2. cell membranes
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/38
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
1
New cards
lipids
diverse group of non polar molecules including fatty acids, triglycerides, phospholipids and cholesterol, they only dissolve in organic (non polar) solvents
2
New cards
emulsion test
test for lipids by adding ethanol, shaking then pouring in to cold water, turns white if lipids present
3
New cards
fatty acid
either saturated or unsaturated, have a hydrocarbon chain and a COOH group at one end
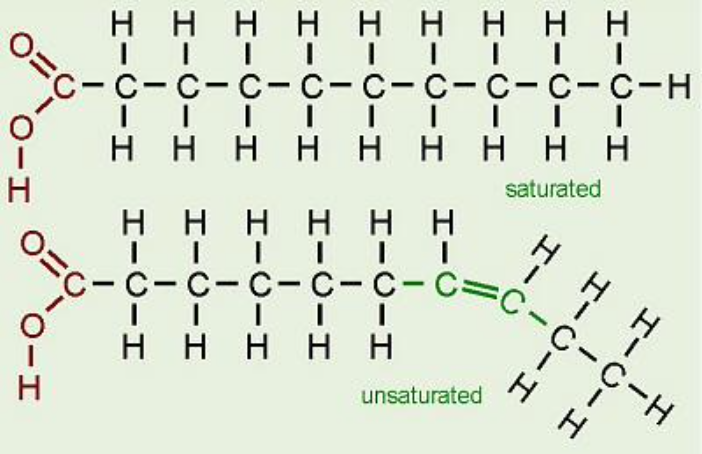
4
New cards
triglycerides
formed by condensation reaction to join 3 fatty acids to glycerol forming 3 ester bonds
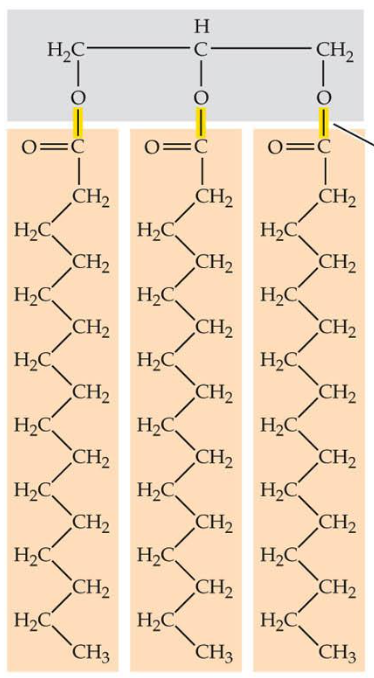
5
New cards
fat
triglycerides with mostly saturated fatty acids, store in animals
6
New cards
oil
triglycerides with mostly unsaturated fatty acids, store in plants
7
New cards
triglycerides use
energy store (adipose tissue in animals/seeds and fruits in plants)
thermal insulation (layer beneath skin)
provides buoyancy
protection- shock absorber for vital organs
thermal insulation (layer beneath skin)
provides buoyancy
protection- shock absorber for vital organs
8
New cards
lipase
enzyme which breaks down triglycerides into fatty acids and glycerol
9
New cards
phospholipid
contains 2 fatty acids joined to a glycerol by ester bonds and has a phosphate group
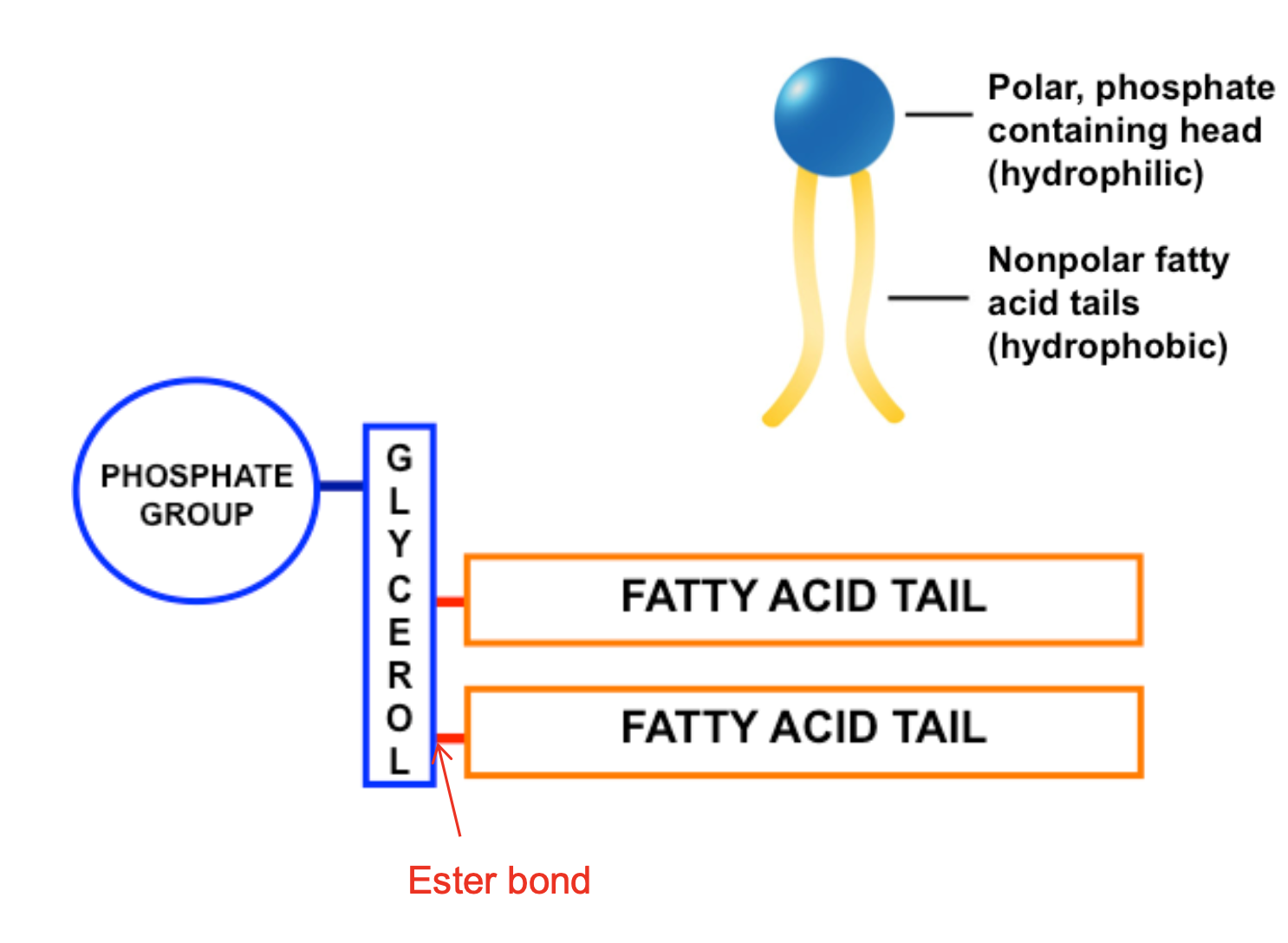
10
New cards
phospholipid bilayer
double membrane made up of phospholipids with hydrophilic heads on outside and hydrophobic fatty acid tails in centre, act as barrier to movement of polar molecules and ion say allow non polar molecules across
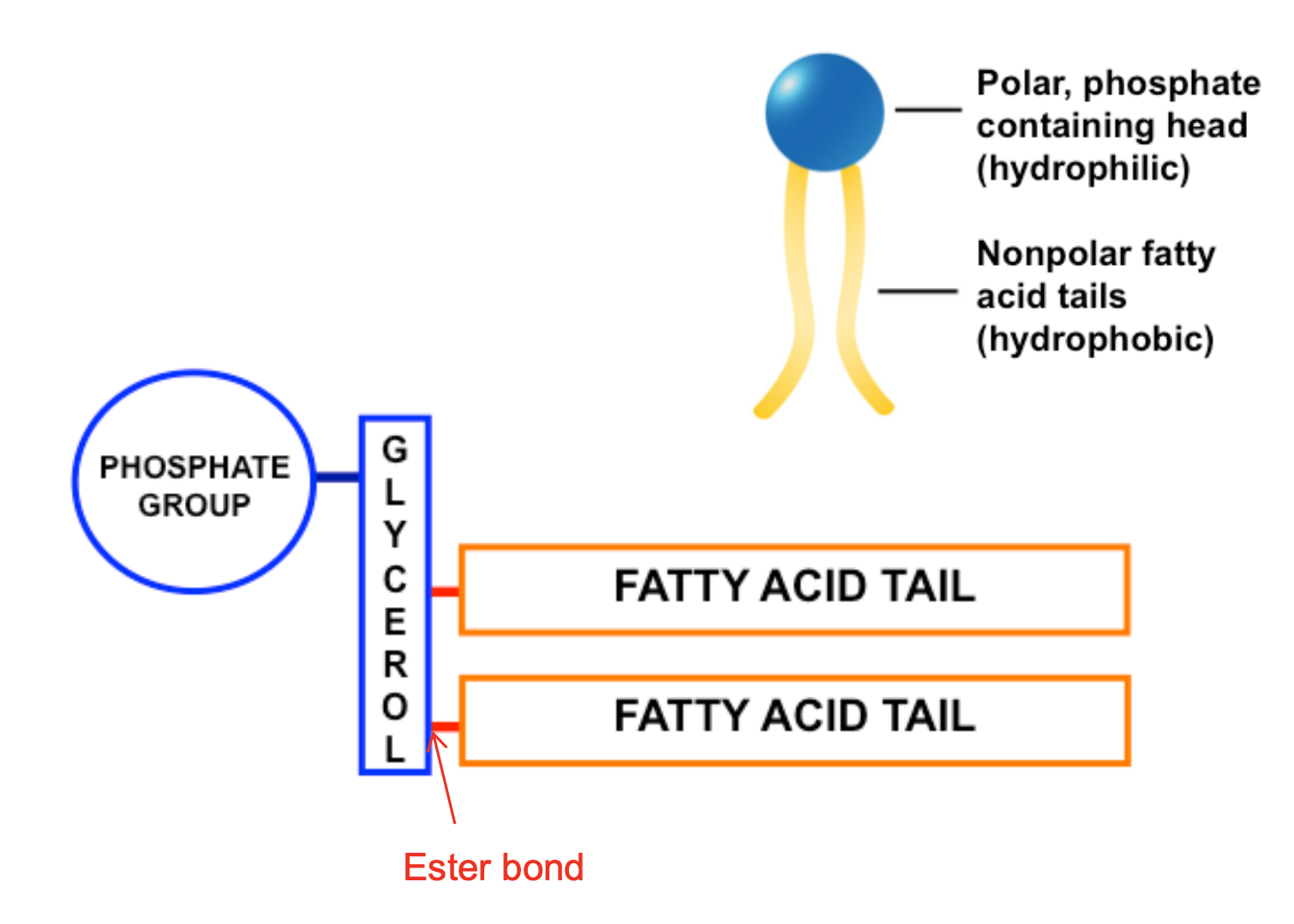
11
New cards
glycolipids
modified phospholipids with a carbohydrate chain (sugar) instead of phosphate group, act as antigens for recognition and adhesion to form tissues
12
New cards
choline and serine
example of what can be added to phospholipids
13
New cards
cholesterol
small non polar molecule with a single polar -oH group at one end, used for synthesis of steroid hormone and in membrane between phospholipids which stabilises them by binding to fatty acid tails, controls fluidity and prevents polar molecules and ions crossing membrane
14
New cards
fluid mosaic model
used to represent the plasma membrane as the molecules are able to move around within monolayer (unless anchored by cytoskeleton) and describes the appearance of the different molecules
15
New cards
outer surface
side which contains carbohydrate chains of glycolipids and glycoproteins that project from cell surface to from glycocalyx
16
New cards
proteins
act ac channels or carrier for polar molecules and ions across membrane by facilitated diffusion or active transport, also act as enzymes eg ATP synthase
17
New cards
glycoproteins
modified in Golgi apparatus by addition of carbohydrate chain, act as antigens for cell recognition as self or non self, act as receptors for chemical signals like hormones, cell adhesion to form tissues
18
New cards
intrinsic
proteins which are embedded in phospholipid bilayer and often span the bilayer
19
New cards
extrinsic
proteins are not embedded in phospholipid bilayer but are associated with one side of the membrane
20
New cards
passive trasport
process of molecules moving by simple diffusion requiring no addition energy
21
New cards
fascinated diffusion
large molecules which cannot pass through membrane without a specific transport protein, they move down their concentration gradient
22
New cards
channel proteins
provide a hydrophilic channel or pore though hydrophobic interior of phospholipid bilayer, specific to small molecule or ion, either open all the time or gated by a ligand or voltage
23
New cards
carrier proteins
bind to specific polar molecule and change shape to relate molecule on other side of membrane
24
New cards
active transport
transport of a molecule from low to high concentration against the gradient, requires specific carrier protein or pump and energy (ATP)
25
New cards
bulk transport
movement of large quantities of materials into or out the cell using vesicles, requiring ATP
26
New cards
exocytosis
movement out the cell eg hormones secretion
27
New cards
endocytosis
movement into the cell eh phagocytosis
28
New cards
4, 1, 3, 2, 5
process of endocytosis and exocytosis
1. Lysosome containing hydrolytic enzymes fuses with phagocytic vesicle
2. Soluble products of digestion are absorbed into the cytoplasm
3. Lysosome releases digestive enzymes into vesicle; these break down the
nutrient particles
4. Nutrient particle is taken up by endocytosis, plasma membrane surrounds the nutrient particle and fuses with itself, pinching off to form a phagocytic vesicle
5. Insoluble, undigested material is removed from the cell by exocytosis as the vesicle fuses with the plasma membrane
1. Lysosome containing hydrolytic enzymes fuses with phagocytic vesicle
2. Soluble products of digestion are absorbed into the cytoplasm
3. Lysosome releases digestive enzymes into vesicle; these break down the
nutrient particles
4. Nutrient particle is taken up by endocytosis, plasma membrane surrounds the nutrient particle and fuses with itself, pinching off to form a phagocytic vesicle
5. Insoluble, undigested material is removed from the cell by exocytosis as the vesicle fuses with the plasma membrane
29
New cards
surface area
allows more diffusion to take place, resulting in faster rate of diffusion
30
New cards
distance
molecules take longer to move further so slows rate of diffusion
31
New cards
concentration gradient
greater the difference between the sides the faster the diffusion
32
New cards
temperature
provides molecules with kinetic energy to move more and increase rate of diffusion
33
New cards
size of particle
larger molecules move slower and don’t fit as easily between phospholipids so slow rate of diffusion
34
New cards
type of particle
non polar can diffuse directly through bilayer, large polar pr charged molecules and ions require transport protein to cross membrane so rate if effected by number or proteins
35
New cards
agar block
used to measure rate pd diffusion by adding pH indicator phenolphthalein and seeing how the block changes from pink to colourless has H+ diffuse from centre
36
New cards
visking tubing
used to separate a solution of starch from the spring iodine and water solution, starch turns blue black after 20 mins and solution turns yellow brown when tested with iodine solution
37
New cards
effect of temperature on membrane fluidity
use beetroot cylinders in different water baths and use a colorimeter to determine the colour change in the water
38
New cards
unsaturated
kind of phospholipid which makes the membrane more permeable and fluid cell
39
New cards
cell signalling
chemical signal binds to receptor in plasma membrane which may lead to production of second intracellular messenger inside the cell to trigger cellular response