40. Antimicrobial Therapy: Antimicrobial Agents 2
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
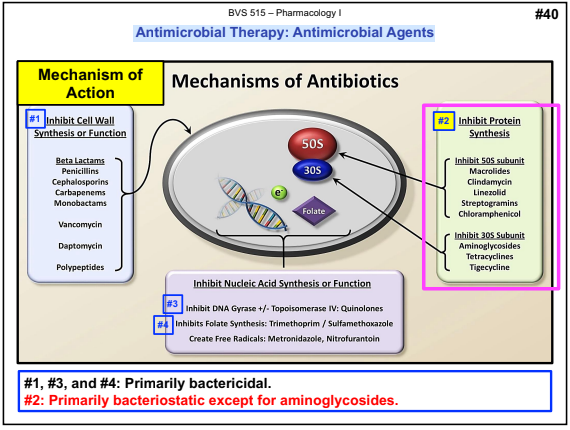
Mechanism of Action: Protein Synthesis Inhibitors
Primarily bacteriostatic except for aminoglycosides.
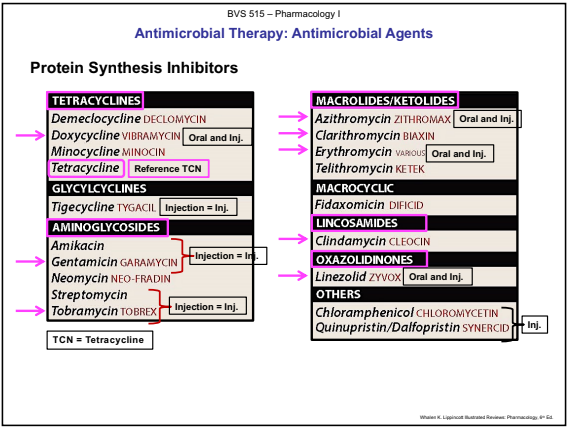
Protein Synthesis Inhibitors Chart
Tetracyclines
Doxycycline and Tetracycline
Macrolides (Ocular Topical Solution)
Azithromycin, Clarithromycin, and Erythromycin
Aminoglycosides (Ocular Topical Solutions, Ointments)
Gentamicin and Tobramycin
Oxazolidinones
Linezolid (Zyvox)
Lincosamides
Clindamycin
Protein Synthesis Inhibitors
targeting bacterial ribosomes and inhibiting bacterial protein synthesis.
Bacterial ribosomes are composed of 30S and 50S subunits
In general, selectivity for bacterial ribosomes minimizes potential adverse consequences encountered with the disruption of protein synthesis in mammalian host cells.
Protein Synthesis Inhibitors: Tetracyclines (Oral)
Mechanism of Action: Inhibits bacterial protein synthesis by binding with the 30S ribosomal subunit
Bacteriostatic as a class.
Indications: respiratory infections, acne and skin infections, sexually transmitted disease secondary to Chlamydia trachomatis.
Adverse Effects
Class Warning in Pediatric Patients: May cause tissue hyperpigmentation, enamel hypoplasia, or permanent tooth discoloration; use of tetracyclines should be avoided during tooth development (children <8 years of age)
Dermatologic: Photosensitivity (caution in the direct sunlight)
Gastrointestinal: Diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting
Avoid use in pregnancy (D).
Drug/Food Interaction
Antacids/Multivitamins/Dairy Products: Iron (Fe) and Calcium (Ca) salts, and food may decrease absorption.
Protein Synthesis Inhibitors: Macrolides (Ocular Topical Solution)
Mechanism of Action: Inhibits RNA-dependent protein synthesis; binds to the 50S ribosomal subunit
Bacteriostatic as a class.
May be used in patients with a penicillin allergy.
Representative agents are:
Erythromycin (oral and injectable)
Azithromycin (oral and injectable)
Indications
Oral azithromycin is indicated for urethritis/cervicitis caused by Chlamydia trachomatis or Neisseria gonorrhoeae.
Oral azithromycin is also used for community acquired pneumonia (CAP) secondary to atypical pathogens (mycoplasma)
Clarithromycin (oral)
Indications
Indicated for the treatment of community acquired pneumonia (CAP)
Indications: Treatment of patients with infections caused by atypical bacteria (atypical pneumonia = Mycoplasma pneumonia, Legionnaires disease, and chlamydia),
Chlamydia, Mycoplasma pneumonia, and Legionnaires disease are considered atypical bacteria.
Atypical bacteria either lack cell walls or lack a rigid cell wall and cannot be identified by gram stain.
Adverse Effects: Systemic Use
Gastrointestinal
Dermatologic (more)
high potential for drug interactions
rare QTc prolongation (cardiac)
Protein Synthesis Inhibitors: Aminoglycosides (Ocular Topical Solution, Ointment)
Mechanism of Action: Interferes with bacterial protein synthesis by binding to 30S ribosomal subunit resulting in a defective bacterial cell membrane.
Bactericidal as a class. ***
Representative agents are:
Gentamicin (injection)
Tobramycin (injection)
Protein Synthesis Inhibitors: Oxazolidinones - Linezolid (Zyvox®)
Mechanism of Action: Inhibits bacterial protein synthesis by binding to bacterial 23S ribosomal RNA of the 50S subunit
Oxazolidinone family of antibiotics.
Linezolid is bacteriostatic against enterococci and staphylococci and bactericidal against most strains of streptococci.
oxazolidinone developed to treat resistant gram-positive organisms, such as methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), vancomycin resistant Enterococcus (VRE), and penicillin-resistant streptococci.
Adverse Effects
Myelosuppression
Peripheral and optic neuropathy with vision loss
Protein Synthesis Inhibitors: Lincosamides - Clindamycin
Mechanism of Action: Reversibly binds to 50S ribosomal subunits preventing peptide bond formation thus inhibiting bacterial protein synthesis