BIO 1202 Test 4
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/141
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 4:19 AM on 12/4/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
142 Terms
1
New cards
Energy
Autotroph:
Photoautotroph- Light
Chemoautotroph- Inorganic Chemicals
Heterotroph:
Photoheterotroph- Light
Chemoheterotroph- Organic Compounds
Photoautotroph- Light
Chemoautotroph- Inorganic Chemicals
Heterotroph:
Photoheterotroph- Light
Chemoheterotroph- Organic Compounds
2
New cards
Nutrients
A substance that provides nourishment essential for growth and the maintenance of life.
3
New cards
Macronutrient
An essential element that an organism must obtain in relatively large amounts.
Carbon, Oxygen, Hydrogen, Nitrogen, Phosphorus, Sulfur, Potassium, Calcium, and Magnesium.
Carbon, Oxygen, Hydrogen, Nitrogen, Phosphorus, Sulfur, Potassium, Calcium, and Magnesium.
4
New cards
Micronutrient
An essential element that an organism must obtain in very small amounts.
Chlorine, Iron, Manganese, Boron, Zinc, Copper, Nickle, Molybdenum
Chlorine, Iron, Manganese, Boron, Zinc, Copper, Nickle, Molybdenum
5
New cards
If C and O make up 90% of the dry tissue mass, from what source do plants get most of their (dry tissue) mass?
Air
6
New cards
If C and O make up 90% of the dry tissue mass, what plant organ collects the materials to make most of their (dry tissue) mass?
leaves
7
New cards
What is the most abundant gas in the atmosphere?
Nitrogen N2
8
New cards
How do plants take up nitrogen? What Organ is used?
Roots
N2-> nitrogen fixing bacteria in soil -> ammonia -> nitrite -> nitrate -> plant roots
N2-> nitrogen fixing bacteria in soil -> ammonia -> nitrite -> nitrate -> plant roots
9
New cards
Where do plants get nitrogen from?
Soil
N2-> nitrogen fixing bacteria in soil -> ammonia -> nitrite -> nitrate -> plant roots
N2-> nitrogen fixing bacteria in soil -> ammonia -> nitrite -> nitrate -> plant roots
10
New cards
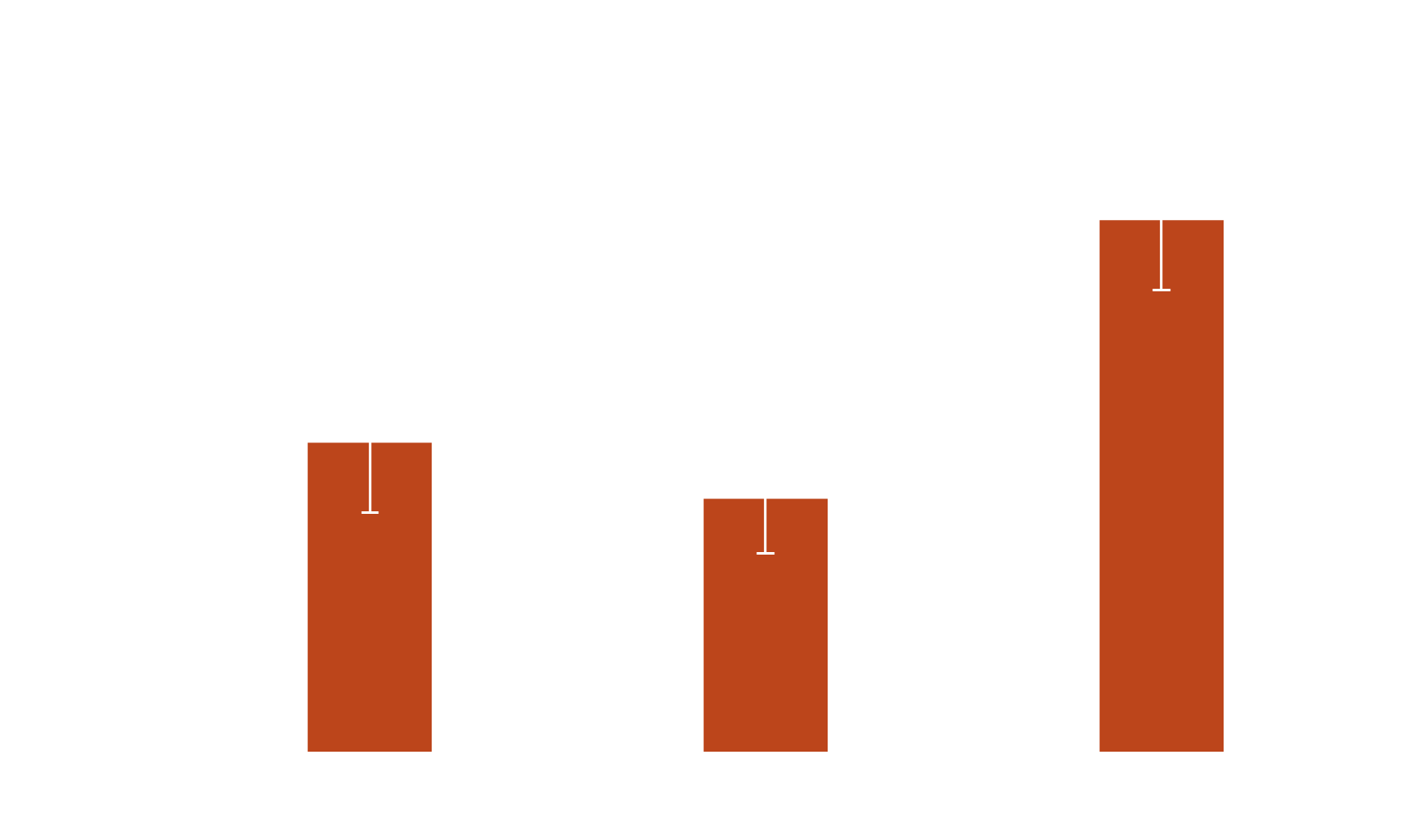
Based on the figure, what nutrient is limiting growth?
Phosphorous P
11
New cards
How do plants grow in environments with low soil nutrients (N).
Relationships with nitrogen fixing bacteria and mycorrhizae that create and the nutrients need to survive (N).
There are also carnivores plants that get there nutrients from insects.
-Venus Flytrap, Sundew, Pitcher Plants
There are also carnivores plants that get there nutrients from insects.
-Venus Flytrap, Sundew, Pitcher Plants
12
New cards
Ectomycorrhiza
Mycorrhizae fungus that lives on outside of root.
13
New cards
Endomycorrhiza
Mycorrhizae fungus that penetrated into the root.
14
New cards
Epiphytes
Plants that grown on other plants.
-Mistletoe (Photosynthetic parasite), Dodder (Nonphotosynthetic parasite), Indian Pipe (Nonphotosynthetic parasite of mycorrhizae)
-Mistletoe (Photosynthetic parasite), Dodder (Nonphotosynthetic parasite), Indian Pipe (Nonphotosynthetic parasite of mycorrhizae)
15
New cards
Mutualism
Both organism that are involved benefit.
Animal - Fungus
Animal - Bacterium
Plant - Fungus
Fungus - Bacterium
Plant - Bacterium
Plant - Animal
Animal - Fungus
Animal - Bacterium
Plant - Fungus
Fungus - Bacterium
Plant - Bacterium
Plant - Animal
16
New cards
Members of Kingdom Animalia are
using ingestive digestion
17
New cards
Animals are
chemoheterotrophs
18
New cards
Herbivores
Eats plant and algae
19
New cards
Carnivors
Eat other animals
20
New cards
Omnivores
Eats plants and animals
21
New cards
Proton Leak
Sa otters have a bad metabolism that leaks protons that actually warms them but they didn't get near as much energy out of there calorie intake causing them to eat more.
22
New cards
Essential Amino Acids
histidine, isoleucine, leucine, lysine, methionine, phenylalanine, threonine, tryptophan, and valine
From meat, eggs and cheese.
From meat, eggs and cheese.
23
New cards
Essentail Fatty Acids
Must be obtained from diet and unsaturated fatty acids (fatty acids with one or more double bonds)
24
New cards
Vitamin requirements of Humans
Vitamin C, D, and Folic Acid
25
New cards
Minerals
Simple inorganic nutrients that are usually required in small amounts.
Calcium, Phosphorus and Iron
Calcium, Phosphorus and Iron
26
New cards
Which of the following has a complete digestive system?
Mollusks
27
New cards
The complete digestive system allowed what to happen?
More specialized absorption abilities
28
New cards
Mechanical Digestion
Chewing or grinding increases the surface area of food.
29
New cards
Chemical Digestion
Stomach splits food into small molecules that can pass through membranes and used to build larger molecules.
30
New cards
Absorbtion
The uptake of small molecules by body cells in the small intestine.
Uses thin membranes with a large surface areas for maximum absorption in to the circulatory system.
Cells take up small molecules
Uses thin membranes with a large surface areas for maximum absorption in to the circulatory system.
Cells take up small molecules
31
New cards
Elimination
The passage of undigested material out of the digestive system.
passing of undigested material
passing of undigested material
32
New cards
Digestion
The process of breaking food down into molecules small enough to absorb.
33
New cards
Incomplete digestion
When there is one opening.
34
New cards
Complete digestion
When there is a mouth and anus.
35
New cards
Enzymes
Breaks down food into particles
36
New cards
Mixing
When food particles are mixed with enzymes and other fluids in the stomach.
37
New cards
Intracellular digestion
When food is directly taken into the cell such as sponges.
38
New cards
Extracellular Digestion
When food is broken down into small pieces outside the cell.
39
New cards
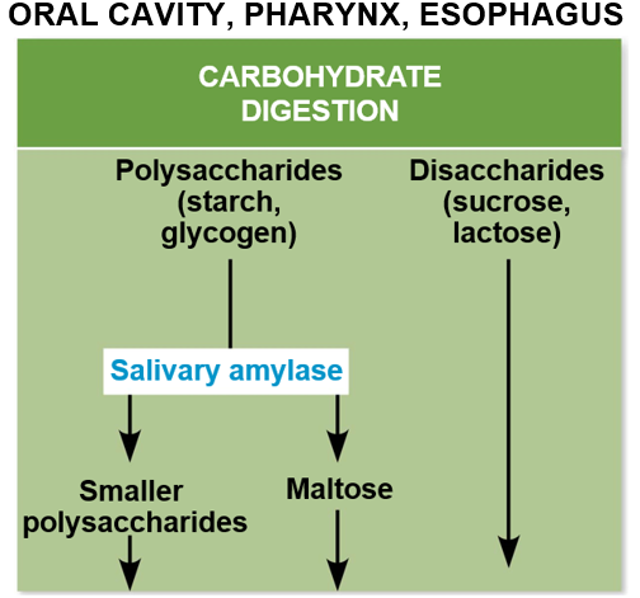
Human Digestion in Mouth
Uses mechanical digestion by chewing and chemical digestion by amylases to break down food.
40
New cards
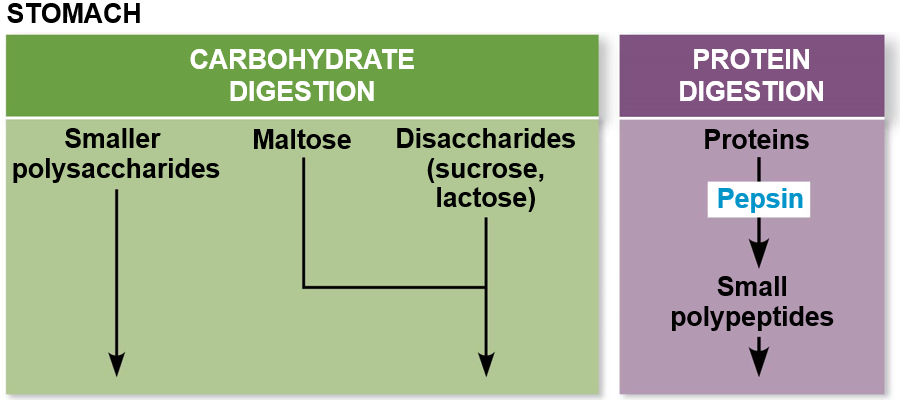
Human Digestion Stomach
Uses chemical digestion with enzymes that are proteins that are secreted as pepsinogen.
41
New cards
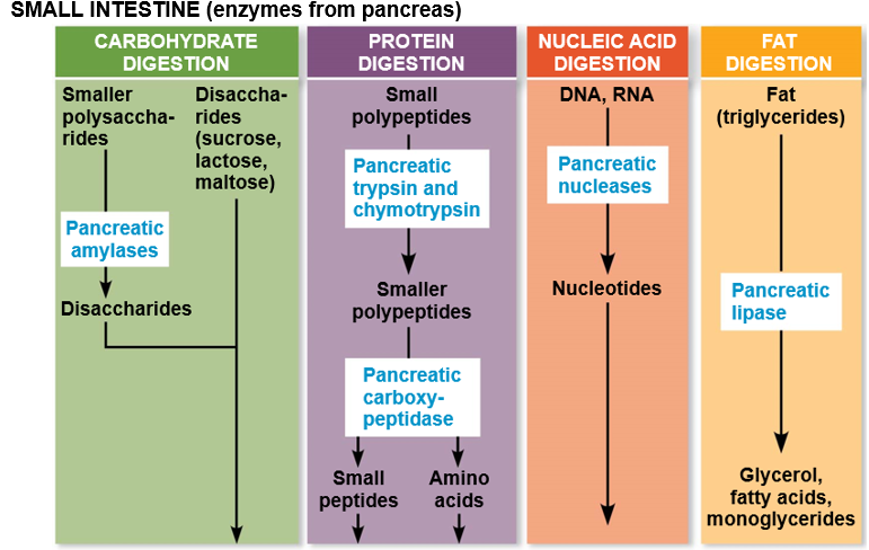
Human Digestion Small Intestine
Chemical Digestion with Enzymes from secreted from the Pancreas and intestinal epithelium and other secretions are also used such as gallbladder, bile and emulsifier.
Absorption happens through the villi and microvilli through capillaries and Lacteals.
Absorption happens through the villi and microvilli through capillaries and Lacteals.
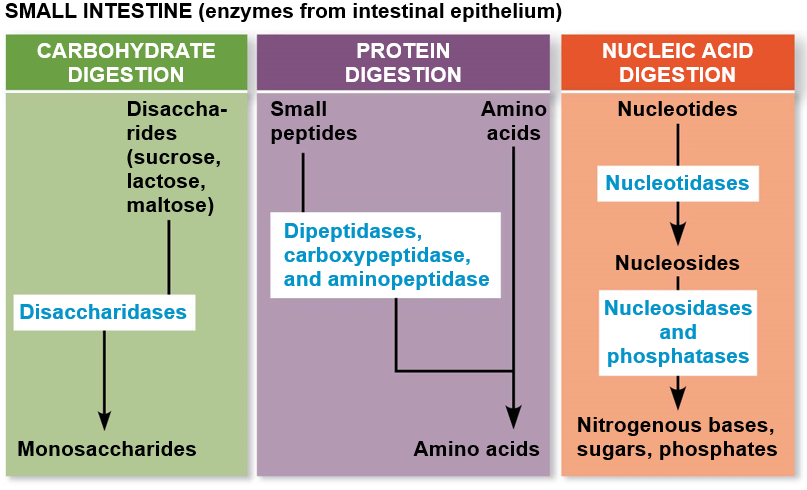
42
New cards
Human Digestion Fat Absorption
Fats enter the intestinal cells but leave via exocytosis and are picked up by the lymphatic system.
43
New cards
Human Digestion Large Intestine
Re absorption of water and vitamin and fermentation by bacteria.
44
New cards
Digestion of carbohydrates, proteins, nucleic acid, and fat.
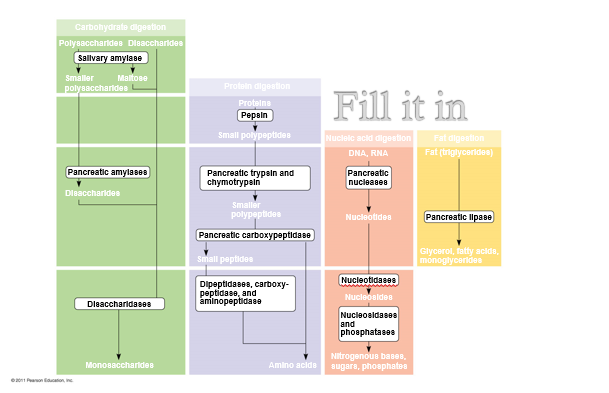
45
New cards
A lipase would be an enzyme that breaks down?
lipids
46
New cards
Which of the following is not digested in the stomach?
nucleic acids
47
New cards
Which of the following undergoes chemical digestion in the oral cavity?
carbohydrates
48
New cards
What dose pepsin do?
Creates smaller polypeptides
49
New cards
Regulation of blood glucose levels to prevent hyperglycemia. Pt.1
Insulin hormones are released from the pancreases and binds to receptors on liver cells and takes on more glucose which is then converted to glycogen to take out excess glucose and less insulin is released.
(Type 1 diabetes dose not make insulin)
Alpha cells release glucagon from the pancreases and bind to receptors on liver cells signaling to break glycogen down to glucose to increase blood glucose levels.
(Type 2 diabetes is when the alpha cells don't respond to insulin)
(Type 1 diabetes dose not make insulin)
Alpha cells release glucagon from the pancreases and bind to receptors on liver cells signaling to break glycogen down to glucose to increase blood glucose levels.
(Type 2 diabetes is when the alpha cells don't respond to insulin)
50
New cards
The release of __________ increases blood glucose concentrations.
Glucagon
51
New cards
Regulation of blood glucose levels to prevent hyperglycemia. Pt.2
Portal System
Blood is taken from the small intestine to the liver to be treated by adding more or less glucose before it is sent to the rest of the body.
Blood is taken from the small intestine to the liver to be treated by adding more or less glucose before it is sent to the rest of the body.
52
New cards
Herbivore digestion
Herbivores have a much larger cecum because plants are a lot harder to break down.
53
New cards
Ingestion, chemical digestion, absorption, and elimination occurring in different parts of the digestive system could only happen in which of the following animals?
fish
54
New cards
Ingestion, chemical digestion, absorption, and elimination occurring in different parts of the digestive system. Which of the following statements about the alimentary canal is TRUE?
-Mutations that created changes in the digestive system occur at random.
55
New cards
An adaptive immune system appears to be unique to vertebrates. This would include?
-mammals
-fish
-amphibians
56
New cards
Innate Immunity
All animal have this immunity to a very broad spectrum of pathogens.
57
New cards
Barriers defense Innate Immunity
-Keeps germs from getting inside (skin)
-Mucous Membranes
-Mucous Membranes
58
New cards
Internal defenses Innate Immunity
-Phagocytic cells, Antimicrobial proteins, inflammatory response (fights pathogens from inside)
-binds to dsRNA (Viruses), lipopolysaccharides (bacteria), flagellin (Bacteria flagella)
-Toll-loke Receptors (TLRs) recognize groups of pathogens
-Pseudopodia surrounds pathogens which are engulfed by endocytosis creating a vacuole which fuse to lysosome and pathogens are destroyed and debris is released.
-binds to dsRNA (Viruses), lipopolysaccharides (bacteria), flagellin (Bacteria flagella)
-Toll-loke Receptors (TLRs) recognize groups of pathogens
-Pseudopodia surrounds pathogens which are engulfed by endocytosis creating a vacuole which fuse to lysosome and pathogens are destroyed and debris is released.
59
New cards
Neutrophils (Phagocytic Cell)
Phagocytic cells that circulate in the blood to engulf and destroy pathogen.
60
New cards
Macrophages (Phagocytic Cell)
Phagocytic cells that migrate through the body or reside permanently in organs and tissues
61
New cards
Dendritic (Phagocytic Cell)
Phagocytic cells that simulate development of adaptive immunity
62
New cards
Eosinophils (Phagocytic Cell)
Phagocytic cells discharge destructive enzymes against parasites.
63
New cards
Mast Cells (innate and adaptive)
Immune cells found in connective tissue.
64
New cards
Histamine
A compound that causes dilation of capillaries and contraction of smooth muscle. It also causes capillaries to me more permeable.
65
New cards
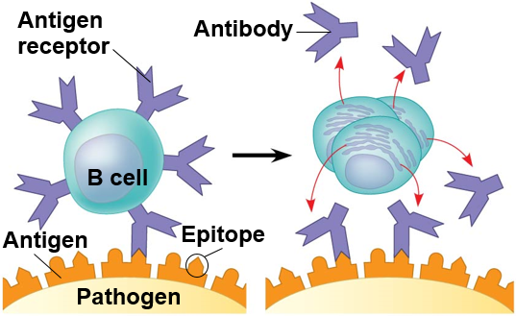
Adaptive Immunity
Unique to vertebrates
-Can learn to fight of certain pathogens
-Immune cells selectively destroy specific invading microbe, and viruses.
-Immunological response remembers the invaders which allows for a rapid response if the invader reappears again.
-Lots of receptors to readily encounter new pathogens
-Must be tolerant of our own cells
-Activation increases specific B and T cells
-Can learn to fight of certain pathogens
-Immune cells selectively destroy specific invading microbe, and viruses.
-Immunological response remembers the invaders which allows for a rapid response if the invader reappears again.
-Lots of receptors to readily encounter new pathogens
-Must be tolerant of our own cells
-Activation increases specific B and T cells
66
New cards
Humoral response Adaptive Immunity
Antibodies defend against infection in body fluids
67
New cards
Cells meditated Response Adaptive Immunity
Cytotoxin cells defense against infection in body cells.
68
New cards
Pathogen
An organism, virus, viroid or prion that causes disease.
69
New cards
Antigen
Any substance that elicits a response from B or T cells. Typicly a pathogen
70
New cards
Epitope
An accessible region of an antigen to which an antigen or anti body binds
71
New cards
A virus would be best described as a
Pathogen
72
New cards
The spike protein on SARS-CoV-2 is an example of a
Antigen
73
New cards
Lymphocytes
White Blood Cells
-Activated by match between receptor and antigen (epitope)
-Activated by match between receptor and antigen (epitope)
74
New cards
B Cell Lymphocytes (Cell mediated Adaptive Immunity)
Arise from stem cells in the bone marrow and develop in the bone marrow.
-Make antibodies
-Has Antigen Receptors
-B effector cells make plasma cells and memory cells
-Ones with antigen receptor reproduce through mitosis which release free antibodies
-Make antibodies
-Has Antigen Receptors
-B effector cells make plasma cells and memory cells
-Ones with antigen receptor reproduce through mitosis which release free antibodies
75
New cards
T Cell Lymphocytes (Cell mediated Adaptive Immunity)
Arise from stem cells in the bone marrow and develop in the thymus gland.
-Has Antigen Receptors
-T effector cells make helper t cells and cytotoxic t cells
-Bind to pieces of antigens on the surface of MHC
-Has Antigen Receptors
-T effector cells make helper t cells and cytotoxic t cells
-Bind to pieces of antigens on the surface of MHC
76
New cards
Antigen Receptor
Surface proteins on B and T cells that bind antigens B cell receptors and T cell receptors.
77
New cards
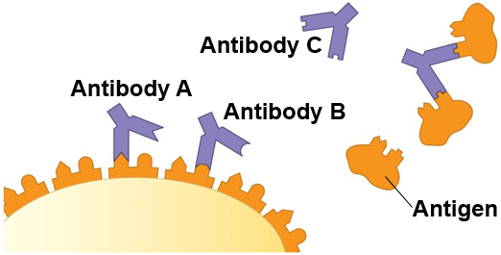
Antibody
A protein that is produced by B cell that combines with a specific antigen and facilitates the destruction of the antigen Y shaped.
-Can bind to free floating antigens
-Can bind to free floating antigens
78
New cards
Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC)
Binds peptide fragments derived from pathogens and display them on the cell surface for recognition by the appropriate T cells.
79
New cards
Effector cells
Short lived and deal with antigen
80
New cards
Clonal Selection
The antigen ends up selecting which lymphocytes will make clones and they have to be activated.
81
New cards
Primary Immune Response
Response following initial infection
82
New cards
Secondary Immune Response
If infected a second time
83
New cards
Sometimes after a vaccine you feel pretty bad (tired, sore, etc.). The cause of these symptoms is
Your bodies primary immune response
84
New cards
Antibodies
-Neutralize virus
-Antibodies bind to antiFgens on pathogen and clumps them up and makes it easier for macrophages to eat it. (opsonization)
-Activates Compliment system- proteins and antibodies trigger a membrane attack complex and pathogens lyses.
-Antibodies bind to antiFgens on pathogen and clumps them up and makes it easier for macrophages to eat it. (opsonization)
-Activates Compliment system- proteins and antibodies trigger a membrane attack complex and pathogens lyses.
85
New cards
Helper T cells (T Cell)
Sends out cytokines after they have encountered MHC molecules on a antigen.
86
New cards
Cytotoxic T Cells (T Cell)
Binds to MHC and begins to punch hole in the membranes of specific pathogens using the protein perforin.
87
New cards
Osmosis is the movement of water from high concentration to low concentration through a semipermeable membrane. Concentration of what?
Water
88
New cards
Think about this definition from the perspective of the solute, then. Water moves from
low to high of solute
89
New cards
The osmolarity of a cell is 9 mOsmol/L and the osmolarity of the interstitial fluid is 20 mOsmol/L. Cell membranes are permeable to water. Will the net movement of water be
out of cell
90
New cards
Continuing with the perspective of the solute, water moves from a (more/less) dilute solution to a (more/less) concentrated solution. This is the more common way that we describe solutions. More concentrated means more solute. More dilute means less solute. You might find it helpful to phrase osmosis in this way.
more, more
91
New cards
A cell with an osmolarity of 275 mOsmol/L is in plasma with an osmolarity of 300 mOsmol/L. Water will move_________ the cell osmotically.
out of
92
New cards
A cell is placed in a solution and shrivels up. The cell was placed in a __________solution.
hypertonic
93
New cards
Do freshwater fish need to drink water? Yes or no. Why or why not?
No, because their body is always taking on water because there body has more solute concentration that the outside water. (They are always excreting water)
94
New cards
Marine Fish
Drinks and loses water because solute concentrations are higher outside of their body and through active transport excrete salt ions through gills.
95
New cards
Seawater has an osmolarity of 1000 mOsmol/L and human blood plasma has an osmalarity of 280 mOsmol/L. If stranded on a life raft in the ocean, drinking seawater
Make you more dehydrated
96
New cards
Osmoregulatory
maintain a constant internal environment for water or ions
97
New cards
Hyperosmoregulators
Maintains higher osmolality than surrounding seawater.
(freshwater fish)
(freshwater fish)
98
New cards
Hypoosmoregulators
Maintains lower osmolality than surrounding seawater.
(marine fish)
(marine fish)
99
New cards
A cell with an osmolarity of 200 mOsmol/L is in plasma with an osmolarity of 100 mOsmol/L. Water will move_________ the cell osmotically.
into
100
New cards
Osmoconformers
Vary as the external conditions vary.