Psychology 1000- Chapters 3, 4, & 5
1/20
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
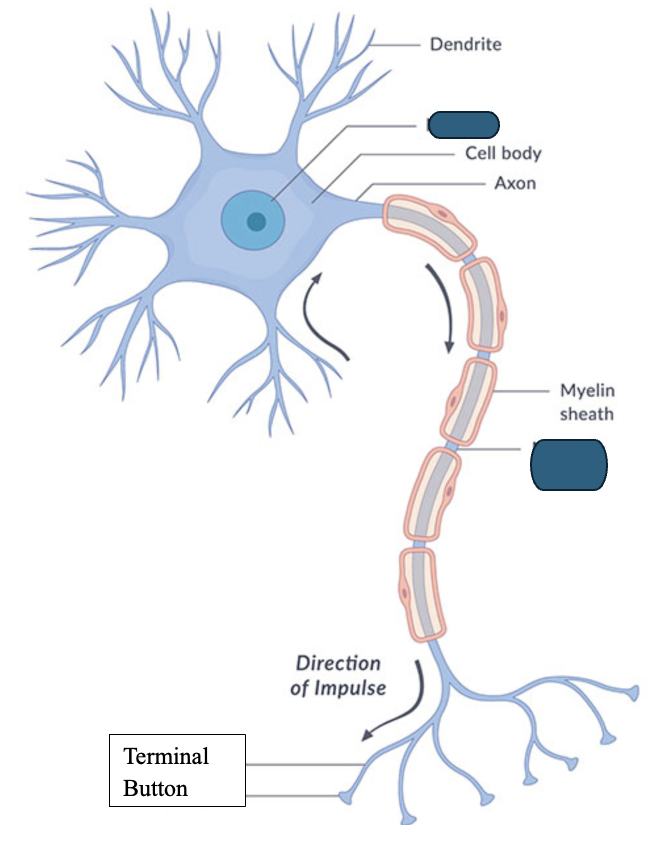
What is the anatomy of the neuron?
What are the types of twins?
Twins can be classified as identical (monozygotic), which develop from a single fertilized egg, or fraternal (dizygotic), which develop from two separate eggs fertilized by two different sperm.
What is the all-or-nothing principle?
Once a neuron is fired, the threshold is passed which triggers this. Once fired, there’s limitations as to how many times it can fire in a minute.
What are the different types of neurotransmitters?
Acetylcholine (ACh): Motor control, Dopamine (DA): Reward pathways, Serotonin: Mood regulation, Endorphins: Natural opiates, and Oxytocin: Hormones and neurotransmitter (attachments and emotional bonds).
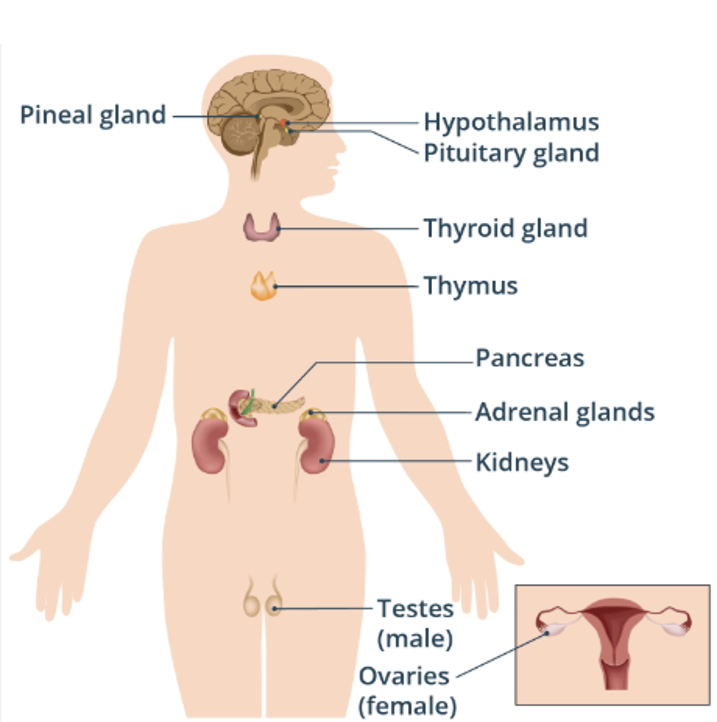
The endocrine cheat sheet
What are the structures/functions of the forebrain and hindbrain?
Hindbrain: Brainstem (Medulla - Coordinates heart rate, circulation, and respiration) (Pons - Relays information from the cerebellum to the rest of the brain).
Cerebellum (Fine motor skills, thinking, communication, attention, and vision).
Forebrain:
Amygdala - Emotional awareness and expression, formation of emotional memories.
Hippocampus - Formation and recall of memories.
Thalamus - Relay station for sensory information and routes to cerebral cortex.
Basal Ganglia - Set of structures that directs intentional movements and damage results in jerky or slow movements.
Hypothalamus - Regulates body temperature, hunger, thirst, and sexual behavior (emotion, stress, and reward).
What is the nature vs. nurture argument?
The nature vs. nurture argument explores the relative contributions of genetic inheritance (nature) and environmental factors (nurture) to human development and behavior. It examines how both elements interact to shape individual traits and characteristics.
What are the processes in sensation?
The processes in sensation include the reception of stimuli through sensory organs, transduction of these stimuli into neural signals, and the transmission of these signals to the brain for interpretation.
What is Weber’s law?
To be perceived as different, two stimuli must differ by a constant minimum percentage (not a constant amount).
What is the absolute threshold vs. just noticeable difference?
Absolute threshold: The minimum amount of energy an organism can detect 50% of the time.
Just noticeable difference: How much stimulus change is necessary for detection.
What is the Stroop Effect vs. cocktail party effect?
Stroop Effect: The delay in reaction time when the color of a word does not match the name of the color itself.
Cocktail Party Effect: Where individuals are able to focus on one particular sound or conversation in a noisy environment, while filtering out other distractions.
What are the color theories?
1st Theory: Trichromatic Theory (Green, blue, and red cones).
2nd Theory: Opponent Process Theory (Complementary color pairs of red-green and blue-yellow).
What are rods and cones?
Rods: Function well in dim light, but don’t see in color.
Cones: Respond to color, operates best under bright light.
What are kinesthetic vs. vestibular senses?
Kinesthetic Sense: Movement, posture, orientation, and proprioceptive feedback.
Vestibular Sense: Three fluid-filled semicircular canals and adjacent organs located next to the cochlea in each inner ear.
What are the sleep stages and disorders?
1) Awake - Alpha Waves.
2) N1 - Theta Waves.
3) N2 - Sleep Spindles, K Complexes.
4) N3 - Delta Waves.
5) REM - Characterized by rapid eye movements and a high level of brain activity (dreaming occurs most often in this stage and body is immobilized).
Insomnia - Being unable to fall asleep and stay asleep.
Sleep Apnea - Breathing disorder in which you stop breathing for 10 seconds or more during sleep.
What is the problem of other minds?
Fundamental difficulty we have in perceiving consciousness of others. (Judging minds according to capacity for experience (feelings) and capacity for agency (self-control, thought).
What are the 2 types of drug dependence?
Psychological dependence and physical dependence
What is drug tolerance?
The need to take increasing amounts of a drug to get the same effect.
What are the 5 levels of consciousness?
1) Higher-level Consciousness: “Fully conscious” and controlled processing.
2) Lower-level Consciousness: Requires little attention, automatic processes.
3) Altered States of Consciousness: Drug states, fatigue, illness, and hypnosis.
4) Subconscious Awareness: Brain activity occurring without your awareness, sleep and dreams.
5) No Awareness: Unconscious thought and non-conscious processes.
What are the dream theories?
Manifest Content: Dream’s apparent topic or superficial meaning.
Latent Content: Dream’s true underlying meaning.
What are the different classes of drugs?
Depressants: Substance that slow down the central nervous system (Alcohol, Barbiturates, Toxic Inhalants, and Narcotics)
Stimulants: Substance that raises levels of physiological or nervous activity in the body (Amphetamines, Ecstasy, Nicotine, and Cocaine)