Chapter 10: Pure Monopoly
Pure monopoly - Single firm is sole producer of product w/ no close substitutes
- Single seller
- No close substitutes
- Price maker - Can change price of product
- Blocked entry - No potential competitors can enter industry
- Non-price competition - Monopolists that have standardized products engage mainly in public relations advertising
Ex. Government-owned public utilities, professional sports teams, etc.
Barriers to entry - Factors that prohibit firms from entering industry
- Block potential competition
- Exists in market structures w/ monopolistic behavior
Economies of scale
- Produce more → Gets cheaper to produce
- Caused by modern technology
- Entry barrier that protects from competition
Legal barriers to entry
- Patent - Exclusive right to use/allow another to use invention
- Protects from rivals
- Monopoly for life of patent
- Funds R&D
- License
- Limits entry into industry/occupation
Ownership of resources
- Owns/controls specific resource → Can prohibit entry of other firms
Pricing
- Slashing prices + increasing advertising → Rivals cannot succeed
Monopoly demand
- Monopolist’s demand curve = Market demand curve
- Down-sloping demand curve
Marginal revenue less than price
- Each additional unit of output sold increases total revenue by an amount equal to its own price less the sum of the price cuts that apply to all prior units of output
- Total revenue increases at diminishing rate
- MR curve below demand curve
Price maker
- Change market supply → Influence product price
- Sets prices in elastic region of demand
- Always avoids inelastic portion of demand curve
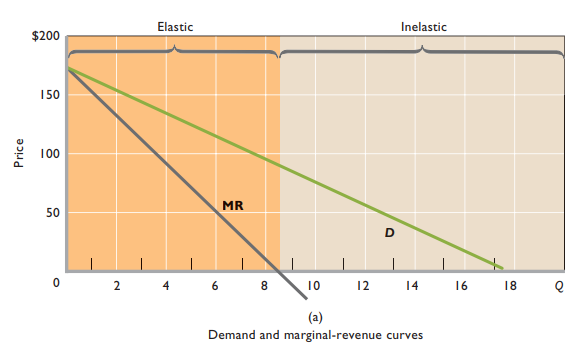
MR = MC
- Vertical line from quantity where MR = MC to demand curve = Price that monopolist charges
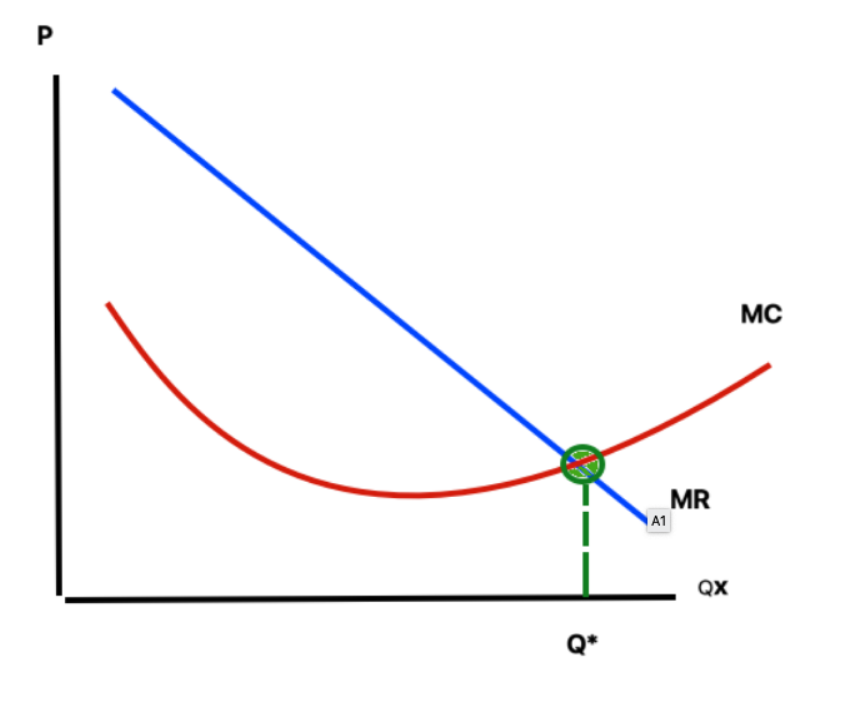
No supply curve
Seeks max total profit, not max prices
Seeks max total profit, not max unit profit
No guaranteed profit
- Not immune to changes in consumer tastes or reduced product demand
- Price greater than average variable cost → Continues to produce instead of shutting down
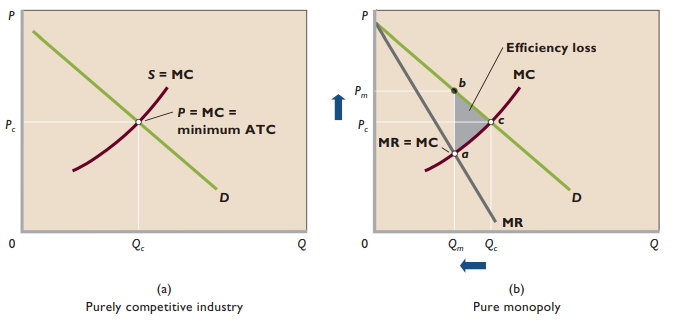
Economic effects
- Neither productive nor allocative efficiency
- Underallocation of resources
- Sum of consumer surplus + producer surplus less than max
Income transfer
- Owners of monopolies benefit at cost of consumers
- Increases income inequality
Cost complications
- Sometimes only natural monopoly can achieve lowest long run average total cost
- Simultaneous consumption - Product’s ability to satisfy large # of consumers at same time
- Network effects - Value of product to each user increases as total number of users increases
- X-inefficiency - Firm produces output at higher cost than necessary to produce
- Caused by lack of competitive pressure
- Rent-seeking behavior - Activity designed to transfer income/wealth to a firm/resource supplier at someone else’s expense
- Pure monopolists are not technologically progressive
Assessment + policy options
- Monopolies are problems
- New technologies can destroy monopolies
- New products circumvent patent advantages
- Possible actions
- Gov’t files charges under antitrust laws
- Gov’t regulates monopoly’s prices + operations
- Society ignores it
Price discrimination - Selling a specific product at more than one price when the price differences are not justified by cost differences
- Conditions
- Monopoly power
- Market segregation
- No resale
- Enhances profit
Regulated monopoly
- Multiple firms would incur higher average total costs than 1 firm
- Socially optimal price - Allocative efficiency; P = MC
- Fair-return price - Permits fair return to firm owners; P = ATC