Alcohol & Phenols
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
making alcohol by fermentation conditions and reagents
Yeast (Zymase), 30-35°C, Anaerobic
Products of alcohol making by fermentation
Alcohol and CO2
making alcohol from alkenes conditions and reagents
hydration/ addition reaction
300°C
60-70 atm
Conc Sulphuric acid/ phosphoric acid catalyst
H2O (g)
making alcohol from haloalkanes conditions and reagents
Nucleophilic substitution reaction, NaOH (aq), reflux/ warm
Reaction of alcohol- dehydration conditions and reagents
Elimination reaction, conc sulfuric acid catalyst, 170°C. Produces steam and alkene.
Reaction of alcohol- partial oxidation conditions and reagents
Acidified potassium dichromate (H+/ K2Cr2O7), reflux and distillation produces an aldehyde or ketone.
Reaction of alcohol- full oxidation conditions and reagents
Acidified potassium dichromate (H+/ K2Cr2O7), reflux. Produces a carboxylic acid.
Reaction of alcohol- esterification conditions and reagents
H2SO4 or HCl catalyst
reflux
carboxylic acid
reducing agents
NaBH4/ Sodium tetraborohydride/ sodium borohydride- weaker reduces aldehydes and ketones
LiAlH4 (in a dry ether solvent)/ lithium aluminium hydride- stronger reduces everything
why are acyl (acid) chlorides extremely reactive
Massive delta + on carbon making it highly susceptible to nucleophilic attack
what gas do acyl chlorides give off when reacting
Fuming Hydrogen chloride gas which is corrosive
How to name an acyd chloride?
and -oyl chloride to the end
reaction of acyl chlorides- making esters
reacts with alcohol
RTP, Add alcohol drop wise, nucleophilic addition-elimination mechanism.
Produces HCl(g)
reaction of acyl chlorides- making carboxylic acids
reacts with water
RTP and add water dropwise, nucleophilic addition-elimination mechanism
Produces HCl(g)
reaction of acyl chlorides- making amides
reacts with ammonia
RTP, add amine/ ammonia dropwise, nucleophilic addition-elimination mechanism
produces white fumes
what is the advantage of acid anhydrides
they react similarly to acid chlorides but do not give off hydrogen chloride gas as a product so do not give of large volumes of gas on an industrial scale
what does anhydride and water produce
2 carboxylic acids
what does anhydride and alcohol produce
2 esters
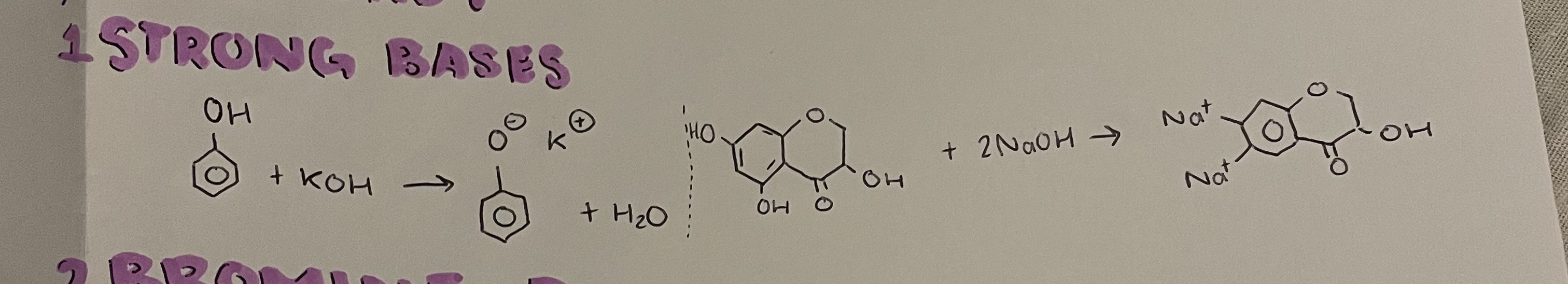
what bases will phenol react and not react with
WILL react with strong bases like NaOH- produces sodium phenoxide and water
WILL N OT react with weak bases such as sodium carbonate
explain the acidity of phenol
phenoxide ion is stable as the -ve charge on the oxygen can be delocalised around the ring structure.
reactions of phenol with strong bases
reactions of phenol with bromine
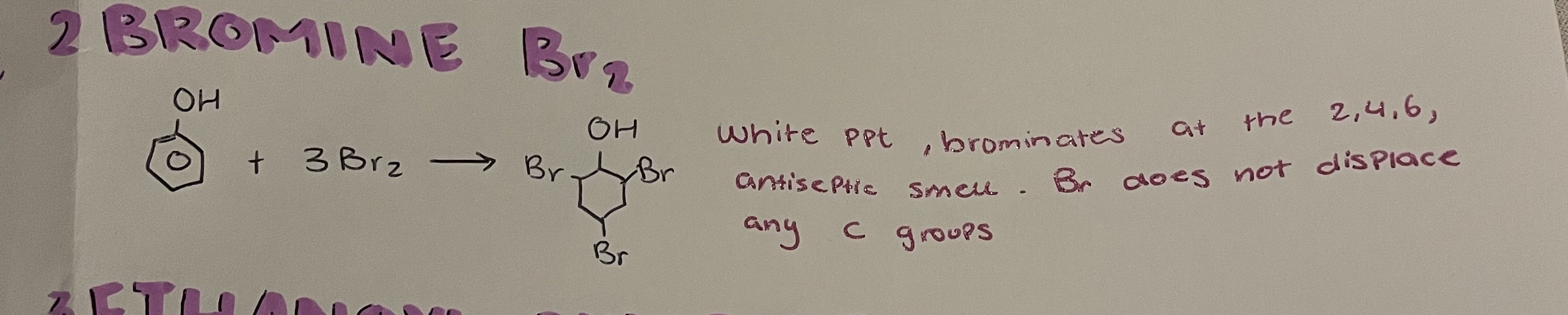
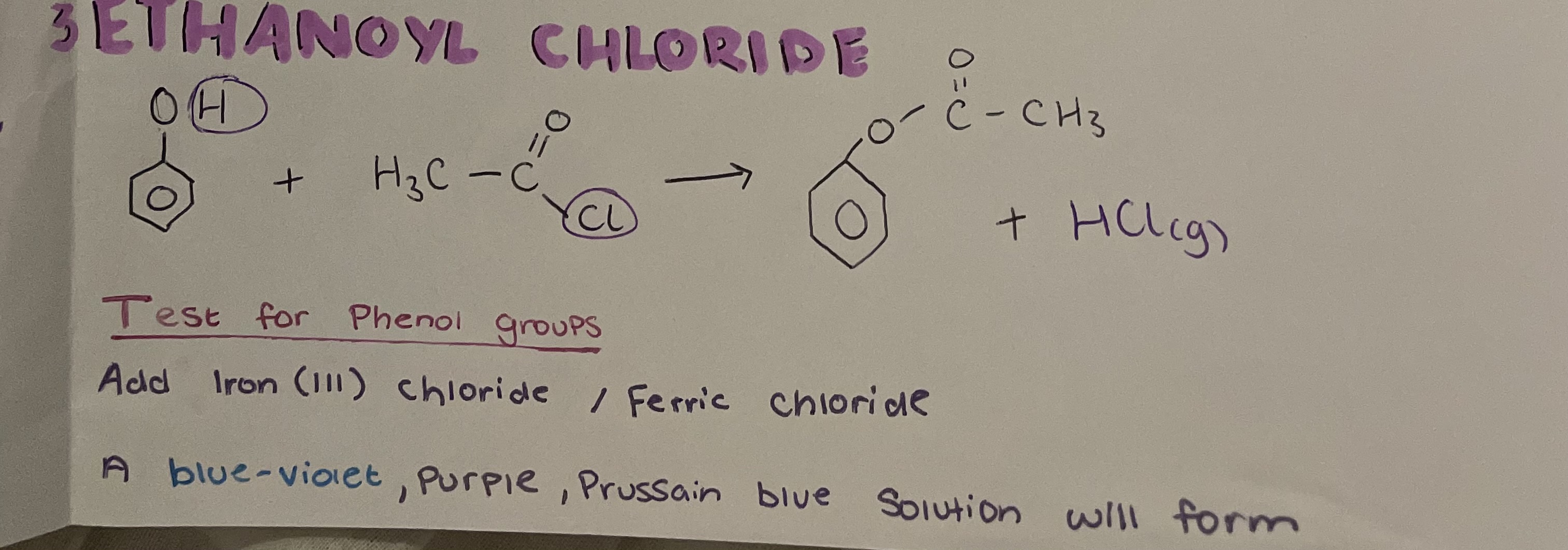
reactions of phenol with ethanoyl chloride
explaining the reactivity of phenol
can readily react whereas benzene needs a catalyst to react
electron density in the benzene ring is greater than that of benzene
oxygen in the OH has a lone pair of p orbitals
test for phenol groups
Add iron (III) chloride / ferric chloride
A Prussian blue/ purple/ blue solution will form if present