Pharm E1- Neuro
1/167
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
168 Terms
What is continuous seizure activity w/o the regaining of mental status (neurological emergency secondary to cerebral ischemia)?
Status epilepticus
What is abnormal behavior that results from abnormal discharges of cortical neurons?
seizure
What is epilepsy?
symptom of disturbed electrical brain activity, w/ periodic recurrence of seizures w/ or w/o convulsions
What are treatment options for epilepsy?
AEDs, vagal nerve stimulator, surgery, and ketogenic diet
How do ketogenic diets help epilepsy?
lower pH / acidosis → higher threshold / harder for seizure to occur
Are AEDs disease modifying?
no
What are the main groups of drugs to treat epilepsy?
Na channel blockers, CCBs, GABA enhancers, glutamate blockers, carbonic anhydrase inhibitors, hormones
AEDs that inhibit which calcium channel are the best for treating absence seizures (ethosuximide)?
T calcium channels
Which GABA receptor is more important in the treatment of seizures?
GABA A (facilitates passage of Cl-)
What drugs modify the NMDA glutamate receptor site?
Felbamate & Levetiracetam
What drugs modify the AMPA/Kainate glutamate receptor set
topiramate
What group of drugs increases the concentration of H ions and decrease the pH, which increases the seizure threshold?
carbonic anhydrase inhibitors
What drug?
inhibit Na channels
highly protein bound to albumin
Michaelis mentan pharmacokinetcs- half life increases as dose& serum conc. increases
CYP3A4 & 2C inducer
requires TDM
Phenytoin (Dilantin)
What is the first line agent for generalized and partial seizures?
Phenytoin (Dilantin)
What are SEs of Phenytoin (Dilantin)?
SJS, rash, lethargy, blurred vision, hirsutism, gingival hyperplasia, vit D deficiency & osteomalacia
Why should phenytoin be avoided IM & IV? (use fosphenytoin instead)
high risk of phlebitis and CV complications
What drug?
Na channel blocker
induces its own metabolism; half life shortens as enzymes are upregulated
induces CYP3A4, 2C9, 2C19
also has anticonvulsant activity
requires TDM & monitor LFTs
Carbamazepine (Tegretol)
What are SEs of Carbamazepine (Tegretol)?
diplopia, dizziness, elevated LFTs, hyponatremia, bone marrow suppression
Both drugs cause hyponatremia, but which one is the bigger offender & more likely to cause SIADH?
Oxcarbazepine
What is Oxcarbazepine (Trileptal) MOA?
Na channel blocker
What is the MOA of valproic acid (Depakote)?
Na channel inhibitor, Ca channel inhibitor, GABA enhancer
What SEs are seen with Valproic Acid (Depakote)?
GI disturbances (MC), hepatotoxicity (monitor LFTs), CYP interactions, sedation, ataxia, tremor, weight gain, pancreatitis, thrombocytopenia, & teratogenic (neural tube defect)
What drug is teratogenic and can cause neural tube defects if given during pregnancy?
Valproic acid (Depakote)
What drugs are Benzodiazepines?
Diazepam (Diastat)
Lorazepam (Activan)
Midazolam (Versed)
Clonazepam (Klonopin)
Clobazam (Onfi)
What is the most common IV agent for acute seizures?
Lorazepam (Ativan)
What drugs?
enhance GABA A activity & increase Cl- influx
C-IV
go to agents for acute seizures (PR/IN/IM/IV); PO better for prevention
SEs: sedation (MC) & withdrawal seizures
Benzodiazepines
What is the drug of choice for neonatal seizures?
Phenobarbital (luminal)
What drug?
activate GABA A to increase Cl- influx
C-IV
rarely used d/t ADRs; reserved for refractory status epileptics or those who failed other AEDs
Phenobarbital (luminal)
What side effects are seen with phenobarbital?
sedation & CNS depression; paradoxical reaction in children (inc excitation)
requires TDM
What drug is used IV for status epileptics and can induce a “pentobarb coma”?
Pentobarbital (Nembutal)
What drug has limited use d/t fatal aplastic anemia, hepatotoxicity, and drug interactions and is used only in refractory epileptic patients?
Felbamate (Felbatol)
What is the drug of choice for absence seizures?
(*Test Q)
Ethosuximide (Zarontin)
What is Ethosuximide’s MOA?
inhibit neuronal Ca channel
What drug?
structure related to GABA- may enhance GABA synthesis & interact with Ca channels
adjust in renal failure
main SE- CNS depression
adjunctive AED & can treat neuropathic pain
Gabapentin (Neurontin) & Pregabalin (Lyrica)
Pregabalin is a _____
C-V
What is Lamotrigine’s (Lamictal) MOA?
inhibit sodium channels, inhibit glutamate release, & modulation calcium channels
What drug?
AED- less sedation than other meds
metabolism inhibited by VPA (higher levels- lower dosage);
induced by carbamazepine & phenytoin (lower levels- increase dosage)
Lamotrigine (Lamictal)
What SEs are seen with Lamotrigine (Lamictal)?
SJS, dizziness, ataxia, N, V
What drug?
bind to synaptic SV2A & prevent glutamate release
becoming first line for epilepsy; used as adjunctive for partial seizures
60% renal elimination - adjust w/ renal issues
Levetiracetam (Keppra)
Which AED is associated with increased aggression, especially in children?
Levetiracetam (Keppra)
What drug?
anticonvulsant- treats seizures & migraine prevention
adjust for for renal
SE: impaired concentration
Topiramate (Topamax)
What is the MOA of Topiramate (Topamax)?
block Na channels, enhance GABA, antagonize AMPA/Kainate
carbonic anhydrase inhibitor - induce mild metabolic acidosis (increase seizure threshold
What drug?
AED- targets Na channels & binds CRMP-2 (prevents hyperexcitability)
C-V
SE: inc PR interval, HA, ataxia, N/V
Lacosamide (Vimpat)
What is a treatment algorithm for status epilepticus?
immediate- secure airway, circulation, protect from injury
early 0-10 min- IV lorazepam, Diazepam PR, Midazolam IN
if unresponsive- phenytoin or fosphenytoin
if unresponsive- Levetiracetam or phenobarbital
if unresponsive- VPA or additional phenobarbital
if unresponsive - general anesthesia or pentobarbital coma
When can a patient stop AED therapy?
seizure free 2-5 yrs on AEDs
single seizure type
normal neuro exam / no brain lesions
normal EEG after treatment
*withdraw slowly, esp benzodiazepines & barbiturates
What are the most common reactions to epileptic treatment?
sedation, dizziness, blurred vision, difficulty concentrating, ataxia (fall risk!)
What AEDs cause less drowsiness than other agents?
Lamotrigine & VPA
What drug is rarely used in school aged children due to interference with learning?
phenobarbital
What would not be a good AED drug to prescribe in a patient with a history of mental illness due to psychosis & suicide attempts observed in clinical trials?
Levetiracetam
What drugs have a a risk of SJS/TEN and should be discontinued immediately with any sign of a rash?
(*test Q)
Oxcarbazepine & lamotrigine
What drug causes aplastic anemia and is reserved for refractory seizure activity?
Felbamate
What drugs should be routinely monitored with CBCs and for sx such as fever, sore throat, mouth ulcers, unusual bleeding/bruising due to possible ADRs such as agranulocytosis, leukopenia, neutropenia, etc?
carbamazepine, felbamate, VPA, phenytoin
What drugs can cause hepatitis / hepatic failure and should be routinely monitored w/ CBCs & LFTS?
carbamazepine, felbamate, phenytoin, VPA (worst one; MC under 2 y/o)
Which AEDs require therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM)?
carbamazepine, phenobarbital, VPA, phenytoin
What forms of birth control are not affected by AEDs?
depo shots & IUDs
What AEDs decrease the effectiveness of OCs?
phenytoin, phenobarbital, carbamazepine, oxcarbazepine, felbamate
What condition is a slowly progressive neurodegenerative disorder caused by too little dopamine & has 4 cardinal features: tremor, rigidity, hypokinesia, & postural instability?
Parkinson’s Disease (PD)
What are 2 main targets for treatment of Parkinson’s?
COMT- metabolizes L DOPA
MOA-B- breaks down dopamine
What can be used as a diagnostic test for Parkinson’s?
response to levodopa or apomorphine
What treatments can be used for early, uncomplicated PD?
Neuroprotection: MAO-B inhibitors, DA agonists
Sx: anticholinergics, MAO-B inhibitors, COMT inhibitors, DA agonists (Ergot & non ergot), DA precursors
What class of drugs irreversibly inhibits MAO-B to reduce metabolism of DA to decrease radical formation/oxidative stress (neuroprotective)?
MAO-B inhibitors
What drugs are MAO-B inhibitors?
Selegiline & Rasagiline
What drug?
MAO-B inhibitor
treats early PD, delays need for levodopa
metabolized to amphetamine derivatives, shows positive on drug screen
SEs: orthostatic hypotension (fall risk), serotonin syndrome, agitation, insomnia, hallucinations
Selegiline (Eldepryl, Zelapar)
What drug?
MAO-B inhibitor
reduces functional decline of PD
not metabolized to amphetamine derivates, fewer SE
risk for serotonin syndrome
Rasagiline (Azilect)
What do both MOA-B inhibitors present a risk for?
serotonin syndrome
What foods should be avoided with MOA-B inhibitors due to risk of tyramine reaction?
Fava beans, aged cheeses, red wine, sausage, salami, etc
What drugs?
used for sx tx in early PD w/ minimal hypokinesia
blocks Ach in SNc → dec tremor
avoid in patients w/ cognitive impairment; not great for elderly
SE: dry mouth, constipation, blurred vision, etc
reduce gradually due to rebound sx
Anticholinergics
What drug?
Unclear MOA- amphetamine like action to release DA, anticholinergic, NMDA antagonist
used as mono or combo tx in early mild PD → can help manage levodopa induced dyskinesia
reduce in renal impairment
se: dizziness, anxiety, insomnia, N, V, anticholinergic
can develop tolerance
Amantadine (Symmetrel)
What drugs may be used as first line monotherapy for PD but are not as effective as cabidopa/levodopa?
Dopamine agonists (ergot & non ergot derivatives)
What class of drugs is Bromocriptine (Parlodel)?
Ergot derivative
What drugs are non-ergot derivatives?
Pramipexole (Mirapex)
Ropinirole (Requip)
Rotigotine (Neupro) - transdermal patch
Apomorphine (Apokyn) - SQ
What are possible SEs of ergot derivatives?
pleuro/retroperitoneal fibrosis and valve regurgitation
What drug?
most effective tx for sx of PD; eventually all pt’s require
crosses BBB
SE: N, V, orthostatic hypotension, hallucinations, insomnia, somnolence, depression
Levodopa / Carbidopa (Sinemet)
What can affect the absorption of levodopa/carbidopa (Sinemet)?
amino acids (compete for absorption; not absorbed as well if taken at same time as proteins)
What forms does Levodopa/Carbidopa come in?
Sinemet, Sinemet CR, Parcopa (ODT)
What should be given along with levodopa to prolong conversion to DA and allow levodopa to act centrally while reducing AE?
Carbidopa
What drug lengthens the half life of levodopa/carbidopa when given in combo?
Entacapone
What drugs?
inc central levodopa & prolong half-life by prevent breakdown through inhibiting peripheral COMT
only as adjunct w/ levodopa/carbidopa (reduce l-dopa by 25%)
contraindication: MOA-AIs
COMT inhibitors
What SE is seen with COMT inhibitors?
urine discoloration (brown/orange)
What drugs are COMT inhibitors?
Tolcapone (Tasmar)
Entacopone (Comtan)
What is the black box warning for Tolcapone (Tasmar)?
hepatotoxicity - monitor LFTs
treatment algorithm for parkinsons
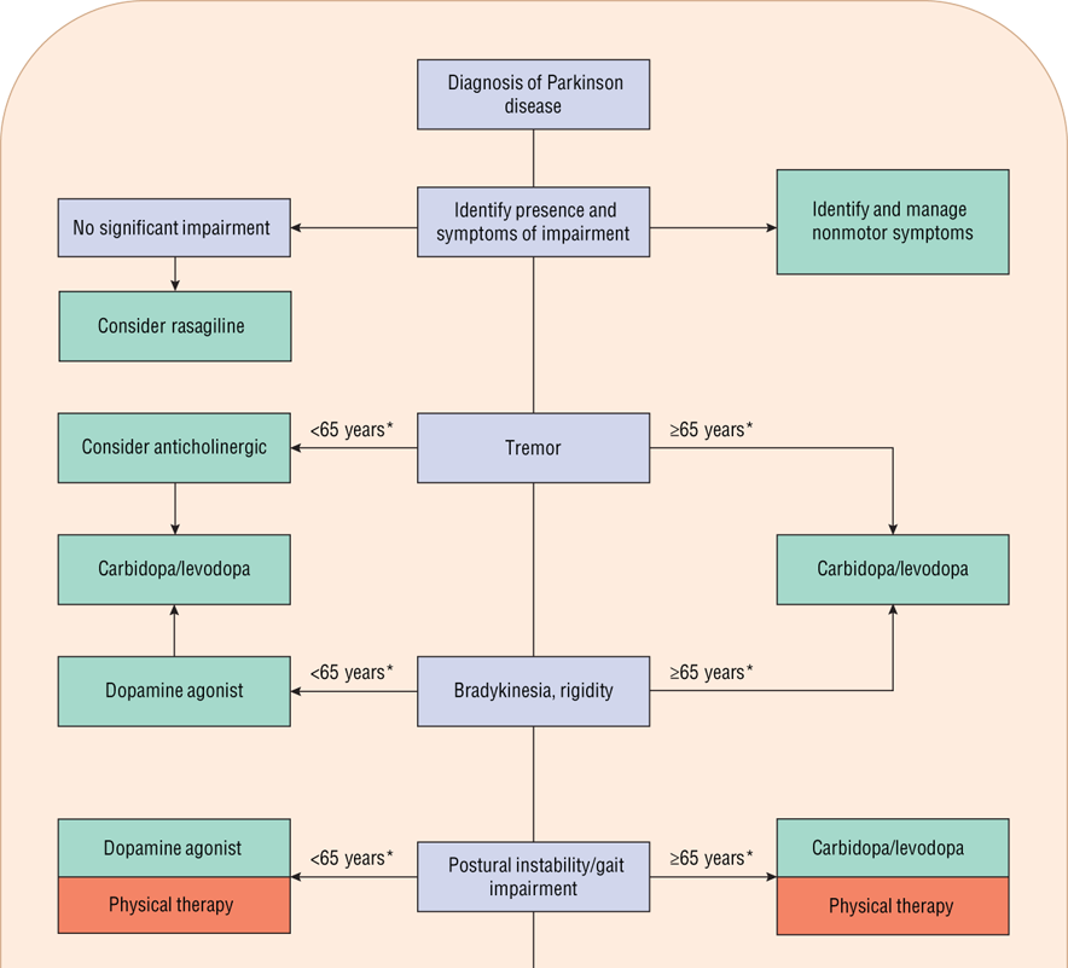
What drug is associated with a “honeymoon” that works great at first and then loses it’s effect?
L-dopa
What are the refractory sx of PD (dysarthria, dysphagia, freezing) treated with?
levodopa oral soln, apomorphine, surgery, PT
What drugs can be added to PD treatment when the medications start wearing off due to loss of presynaptic neurons?
entacapone, DA agonist, MAO-B inhibitor, apomorphine injections, duodenal L dopa infusions
administer Sinemet more frequently or switch to oral soln or sinemet CR
What can be added to PD treatment for “off” dystonia?
DA agonist, rotigotine, botox
add bedtime dose of sinemet CR & take first thing in the morning
What can be added to treatment for PD if meds unpredictably wear on-off?
DA agonist or try a different one, MOA-Bi, COMTi, protein redistribution (separate meals), sinemet oral soln, apomorphine injections, continuous duodenal l dopa infusion
*trial and error
How can PD treatment be modified for dyskinesias associated with peak dose or “on” (too much DA/too much effect)?
lower sinemet dose or discontinue agents that potentiate L dopa (COMTi / MAO-Bi)
add DA agonist, amantadine, clozapine, or propranolol
How can PD treatment be modified for biphasic dyskinesias?
short dosing interval to produce over lapping of effects; add DA agonist; switch to CR
What condition is the progressive loss of hippocampus and cortical cholinergic neurons associated with memory and cognition?
Alzheimer’s Disease (AD)
What drugs?
treat mild-mod AD by preventing breakdown of post synaptic Ach to enhance cholinergic transmission (helps improve memory and cognition)
SE: cholinergic toxidrome- DUMBBBELS
Cholinesterase inhibitors (ChEI)
What drugs are cholinesterase inhibitors?
Donepezil (Aricept)
Rivastigmine (Exelon)
Galantamine (Razadyne)
Tacrine
What drug?
cholinesterase inhibitor specific for AChE over BuChE
high plasma protein binding & long half life (70 h)
CYP interactions (ketoconazole, quinidine)
reduced response in long term use
Donepezil (Aricept)
What drug?
cholinesterase inhibitor for both AChE & BuChE
short plasma half life (1-1.5 hr) but covalently binds ChE to stick around longer
twice daily dosing
sustained effect in long term use
Rivastigmine (Exelon)
What drug?
cholinesterase inhibitor very specific for AChE
moderate half life (7h); twice daily dosing
reduced response in long term use
CYP drug interactions
Galantamine (Razadyne)
What drug?
NMDA glutamate receptor antagonist - prevents Ca entry = less stress & reduced excitatory activity
tx mod-severe AD
well tolerated; improve cognitive function & daily activities
long half life; minimal drug interactions
Memantine (Namenda)
What condition is an inflammatory/demyelination disease of the CNS producing progressive neurological symptoms and plaques/sclerosed areas?
Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
What are the 3 categories of treatment for MS?
exacerbations - shorten duration & lessen severity
disease modifying therapy (DMT)
symptom management
How are MS exacerbations managed?
IV methylprednisolone w/in 2 wks of sx onset
Plasma exchange if severe
DMTs reduce relapse rates & white matter lesions in MS, but how long does it take to have an effect on symptoms in MS patients?
1-2 yrs