Limbic System
1/39
Earn XP
Description and Tags
finished 5/8
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
What are the gyri/cortices included in the limbic system?
cingulate gyrus, parahippocampal gyrus, medial orbitofrontal cortex, and entorhinal cortex
What are the nuclei of the limbic system?
amygdala, hippocampus, septal nuclei, thalamus/hypothalamus, mammillary bodies, nucleus accumbens
what are the connections of the limbic system?
fornix, mammillothalamic tract, cingulum, and the medial forebrain bundle
the ___ is located near the temporal pole. it receives projections from the olfactory system and the temporal cortex, and has reciprocal connections with the septum.
amygdala
the hippocampal formation is made up of
the hippocampus, dentate gyrus, and parahippocampal gyrus
the ___ receives fibers from the entorhinal cortex and projects via the fornix to the mammillary body of the hypothalamus
hippocampal formation
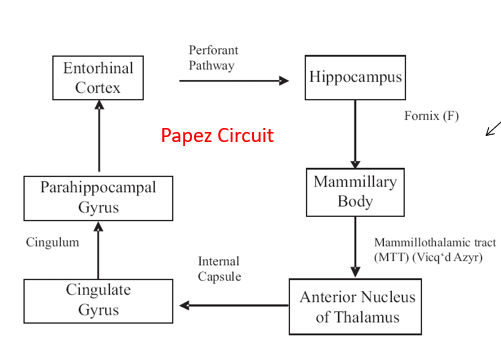
the principle components of the limbic system are interconnected in the
Papez circuit
list the parts of the papez circuit, starting from the hippocampus
hippocampus → through fornix → mammillary body → through mammillothalamic tract → anterior nucleus → through internal capsule → cingulate gyrus → through cingulum → parahippocampal gyrus → entorhinal cortex → through perforant pathway → back to hippocampus
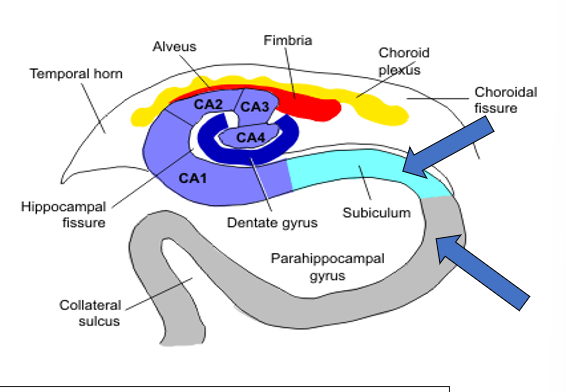
what are the interlocking C shapes of the hippocampal formation
CA1-CA3 of the hippocampus and the dentate gyrus
what are the segments of the hippocampal formation?
subiculum, CA1, CA2, CA3, CA4, dentate gyrus
input to the entorhinal cortex from the amygdala goes through what pathway?
the amygdalofugal pathway
from what point(s) does the hippocampus receive information?
information goes to the subiculum directly, or to the entorhinal cortex before the subiculum
what are the two outputs from the hippocampus?
back to subiculum, then to the cortex
to fornix, to subcortical areas
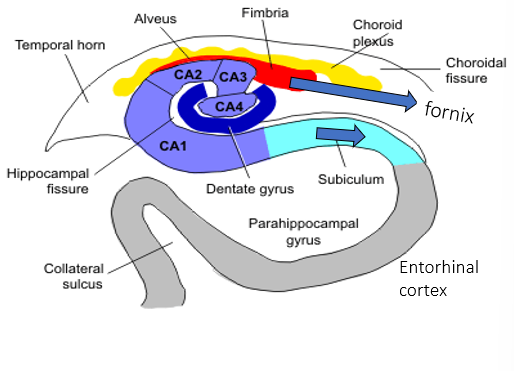
the ___ converge in the midline to become the fornix
fimbriae
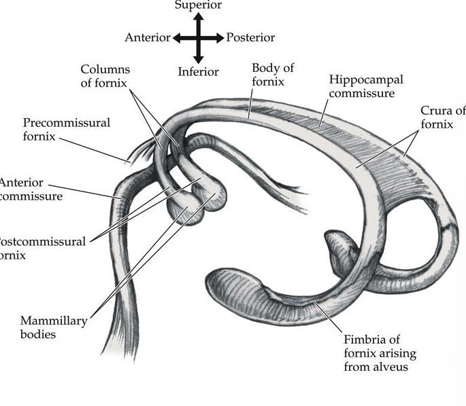
on the anterior end of the fornix, there are split ends. what are they?
anterior to the anterior commissure are the precommissural branches of the fornix. they go to the septum.
posterior to the anterior commissure are the postcommissural branches that go to the mammillary bodies
memory loss (profound anterograde amnesia, some retrograde) caused by lack of thiamine, especially in chronic alcoholics. they may confabulate (fill a gap in memory with falsification)
Korsakoff’s syndrome
Korsakoff’s syndrome is a lesion to the
mammillary bodies
the cingulate gyrus has inputs from
anterior nucleus of thalamus and the frontal, somatosensory, and visual cortices
what are the functions of the cingulate gyrus?
emotion processing, learning, emotional memory, attention flexibility, empathy
involved in anger and fear recognition
amygdala
the amygdala projects to the ___
cerebral cortex and hypothalamus
the amygdalae send impulses to the hypothalamus for important activation of the ___ nervous system
sympathetic
the amygdalae send impulses to the reticular nucleus for ___
increased reflexes
the amygdalae send impulses to the trigeminal nerve and facial nerve for ___
facial expressions of fear
the amygdalae send impulses to the ___ for the activation of dopamine, norepinephrine, and epinephrine
ventral tegmental area, locus coeruleus, and the laterodorsal tegmental nucleus
the centromedial nuclei are the main outputs for the basolateral complexes, and are involved in ___
emotional arousal
what nuclei serve as a relay of hippocampus to the hypothalamus?
the septal nuclei
emotional memory and rage are associated with the ___
septal nuclei
the ventral striatum and the ___ are the same
nucleus accombens
where is the nucleus accumbens?
where the caudate and putamen meet
the nucleus accumbens is important for ___
reward and pleasure
projections from the VTA to the nucleus accumbens go through the
medial forebrain bundle
overall, what are the functions of the limbic system?
fight/flight, fear and emotions, memory, sexual behavior
Klein-Levin syndrome
hypothalamic hamartoma. recurring episodes of severe sleepiness, accompanied by behavioral changes, such as sexual aggressiveness, hyperphagia, hallucinations, excessive hunger.
Kluver Bucy syndrome
memory loss, hypersexuality, excessive hunger, chewing, flattened affect
lung carcinoma can be associated with
limbic encephalitis
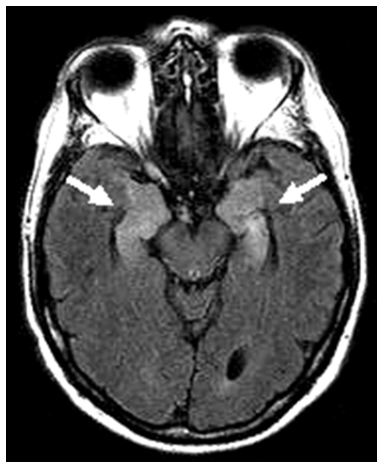
limbic encephalitis symptoms
seizures, apathy, confusion, short-term memory difficulty, sexual disinhibition, episodic agitation, emotional lability, disorientation. gradual onset
what is abulia?
decreased motivation/drive to perform actions necessary for taking care of oneself, communicating, etc. no motor issues, but not moving, speaking, using the restroom on their own, etc. associated with frontal lobe damage
how are the voluntary and spontaneous smile circuits different?
the spontaneous smile circuit involves the limbic system and only involves the direct pathway.
the voluntary smile circuit involves the motor cortex and both indirect and direct pathways.
if someone’s basal ganglia is not damaged by a stroke, the ___ circuit is intact
spontaneous smile circuit