Bio 30 Unit 3 Ch. 17 _ Genetics
Genetics Chapter 17
Selective Breeding - choosing parents with particular characteristics to breed together and produce offspring with more desirable characteristics
Selective breeding of wheat began as early as 9000 BC in the Middle East
Farmers collected and planted the seeds of one variety of wheat more easily than the other, unknowingly “selecting for” this former strain
True Breeding- a kind of breeding wherein the parents would produce offspring that would carry the same phenotype
alleles- one of two or more versions of DNA sequence (a single base or a segment of bases) at a given genomic location
Phenotype - refers to how a trait is physically expressed
genotype - refers to the combination of alleles for a given trait
Example of phenotype and genotype: Child's eye colour determined by dominant and recessive alleles from parents
Dominant allele controls the expressed characteristic
complete dominance - the effect of one allele in a heterozygous genotype completely masks the effect of the other
Recessive allele controls the repressed characteristic
Allele combinations- Traits are influenced by the interaction of two alleles, with one always dominant over the other
BB (homozygous dominant) results in a dominant phenotype
Bb (heterozygous) results in the dominant phenotype
bb (homozygous recessive) results in recessive phenotype
Homozygous - two identical alleles for a trait (RR or rr)
Heterozygous - Having two different alleles for a particular trait (Rr)
Gregor Mendel - first described the idea of dominant/recessive alleles
Mendel conducted test crosses with peas and observed that offspring displayed either the maternal or paternal phenotype, not a blending of the two
Mendel concluded that certain traits were dominant over others
Law of Segregation- Offspring display either the maternal or paternal phenotype, allowing for the random segregation of genes during gamete formation
Monohybrid Crosses- where only a single trait is considered
Chromosome theory of inheritance - the alleles that determine a trait are in the genes within specific chromosomes. This theory also explains how dominant and recessive alleles are transmitted from parent to child, and that each trait is transmitted independently.
MODE OF INHERITANCE
Autosomal dominant mode of inheritance= the trait is dominant & inherited on an autosome (as opposed to the sex chromosomes)
Autosomal recessive mode of inheritance= the trait is recessive & inherited on an autosome (as opposed to the sex chromosomes)
DIHYBRID CROSSES - crosses involving 2 genes
Law of independent assortment- The two alleles for one gene segregate independently of alleles for other genes during gamete formation
incomplete dominance - a condition where neither of the two alleles for the same gene have complete dominance over the other
Co-dominance - a situation where both alleles are fully expressed
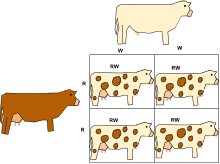
Heterozygote - the result of incomplete dominance or co-dominance
sex-linked traits- genes that are located on the X or Y chromosome
Barr Bodies- the inactive X-chromosomes in females
Multiple Alles- often more than two alleles may exist for a particular trait (one organism can only have 2, but more than one can exist among a population creating variation)
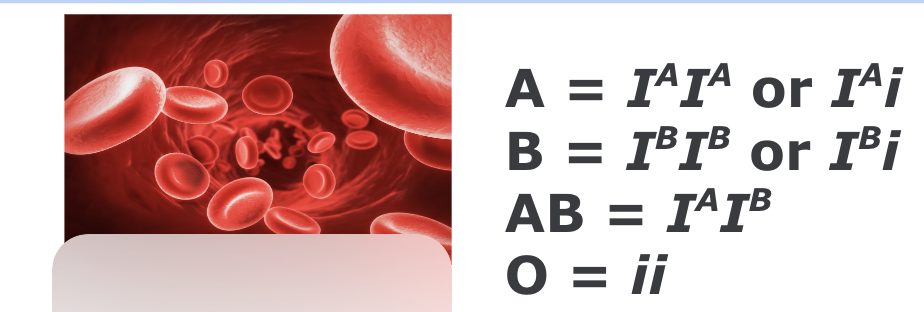
Blood types- A, B, AB, or O
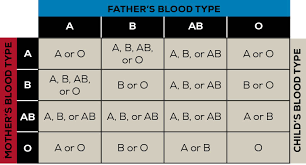
Epistasis- describes a certain relationship between genes, where an allele of one gene (e.g., 'spread') hides or masks the visible output. ex: The recessive c allele does not produce pigment, and a mouse with the homozygous recessive cc genotype is albino regardless of the allele present at the A locus.
Pedigrees- a type of flowchart that uses symbols to show the expression of a particular trait through multiple generations of a single family.
Roman numerals are used to indicate generations. Numbers are used to indicate individuals within each generation
GENE LINKAGE - the inheritance of a particular trait is thought to follow Mendel’s law of independent assortment, allowing us to predict the phenotypic and genotypic ratios of offspring accurately.
Recombinant- An event where crossing over takes place and forms 2 distinct pairs of alleles from what the parents had.
Non-linked genes = 50% parental gametes, 50% recombinants
Linked genes = less than 50% recombinants
Gene Mapping-
