05 NPTE Metabolic, Endocrine, Gastrointestinal, and Genitourinary Systems Review
1/134
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
135 Terms
Metabolic System Functions
-Conversion of food to energy to run cellular processes
-Conversion of food to fuel for proteins, lipids, nucleic acids, and carbs
-Elimination of metabolic waste
Catabolism breaks down organic processes
Anabolism combines simple molecules for tissue growth
Metabolic rate
speed at which an organism carries out its metabolic process
Inherited Metabolic Disorders
Classified by particular building block that is affected.
-Enzyme deficiency leads to accumulation of substrate and deficiency in the product of the enzyme
Diagnosis: Amniocentesis in utero, or chorionic villus sampling
-Phenylketonuria
-Tay-Sachs disease
-Mitochondrial disorders
-Wilson's Disease
Must have awareness of dietary restrictions
chorionic villus sampling (CVS)
Prenatal diagnostic technique that involves taking a sample of tissue from the chorion (outermost membrane of embryo)
Phenylketonuria (PKU), amino acid metabolic disorder
Inherited deficiency in phenylalanine hydroxylase, which normally converts phenylalanine to tyrosine. Excess buildup of phenylalanine leads to brain damage resulting in behavioral and cognitive deficits
Sxs: Intellectual disability, hyperactivity, psychoses, abnormal body order, lighter features than family members.
Tx: Dietary restriction of phenylalanine (diet drinks, anything with aspartame, breast milk, eggs, chicken, beef, liver, milk.)

Tay-Sachs Disease (Lysosomal storage disorder)
Inherited deficiency of Hexosaminidase A, producing an accumulation of gangliosides (GM2) in the brain, typically in Eastern European (Ashkenazi) Jewish population
Sxs: At 6 months of age, child will start to miss developmental milestones and continue to deteriorate in motor and cognitive skills. Patient will develop significant intellectual disability and paralysis, dying by age 5
Tx: No effective treatment. Genetic testing in high risk pops.
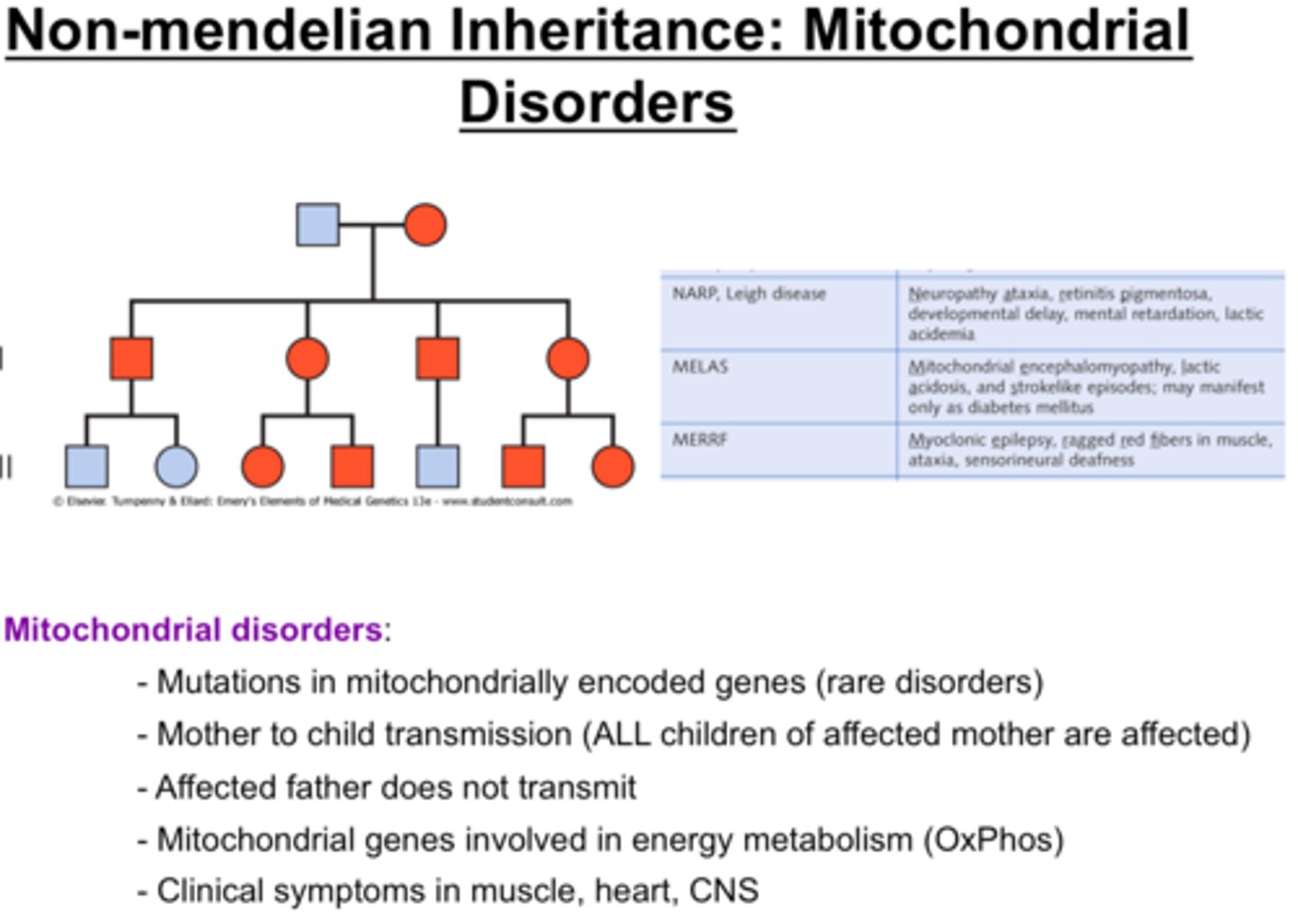
Mitochondrial disorders
LHON (Leber Optic Atrophy), MELAS, Leigh syndrome
Caused by mutations in DNA that lead to impaired mitochondrial protein function, resulting in loss of muscle coordination or strength, visual/hearing problems, learning disabilities, heart/liver/kidney disease, respiratory, neuro and GI disorders, dementia
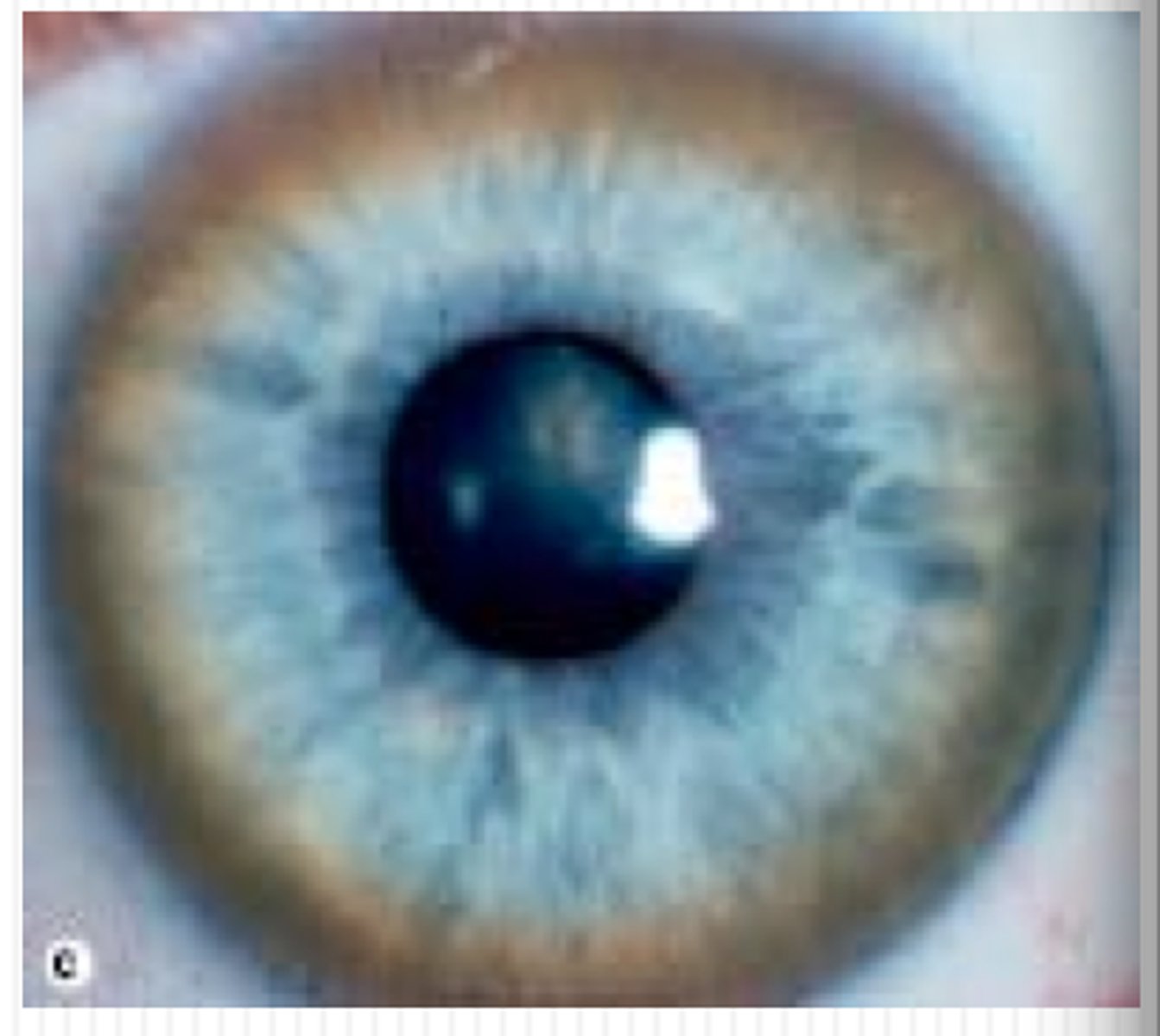
Wilson's disease (hepatolenticular degeneration)
Inherited disorder most common in eastern Europeans, Sicilians, and southern Italians that appears in people under 40, usually between 4 and 6 years old.
Inherited defect in body's ability to metabolize copper, which accumulates in brain, liver, cornea, and kidney.
Sxs: Kayser-Fleischer rings surrounding iris of eye, degenerative changes in basal ganglia, hepatitis, cirrhosis of liver, athetoid movements, ataxic gait patterns, emotional/behavioral changes as copper accumulates.
Over time, deformities in msk system, fractures, osteomalacia, contractures
Tx: Vitamin B6 and D-Penicillamine, and treatment of hepatic disease
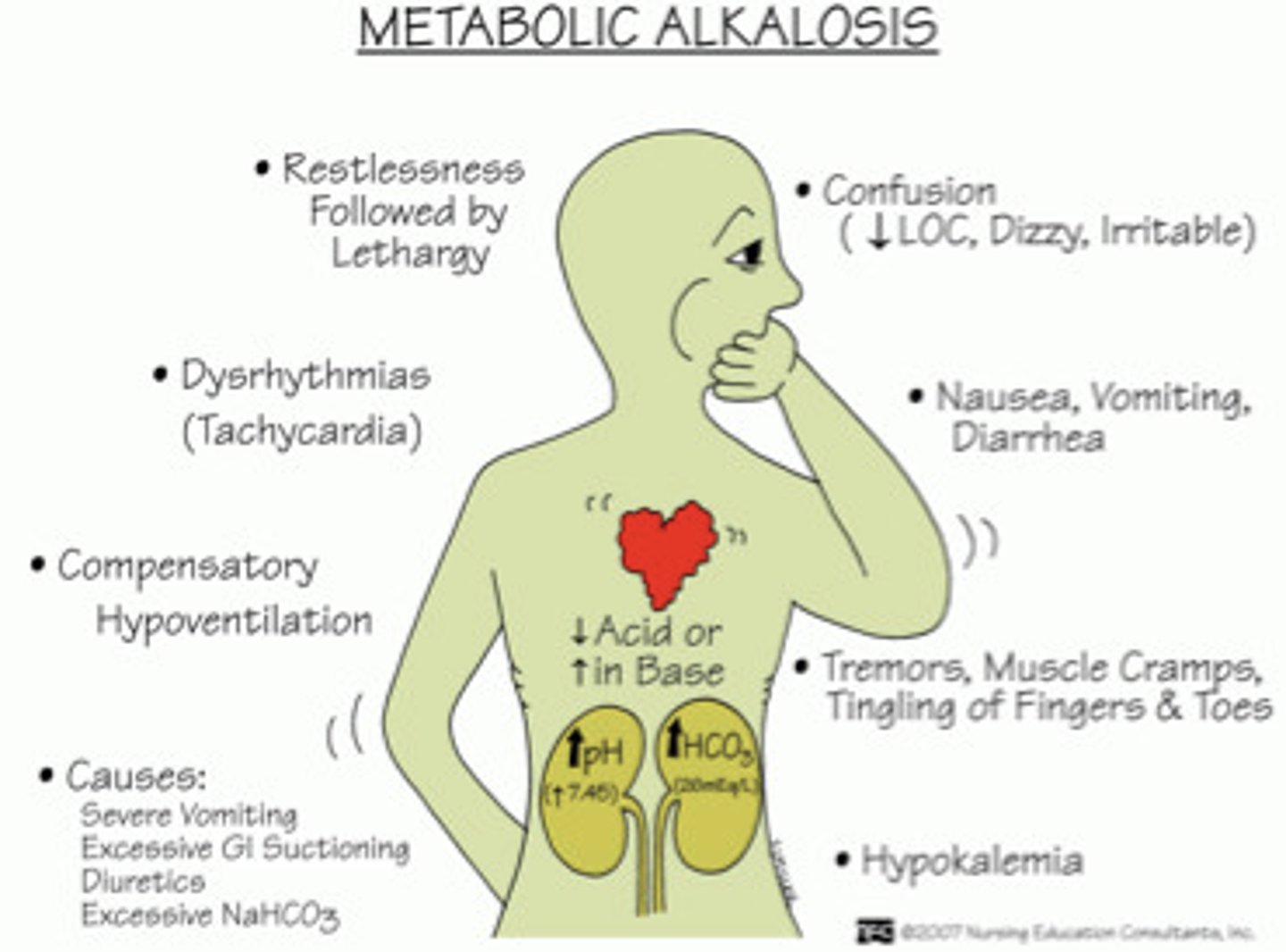
Metabolic Alkalosis
Increase in bicarbonate accumulation or abnormal loss of acids, leading to pH rising above 7.45. Can be a result of vomiting too much, taking too many antacids, or diuretic therapy.
Sxs: Nausea, diarrhea, vomiting, confusion, fasciculations, muscle cramping, hypoventilation. Can result in coma, seizures, and respiratory paralysis
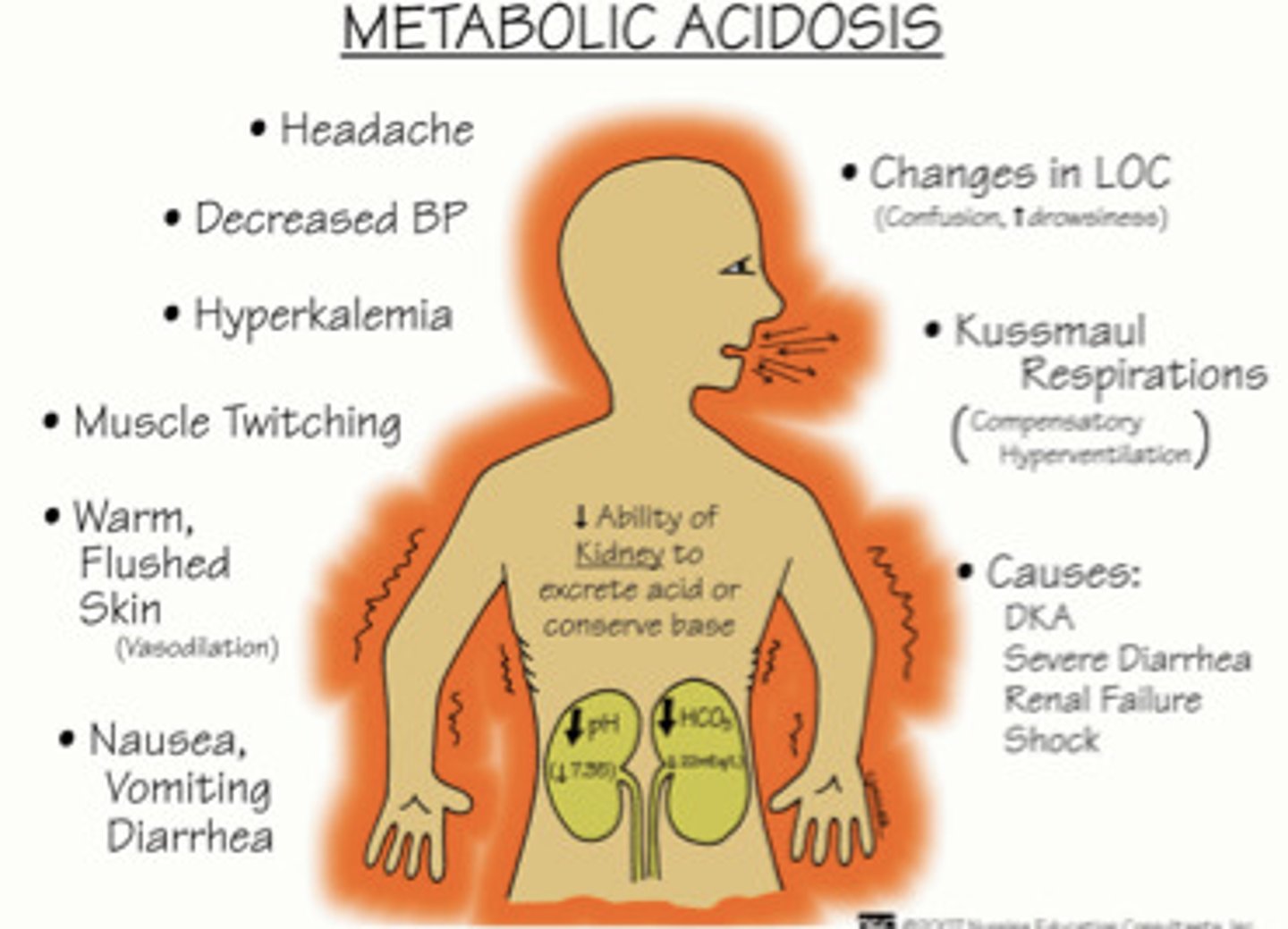
Metabolic Acidosis
Accumulation of acids or deficit in bicarbonate results in pH dropping below 7.35. Can be a result of renal failure, lactic acidosis, diabetic/alcoholic ketoacidosis, diarrhea, or poison.
Sxs: Compensatory hyperventilation (to blow off excess CO2), vomiting, diarrhea, headache, weakness, hyperkalemia, cardiac arrhythmias. Can lead to coma and death.
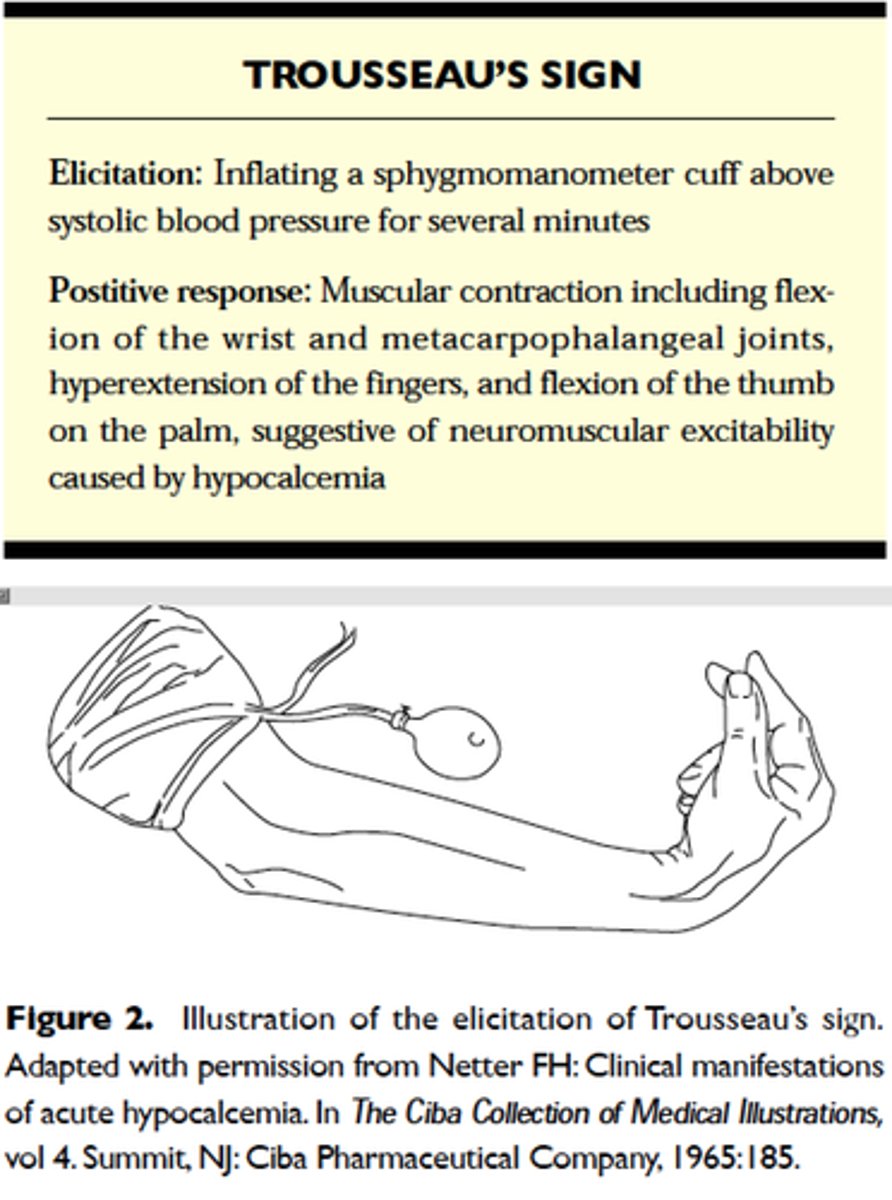
Trousseau's sign
A sign of hypocalcemia and early stages of tetany. Carpal spasm caused by inflating a blood pressure cuff above the client's systolic pressure and leaving it in place for 3 minutes.
Metabolic Bone Disease
- Disruption in normal skeletal metabolism
- Results in deformity, bone loss, fx's, softening
of the bones, arthritis, and pain.
-Skeletal system uses calcium and phosphorous to balance remodeling of cortical and trabecular bone to optimize skeletal structure
-Osteomalacia
-Osteoporosis
-Paget's Disease
Osteomalacia
Bones become soft secondary to calcium (decreased intestinal absorption) or phosphorous deficiency (increased renal excretion) or deficiency in vitamin D. Bone matrix is adequate, insufficient calcification of matrix.
Sxs: Vague presentation of aching, fatigue, weight loss. Myopathy and sensory polyneuropathy with periarticular tenderness and pain, thoracic kyphosis and bowing of lower extremities.
Tx: Fix underlying etiology.
Osteoporosis
Decrease in trabecular and cortical bone mass leading to increased risk of fracture. Can be idiopathic, post-menopausal, or involutional (senile) osteoporosis. Declining osteoblast function coupled with loss of calcium and bone salts will cause bones to be brittle
Sxs: Compression and other bone fractures, low thoracic/lumbar pain, loss of lumbar lordosis, kyphotic deformity, decrease in height, dowager's hump, postural changes
Tx: Vitamin and pharmacological intervention
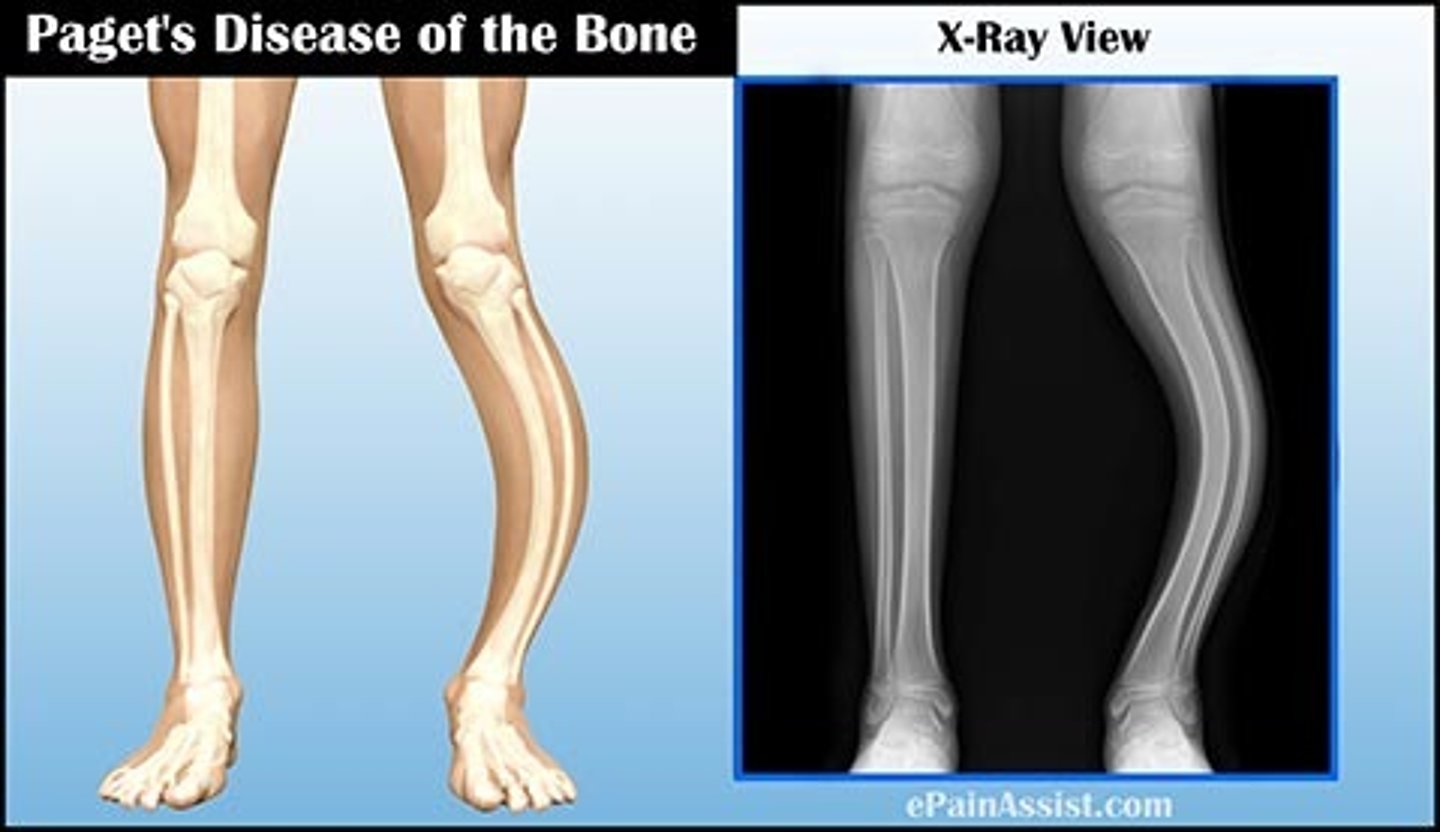
Paget's Disease
Heightened osteoclast activity, causing excess bone formation that lacks true structural integrity. Bone is large but lacks strength.
Sxs: MSK pain, bony deformities at skull, clavicle, pelvis, femur, spine, and tibia. Progresses to HA, vertigo, hearing loss, mental deterioration, fatigue, increased CO and heart failure
Tx: Biphosphonates to limit bone resorption and improve quality of involved bone.
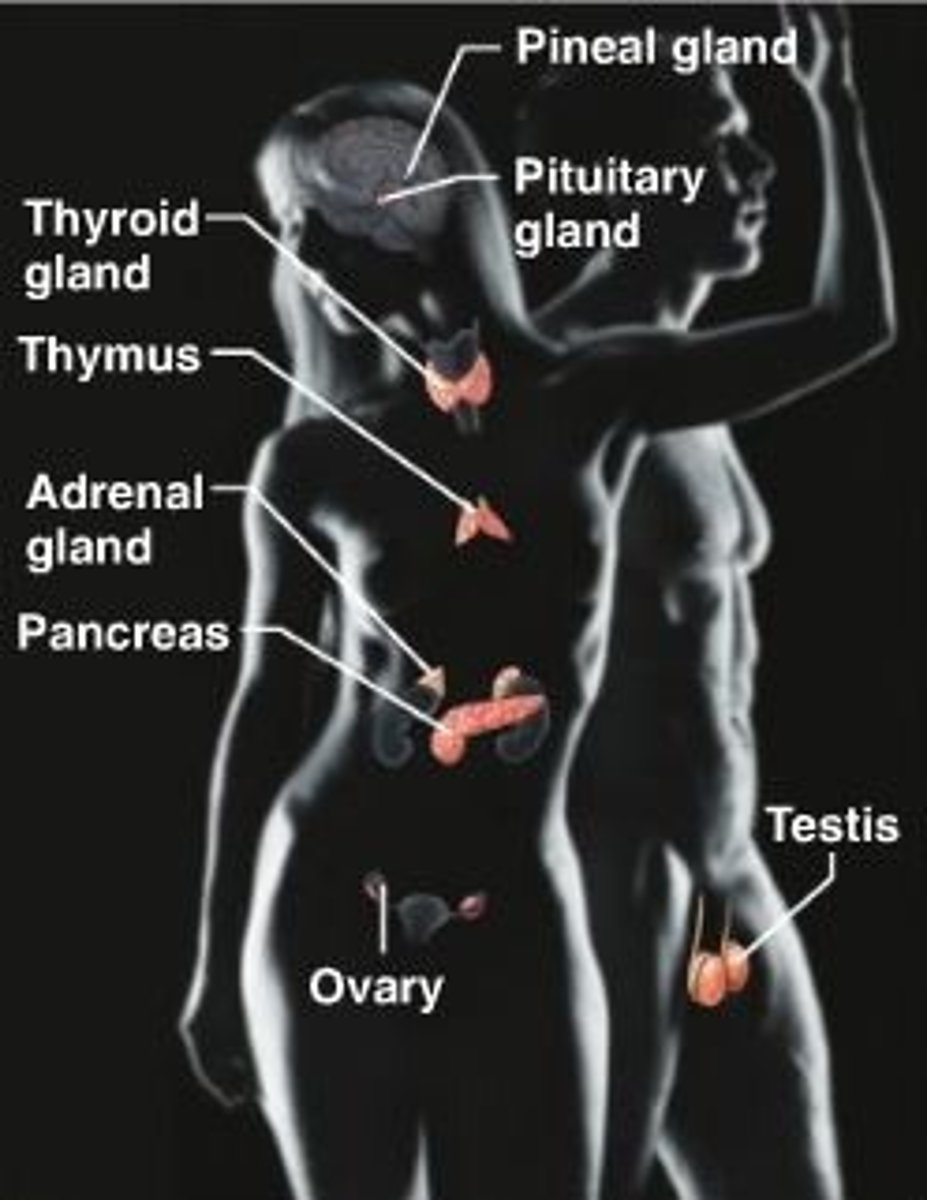
Endocrine System
the body's "slow" chemical communication system; a set of ductless glands that secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream. Hormones travel through the body to target organs, where they selectively bind to receptor cells.
Hormones travel to virtually every area of the body.
Key Glands:
-Hypothalamus
-Pituitary Gland
-Thyroid Gland
-Parathyroid Gland
-Adrenal Gland
-Pancreas
-Ovaries
-Testes
Hypothalamus
A neural structure lying below the thalamus; it directs autonomic nervous system, the feed & breed (hunger, thirst, sexual behavior, body temperature), helps govern the endocrine system via the pituitary gland
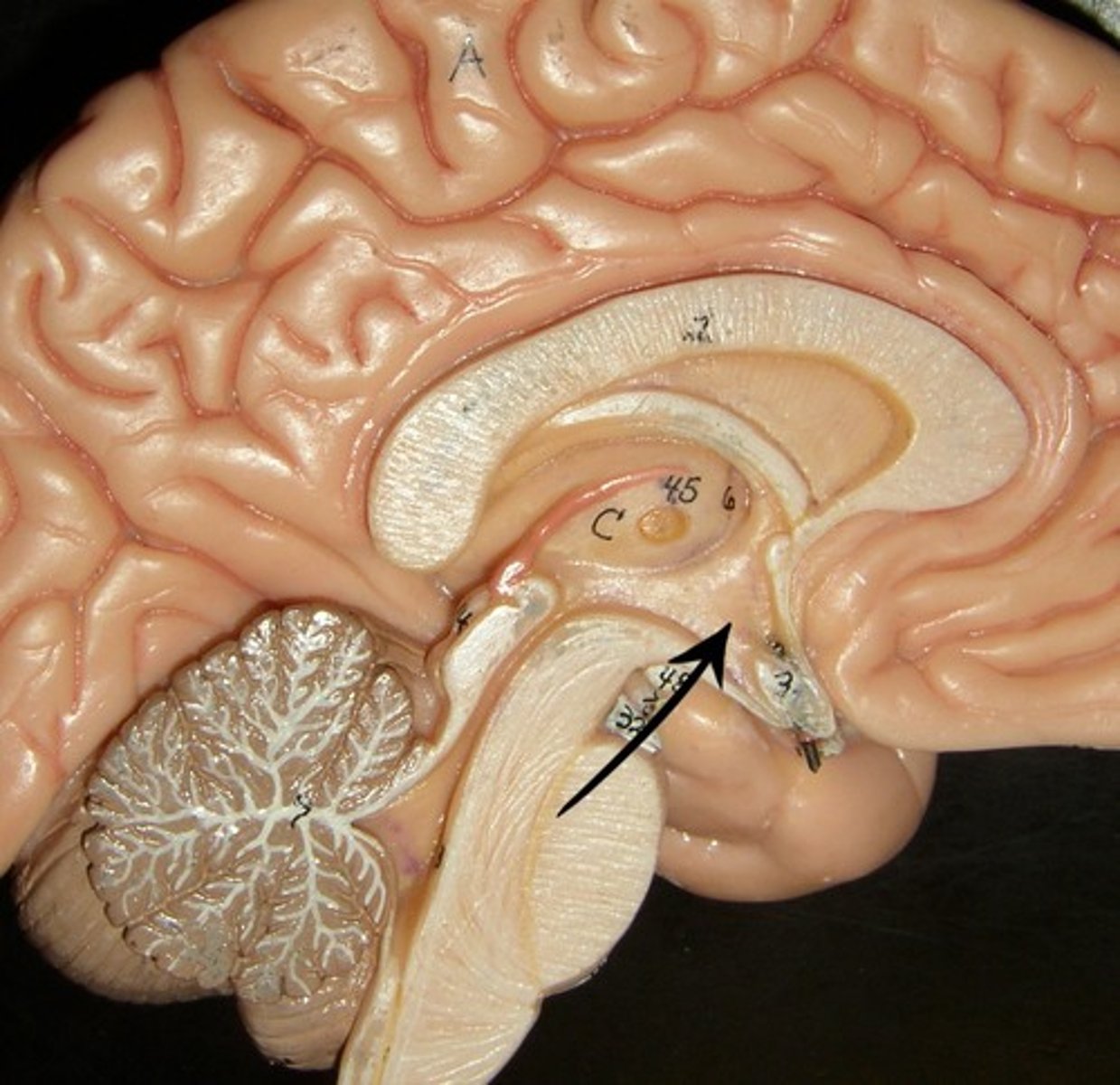
Pituitary Gland
Located at base of brain below hypothalamus, and is controlled by the hypothalamus. Consists of two glands (adenohypophysis anterior, and neurohypophysis in posterior). Considered the "master gland" and releases hormones that regulate other endocrine glands, and is influenced by seasonal changes or emotional stress.
Creates sex hormones, controls ovulation
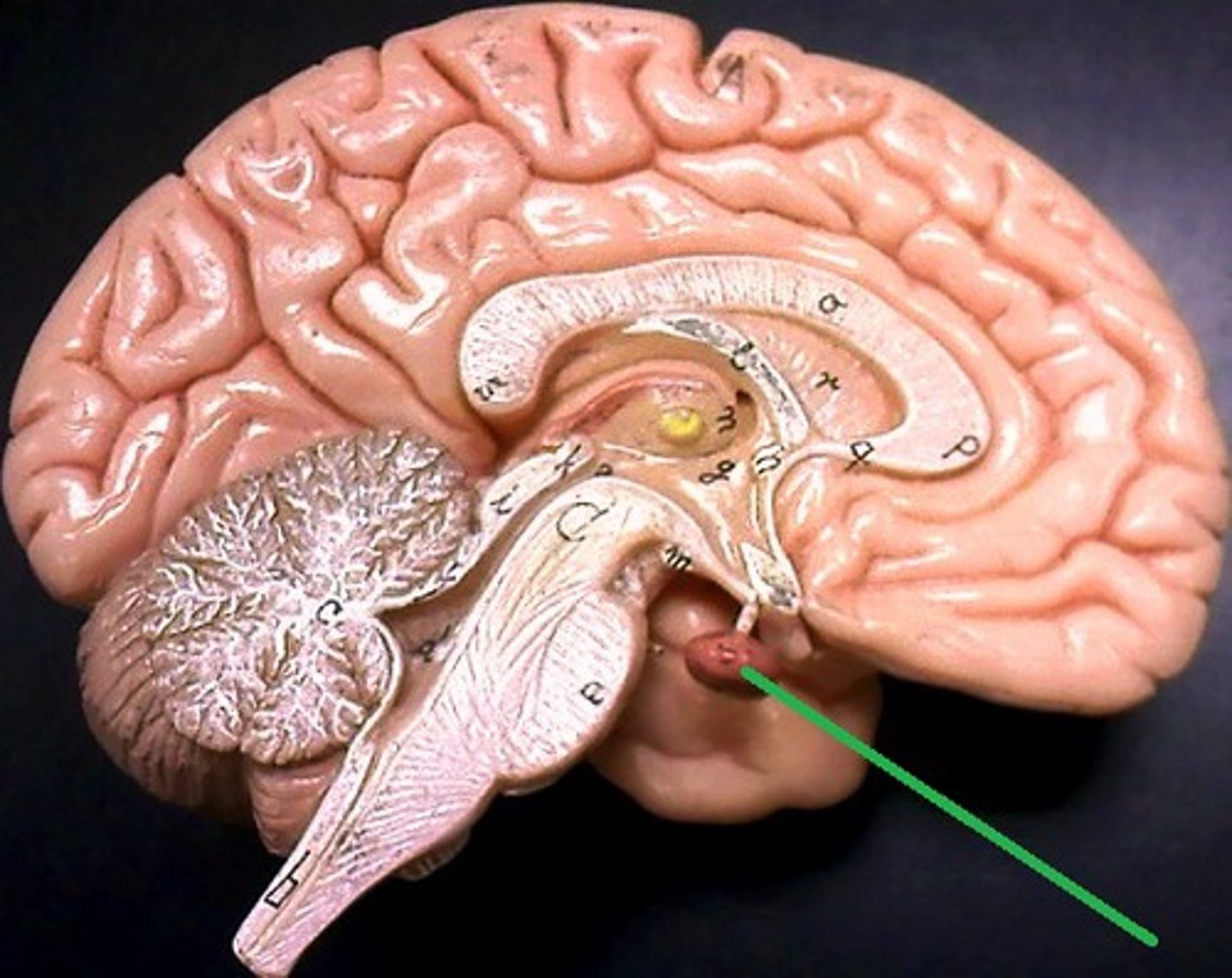
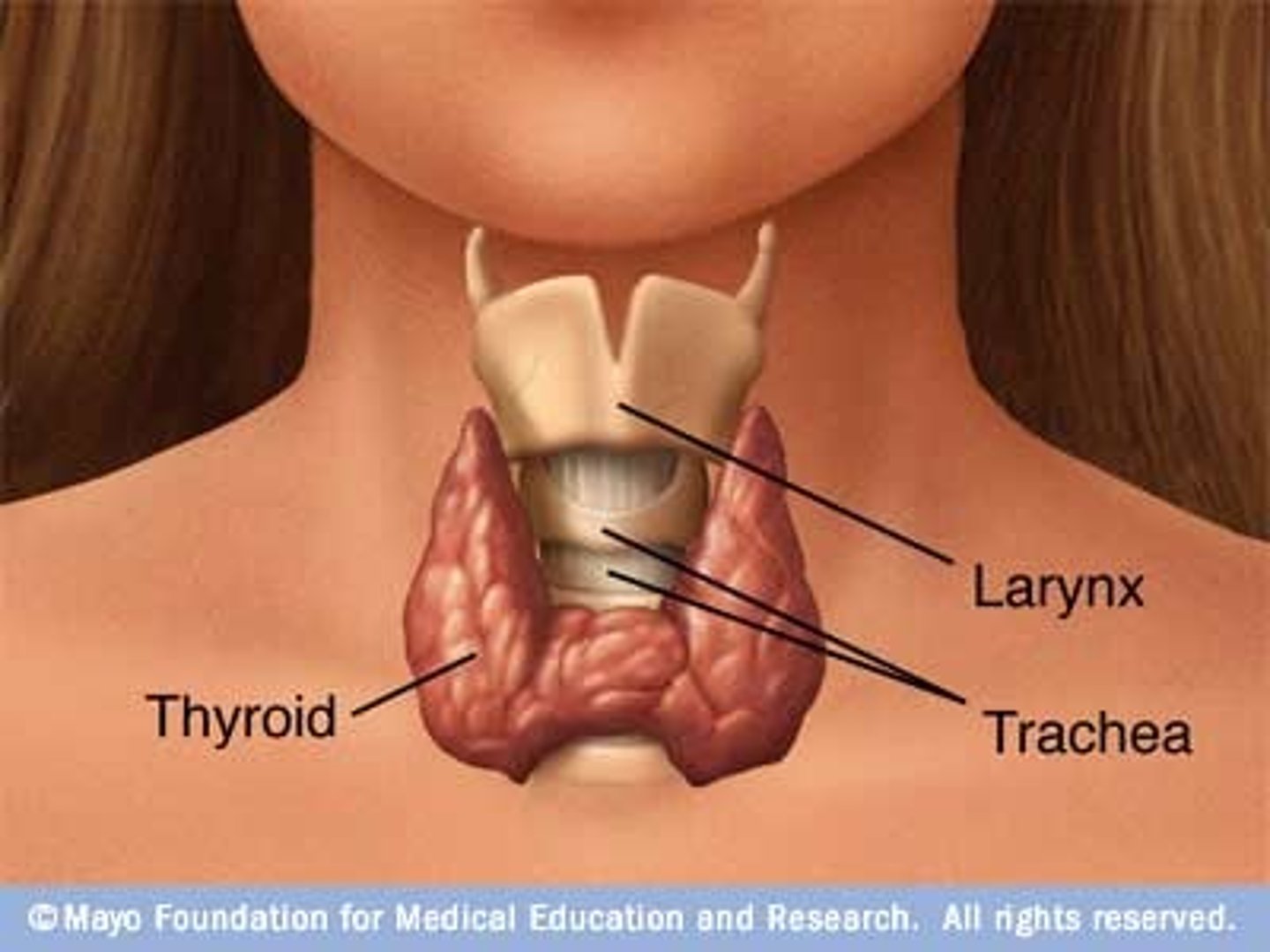
Thyroid Gland
Controls body's metabolism. Produces thyroxine and triiodothyronine to control the rate at which cells burn fuel from food. Increased thyroid hormones increases rate of chemical reactions in body.
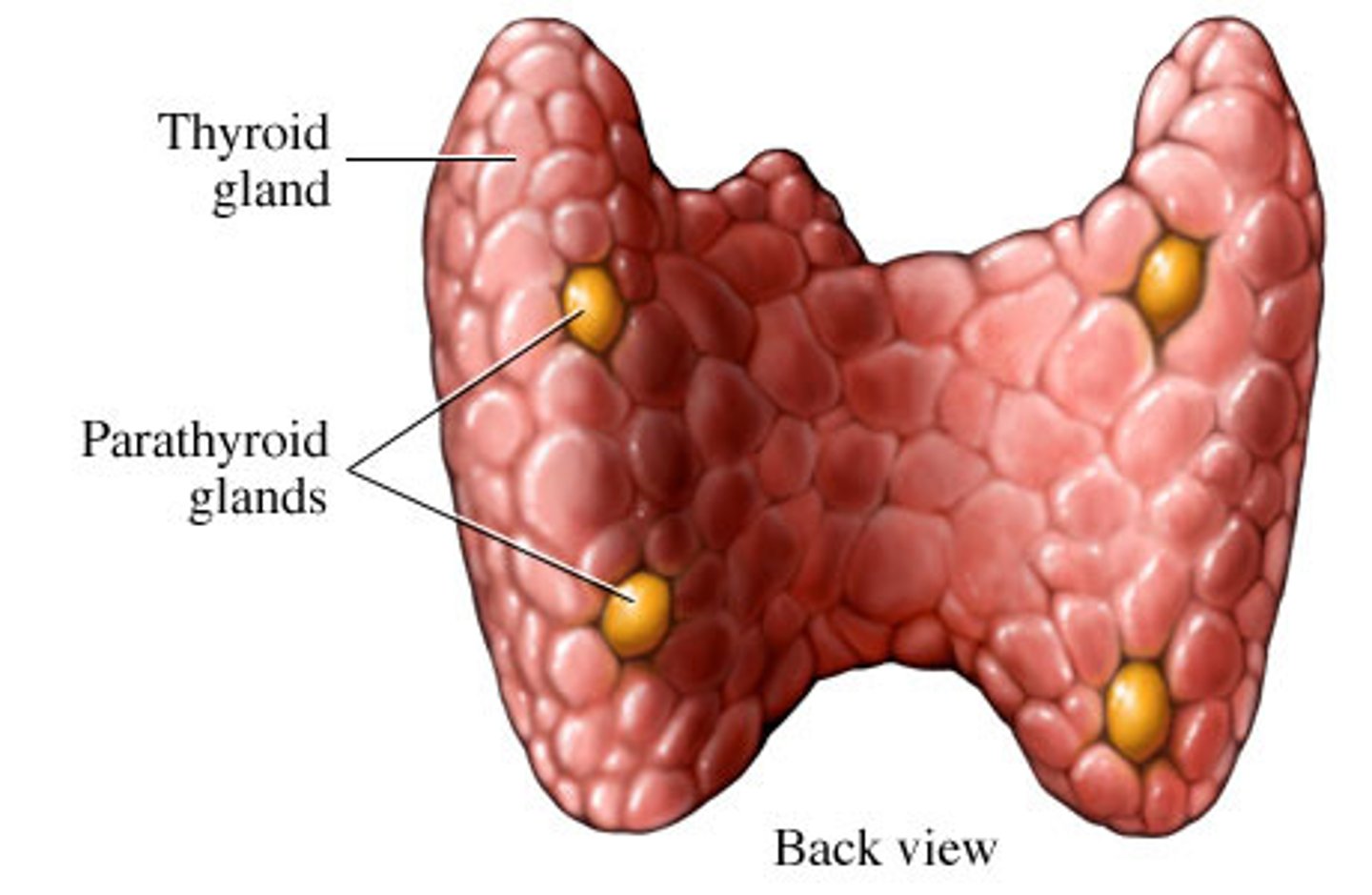
Parathyroid Glands
-Produce parathyroid hormone, which is an antagonist to calcitonin and helps maintain normal blood levels of calcium and phosphate
-Increased PTH increases reabsorption of calcium and phosphate from bones to blood.
-Low blood calcium stimulates PTH, high blood calcium inhibits it.
-Calcium levels control clotting, neuromuscular excitability, and cell membrane permeability.
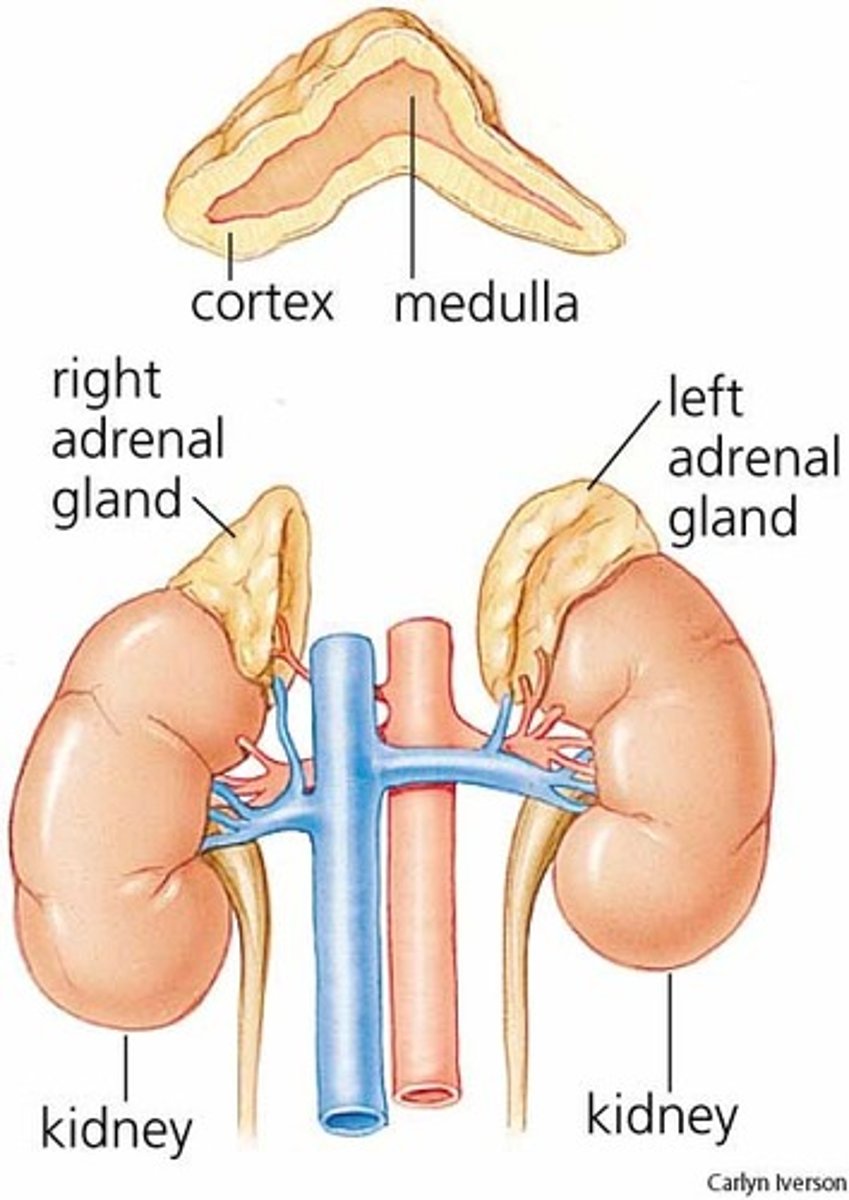
Adrenal Glands
-Adrenal Cortex: Corticosteroids that regulate water/sodium balance, stress response, immune system, sexual development, and metabolism
-Adrenal Medulla: Epinephrine that increases HR and BP in response to stress
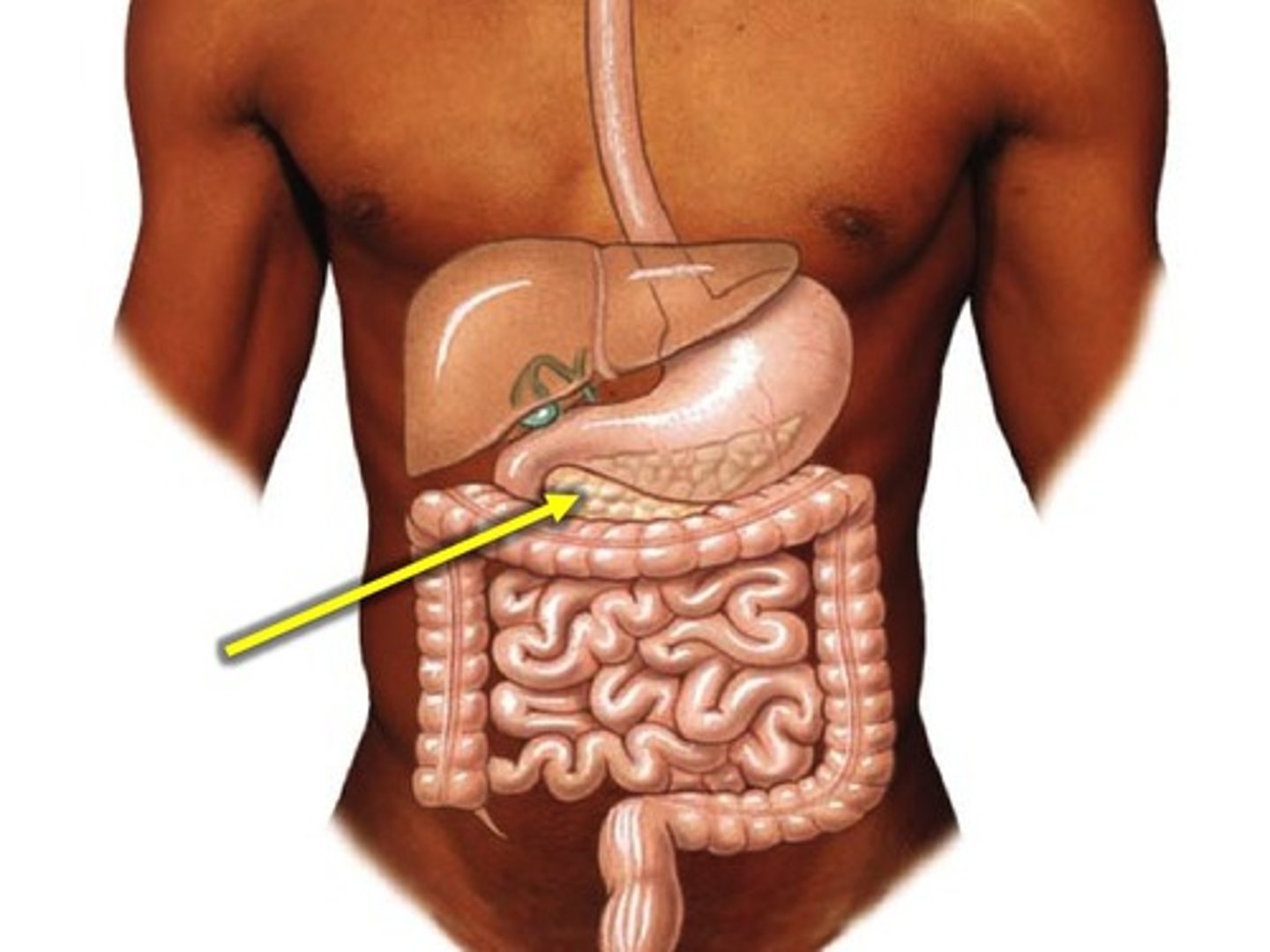
Pancreas
Housed in upper left quadrant of abdominal cavity.
-Functions mostly as endocrine organ but also an exocrine gland, secreting bicarbonate and enzymatic pancreatic juice to neutralize stomach acid in intestines and break down food.
-Islets of Langerhans are the hormone-producing cells of pancreas, containing Alpha cells to produce glucagon and Beta cells tp produce insulin
-Those two hormones regulate glucose in bloodstream
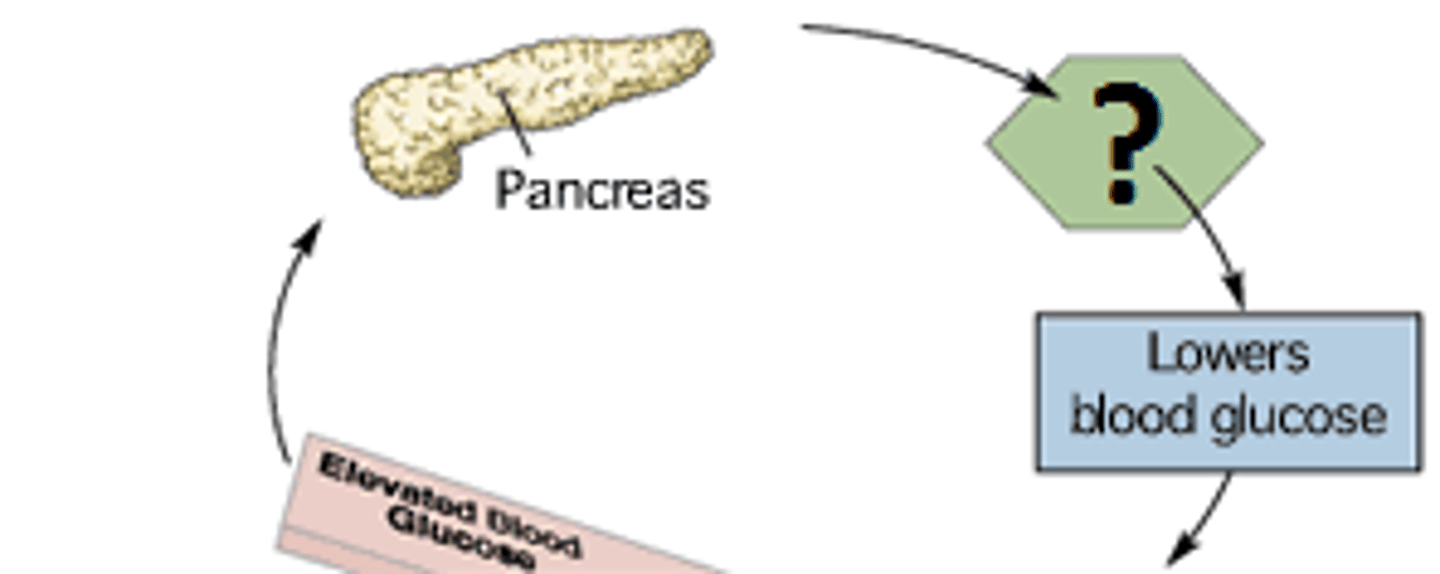
Glucagon
A hormone secreted by the pancreatic alpha cells that increases blood glucose concentration, and is released into bloodstream when blood glucose is low.
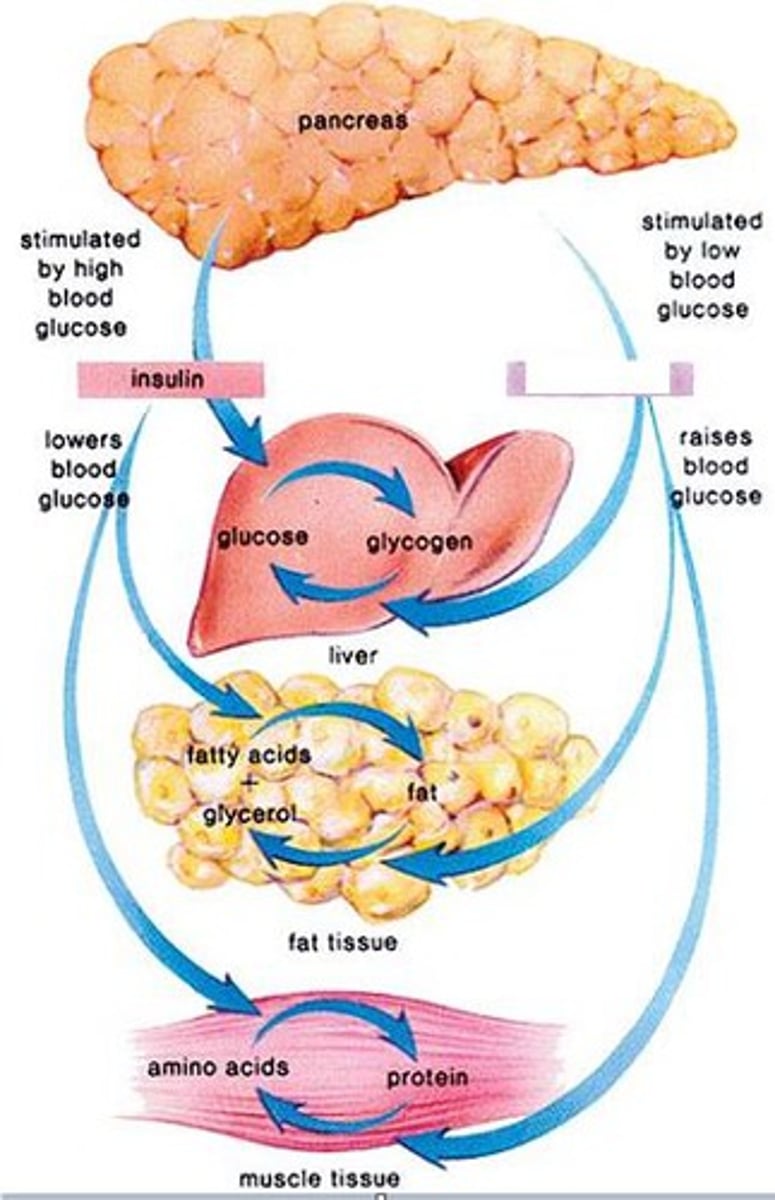
Insulin
A protein hormone synthesized in the pancreas that regulates blood sugar levels by facilitating the uptake of glucose into tissues. High blood glucose levels increase this hormone's activity to achieve homeostasis.
Ovaries
Located in pelvic cavity on each side of uterus, providing estrogen and progesterone that contribute to regulation of menstrual cycle and pregnancy.
Ovarian follicles secrete estrogen, responsible for female sex characteristics
Corpus Luteum secretes progesterone, which maintains uterus lining
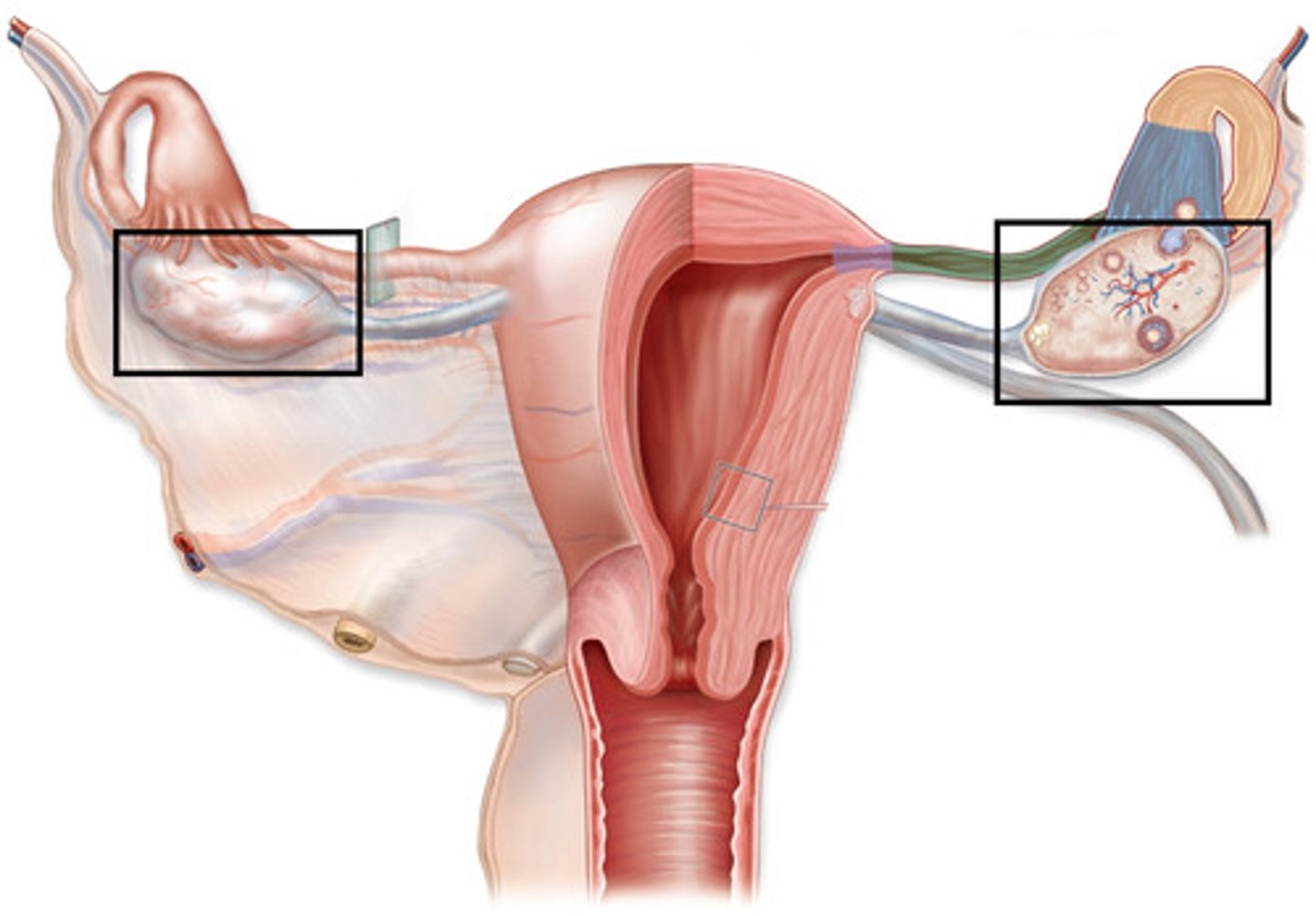
Testes
Located in scrotum. Secrete androgens such as testosterone that regulate body changes associated with sexual development and support sperm production
Steroid Hormones (prostaglandins)
Do not circulate in blood, just exert effects where they are produced.
All cells create prostaglandins from phospholipids of cell membrane
Can produce wide variety of effects: inflammation, pain, vasodilation/constriction, nutrient metabolism, blood clotting
Amine hormones (catecholamines)
Epinephrine
Norepinephrine
Dopamine
Synthesized from chromaffin cells in adrenal medulla, and released into the bloodstream after sympathetic nervous system stimulation to activate glycogen breakdown for fuel, block insulin, increase metabolic rate, and dilate lung airways.
Epinephrine
Neurotransmitter secreted by the adrenal medulla in response to stress. Also known as adrenaline.
Targets cardiovascular and metabolic systems.
Sarcoidosis
chronic inflammatory disease in which small nodules (granulomas) develop in lungs, lymph nodes, and other organs
Hypothalamus Dysfunction
Tumors (ependyomas), inflammatory process (sarcoidois), surgical transection, trauma (skull fracture)
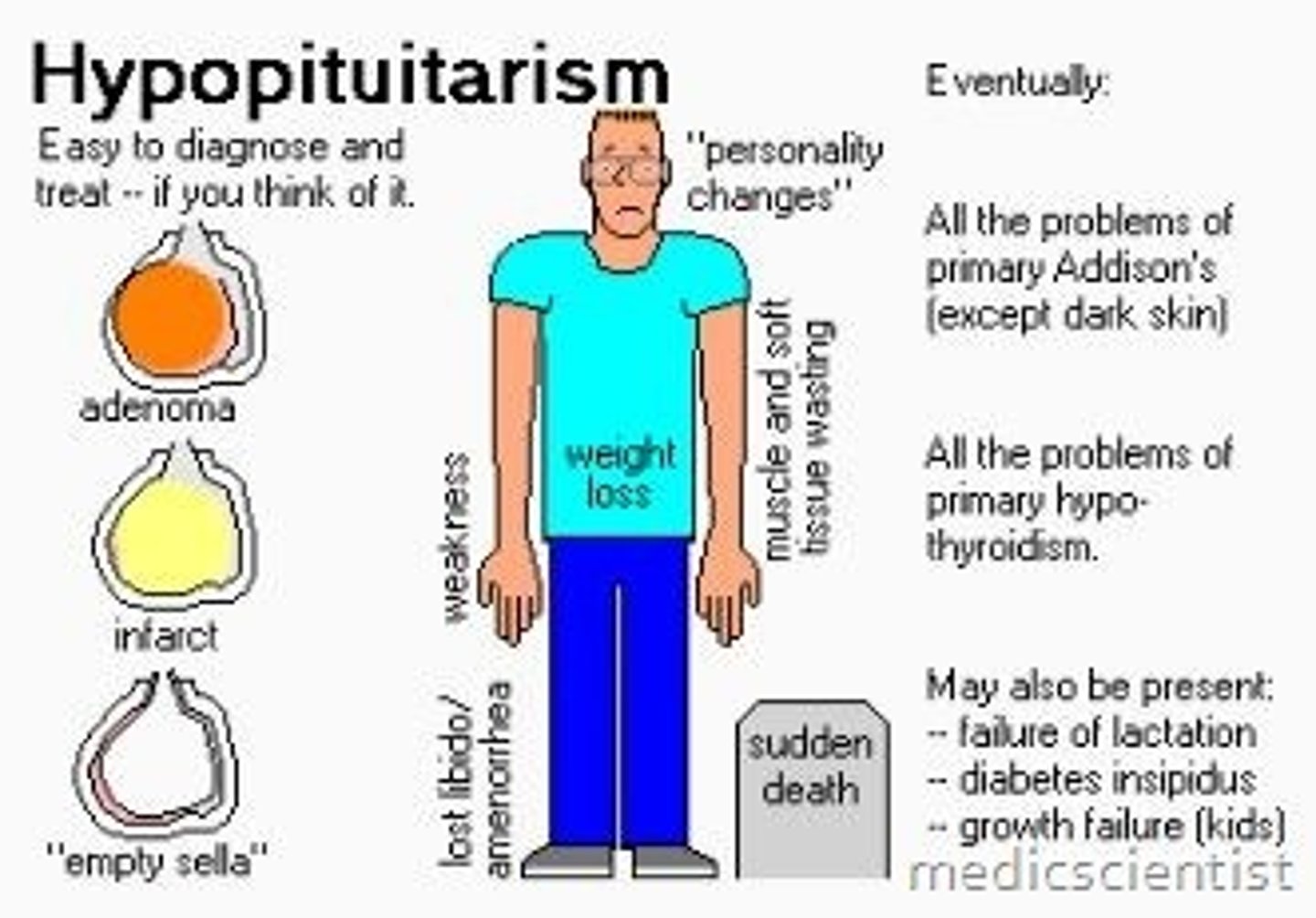
Hypopituitarism
Decreased/absent secretion from anterior pituitary gland, causing dwarfism, delayed growth/puberty, diabetes insipidus. Often caused by pituitary adenoma (usually benign tumor) or a pituitary infarction
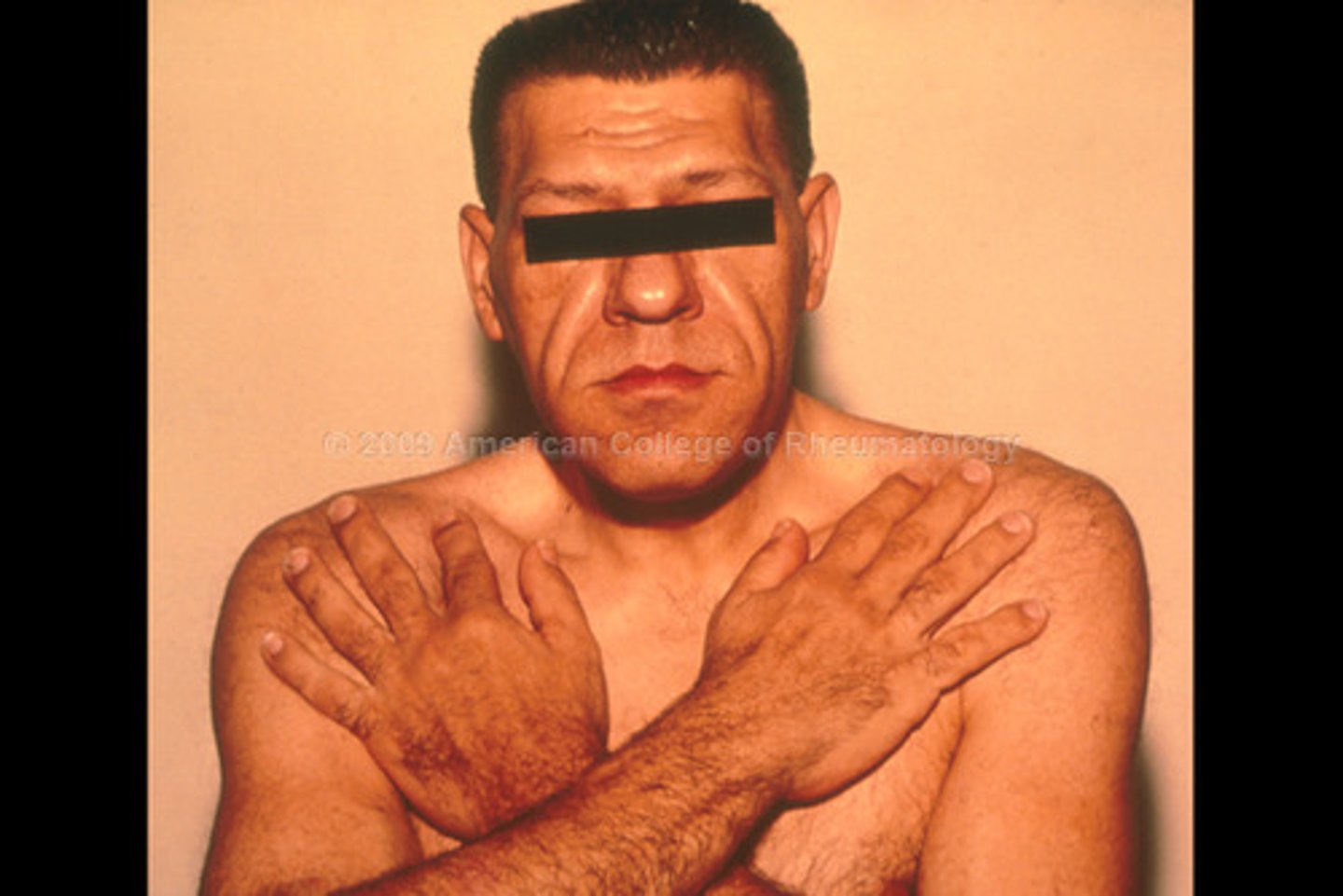
Hyperpituitarism
Excess secretion of growth hormone, causing gigantism, acromegaly, hirsutism (excess hair growth), galactorrhea (abnormal lactation), amenorrhea, infertility, or impotence.
Addison's Disease
Adrenal Hypofunction. Occurs when the adrenal glands do not produce enough of the hormones cortisol or aldosterone
Sxs: Hyperpigmentation, GI pain, nausea, hypotension, weakness, fluid/electrolyte imbalance secondary to aldosterone dysfunction, metabolic dysfunction secondary to cortisol deficiency

Aldosterone
"salt-retaining hormone" which promotes the retention of Na+ by the kidneys. na+ retention promotes water retention, which promotes a higher blood volume and pressure
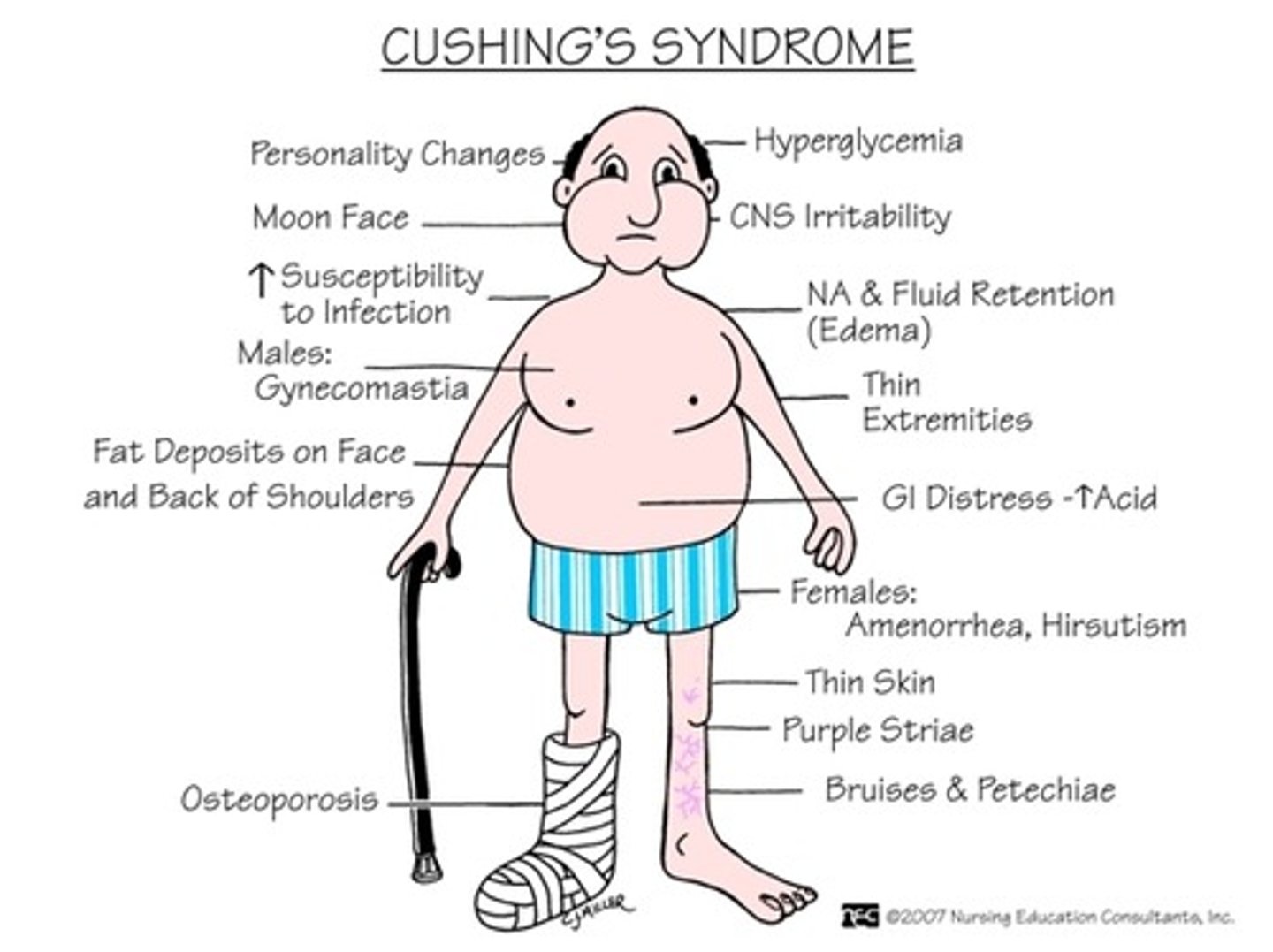
Cushing's Syndrome
Adrenal Hyperfunction. Excessive amounts of cortisol production.
Sxs: Moon Face, buffalo hump, hyperglycemia, truncal obesity, acne, hypertension, depression, memory loss
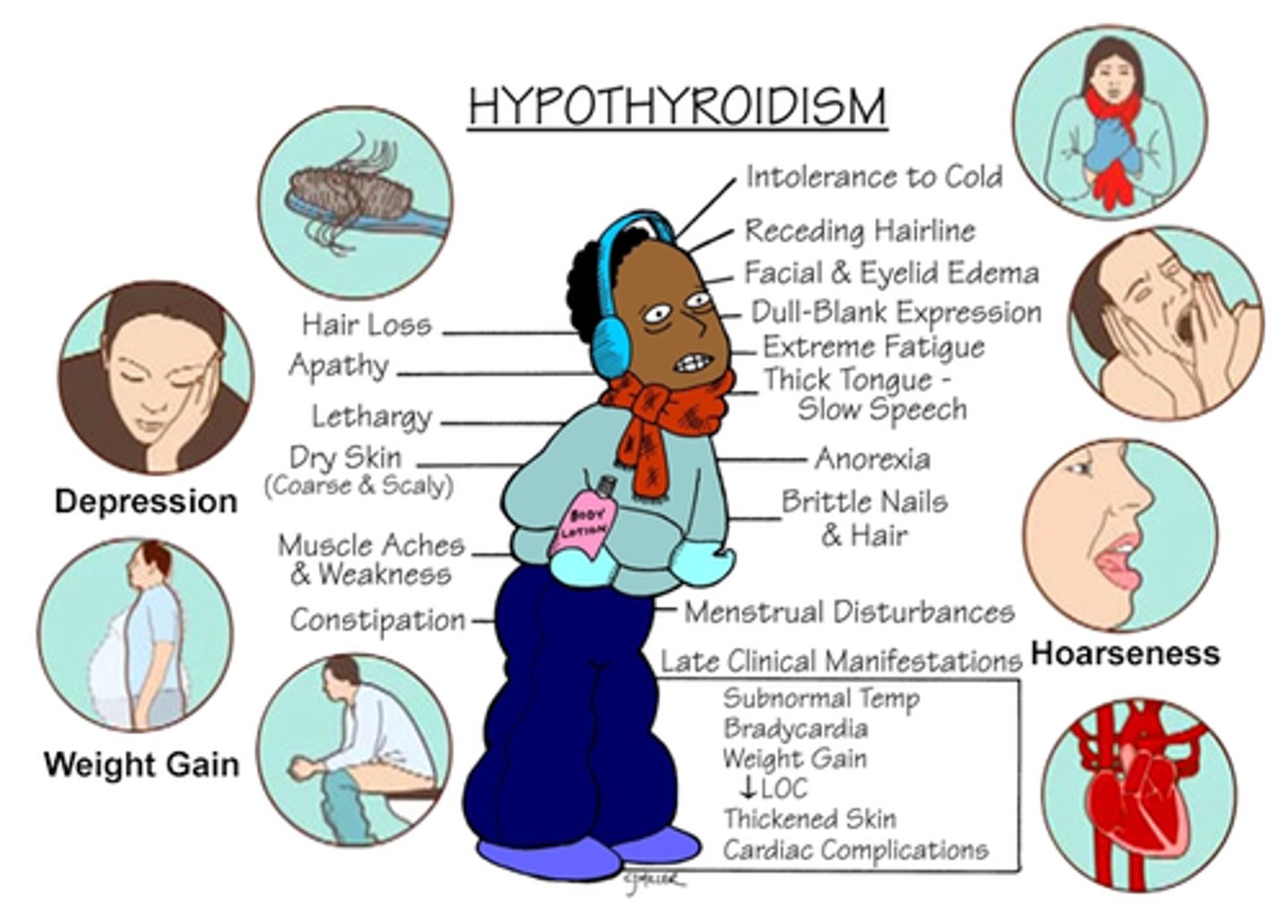
Hypothyroidism
Decreased thyroid hormon secretion, slowing metabolic processes in the body. Hashimoto's or underdeveloped thyroid gland.
Sxs: Fatigue, weight gain, decreased HR, constipation, slowed growth
PT implications: Risk of rhabdomyolsysis
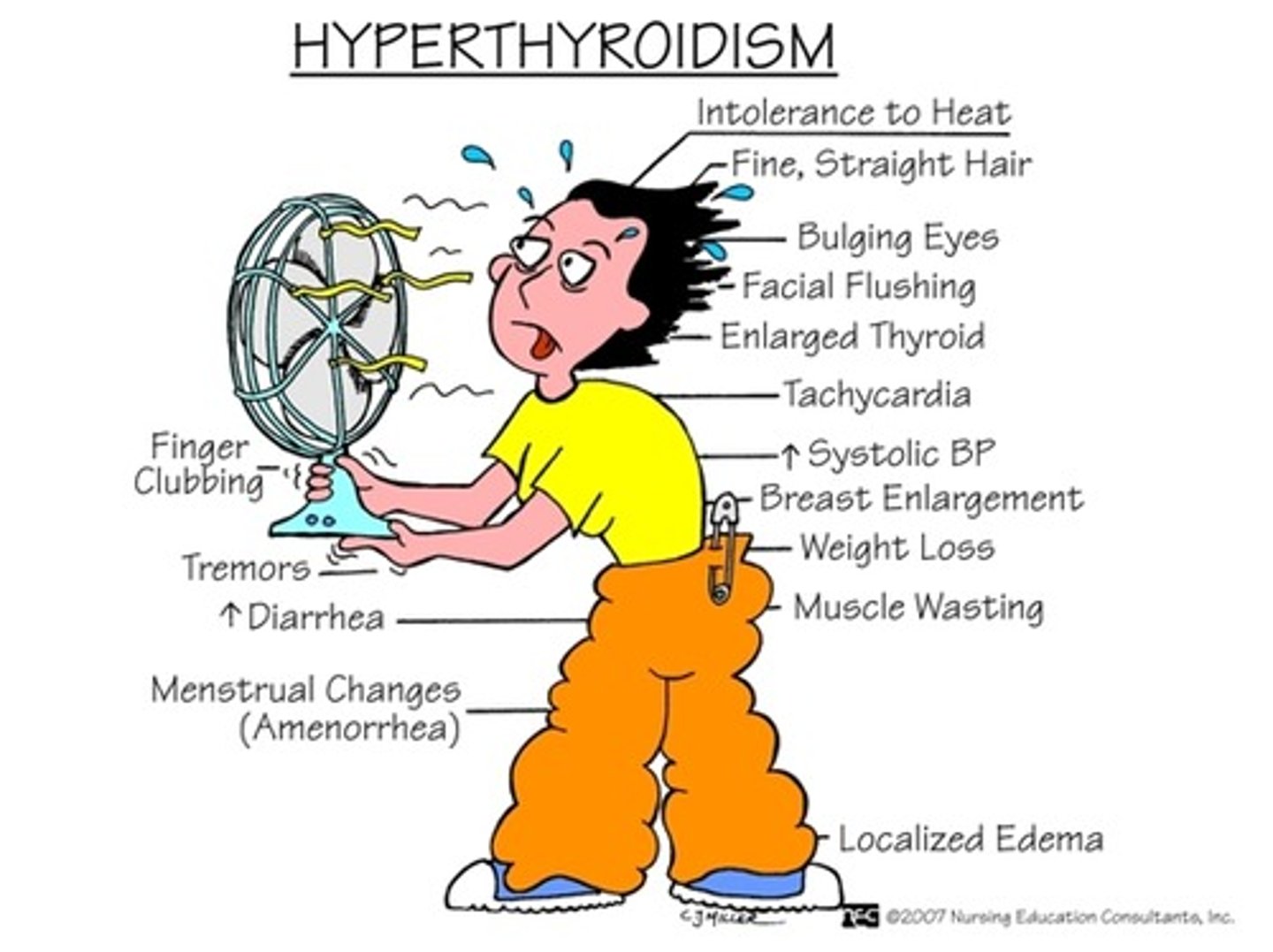
Hyperthyroidism
Excess thyroid hormones in bloodstream. Most specific cause is Grave's disease, an autoimmune disorder.
Sxs: Increase in nervousness, excess sweating, exophthalmos weight loss, increased BP, myopathy chronic periarthritis, enlarged thyroid gland
PT implications: Avoid treatments that exacerbate, avoid hot settings, avoid cardiovascular stress
Hypoparathyroidism
Hypofunction of parathyroid gland
Sxs: Hypocalcemia, seizures, cognitive deficits, tetany, cramps, muscle pain, cardiac arrhythmias. May see Trousseau's Sign
Tx: Intravenous calcium

Hyperparathyroidism
Hyperfunction of the parathyroid gland
Sxs: Renal stones, kidney damage, depression, memory loss, muscle wasting, bone deformities and vertebral compression fractures
Tx: Lowering serum calcium with diuretics or antiresorptive meds

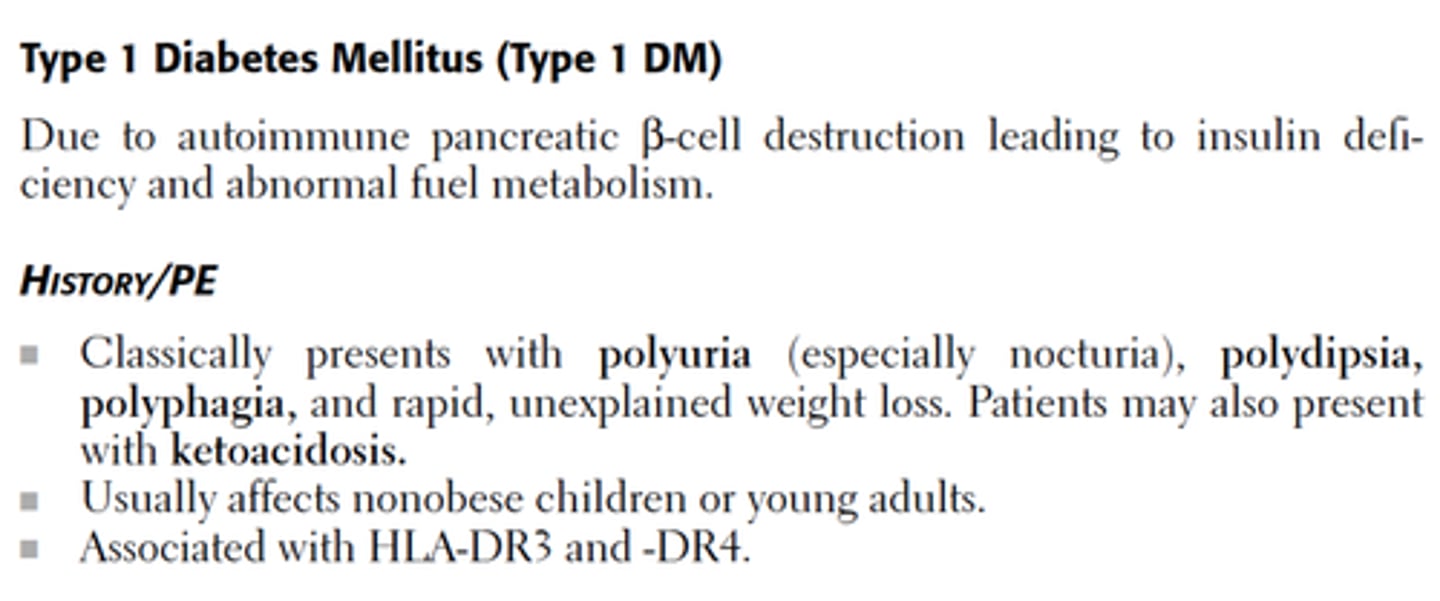
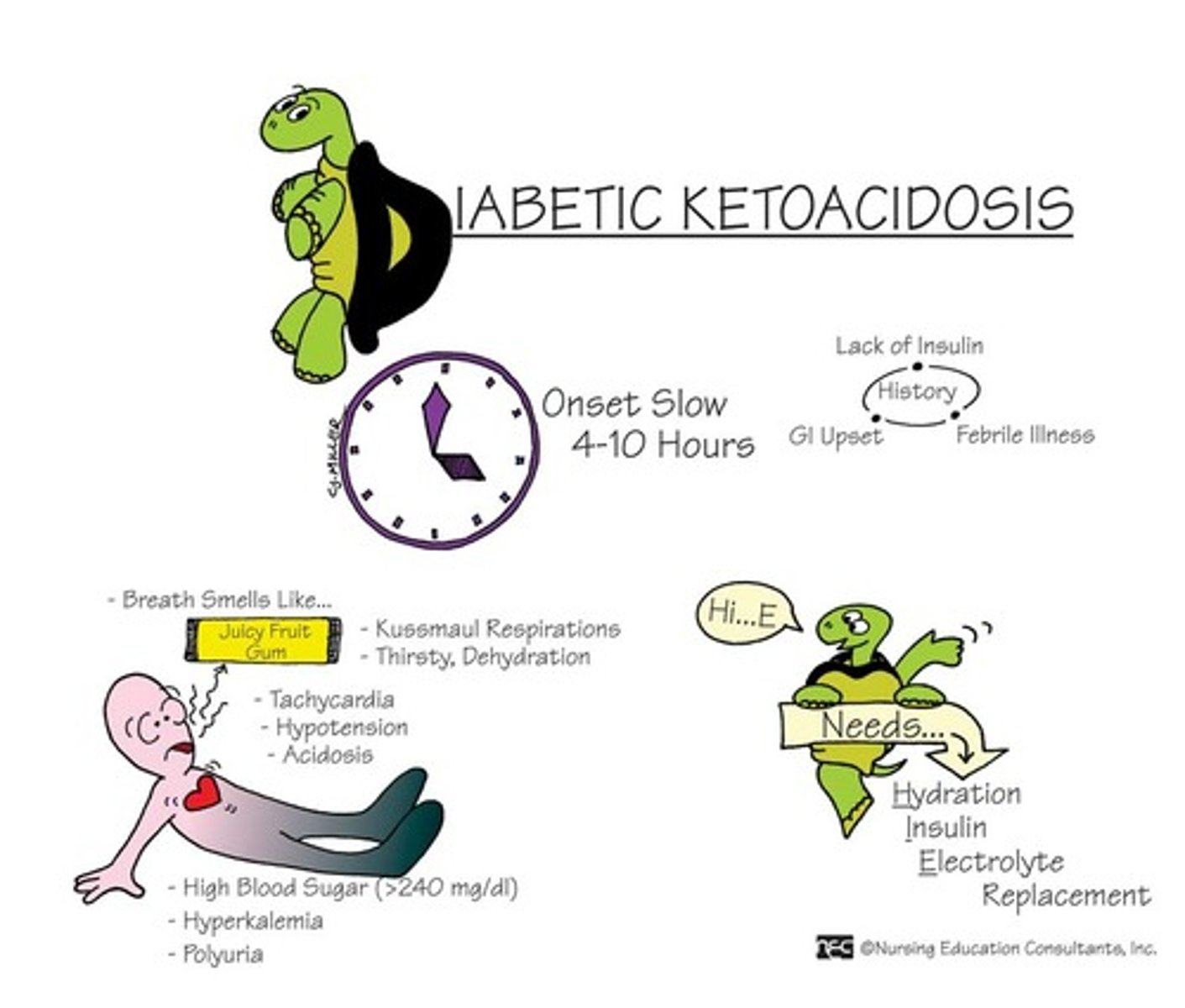
Type I Diabetes Mellitus
Pancreas fails to produce enough insulin due to genetic disposition and/or exposure to trigger causing an immune reaction. Also called insulin-dependent or juvenile diabetes.
Sxs: Rapid onset, weight loss, ketoacidosis, polyuria (urination), polydipsia (thirst), polyphagia (hunger), blurred vision, dehydration, fatigue
Tx: Insulin injections to maintain glucose blood levels.
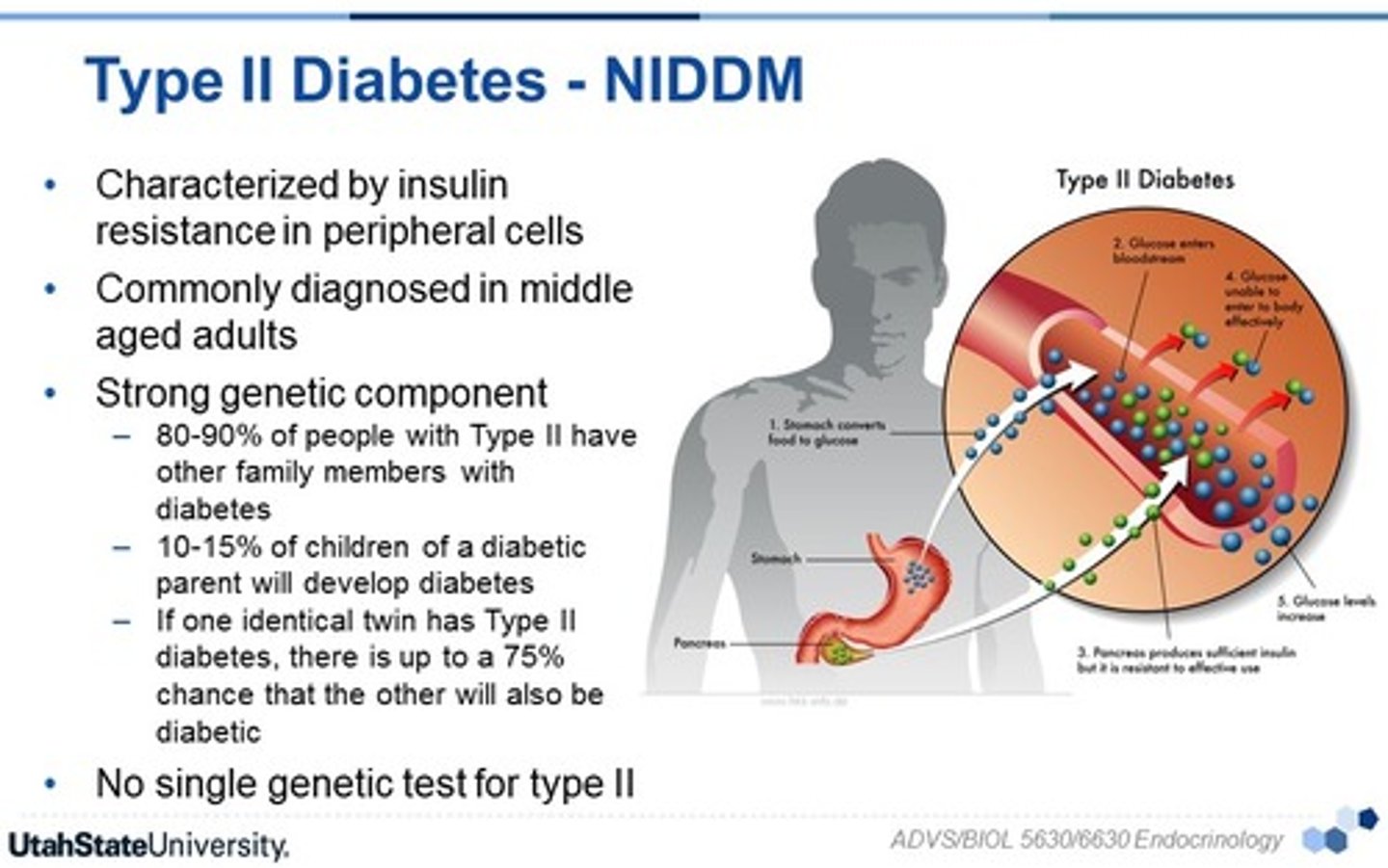
Type II Diabetes Mellitus
Typically occurs over age of 45. Resistance to insulin action at receptor site, inadequate insulin secretion, and hyperglycemia when body cannot properly respond to insulin. Exacerbated by obesity.
Sxs: Polyphagia, polydipsia, polyuria, dehydration, fatigue, no ketoacidosis.
Tx: Blood glucose control through diet, exercise, and medications.
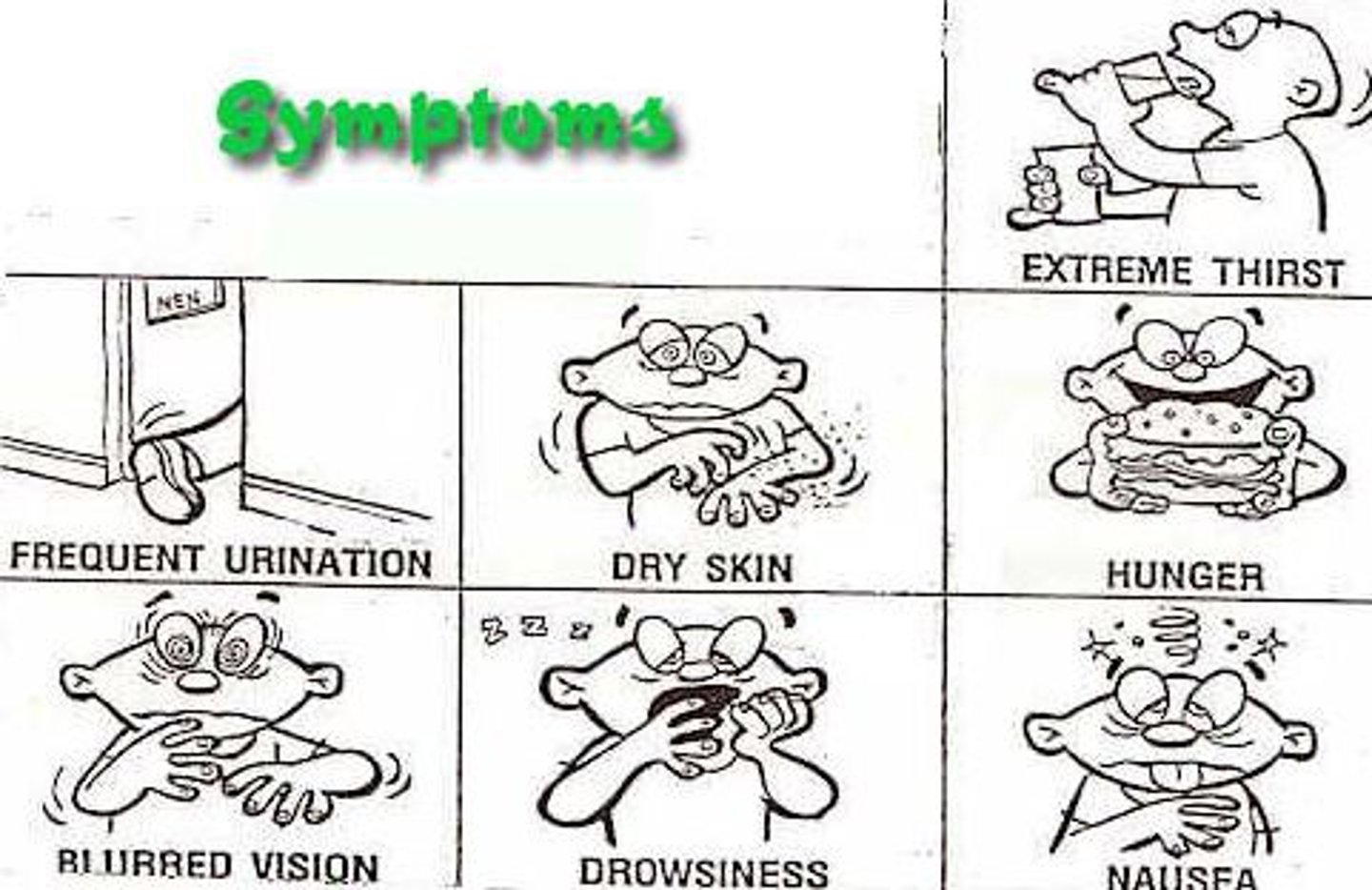
Hyperglycemia
Blood glucose over 180-200 mg/dL.
Increased thirst and frequent urination, dyspnea, fruity breath odor, dry mouth, nausea, confusion, LOC.
Ketoacidosis
excessive production of ketones, making the blood acidic
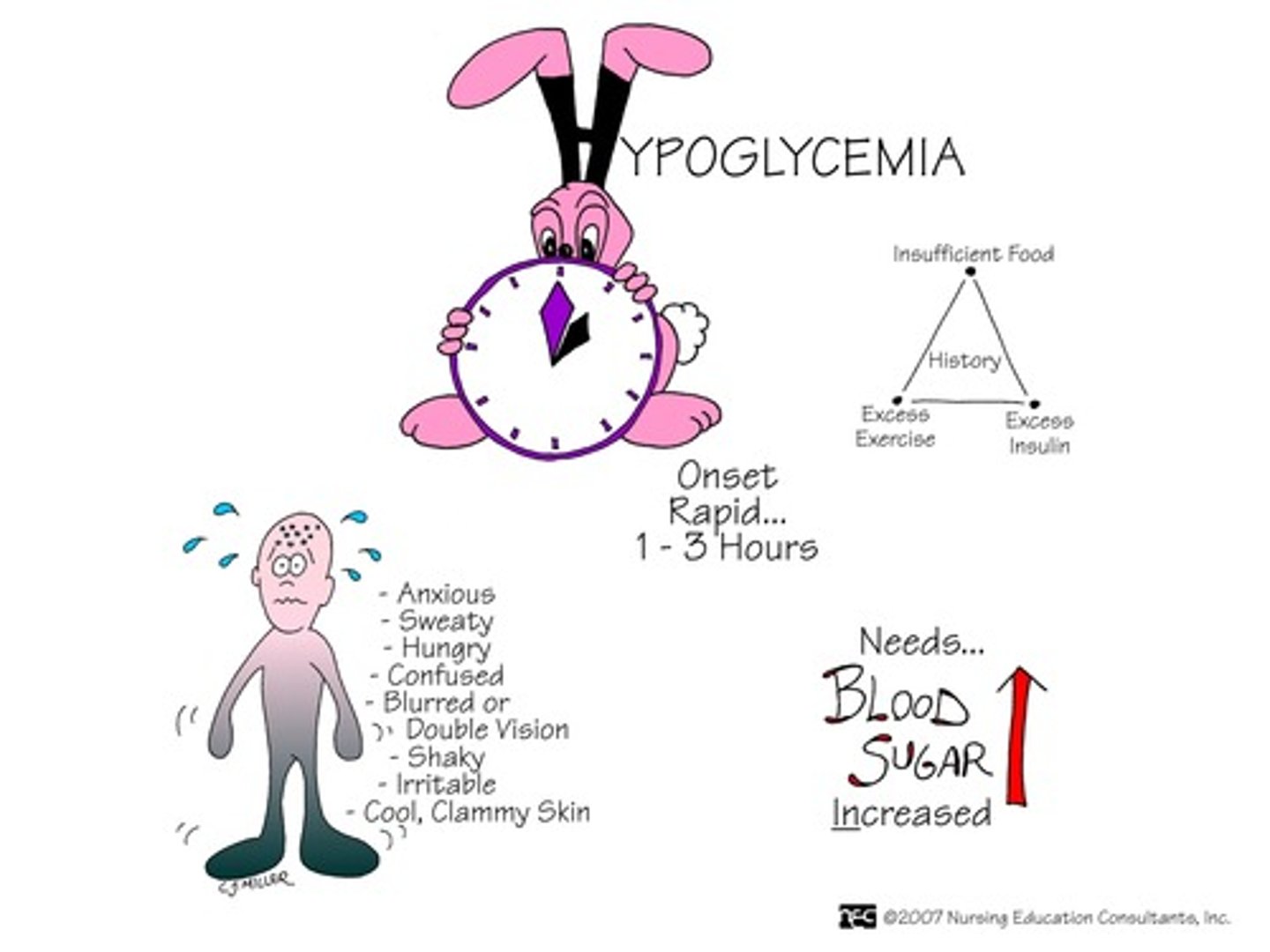
Hypoglycemia
Blood glucose less than 70 mg/dL
Sweating, shaking, dizziness, clumsiness, headache. May lose consciousness. Counteracted with glucose or carb rich substace (sugar, honey, crackers, juice)
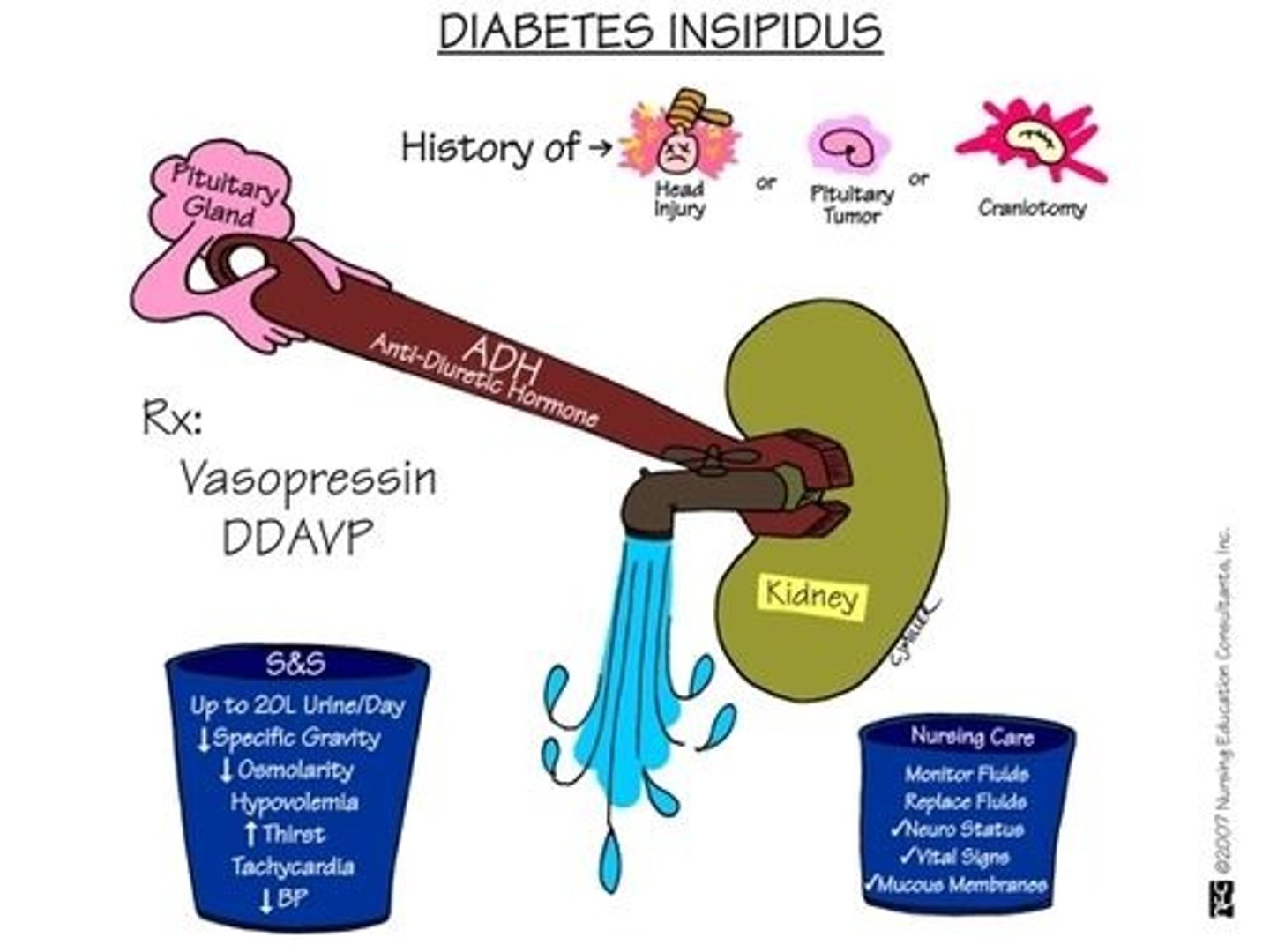
Diabetes Insipidus
Large amounts (almost 20 L per day) of urine, excessive thirst. Variety of causes
Central: lack of anti-diuretic hormone
Nephrogenic: Kidneys don't respond to ADH
Dispogenic: Hypothalmic thirst mechanism is damaged from trauma or meds
Gestational diabetes
Increase in insulin resistance and blood glucose levels during pregnancy, usually last trimester.
Babies born to women with gestational diabetes have increased levels and are usually big, increasing difficulty of delivery. Baby will have breathing difficulties, jaundice, or hypoglycemia following birth
In childhood, will be more likely to have insulin resistance, obesity, behavioral healthy disorders, delays in fine/gross motor skills
Fasting Plasma Glucose
measures circulating glucose level in a patient who has fasted at least 8 hours.
Positive for DM if blood glucose level is over 125 mg/dL
(normal is 100)
Oral glucose tolerance test
Glucose testing after two hours post injection of sugary drink.
positive for DM if level is 200 mg/Dl or higher (normal is less than 140)
A1C Testing
Blood test based on attachment of blood glucose to hemoglobin, measuring patient's glucose level over 2-3 months.
Positive if A1C level is 6.5% or higher (normal is below 5.7%)
Male Hypogonadism
Primary hypogonadism: deficiency of testosterone secondary to failure of testes to respond to FSH and LH. Most common cause is Klinefelter's
Secondary hypogonadism: Failure of hypothalamus or pituitary to produce hormones to stimulate testosterone production.
Sxs: Pre-puberty--sparse body hair, underdeveloped msk, long arms/legs secondary to no growth plate closure
Adult-onset--decreased libido, ED, infertility, decreased cognitive skills, mood changes, sleep disturbances.
Female Hypogonadism
Primary: Gonads do not produce the amount of sex steroid sufficient to supress secretion of LH and FSH at normal levels. Most common cause is Turner's (X).
Secondary: Failure of hypothalamus or pit to produce the hormones which will subsequently stimulate estrogen production. If this happens before puberty symptoms will include gonadal dysgenesis, short stature, failure to progress through puberty or primary amenorrhea and premature gonadal failure. The main post-puberty symptom is secondary amenorrhea.
Bone mineral regulating agents
- Prevent bone loss
- Examples: calcium (calcium carbonate Tums, Calderol), calcitonin (Cibacalcin), biphosphonate (Fosamax), anabolic agents (Premarin)
- Indications: Paget's disease, osteoporosis,
hyperparathyroidism, rickets, hypoparathyroidism,
cardiac arrhythmias
- Implications for PTs: Risk for fractures and side effects
Upper GI function
Mouth, Esophagus, and Stomach mechanically and chemically digest food.
Stomach uses HCl acid and digestive enzymes from liver, pancreas, and gallbladder to assist digestion
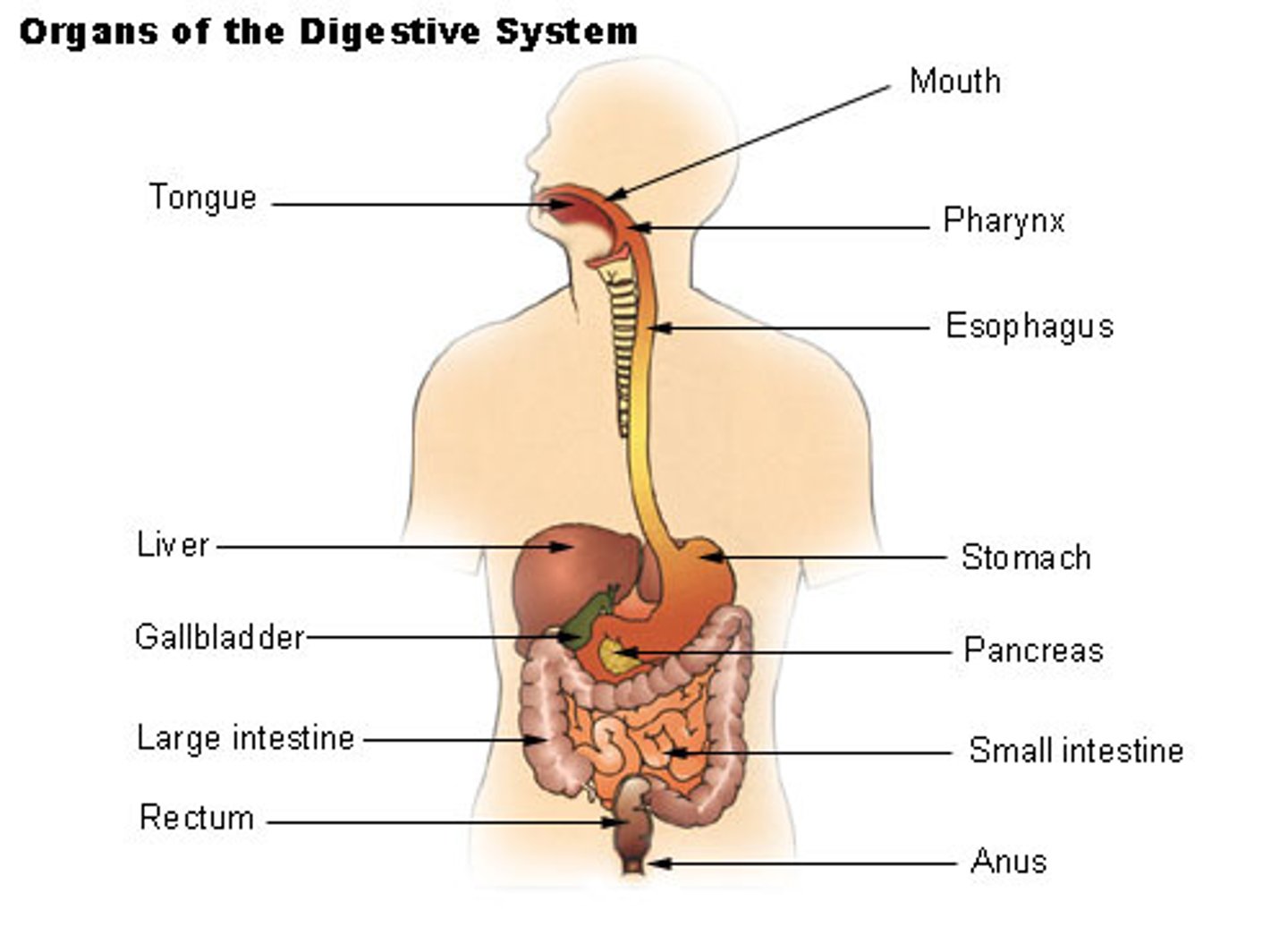
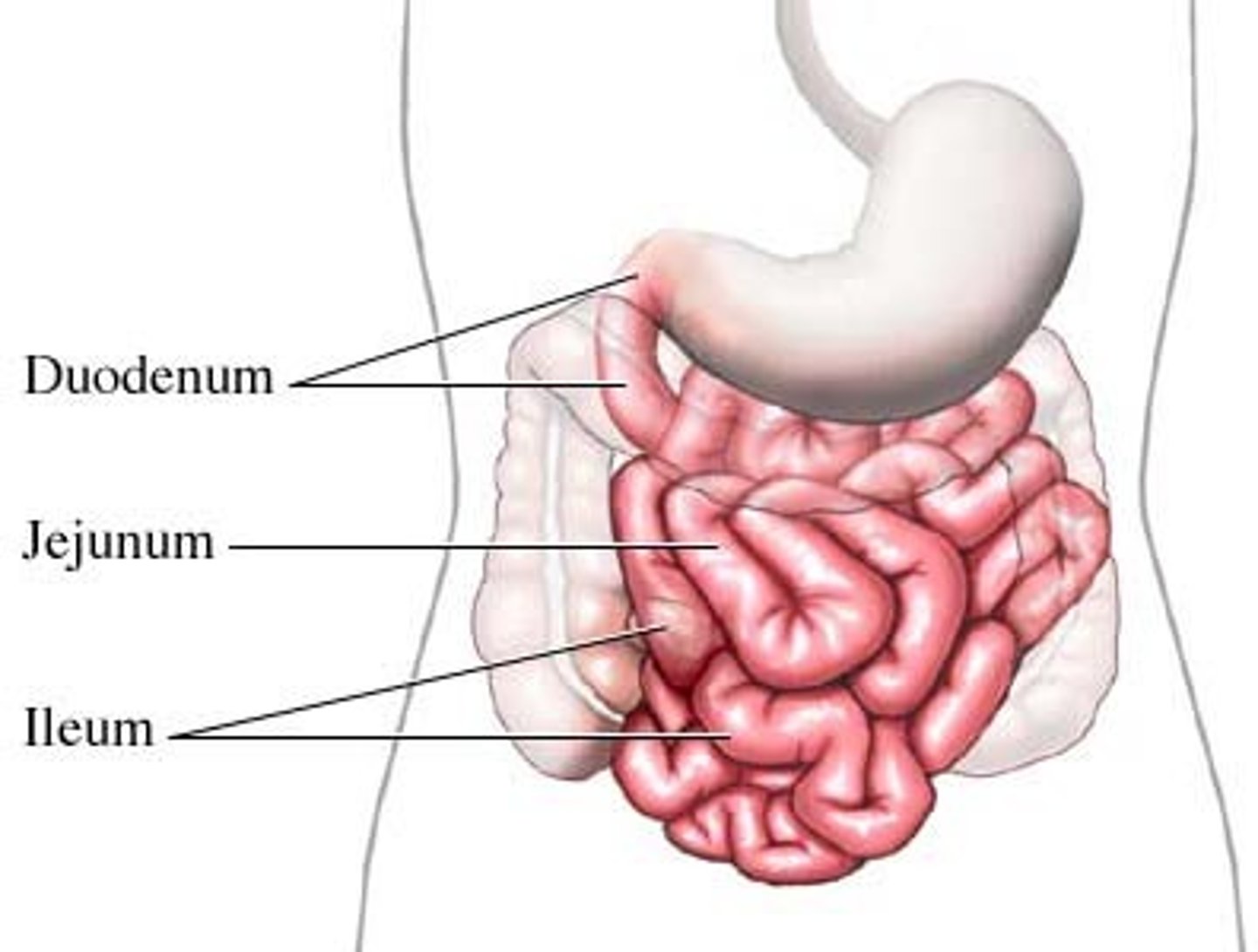
Small Intestine Function
Absorbs most nutrients; Main absorption organ of the digestive tract
Duodenum: Neutralizes stomach acid
Jejunum: Absorbs water, electrolytes, nutrients
Ileum: Absorbs bile and intrinsic factors to be recycled
Large Intestine Function
Reabsorbs water and stores and eliminates undigested food as feces
Ascending colon
Transverse Colon
Descending colon
Sigmoid Colon
Rectum
Anus
Gallbladder
Stores and releases bile into duodenum to assist digestion
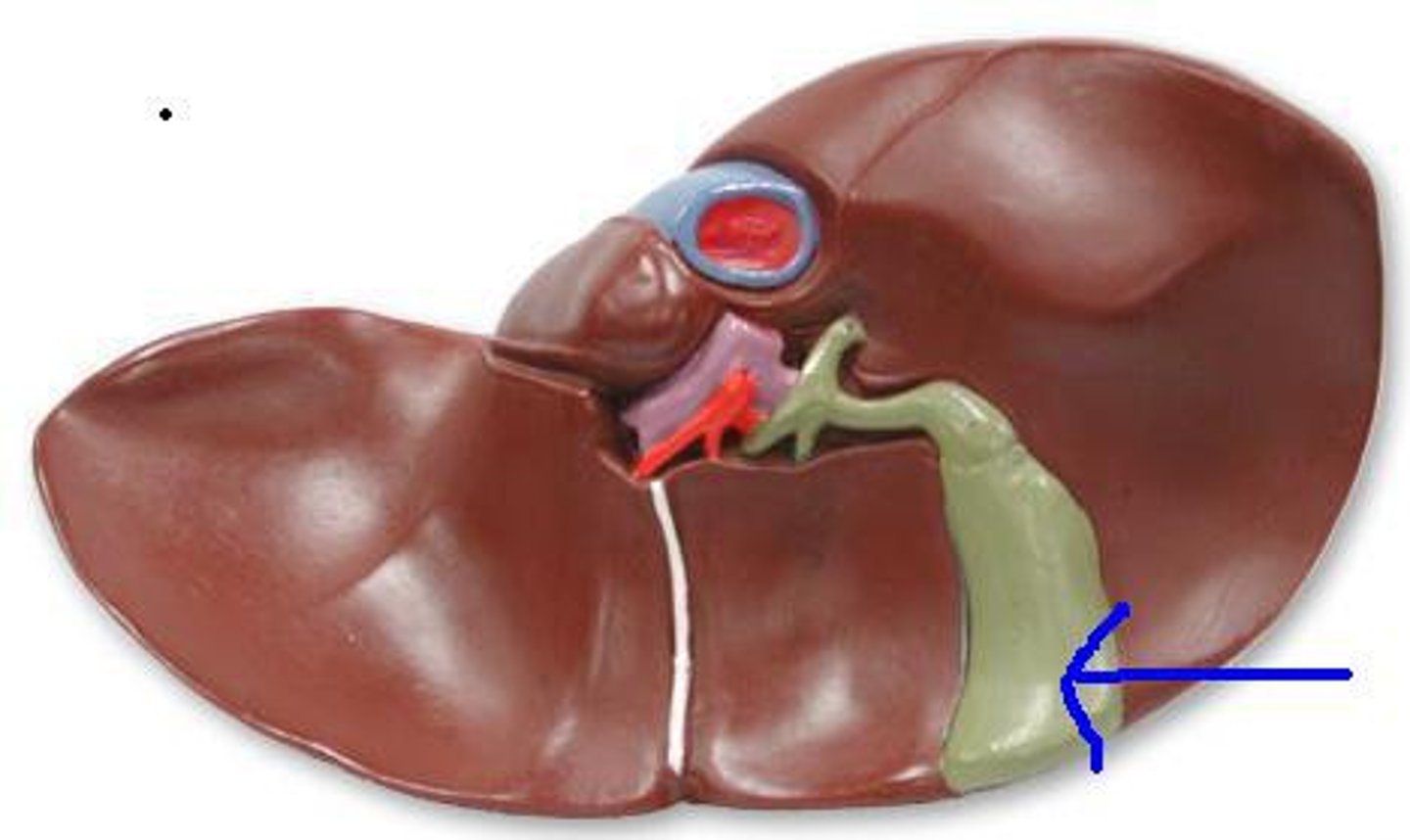
Liver
Produces bile which emulsifies fat, produces RBCs and vitamin K, regulates serum level of carbs, proteins, and fats
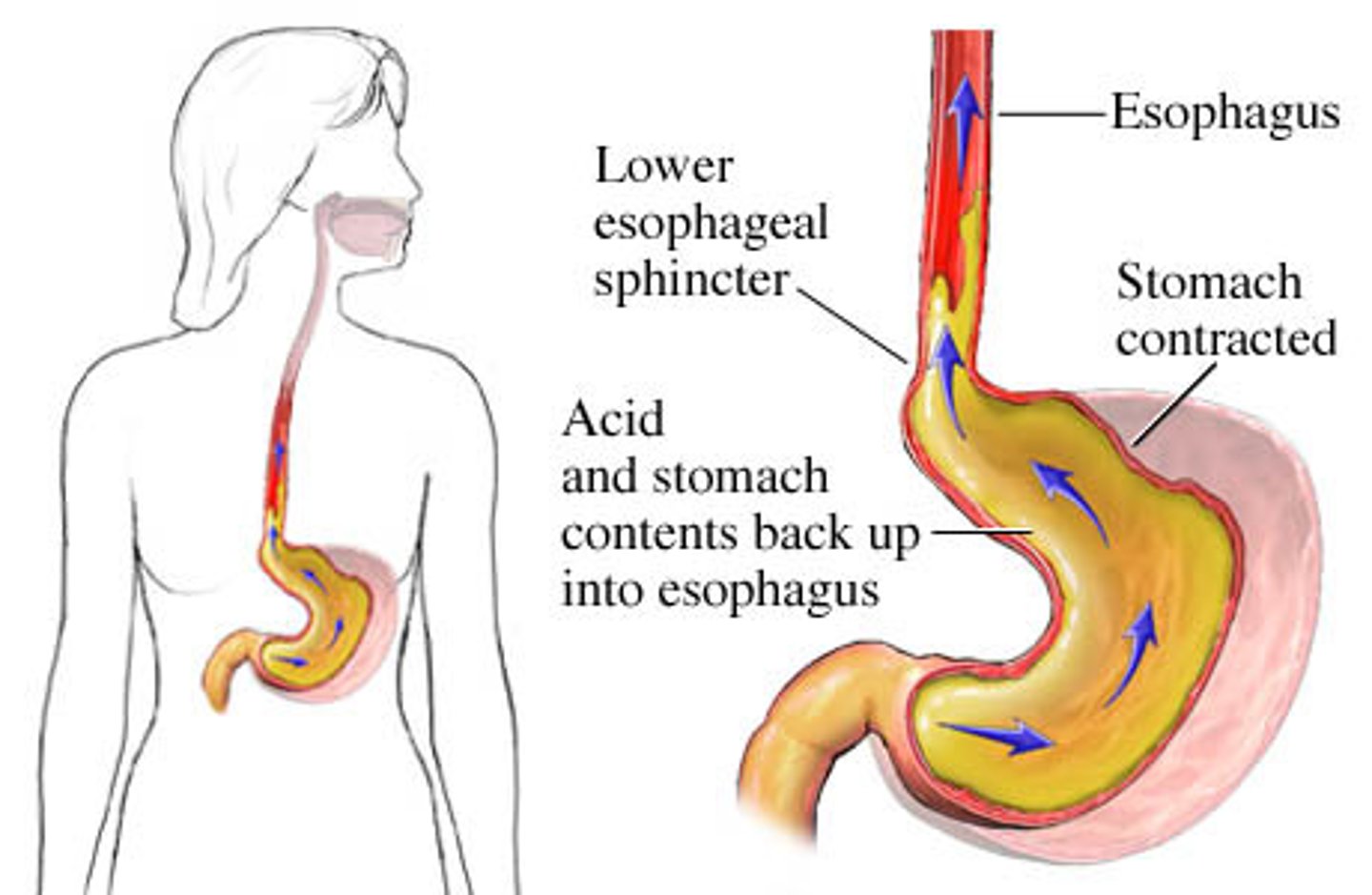
gastroesohageal reflux disease (GERD)
Incompetent lower esophageal sphincter allows gastric contents to move backward, causing esophageal tissue injury over time. Occurs in 20-30% of adults and some newborns or infants
Sxs: Heartburn, belching, chest pain, coughing, esophagitis, hematemesis. If untreated, may develop esophageal strictures, esopaghitis, aspiration pneumonia, asthma, and esophageal adenocarcinoma
PT Rehab Considerations: Avoid certain exercises, recumbency will induce symptoms. Head/neck discomfort secondary to perception of lump in throat and subsequent compensation. Tight clothing, exercise, and constipation may precipitate it. Chronic bronchitis, asthma, and pulmonary fibrosis may present with GERD.
Have them sleep in left sidelying with pillows elevated (lower esophagus bends to left, so reflux is minimized)
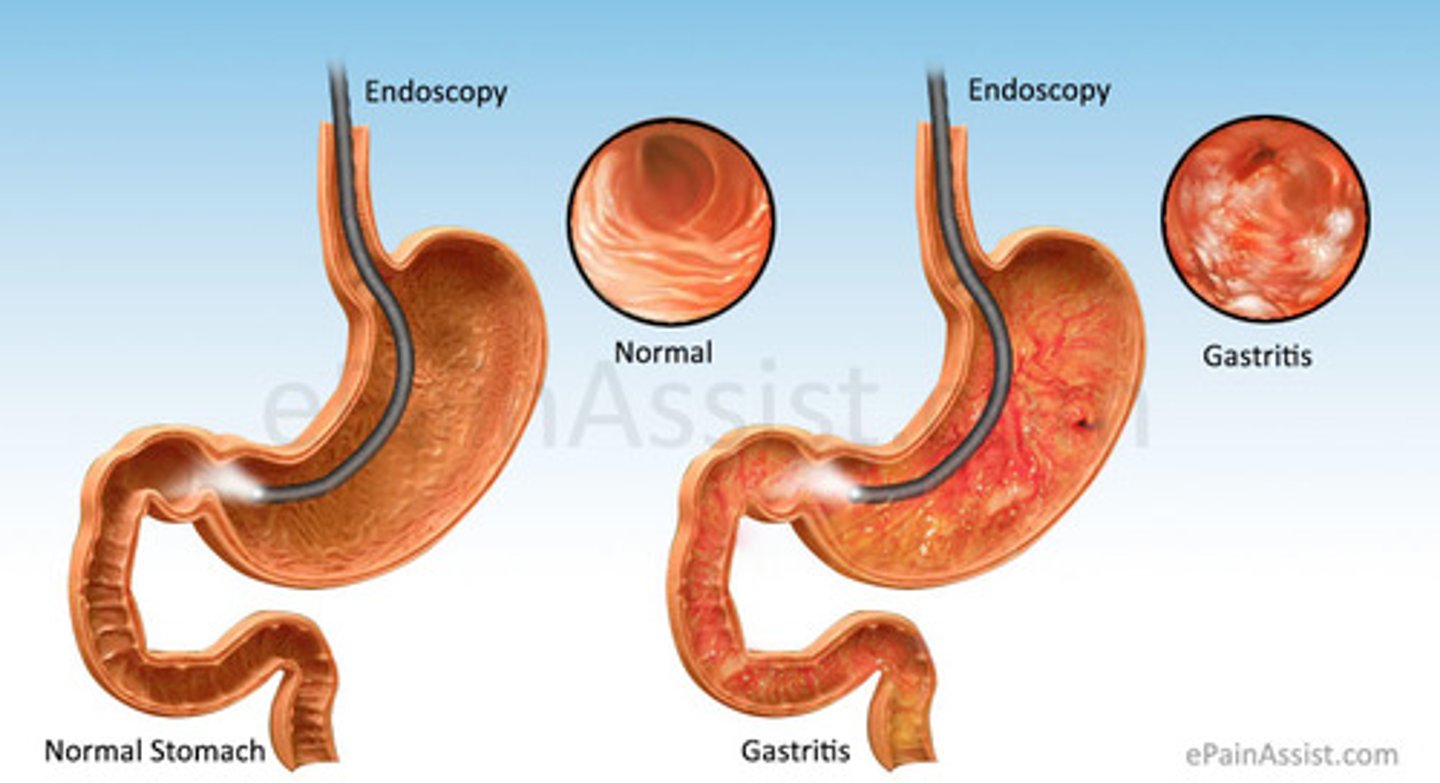
Gastritis
Inflammation of gastric mucosa (stomach lining) with similar symptoms to GERD but greater intensity. Can be erosive (acute) or non-erosive (chronic type B).
Patients should avoid all aspirin containing compounds. If blood in stool, initiate physician referral.
Erosive Gastritis
Inflammation and bleeding of gastric mucosa due to stress, NSAIDs, alcohol, viral infection, or direct trauma.
Sxs: Dyspepsia, nausea, vomiting, and hematemesis. Pt may be asymptomatic. May progress to gastric ulcer
Non-erosive Gastritis
Inflammation of gastric mucosa as a result of H.Pylori bacterial infection.
Sxs: May be asymptomatic, but will show symptoms in progression.
Tx: H. Pylori is a carcinogen and should be treated with aggressive pharmacological intervention, including proton pump inhibitor and antibiotics
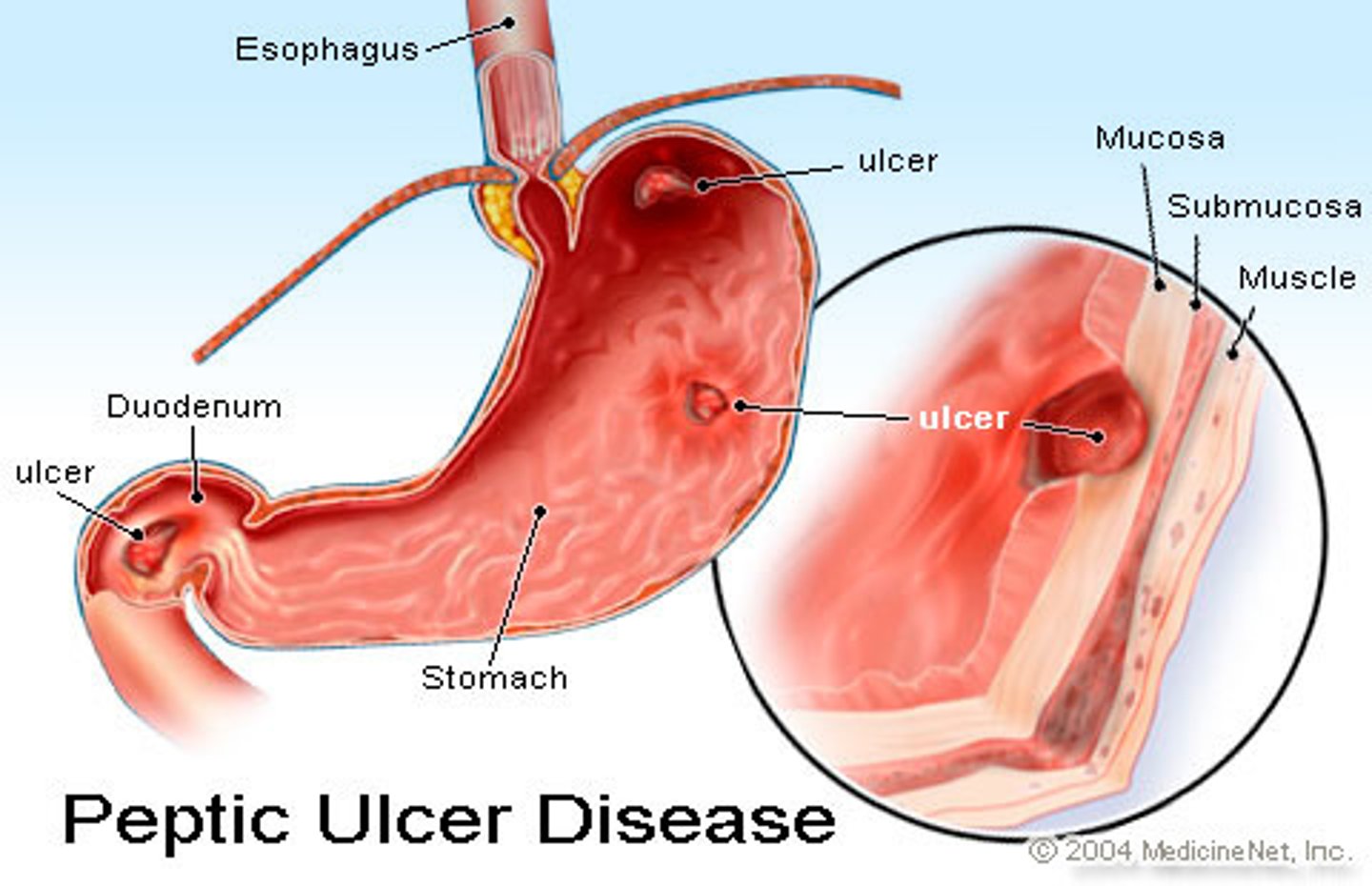
Peptic Ulcer Disease
Disruption or erosion in GI mucosa due to imbalance between protective mechanisms of stomach and secretion of acids in stomach. Causes include H pylori, chronic NSAId use, stress, alcohol, some meds and food, smoking
Sxs: Dependent on location and severity. Can include epigastric pain, burning or heart burn, nausea, vomiting, bleeding, bloody stools, pain in waves that is relieved by eating.
Specific to H. Pylori: halitosis, rosacea, and flushing.
HR increase or BP decrease may be signs of bleeding
Perforated ulcer on posterior wall of stomach may present as back pain!
Midthoracic to Right upper quadrant and shoulder may signify blood in peritoneal cavity secondary to perforated ulcer
Malabsorption Syndrome
Group of pathologies where intestinal absorption and nutrition are inadequate. Occurs secondary to defects in digestion, or inability of intestinal mucosa to absorb nutrients
-Celiac
-CF
-Pancreatic Carcinoma
-Pernicious Anemia
-AIDS
-Crohn's
-Addison's Disease
Risk for osteoporosis and fractures, and swelling/spasms secondary to electrolyte imbalances and protein depletion.
Irritable Bowel Syndrome
Colon or large intestine are sensitive to certain foods or stress. Symptoms may be triggered by anxiety, caffeine, smoking, alcohol, or fat intake.
Sxs: Abdominal pain/bloating/distension, nausea, vomiting, changes in form/frequency of stool, passing of mucus in stool
Tx: Diagnosis of exclusion from other GI diagnoses. Change in lifestyle, nutrition, stress, adequate sleep and exercise. Avoid milk, wheat, rye, barley, alcohol, and caffeine.

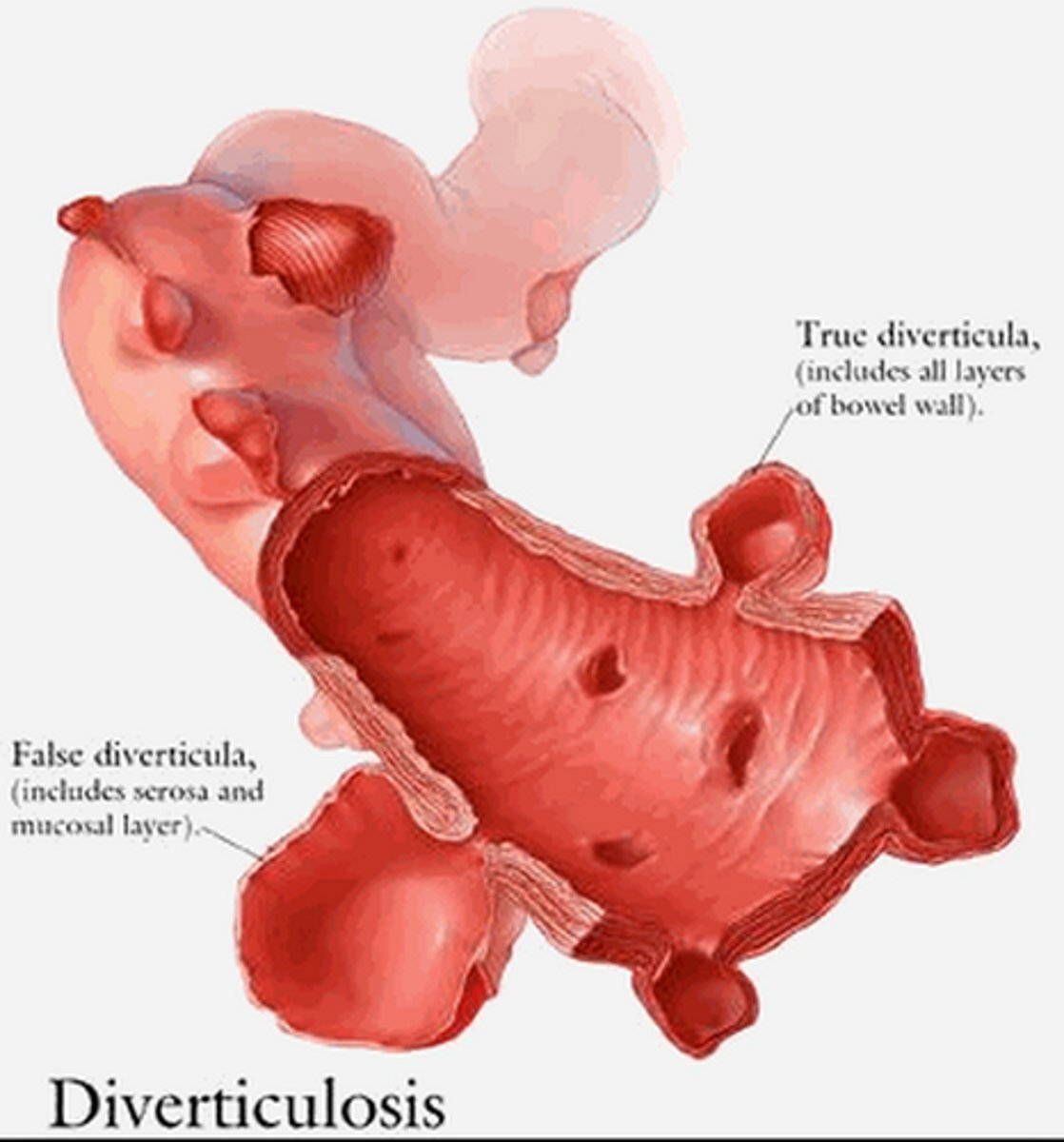
Diverticulitis
Inflammation in diverticula (pouch-like protrusions in colon). 80% of diverticulosis is asymptomatic, but 20% may progress to diverticulitis. May be a result of low fiber diet.
Sxs: Abdominal pain, with tenderness over left side of lower abdomen. Cramping, constipation/diarrhea, nausea, fever, chills, vomiting.
Tx: Diet modification, lower internal colonic pressure through increased fiber. Nasogastric tube for severe cases.
Hepatitis A
Ends in a vowel, comes from the bowel. Transmission is by close personal contact with someone who has the infection or through fecal-oral route (contaminated water or food source).
Flu like symptoms, usually does not progress to chronic disease or liver cirrhosis. Pts recover in 6-10 weeks
Hepatitis B
B= blood and body fluids (hep c is the same)
Transmitted via blood and bodily fluids (sharing of needles, intercourse, exposure to blood, semen, or maternal-fetal exposure)
10% of cases progress to chronic Hep
Tx: Hepatitis B Immunoglobulin, then vaccination series.
Hepatitis C
Blood, semen, or bodily fluid transmission.
90% of post-transfusion hep cases. Often asymptomatic, acute infection can be mild Increased frequency of hashimoto's, DM, and corneal ulceration. No vaccine available. Chronic hep occurs in 50% of cases, 20% of those progress to liver cirrhosis
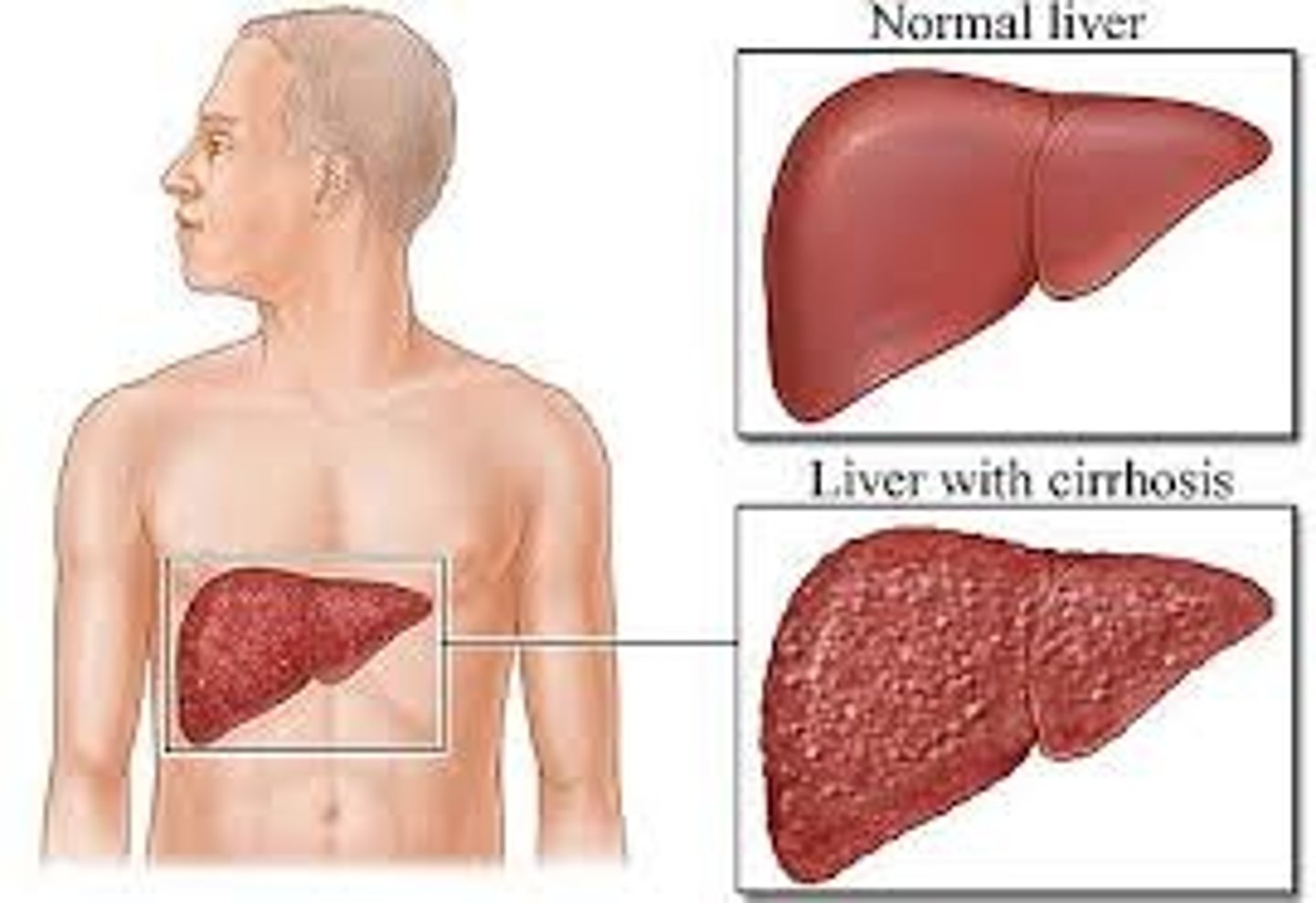
Cirrhosis of the Liver
Healthy tissue of liver replaced with scar tissue which blocks blood flow through liver and prevents liver from properly functioning.
Etiology: Alcoholism (over a decade), hep C, B, D, certain drugs, infections, toxins, heredity, steatohepatitis, blocked bile ducts.
Alcohol blocks normal metabolism of protein fats and carbs. Cirrhosis occurs after >a decade of alcoholism. Hep C causes inflammation - results in cirrhosis after > 2 decades.
Sxs: Fatigue, decreased appetite, abdominal pain, spider angiomas, weight loss. Ascites, LE edema, jaundice, gallstones, bleeding, immune system dysfunction, varices.
Cholecystitis
Inflammation of the gallbladder, usually associated with cholelithiasis (gallstones).
Sxs: Can be asymptomatic, but most common symptom is RUQ pain. If gallstone is lodged in cystic duct, patient can have severe pain that radiates to interscapular region.
Tx: Low fat diet to decrease gallbladder stimulation. Lithotripsy if symptomatic to break up stones. Can use laparoscopic cholecystectomy to completely remove gallbladder.
Acute cholecystitis resolves in a week.
Antibiotics for H. Pylori
Clarithromycin
Amoxicillin
Tetracycline
Metronidazole
Antacids for GERD, peptic ulcer, gastric indigestion
Basaljel (Aluminum carbonate)
Tums (Calcium carbonate)
Milk of magnesia (magnesium hydroxide)
Bromo Seltzer (sodium bicarbonate)
Antidiarrheals
Pepto Bismol (bismuth subsalicylate)
Motofen (difenoxin)
Imodium (loperamide)
Donnagel (attapulgite)
Kapectolin (Kaolin)
Antiemetics
Meclizine
Scopolamine
Dolasetron
Phenergan
Emetics
Apomorphine, Ipecac
H2 Receptor Blockers
Prevents the release of stomach acid to promote ulcer healing
Pepcid (famotidine)
Zantac (ranitidine)
Tagamet (cimetidine)
Laxatives
Metamucil (Psyllium)
Colace (Docusate)
Glycerin Suppository
Milk of Magnesia
Correctol (Bisacodyl)
Senokot (Senna)
Citrucel (Methylcellulose)
Proton Pump Inhibitors
Inhibit the action of the gastric proton pump, thereby reducing gastric acid production. They usually have the suffix "PRAZOLE". Used for dyspepsia and GERD
Nexium (Esomeprazole)
Prilosec (Omeprazole)
Protonix (Pantoprazole)
Prevacid (Lansoprazole)
AcipHex (Rabeprazole)
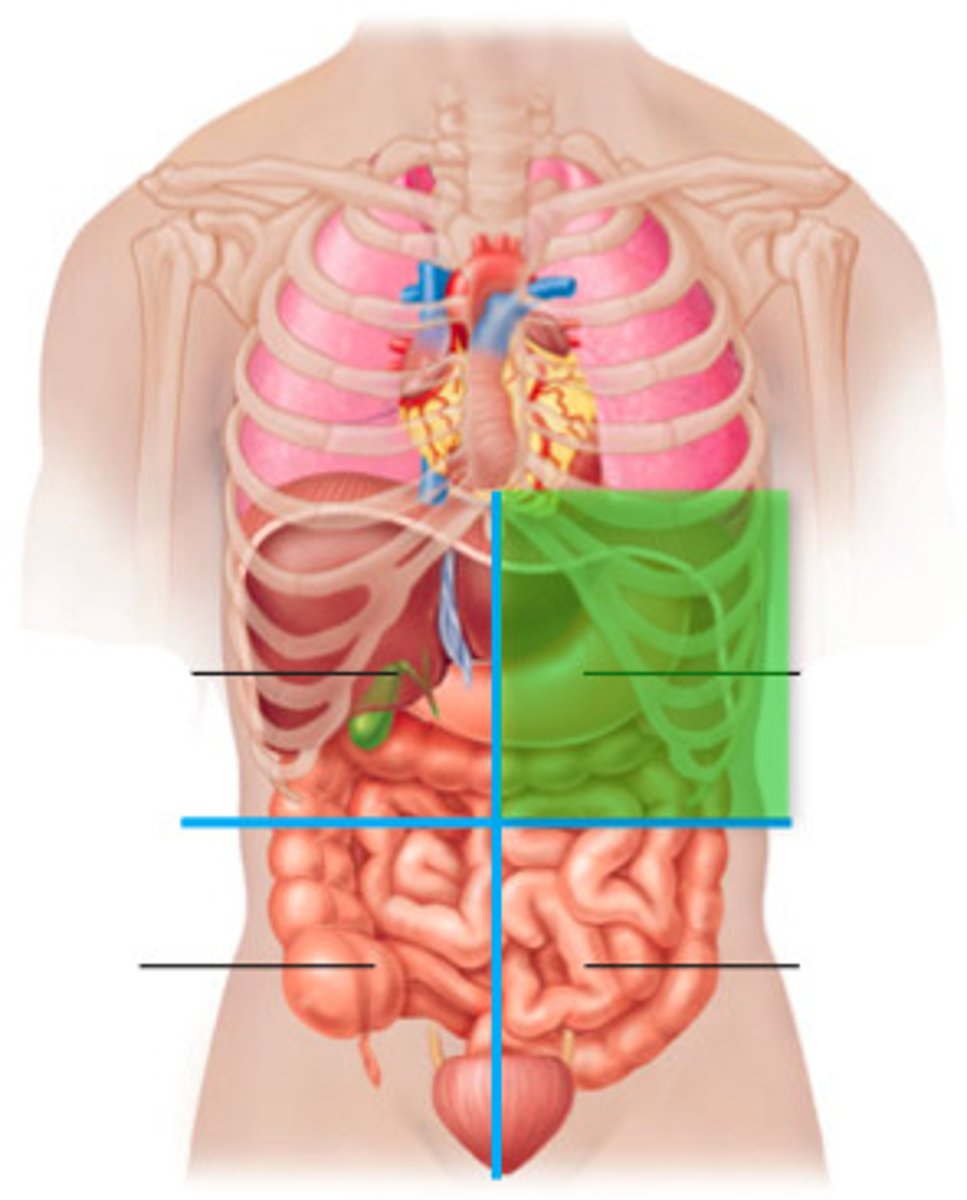
LUQ pain
Gastric Ulcer
Pancreatitis
Perforated Colon
Spleen injury or rupture
Pneumonia
Aortic Aneurysm
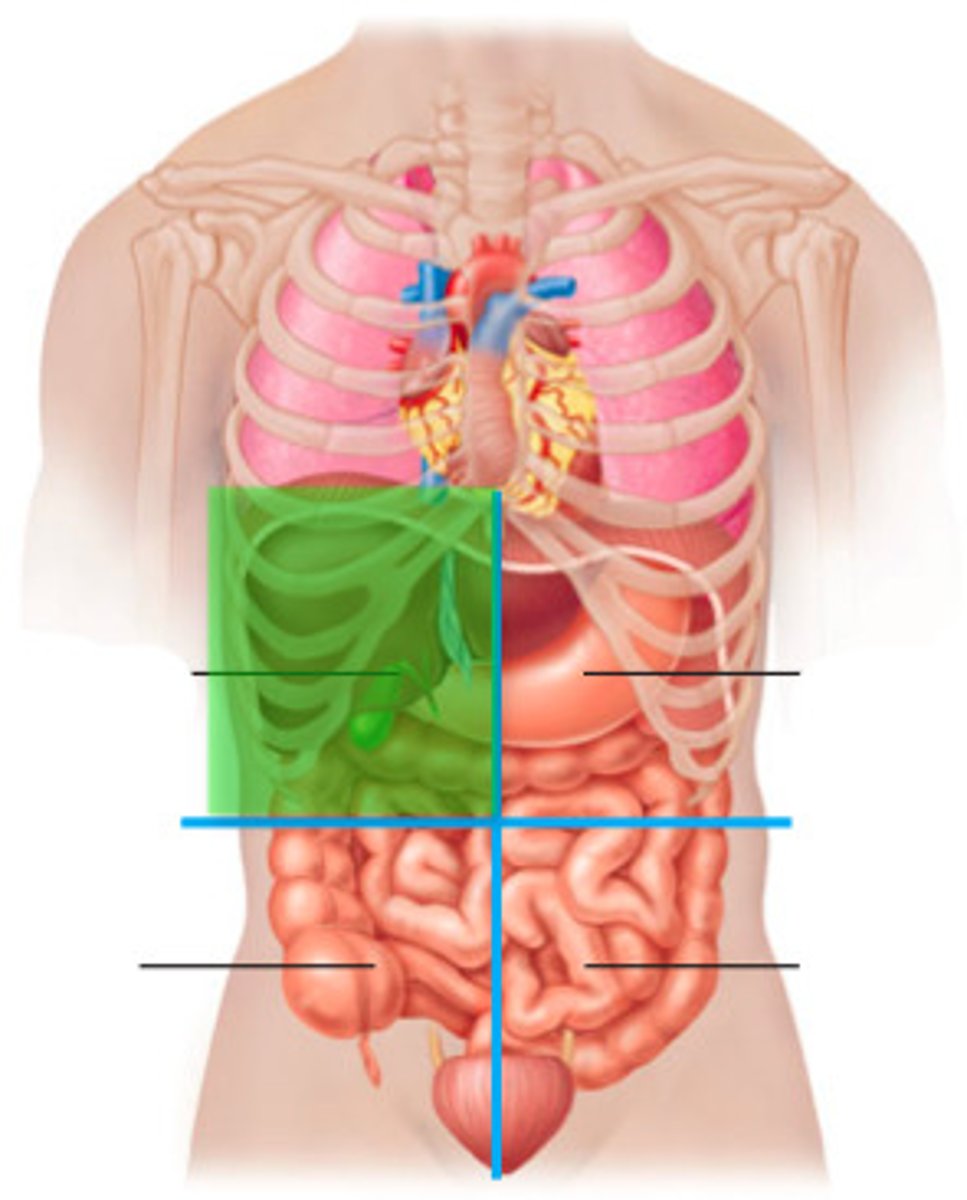
RUQ pain
Cholecystitis
Hepatitis
Duodenal Ulcer
Biliary Stones
LLQ pain
Kidney stone, ureteral stone
Intestinal Obstruction
Sigmoid Diverticulitis
Perforated Colon
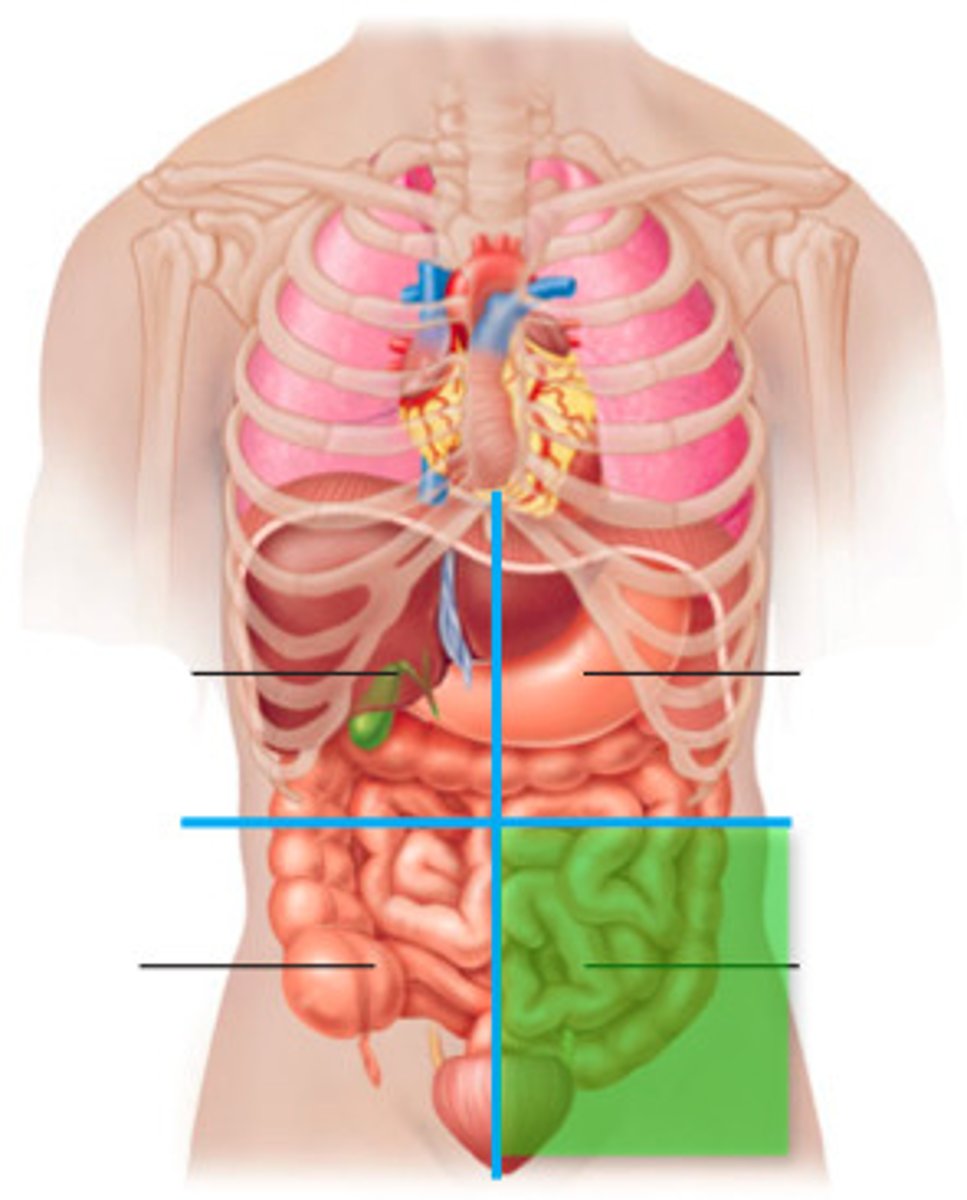
RLQ pain
Appendicitis
Kidney stone/Ureteral Stone
Meckel Diverticulum
Cholecystitis
Intestinal Obstruction
Kidneys
Filter water, salt, and metabolic waste from blood through urine excretion
Contributes to homeostasis--acid/base balance, regulation of electrolytes, blood volume control, BP control via hormone

Ureters
the tubes connecting the kidneys to the bladder
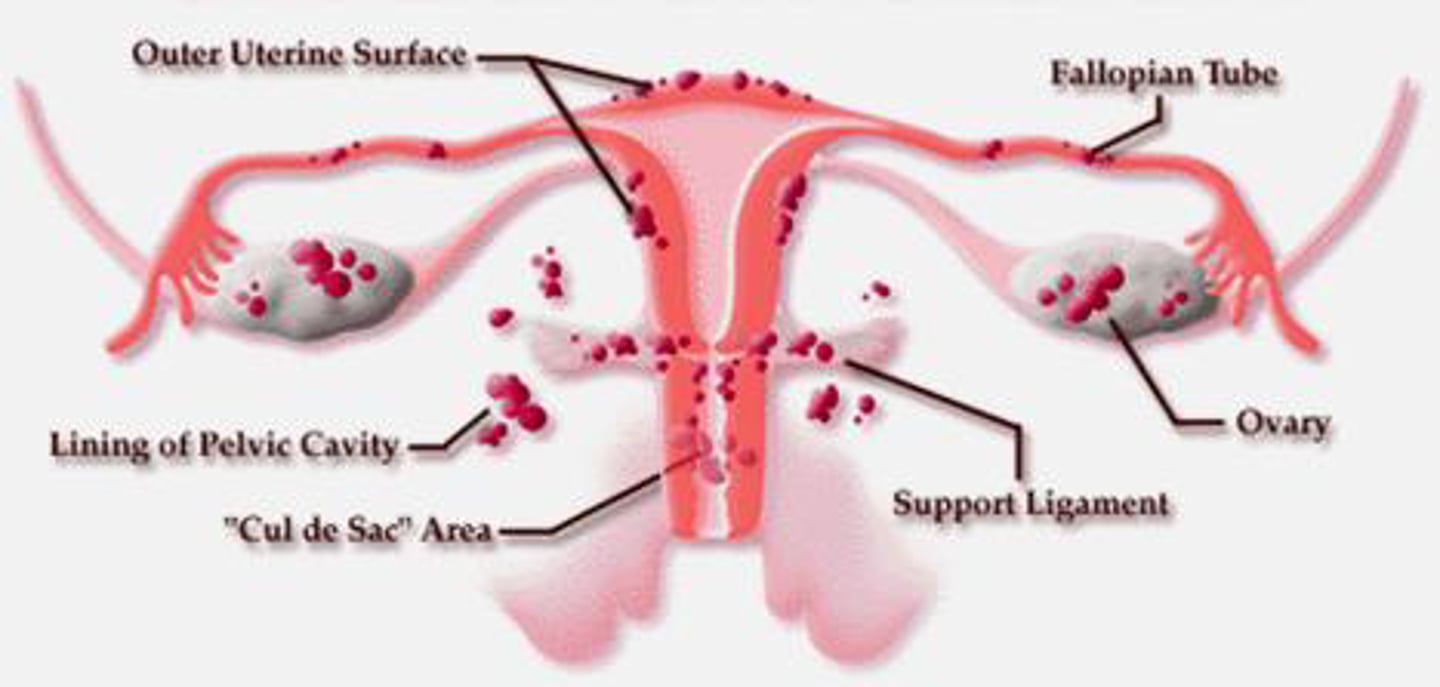
Endometriosis
Development of endometrial tissue normally lining the uterus in extrauterine locations in abdomen and pelvis, most commonly the uterosacral ligaments. Each menstrual cycle the tissue bleeds, causing scarring and adhesions.
Sxs: Mod to severe abdominal, pelvic, or LBP before/during menstruation, irregular cycles, PM spotting, dyspareunia, pain during defecation, infertility
Tx: Manual therapy to break up scar tissue/adhesions, mobility to sustain elongation of tissues, surgery to remove endometrial tissue or total hysterectomy
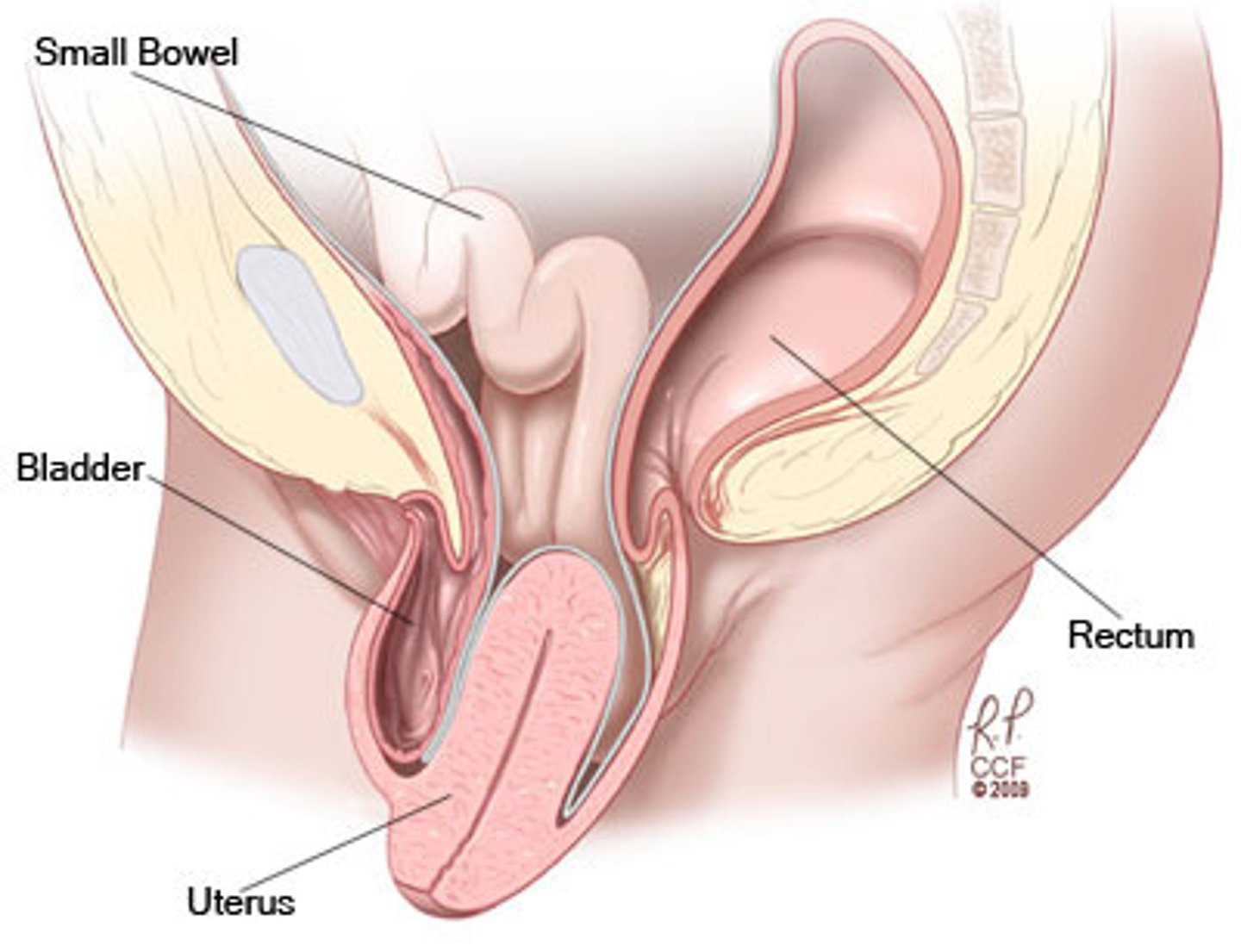
Uterine Prolapse
Descent of uterus and cervix into vagina due to genetics, denervation, or muscular trauma from labor and delivery.
-Classified using Baden-Walker system using 5 point grading scale (0 = no prolapse, 5 = max descent of tissue outside body)
Sxs: Pelvic pressure with exertion, urgency/frequency, urinary incontinence, incomplete bladder emptying, discomfort, vaginal dryness, dyspareunia, lower back pain relieved by lying down
Tx: Pessary for severe cases. Positioning and pelvic floor training
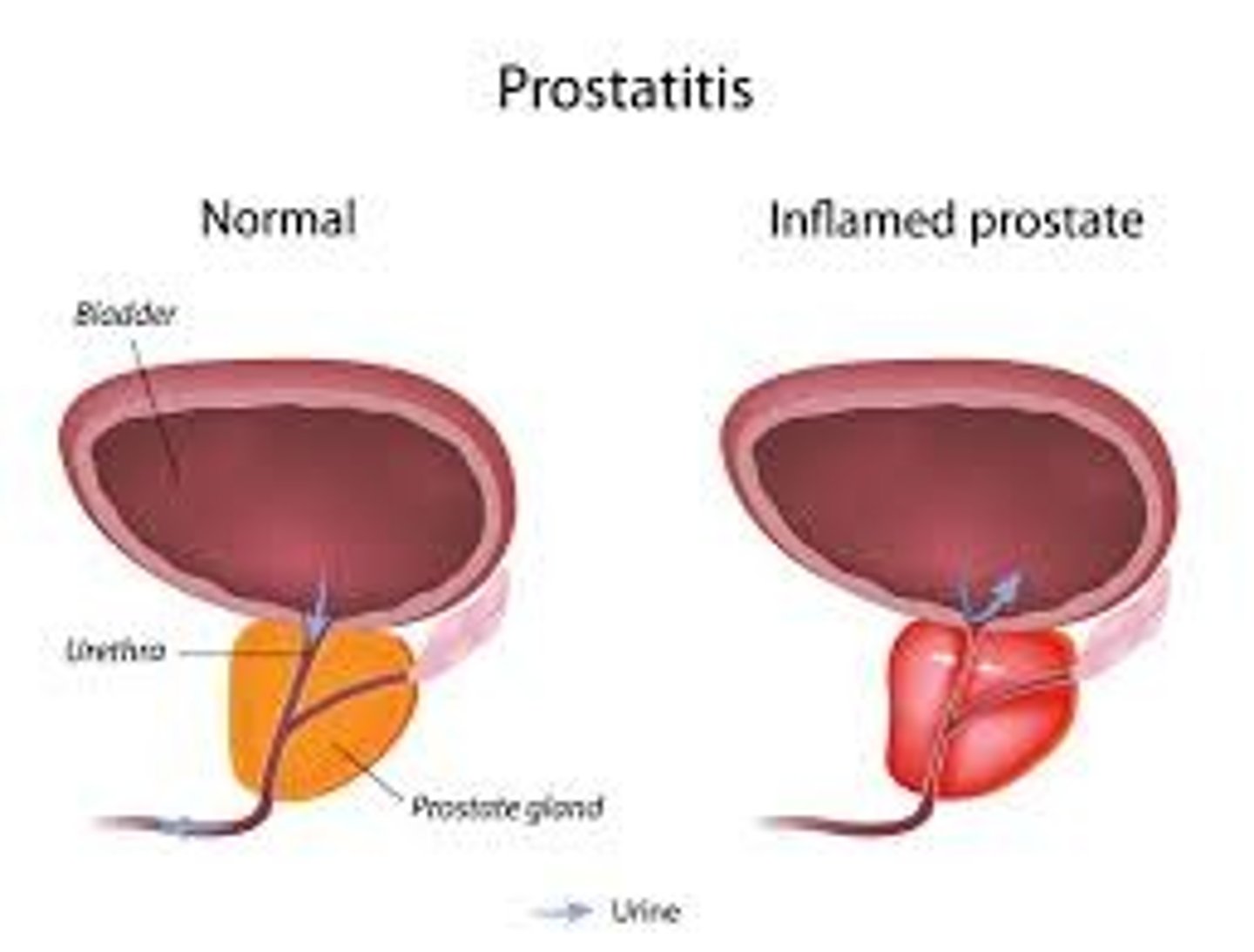
Prostatitis
Inflammation of prostate gland due to bacterial infection, or back up of prostate secretions in the gland.
I. Acute Bacterial
II. Chronic Bacterial
III. Chronic Pelvic Pain Syndrome
IV. Asymptomatic Inflammatory Prostatitis
Sxs: Urgency, frequency, discomfort with urination and pain with ejaculation.
-Chronic pelvic pain syndrome--pain in perineum, rectum, prostate, penis, testicles, abdomen.
-Asymptomatic inflammatory prostatitis--prostate inflammation in absence of genitourinary tract symptoms
Erectile Dysfunction
Inability of adult male to achieve or maintain an erection. Caused mainly by diabetes, CHD, HTN, hypothyroidism, hypopituitarism, MS, excess alcohol, hormonal imbalances
Renal Failure
Kidneys experience a decrease in glomerular filtration rate, and fail to adequately filter toxins and waste from blood. Occurs due to DM or HTN, or from poison, trauma, and genetics, damaging nephrons so they cannot filter blood.
Can be:
Acute
Chronic
End-stage
Sxs: Nausea, vomiting, lethargy, pruritus, GI ulcers, sleep disorder, anemia, PE, seizure, coma
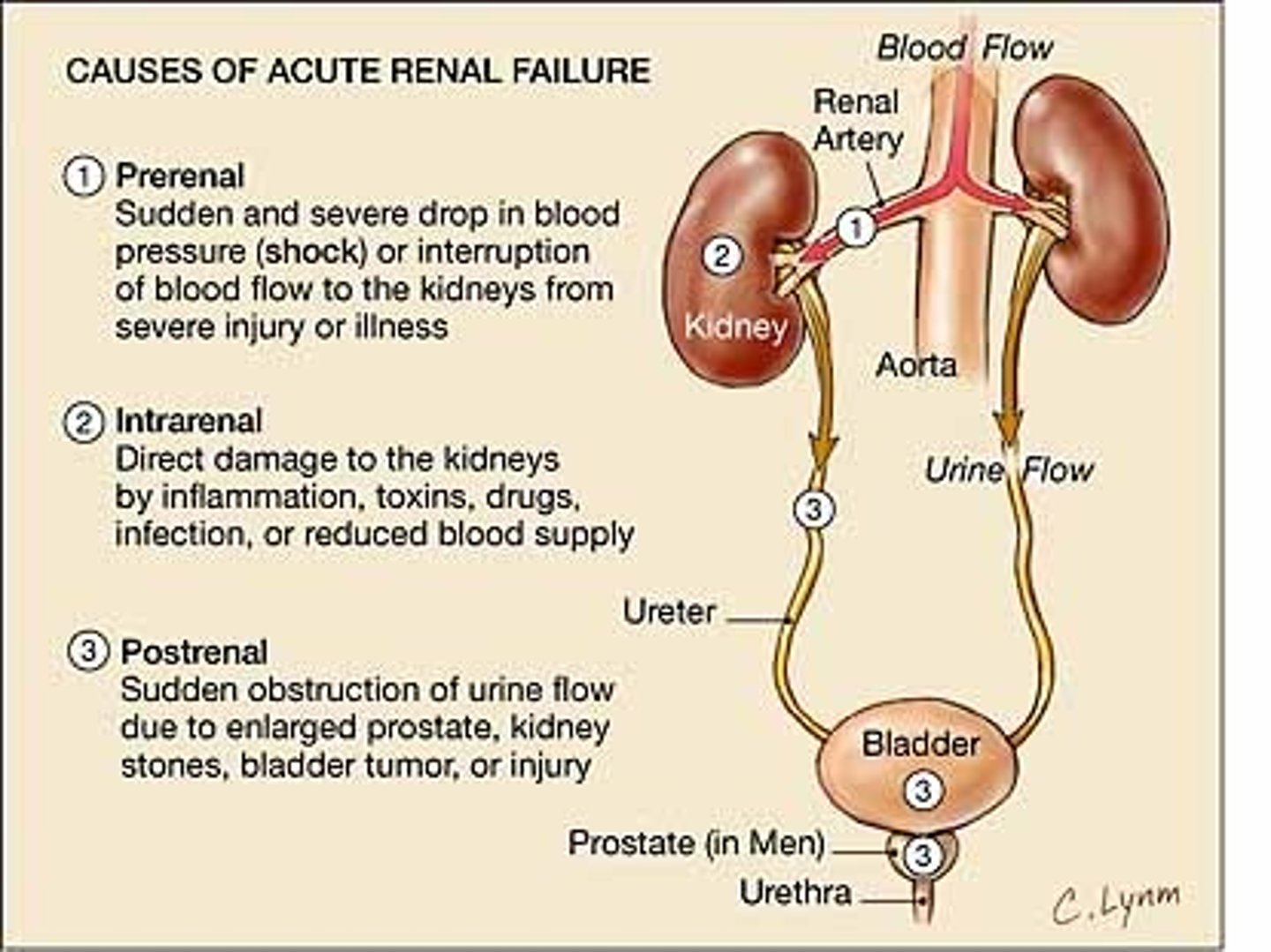
Acute Renal Failure
Sudden decline in kidney function increase in BUN and creatine, oliguria, hyperkalemia, and sodium retention
-Prerenal--Shock, hemorrhage, burn, or PE
-Postrenal--Neoplasm, kidney stone, prostate hypertrophy
-Intrarenal--Toxins, intrarenal ischemia, vascular disorders
Chronic Renal Failure
Progressive deterioration in renal function due to DM, severe HTN, glomerulopathies, obstructive uropathy, interstitial nephritis, or polycystic kidney disease
Stages of Kidney Disease
1 - Kidney damage with normal GFR (>90)
2 - Mild decrease in GFR (60-89)
3 - Moderate decrease in GFR (30-59)
4 - Severe reduction in GFR (15-29)
5 - Kidney failure (GFR <15)
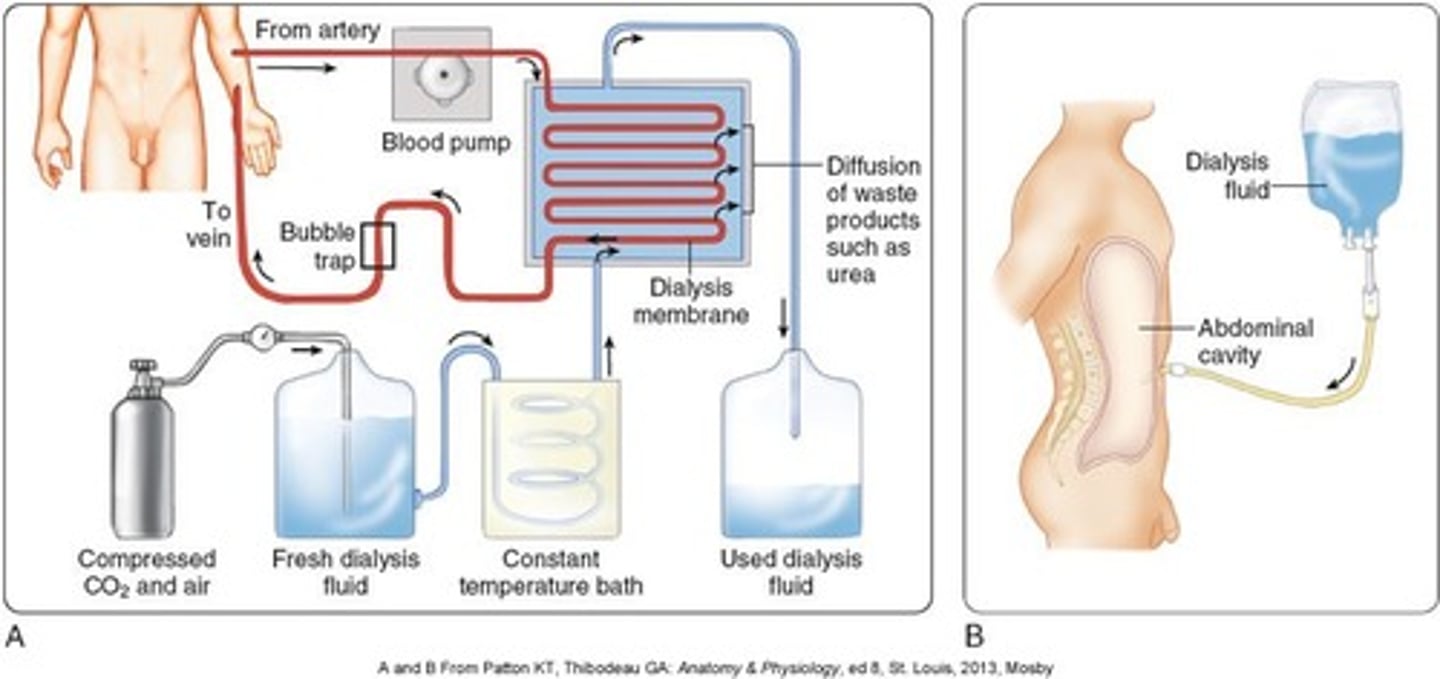
Hemodialysis
Treatment process for patients with advanced and permanent kidney failure. This process removes blood from the body, cleanses the blood, and returns it to the body. Patient must attend 3x/week for 3-5 hours at a time.
Side effects may include anemia, pruritus, sleep disorders, and amyloidosis (amyloid deposits in organs and tissue)
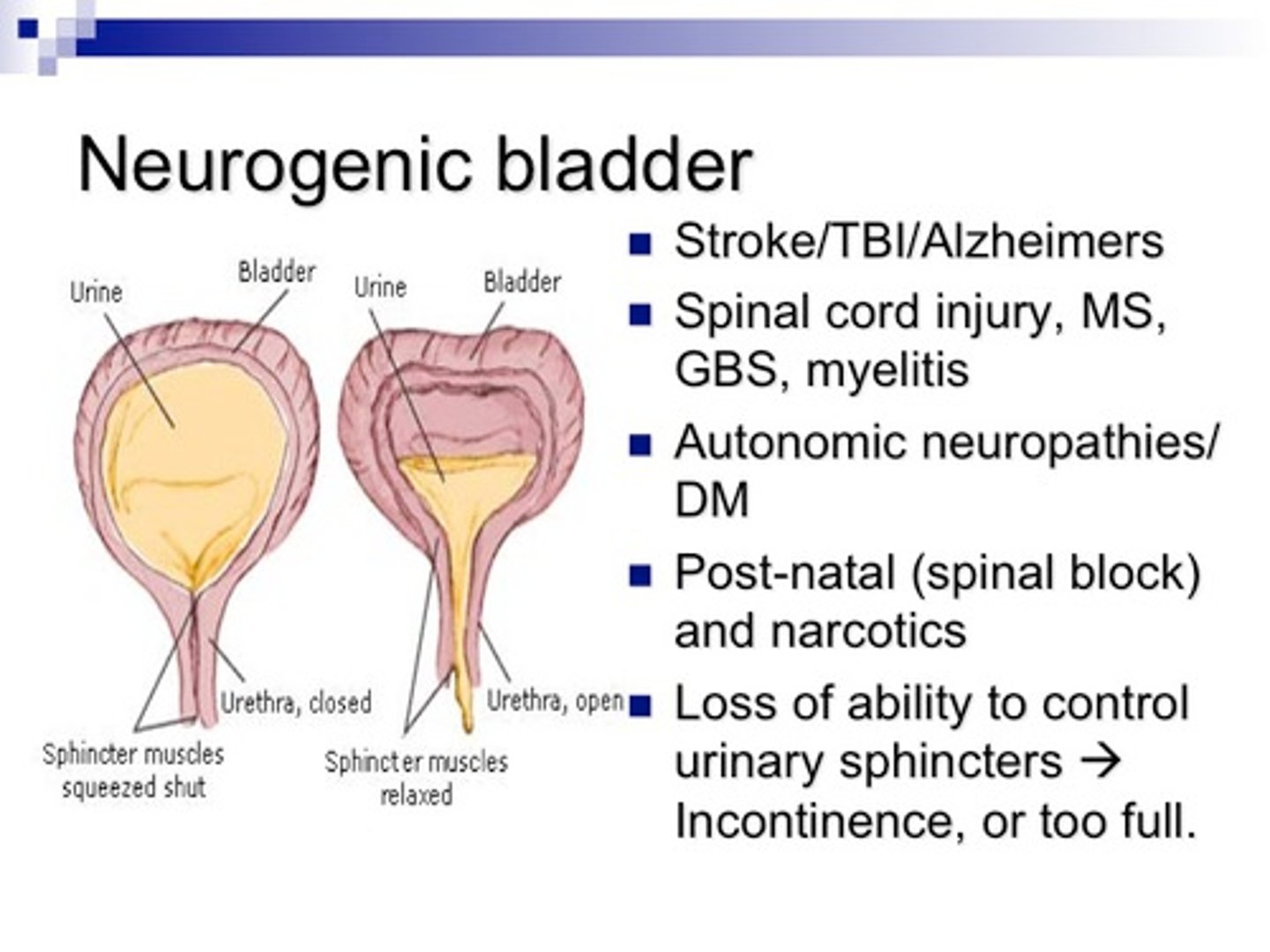
Neurogenic Bladder
Damage to cerebral control of bladder from diabetes, CVA, or nerve damage, and allows for urinary dysfunction that can increase UTIs and kidney damage.
Sxs: Frequent UTIs, urine leakage, inability to empty or los of urge to urinate with full bladder. Urodynamics to diagnose.`
Urinary Incontinence
Involuntary loss of urine great enough to be problematic for the person, typically when bladder pressure exceeds sphincter resistance.
Classified as:
Stress Urinary Incontinence
Urge Urinary Incontinence
Overflow Urinary Incontinence
Functional Urinary Incontinence
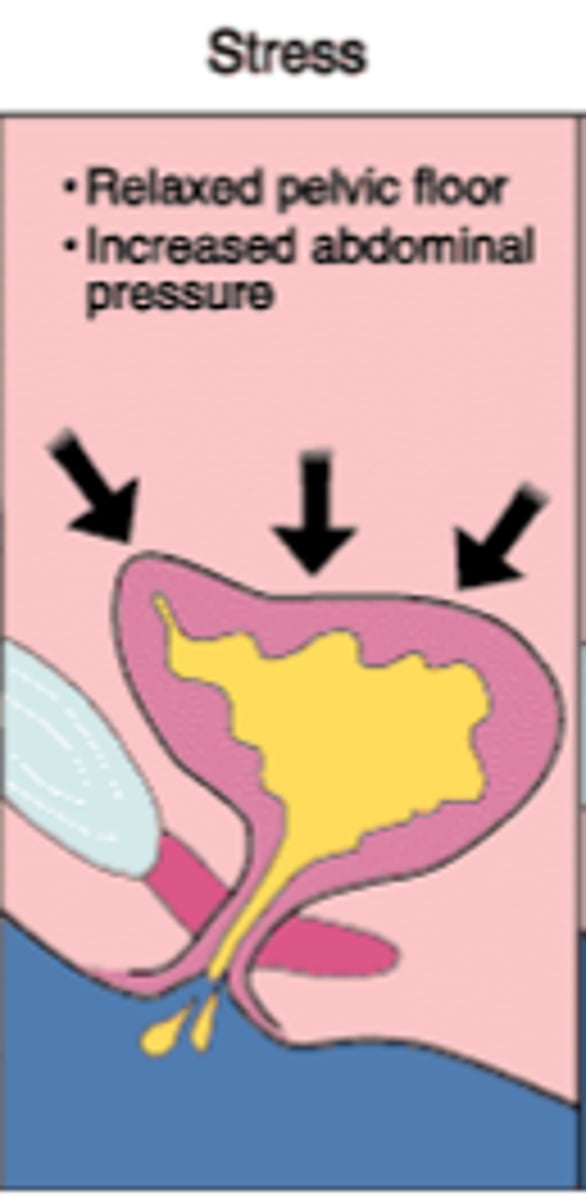
Stress Urinary Incontinence
Loss of urine due to activities that increase intra-abdominal pressure, such as sneezing, coughing, laughing, running, and jumping.
Urge Urinary Incontinence
loss of urine after a sudden, intense urge to void due to the detrusor muscle of the bladder involuntarily contracting during bladder filling. Common in geriatric population and among residents in long-term care facilities
Sxs: Urination triggered due to conditioned reflex, i.e. "key in lock" syndrome or running water
Tx: Behavior modification, biofeedback, pelvic floor strengthening, and bladder retraining via scheduled voiding
Detrusor
the smooth muscle that forms most of the bladder wall and aids in expelling urine
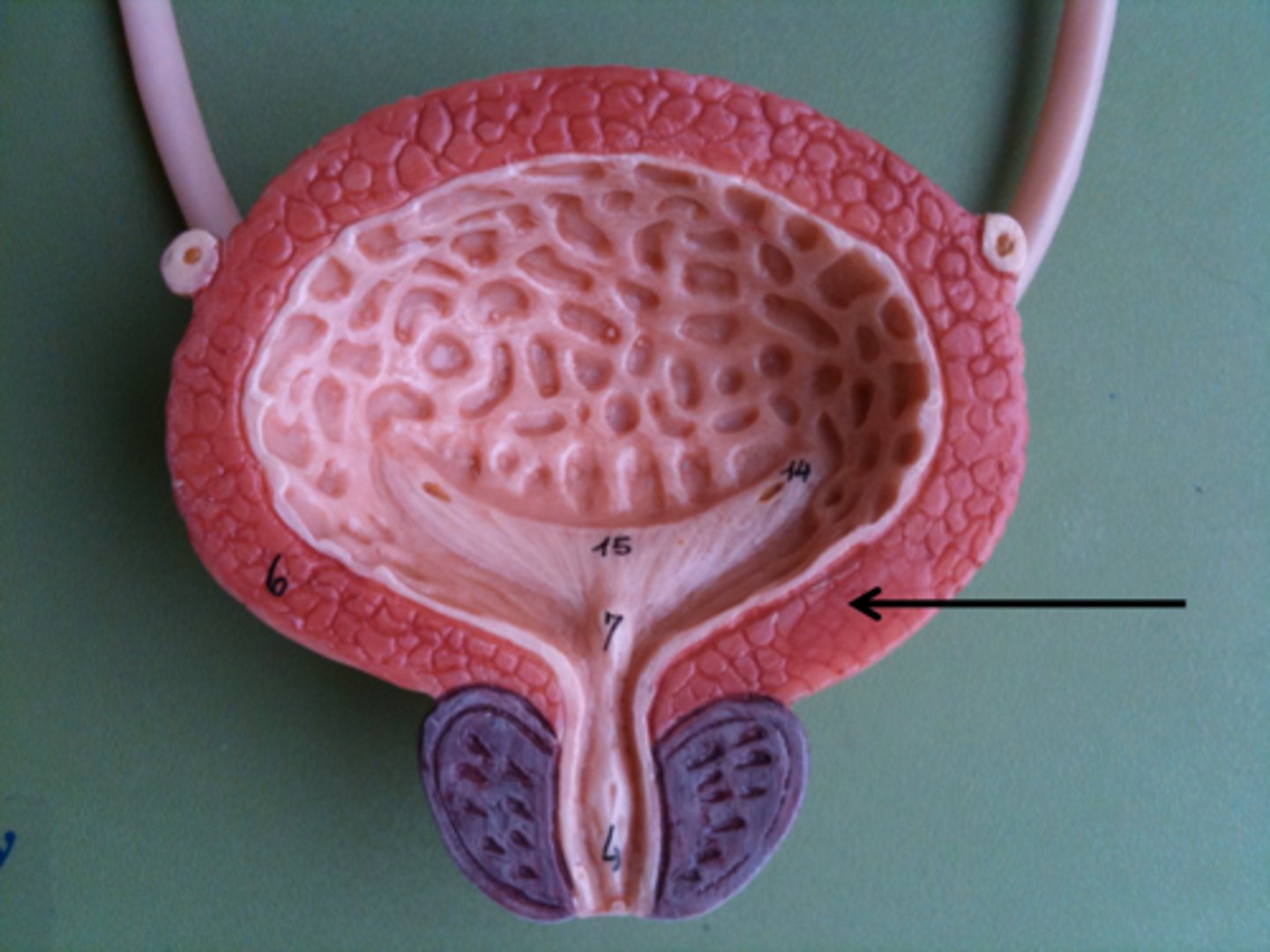
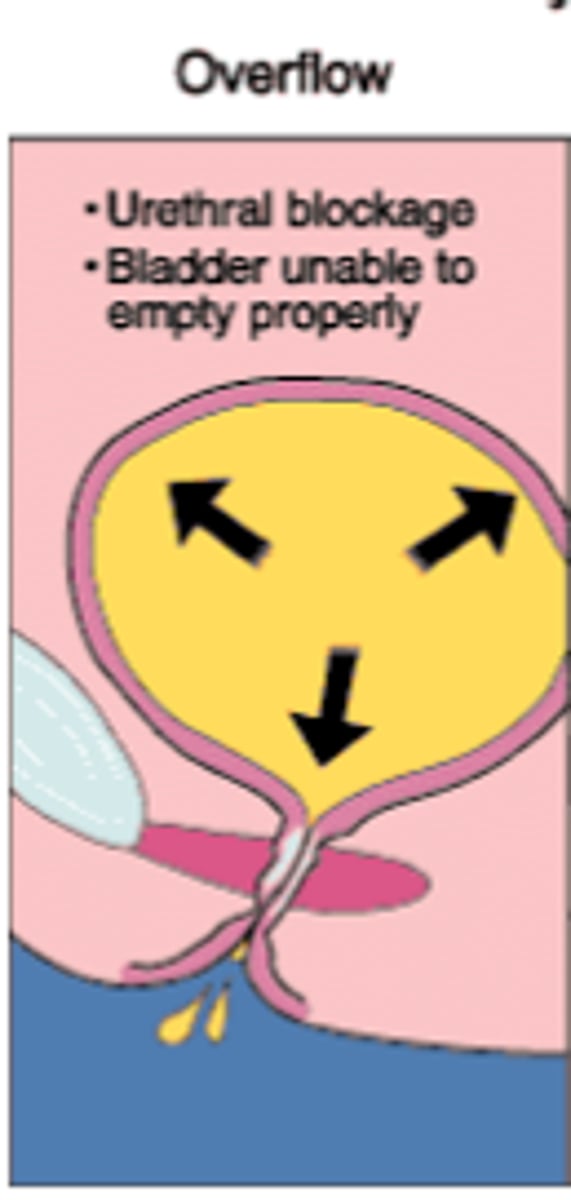
Overflow Urinary Incontinence
Loss of urine when intra-bladder pressure exceeds the urethra's capacity to remain closed due to urinary retention.
Caused by outflow obstruction secondary to narrow/obstructed urethra from prolapsed pelvic organ, stricture, enlarged prostate, chronic constipation, or neurological disease.
Sxs: Difficulty initiating urine stream, weak stream with post-void dribble when initiated.
Tx: Double voiding for patients with weak detrusor. Surgical intervention for obstruction