draft - fashion study guide
1/82
Earn XP
Description and Tags
mc qs (1 answer), multiple answer
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
83 Terms
What is fashion?
The industry of creativity(cultural trends); a seasonal(short product cycle, long industrial pipeline) and risky business(demand is cray)
What is seasonality?
traditional - 2 collections/seasons a year
trends originated from a long and complex pipeline (takes time, from raw material —> product)
make capsules (curated collections) to refresh the assortment
basic vs fashion items
co-existence of basics and fashionable items with different business logics.
Basic = never out of stock, not seasonable (white polo shirt)
Traditional seasonal collections are 2 (SS and AW) with capsules and special deliveries (Christmas, cruise, Valentine day…) in season
Basic/carry over | Fashion/seasonal | |
Style | Classic, carry-over | Trendy |
Market | Demand stable and predictable | Volatile |
Variety (of products) | Low | High |
Product Lifecyle | Medium to Long | Short |
Profit Driver | Traffic and brand awareness | Brand image |
Negative impact of stock-outs | Medium-low | Very High |
Discounts | Not on classic items | Yes (end of season) |
Two main drivers behind the future of fashion
solving the issue of sustainability (which examples and challenges?)
delivering and an omnichannel go to market strategy
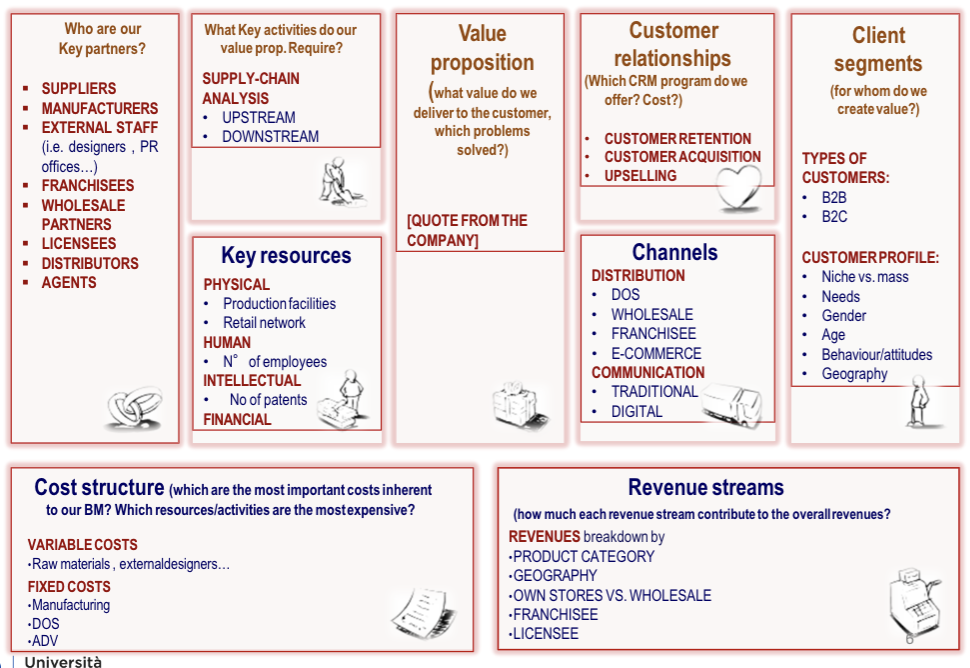
Business Model Canvas
the way you make money - 9 components
client segments
channels
customer relationship
value proposition
key resources
key activities
key partners
revenue streams
cost structure
Brand VS Retailer
BRAND
Value proposition: unique product design & brand narratives as the result of a design-driven approach
• Go to market strategy: BTB and/or BTC. They can develop their business through a direct channel (Direct to Consumer strategy) therefore integrating the entire value chain and/or they can work with hundreds of retailers (wholesales) to effectively distribute inventory risk and disseminate the brand narrative to ‘get the word out’. The revenue model is sell-in revenue with a wholesale price when the brand has a BTB strategy, while is a sell- out revenue with a retail price when it operates BTC.
•Evolution: brands begin life by focusing on one product vertical (i.e. Cucinelli of knits or Adidas on sneakers) and progressively expand in terms of product categories, markets and channels (Gucci) à continue to open more stores
•
RETAILERS
• Value proposition: The product is the retail assortment direct to the final consumer. Have extensive customer insights that enables retailers to optimize their merchandising assortment of different brands, styles, and inventory quantities dynamically for each location
• Go to market strategy: BTC only. The entire organization is built around the customer side and the revenue model is BTC only sell out revenue and retail price.
• Evolution: derive long-term value from major investments in building customer mindshare (i.e. ‘I think that I am going to stop by Harrods or Rinascente on Saturday’) and it grows by opening new stores and might decide to launch a private label in addition to the re-sale of brands (i.e. Sephora).

sell in business VS sell out business
BTB vs BTC
Luxury conglomerates (category focused, vertical integration, contribution of cash cows,
advantages of the conglomerate status)
Luxury conglomerates- vertical integration
Luxury conglomerates -contribution of cash cows
Luxury conglomerates - advantages of the conglomerate status
Designers (different supply chains by category and multi-channel distribution)
Designers licensing business
fast vs mass retailers - speed vs cost
fashion pricing : sell in and sell out
what are DTC advantages?
Sell in with fashion platforms
Objectives of an industry analysis
How to define a business
Margin structure in luxury and its determinants
What are strategic groups in that business?
How to define the KSF of your strategic group?
How to define the value proposition?
what a brand offers to the market - unique benefits, quality, price positioning, and emotional or functional appeal that differentiate the brand and attract its intended audience.
ex - Convenience to the mass, trend to the fashionista, timlessness luxury to the investor….
Internationalization - what does it mean (global)? 4 points
Brand & line extension in fashion - definitions
Brand & line extension in fashion - risks
Brand & line extension in fashion - key success factors
vertical integration - retail and wholesale formats
vertical integration - advantage / disadvantage of different channels for the brand
how to identify business ideas/opportunities
Why write a BP?
What is a BP?
Types of BP
structure of BP
Marketplace
Company
Business idea & strategy
Marketing & sales
Organizational Concept
Financial Concept
Sources of Funding
BP model - assumptions
BP model - key financials
BP model - performance ratios
BP model - scenario/sensitivity analysis
IP RIGHTS in fashion - what are characteristics of trademarks and their use?
IP RIGHTS in fashion - what are characteristics of designs and their use?
IP RIGHTS in fashion - what are characteristics of copyrights and their use?
IP RIGHTS in fashion - what are characteristics of patents and their use?
Value proposition of Velasca
value chain design of Velasca
Revenue model of Velasca
Value proposition of Moncler
Value Chain Design of Moncler
Revenue Model of Moncler
Value Proposition of Sephora
Value Chain Design of Sephora
Revenue Model of Sephora
Value Proposition of Rent the Runway
Value Chain Design of Rent the Runway
Revenue Model of Rent the Runway
Value Proposition of Stitch Fix
Value Chain Design of Stitch Fix
Revenue Model of Stitch Fix
Value Proposition of Farfetch
Value Chain Design of Farfetch
Revenue Model of Farfetch
True or false. Rent The Runway’s relies on a subscription based business mode
True
True or False- the value proposition of Farfetch is to make shoppers’ lives easier by periodically delivering right to their door boxes of clothing and accessories carefully selected according to subscribers’ taste, body type and budget
False
Definition of supply chain
5 Transformative forces behind global supply chains evolution
Supply chain risk dimensions
(operational, strategic)
4 Supply chain governance models
(open market, hierarchical, integrated, ecosystem -
exibit 1 pag. 74)
Definition of supply chain transparency
visibility, disclosure
Mandatory and voluntary regulation in fashion
Definition of blockchain and main benefits
Benefits of a BP
BP Contents and executive summary
Business model and strategy
BP different sections (ownership, the team, marketing plan, operating plan, financial plan)
BP types and styles