AP Biology Unit 2
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
82 Terms
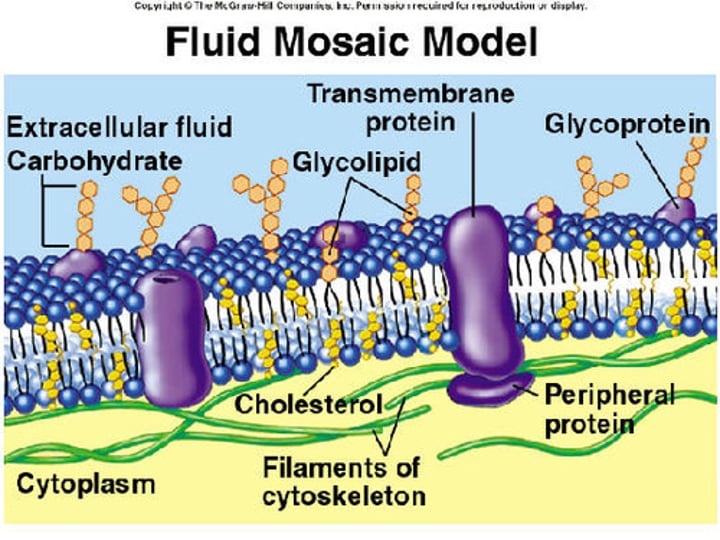
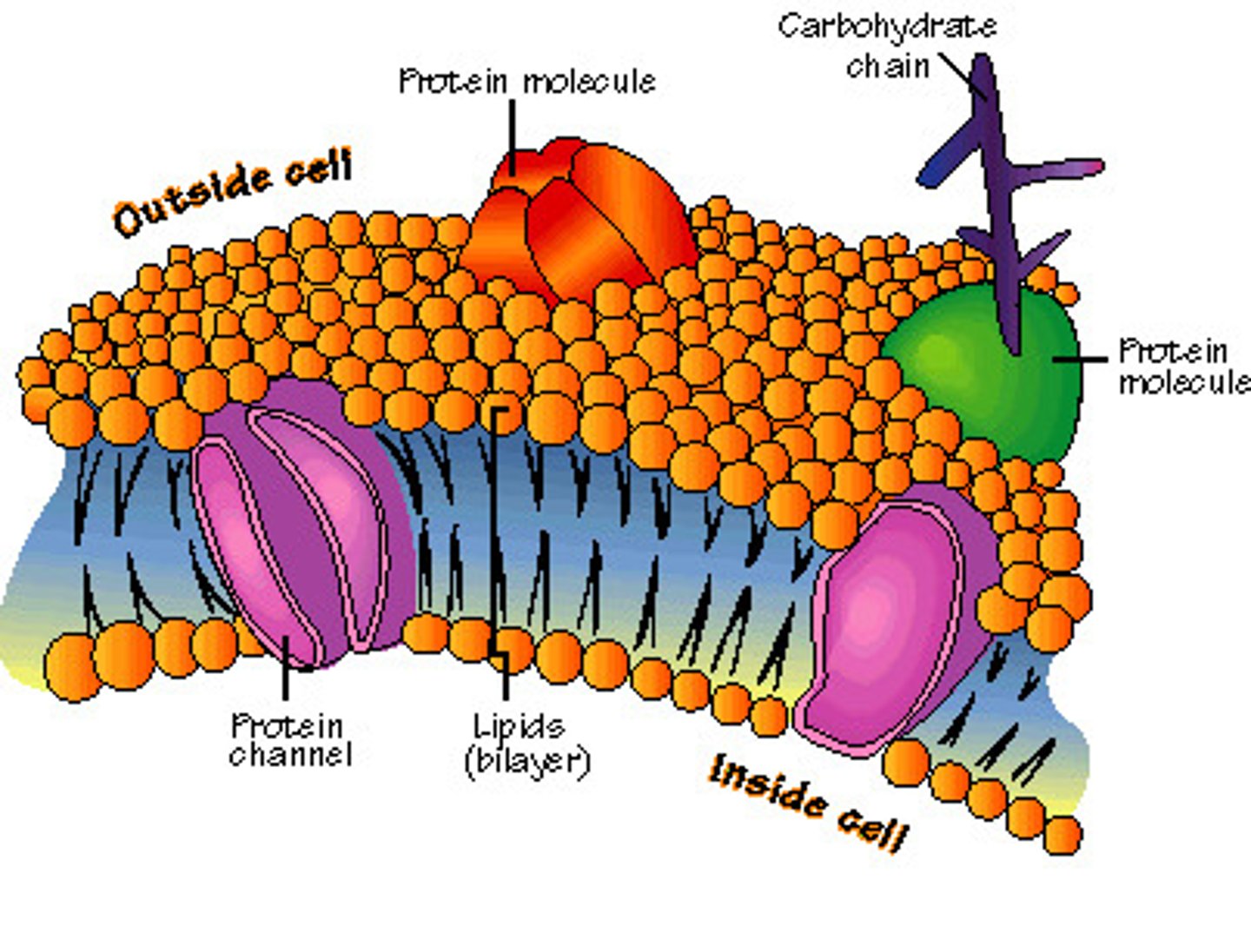
Fluid Mosaic Model
The currently accepted model of cell membrane structure, which envisions the membrane as a mosaic of protein molecules drifting laterally (Move continually and form changing patterns) in a fluid bilayer of phospholipids (Molecules are not attached side to side and are free to slide next to each other)
Methods that Keep Cell Membranes Fluid
Phospholipid changes or shifts; Cold hardening of plants: Shift to unsaturated fatty acids; Hibernating Animals: Increase cholesterol (Decreases fluidity)
Methods for Transporting Small Molecules Across the Cell Membrane
If hydrophobic, can cross phospholipid bilayer
Methods for Transporting Large Molecules Across the Cell Membrane
Can cross through certain transport proteins; Exo/endocytosis
Selective Permeability
A property of biological membranes that allows them to regulate the passage of substances across them
Membrane Composition of Plant in Hot Climates
Membrane might contain phospholipids with more saturated hydrocarbons and contain more cholesterol to decrease the fluidity of the membrane
Membrane Protein Functions
Transport, enzymes, signal transduction, cell to cell recognition, intercellular joining, attachment to the cytoskeleton
Glycolipid and Glycoprotein
Membrane carbohydrates that vary from cell to cell, which enable membrane carbohydrates to function as markers that distinguish one cell from another; Attach cells, cell-cell recognition, cell communication
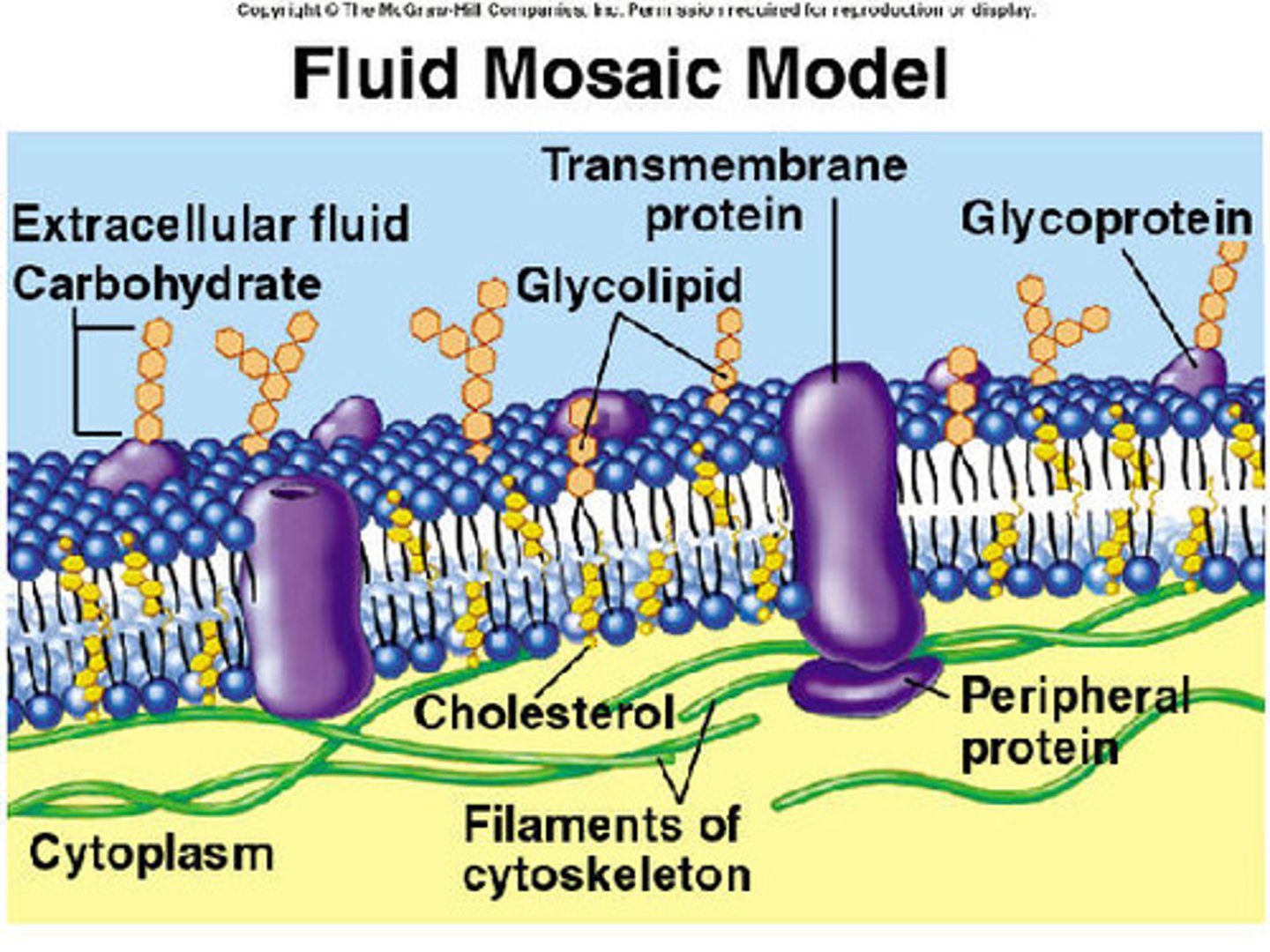
Integral Proteins
A transmembrane protein with hydrophobic regions that extend into and often completely span the hydrophobic interior in contact with the aqueous solution on one or both sides of the membrane (or lining the channel in the case of a channel protein); Pass through the phospholipid bilayer; Act as enzymes, help in communication and structure; Act as transport proteins; Have polar amino acids to match the head areas and non-polar amino acids in the fatty acid area
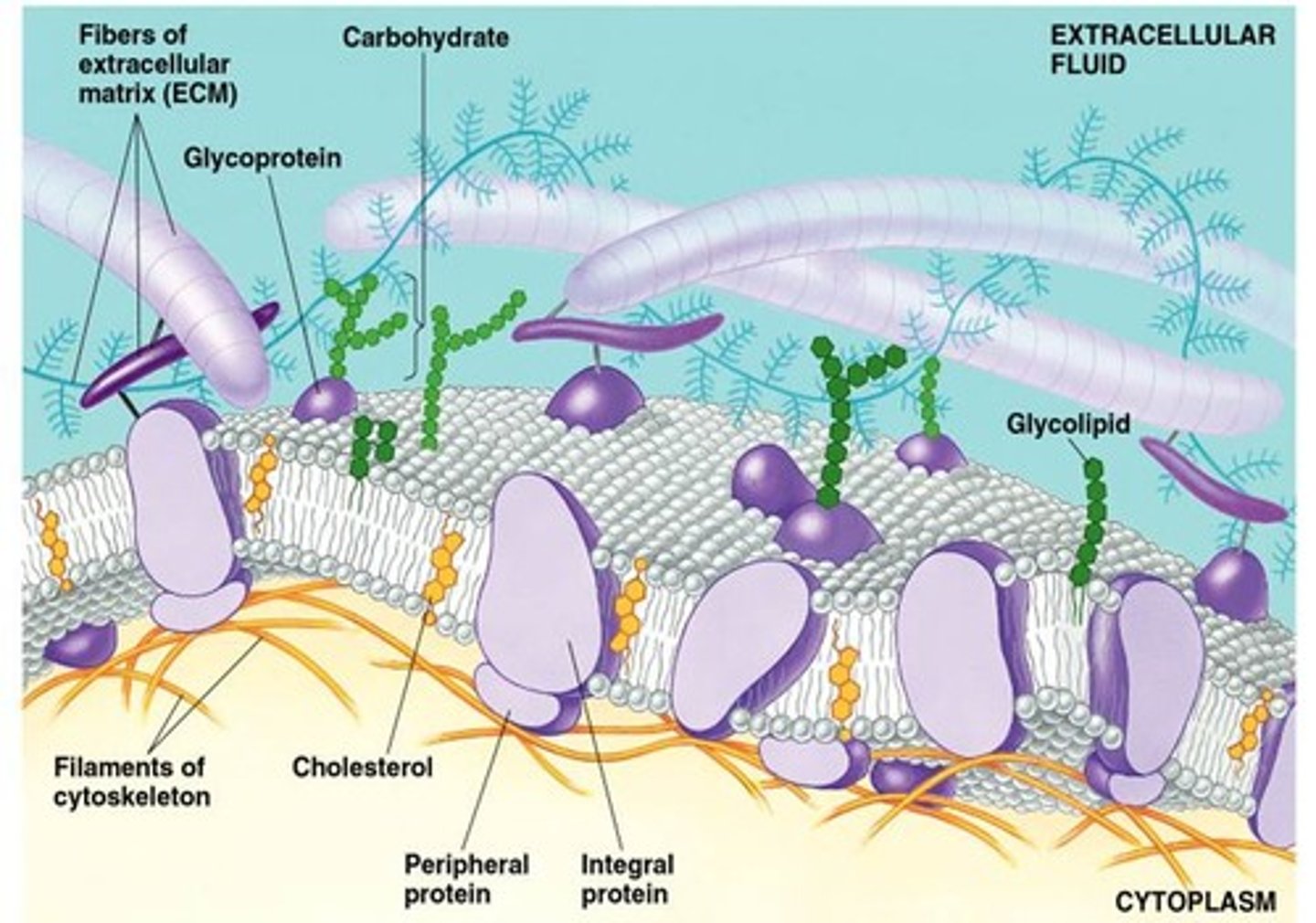
Peripheral Proteins
A protein loosely bound to the surface of a membrane or to part of an integral protein and not embedded in the lipid bilayer; On cytoplasmic side of the membrane; Act as enzymes, help in communication and structure
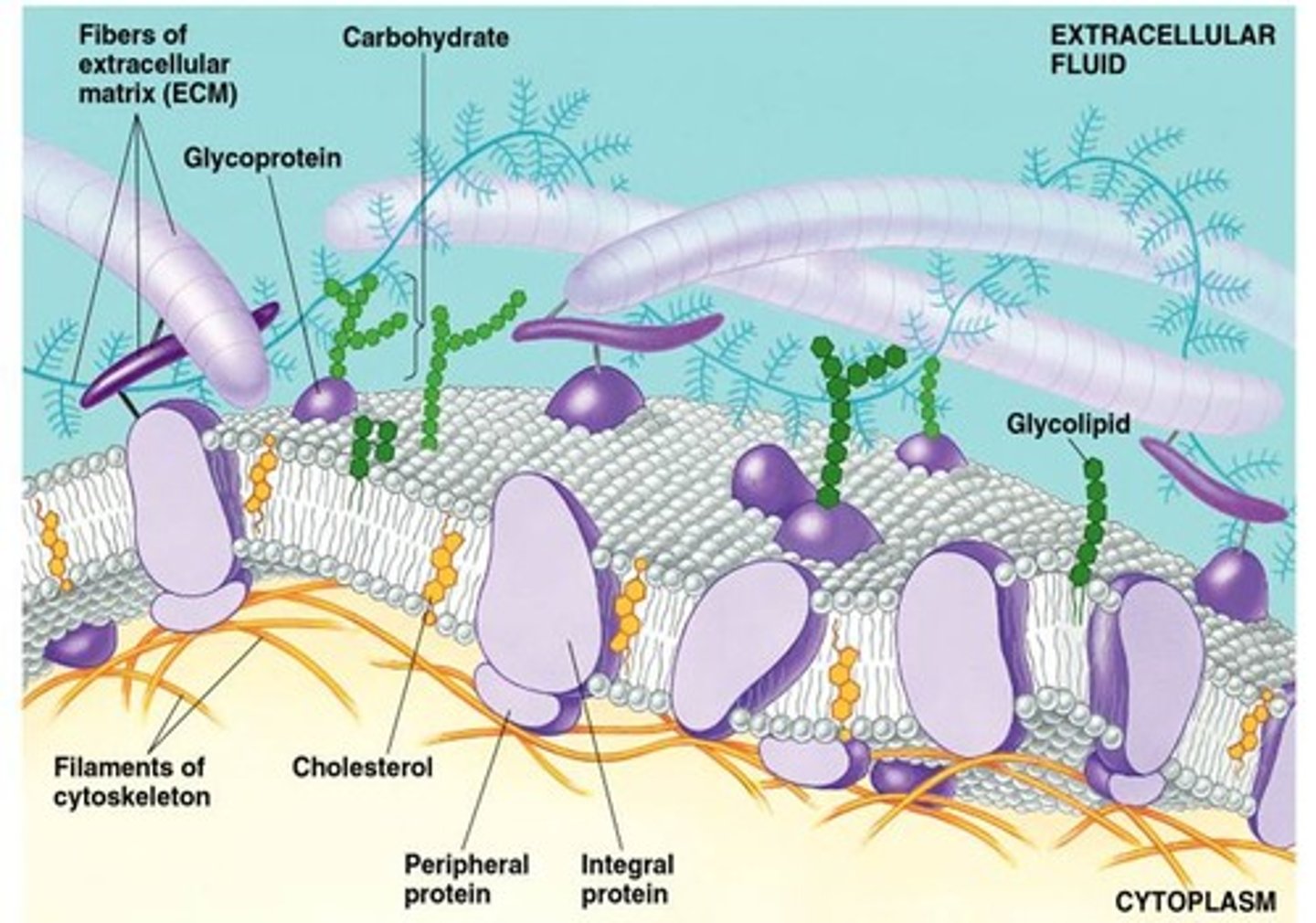
Outer Membrane vs. Inner Membrane
Outer membrane has oligosaccharides attached while the inner membrane does not, the ECM or cytoskeleton are only found on one side of the membrane
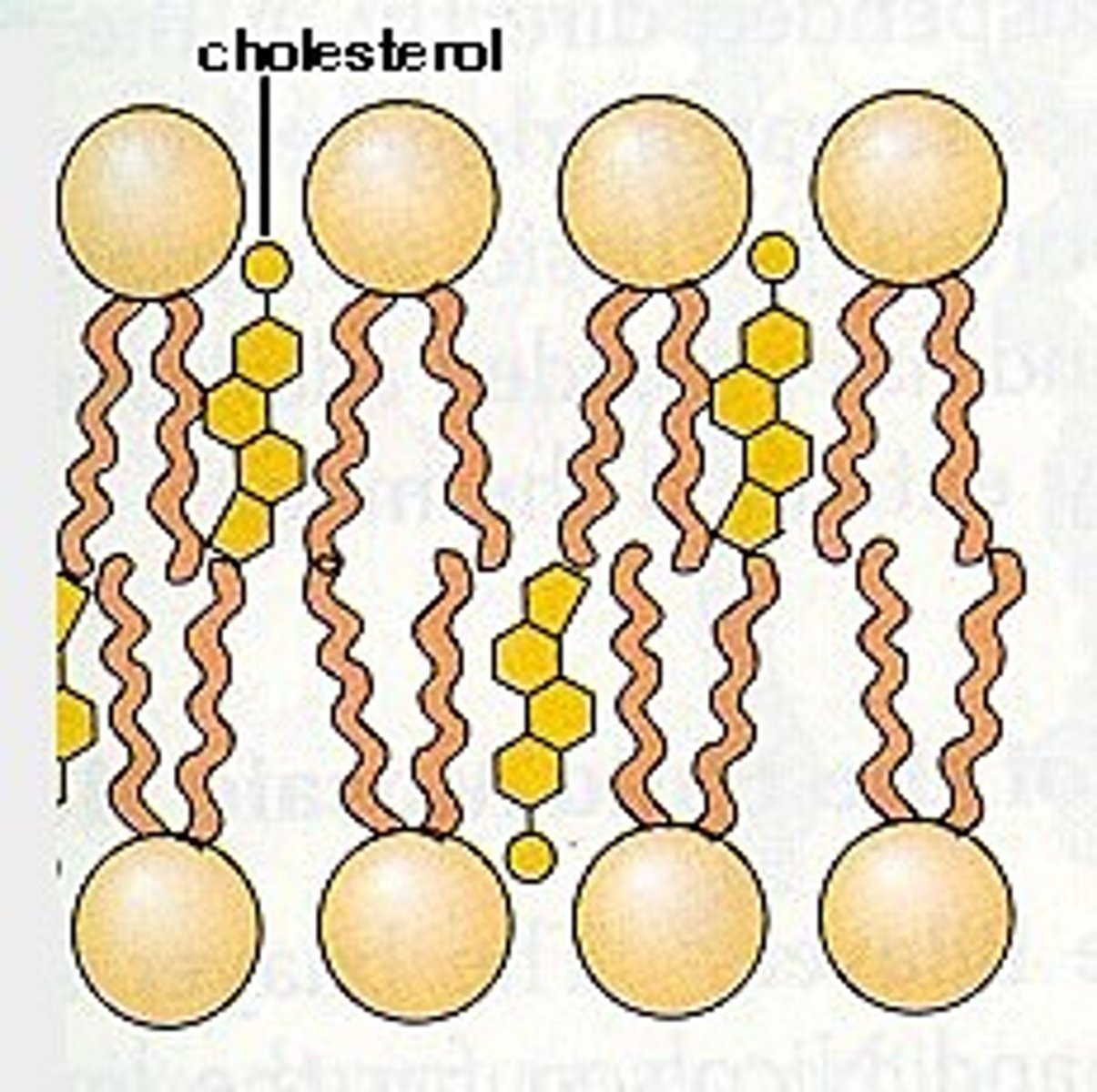
Cholesterol
Helps to regulate membrane fluidity; Makes membrane less fluid by restraining phospholipid movement; Also lowers temperature required for membrane to solidify; Helps resist changes in fluidity as temperature changes; Decreases fluidity
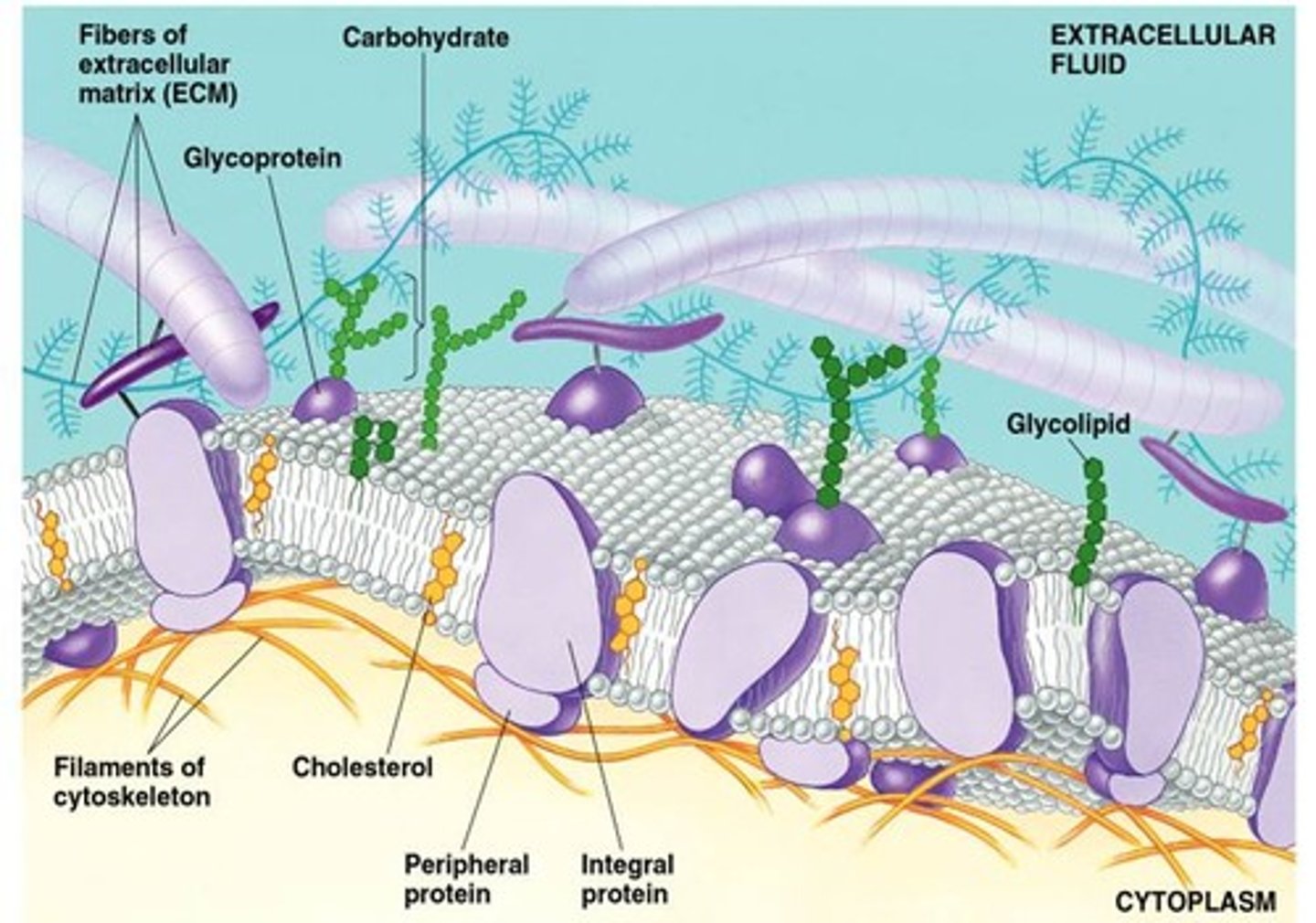
Membrane Carbohydrates
Branched oligosaccharides form glycophospholipids and glycoproteins on external surface; Recognition of "self" vs. "other"
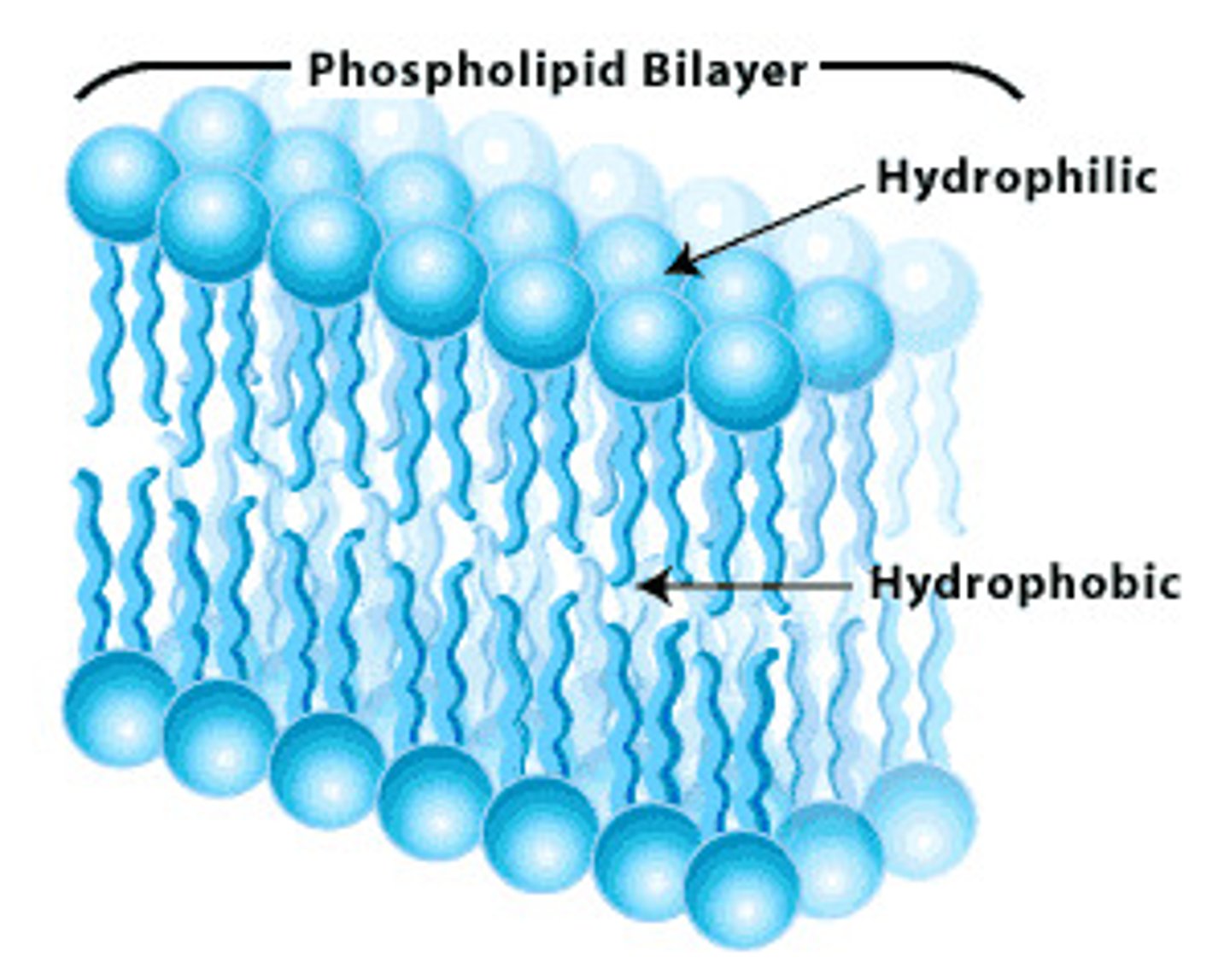
Phospholipid Bilayer
O2 and CO2 are small molecules that can diffuse across; Hydrophilic molecules (polar), large molecules, and ions can't cross the phospholipid bilayer
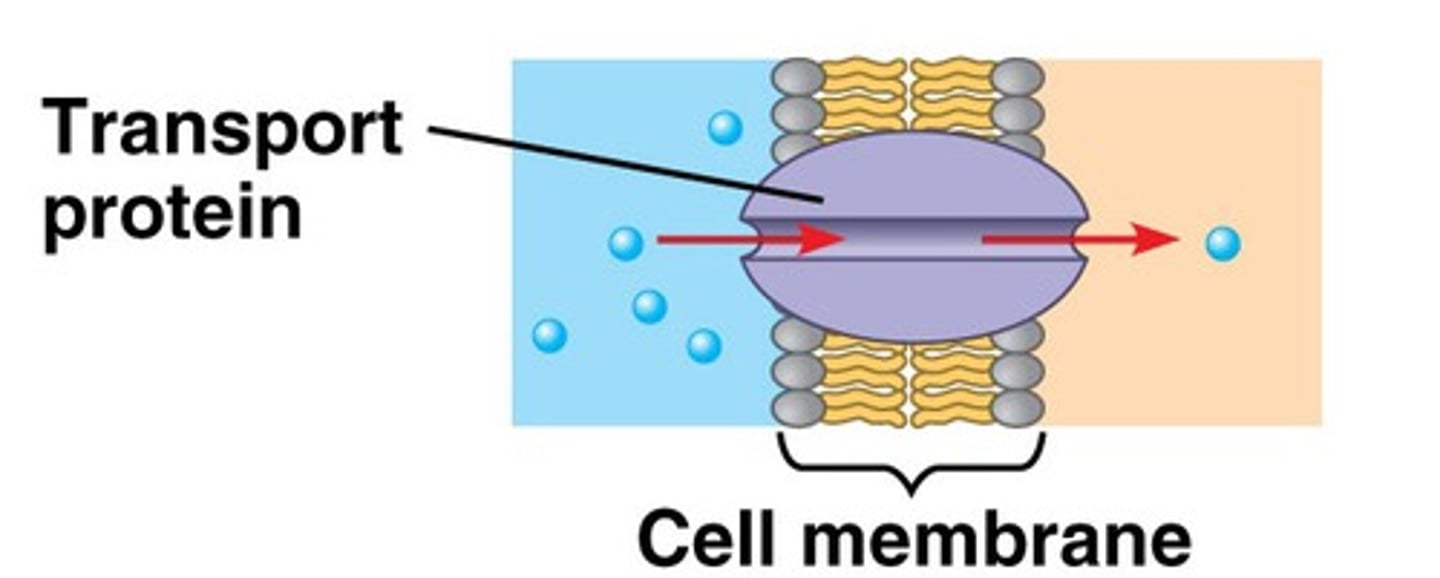
Transport Proteins
A transmembrane protein that helps a certain substance or class of closely related substances to cross the membrane; Provides a polar (hydrophilic) environment for ions and polar molecules to diffuse through
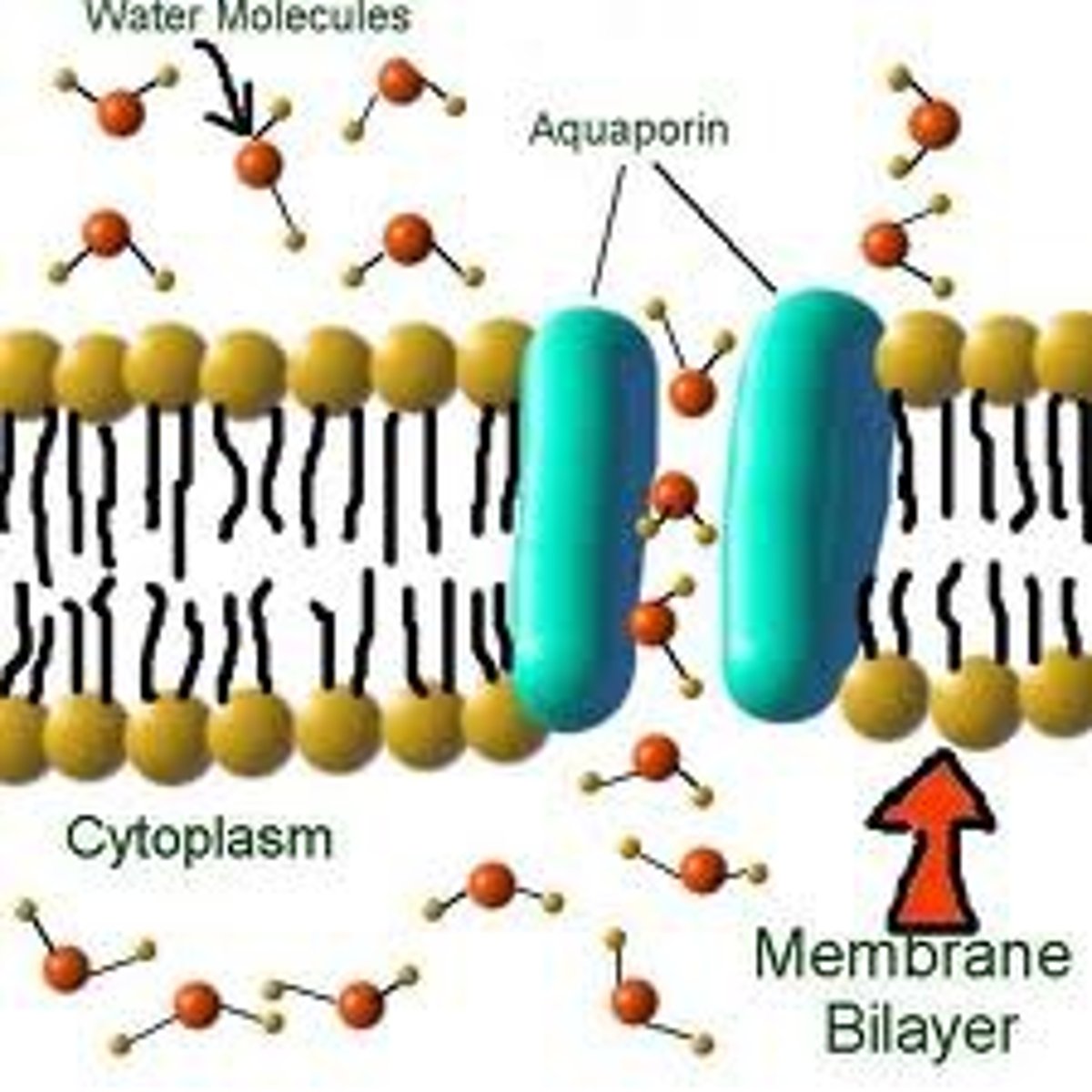
Aquaporins
Facilitated diffusion channels that allow water to cross membranes
Diffusion
The random thermal motion of particles of liquids, gases, or solids. In the presence of a concentration or electrochemical gradient, diffusion results in the net movement of a substance from a region where it is more concentrated to a region where it is less concentrated; Affected by concentration, temperature, pressure, particle size, and mixing (stirring)
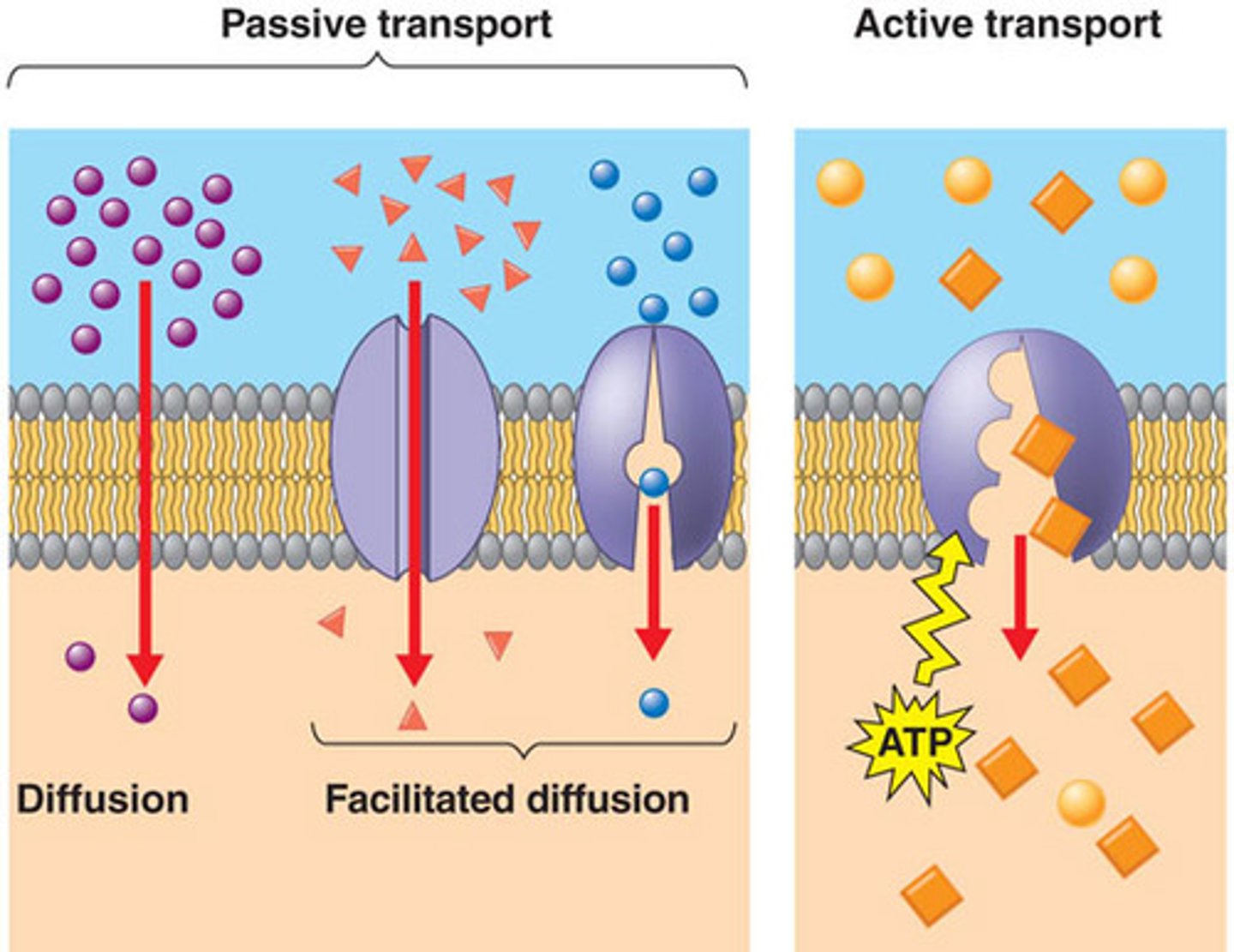
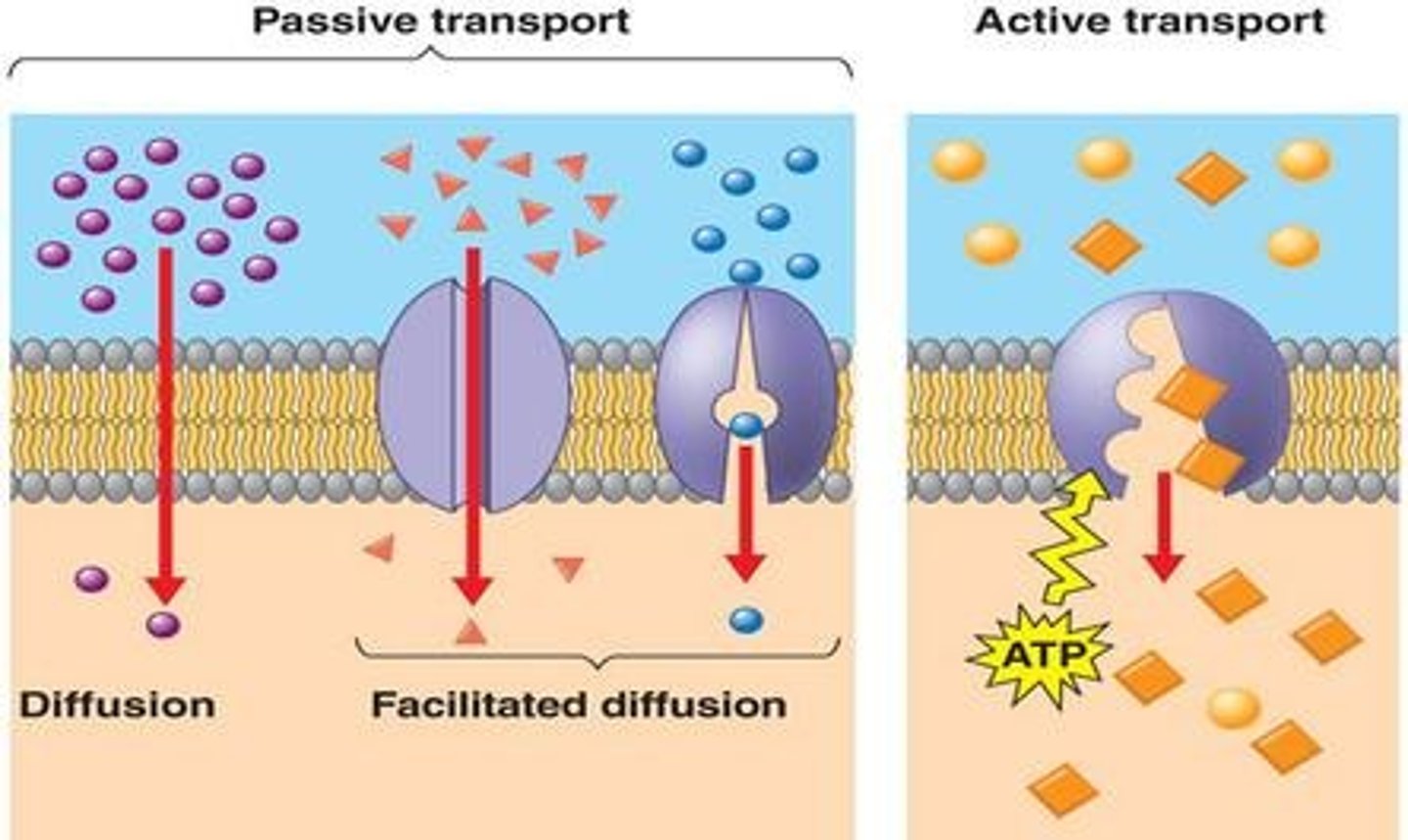
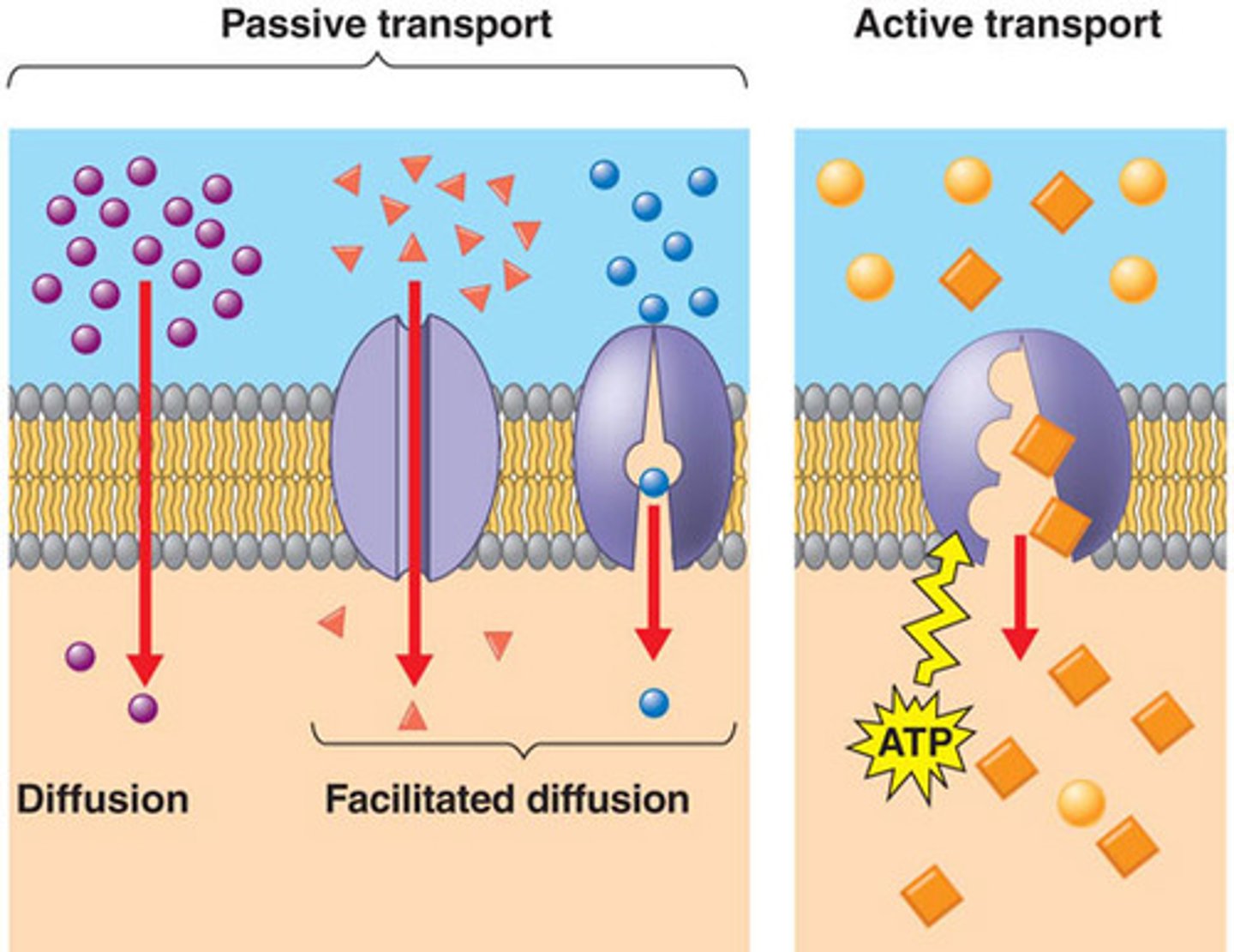
Passive Transport
The diffusion of a substance across a biological membrane with no expenditure of energy; Diffusion, osmosis, facilitated diffusion
Concentration Gradient
A region along which the density of a chemical substance increases or decreases; In passive transport, substances move down the concentration gradient
Osmosis
The diffusion of free water molecules across a selectively permeable membrane
Tonicity
The ability of a solution surrounding a cell to cause that cell to gain or lose water; (Hypo, hyper, iso); Hypotonic = Low; Hypertonic = High
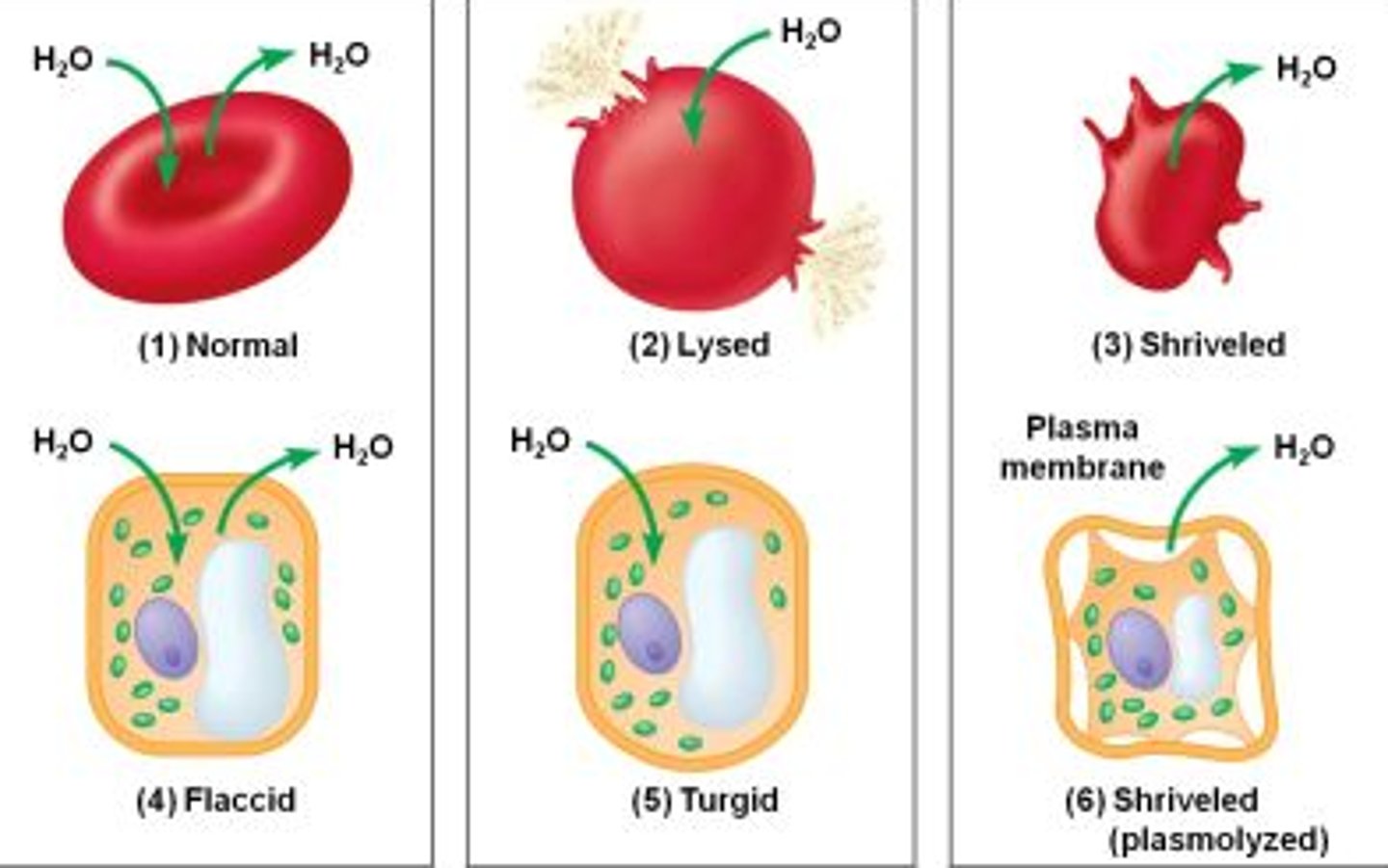
Hypertonic
Referring to a solution that, when surrounding a cell, will cause the cell to lose water
Hypotonic
Referring to a solution that, when surrounding a cell, will cause the cell to take up water
Isotonic
Referring to a solution that, when surrounding a cell, causes no net movement of water into or out of the cell
Osmoregulation
Regulation of solute concentrations and water balance by a cell or organism
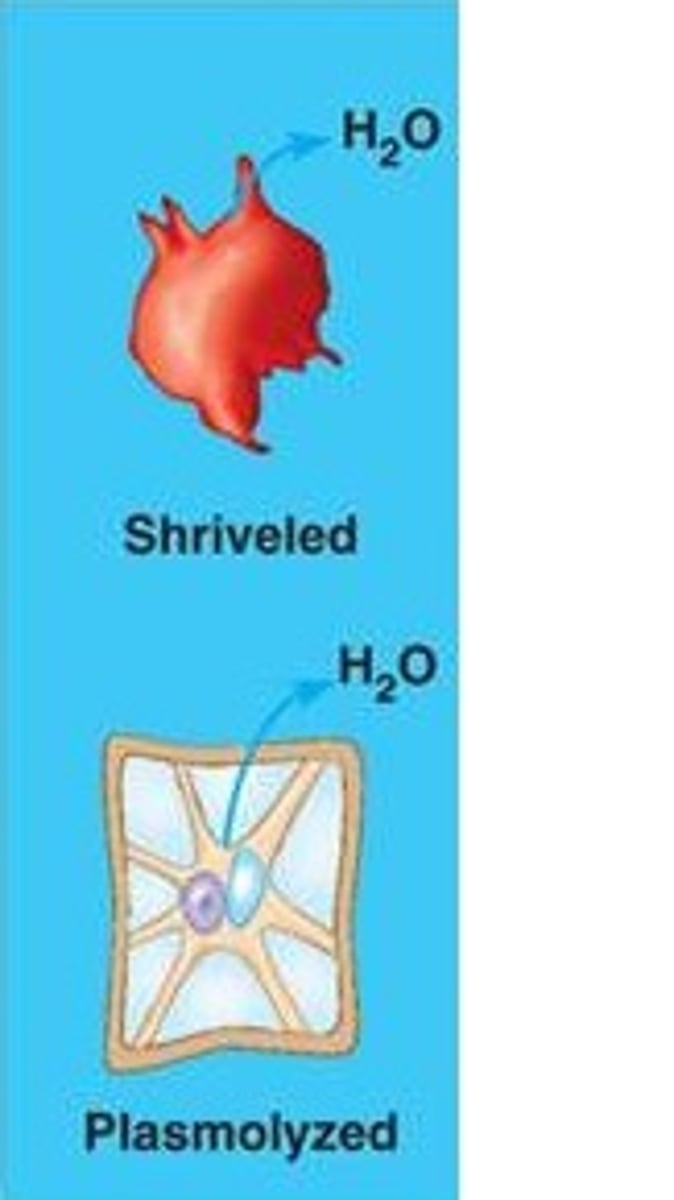
Plasmolysis
A phenomenon in walled calls in which the cytoplasm shrivels and the plasma membrane pulls away from the cell wall; occurs when the cell loses water to a hypertonic environment
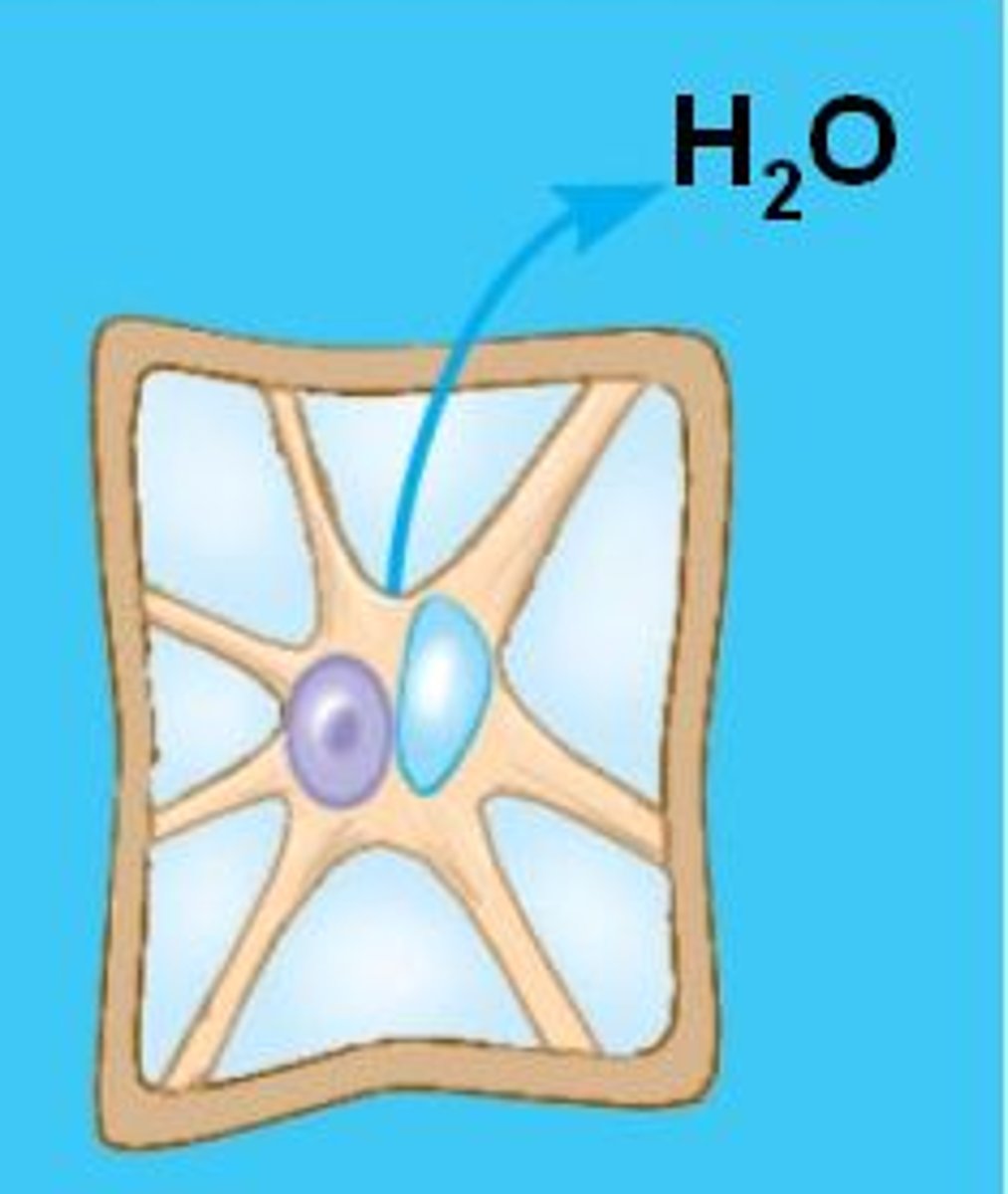
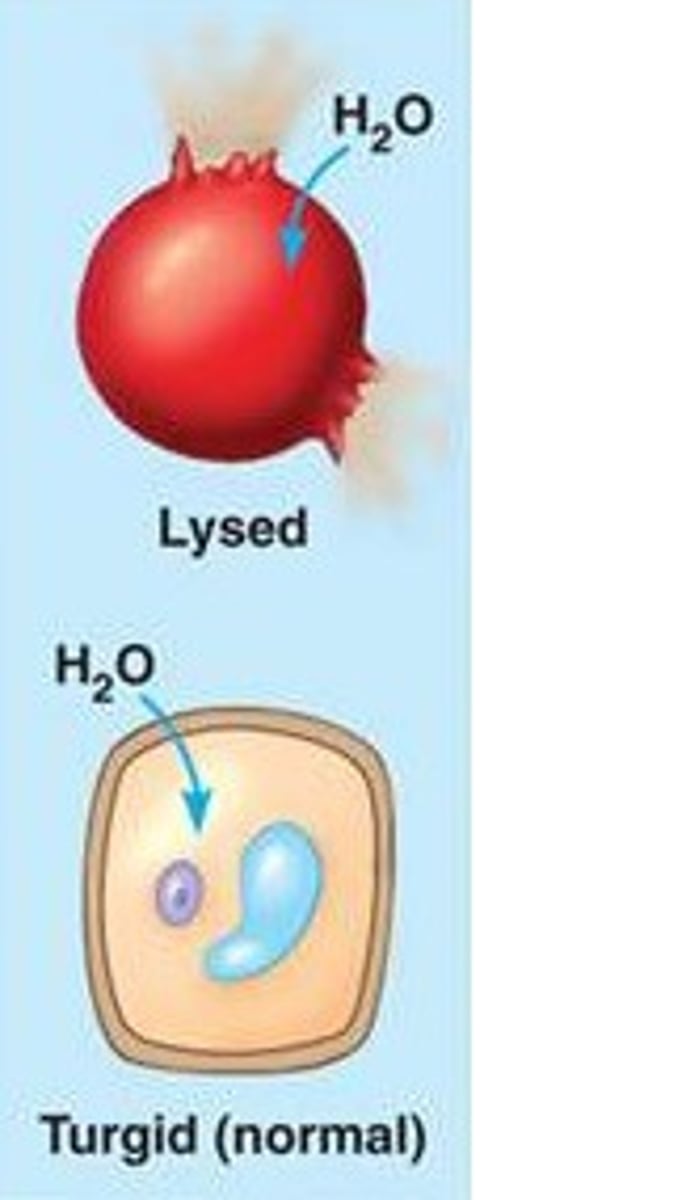
Turgid
Swollen or distended, as in plant cells (A walled cell becomes this if it has a lower water potential than its surroundings, resulting in entry of water)
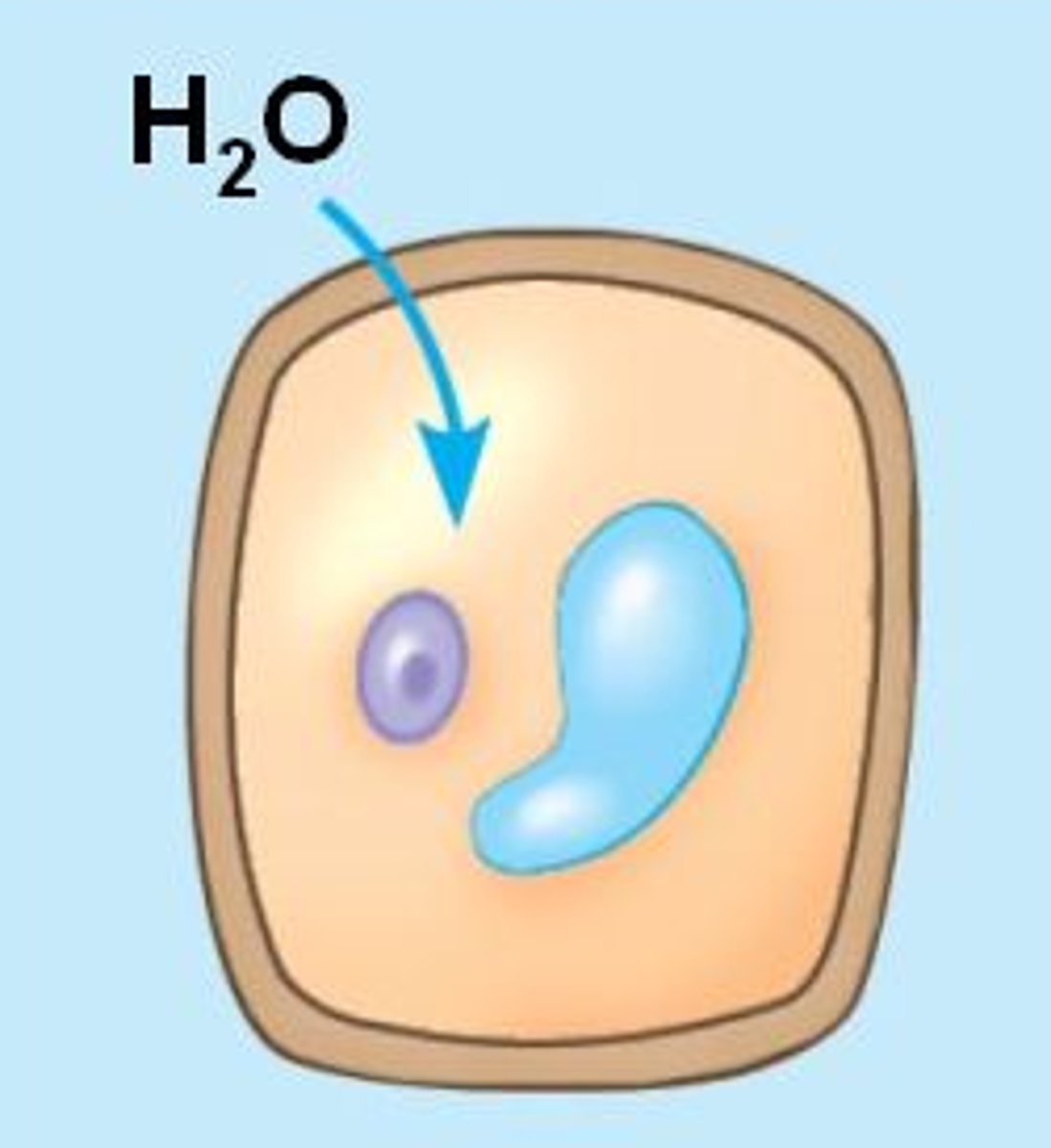
Flaccid
Limp. Lacking turgor (stiffness or firmness), as in a plant cell ins surroundings where there is a tendency for water to leave the cell (A walled cell becomes this if it has a higher water potential than its surroundings, resulting in the loss of water).
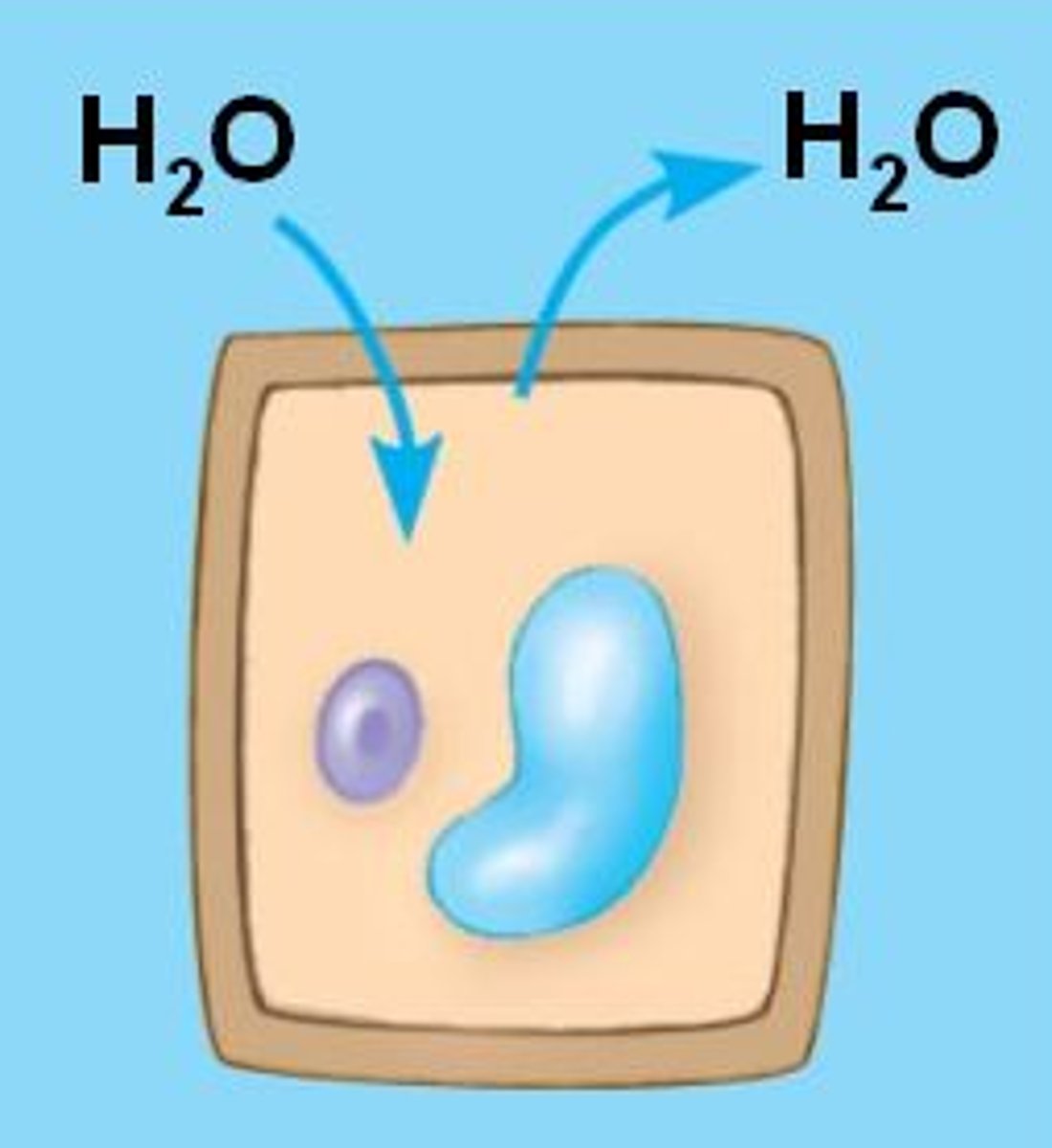
Facilitated Diffusion
The passage of molecules or ions down their electrochemical gradient across a biological membrane with the assistance of specific transmembrane transport proteins, requiring no energy expenditure
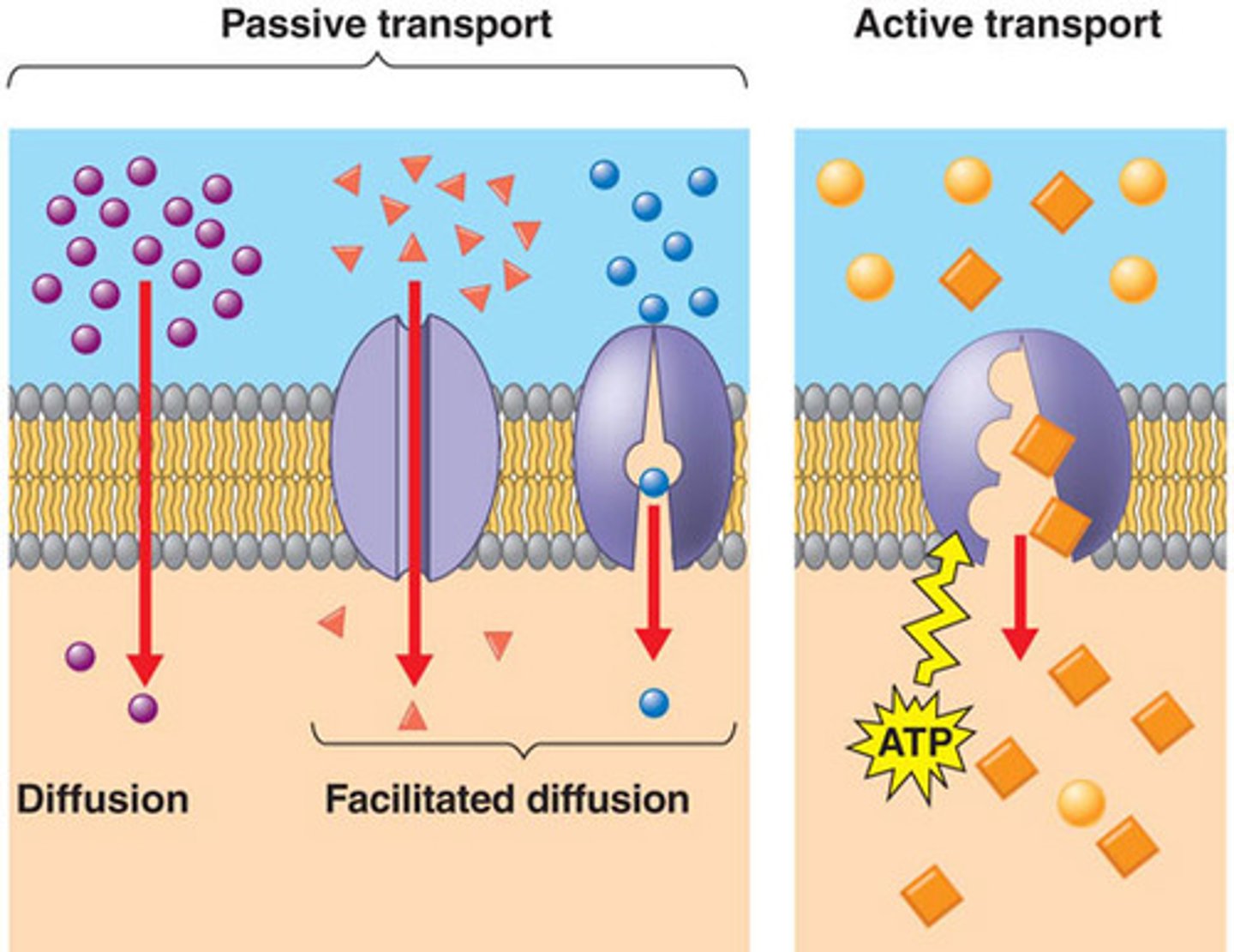
Active Transport
The movement of a substance across a cell membrane against its concentration or electrochemical gradient, mediated by specific transport proteins and requiring an expenditure of energy (ATP); Carrier-mediated, endocytosis, exocytosis
Carrier-Mediated Transport
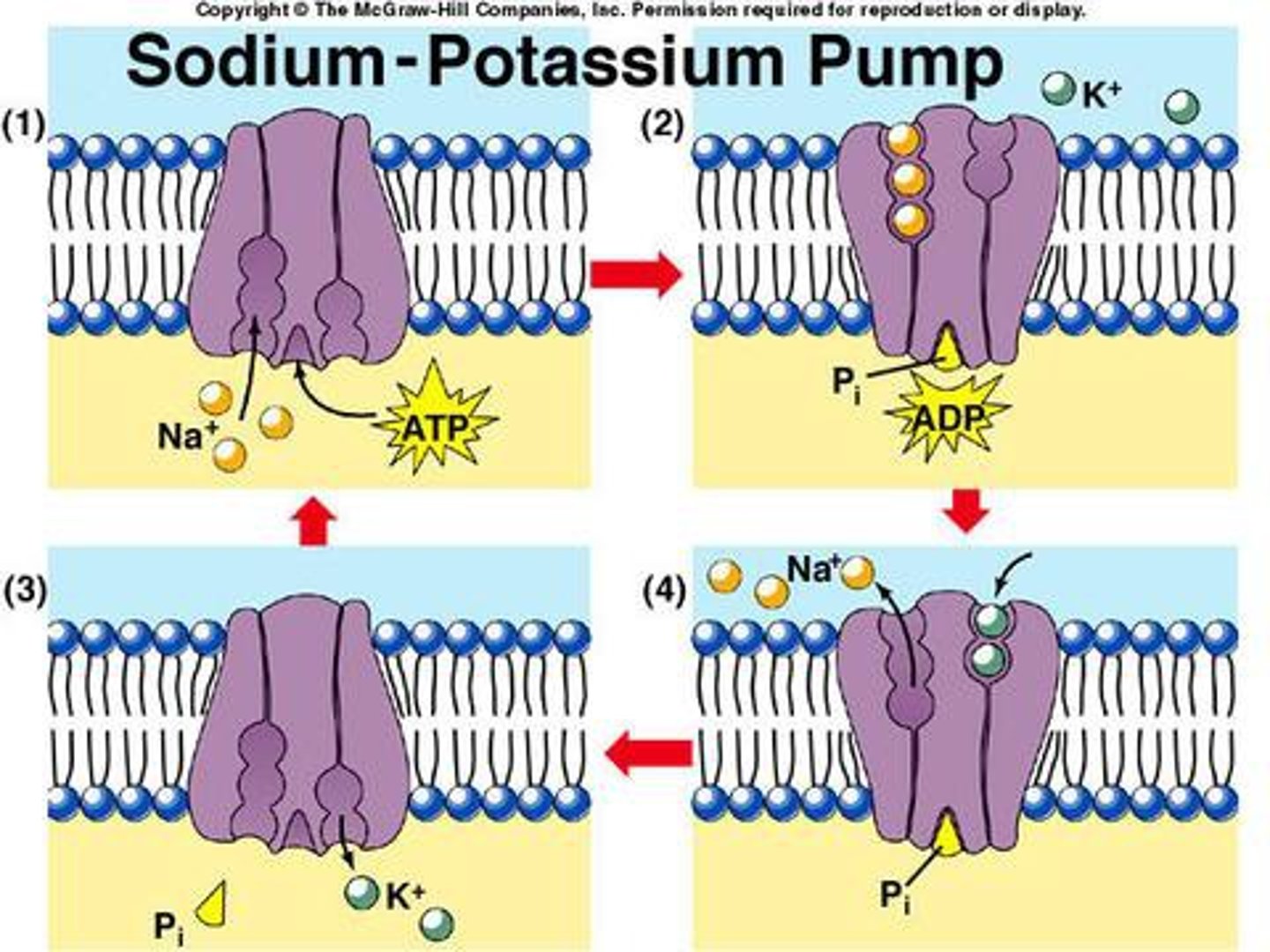
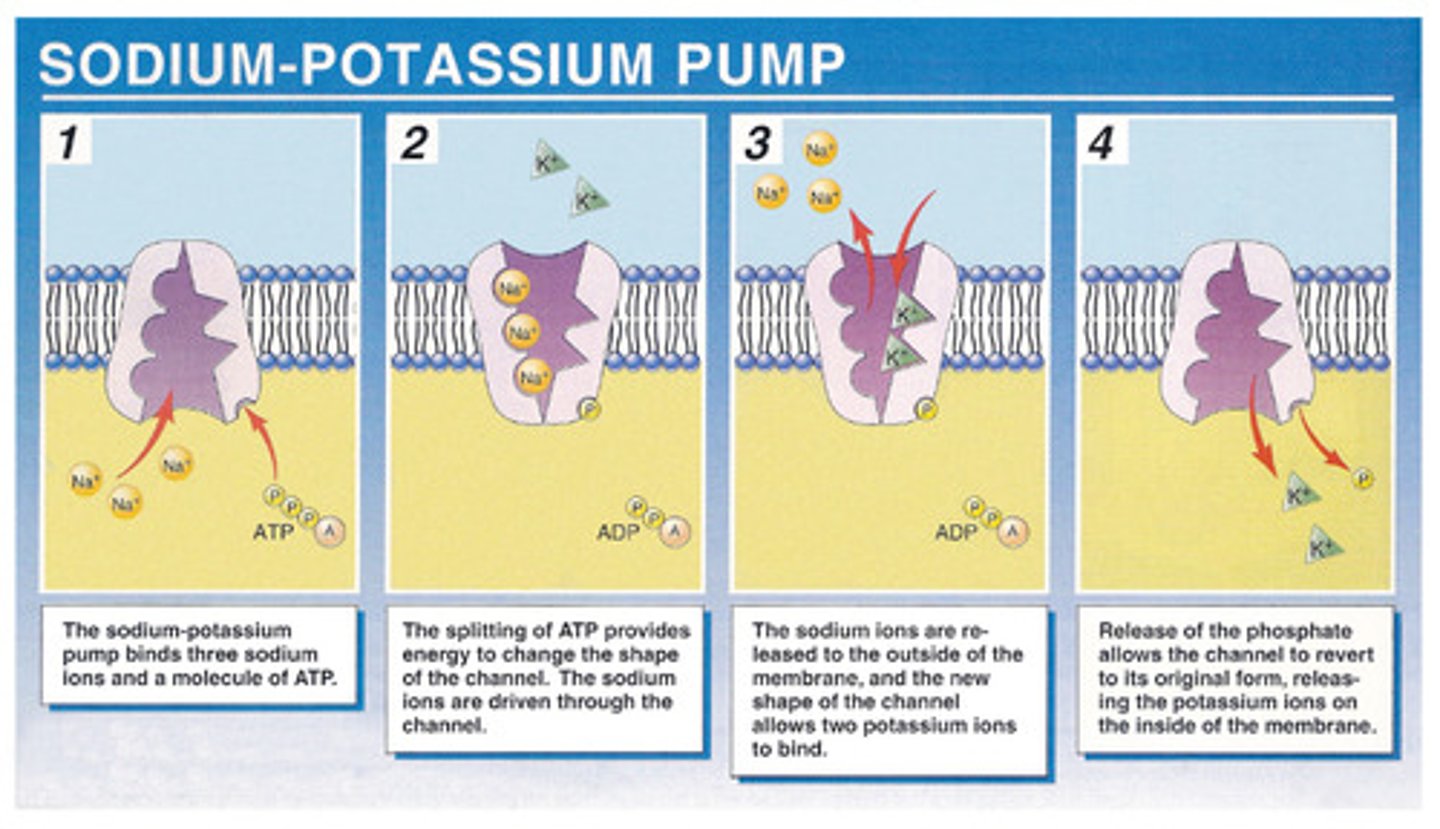
Active transport of materials into cells against concentration gradients (Low to high); Ex. Na+ and K+ pump, electrogenic or H+ pump, cotransport
Membrane Potential
The voltage (charge) difference between two sides of a membrane; Inside of cells is usually negatively charged relative to the outside
Electrochemical Gradient
Made up of concentration gradient (chemical) and membrane potential (electrical)
Na+ and K+ Pump
Major electrogenic pump in animal cells; Exchanges sodium ions for potassium ions, both of which are cations; Because the cations are not in equal concentration, a membrane potential or difference in electrical charge, giving one side a more positive charge as compared to the other; Carrier-mediated (active) transport
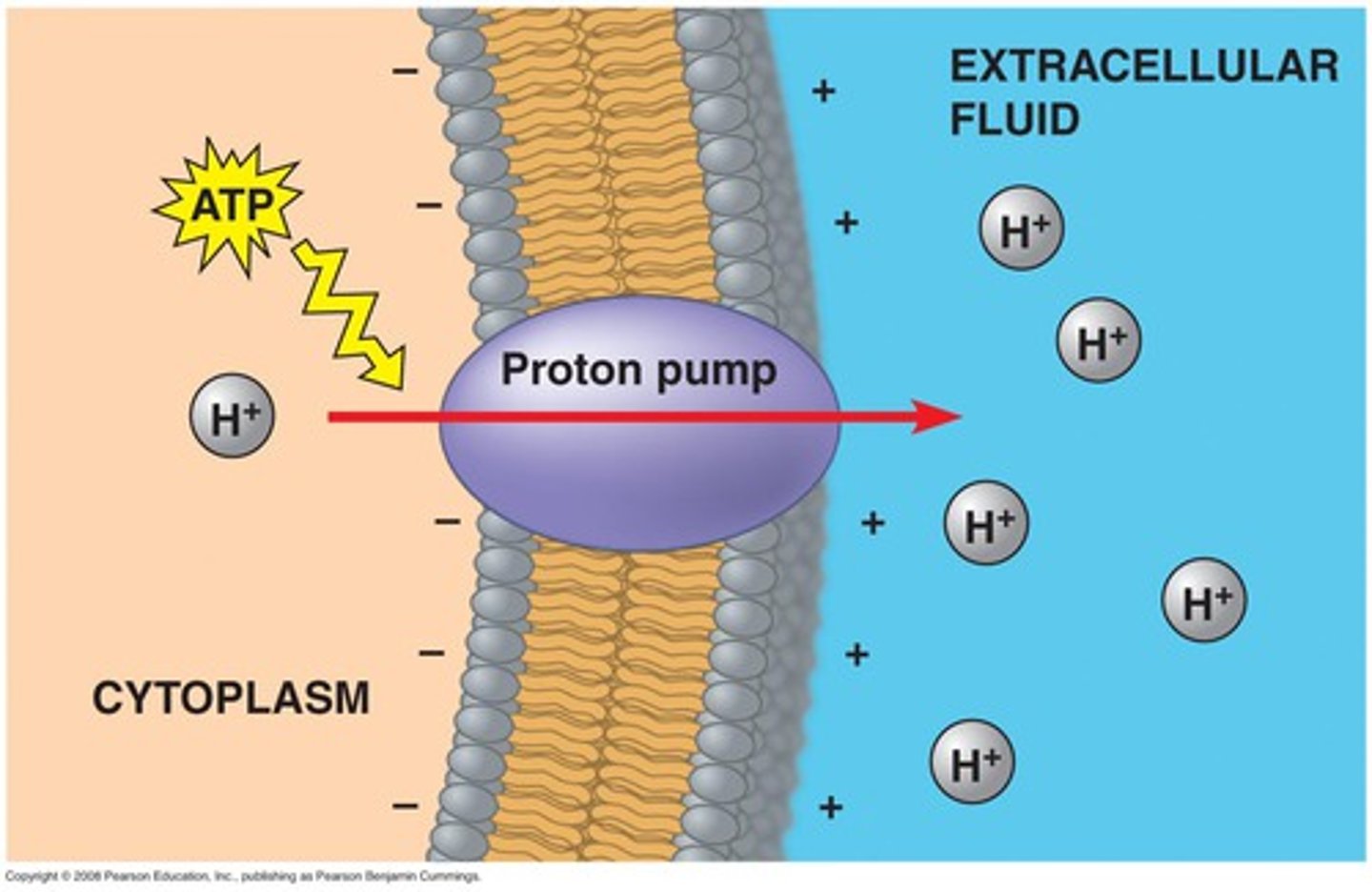
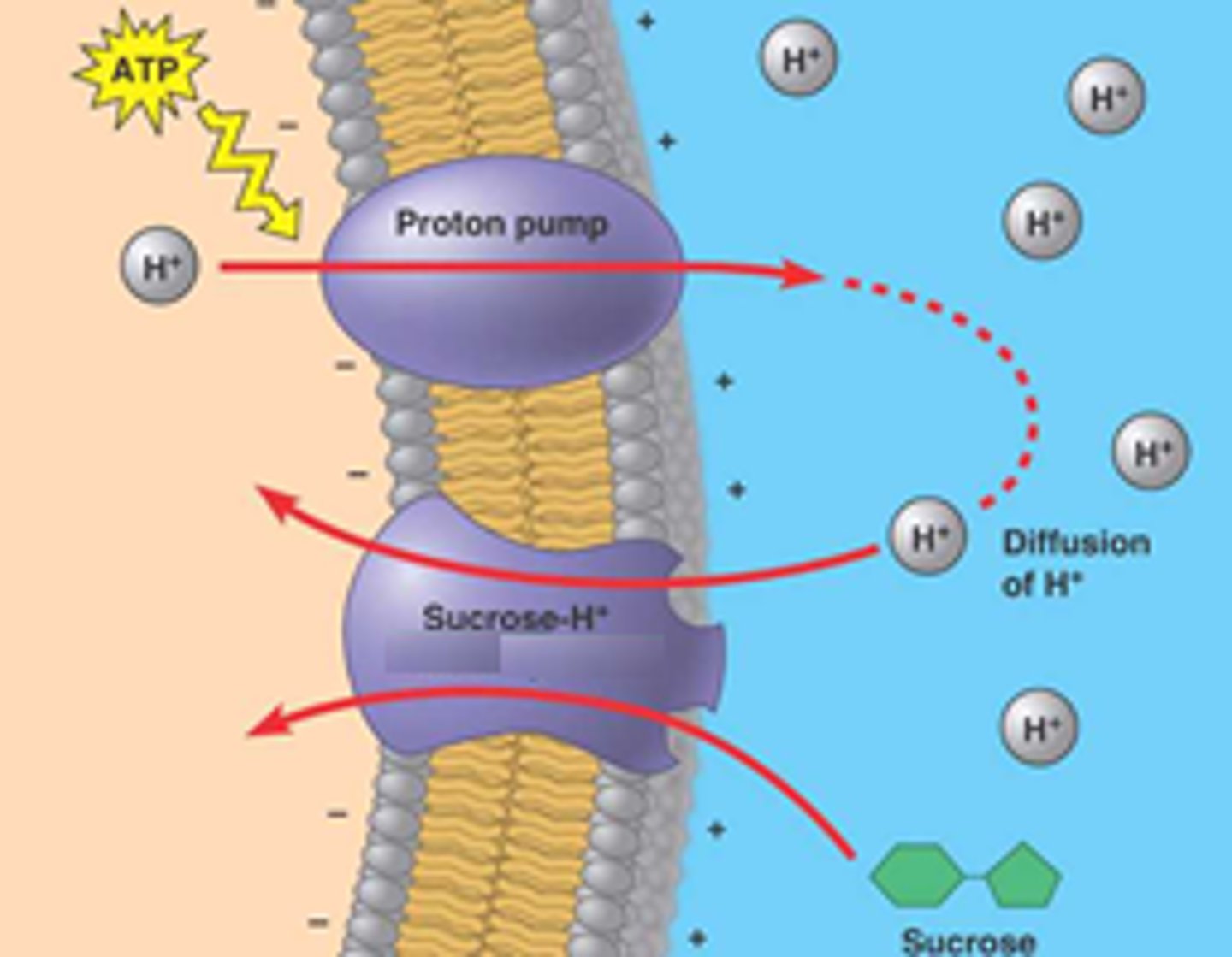
Electrogenic or H+ Pumps
AKA Proton pumps; active; Carrier-mediated transport; Create voltages across membranes for other cell processes; Used by plants, fungi, and bacteria
Cotransport
The coupling of the "downhill" diffusion of one substance to the "uphill" transport of another against its own concentration gradient; Sucrose transport; Active
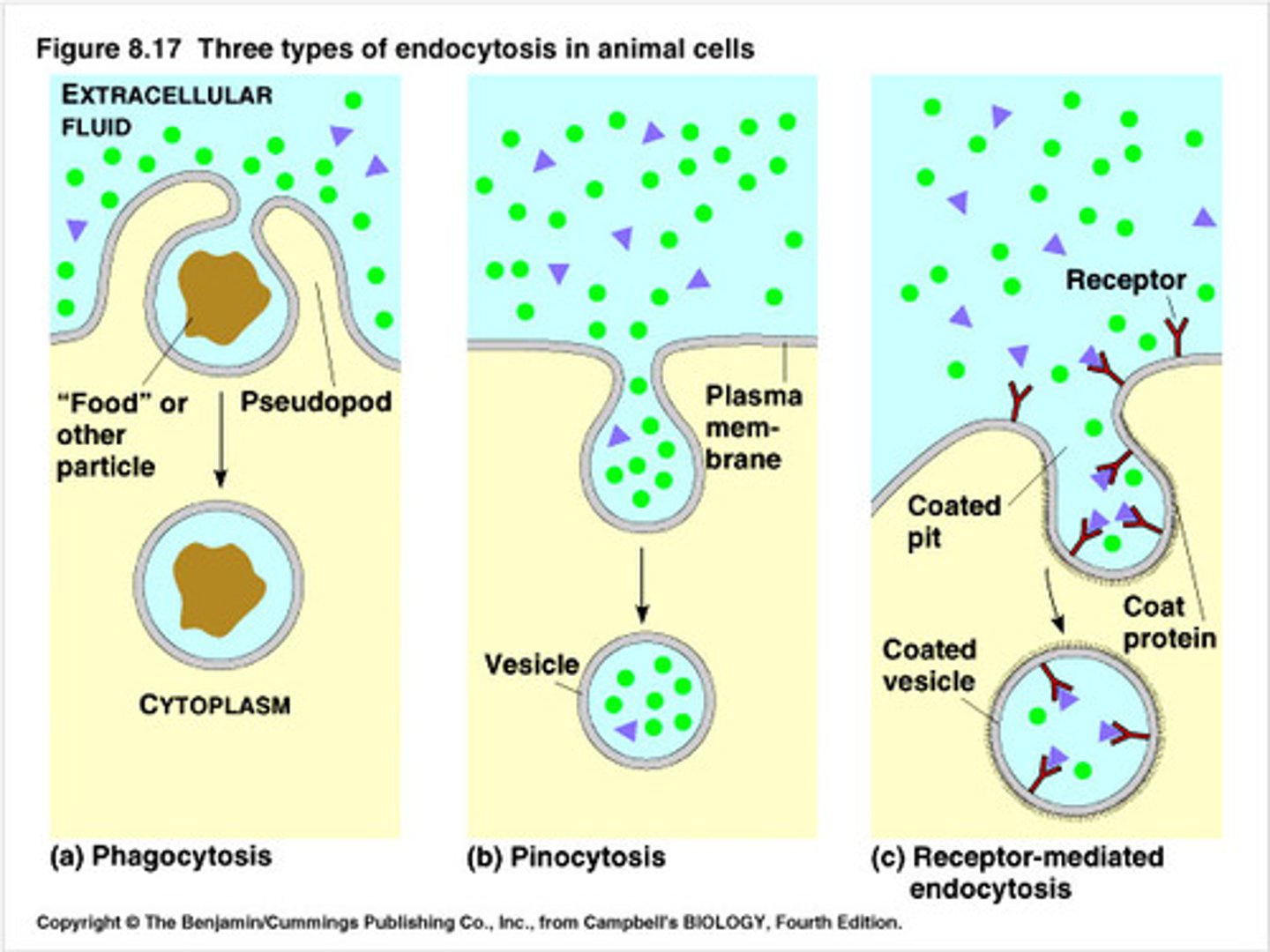
Endocytosis
Cellular uptake of biological molecules and particulate matter via formation of vesicles from the plasma membrane; Active transport; Used when the molecules are large or needed in large quantities; Exocytosis in reverse
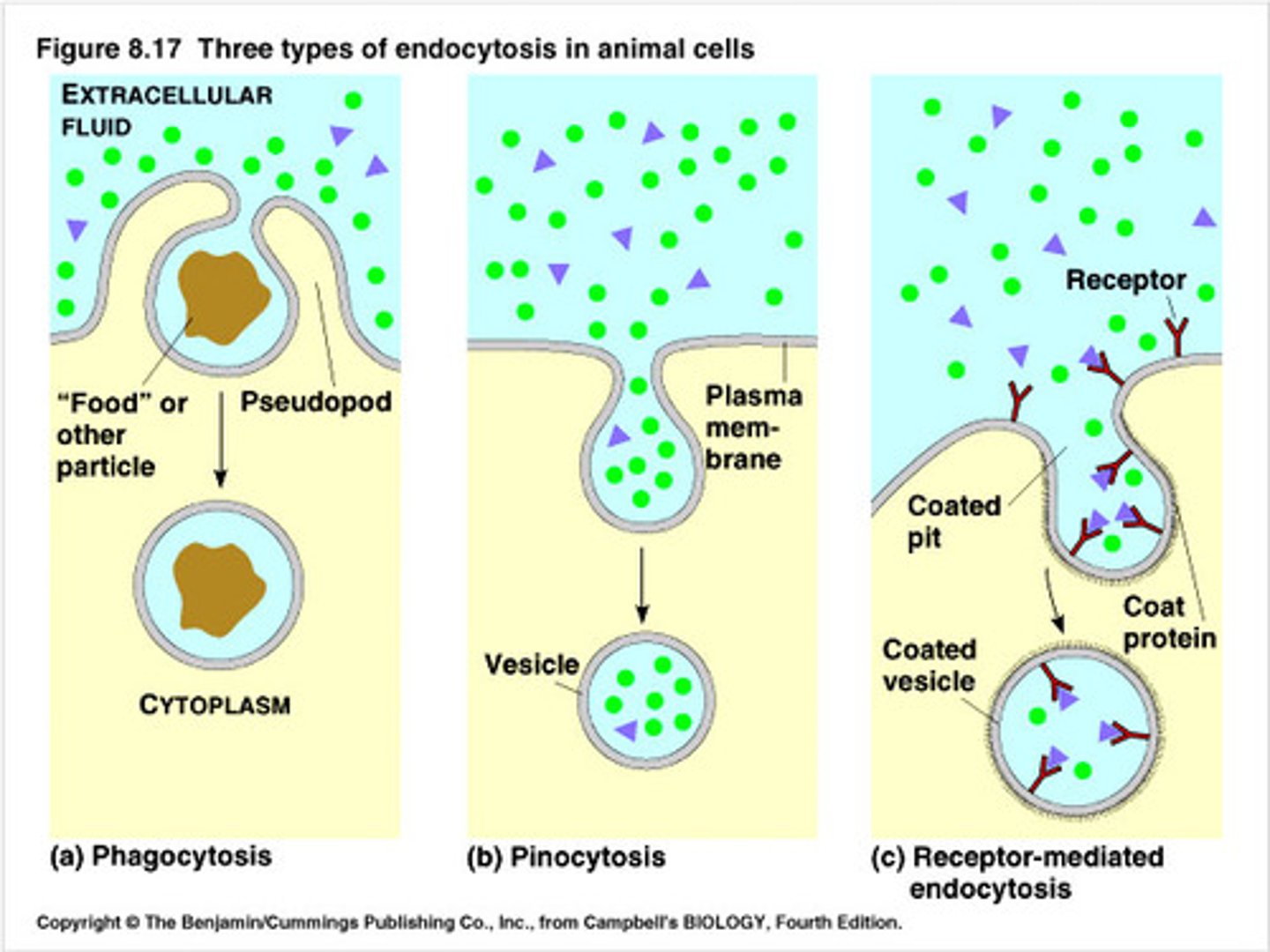
Phagocytosis
A type of endocytosis in which large particulate (solid) substances or small organisms are taken up by a cell. It is carried out by some protists and by certain immune cells of animals (In mammals, mainly macrophages, neutrophils, and dendritic cells); What the white blood cell known as a macrophage uses to engulf bacteria
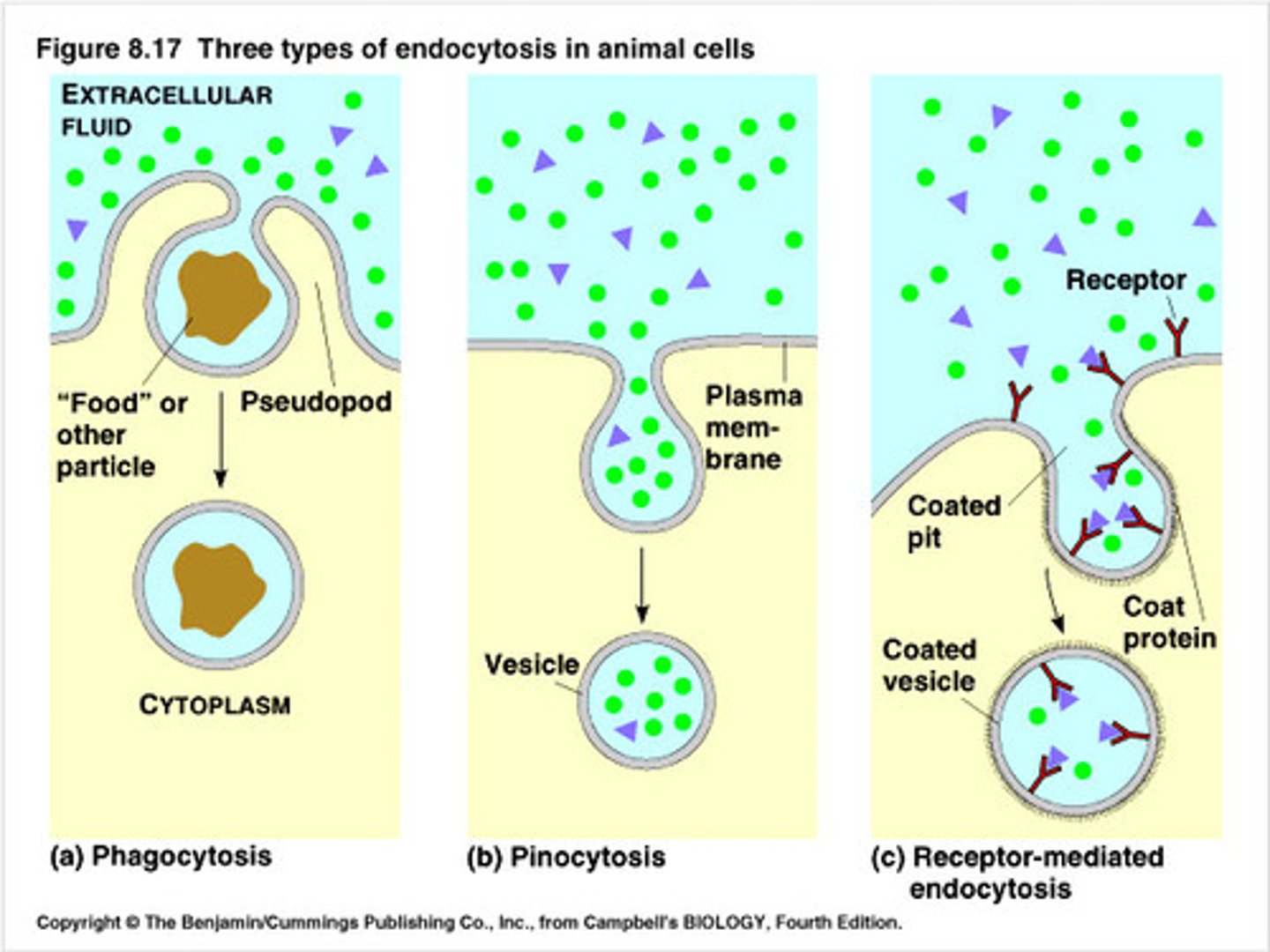
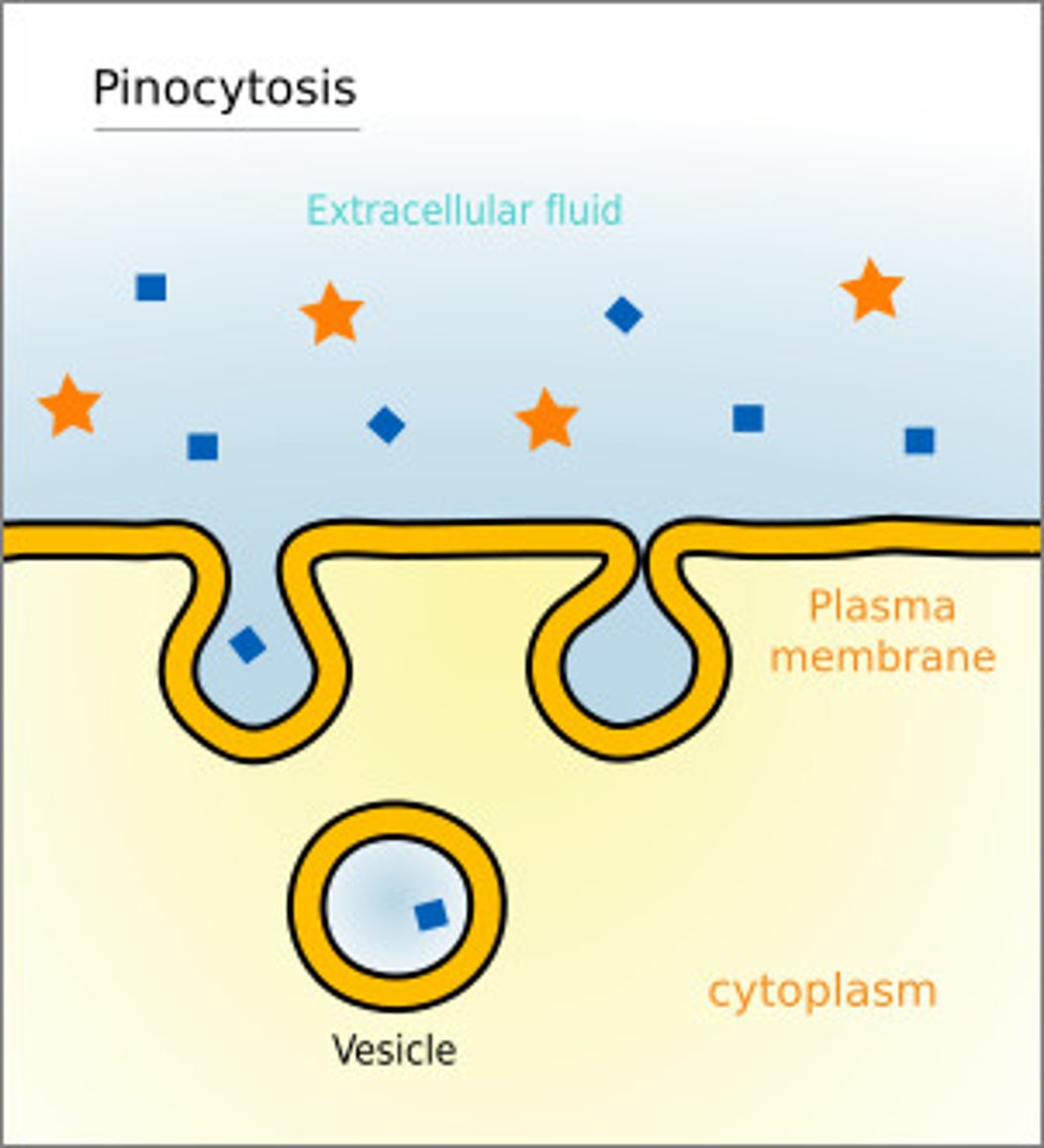
Pinocytosis
A type of endocytosis in which the cell ingests extracellular fluid and its dissolved solutes; Liquids
Receptor-Mediated Endocytosis
The movement of specific molecules into a cell by the inward budding of vesicles containing proteins with receptor sites specific to the molecules being taken in; enables a cell to acquire bulk quantities of specific substances
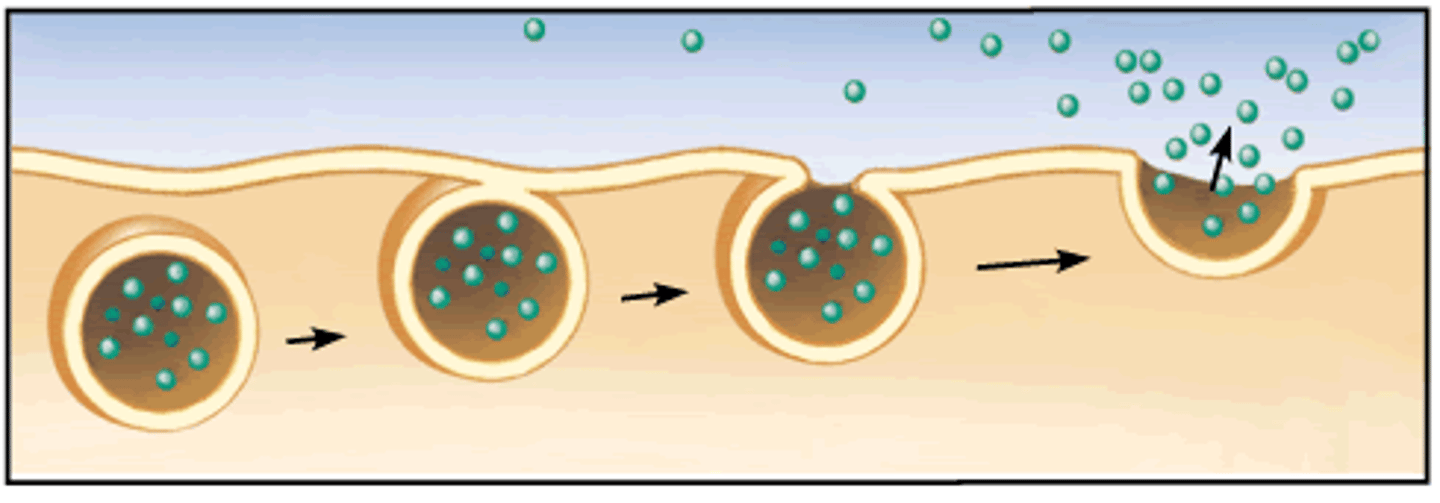
Exocytosis
The cellular secretion of biological molecules by the fusion of vesicles containing them with the plasma membrane; Active transport; Transport vesicles carrying proteins fuse to plasma membrane, then the vesicle opens up to the outside releasing the protein and becoming part of the plasma membrane; Ex. Secretion of enzymes
Limitations on Cell Size
Surface area to volume ratios, cytoplasm to nucleus ratios, metabolic requirements
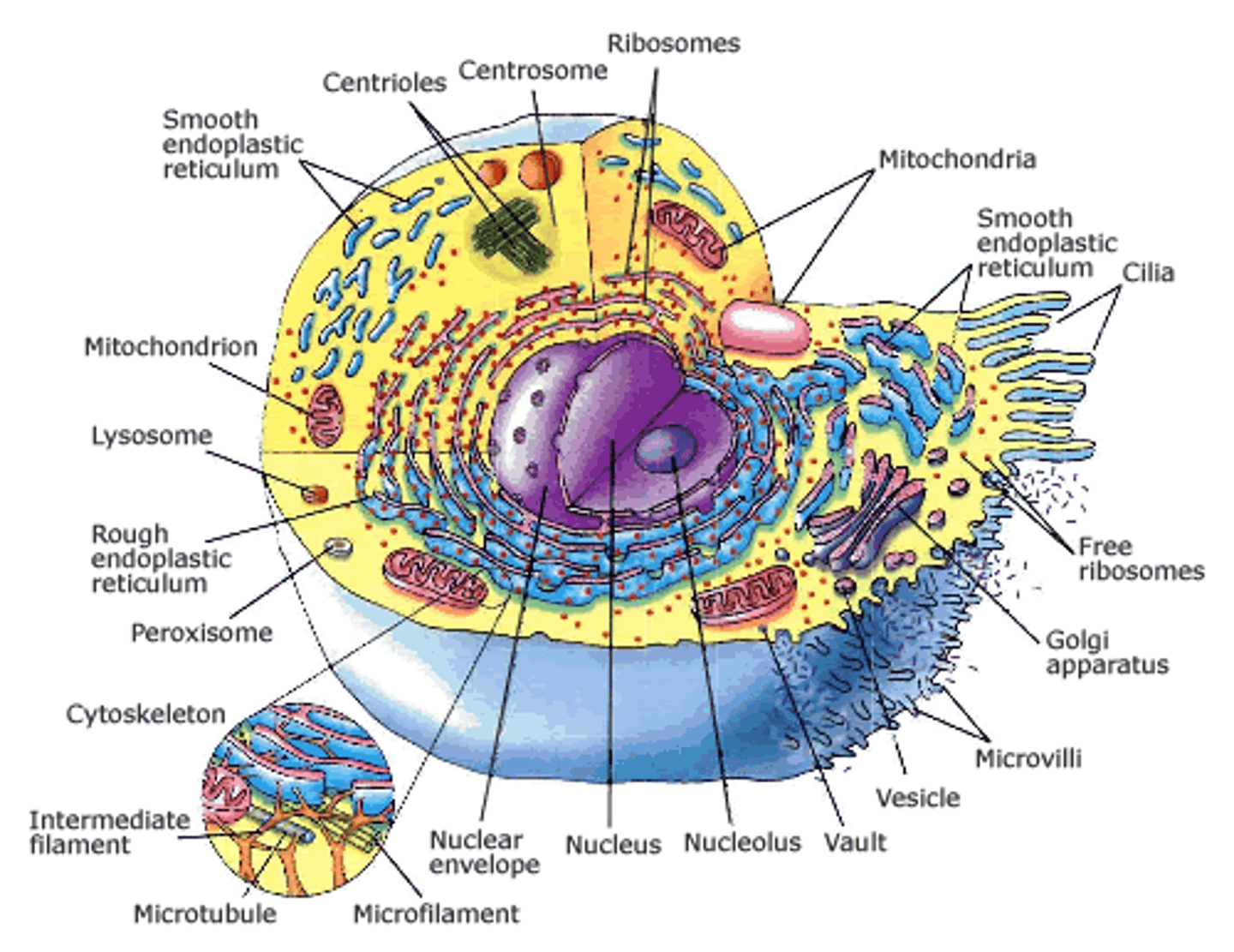
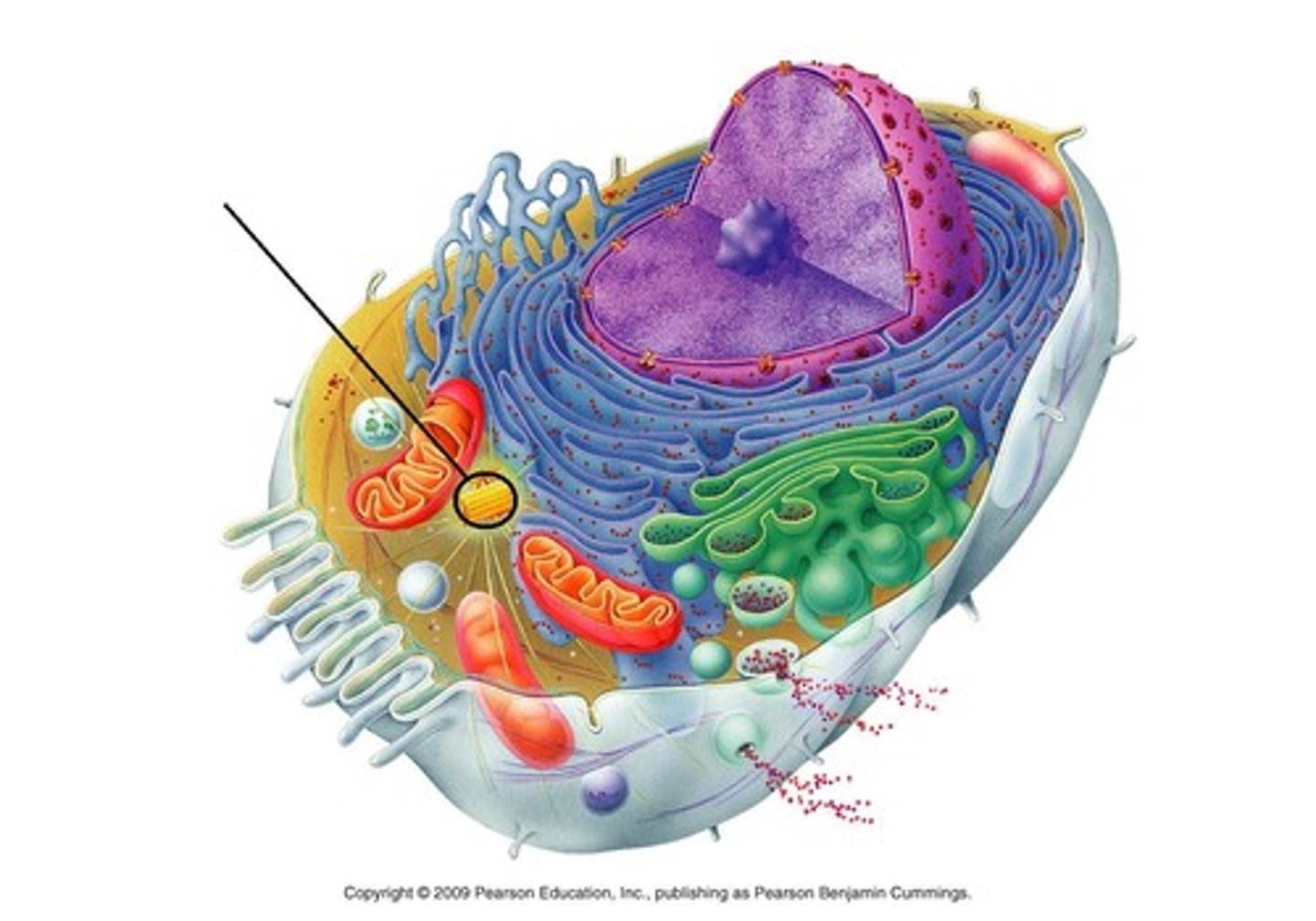
Organelle
Any of several kind of membrane-enclosed structures with specialized functions, suspended in the cytosol of eukaryotic cells
Cytoskeleton
A network of microtubules, microfilaments,and intermediate filaments that extends throughout the cytoplasm and serves a variety of mechanical, transport, and signaling functions
Cell Theory
All living matter is composed of 1+ cells; Cell is structural and functional unit of life; All cells come from cells
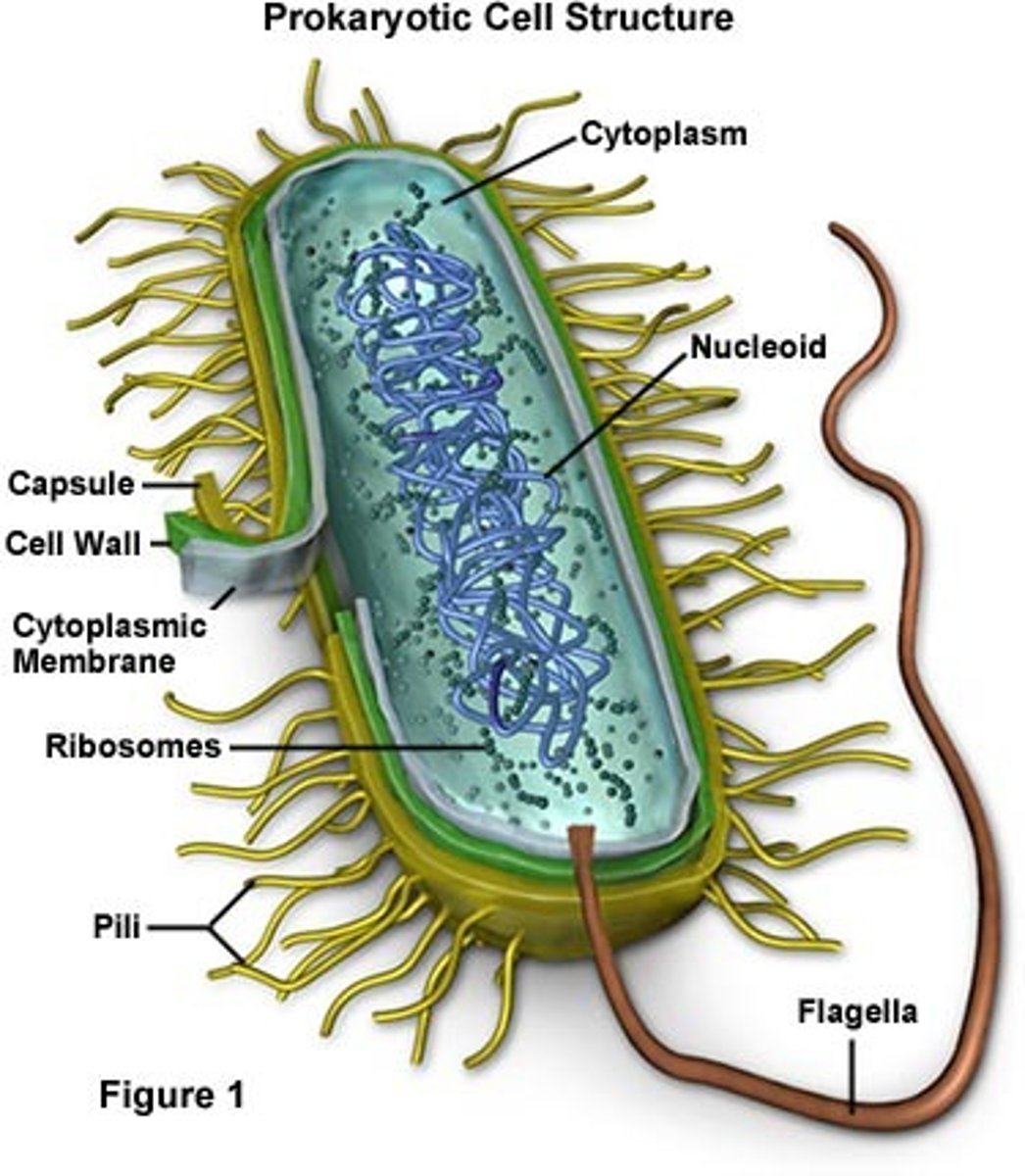
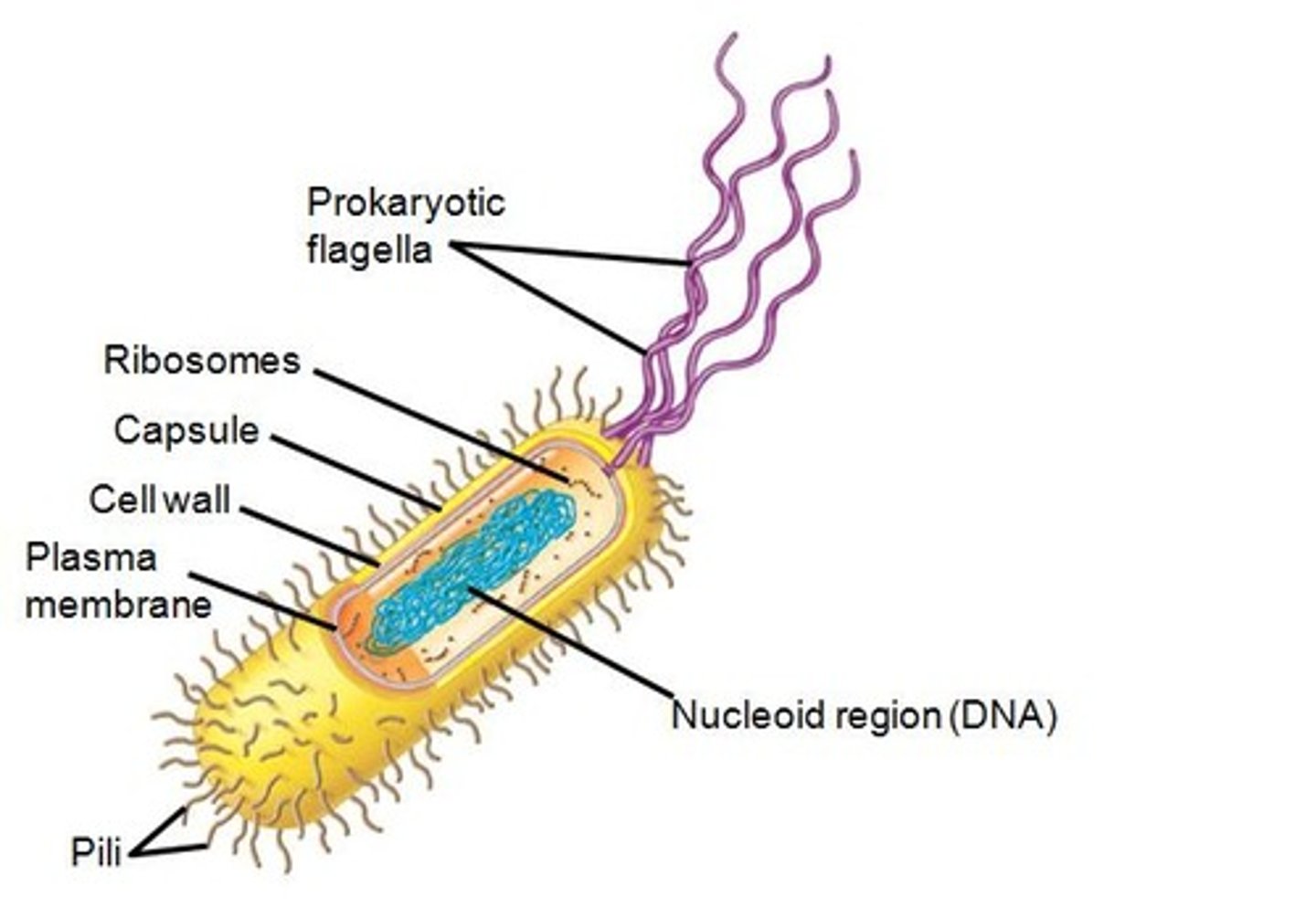
Prokaryotic Cell
A type of cell lacking a membrane-enclosed nucleus (Has a nucleoid instead) and membrane-enclosed organelles; Bacteria and archaea; Cytoplasm contains regions surrounded by proteins for specific reactions; Evolved first
Similarities Between Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes
Both have plasma membrane, cytosol, chromosomes, and ribosomes
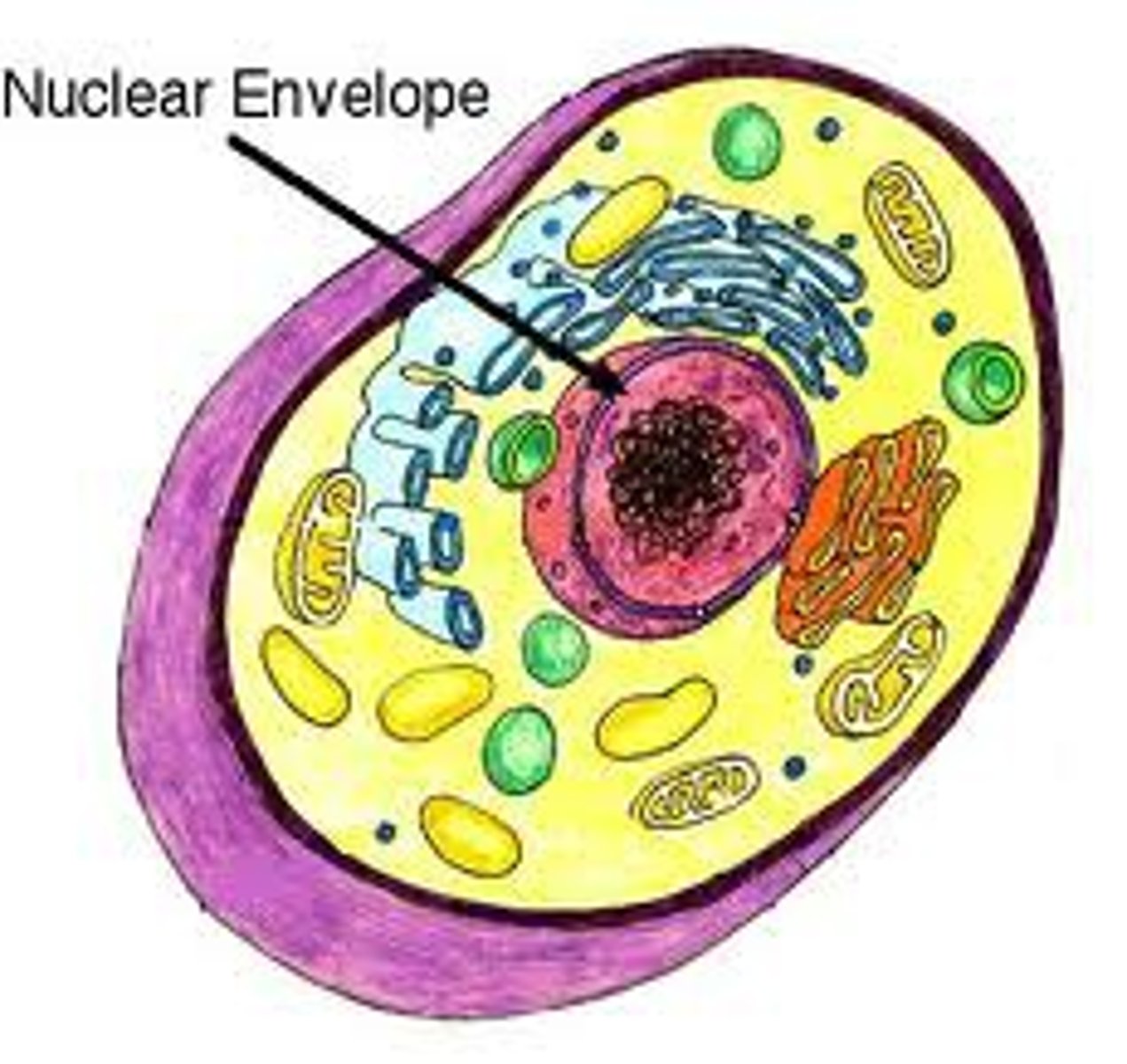
Eukaryotic Cell
A type of cell with a membrane-enclosed nucleus and membrane-enclosed organelles (Protists, plants, fungi, and animals); Has internal membranes that divide it into organelle compartments that provide different local environments that support specific metabolic functions so incompatible processes can go on simultaneously (Compartmentalization)
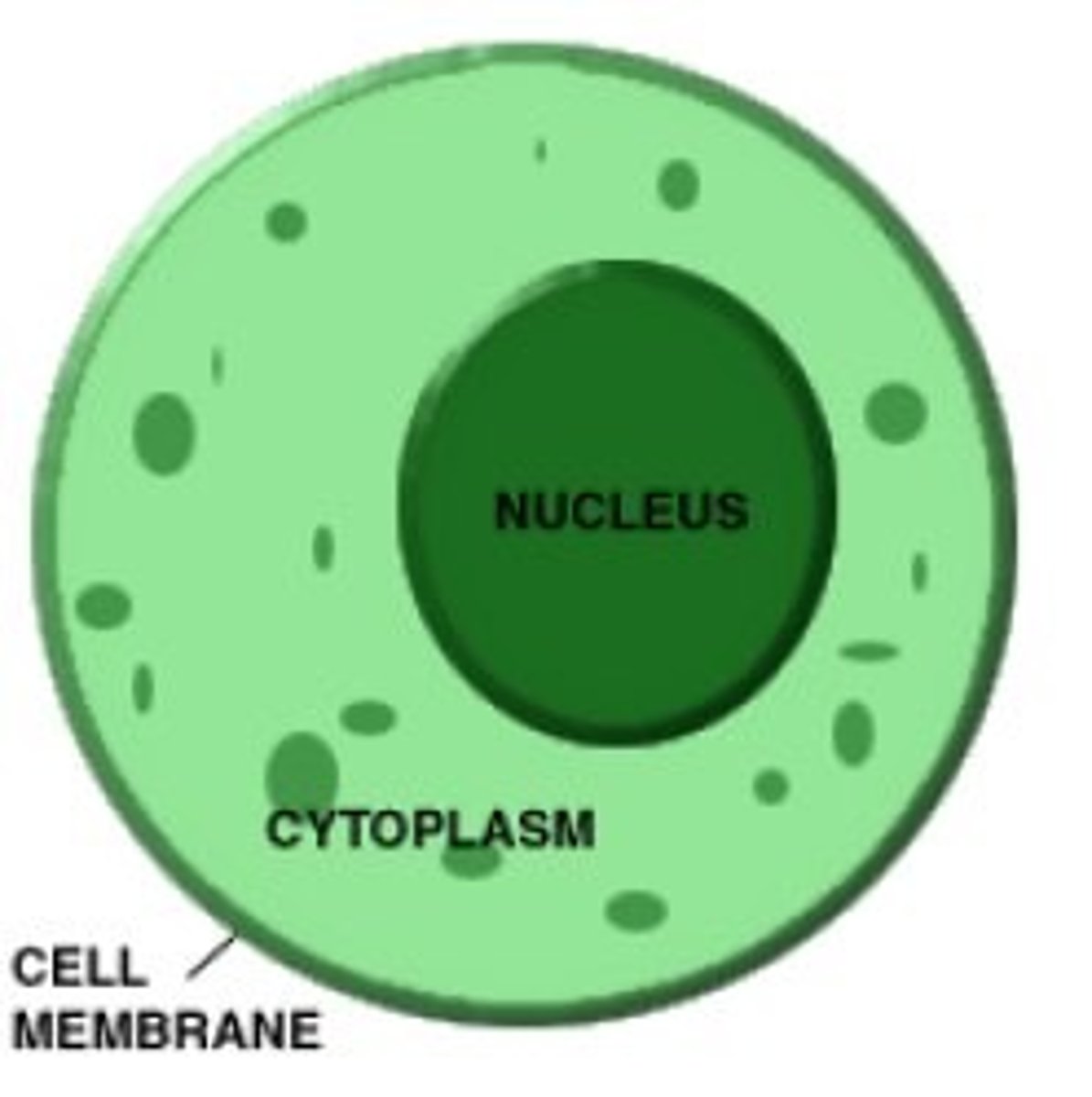
Plasma Membrane
The membrane at the boundary of every cell that acts as a selective barrier, regulating the cell's chemical composition; Made of phospholipids and proteins
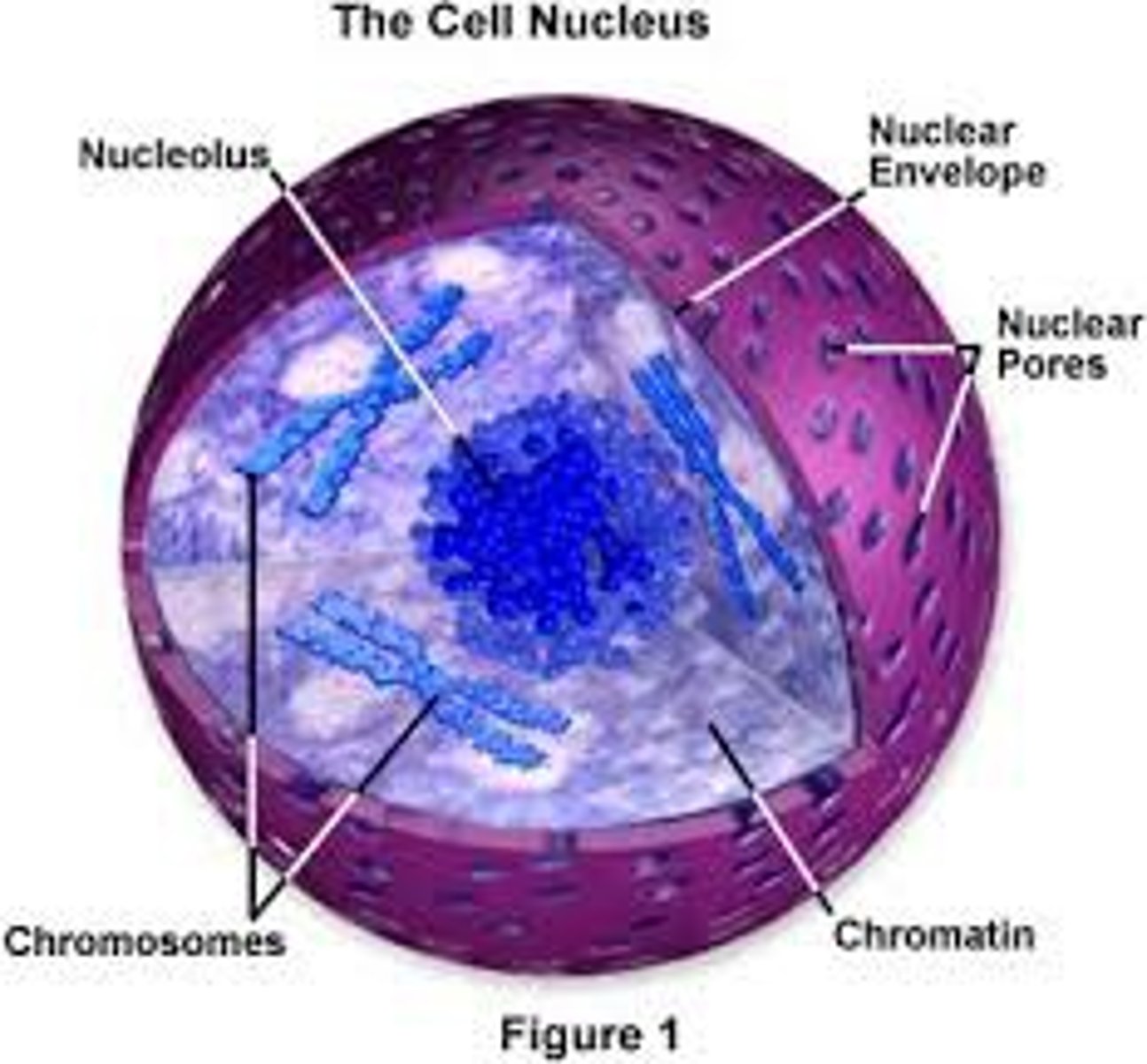
Nucleus
The organelle of a eukaryotic cell that contains the genetic material in the form of chromosomes, made up of chromatin
Cytoplasm
The contents of the cell enclosed by the plasma membrane
Nucleoid
A non-membrane-enclosed region in a prokaryotic cell where its chromosome is located
Nuclear Envelope
In a eukaryotic cell, the double membrane that surrounds the nucleus, perforated with pores that regulate traffic with the cytoplasm; Outer membrane is continuous with the ER
Nuclear Pores
Perforate the nuclear envelope and regulate traffic between the nucleus and the cytoplasm
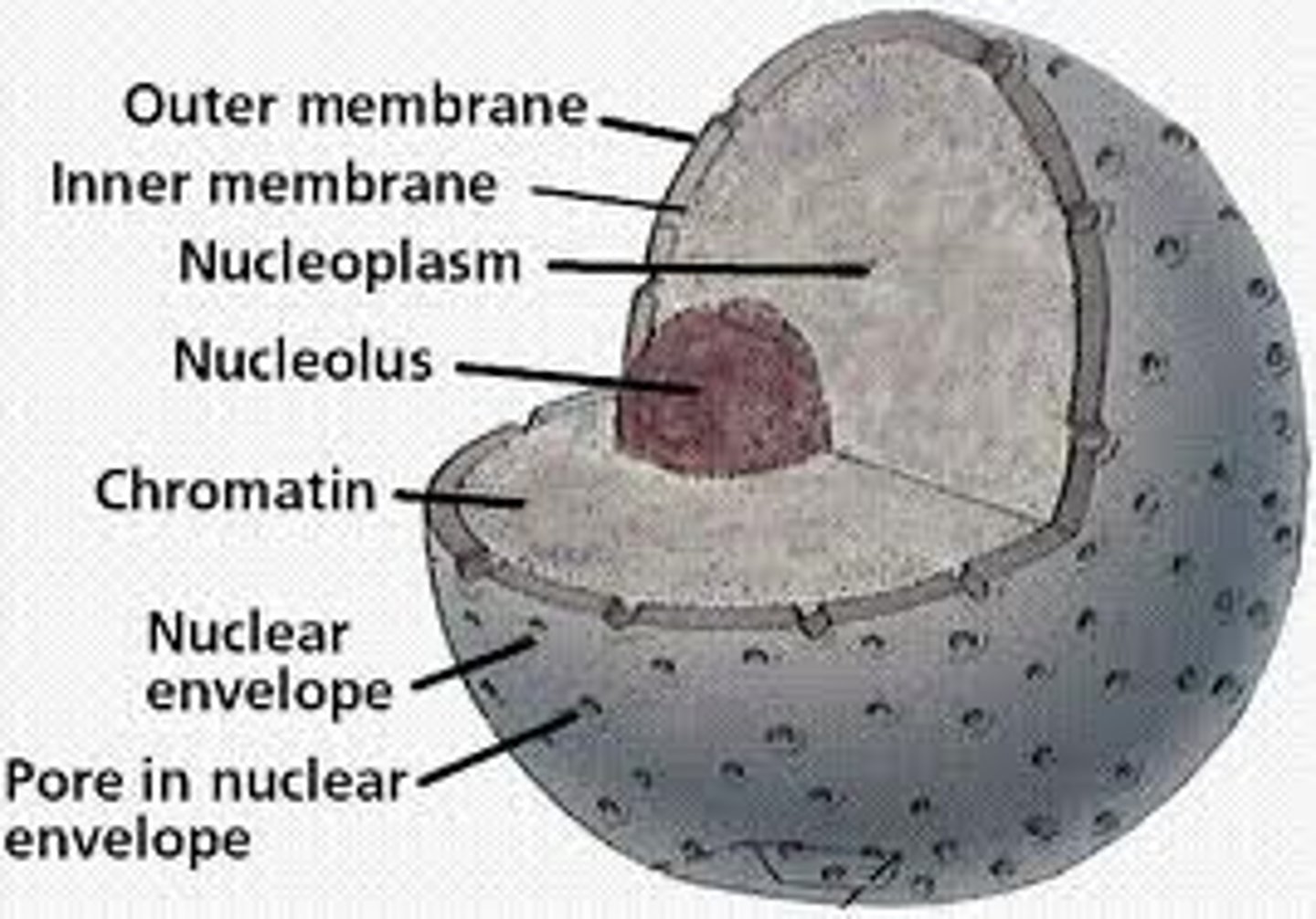
Nucleolus
A specialized structure in the nucleus consisting of chromosomal regions containing rRNA genes along with ribosomal proteins imported from the cytoplasm; sites of rRNA synthesis (Using DNA instructions) and ribosomal subunit assembly; Mass of densely stained granules and fibers adjoining part of the chromatin
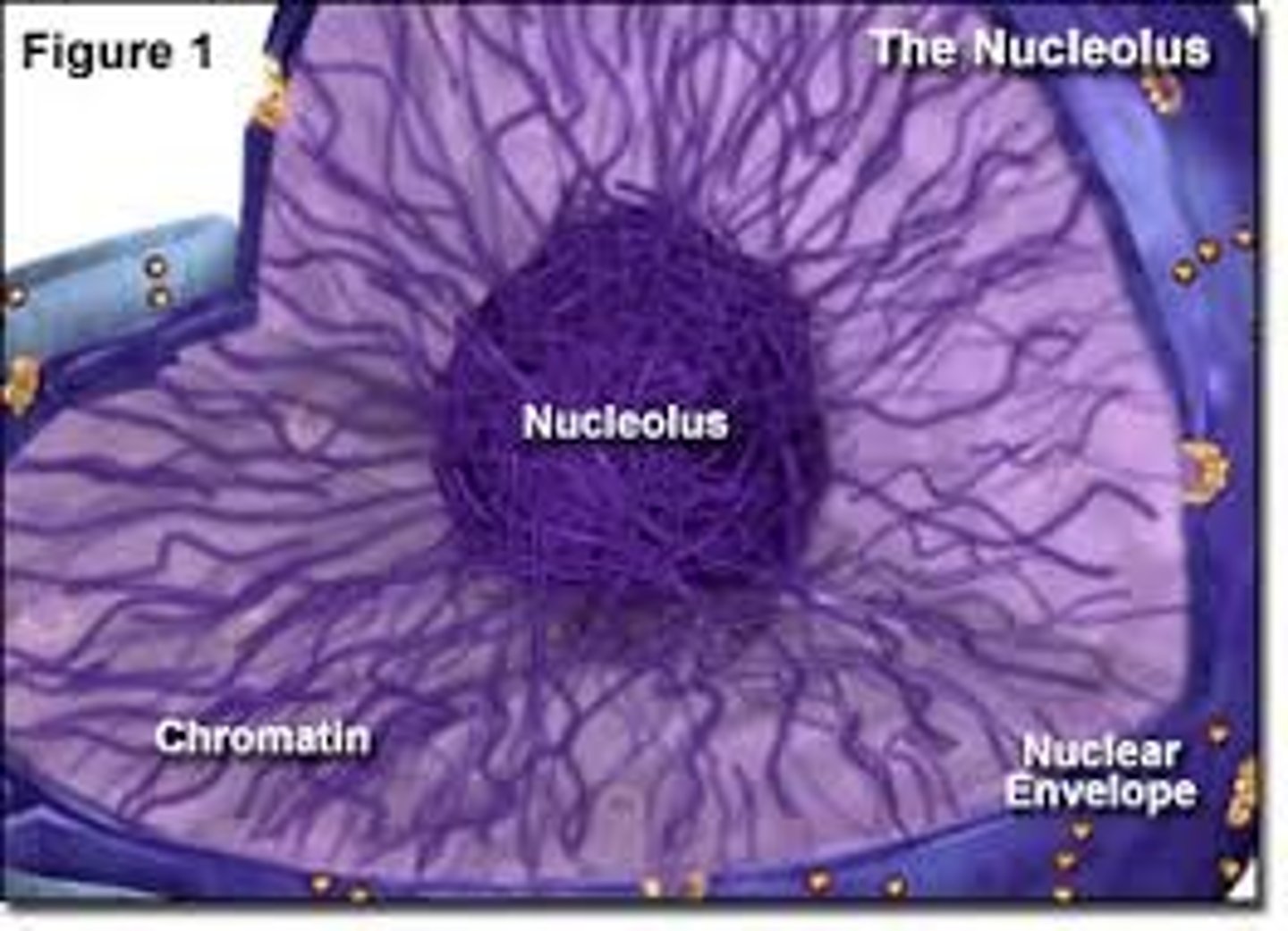
Chromatin
The complex of DNA and proteins that makes up eukaryotic chromosomes; When the cell is not dividing, this exists in its dispersed form, as a mass of very long, thin fibers that are not visible with a light microscope
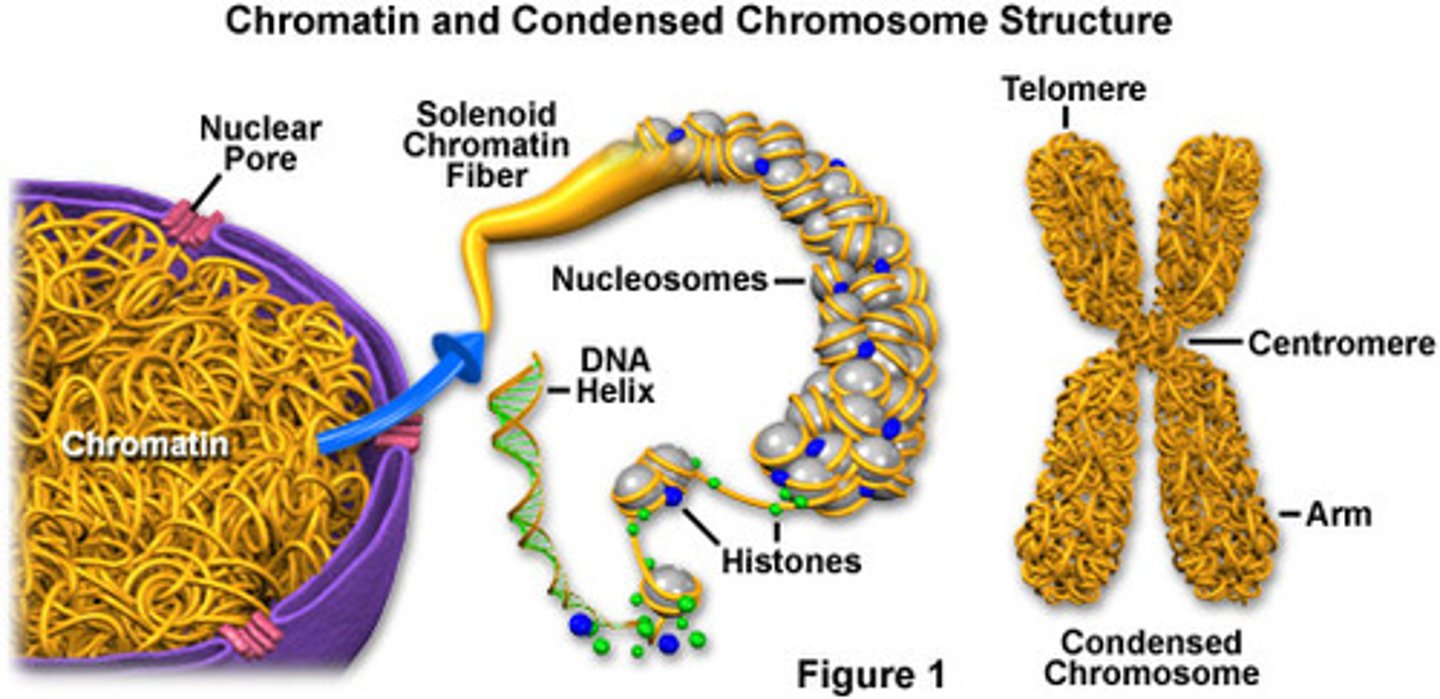
Ribosomes
A complex of rRNA and protein molecules that functions as a site of protein synthesis in the cytoplasm; consists of a large subunit and a small subunit; In eukaryotic cells, each subunit is assembled in the nucleolus
rRNA
RNA molecules that, together with proteins, make up ribosomes; the most abundant type of RNA
Cells that Produce a Lot of Protein...
Have lots of ribosomes and prominent nucleoli, as well as rough ER and Golgi apparatus
Free Ribosomes
Produce proteins for use within the cell; Suspended in the cytosol; Consists of 2 subunits; Composed of rRNA and proteins
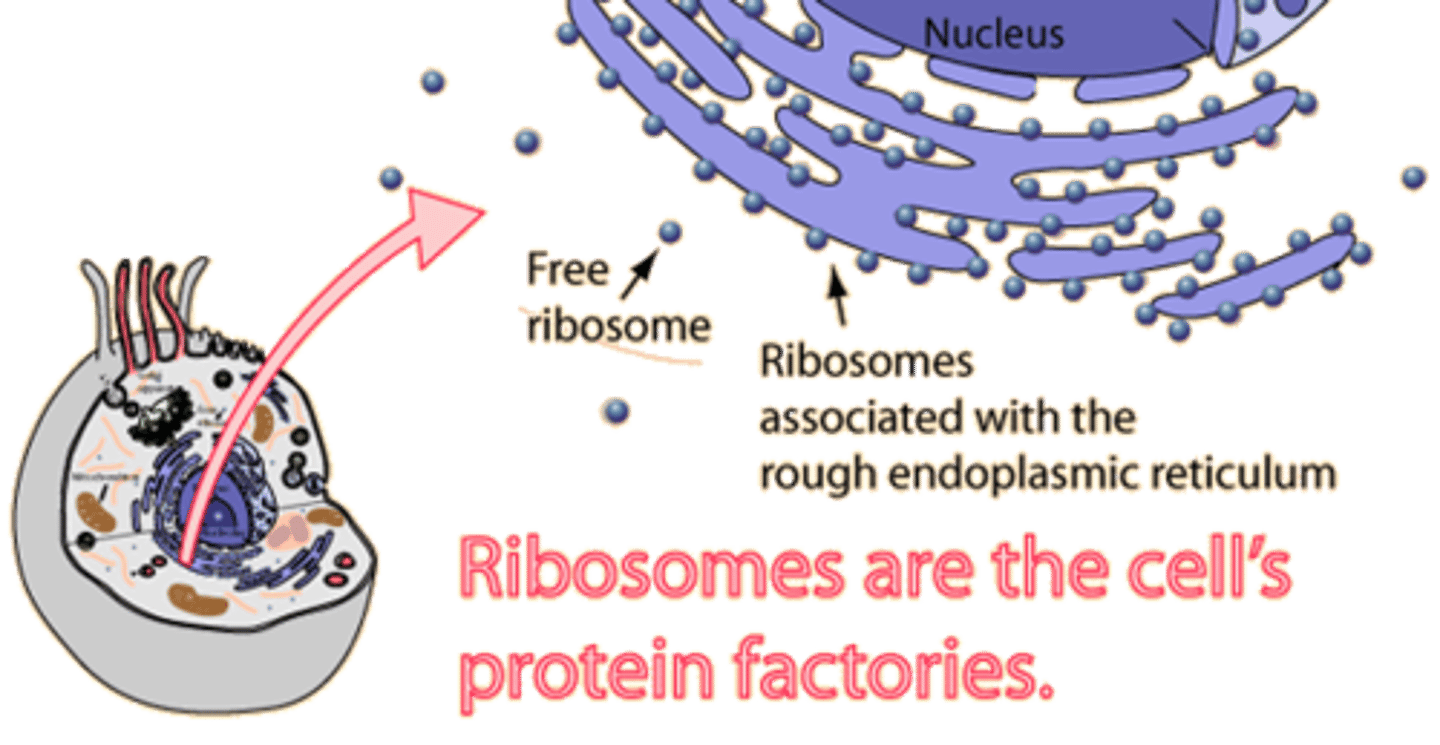
Bound Ribosomes
Produce proteins for export/secretion; Attached to the rough ER or nuclear envelope; Consists of 2 subunits; Composed of rRNA and proteins
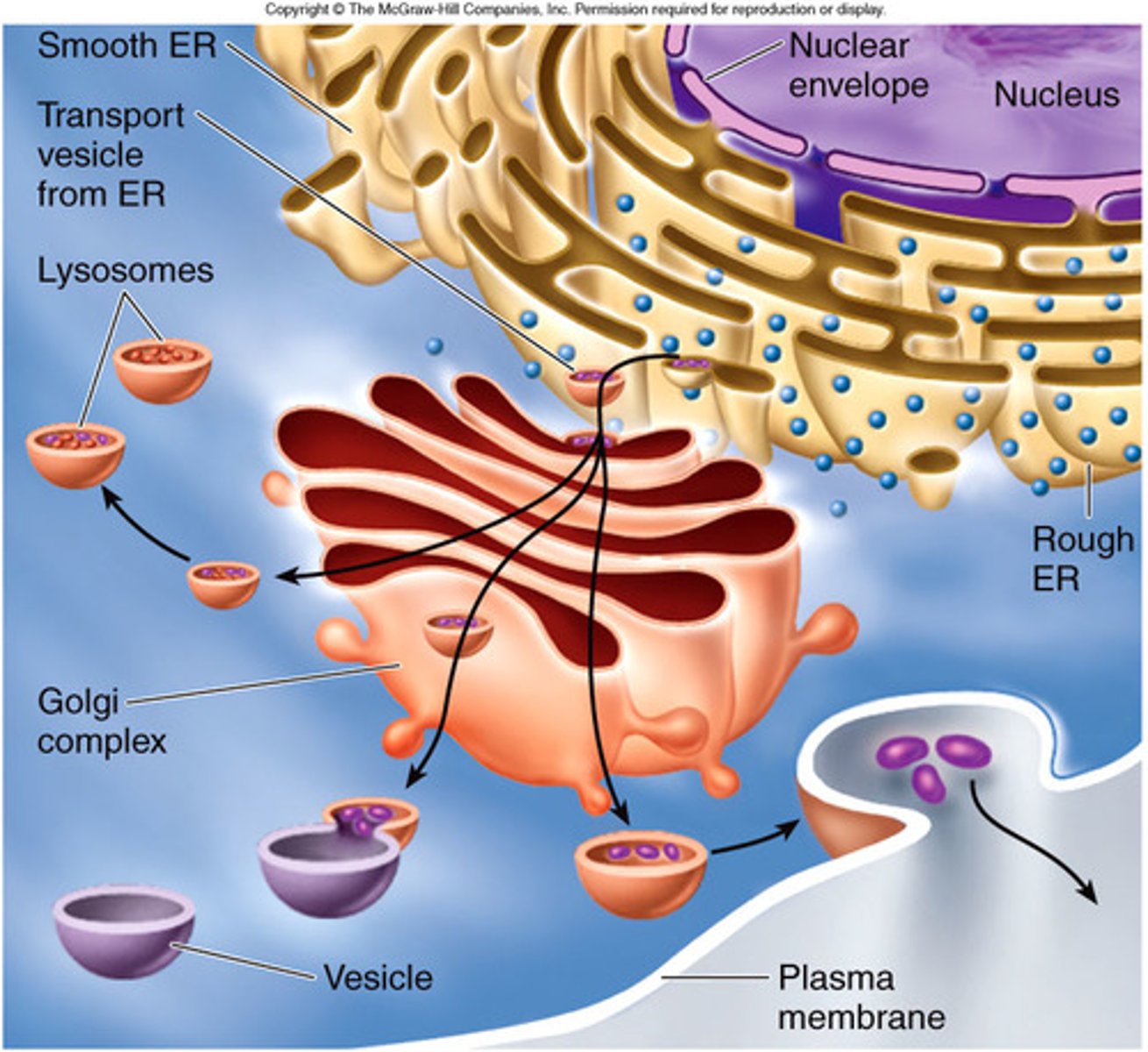
Endomembrane System
Membranes that are related through direct physical continuity or by the transfer of membrane segments called vesicles; Nuclear envelope, ER, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, vesicles, vacuoles, and plasma membrane
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
An extensive membranous network in eukaryotic cells, continuous with the outer nuclear membrane and composed of ribosome-studded (rough) and ribosome-free (smooth) regions
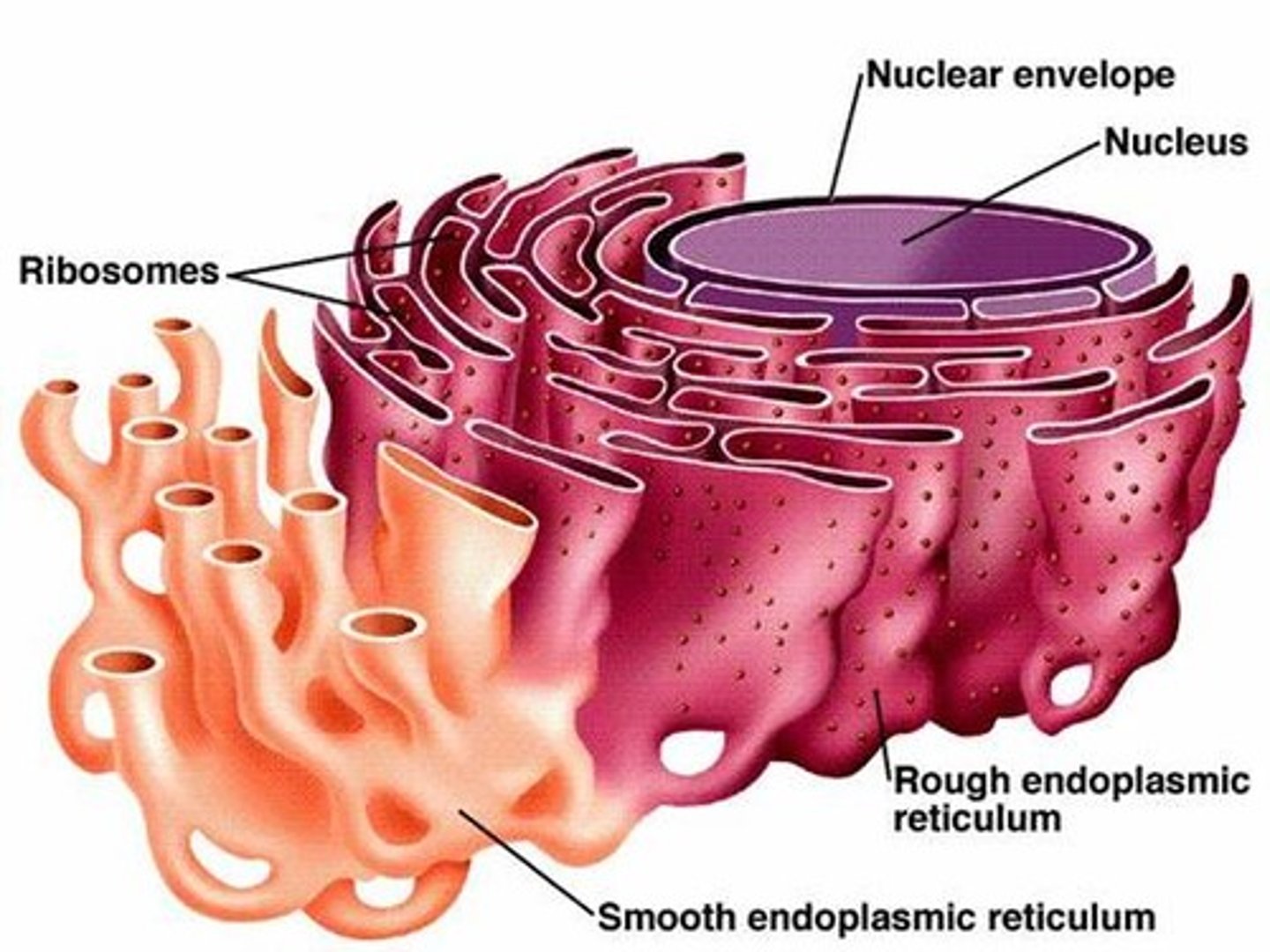
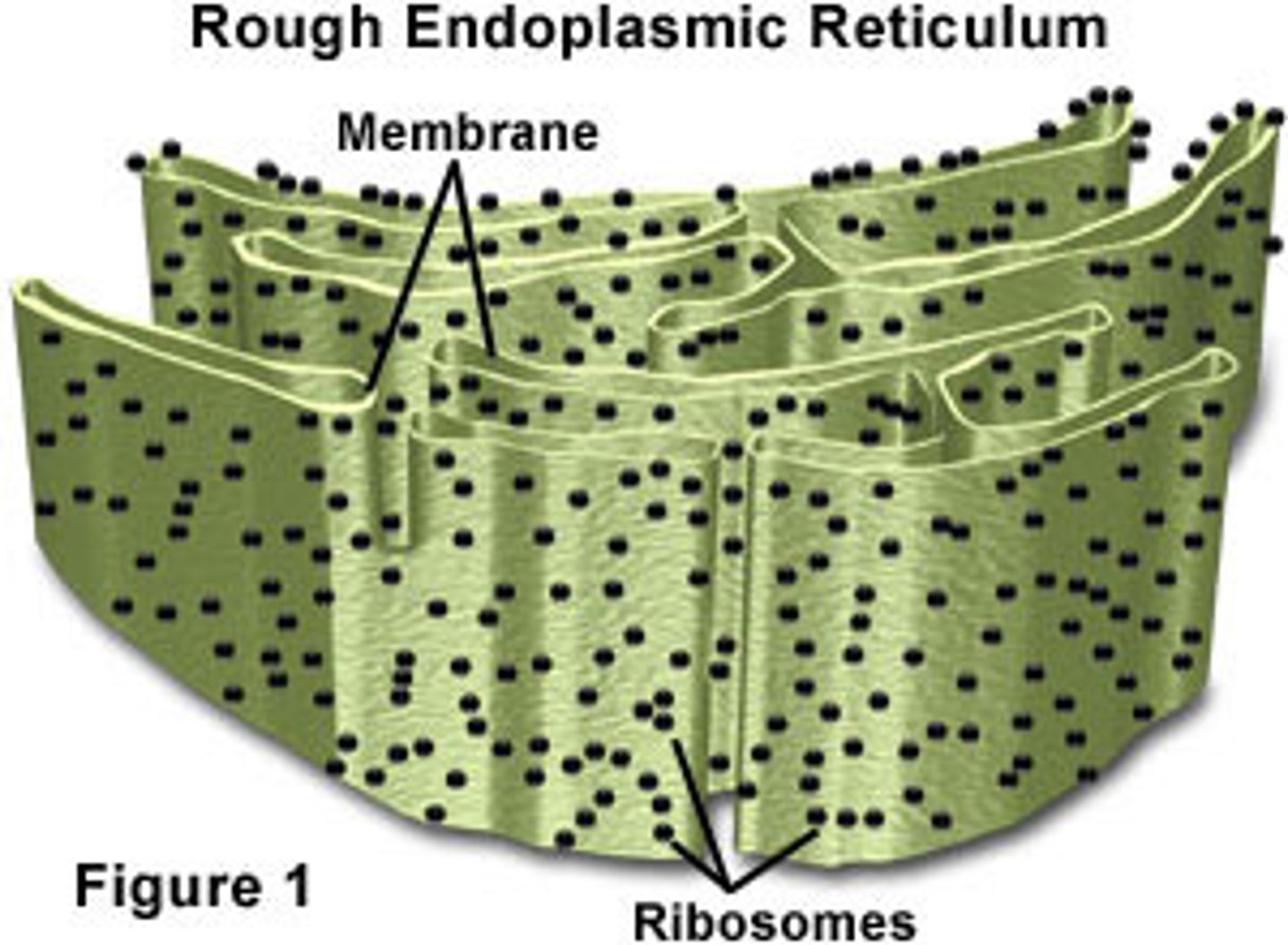
Rough ER
The portion of the endoplasmic reticulum with ribosomes attached; Create secretory proteins (Mostly glycoproteins); Makes membrane phospholipids; Sheets; Lots in pancreatic cells
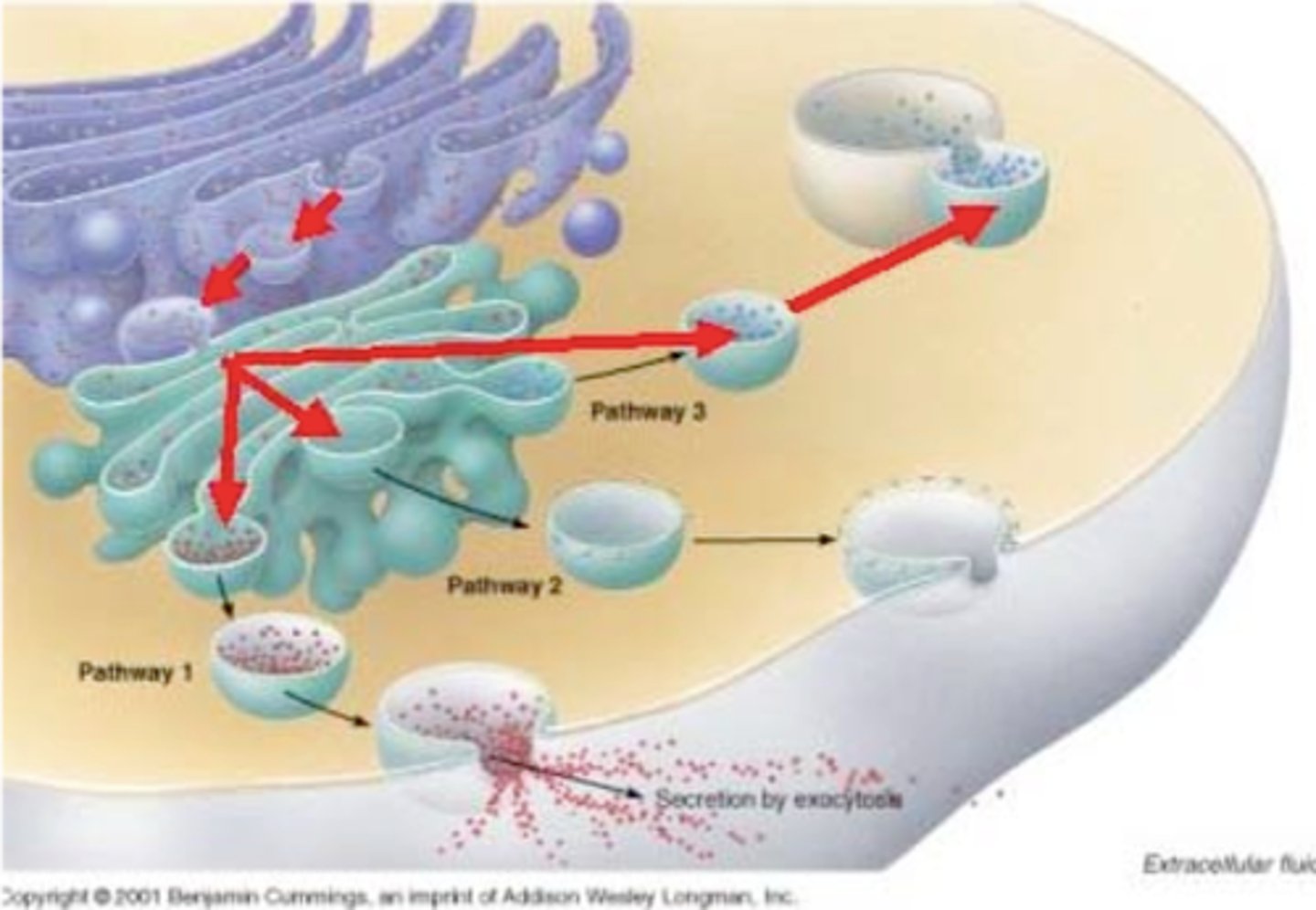
Protein Pathway
1) Amino Acids imported into the cell and bound ribosomes use the amino acids to produce proteins; 2) Proteins routed by ER and proteins may be modified; 3) Formation of transition vesicle; 4) Transition vesicle carries contents to the Golgi; 5) Golgi modifies proteins; 6) Secretory vesicle produced; 7) Secretory vesicle contents released to the outside; 8) Lysosomes produced that contains hydrolytic enzymes; 9) Lysosomes fuses with vacuole
Smooth ER
The portion of the ER that is free of ribosomes; Synthesis of lipids; Detoxification of drugs and poison; Stores calcium ions; Tube; Lots in liver cells
Golgi Apparatus
An organelle in eukaryotic cells consisting of stacks of flat membranous sacs that modify, store, and route products of the ER (Proteins) and synthesize some products, notably non cellulose carbohydrates
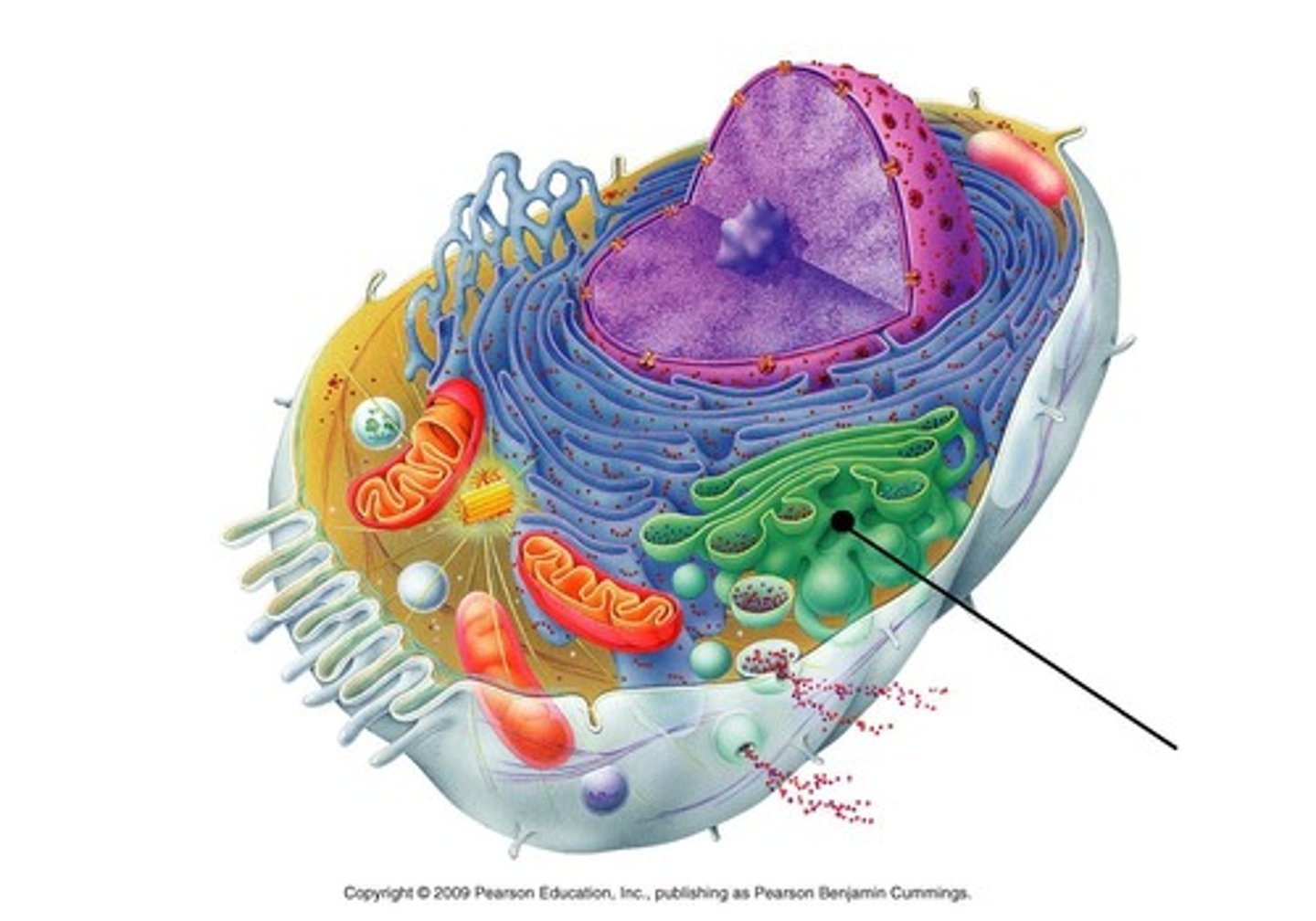
Golgi Vesicles
Small sacs of membranes that bud off Golgi body; Transport vehicle for modified ER products
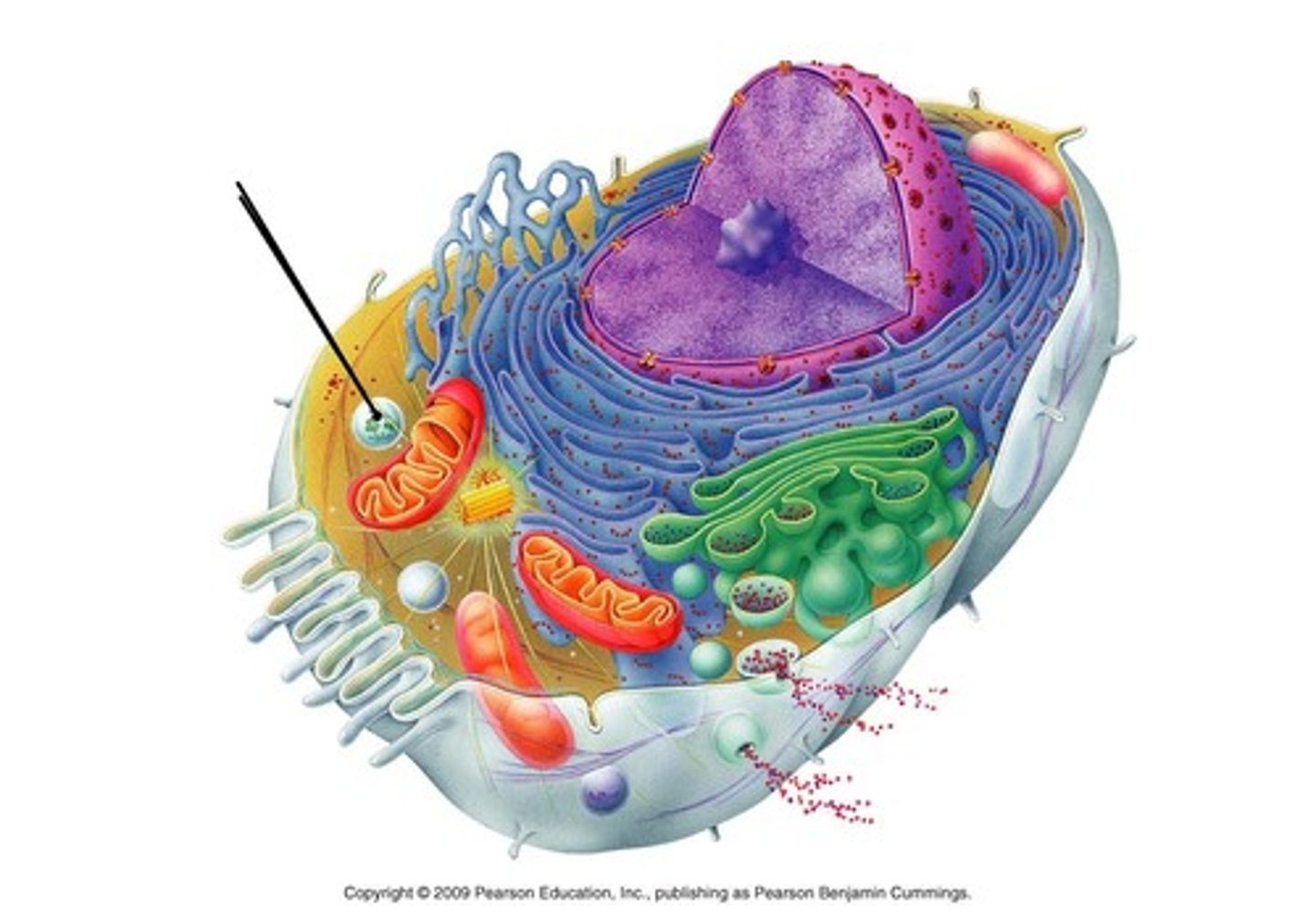
Lysosomes
A membrane-enclosed sac of hydrolytic enzymes found in the cytoplasm of animal cells and some protists
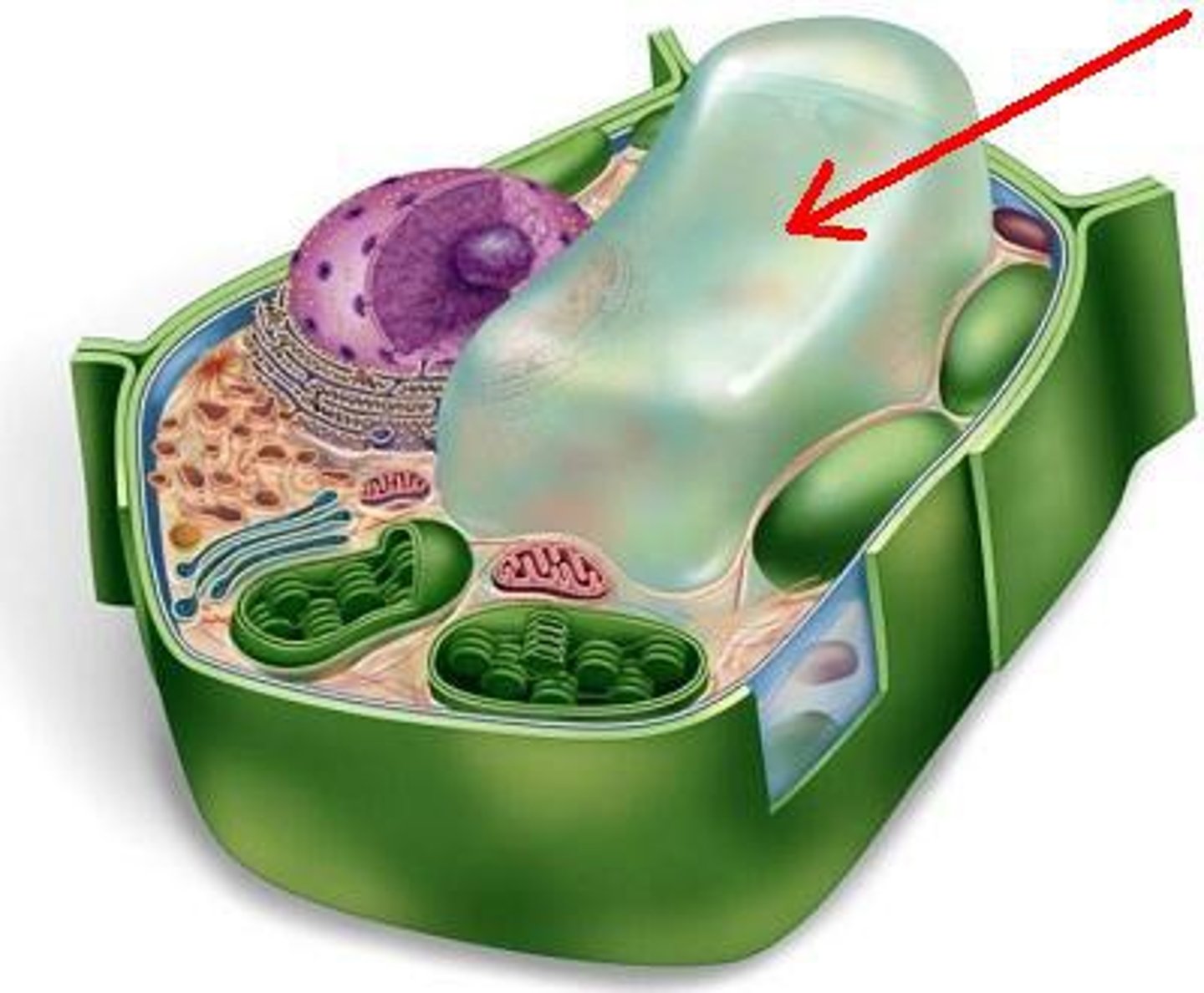
Central Vacuole
In a mature, plant cell, a large membranous sac with diverse roles in growth, storage, and sequestration of toxic substances; Water regulation, storage of ions and hydrophilic pigments, enlarge cells and create turgor pressure, store toxins, coloration
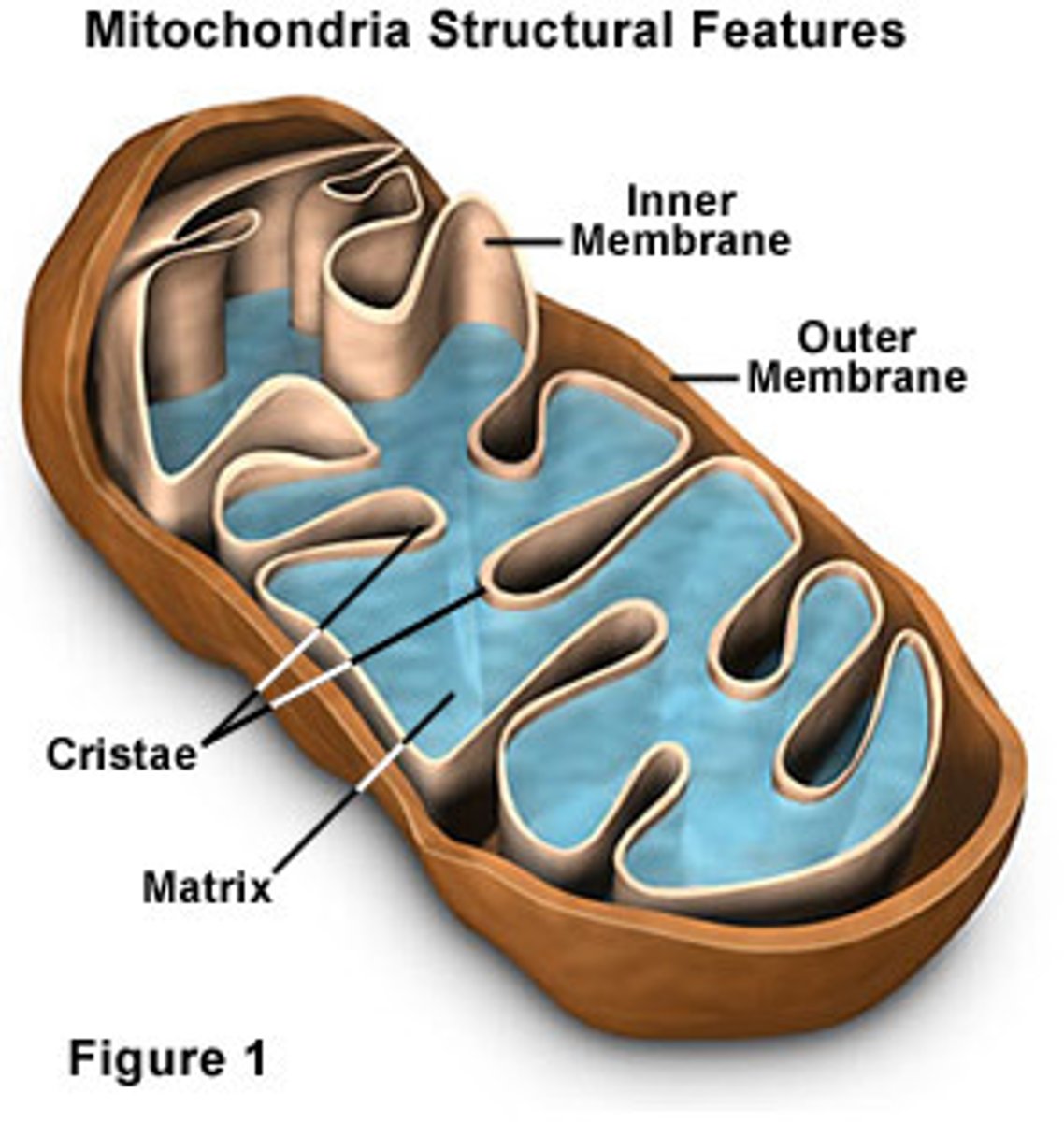
Mitochondria
An organelle in eukaryotic cells that serves as the site of cellular respiration; uses oxygen to break down organic molecules and synthesize ATP; Structure: Outer membrane, inner membrane and cristae, matrix; Has its own DNA and ribosomes; The folded inner membrane provides a large surface area, which results in more productive cellular respiration and more ATP; 2 Compartments
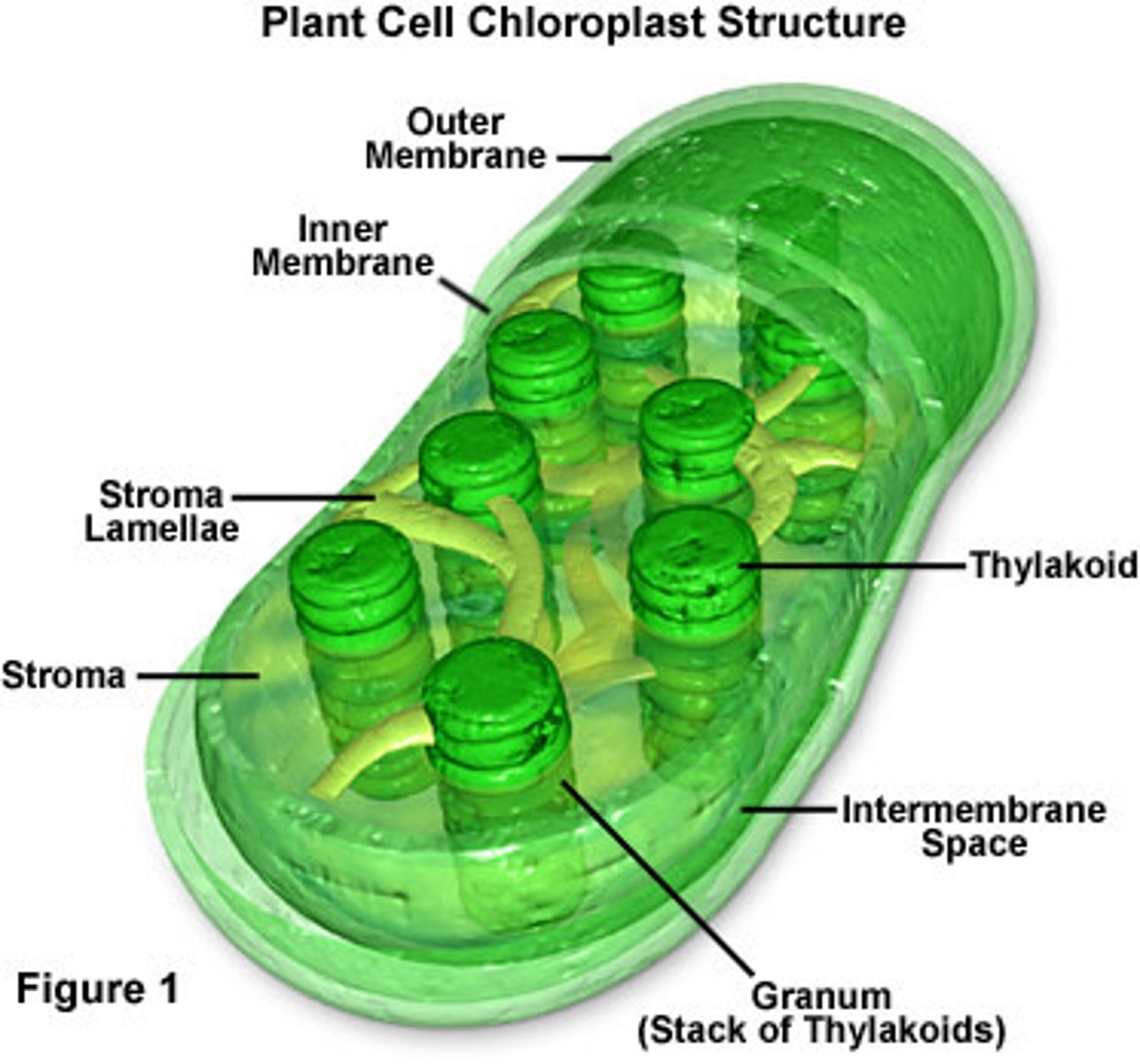
Chloroplasts
An organelle found in plants and photosynthetic protists that absorbs sunlight and uses it to drive the synthesis of organic compounds from carbon dioxide and water (Photosynthesis); Uses chlorophyll; Structure of thylakoids, granum, and stroma; 3 compartments: Intermembrane space, stroma, and thylakoid; Has its own DNA and ribosomes
Endosymbiotic Theory
Early ancestor of eukaryotes engulfed an oxygen-using non-photosynthetic prokaryote; Engulfed cell formed a relationship with host cell and was enclosed and merged into eukaryote with mitochondria and/or chloroplasts; Mitochondria and chloroplasts have 2 membranes, ribosomes, DNA, and are autonomous organelles that grow and reproduce within the cell
Plastid
One of a family of closely related organelles that includes chloroplasts; Found in the cells of photosynthetic eukaryotes (i.e. Tomato)
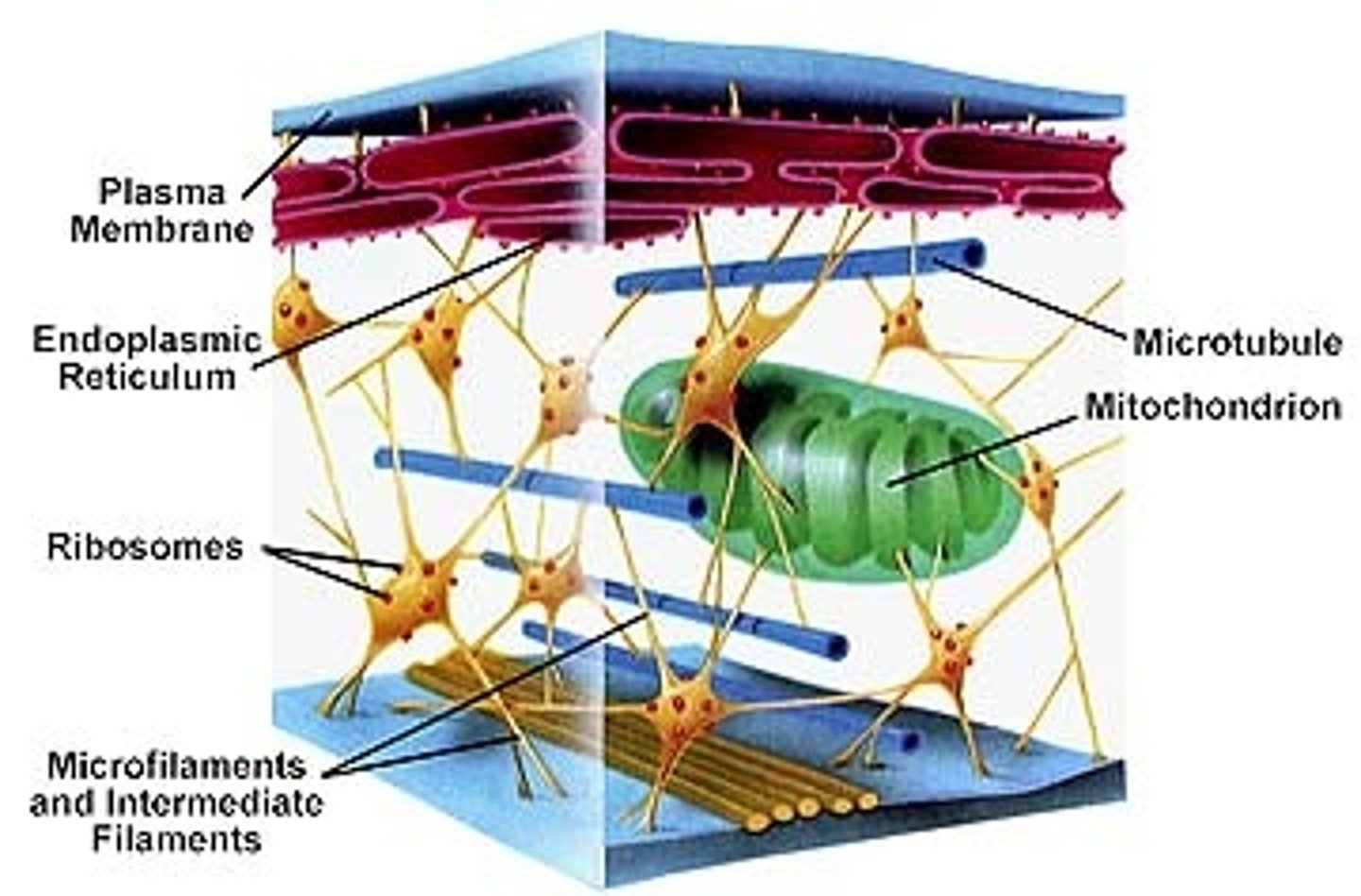
Microtubules
A hollow rod composed of tubulin proteins that makes up part of the cytoskeleton in all eukaryotic cells and is found in cilia, flagella, spindle fibers, and centrioles; Move big stuff, shape and support cell, separation of chromosomes in cell division; Provides tracts for organelle movement; Resists compression
Centriole
A structure in the centrosome of an animal cell composed of a cylinder of microtubule triplets arranged in a 9 + 0 pattern; A centrosome has a pair of these; Help in cell division
Basal Bodies
A eukaryotic cell structure consisting of a "9 + 0" arrangement of microtubule triplets; Anchor cilia and flagella
Microfilaments
Thin, solid rods composed of actin proteins in the cytoplasm of almost every eukaryotic cell, making up part of the cytoskeleton and acting alone or with myosin to cause cell contraction (Forms a contracting belt that pinches dividing animal cell forming a cleavage furrow); AKA actin filament; Gives support and structure to membrane; Microvilli; Cell division; Provides tracts for organelle movement; Resists tension
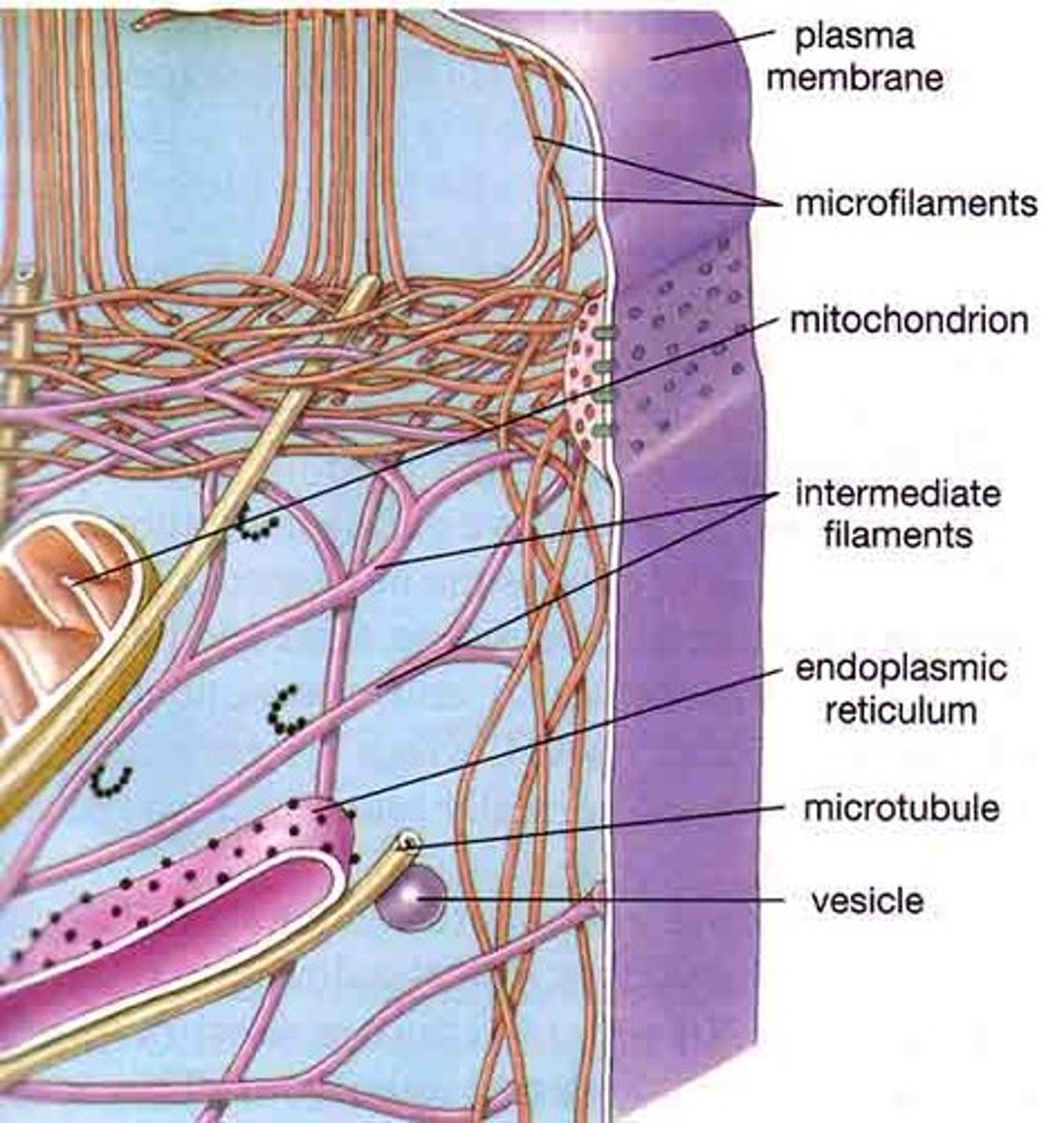
Intermediate Filaments
A component of the cytoskeleton that includes filaments intermediate in size between microtubules and microfilaments; Reinforce cell shape, fix organelle position
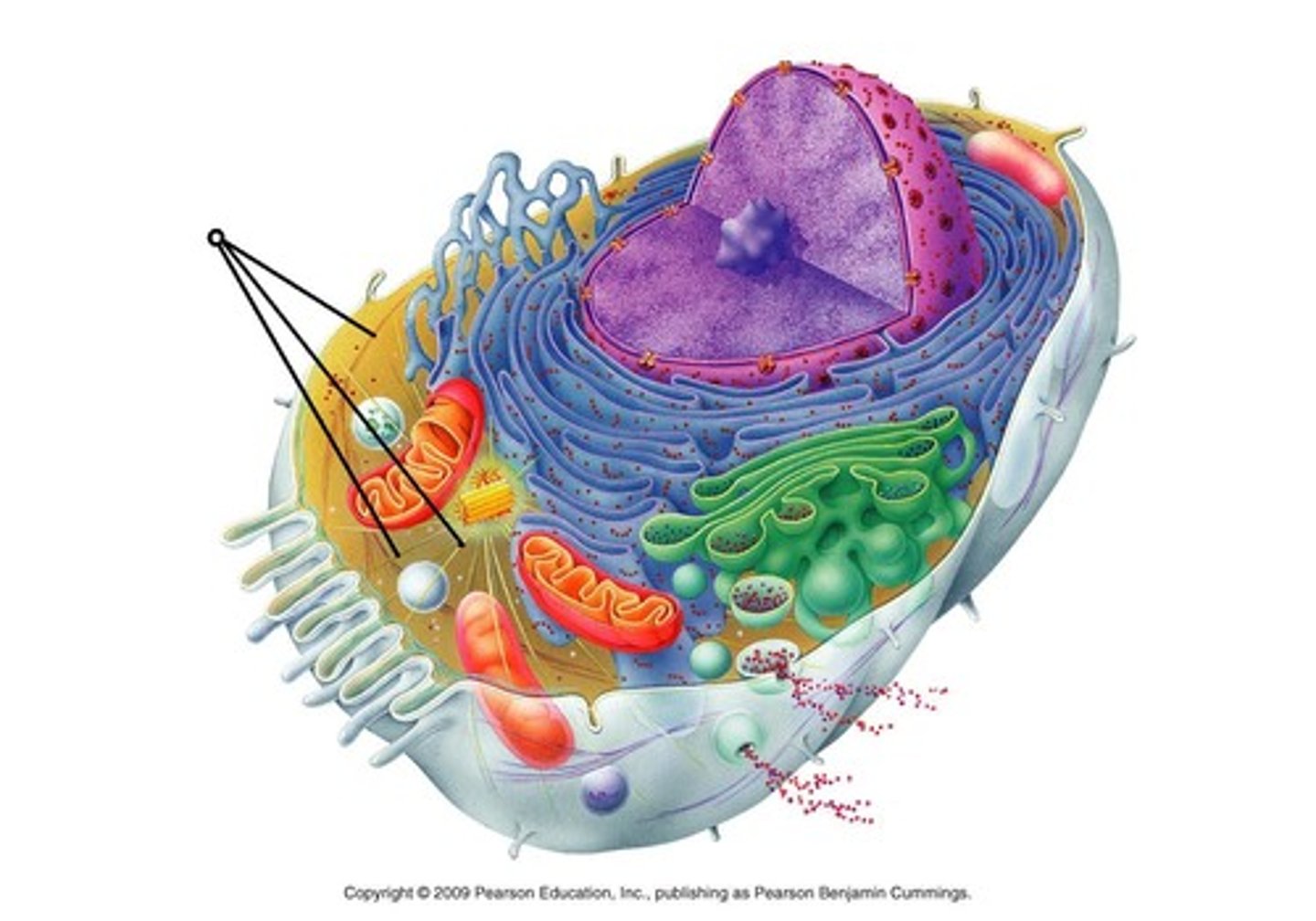
Cell Wall
A protective layer external to the plasma membrane in the cells of plants, prokaryotes, fungi, and some protists; Polysaccharides such as cellulose (In plants and some protists), chitin (in fungi), and peptidoglycan (in bacteria) are important structural components of cell walls
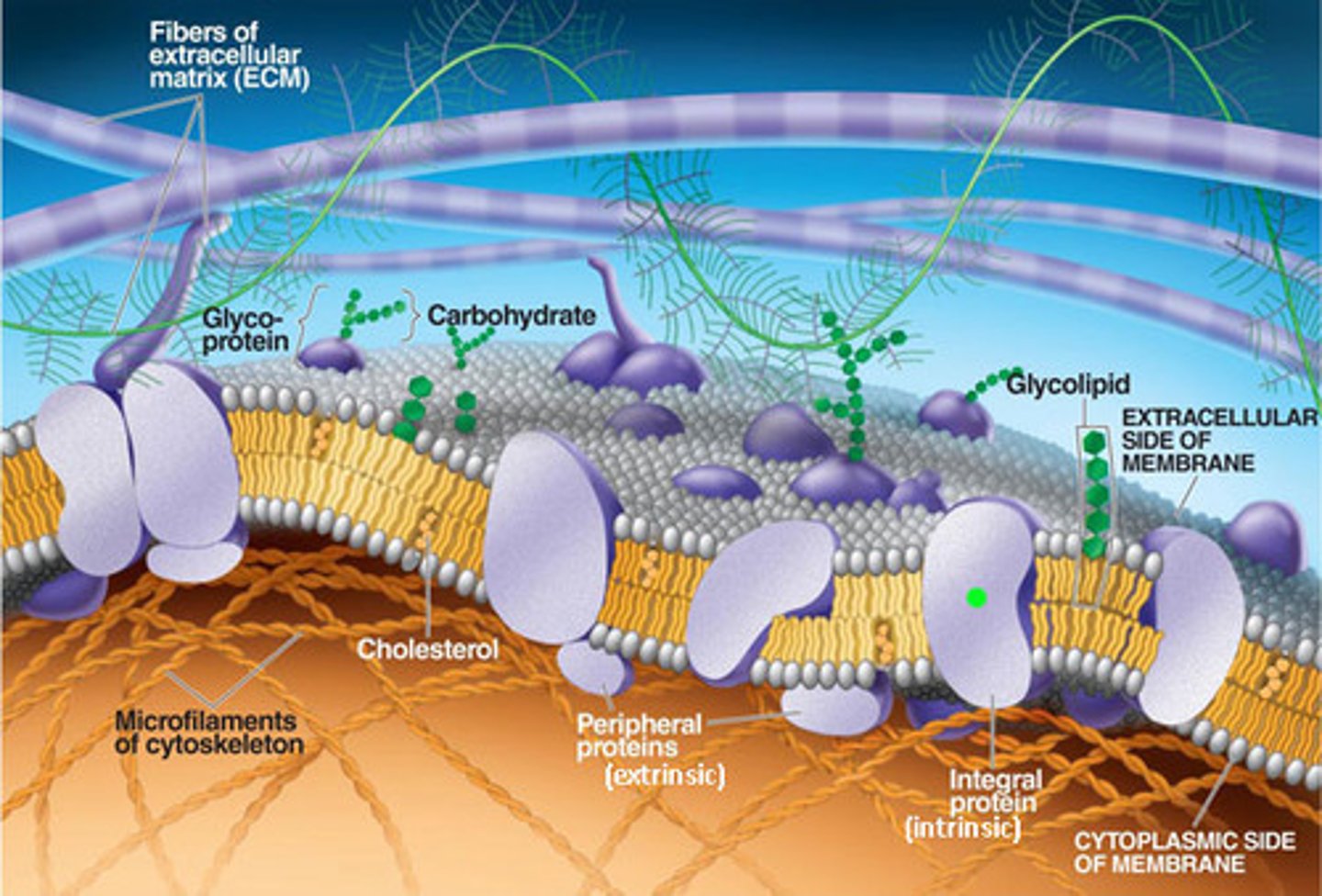
Extracellular Matrix
The meshwork surrounding animal cells, consisting of glycoproteins, polysaccharides, and proteoglycans synthesized and secreted by the cells; Made of collagen- Forms strong fibers outside cell; Communicate with cell through integrins, regulate cell behavior; Influence activity of genes in the nucleus; Helps glue cells together
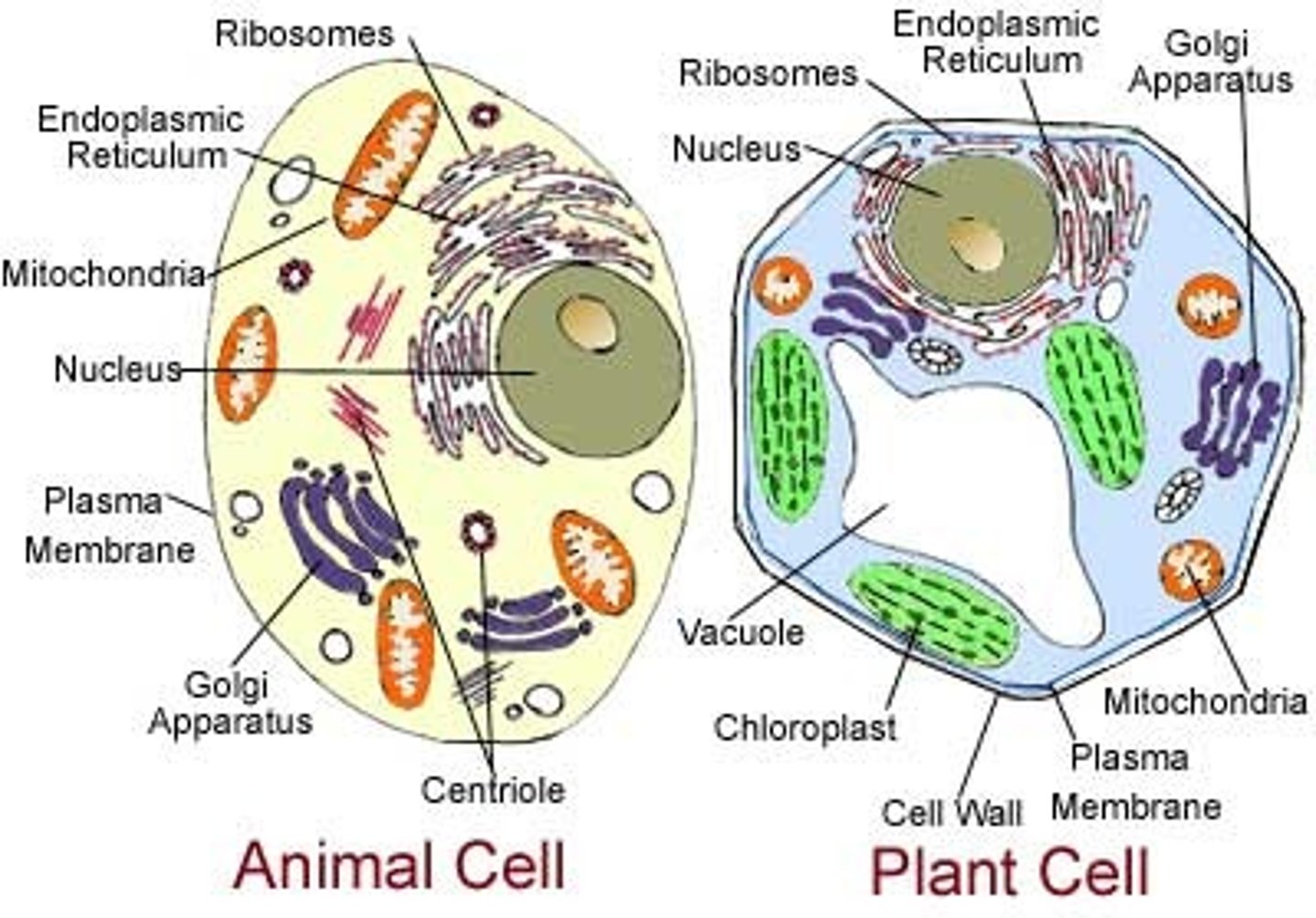
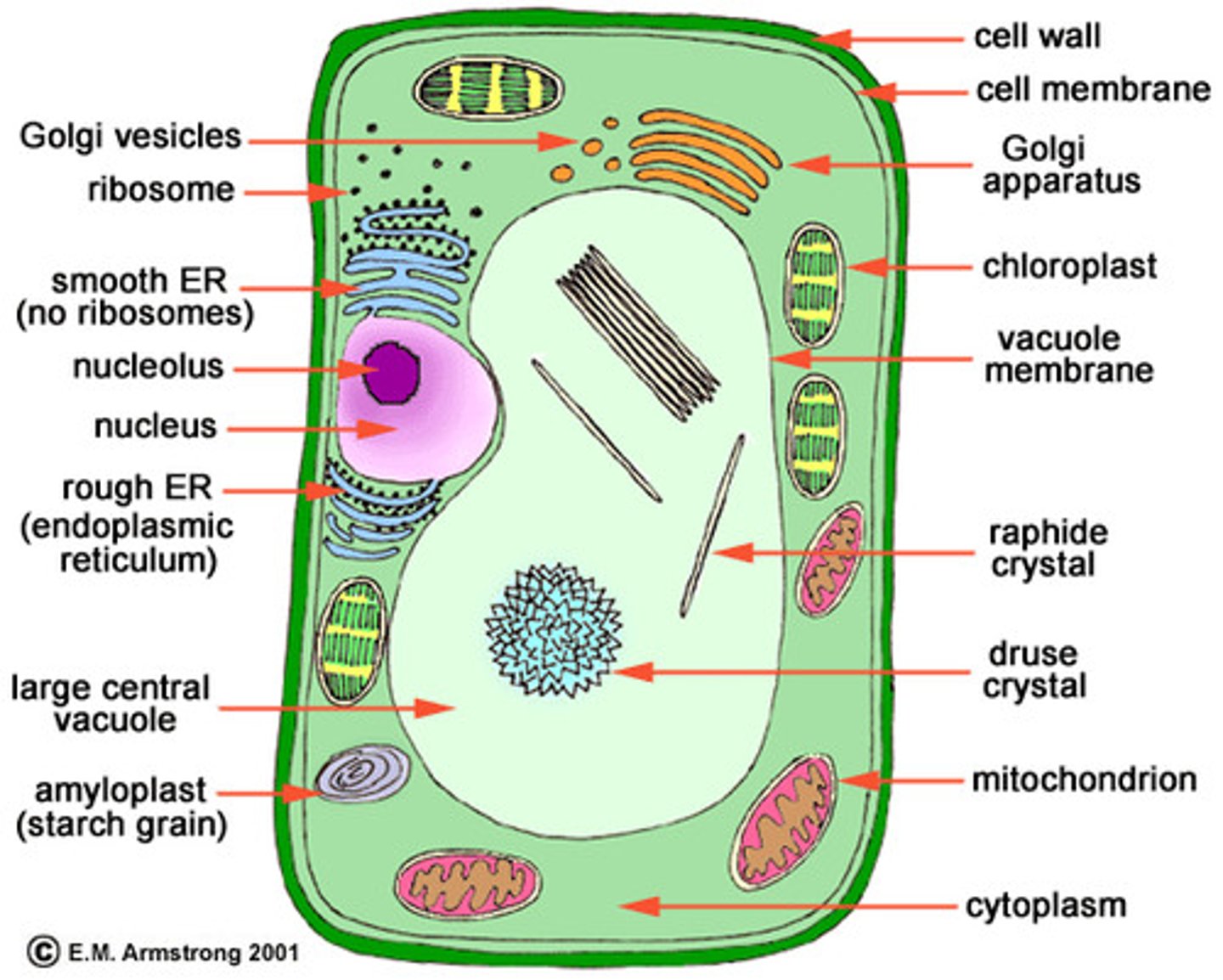
Plant Cells vs. Animal Cells
Plant cells have large central vacuoles, cell walls, plasmodesmata, chloroplasts, and mitochondria, while animal cells have extracellular matrix, tight junctions, desmosomes, gap junctions, and mitochondria