HAMEX VOCAB QUIZ Intro Terms 2025
1/29
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
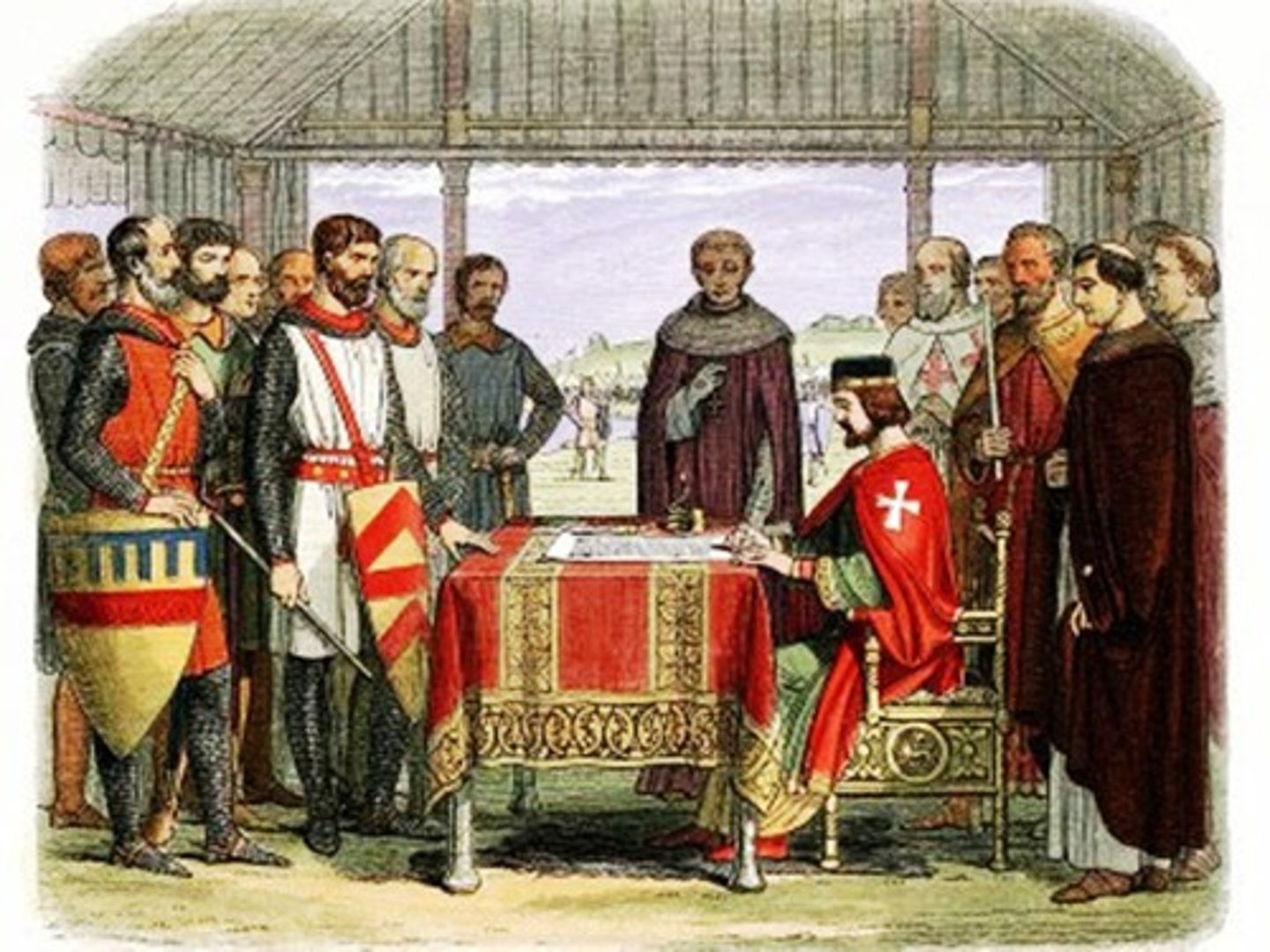
Magna Carta
A 1215 English Document forced on King John by his barons, which established that everyone, INCLUDING THE KING, was subject to the law.
It set a precedent for the American founders to protect individual rights and ensure that the President does not have too much power.

Constitution
The system of fundamental principles according to which a nation, state, corporation, or the like is governed.
The US Constitution is the supreme law of the United States, establishing the framework of the federal government and the rights of the people

Social Contract
The voluntary agreement among a population by which they abide by laws appointed by a governing body, while the government promises to protect and serve the people.
An agreement between people and their government where citizens give up some freedoms in exchange for protection and the benefits of living in an organised society, such as security and welfare.
People pay taxes to the government in exchange for public services, such as schools and roads.

Higher Law
An ethical or religious principle considered as taking precedence over the laws of society, and to which one may appeal to justify disobedience.
A fundamental set of moral principles that are considered superior to the law, and are meant to ensure that human-made laws are just and protect the basic rights of the people.
The US Constitution is considered higher law because it protects people's rights and limits government power.

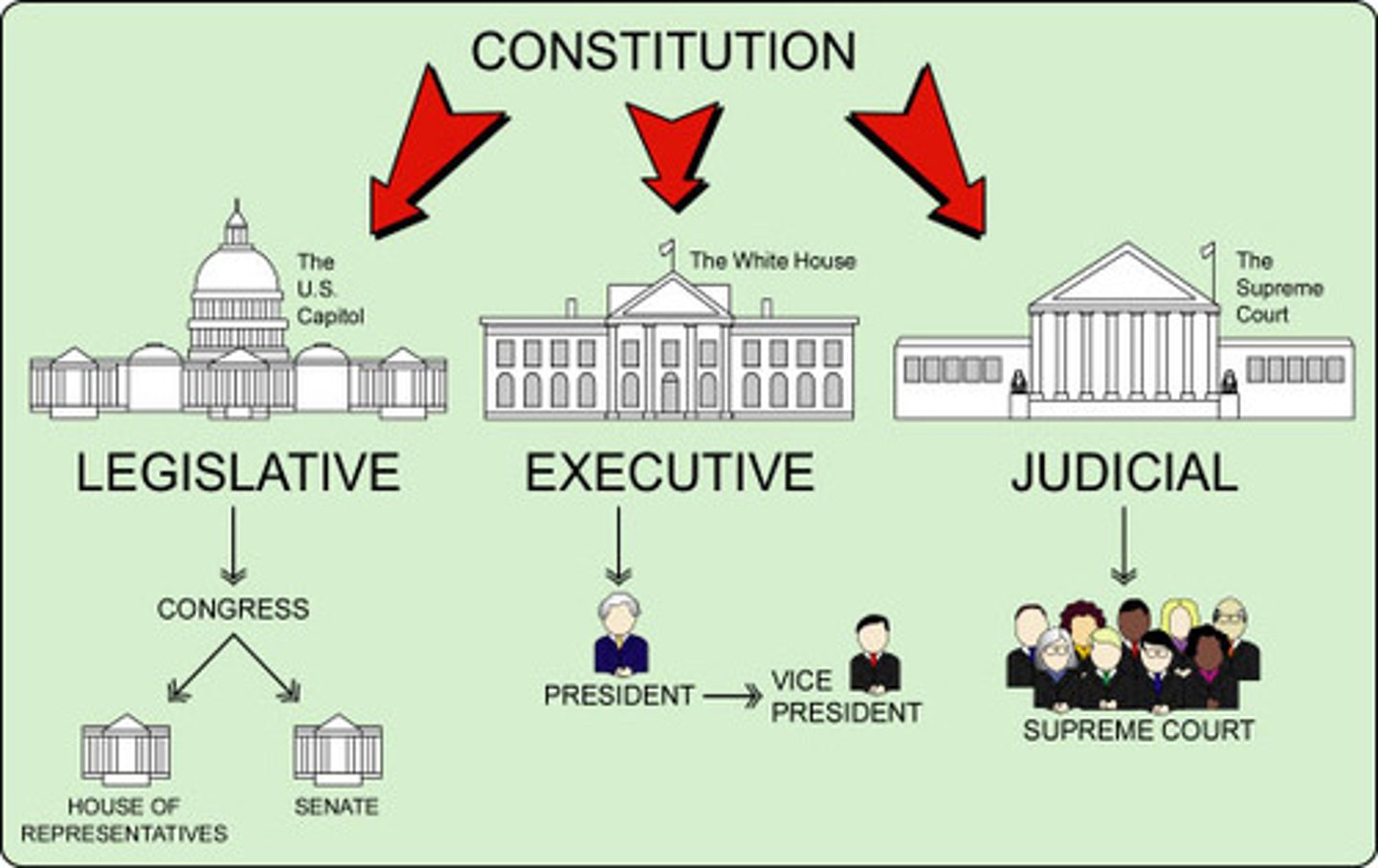
Judicial Branch
The branch of government also called the court system charged with the interpretation of laws, resolving disputes and making sure the laws are being applied fairly.
The Supreme Court and lower federal courts can declare laws unconstitutional.

Executive Branch
The Executive Branch is the part of the government that is responsible for the enforcement of laws passed by the legislative branch, managing foreign relations, appointing officials, and issuing executive orders.
In the US, the executive branch is made up of the President, Vice President, and the Cabinet.

Dictatorship
A dictator is someone who has ultimate power in a nation, with no limitations from anyone or anything.
King George's rule over the colonies was slowly becoming a dictatorship, which went against American beliefs, causing them to rebel.

Bill
A bill is a draft or blueprint for a new law or a change to an existing law that is introduced by the Legislative branch. It has to go through both chambers of Congress before it can be sent to the president for approval, before becoming a law.
An example of a bill is The Big Beautiful Bill, passed by Donald Trump.

Legislative Branch
The Legislative Branch is the part of the government that is responsible for creating, debating, and enacting laws. It also has the power to impeach elected officials and declare war.
In the U.S, the legislative branch is Congress, which is made up of the Senate and the House of Representatives.

Government
A government is a group of people who work together to organize and lead a community. There are many different types and examples of a government.
For instance, the US government is a democracy, which is a "rule by the people.
Monarchy
Monarchy is a form of government ruled by a ruler, where the power is passed down through the family.
The US was created in direct opposition to this system of government. The founders built a republic after breaking away from King George III, where the power came from the people and not the royal family.

Jurisdiction
What one entity of the government has the power to do.
State and federal courts in the United States have different areas of authority.
For instance, state courts handle matters like local crime or contracts, whereas federal courts handle constitutional issues.

Articles of Confederation (AOC)
First Constitution of the United States. Most power was held by states and created a weak central government.
This caused a few problems, like the inability to tax or effectively raise a national army.

Shays' Rebellion
It was an armed uprising in 1786-1787 by farmers in Massachusetts who were protesting economic justice and high taxes.
It showcased the weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation and pushed leaders to consider creating a stronger national government.
Framers feared factions, and today, factions still cause political issues.
Forced the American government to change

Constitutional Convention
It was held in Philadelphia in 1787 to fix the issues/problems of the Articles of Confederation. They decided to write a whole new constitution instead of just making a few changes.
The strong federal government we have today had its foundation laid from that meeting called the constitutional convention.`

Judicial Review
The power of the courts of a country to examine the actions of the legislative and executive branches of government and determine whether their actions are constitutional.

Enumerated Powers
The specific and explicit powers granted to the federal government by the Constitution. These include powers such as the ability to collect taxes, borrow money, regulate commerce, coin money, declare war, and establish post offices and lower federal courts.
Article One Section 8

Representative Democracy
A form of government where citizens elect representatives to make decisions, laws, and policies on their behalf, instead of voting on every issue directly.
Federalists
Federalists were a group of individuals who battled for the adoption of the Constitution. They supported a strong central government and a representative democracy. Examples include Alexander Hamilton and George Washington.

Federalism
A political philosophy and a system of government that divides power between a central government and regional governments, with each level having its own distinct responsibilities and authority.
Power is divided between the federal government and the state governments
States decide their own minimum wage, and the federal government can declare war
Common Good
Making something that is accessible to society and benefits them.
For example, charities since the money and supplies go to the people who can't afford them.

Seperation of Powers
The three branches of government: The Legislative (they make the laws), Judicial (interprets the law), and the Executive (who pass the law out).
How it relates is when Congress is going to pass a law, it has to pass through the 3 branches.

Checks and Balances
It limits the powers of each branch so that the powers they have are in balance.
For example, if the president executes the law, Congress has the power to override it if it disagrees with it.

Delegates
People who represent the people and vote on their behalf.
For example, they are voted on by citizens and are part of the Representative democracy. Constitutional Convention men. Maddison, Washington, etc.

Factions
Small groups inside a larger group to share ideas/goals; usually negative. More extreme, farmers feared factions.
Political parties, Democrats, and Republicans are examples since they share their viewpoints and ideas. Today, factions often cause conflicts.

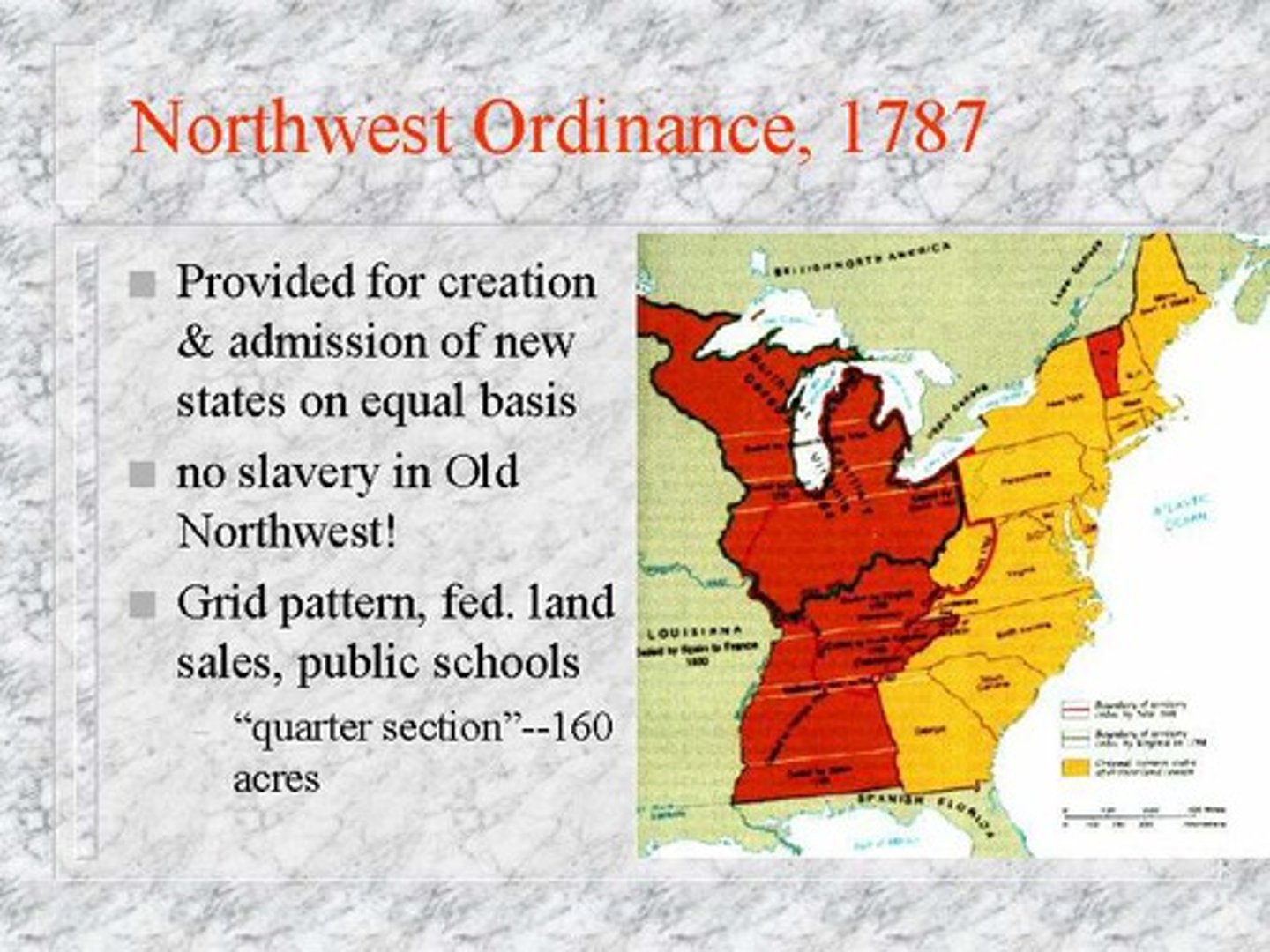
Northwest Ordinance
It was a landmark act of 1787 that established a process of admitting new states and set a "blueprint" for westward expansion. It also banned slavery in those new states and promised basic rights. It was the only law passed under the Articles of Confederation.
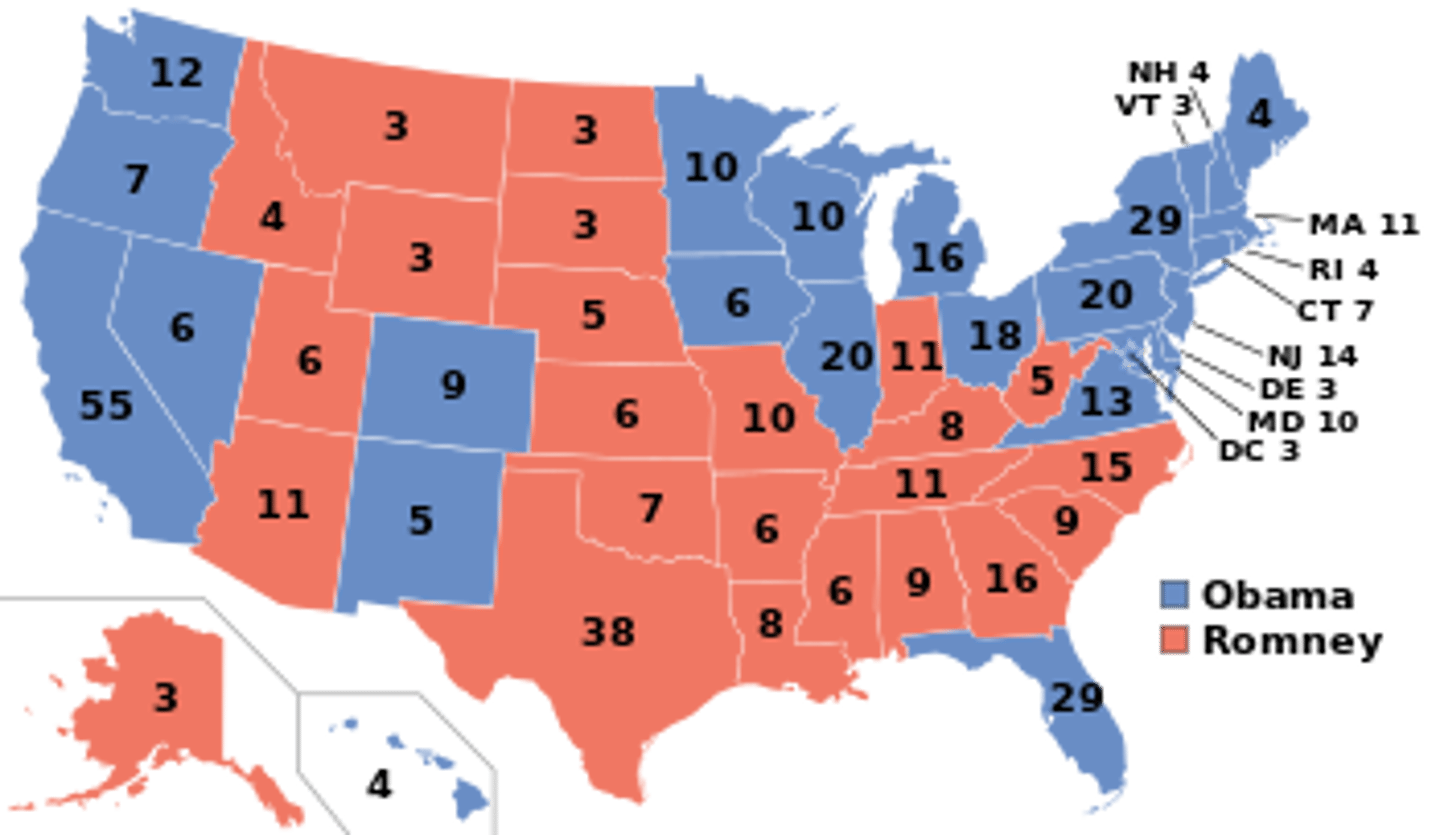
Electoral College
A system the U.S uses to elect the President and Vice President. Citizens vote for the number of electors in their state. A candidate needs at least 270 electoral votes to win.
The Veto
The President's power to reject laws passed by Congress. It is part of the "checks and balances" system, so no other branches of government have too much power.

Bill of Rights
The first 10 amendments to the Constitution. It lists basic freedoms and rights that all citizens should have. Our government has the Bill of Rights to protect everyone's freedoms and equal protection.

Political Ideology
A set of beliefs and values that shapes a person's understanding of how the government works and how society should be organized. Ideologies influence how people vote and what laws the government makes.
Someone's views on political issues will impact how they vote
Liberal and Conservative