602: Pterygopalatine Fossa
1/207
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
208 Terms
- Maxillary nerve blocks
- Panoramic radiograph interpretation
- Bleeding complications
- Facial trauma
- Odontogenic maxillary sinusitis
- Maxillary surgery
Why study the nasal cavity and PFF?
Pyramidal space medial to the infratemporal fossae between the sphenoid, maxilla, and palatine bone
- Posterior to the maxillary sinus
- Posteroinferior to the orbit
What is the pterygopalatine fossae?
- Maxillary artery (3d part or pterygopalatine part)
- Maxillary nerve (V2, 2nd division of the trigeminal)
- Pterygopalatine ganglion-associated autonomic nerves
The pterygopalatine fossa is the major distribution site for:
Major somatic sensory nerve for:
- Face
- Nasal cavity and nasopharynx
- Maxillary sinuses
- Meninges (dura)
- Oral cavity: maxillary teeth, hard and soft palate, gingiva
What does CN V2 do?
Greater petrosal n (from CN VII)
What parasympathetic autonomics are associated with the pterygopalatine ganglion?
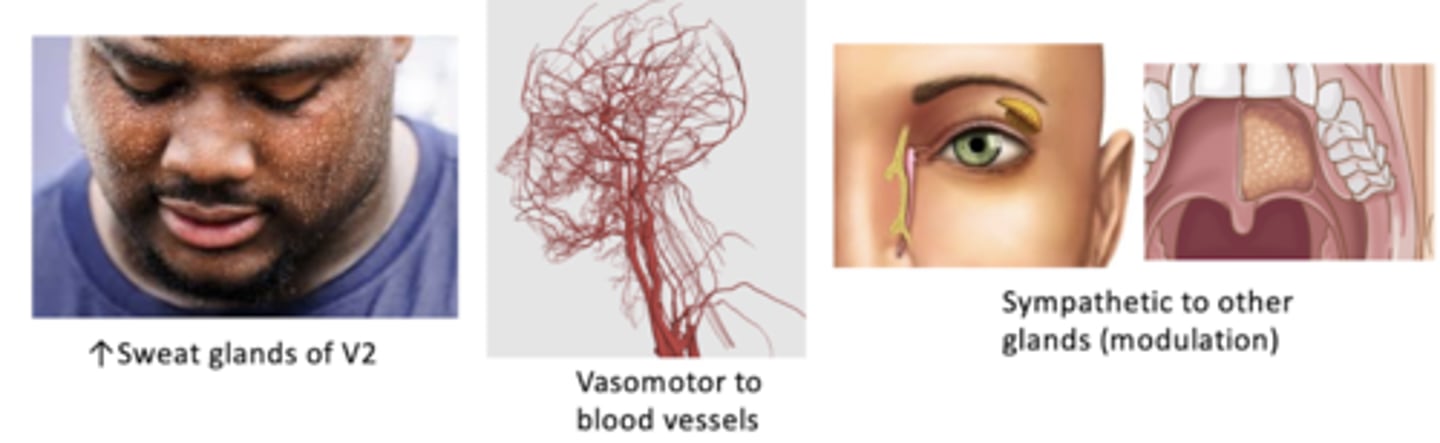
Deep petrosal n (from internal carotid plexus)
What sympathetic autonomics are associated with the pterygopalatine ganglion?
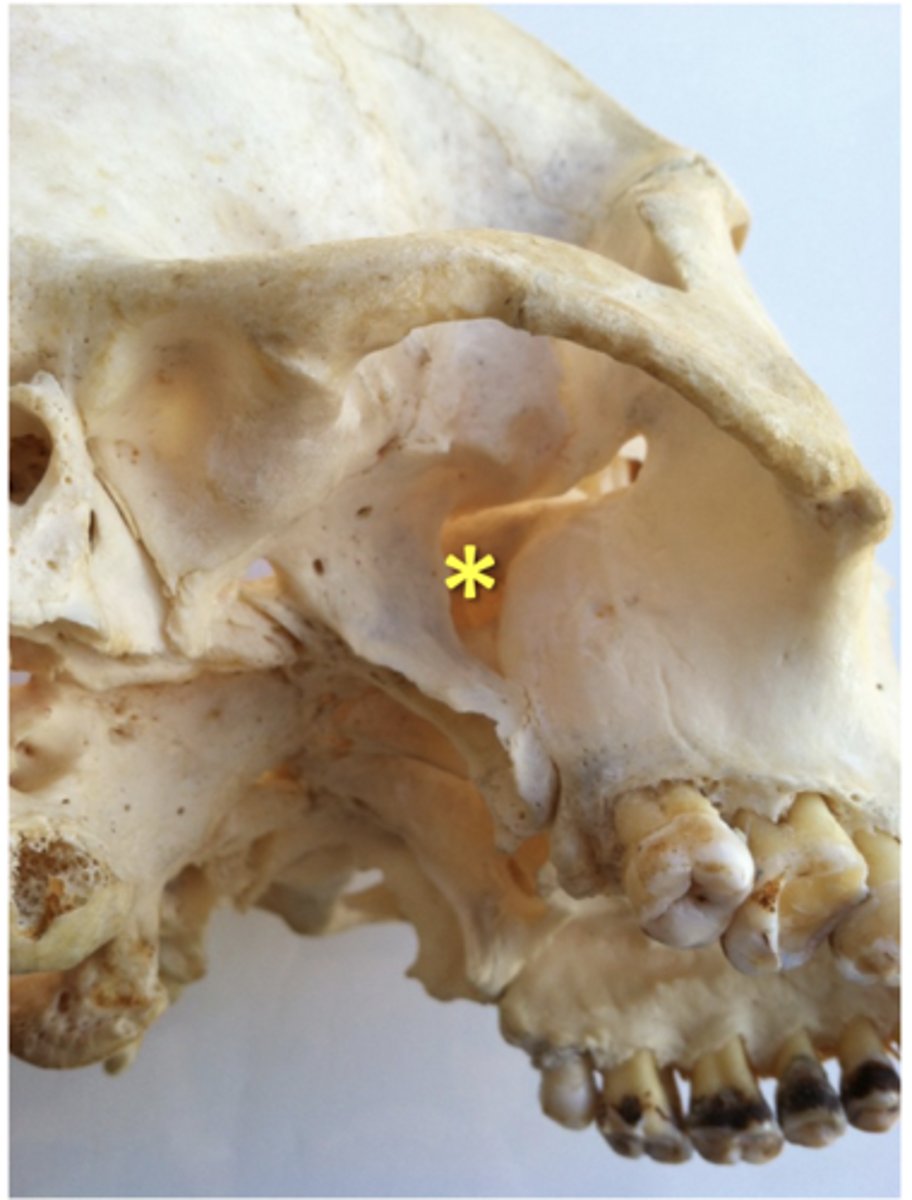
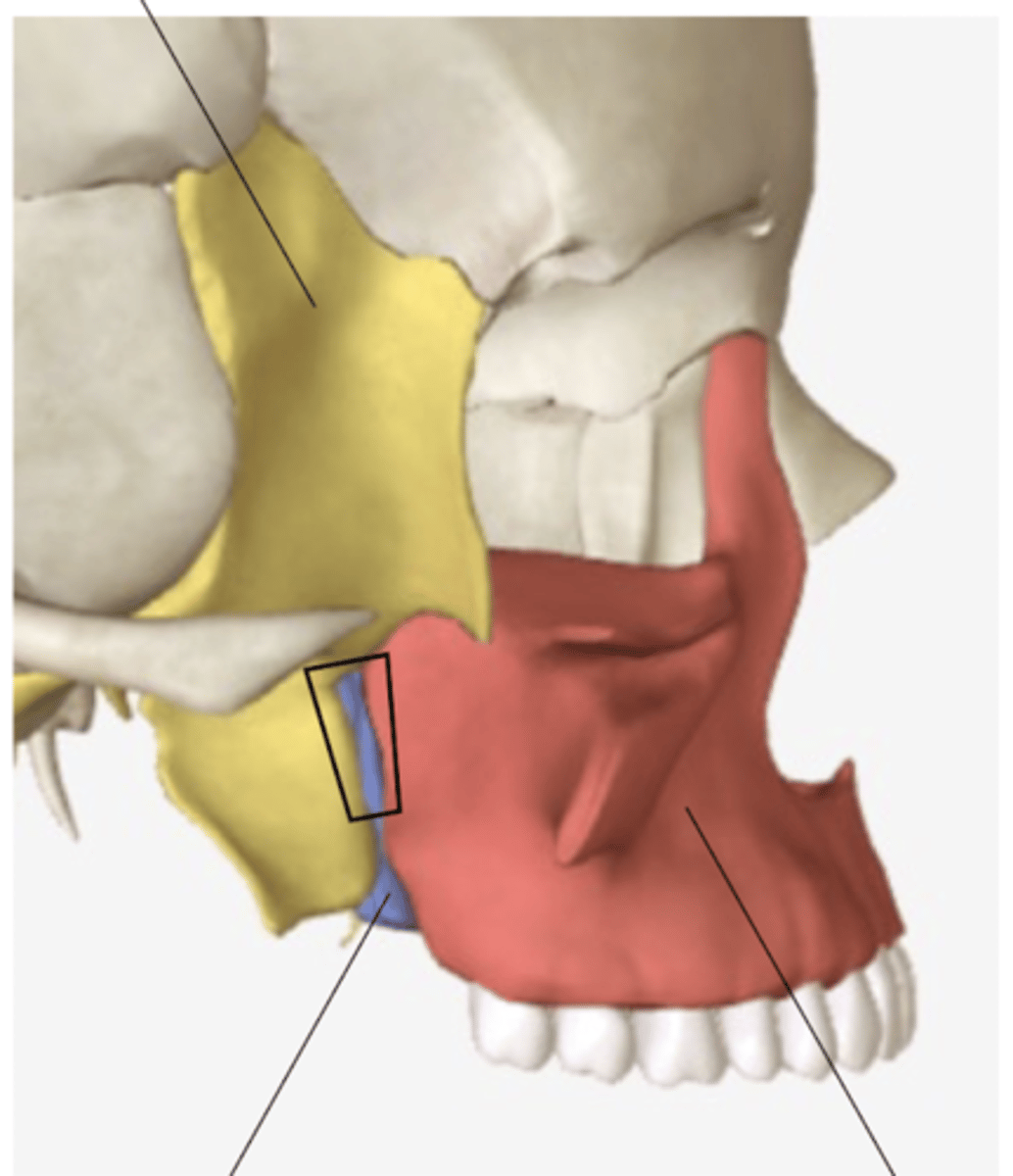
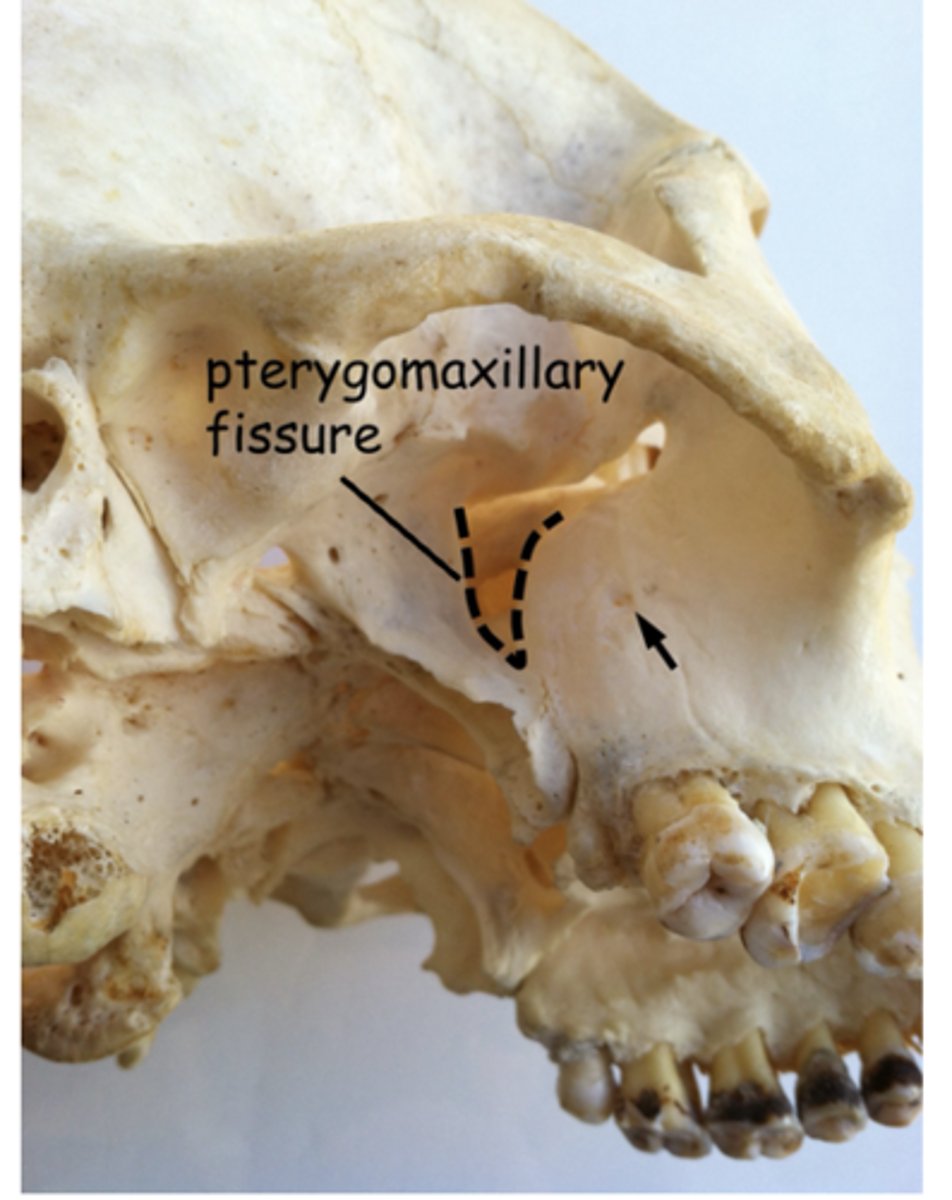
pterygomaxillary fissure
what structure leads to the pterygopalatine fossa?
pterygopalatine fossa
traveling medially from the pterygomaxillary fissure will place you in the:
inferior
The pterygopalatine fossa is ________to the apex of the orbit.
lateral
The pterygopalatine fossa is ________ to the sphenopalatine foramen
foramen rotundum
pterygoid (vidian) canal
pharyngeal canal
what 3 foramen are located on the posterior wall of the pterygopalatine fossa?
sphenopalatine foramen
if you move a probe medially in the pterygopalatine fossa to get to the nasal cavity, you must go through the:
Pterygoid process of the sphenoid
the posterior boundary of the pterygopalatine fossa is the:
Posterior border of the maxilla
the anterior boundary of the pterygopalatine fossa is the:
Perpendicular plate of the palatine
the medial boundary of the pterygopalatine fossa is the:
Part of the greater wing of the sphenoid
the superior boundary of the pterygopalatine fossa is the:
pterygomaxillary fissure, open to the infratemporal fossa
the lateral boundary of the pterygopalatine fossa is the:
Pyramidal process of the palatine
the inferior boundary of the pterygopalatine fossa is the:
pterygopalatine canal
the floor of the pterygopalatine fossa is the:
maxilla
the anterior wall of the pterygopalatine fossa is formed by the:
maxilla
sphenoid
palatine
what 3 bones make up the pterygopalatine fossa
sphenoid bone
the posterior wall and roof of the pterygopalatine fossa is formed by what bone?
- 3rd part of maxillary a.
- Maxillary nerve (V2)
- Pterygopalatine ganglion
What three main contents are in the pterygopalatine fossa?
pterygomaxillary fissure
inferior orbital fissure
name the 2 fissures associated with the pterygopalatine fossa:
foramen rotundum
sphenopalatine foramen
name the 2 foramen associated with the pterygopalatine fossa:
vidian canal/ pterygoid canal
pterygopalatine canal
pharyngeal canal
name the 3 canals associated with the pterygopalatine fossa:
inferior orbital fissure
what hole is located anterior and superior on the maxilla bone in the pterygopalatine fossa?
orbit
a probe from the pterygopalatine fossa through the infraorbital fissure, you would arrive in the:
inferior orbital fissure
if you wanted to go from the orbit to the pterygopalatine fossa, you'd take the
sphenopalatine foramen
what hole is located superiorly on the palatine bone?
nasal cavity
a probe from the pterygopalatine fossa through the sphenopalatine foramen, you would arrive in the:
sphenopalatine foramen
if you wanted to go from the nasal cavity to the pterygopalatine fossa, you'd take the
middle cranial fossa
a probe from the pterygopalatine fossa through the foramen rotundum, you would arrive in the:
foramen rotundum
what hole is located superiorly on the sphenoid bone?
foramen rotundum
if you wanted to go from the middle cranial fossa to the pterygopalatine fossa, you'd take the
nasopharynx
a probe from the pterygopalatine fossa through the pharyngeal canal, you would arrive in the:
pharyngeal canal
if you wanted to go from the nasopharynx to the pterygopalatine fossa, you'd take the
foramen lacerum in the middle cranial fossa
a probe from the pterygopalatine fossa through the vidian canal/ pterygoid canal, you would arrive in the:
vidian canal/ pterygoid canal
if you wanted to go from the foramen lacerum to the pterygopalatine fossa, you'd take the
oral cavity
a probe from the pterygopalatine fossa through the pterygopalatine canal, you would arrive in the:
pterygopalatine canal
if you wanted to go from the oral cavity to the pterygopalatine fossa, you'd take the
Palatine canal
If you wanted to go to the palate from the pterygopalatine fossa, you'd take the
Pterygomaxillary fissure
If you wanted to go to the infratemporal fossa from the pterygopalatine fossa, you'd take the
Zygomatic n.
Infraorbital n.
Infraorbital vv.
What are the nerves and vessels that travel through the infra-orbital fissure?
3rd part of maxillary artery
Posterior superior alveolar nn.
What are the nerves and vessels that travel through the pterygomaxillary fissure?
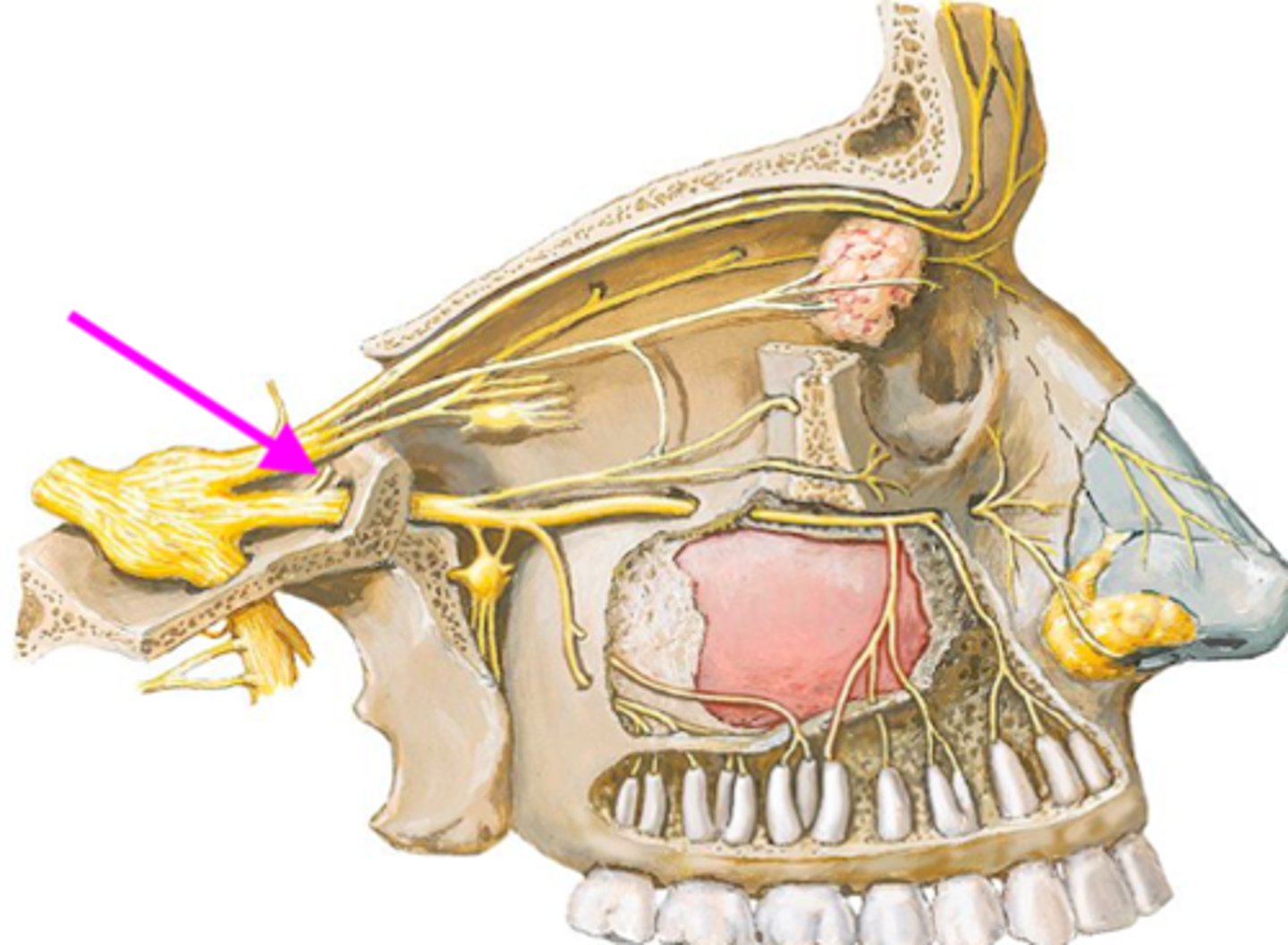
Opening for posterior superior alveolar n.
Identify the structure at the arrow
Sphenopalatine a.
Nasopalatine n.
Posterior superior lateral nasal n.
What are the nerves and vessels that travel through the sphenopalatine foramen?
Descending palatine artery
Greater palatine n.
Lesser palatine n.
What are the nerves and vessels that travel through the palatine canal?
Pharyngeal n.
Pharyngeal a.
What are the nerves and vessels that travel through the pharyngeal canal?
N. of the pterygoid canal (greater petrosal n. and deep petrosal n.)
A. of the pterygoid canal
What are the nerves and vessels that travel through the pterygoid canal?
Greater petrosal n. (parasympathetic)
Deep petrosal n. (sympathetic)
What nerves make up the nerve of the pterygoid canal (vidian n.)?
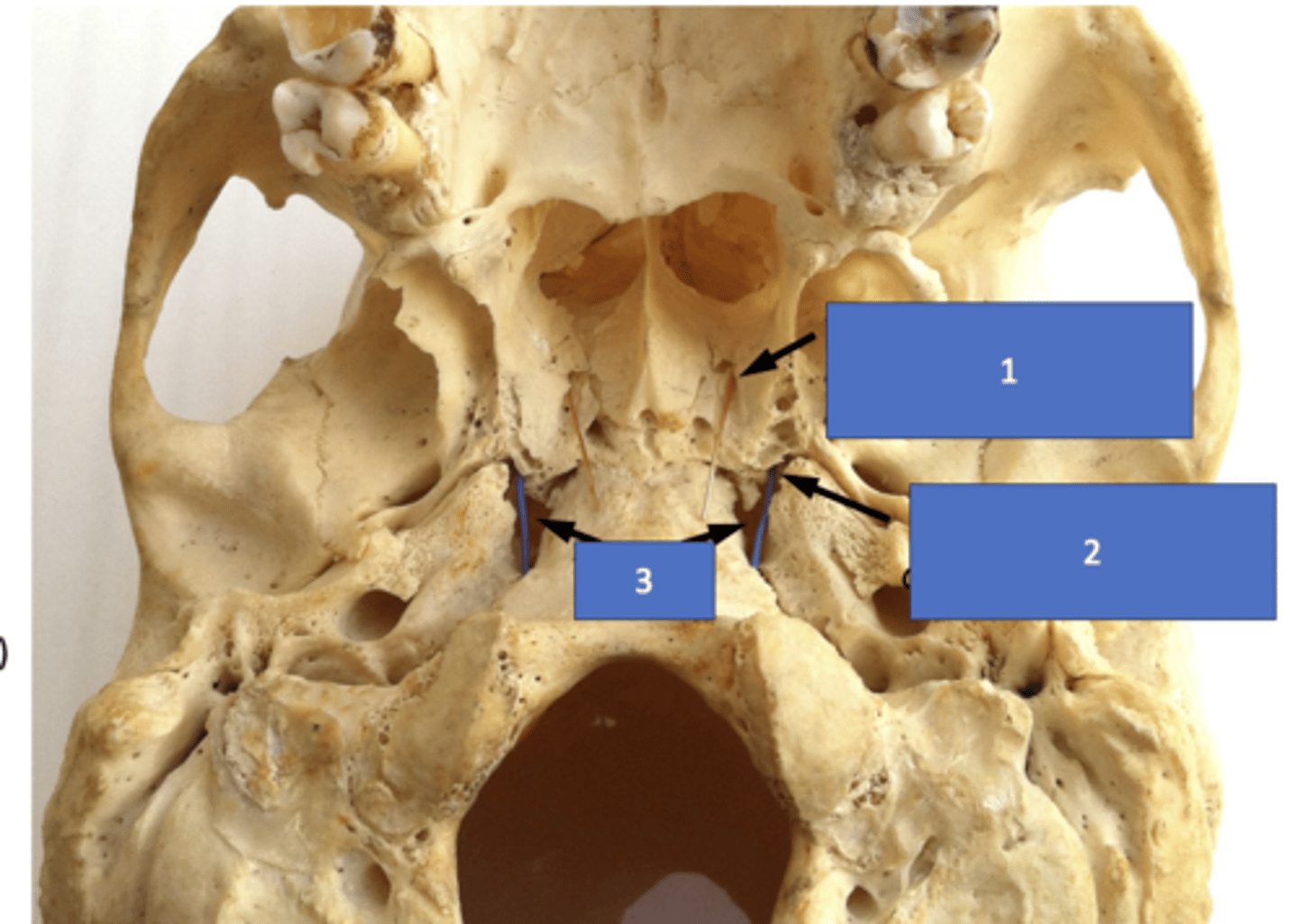
Pharyngeal canal (aka palatovaginal canal)
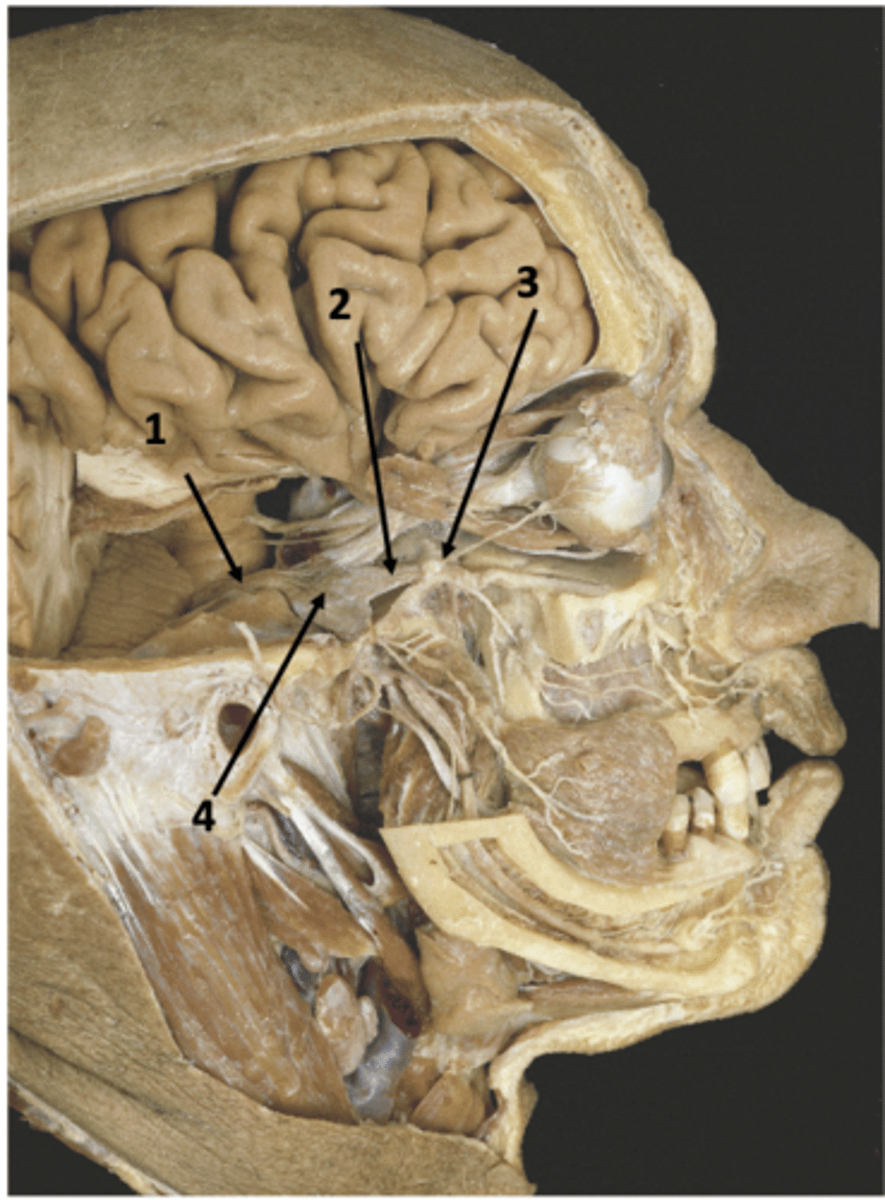
Identify the structure at #1
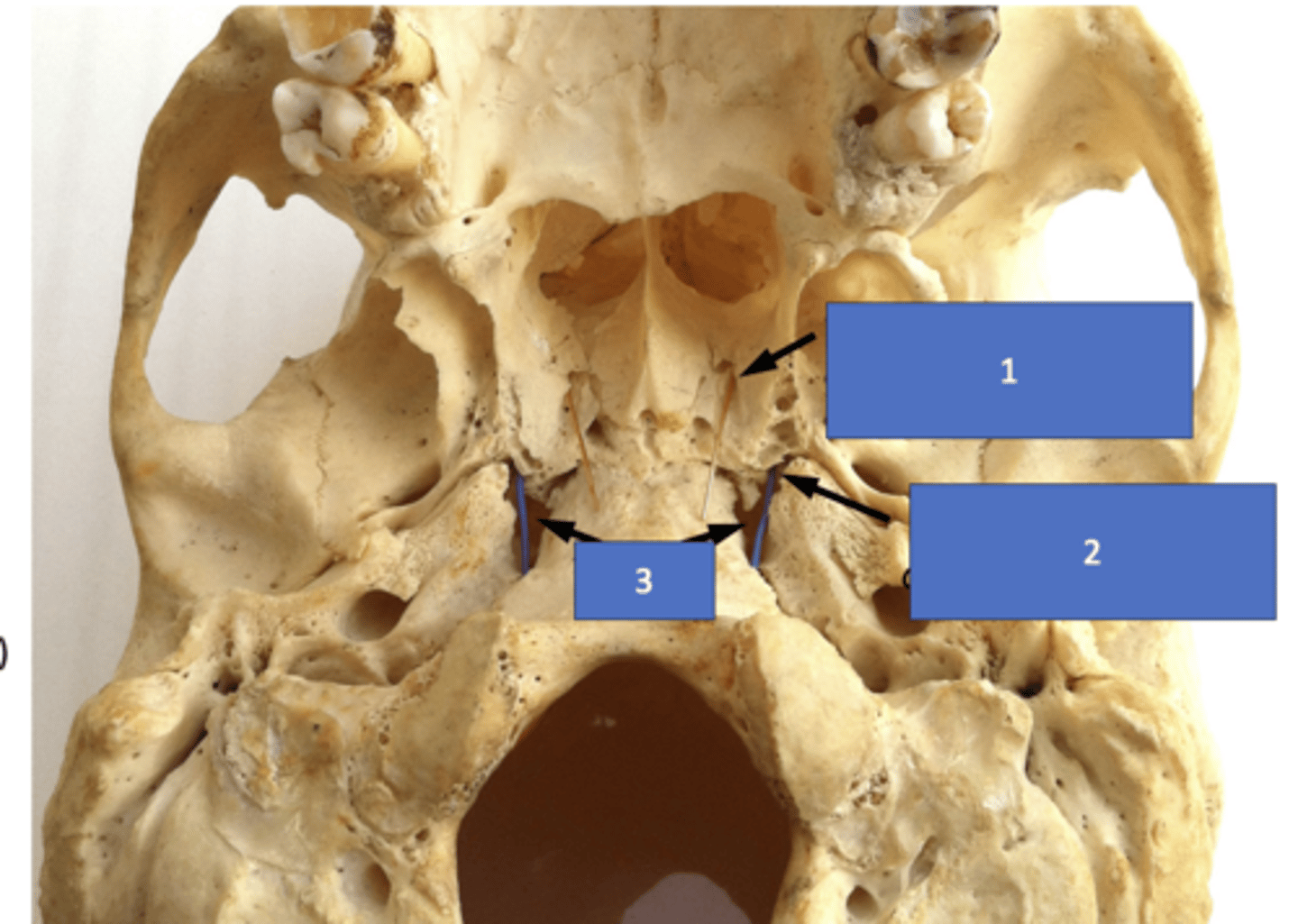
Pterygoid (vidian) canal
Identify the structure at #2
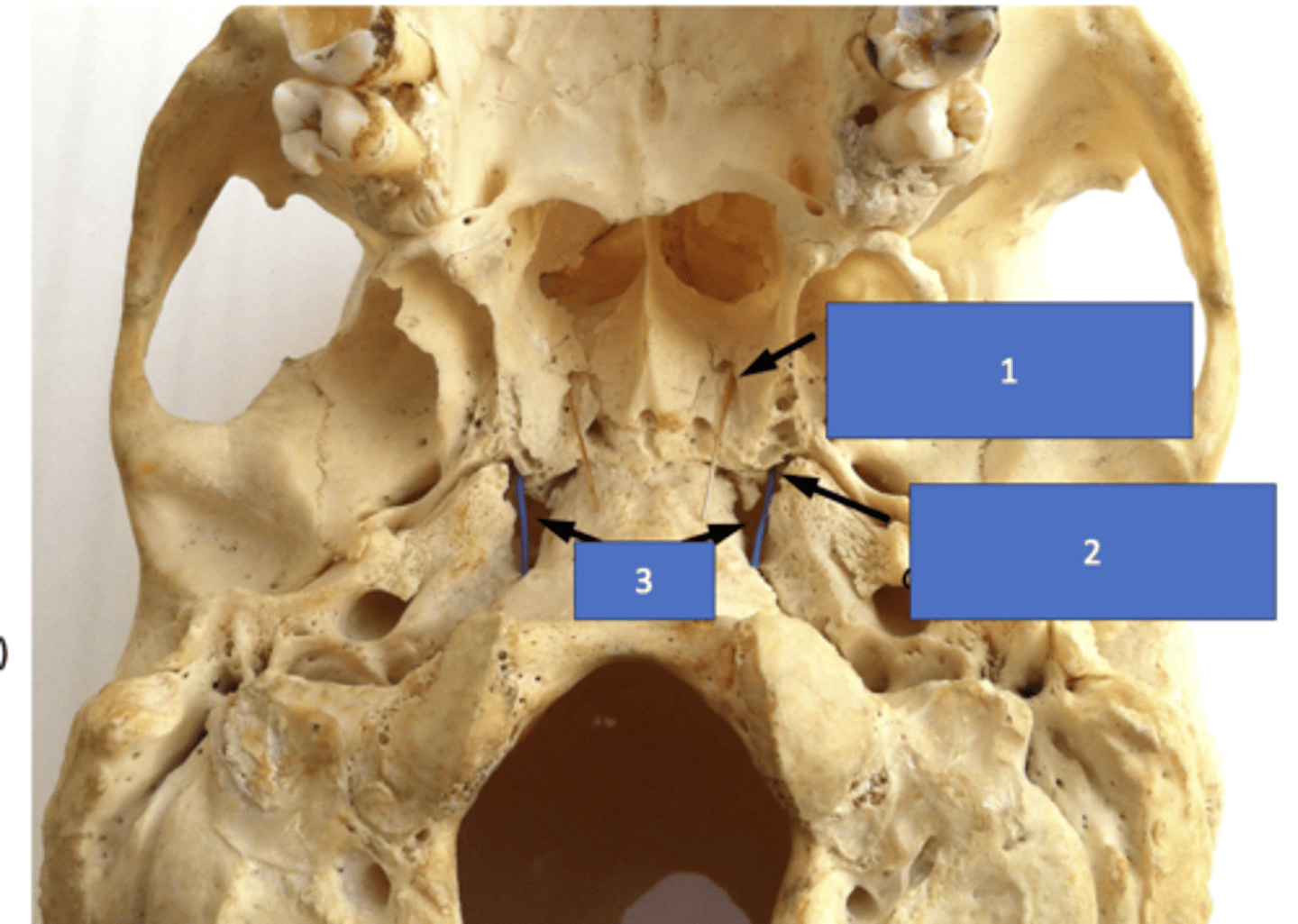
Foramen lacerum
Identify the structure at #3
CN V
Identify the structure at #1
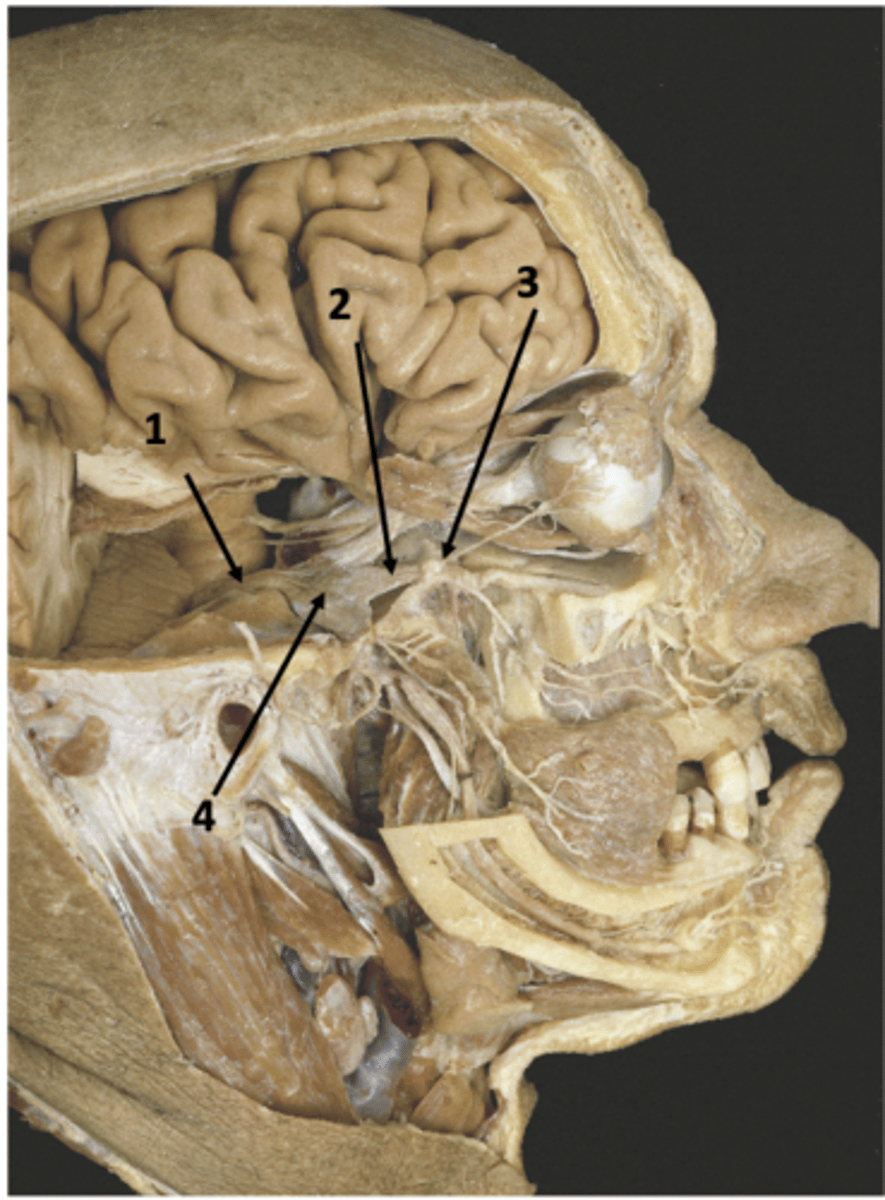
V2
Identify the structure at #2
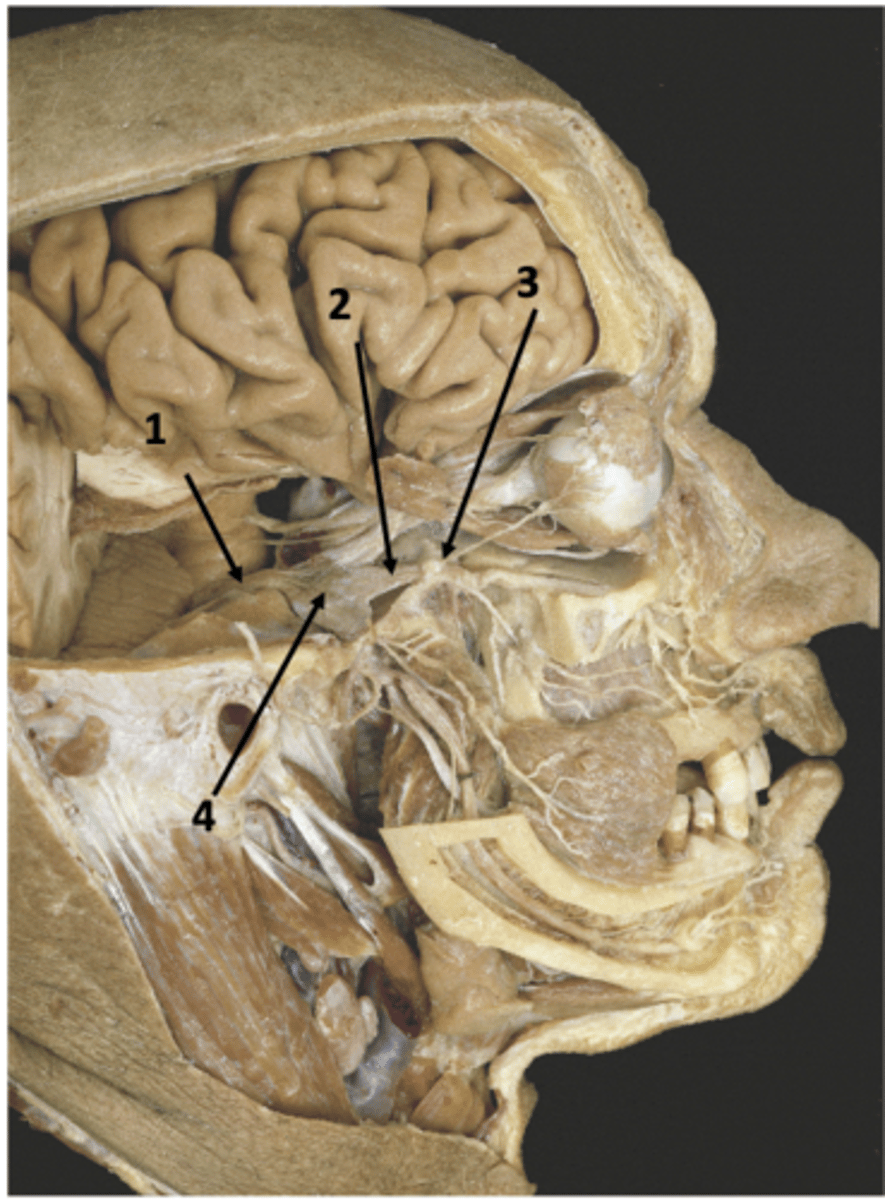
Foramen rotundum
Identify the structure at #3
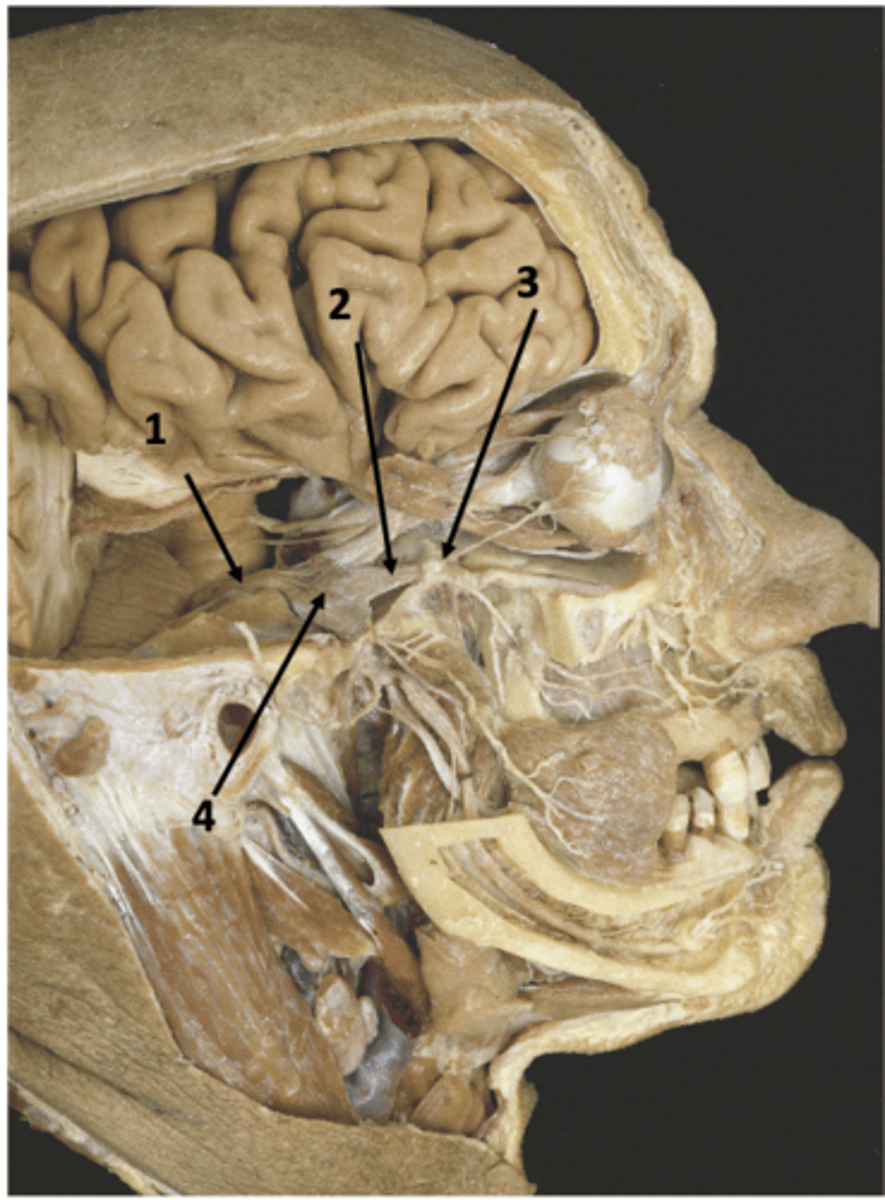
Trigeminal ganglion
Identify the structure at #4
Pterygomaxillary fissure
Identify the structure at #1
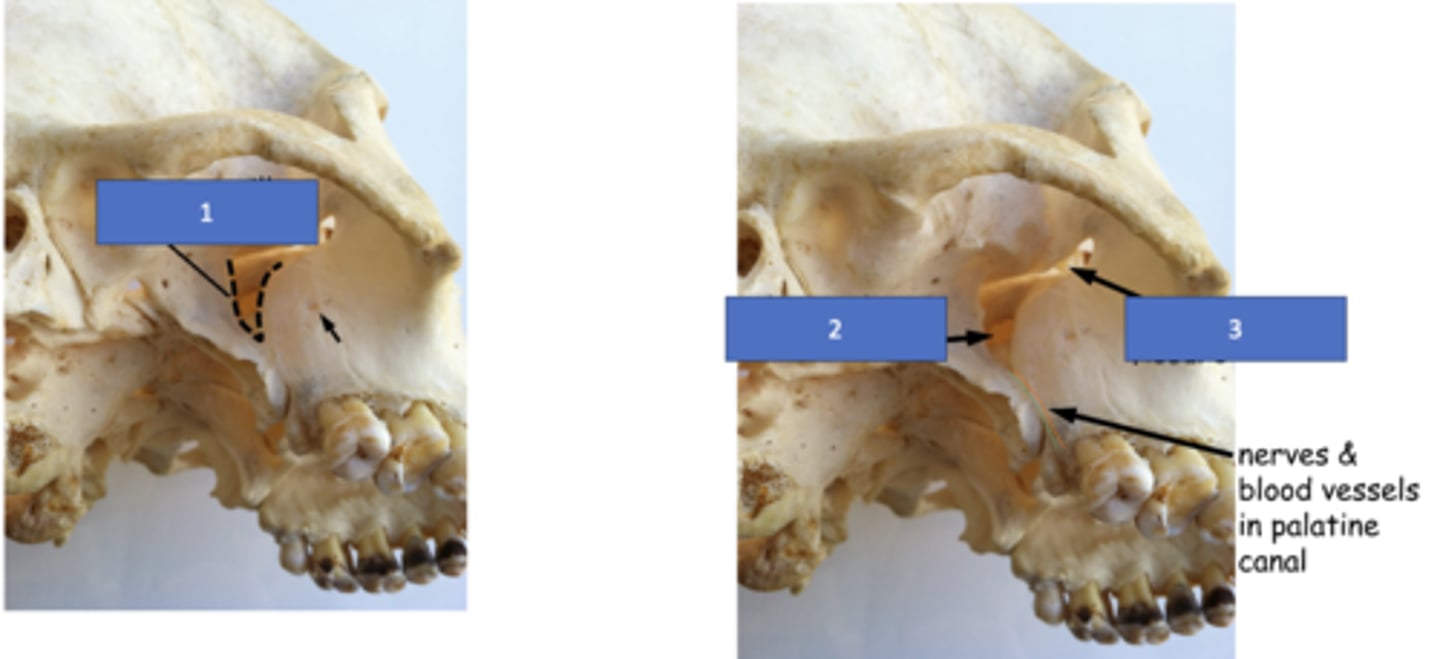
Sphenopalatine foramen
Identify the structure at #2
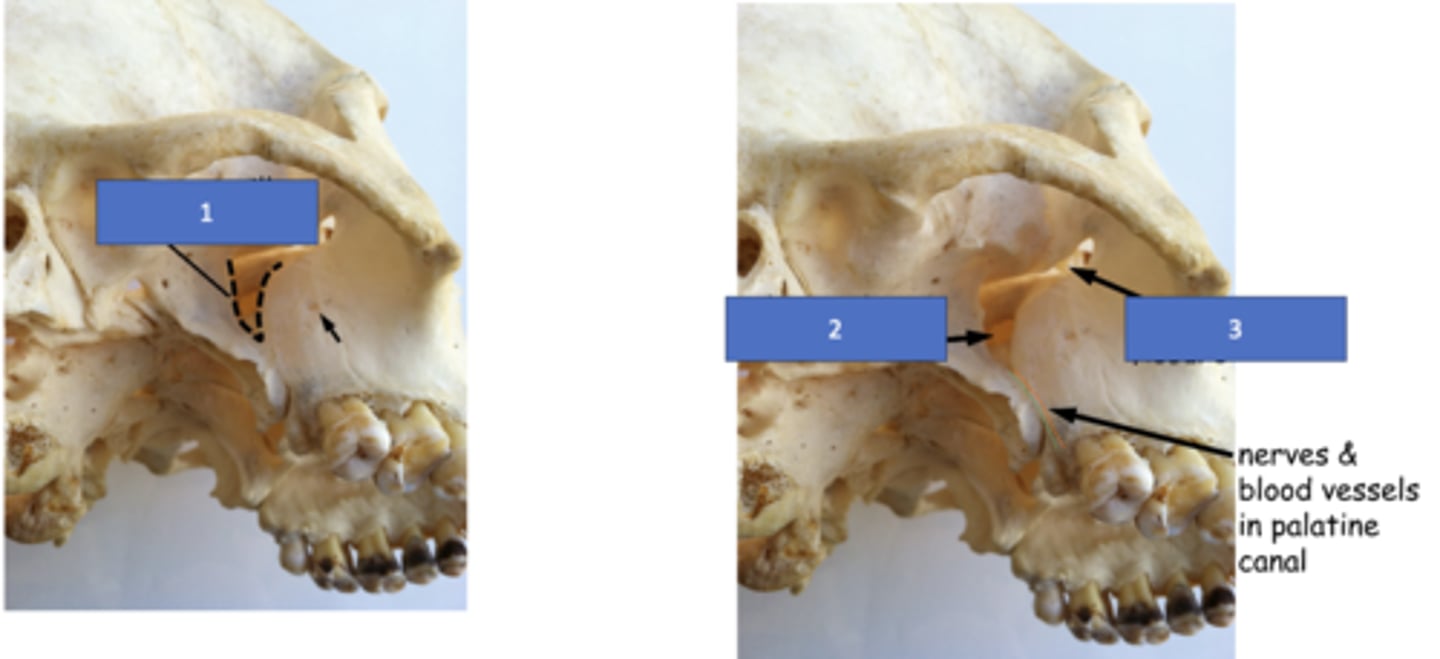
Inferior orbital fissure
Identify the structure at #3
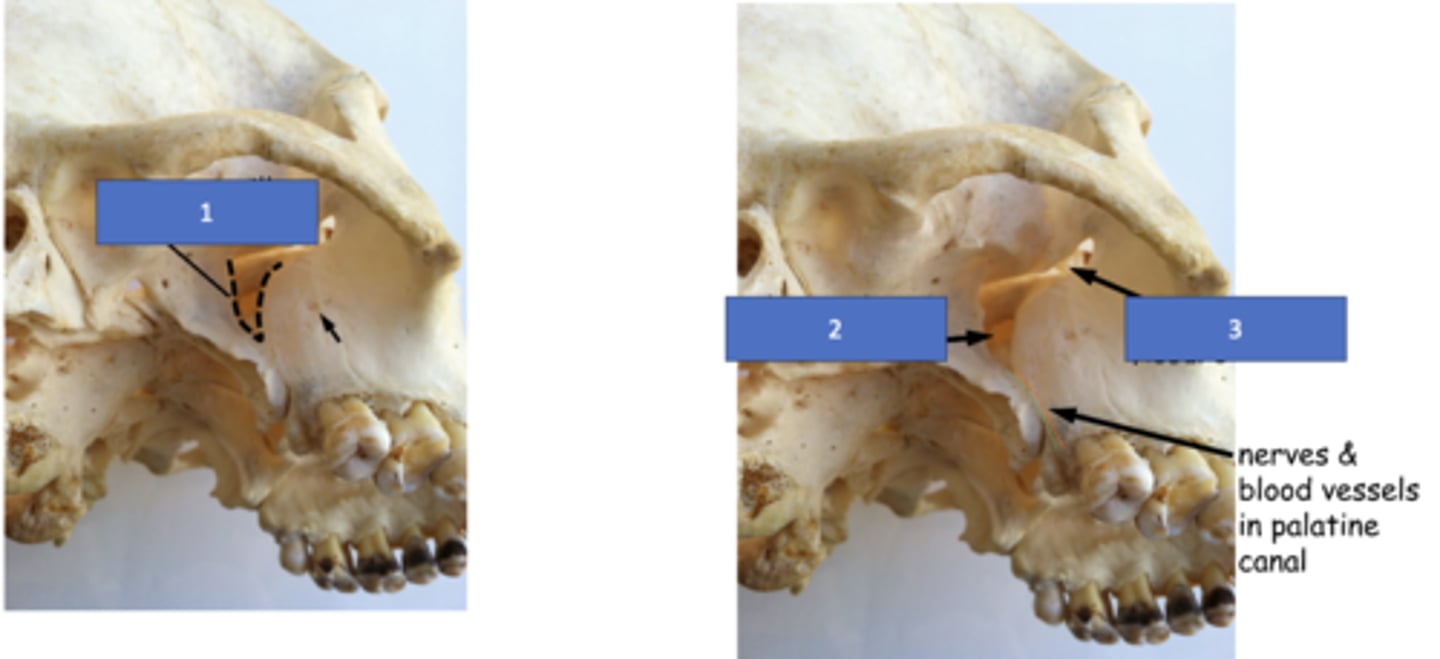
Infraorbital foramen
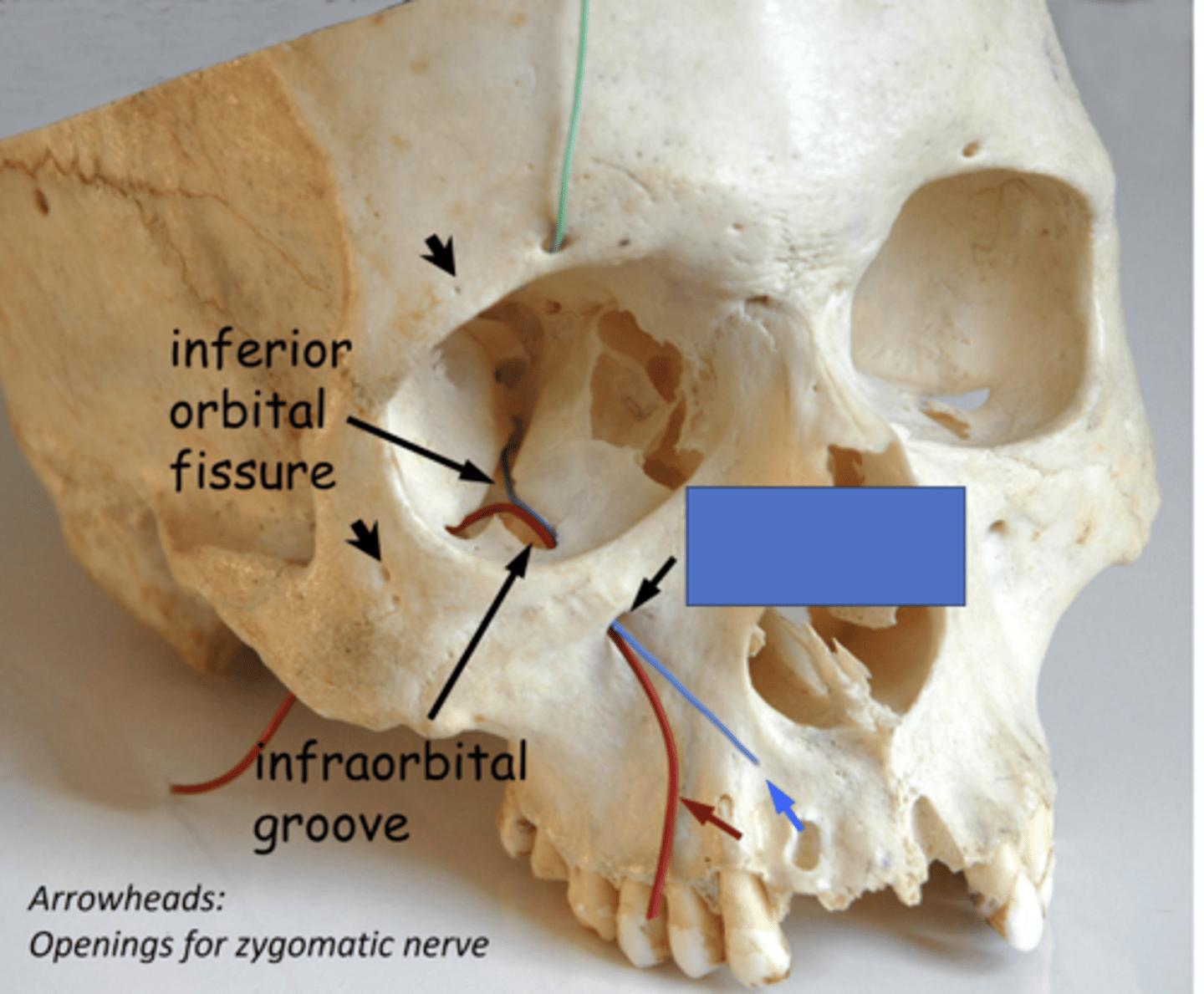
the infraorbital nerve (ION) passes through the inferior orbital fissure, travels through the infraorbital groove and exits onto the face through the...
True - there are NO somatic motor fibers
T/F: V2 is entirely somatic sensory
Dura
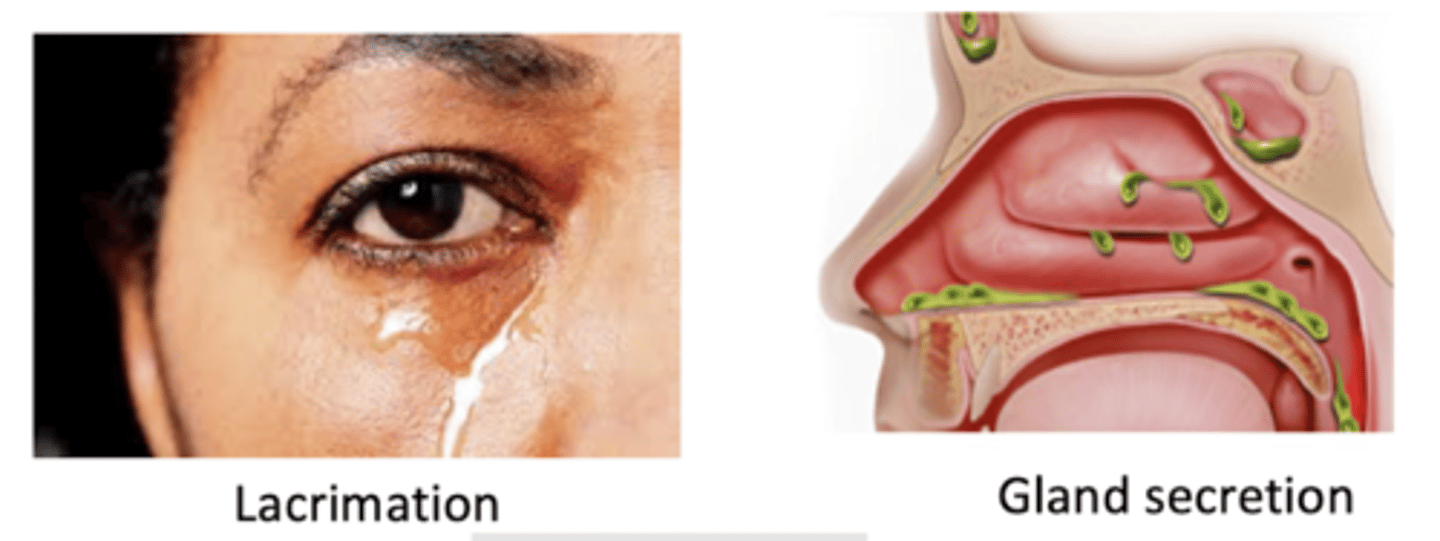
Lacrimal gland
Face
Maxillary teeth/sinus
Nasal cavity
Palate
Pharynx
What are the targets of V2?
Face > Orbit > Pterygopalatine fossa > Middle cranial fossa > Trigeminal ganglion
What spaces does V2 travel from the face to the trigeminal ganglion?
Middle cranial fossa
Identify the region in blue
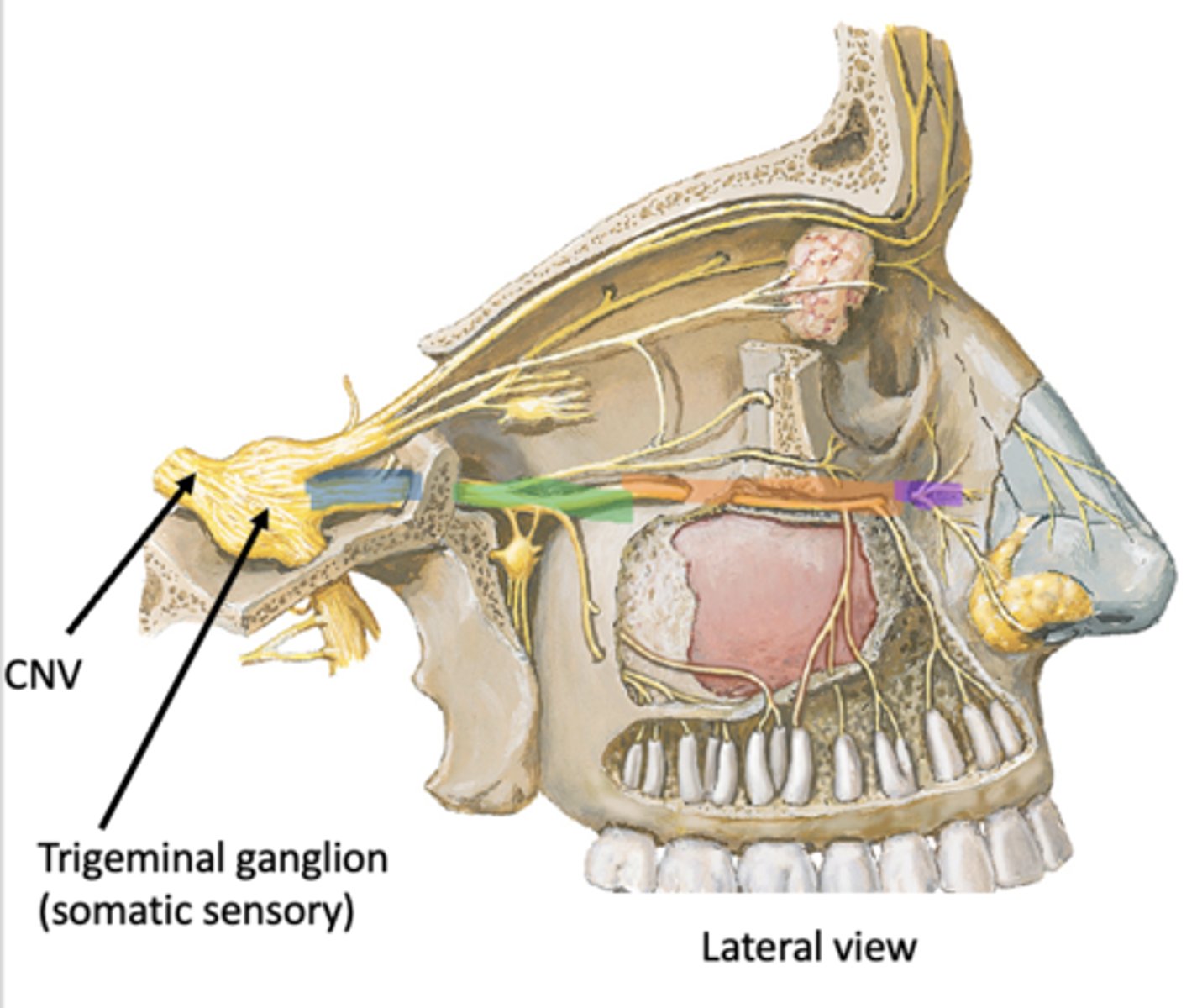
Pterygopalatine fossa
Identify the region in green
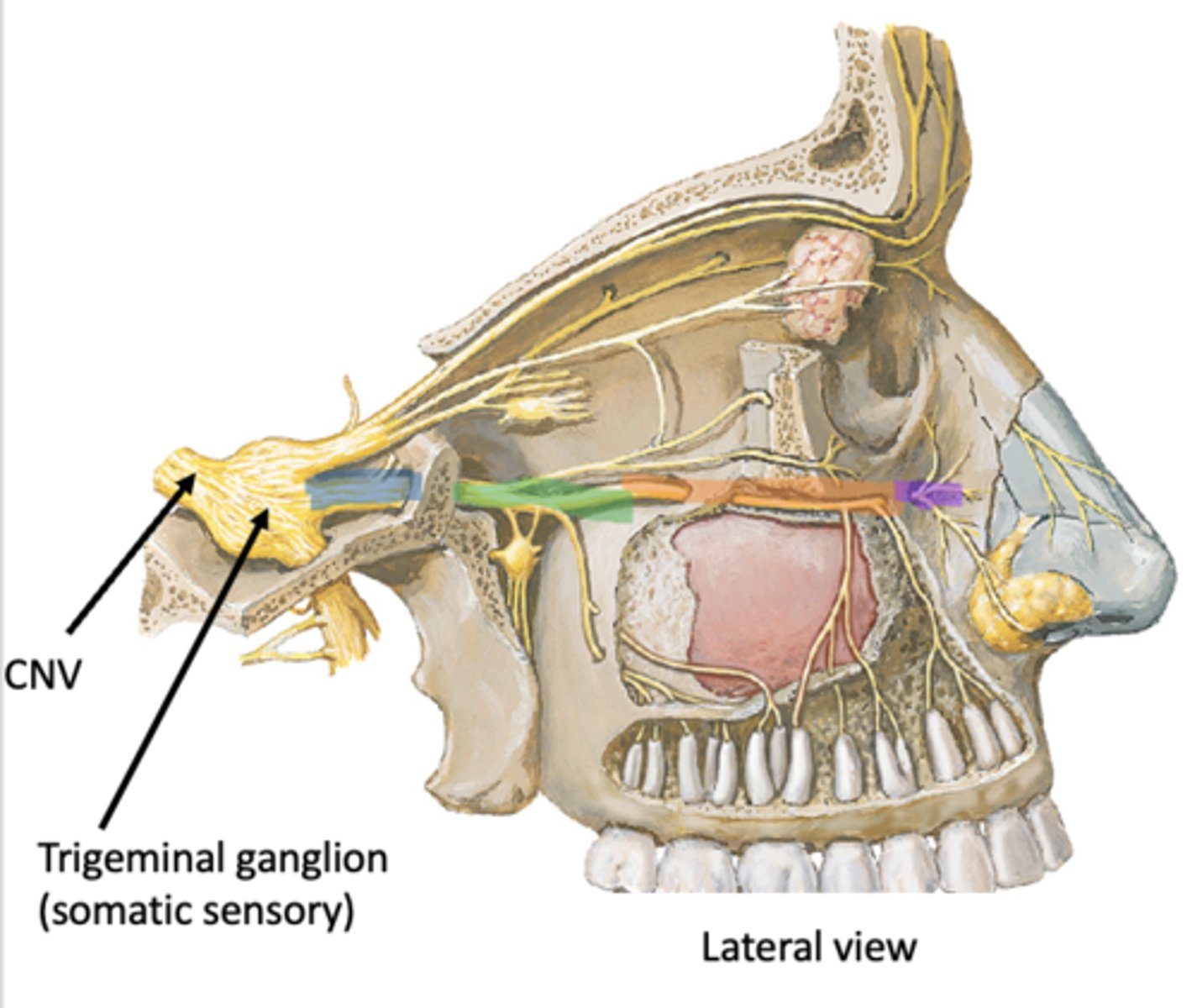
Orbit
Identify the region in orange
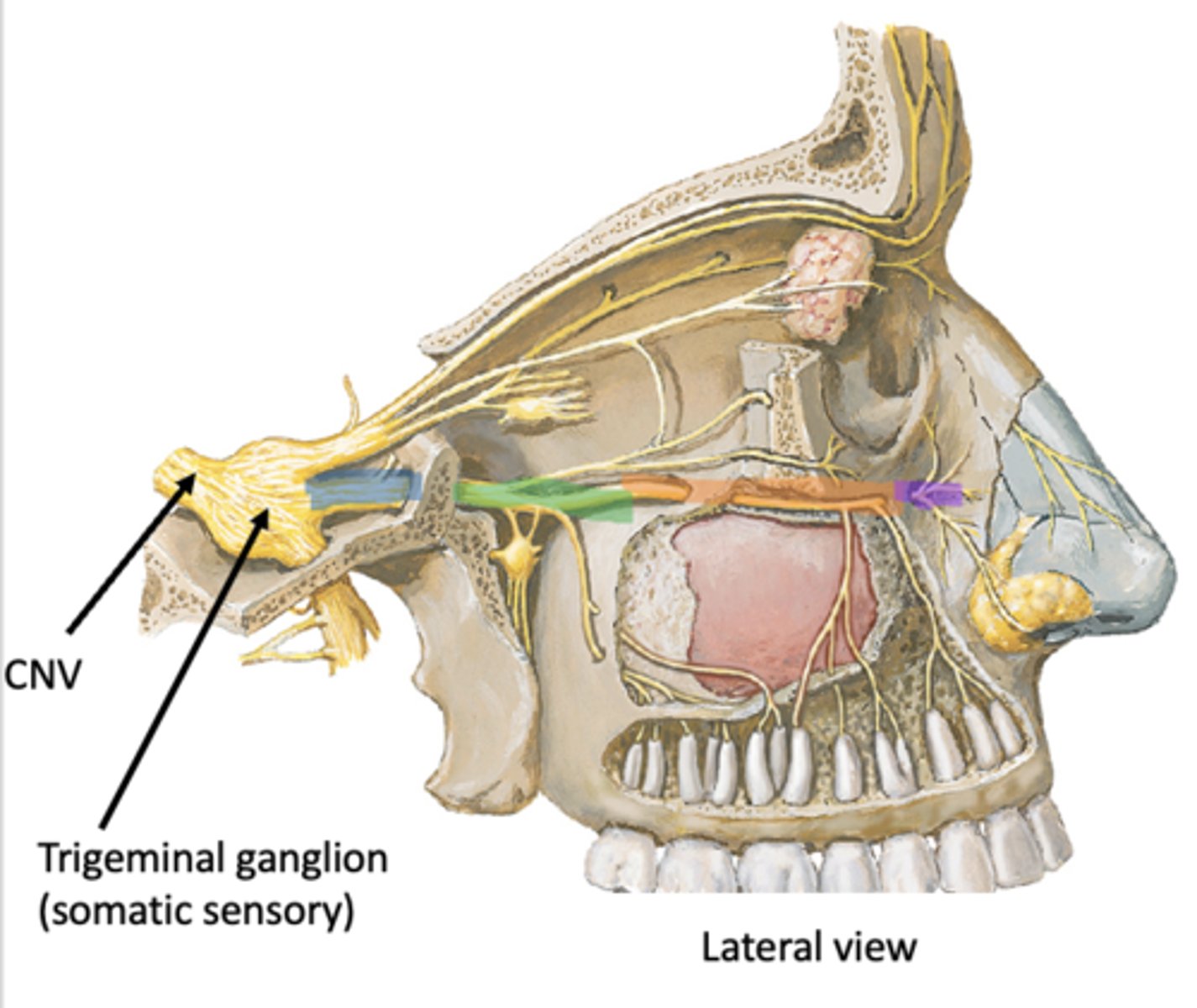
Face
Identify the region in purple
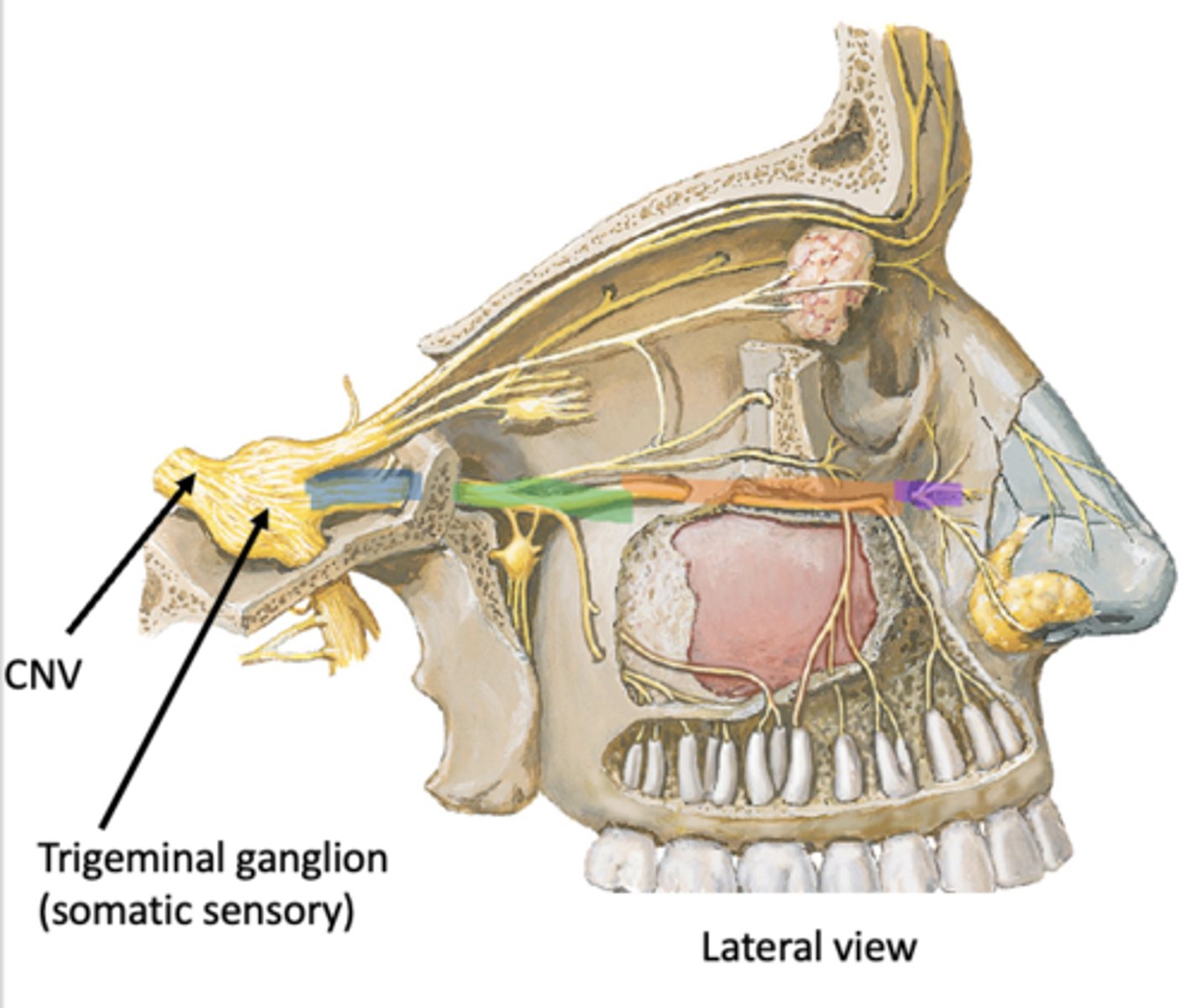
Trigeminal ganglion (outside fossa in middle cranial fossa)
Pterygoplaatine ganglion (in fossa)
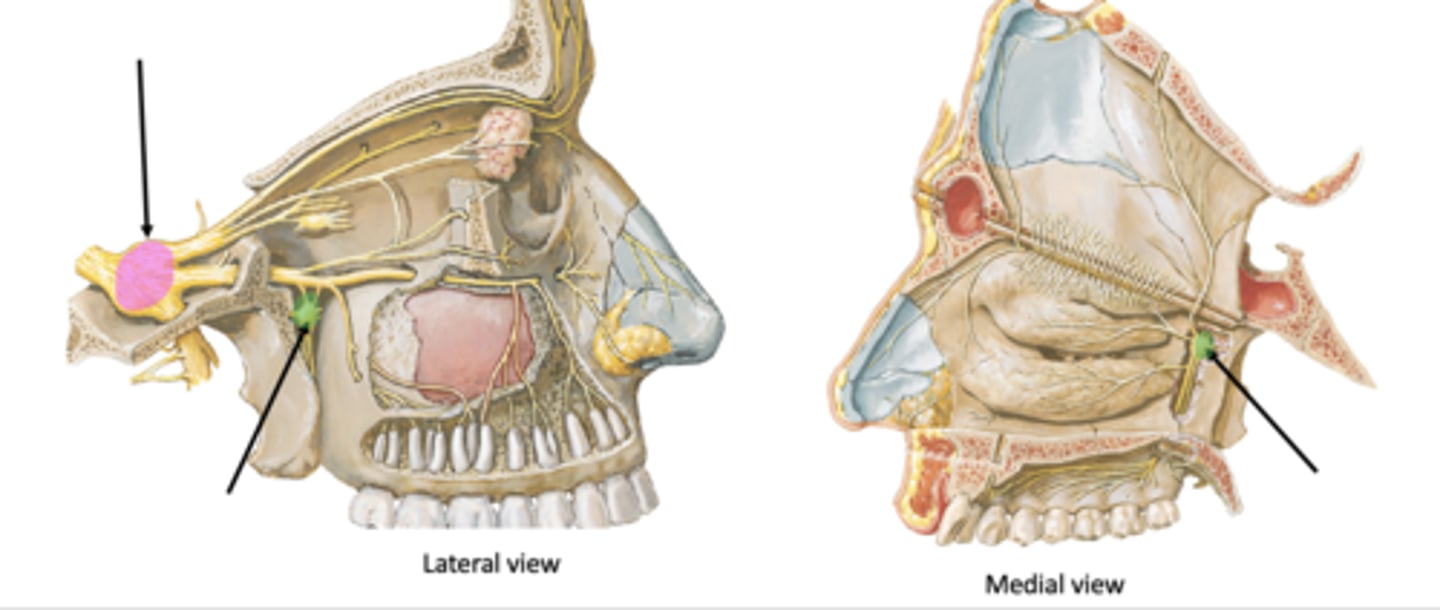
What are the two ganglia associated with pterygopalatine fossa?
Trigeminal ganglion
Identify the ganglion:
• Houses all of the trigeminal somatic sensory nerve cell bodies.
• These are unipolar neurons carry sensation from the periphery to the brainstem
Pterygopalatine ganglion
Identify the ganglion:
• Preganglionic parasympathetic fibers (from greater petrosal n) synapse here
• Sympathetic and sensory fibers travel through the ganglion without synapsing
• Autonomic fibers leave the ganglion and travel with V2 branches
Trigeminal ganglion (somatic sensory)
Identify the structure in pink
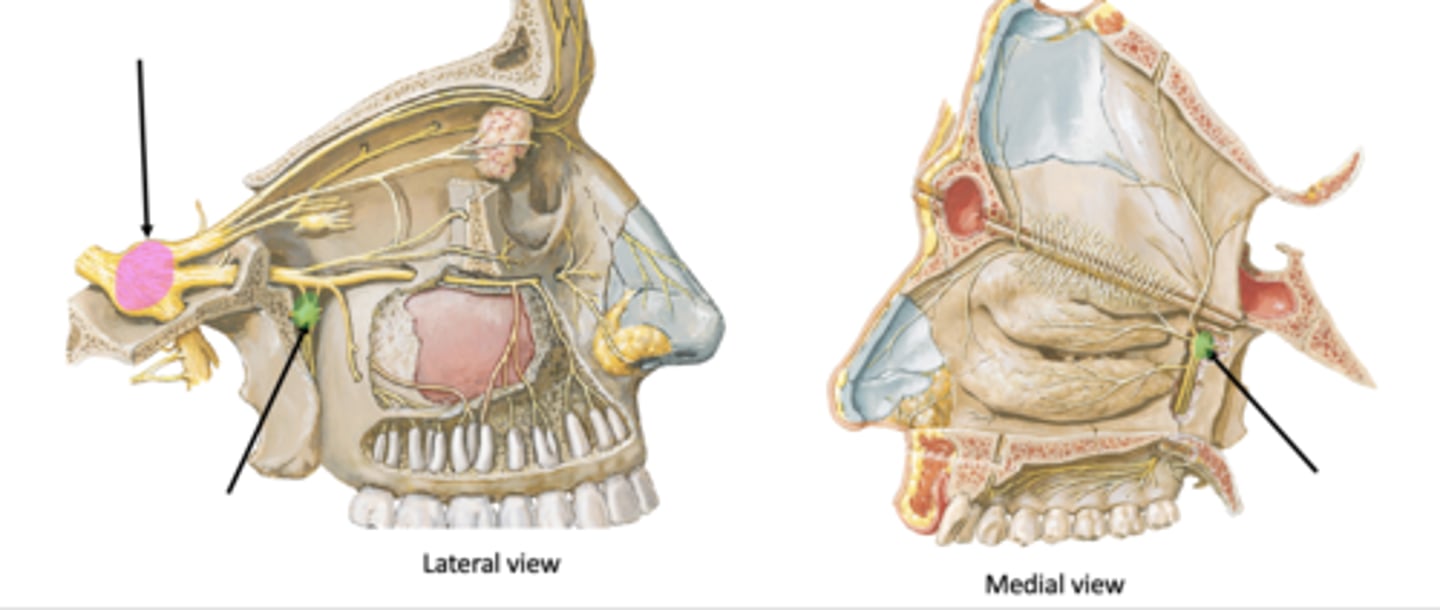
Pterygopalatine ganglion (parasympathetic)
Identify the structure in green
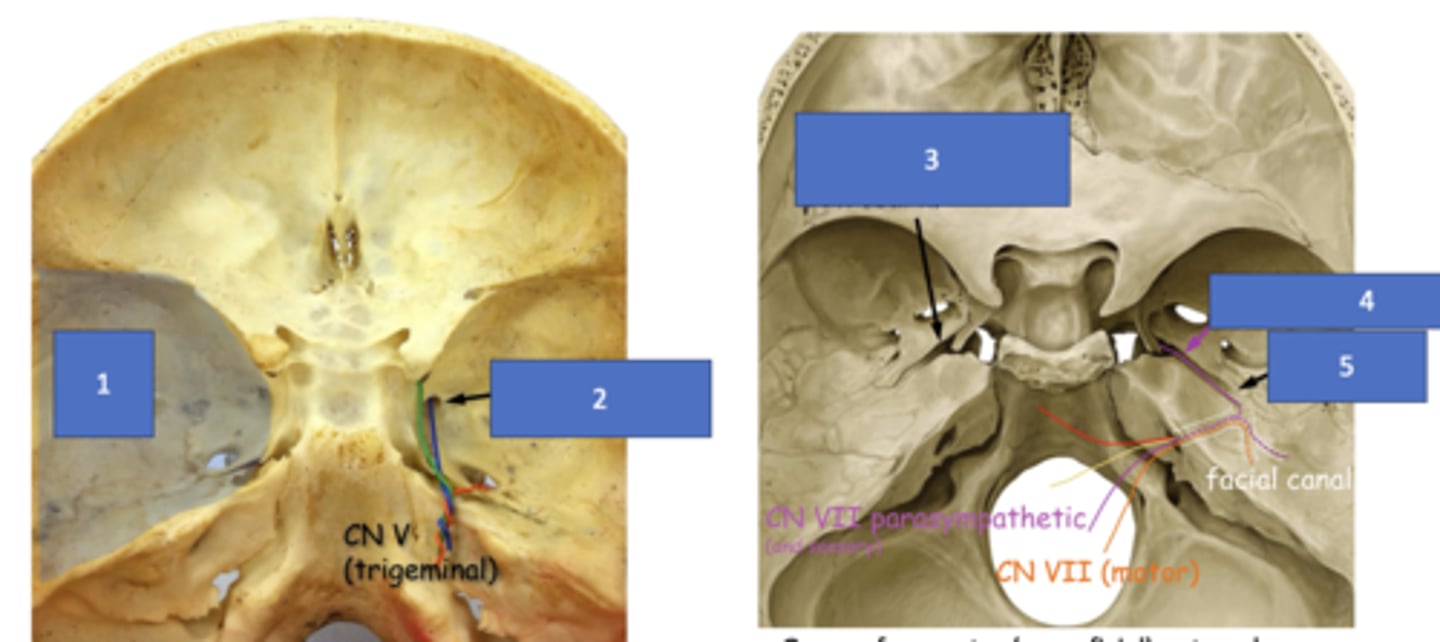
foramen rotundum
the maxillary division of CN V enter the pterygopalatine fossa via the:
infraorbital n.
V2 after fibers pass through the infraorbital fissure is called the:
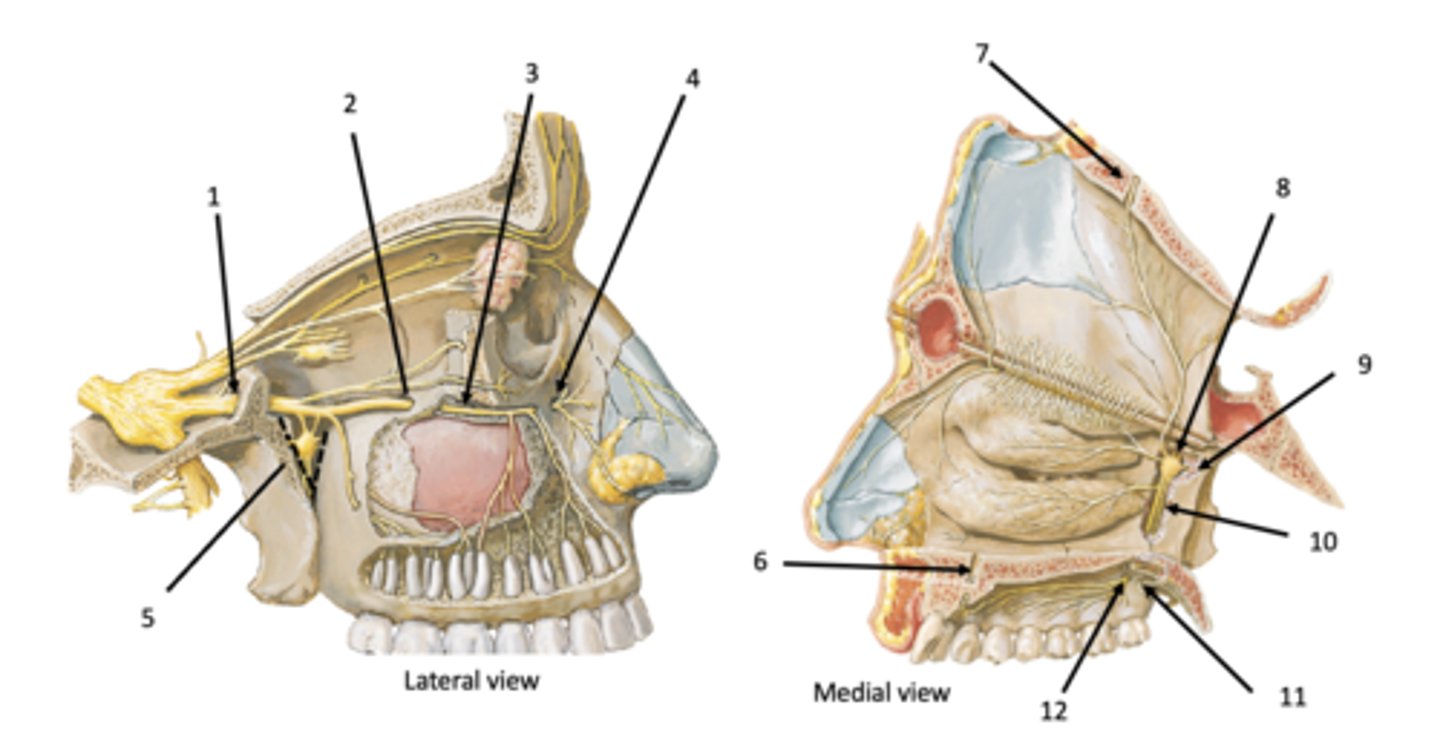
Foramen rotundum
Identify the structure at #1
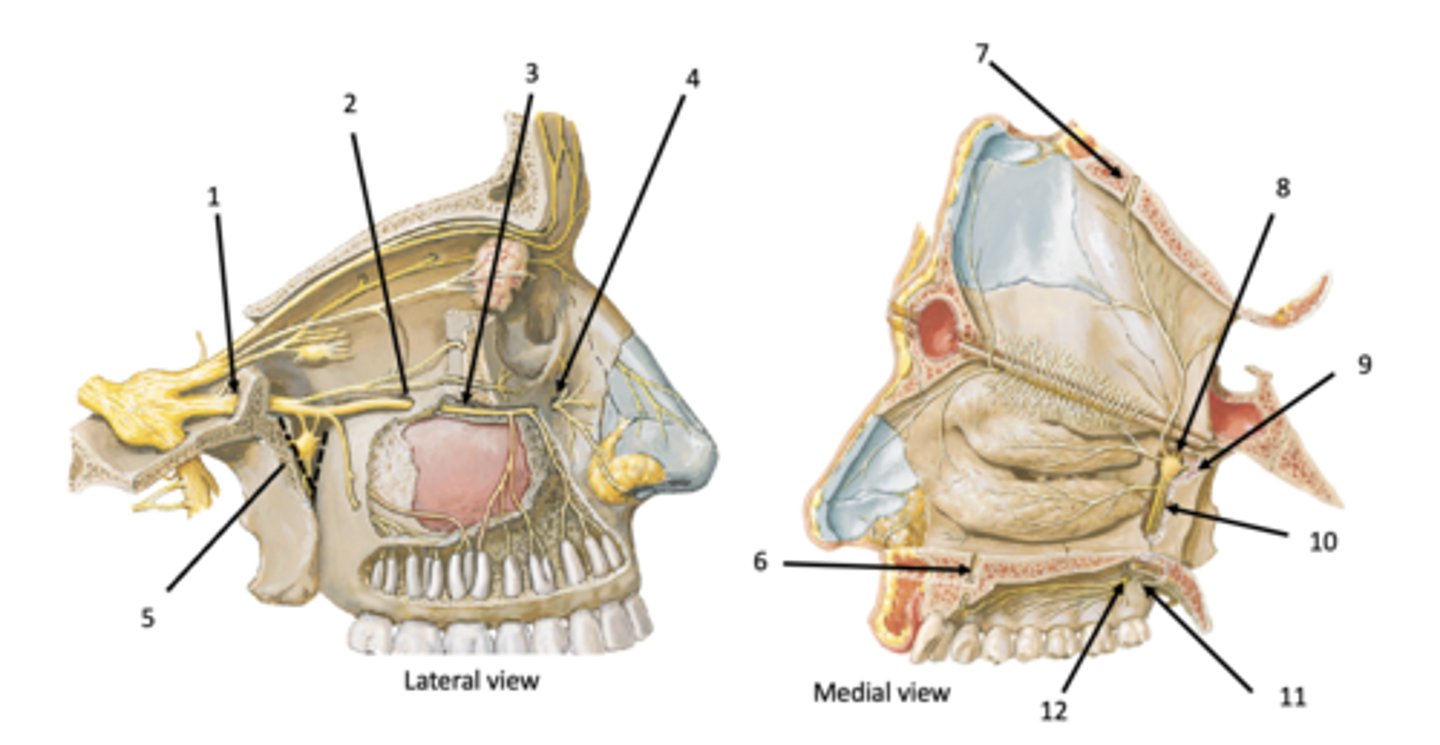
Infraorbital fissure
Identify the structure at #2
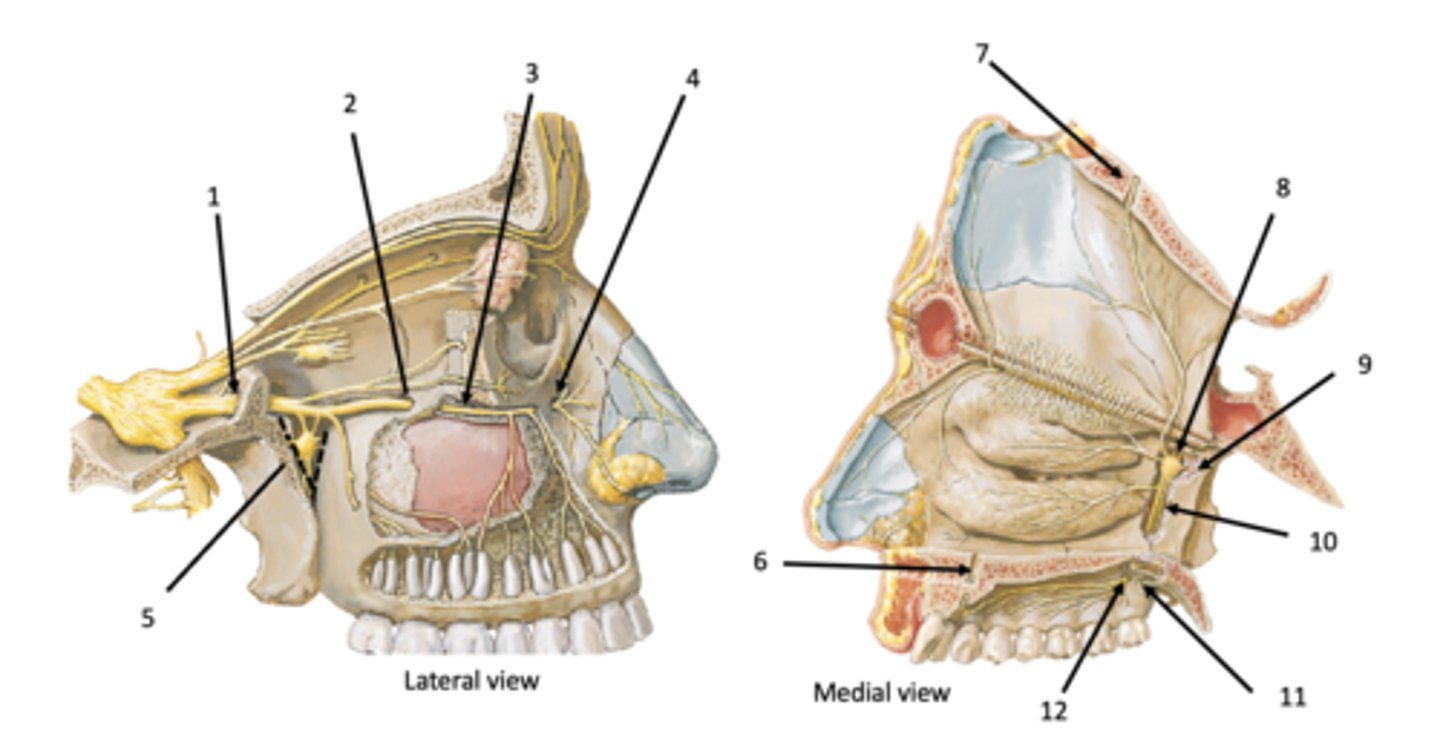
Infraorbital groove and canal
Identify the structure at #3
Infraobrital foramen
Identify the structure at #4
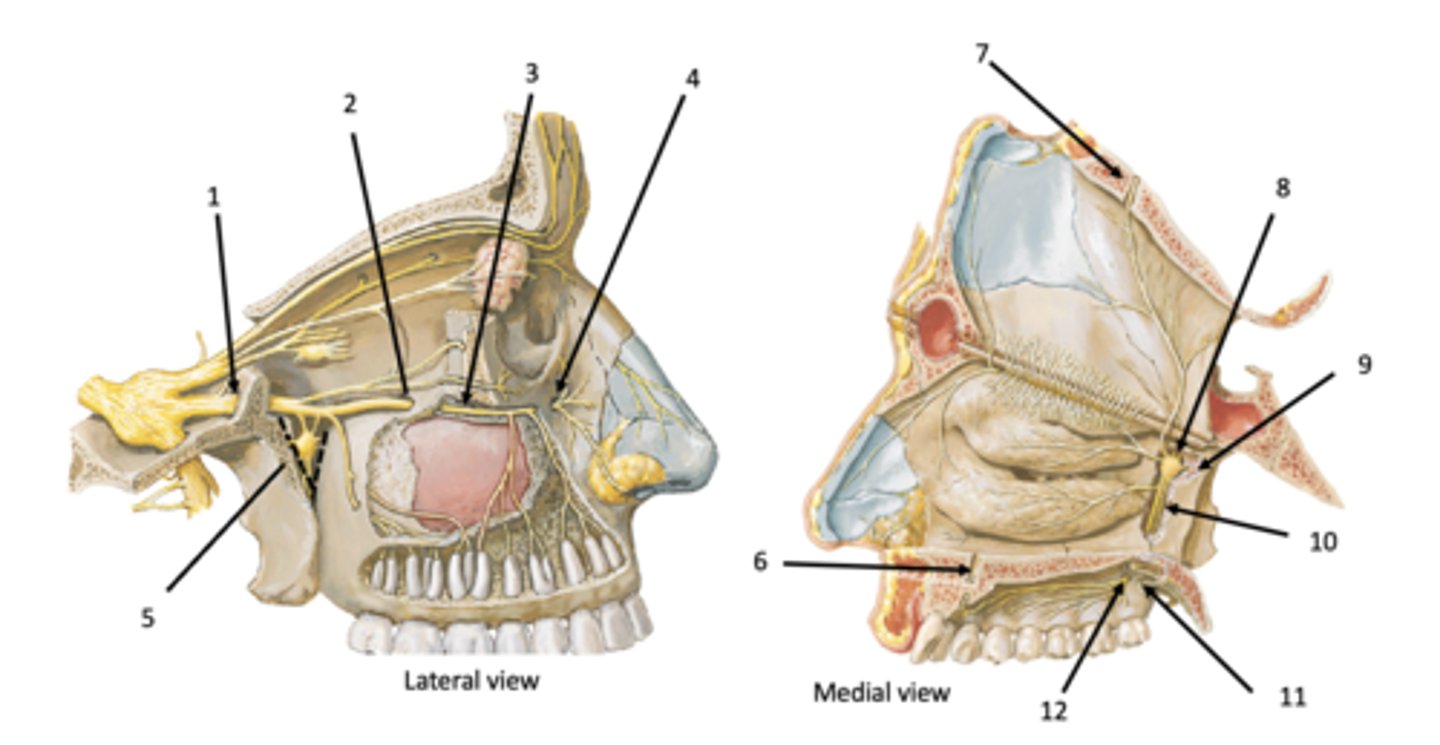
Pterygomaxillary fissure
Identify the structure at #5
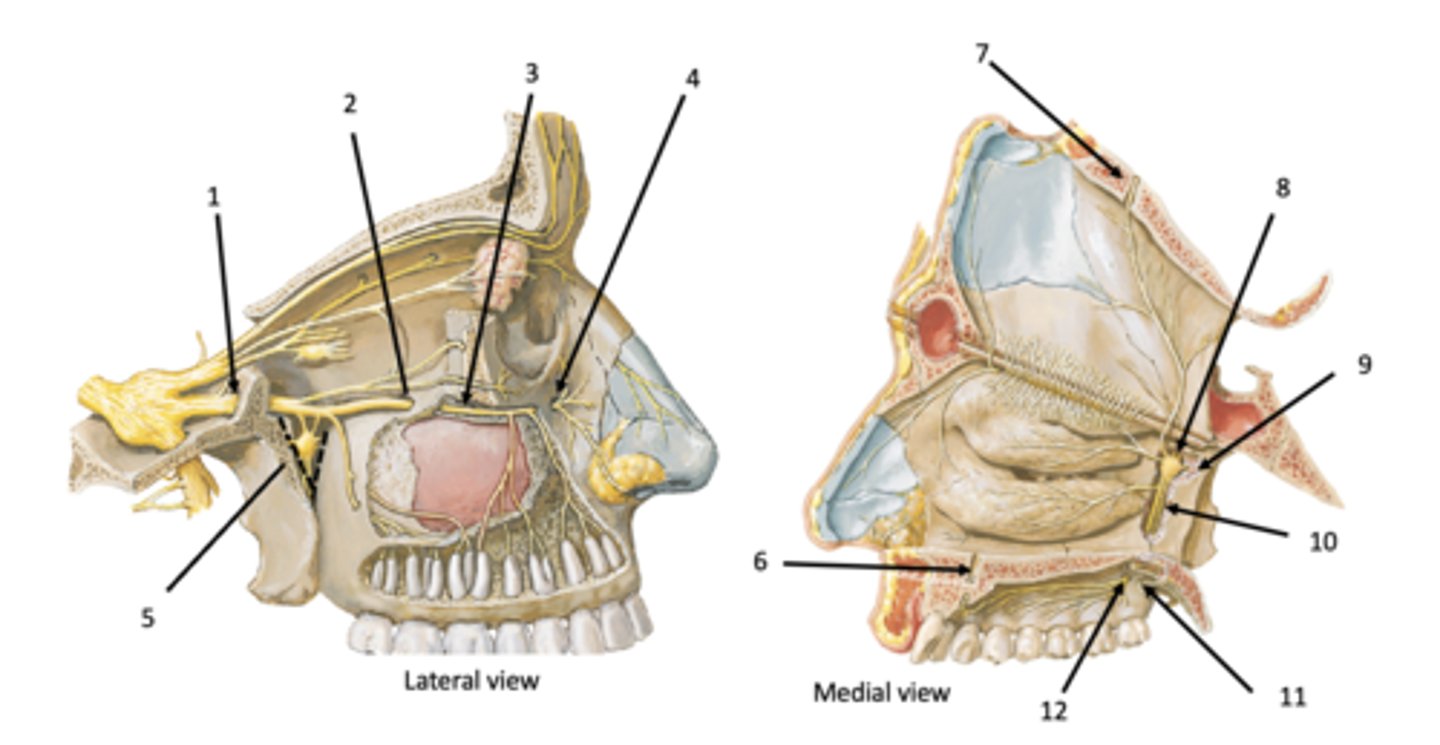
Incisive canal
Identify the structure at #6
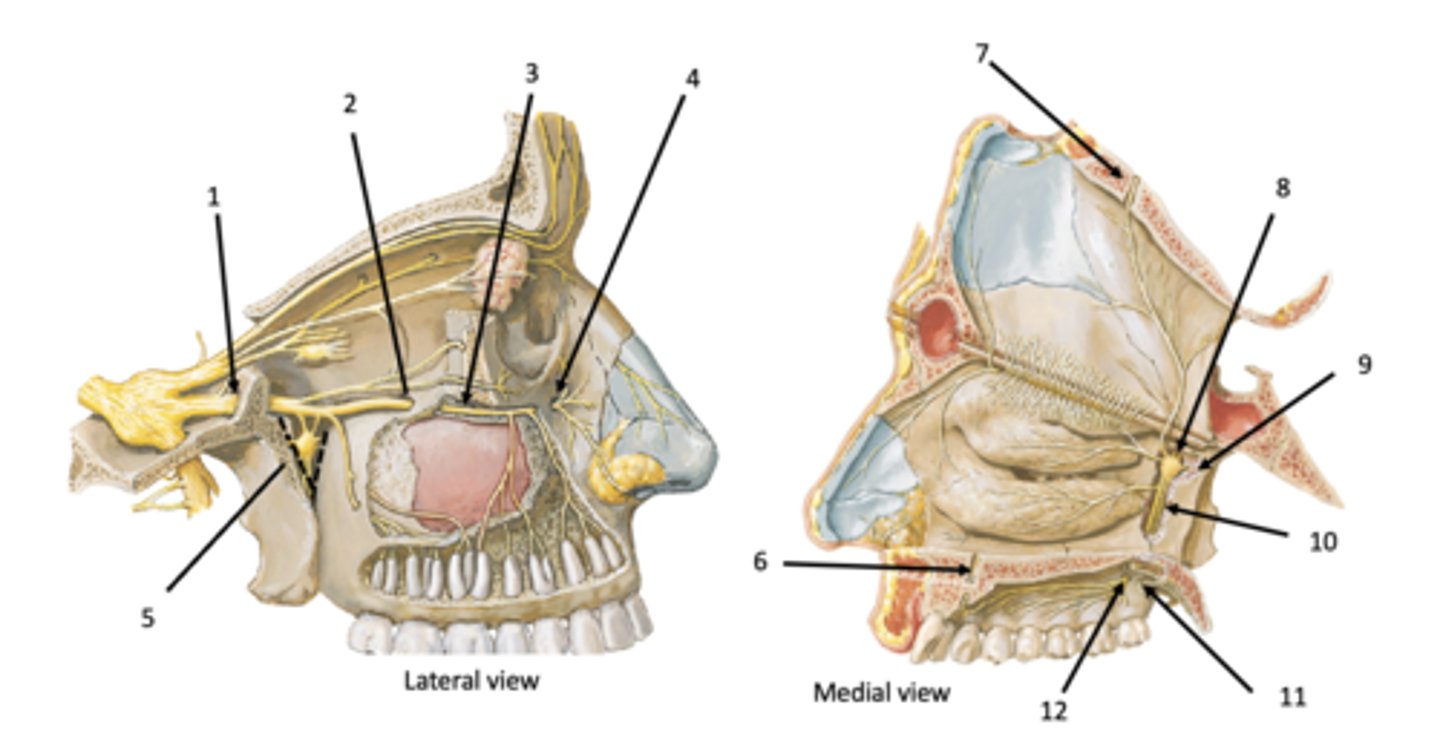
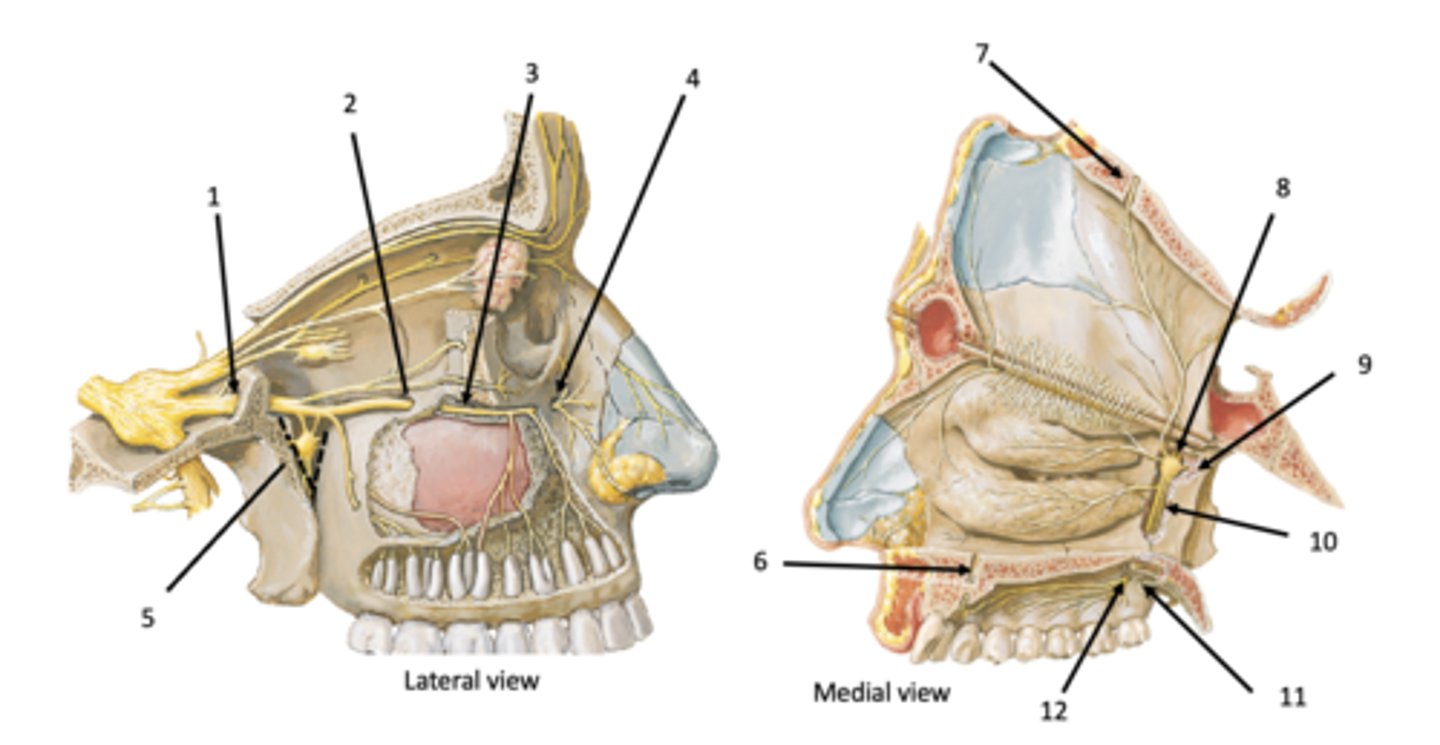
Incisive canal
Identify the structure at #7
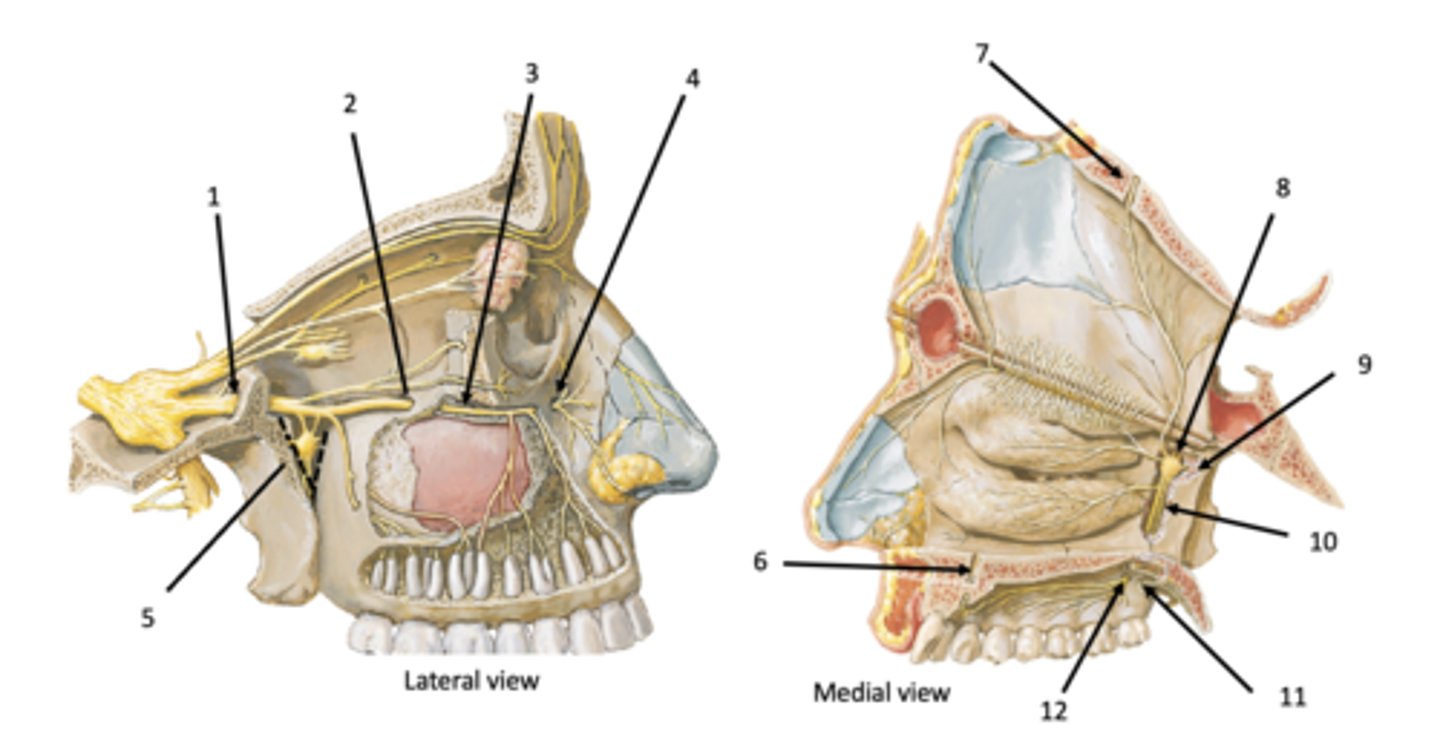
Sphenopalatine foramen
Identify the structure at #8
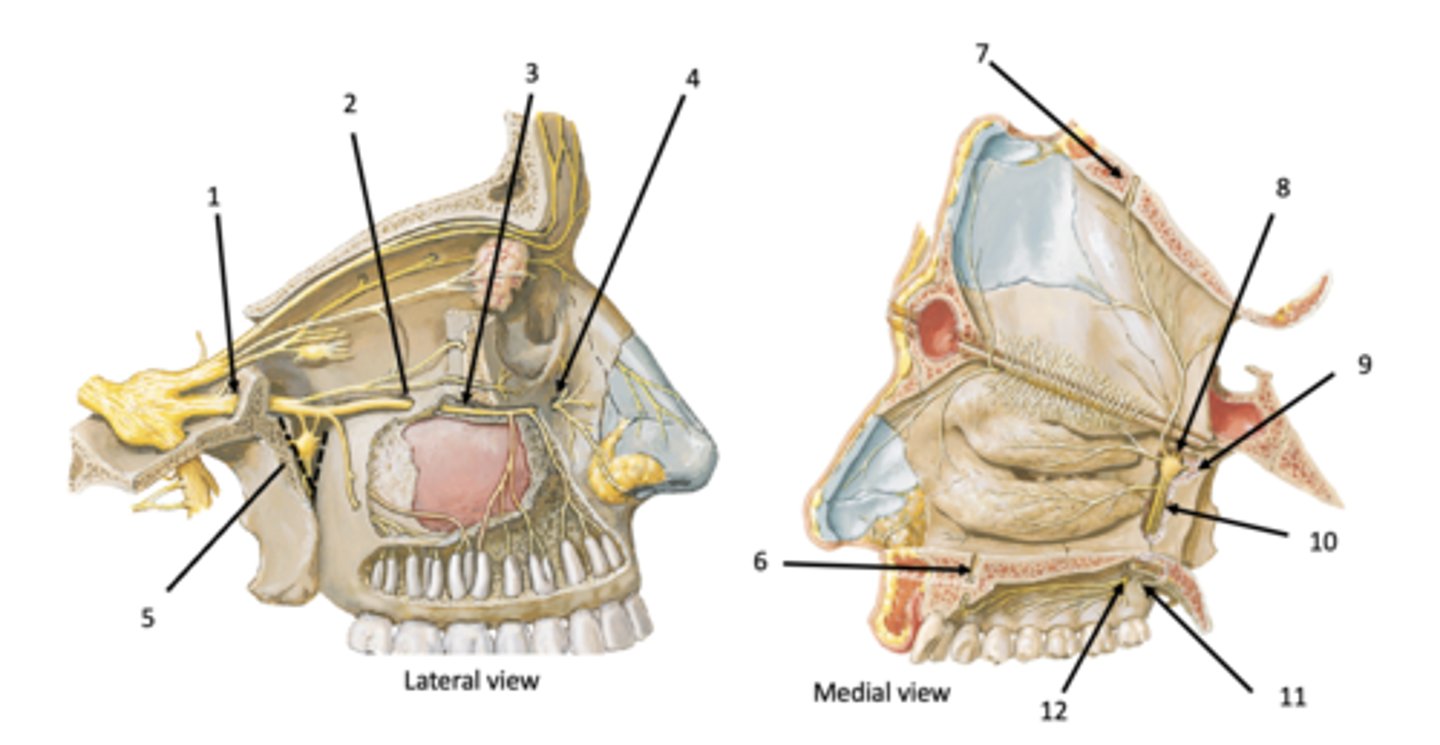
Pterygoid (vidian) canal
Identify the structure at #9
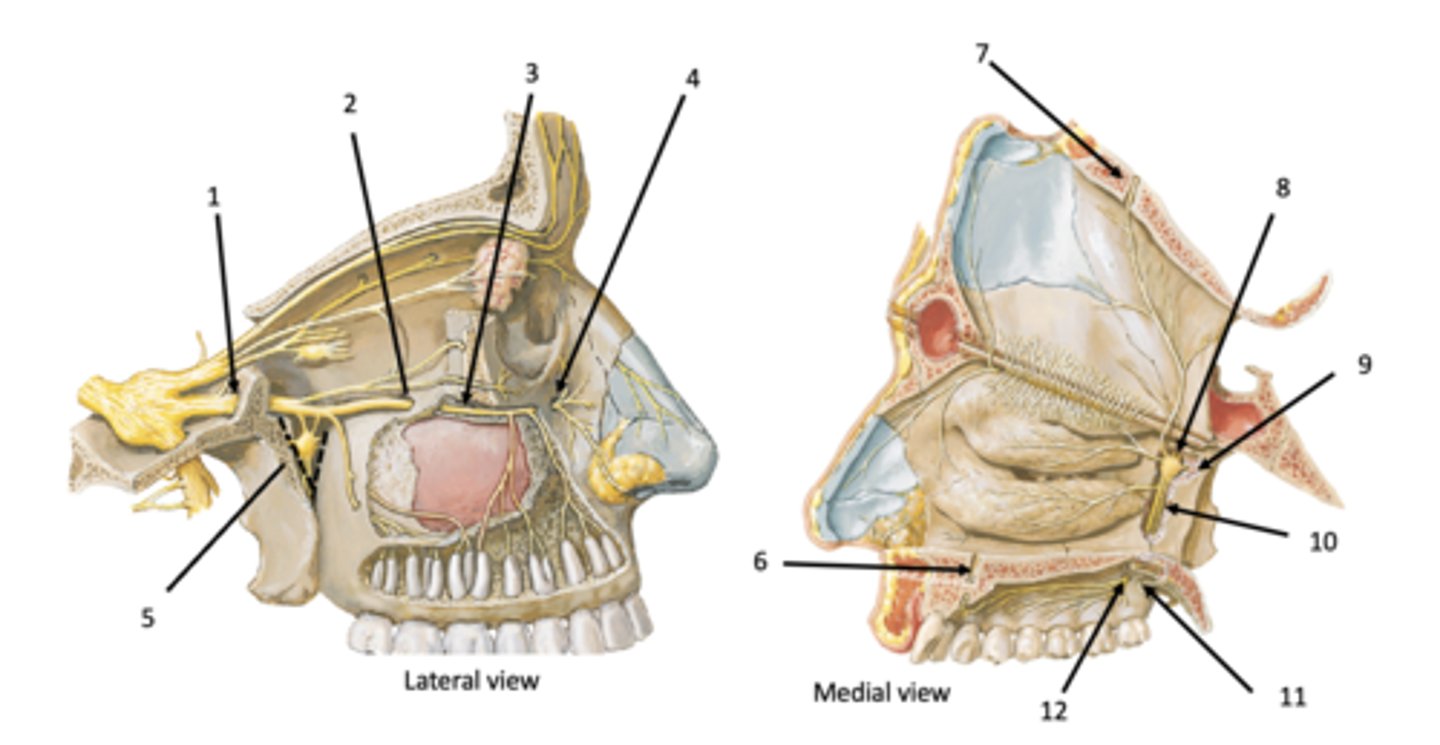
Palatine canal
Identify the structure at #10
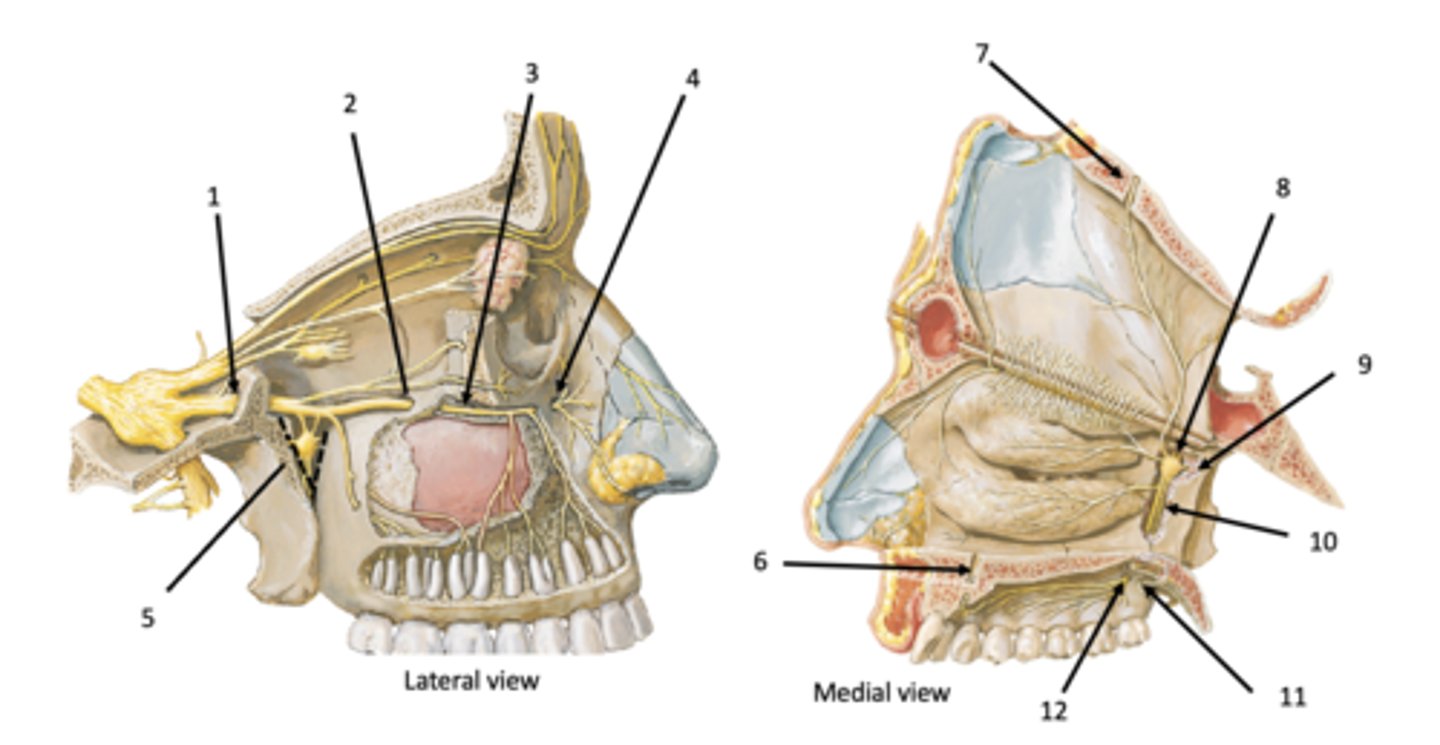
Lesser palatine foramen
Identify the structure at #11
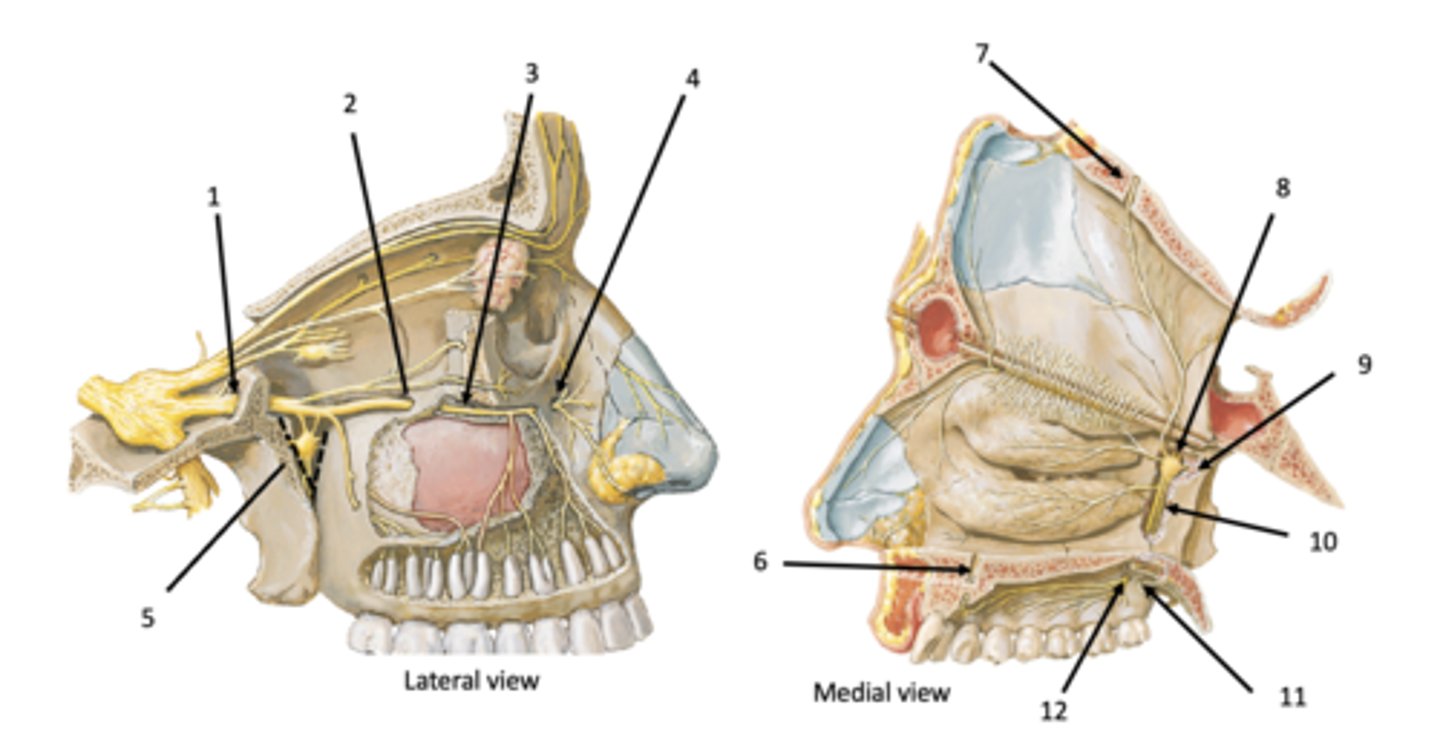
Greater palatine foramen
Identify the structure at #12
Middle cranial fossa
Identify the structure at #1
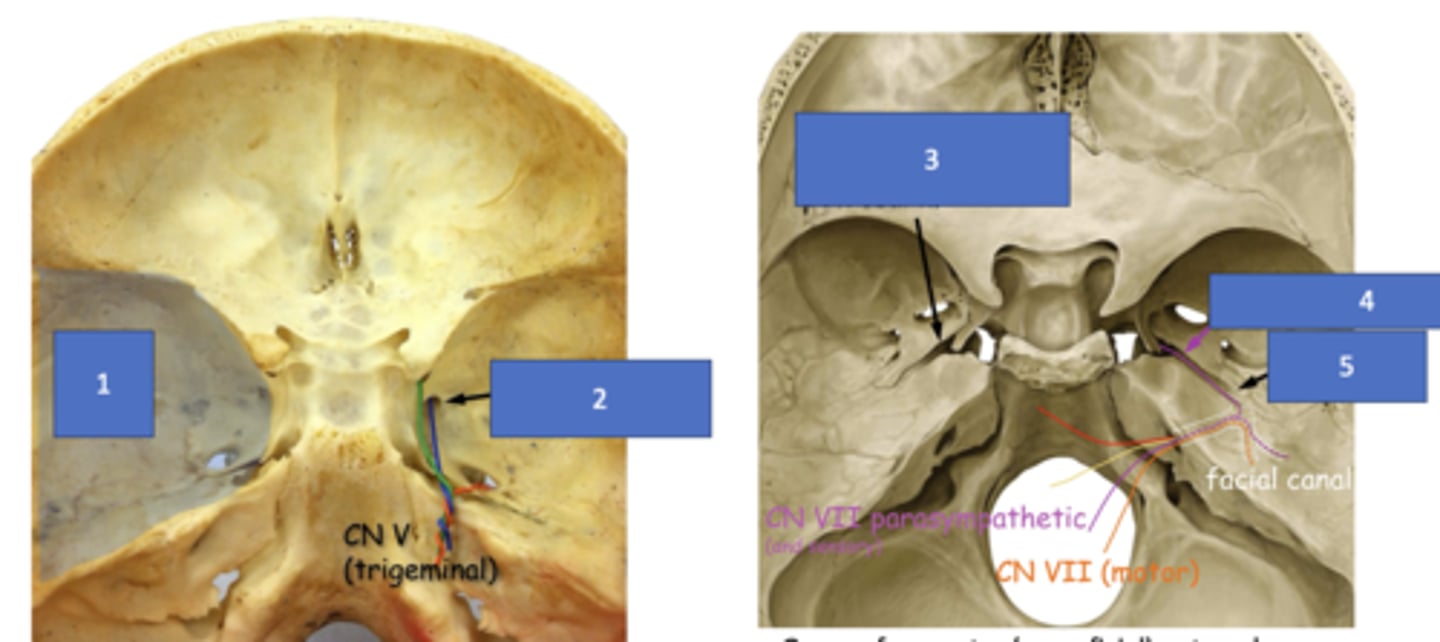
Foramen rotundum
Identify the structure at #2 (foramen)
Groove for greater (superficial) petrosal n.
Identify the structure at #3
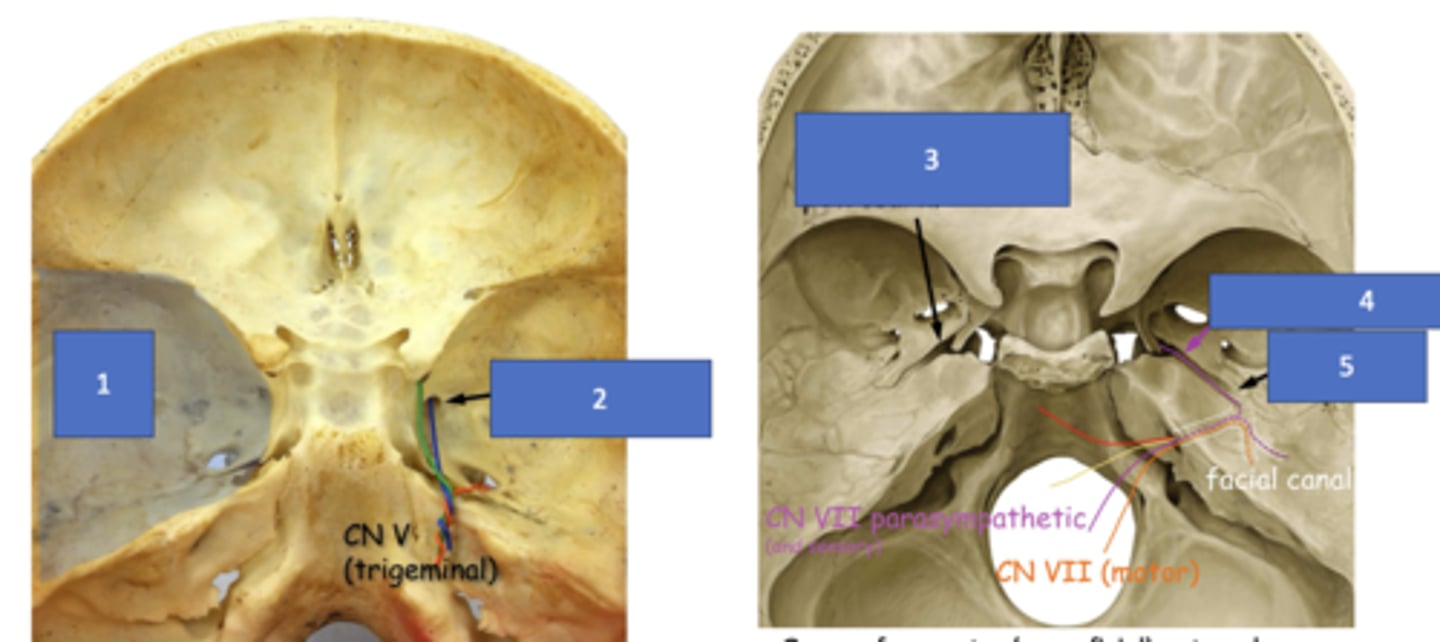
Greater petrosal n.
Identify the structure at #4
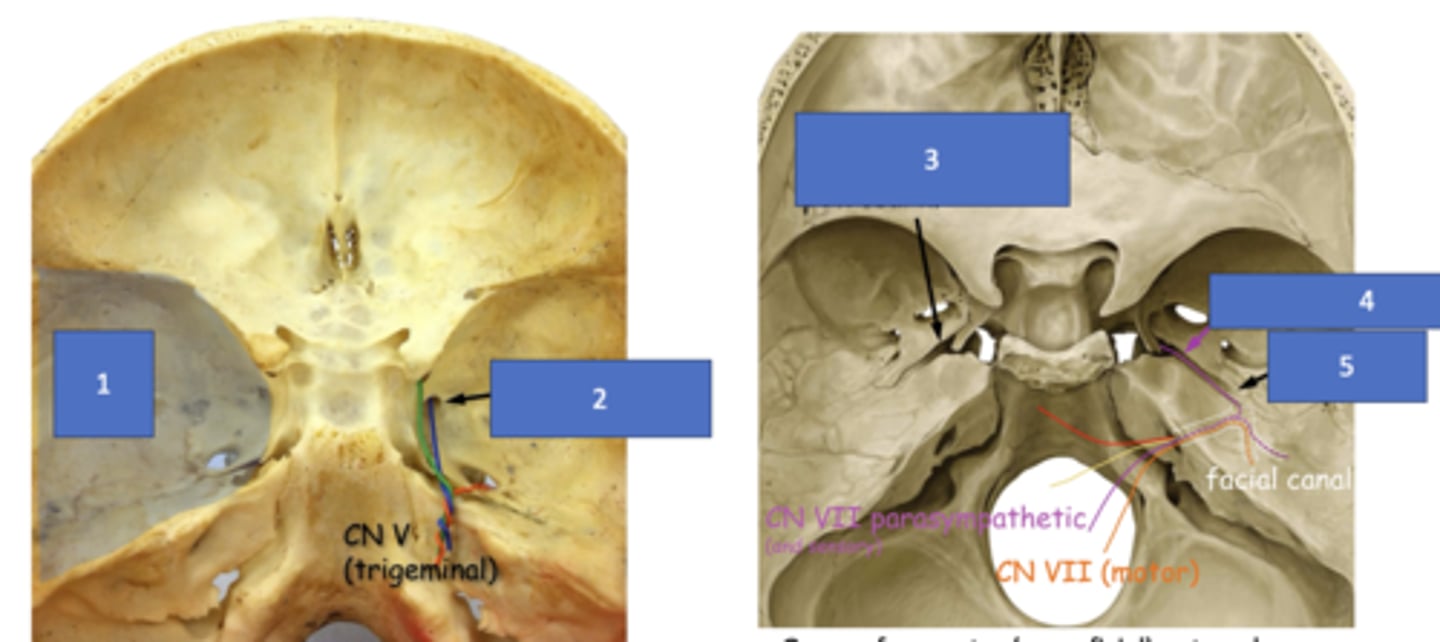
Hiatus of facial canal
Identify the structure at #5
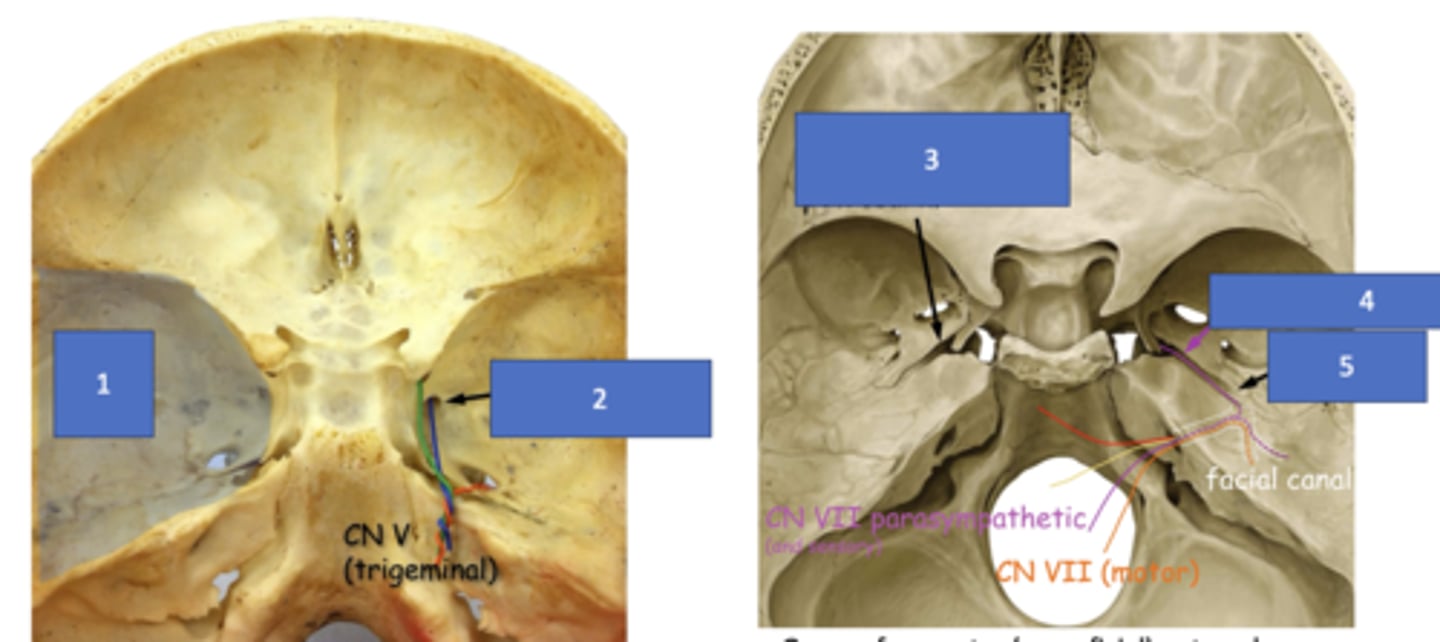
Pterygopalatine fossa, pterygoid canal
The greater petrosal nerve will travel through the groove for greater (superficial) petrosal nerve and the parasympathetic fibers from VII will enter the __________ through the __________
meningeal n. branch
which branch from V2 does NOT pass through the foramen rotundum?
meningeal n. branch
provides sensory innervation to the dura mater:
V2
meningeal nerve branch is a branch of:
middle meningeal a.
meningeal nerve branch travels with what structure?
meningeal n. branch
identify the structure:
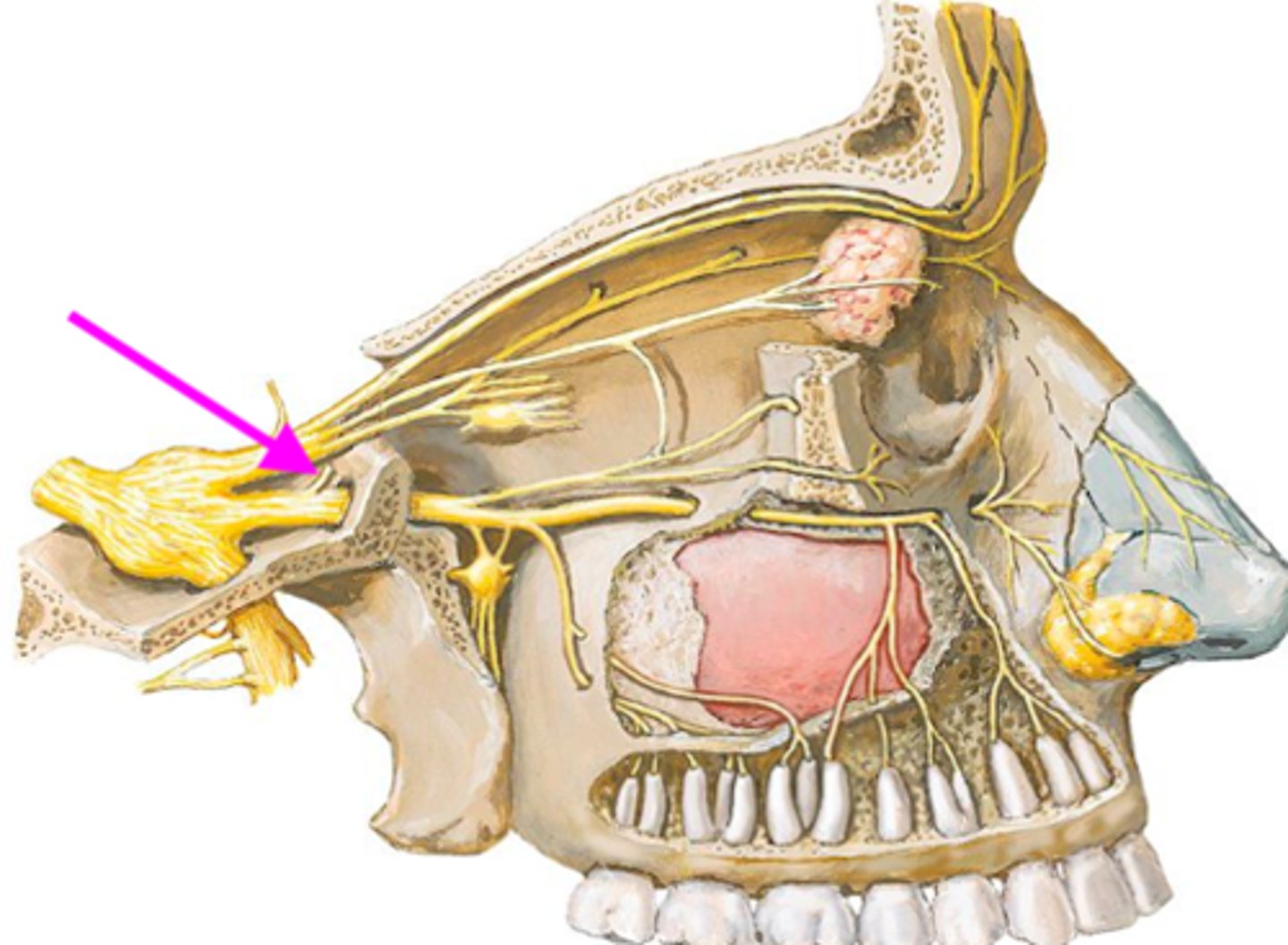
sensory innervation of dura mater
if this structure was lacerated, what function would be diminished