lec 3 (mcbride) - lipids, carbohydrates part 2: roles in health and disease
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
maintaining homeostasis requires…
metabolic regulation that coordinates the use of nutrient pools
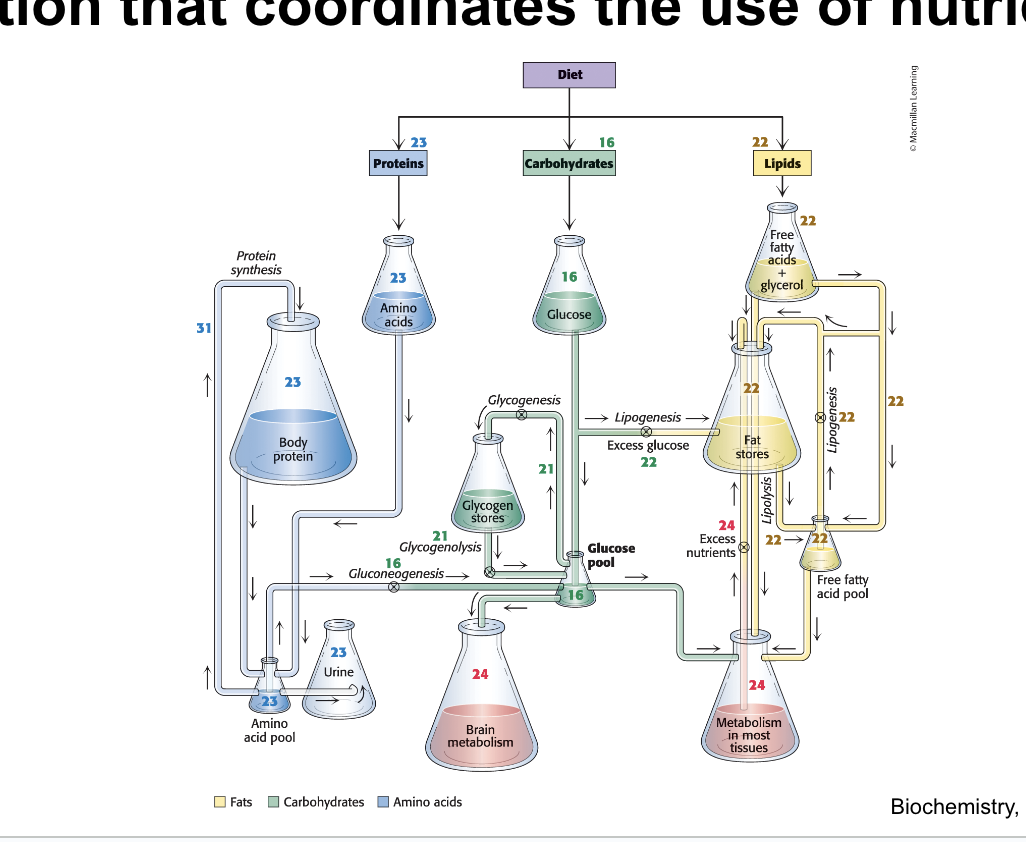
homeostasis adjusts…
production and consumption rates to maintain physiological levels while also meetinhg essential demands
homeostatic mechanisms adjust these rates to achieve production = consumption to maintain a physiological concentration required for life
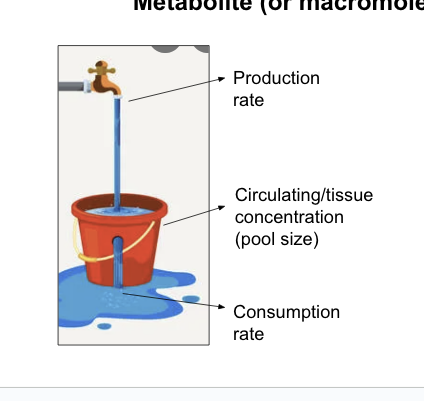
caloric homeostasis…
is a means of regulating energy stores
caloric homeostasis (energy homeostasis) = the ability to maintain adequate but NOT excessive energy stores
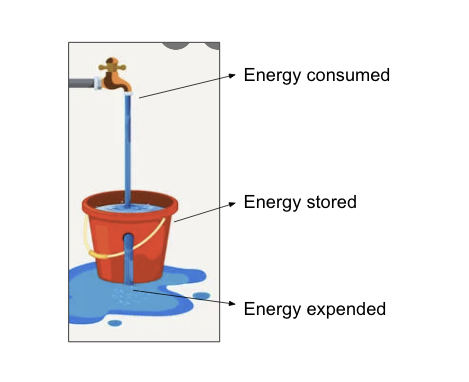
excess energy fuels (nutrients) must be…
if fuels are consumed in excess of energy needs → fuels are stored
excess energy molecules ultimately converted to triacylglycerols which are stored in adipocytes
diagram
fuel consumed = dietary protein, fats, and carbs
energy stored as triacylglycerols
fuel expended = AAs, fatty acids and monosaccharides oxidized in TCA cycle
excessive triacylgylcerol storage
has adverse health effects
excess storage of triacylglycerols is great when there is scarcity of food to maintain energy supply
continued energy storage leads to accumulation of triacylglycerols, enlarged adipocytes, and body weight gain
health consequences of increased body fat
coronary heart disease
type 2 diabetes
cancers
hypertension
dyslipidemia (disruption of lipid metabolism)
stroke
liver and gallbaldder disease
sleep apnea and respiratory problems
osteoarthritis (degeneration of joint cartilage/bone)
gynecological problems
male infertility problems
energy balance
is controlled by both behavioral and biochemical factors
behavior factors
diet/nutrient consumption
exercise
biochemical factors
short term and long term signals
resting metabolic rate
hormones
caloric homeostasis
brain plays a key role in caloric homeostasis
2 types of signals in the GI tract, the β cells of the pancreas and fat cells
short term signals are active during a meal
long term signals report on the overall energy status of the body
these signals target the brain’s arcuate nucleus, a group of neurons in a region of the hypothalamus
small peptide hormones
secreted from small intestine signal distal organs such as brain and pancreas
short term signals relay feelings of satiety from gut → various regions of the brain, reducing the urge to eat
cholecystokinin (CCK) and glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) = small peptide hormones secreted into the blood by cells of the small intestine after a meal
bind to their respective GPCRs in peripheral neurons, relaying satiety signals
CCK stimulate the secretion of pancreatic enzymes and bile salts from the gall bladder
GLP-1 enhances glucose-induced insulin secretion and inhibits glucagon secretion
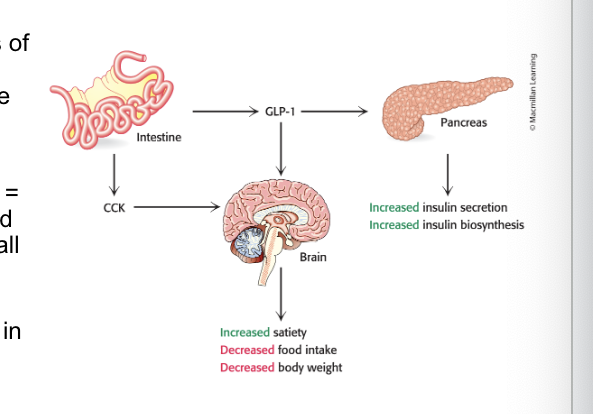
GLP-1 secretion…
promotes energy storage through increase in insulin secretion
insulin promotes energy storage
increases glycogen synthesis and lipogenesis
decreases lipolysis
promotes energy storage through inhibition of glucagon secretion
glucagon decreases energy storage
activates lipases to catalyze the hydrolysis of triacylglycerols → fatty acids
GLP-1 agonists
are a new line of medication for regulating blood sugar and lipid storage
Glucagon-like peptide-1 agonist medication work by mimicking the GLP-1 hormone
triggering insulin release from the pancreas
decreasing glucagon secretion
decreasing rate of stomach emptying (digestion)
increasing feelings of fullness from eating (satiety)
leptin
in addition to insulin, leptin regulates long term control over caloric homeostasis
insulin = signal molecule that communicates the status of glucose in the blood
secreted by the pancreatic β cells
leptin = signal molecule that communicates the status of triacylglycerol stores
secreted by adipocytes
secreted in direct proportion to amt of fat present
binding to its receptors increases the sensitivity of muscle and the liver to insulin, stimulates β oxidation of fatty acids and decrases triacylglycerol synthesis
leptin also suppresses…
appetite by binding the leptin receptor in brain
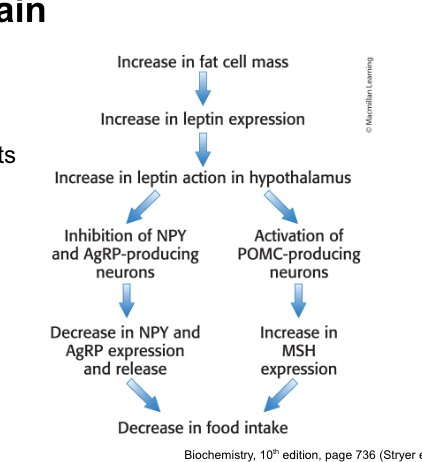
leptin = adipokine secreted by adipose tissue in direct relation to fat mass
when fat mass increases → leptin inhibits appetite-stimulating peptide (NPY and AgRP) secretion while stimulating the release of appetite-suppressing hormone (MSH)
blood sugar levels
must be maintained between meals
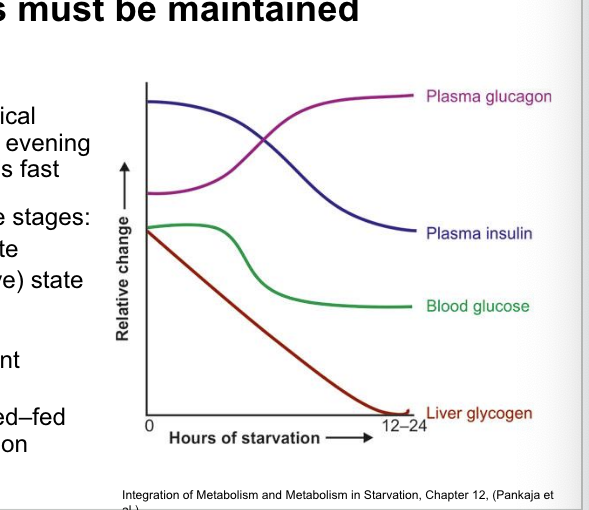
fasted-fed cycle = a physiological condition experienced after an evening meal and throughout the night’s fast
3 stages
well-fed (post-prandial) state
early fasting (postabsorptive) state
refed state
glucose homeostasis = constant blood-glucose concentration
maintained during the fasted-fed cycle by insulin and glucagon
postabsorptive state
occurs at the beginning of a fast
postabsorptive (fasted) state = state that immediately follows the absorption of glucose from the previous meal blood-glucose concentration begins to drop
leads to decrease in insulin secretion and rise in glucagon
glucagon
stimulates glycogen breakdown
inhibits glycogen synthesis
inhibits fatty acid synthesis
stimulates the gluconeogenic state in the liver
blocks glycolysis
gluconeogensis
is production of glucose from pyruvate
pyruvate → PEP → fructose 1,6-biphosphate → fructose 6-phosphate → glucose 6-phosphate → glucose
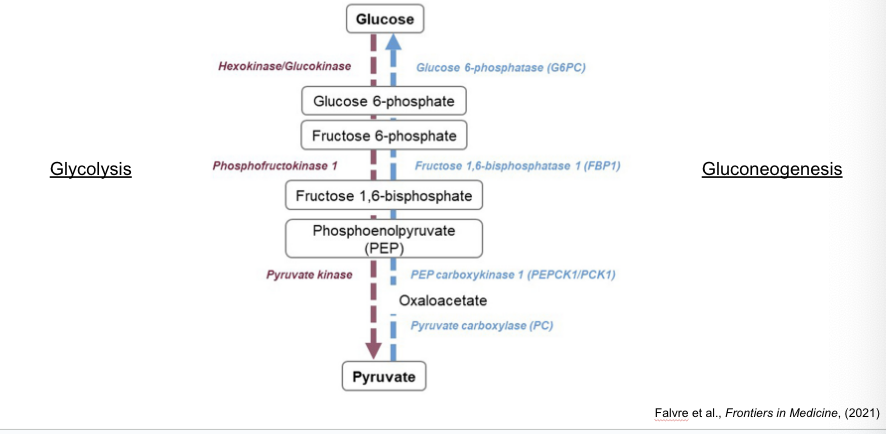
glycolysis and gluconeogenesis
are reciprocally regulated
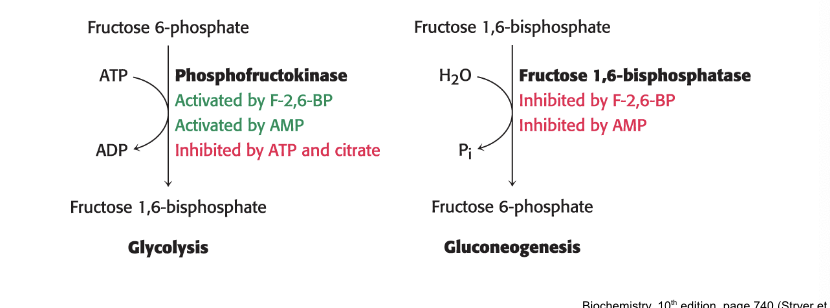
phosphofructokinase = key enzyme in regulation of glycolysis
activated by F02,6-BP; AMP
inhibited by ATP; citrate
fructose 1,6-biphosphatase = principal enzyme for controlling rate of gluconeogenesis
inhibited by F-2,6-BP; AMP
upon eating after a long fast…
liver will use glucose to replenish glycogen stores
fat is processed the same in the normal fed state and refed state
after long fast, liver does NOT initially absorb glucose from blood, leaving it for other tissues
liver remains in gluconeogenic mode → replenishing liver’s glycogen stores
after glycogen stores are replenished → liver processes excess glucose for fatty acid synthessi
diabetes
is a disease of disrupted glucose homeostasis resulting from insulin resistance
diabetes mellitus = disease resulting from disruption of caloric homeostasis
characterized by overproduction of glucose by the liver and underutilization by other organs
named for common symptom of excessive urination
diabetes and glucose
diabetes leads to increased glucose elevation and slower clearance after meal
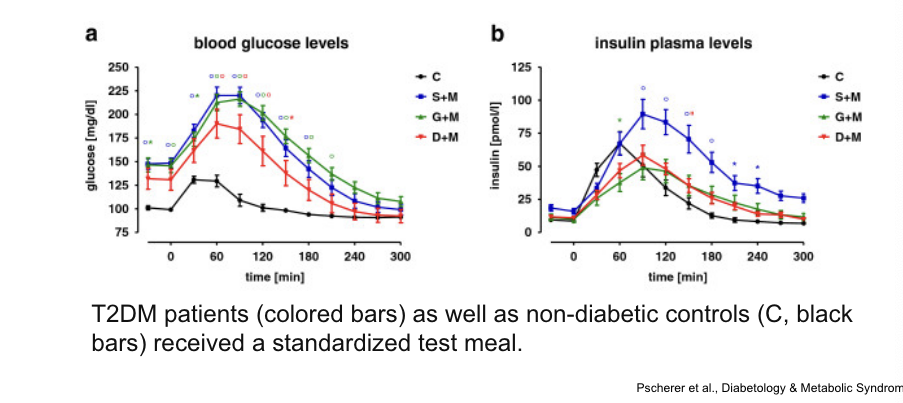
2 forms of diabetes
type 1 diabetes (insulin dependent diabetes) = diabetes caused by destruction of the insulin-secreting β-cells of the pancreas
typically autoimmune disorder
begins before age 20
insulin resistance = characteristic by which individuals are poorly responsive to insulin
type 2 diabetes = diabetes caused by insulin resistance
arises later in life than type 1
obesity = significant predisposing factor
accounts for 90% of cases in the world
metabolic syndrome
is closely associated with type 2 diabetes
metabolic syndrome = cluster of pathologies, including insulin resistance, hyperglycemia, and dyslipidemia (high blood triacylglycerol levels) that often develop together
thought to be a predecessor of type 2 diabetes
hepatic steatosis = condition in which tissues other than adipose tissue accumulate fat
often occurs in liver and muscle
results in insulin resistance and pancreatic failure
storage capacity of adipose tissue
can be exceeded leading to lipid accumulation in other tissues
in caloric excess, the storage capacity of adipocytes can be excessed with deleterious results
excess fat accumulates in other tissues → results in biochemical malfunction of tissues
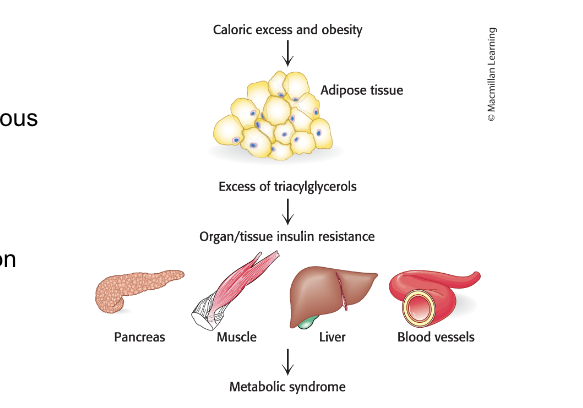
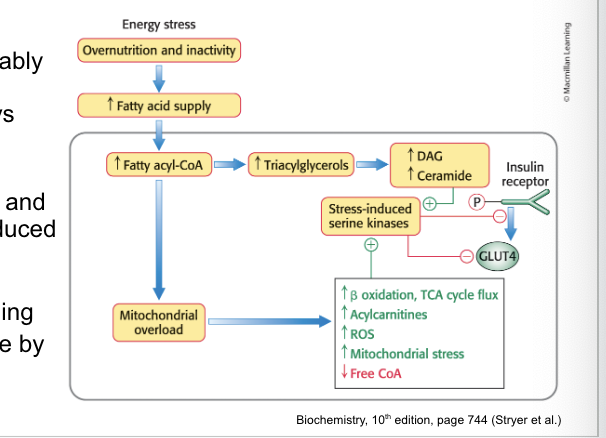
excess tissue triaglycerides
can disrupt signal-transduction pathways leading to insulin resistance
excess fat accumulation in peripheral tissues, most notably muscles, can disrupt some signal-transduction pathways and inappropriately activate others
in particular, diacylglycerols and ceramide activate stress-induced pathways that interfere with insulin signaling
decrease insulin signaling
decrease glucose uptake by transporter GLUT4
results in tissue insulin resistance
possible health benefits of high fat, low carb ketogenic diet
ketogenic diets = diets that promote ketone-body formation
used as therapeutic option for children with drug-resistant epilepsy
diets are rich in fats and low in carbs with adequate amounts of protein
recent research in mice suggests ketogenic diets:
alter the microbiome → results in therapeutic effects
may extend lifespan, improve memory and maintain long-term health
nutritional ketosis occurs when…
liver produces ketones from lipid degradation
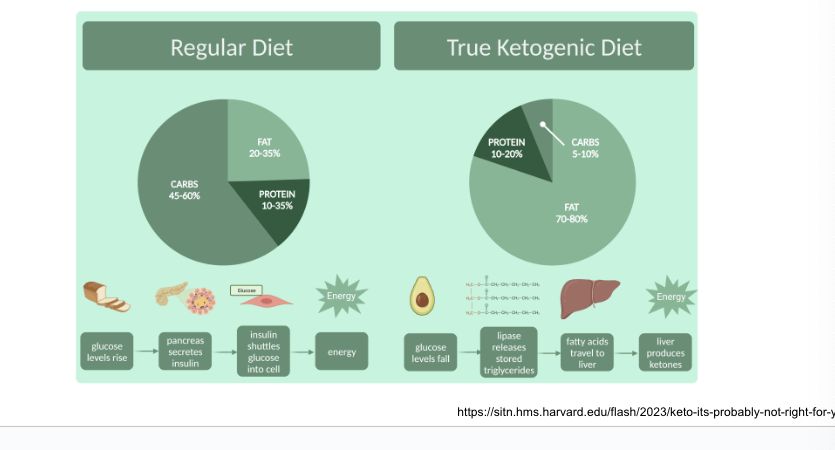
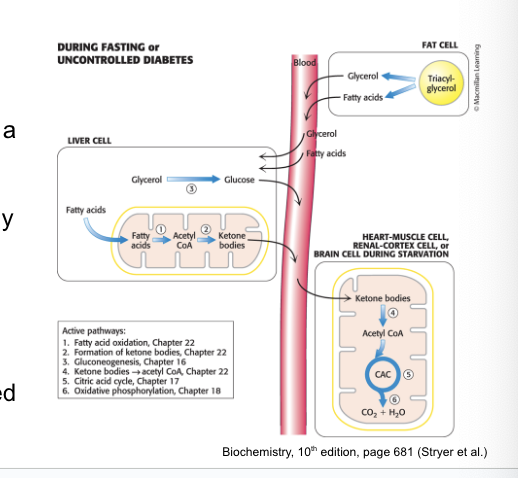
liver produces…
ketone bodies from acetyl coA when insulin signaling is low
3 molecules known as ketone bodies: acetoacetate, D-3-hydroxybutyrate and acetone
liver enzymes catalyzing the ketone body formation rxns are
3-ketothiolase
hydroxymethylglutaryl CoA synthease
hydroxymethylglutaryl CoA cleavage enzyme
D-3-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase
acetoacetate spontaneously decarboxylates to form acetone
liver supplies…
ketone bodies to peripheral tissues
during fasting or in untreated diabetics, liver converts fatty acids → ketone bodies which are a fuel source for number of tissues
ketone-body production = especially important during starvation when ketone bodies = predominant fuel
provides health benefits by shifting the energy balance towards increased triglyceride degradation
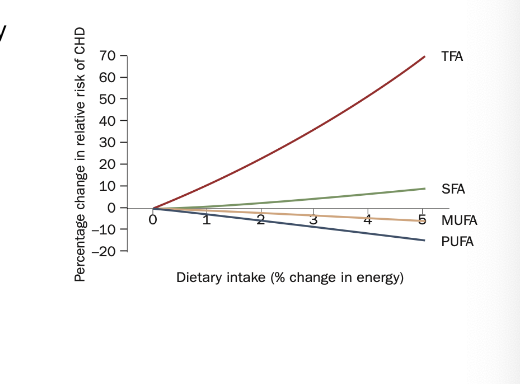
dietary consumption of trans fats…
increases CV disease
changes in relative risk of coronary heart disease for each 1% energy fom carbohydrate that is isocalorically replaced with:
trans fatty acids (TFAs)
saturated fatty acids (SFAs)
monounsaturated fatty acids (MUFAs)
polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs)
most dietary trans fats derive from…
industrial, partial hydrogenation of vegetable oils
partially hydrogenated vegetable oils are typically less expensive than animal fats and have commericial advantages over some nonhydrogenated vegetable oils
longer shelf life
greater solidity at room temp
greater stability during repeated deep-frying at high temps
example: margarine
partial hydrogenation of vegetable oil provides the soft, spreadable texture
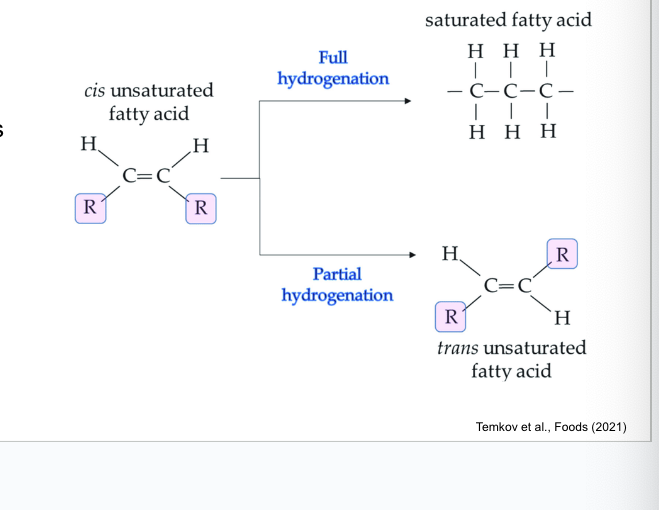
naturally occurring unsaturated fatty acids are…
in the cis form
if the hydrogen bonded to each of the carbons in the double bond are on the same side = cis and leads to bent molecular chain
if 2 hydrogens are on opposite sides = trans and leads to straight chain
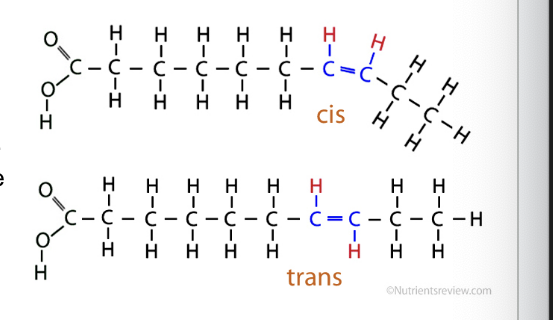
trans fats are formed…
by partial hydrogenation of cis fats
hydrogenation occurs by adding hydrogen gas (H2) to oil with high pressure and heat
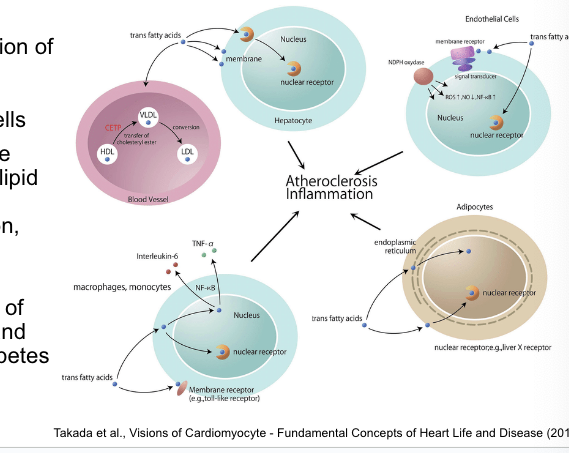
trans fats have numerous adverse effects…
contributing to heart disease
dietary TFAs influence the function of multiple cell types including…
hepatocytes
adipocytes
macrophages
endothelial cells
TFA consumption affects multiple metabolic risk factors including
lipid and lipoprotein levels
systemic inflammation
endothelial function
adiposity
glucose-insulin homeostasis
TFA consumption increases risk of clinical coronary heart disease and likelihood of development of diabetes
cholesterol is an important component of…
cell membranes
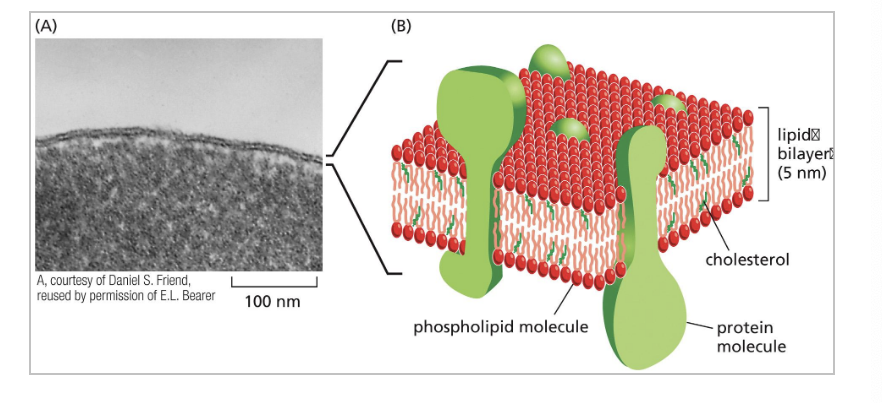
phospholipids are major component of…
lipid bilayer
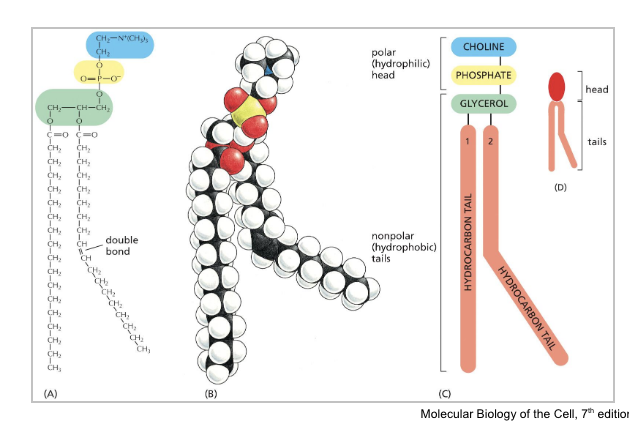
cholesterol molecules have a…
rigid planar steroid ring structure
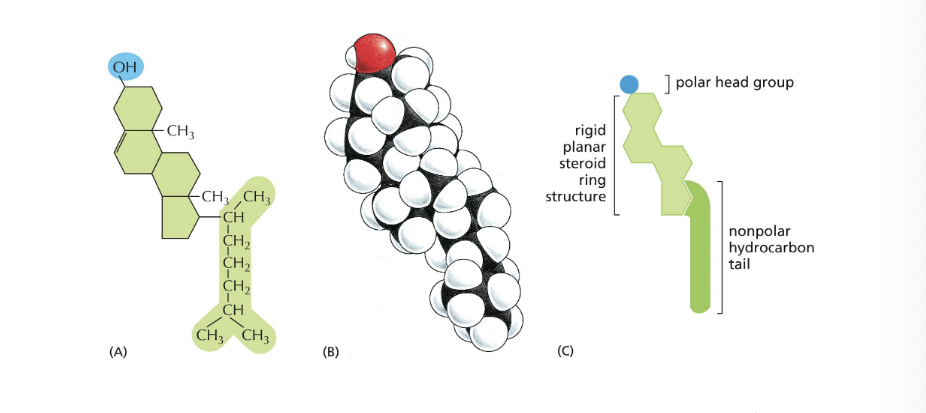
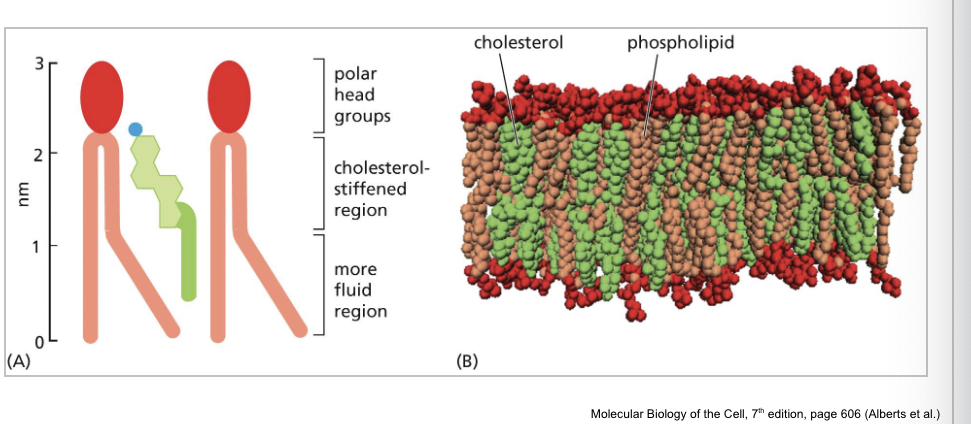
cholesterol interact with…
phospholipid molecules in lipid bilayer to control membrane fluidity
cholesterol stiffens region of the fatty acid tail
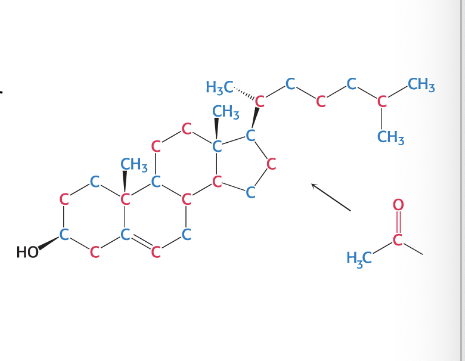
cholesterol is synthesized from…
acetyl coenzyme A
27 carbon atoms of cholesterol are derived by acetyl coA in 3 stage synthetic process
cholesterol can be obtained form the diet or cells can synthesize it de novo (produce from scratch)
liver and intestine are primary sites of cholesterol biosynthesis
rate of cholesterol formation is mediated primarily by changes in the amount and activity of HMG CoA; the enzyme that catalyzes the synthesis of mevalonate (intermediate)
HMG CoA: 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl CoA reductase
lipoproteins transport…
cholesterol and triacylglycerols throughout the organism
lipoprotein particles = the means by which cholesterol and triacylglycerols are transported in body fluids → tissues for use as fuel or for storage
fatty acids constituents of the triacylglycerol components of the lipoprotein particles are incorporated in phospholipids for membrane synthesis
cholesterol = vital component of membranes and is precursor to steroid hormones
cells are NOT able to degrade the steroid nucleus so cholesterol must be used or excreted by liver
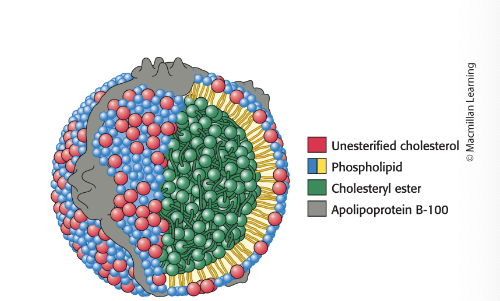
lipoprotein particles consist of…
both hydrophobic and polar components
lipoprotein particles consist of:
a core of hydrophobic lipids
shell of more-polar lipids and proteins
protein components of lipoprotein particles (apoproteins) have 2 roles:
solubilizing hydrophobic lipids
containing cell-targeting signals
low-density lipoprotein (LDL) particles…
are the main carrier of cholesterol in circulation
LDL = particles that are a major carrier of cholesterol in blood and regulate de novo cholesterol synthesis at peripheral tissues
contains a core of ~1500 cholesterol molecules esterified to fatty acids (most commonly linoleate)
contains a shell of phospholipids, unesterified cholesterol and a single copy of apoB-100 which is recognized by target cells
cells outside the liver and intestine obtain cholesterol from LDL in plasma rather than synthesizing it de novo
process of LDL uptake is called receptor-mediated endocytosis
excess cholesterol causes…
arterial plaques, increasing risk of stroke and CV disease
excess cholesterol collects in various tissues of the body
excess LDL becomes oxidized and taken up by macrophages → become engorged and form foam cells
foam cells become trapped in blood vessels and contribute to formation of atherosclerotic plaques
high-density lipoprotein particles transport…
cholesterol to liver for excretion
HDL = particles that pick up cholesterol released into plasma → deliver to liver for excretion
excretion occurs by converting the cholesterol biosynthetically into bile salts or by secreting it as unesterified cholesterol into bile
in process called reverse cholesterol transport, HDL removes cholesterol from cells, especially macrophages, and returns it to liver for excretion
when transport fails, macrophages → foam cells and facilitate the formation of plaques
the more HDL → more readily this transport takes place and less likely that MPs will → foam cells
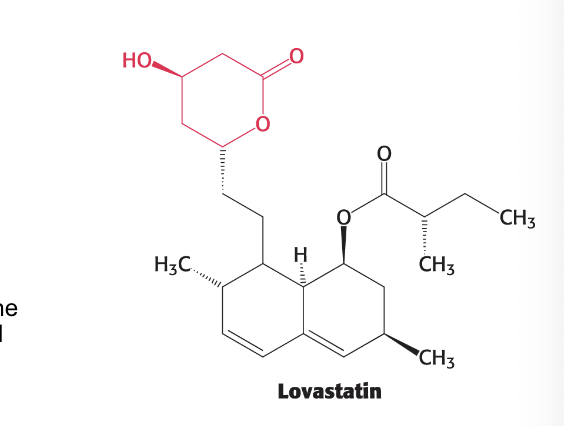
statins are a major class of drug for treating…
heart disease
goal is to reduce blood cholesterol levels
statins are competitive inhibitors of HMG-CoA reductase so block de novo synthesis of cholesterol
part of lovastatin structure that resembles the 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl (HMG) moiety is in red

ANSWER: C → increase by 20 moles
EXPLANATION
+120
2×24 = -48
0.5×24 = -12
60 mols of fatty acids but question is asking how many triglyceride so per 1 mol of TAG = 3 mols of fatty acid

ANSWER = B; weight gain
leptin is responsible for suppressing appetite; if no leptin → no suppression of appetite → keep eating → fat

ANSWER = decrease by 19 moles
EXPLANATION
2000 × 10 = 20,000 = consumption
100 × 10 = 1000
20,000 - 1000 = 19,000 → 19,000/1000 = 19 mols
20,000 are being consumed and 1000 of that 20,000 comes from gluconeogenesis which means 19,000 comes from glycogen pools

ANSWER = PATIENT B
EXPLANATION
pt B has a lower circulating glucose concentration which means the tissue has absorbed more glucose