P1: bio-molecules: poly, mono and carbs
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Paper 1 Topic 2 biological molecules. If it’s helpful feel free to save or check the other sets :)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
Define monomer
Smaller units that join together to form larger molecules
Eg. monosaccharides (fructose, glucose and galactose)
Amino acids
nucleotides
Define Polymer
molecules formed when many monosaccharides join together
eg. Polysaccharides
proteins
DNA/RNA
What happens in a condensation reaction?
A chemical bond forms between 2 molecules and a molecule of water is produced
What happens in a hydrolysis reaction?
A water molecule is used to break a chemical bond between 2 molecules
Name 3 hexose monosaccharides
glucose, fructose and galactose
All have molecular formula C6H12O6
Name the type of bond formed when monosaccharides react
(1,4 or 1,6) Glycosidic bond
2 monomers→ 1 chemical bond=disaccharide
Multiple monomers→ many chemical bonds=polysaccharide
Name 3 disaccharides. Describe how they form
Condensation reaction forms glycosidic bond between 2 monosaccharides
maltose: glucose+glucose
sucrose: glucose+fructose
lactose: glucose+galactose
All have molecular formula C12H22O11
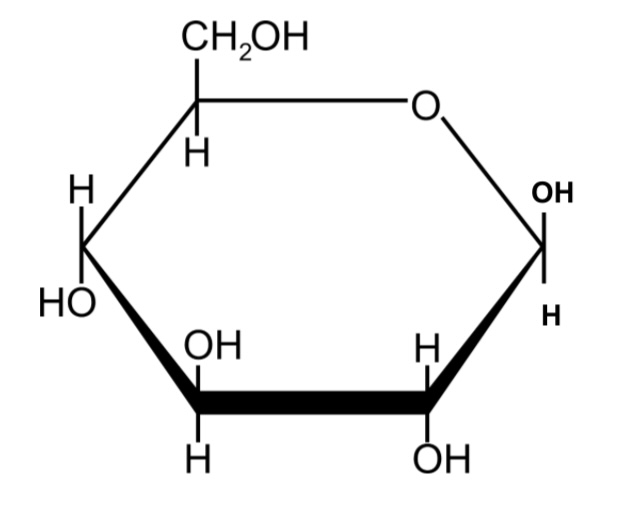
Draw the structure of B-glucose
OH on carbon 1 is above the ring
Describe the structure and functions of starch
Storage polymer of a-glucose in plant cells
insoluble=no osmotic effect on cells
large=does not diffuse out of cells
Made from amylose:
1,4 glycosidic bonds
Helix w intermolecular H-bonds=compact
Made from Amylopectin:
1,4 and 1,6 glycosidic bonds
Branched=many terminal ends for hydrolysis into glucose
Describe the structure and functions of glycogen
Main storage polymer of a-glucose in animal cells (but also found in plant cells)
1,4 and 1,6 glycosidic bonds
Branched=many terminal ends for hydrolysis
Insoluble=no osmotic effect & does not diffuse out of cells
compact
Describe the structure and function of cellulose
Polymer of B-glucose gives rigidity to plant cell walls (prevents bursting under turgor pressure, holds stem up)
1,4 glycosidic bonds
Straight chain, unbranched molecule
alternate glucose molecules are rotated 180 degrees
H-bonds cross links between parallel strands on oxygen molecules form microfibrils=high tensile strength
Describe the Benedict’s test for reducing sugars
Add an equal volume of Benedict’s reagent to a sample
Heat the mixture in an electric water bath at 100 degrees C for 5 mins
Positive result: colour change from blue to orange & brick-red precipitate forms
Describe the Benedict’s test for non-reducing sugars
Negative result: Benedict’s reagent remains blue
Hydrolyse non-reducing sugars eg. Sucrose into their monomers by adding 1cm³ of dilute acid e.g HCL. Heat in a boiling water bath for 5 mins
Neutralise the mixture using an alkali
Proceed with the Benedict’s test as usual
Describe the test for starch
Add the iodine solution
Positive result: colour change from orange to blue-black
Outline how colorimetry could be used to give quantitative results for the presence of sugars and starch
Make standard solutions with known concentrations. Record absorbance or % transmission values
Plot calibration curve:absorbance or % transmission (y axis) concentration (x-axis)
Record absorbance or % transmission values of unknown samples. Use calibration curve to read off concentration
Exam Q: Cellulose is a polysaccharide of B-glucose molecules. Describe how two B-glucose molecules are able to join together
OH group on carbon 1 is above the ring but OH group on carbon 4 of adjacent B-glucose molecule is below the ring (1)
only hydrogen available to form water with OH so no oxygen available to form glycosidic bond (1)
Every other B-glucose ‘flips’ through 180 degrees to place two OH groups adjacent to each other (1)
1,4 glycosidic bonds are formed to created unbranched chains
draw the shorthand structural formula of alpha-glucose
note that the5 corners of the corners of the hexagon are C atoms while one is O. each of the C atoms is designated by a number, increasing by 1 starting at the O atom.
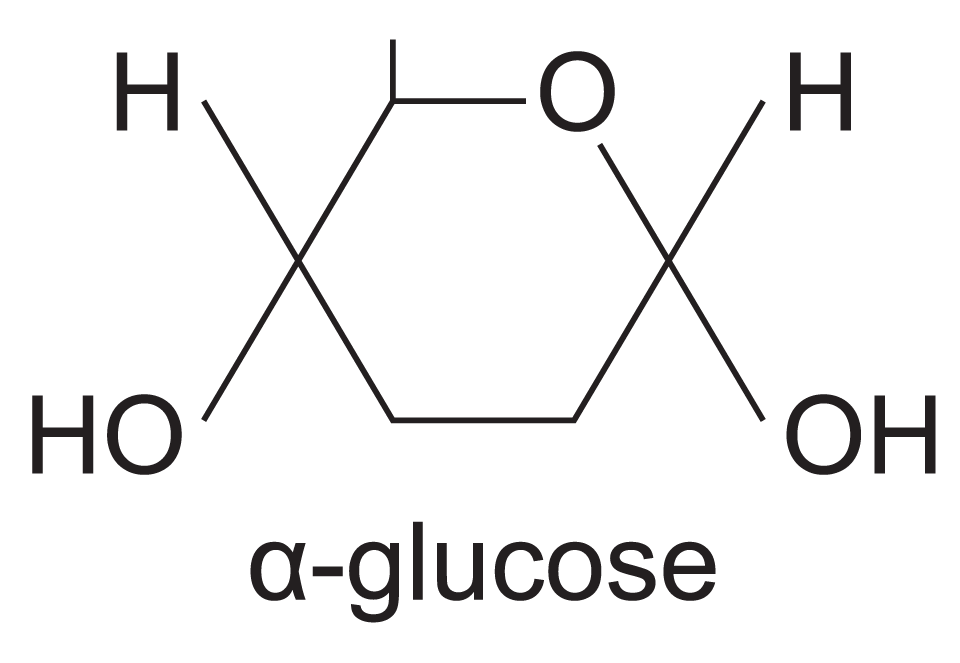
differences between beta and alpha glucose?
carbon 1 hydroxyl (OH) group lies below the ring
What is the general formula of monosaccharides?
(CH2O)n
name the 3 key polysaccharides:
glycogen, starch and cellulose.