Organic chemistry
1/21
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
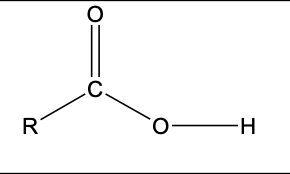
R-COOH
functional group: carboxyl
homologous series: carboxylic acid
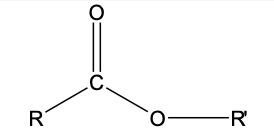
R-COO-R’
functional group: ester
homologous series: ester
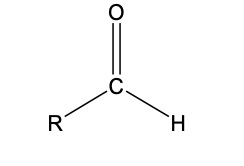
R-CHO
functional group: aldehyde
homologous series: aldehyde
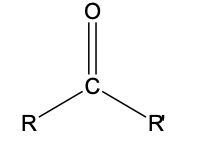
R-CO-R’
functional group: carbonyl
homologous series: ketone
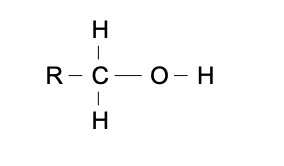
R-OH
functional group: hydroxyl
homologous series: alcohol
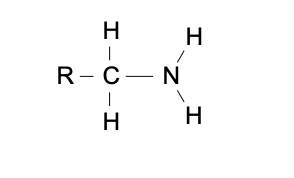
R-NH2
functional group: amino
homologous series: amine
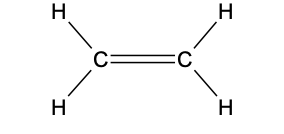
-C=C-
functional group: alkenyl
homologous series: alkene
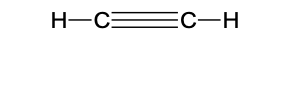
-C≡C-
functional group: alkynl
homologous series: alkyne
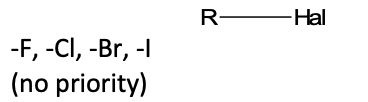
R-Hal
functional group: halide
homologous series: halogenoalkane
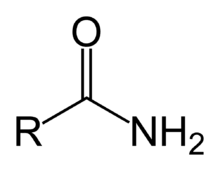
R-CONH2
functional group: carboxamide
homologous series: amide
free radical substitution
for alkanes only
produce hydrogen halide
each halogen molecule only substitute out one hydrogen
uv/heat needed
combustion
complete combustion = carbon dioxide + water
incomplete combustion = carbon monoxide / carbon + water
addition reaction - hydrogenation
for alkenes only
require Ni catalyst and heat
no additional products
addition of halogens
for alkenes only
no requirement for catalyst
no additional products
alcohols forms
water (steam) added to a double bond
sulphuric acid catalyst
test for saturation
add bromine solution see if there is colour change from brown to colourless
addition polymerisation
addition between alkene monomer units
catalyst needed
oxidation of alcohols
using oxidising agent (catalyst):
acidified dichromate H+&Cr2O72-
acidified permanganate H+&MnO4-
oxygen (natural oxidation)
primary alcohol
distillation → aldehyde →reflux → carboxylic acid
secondary alcohol
reflux → ketone
tertiary alcohol
no reaction
esterification
alcohol + carboxylic acid →(acid) ester + water
substitution - halogenoalkane to alcohol
via nucleophilic substitution reactions
nucleophile = lone pair donor e.g. (OH-)
electrophile = electron/lone pair acceptor
electrophilic substitution reactions of benzene
benzene + halogen → (heat & Fe(Hal)3) halogenobenzene
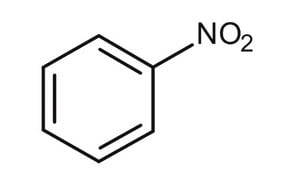
nitration
benzene + HNO3 → (H2SO4 & heat) nitrobenzene