Biochemistry - Chapter 14: Nucleic Acids & Protein Synthesis
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/101
Last updated 11:35 PM on 8/14/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
102 Terms
1
New cards
unchanged
Living cells are able to produce nearly exact replicas of themselves through hundreds of generations. THis requires certain information to be passed ___________.
2
New cards
Nucleic Acids
A biomolecule involved in the transfer of genetic information from existing cells to new cells, are high molecular weight compounds with nearly __infinite varieties__ of possible structures. This enables them to represent a huge amount of information that can be transmitted sexually or asexually to reproduce an organism.
3
New cards
RNA
Found in the cytoplasm of living cells, unbranched polymers of linear molecules, contains A C G and U bases, the sugar component is D-ribose, and the phosphate is derived from phosphoric acid.
4
New cards
DNA
Found primarily in the nuclei of cells, polymers of linear molecules, contains A C G and T bases, the sugar component is D-deoxyribose, and the phosphate is derived from phosphoric acid.
5
New cards
Nucleotides
The monomers that make nucleic acids.
__Three Chemical Components:__
1) Nitrogenous Base
2) Sugar (Carbohydrate)
3) Phosphate
__Three Chemical Components:__
1) Nitrogenous Base
2) Sugar (Carbohydrate)
3) Phosphate
6
New cards
heterocyclic compounds
Each of the five bases found in nucleic acids are _______________________ that can be classified as a pyrimidine or a purine, the parent compounds from which the bases are derived.
7
New cards
Pyrimidine Bases
Uracil (U), Thymine (T), and Cytosine (C)
8
New cards
Purine Bases
Adenine (A) and Guanine (G)
9
New cards
beta
Both RNA and DNA have their anomeric carbon in the _____ position.
10
New cards
cellular pH
The phosphate in RNA and DNA is derived from phosphoric acid (H3PO4), which under __________ conditions exists in ionic form.
11
New cards
water
A nucleotide can be formed by the rx of the three components with two moles of _______ being removed.
12
New cards
1’, 5’
In a nucleotide, the base is always attached to the __ position of the sugar (anomeric carbon) and the phosphate is located at the __ position. The carbon atoms in the sugar are designated with a number followed by a prime to distinguish them from the atoms in the nitrogenous base.
13
New cards
100 million
DNA molecules are among the largest molecules known, they can contain between 1 and ___________ nucleotide units.
14
New cards
phosphodiester bonds
The linkages between the nucleotides that are joined together by the phosphate groups that connect the 5’ carbon of one nucleotide to the 3’ carbon of the next in the chain.
15
New cards
Nucleic Acid Backbone
The linkage of alternating phosphate and sugar units to which the bases are attached, constant throughout the entire nucleic acid molecule.
16
New cards
primary structure
One DNA molecule only differs from another only in the sequence of the bases along the backbone (____________________).
17
New cards
James Watson, Francis Crick
The secondary structure of DNA was proposed in 1953 by ________________ (American molecular biologist) and ________________ (English biologist). This was perhaps the greatest discovery of modern biology and it earned both of them the Noble Prize in Physiology & Medicine in 1962.
18
New cards
equal
The analysis of DNA from many different forms of life revealed an interesting pattern. The relative amounts of each base often varied from one organism to another, but in all DNA percentages of __adenine & thymine__ were always _______ to each other as were the percentages of __guanine & cytosine__.
19
New cards
20, 30
Human DNA contains __% guanine & cytosine, and __% adenine & thymine. This led Watson and Crick to conclude that DNA is composed of two strands entwined around each other in a double helix.
20
New cards
antiparallel
The two intertwined polynucleotide chains of the DNA double helix run in opposite (___________) directions. Each end of the double helix contains the 5’ end on one chain and the 3’ end of the other.
21
New cards
outside, inside
The sugar-phosphate backbone is on the ________ of the helix and the bases are on the ________. The chains are held together and stabilize the molecule through H-bonds between the bases that extend inward from the sugar-phosphate backbone.
22
New cards
spacing
The ________ in the interior of the double helix is such that adenine always H-bonds to thymine, and guanine always H-bonds to cytosine.
23
New cards
Complementary
The two DNA strands with these matched sequences are said to be ______________ (not identical) to each other.
24
New cards
genetic material
DNA is responsible for the storage and transmission of _______________ (one of the most essential functions of an organism).
25
New cards
Chromosome
Protein-coated strand of multi coiled DNA. A tightly packed bundle of DNA and protein that is involved in cell division (A normal human cell contains 46).
26
New cards
Histones
Each chromosome contains one molecule of DNA coiled tightly about proteins called _________.
27
New cards
Genes
Made up of individual sections of DNA, are the fundamental unit of heredity, and direct the synthesis of a specific protein.
* Viruses contain several hundred.
* Bacteria like E. Coli contain about 1,000.
* Human cells contain approximately 25,000.
* Viruses contain several hundred.
* Bacteria like E. Coli contain about 1,000.
* Human cells contain approximately 25,000.
28
New cards
Karyotype
Shows the 46 chromosomes of a human cell.
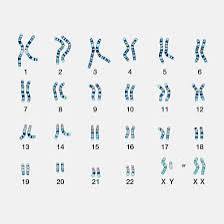
29
New cards
True
T or F: Watson and Crick’s model was the first to explain the transmission of heredity information (it explains how DNA is duplicated for the next generation).
30
New cards
Replication
The process by which an exact copy of DNA molecule is produced. Occurs when two strands of DNA separate and each serves as a template (pattern) for the construction of its own complement. It generates DNA double-stranded molecules that are exact replicas of the original DNA molecules.
31
New cards
Daughter molecules
The two ______________________ have exactly the same base sequences as the original parent DNA. EAch contains one strand of the parent and one new complementary strand.
32
New cards
Semiconservative Replication
Replication where one strand of the daughter DNA molecule comes from the parent DNA molecule and the other is a new complementary strand.
33
New cards
Steps of Replication
1) Unwinding the Double Helix
2) Synthesis of DNA Segments
3) Closing the Nicks
2) Synthesis of DNA Segments
3) Closing the Nicks
34
New cards
Unwinding the Double Helix
(Step of Replication) An enzyme called __helicase__ catalyzed the separation and unwinding of the nucleic acid strands at a specific point on the DNA helix. The hydrogen bonds are broken and the strand unwinds.
35
New cards
Replication Fork
The point of unwinding.
36
New cards
Synthesis of DNA Segments
(Step of Replication) Synthesis occurs on both nucleic acid strands that were separated. The process goes from 3’ to 5’ on the template and the new strand is synthesized from 5’ to 3’. One of the new strands synthesized proceeds towards the replication fork and the other proceeds away from it. The enzyme that synthesizes the new strand (add the correct nucleotides) is called __DNA polymerase__. The new strands are antiparallel. One of the strands grows smoothly towards the fork while the other is synthesized in fragments.
37
New cards
Okazaki Fragments
Discovered by Reiji Okazaki, the strand synthesized in segments.
38
New cards
Nicks
The gaps between Okazaki fragments.
39
New cards
Closing the Nicks
(Step of Replication) One daughter DNA strand is synthesized without any nicks, but the Okazaki fragments of the other strand must be joined together. The result is two DNA double-helical molecules that are identical to the original molecule.
40
New cards
Ligase
Enzyme catalyzing the connection of the Okazaki fragments.
41
New cards
Kary Mullis
(1983) Discovered a revolutionary laboratory technique called polymerase chain reaction (PCR).
42
New cards
eukaryotic cells
Through observations with electron microscopes, it has been found that replication in _________________ occurs simultaneously at many points along the original DNA molecule. This allows the molecules to be replicated rapidly.
43
New cards
PCR
Mimics the natural process of replication in that the helix unwinds and DNA polymerase makes a new copy.
Procedure:
1. Target DNA is added to a buffer solution containing DNA polymerase, the cofactor MgCl2, the four nucleotide building blocks, and primers.
2. The mixture is heated at 95C for 1-10 minutes to unravel (denature) the DNA into single strands.
3. The tube is cooled to 50-65C for 1-10 minutes and the primers hydrogen bond to the separated strands of DNA.
4. The tube is heated to 72C for 1-10 minutes where DNA polymerase make new DNA strands.
Procedure:
1. Target DNA is added to a buffer solution containing DNA polymerase, the cofactor MgCl2, the four nucleotide building blocks, and primers.
2. The mixture is heated at 95C for 1-10 minutes to unravel (denature) the DNA into single strands.
3. The tube is cooled to 50-65C for 1-10 minutes and the primers hydrogen bond to the separated strands of DNA.
4. The tube is heated to 72C for 1-10 minutes where DNA polymerase make new DNA strands.
44
New cards
Primers
Short nucleotide segments that will bind to the separated DNA strands and serve as starting points for new chain growth.
45
New cards
doubles
Each PCR cycle _________ the amount of DNA, therefore 30 cycles theoretically amplifies the amount to 1 billion.
46
New cards
PCR Purposes
1. Detect mutations associated with genetic diseases.
2. Detect the presence of unwanted DNA from a pathogen (microorganism).
3. Utilize degraded DNA samples in forensics.
4. Analyze and examine ancient DNA.
47
New cards
single stranded, loops
RNA consists of nucleotides joined by 3’ → 5’ phosphodiester bonds (like DNA), the number of nucleotides range from __73__ to thousands, the secondary structure of RNA is ___________________, does not contain a base ratio of 1:1, but do contain regions of double-helical structure where they form _______ (\~50%).
48
New cards
nucleus, cytoplasm, mitochondria
RNA is distributed throughout cells so it can be found in many areas including the _________, ______________, and ________________.
49
New cards
Messenger RNA
RNA that functions as the carrier of genetic information from the DNA of the cell nucleus directly to the cytoplasm where it is used in protein synthesis.
The bases in the sequence are __complementary__ to the bases of one of the strands of nuclear DNA. Has a short lifespan (\~1 hour), then degrades into the nucleotide parts that make it up.
The bases in the sequence are __complementary__ to the bases of one of the strands of nuclear DNA. Has a short lifespan (\~1 hour), then degrades into the nucleotide parts that make it up.
50
New cards
Transfer RNA
RNA that delivers individual amino acid molecules to the site of protein synthesis.
Smallest of all nucleic acids (73-93 nucleotides), cells contain at least one specific type for each of the 20 amino acids found in proteins, has regions of H-bonds between complementary bases and regions with no H-bonds called loops. Has anticodons and the site of amino acid attachment.
Smallest of all nucleic acids (73-93 nucleotides), cells contain at least one specific type for each of the 20 amino acids found in proteins, has regions of H-bonds between complementary bases and regions with no H-bonds called loops. Has anticodons and the site of amino acid attachment.
51
New cards
Ribosomal RNA
RNA that constitutes 65% of the material in ribosomes (other 35% is protein).
Constitutes 80-85% of the total RNA of the cell.
Constitutes 80-85% of the total RNA of the cell.
52
New cards
Anticodon
A three-base sequence in tRNA that is complementary to one of the codons of mRNA.
53
New cards
3’, ester bond
The ___ end of the tRNA molecule contains a hydroxy group which is the site of amino acid attachment. Each amino acid is joined to the 3’ end of its specific tRNA by an ____________ that forms between the carboxyl group of the amino acid and the 3’ hydroxy group of ribose.
54
New cards
Ribosomes
The organelles responsible for protein synthesis.
55
New cards
Central Dogma of Molecular Biology
The well-established process by which genetic information stored in DNA molecules is expressed in the structure of synthesized proteins.
56
New cards
genes, proteins
Segments of DNA called ______ direct the synthesis of specific proteins, there is a specific one for every protein in the body. __________ manufacture all the other substances essential for life (carbs, lipids, etc.) In higher organisms (eukaryotes) the DNA is in the nucleus and protein synthesis occurs in cytoplasm.
57
New cards
Transcription
The transfer of genetic information from a DNA molecule to a molecule of messenger RNA.
58
New cards
Translation
The conversion of the code carried by mRNA into the amino acid sequence of a protein.
59
New cards
RNA polymerase, ribonucleotides
_________________ catalyzes RNA synthesis. First, the DNA double helix unwinds at a point near the gene that is to be transcribed and only one strand is transcribed. ______________ are linked together along the unwound DNA strand in a sequence determined by complementary base pairing of the DNA strand base.
60
New cards
starting point, termination point
During RNA synthesis, the DNA strand always has one sequence of bases recognized by RNA polymerase as the ______________________ and catalyzes the synthesis of mRNA in the 5’ to 3’ direction. It continues until it reaches another sequence of bases that is the _____________________. Once the mRNA molecule has been synthesized, it moves away from the DNA template (which rewinds).
61
New cards
template
tRNA and rRNA are synthesized in the same way with DNA serving as a __________.
62
New cards
Prokaryotic Translation
Each gene exists as a continuous segment of a DNA molecule and transcription produces mRNA that undergoes translation into a protein almost immediately due to there being no nucleus.
63
New cards
Eukaryotic Translation
Genes are in segments that are “interrupted”by segments that do not code for proteins. Both introns and exons are then transcribed into mRNA that produces hnRNA that undergoes a series of enzyme-catalyzed rx. The introns get cut out and the exons are spliced together to make mRNA. The results only contain the sequence of bases that actually code for protein synthesis.
64
New cards
Introns
The DNA segments that carry no amino acid codes, they remain in the nucleus (junk DNA).
65
New cards
Exons
The DNA segments (genes) that code for proteins, they exit the nucleus.
66
New cards
Heterogeneous Nuclear RNA
(hnRNA) Has both introns and exons.
67
New cards
Codon
Triplet of RNA nucleotide bases that code for a specific amino acid.
68
New cards
amino acid
In the early 1960’s it was proposed that a combination of mRNA bases (A,U,C,G) code for each _____________.
69
New cards
Marshall Nirenberg
In 1961, __________________ and his coworkers began to break the genetic code by making a synthetic molecule of mRNA consisting of uracil bases (UUU) and they incubated the synthetic mRNA with ribosomes, amino acids, tRNAs, and enzymes. The resulting polypeptide only contained phenylalanine amino acids.
70
New cards
1967
Many experiments followed Marshall Nirenberg’s and by ______ the entire genetic code had been broken.
71
New cards
Degeneracy
The genetic code is universal in almost every organism. Most amino acids are represented by more than one codon this is called _______________.
72
New cards
Methionine, Tryptophan
Only ______________ and _______________ are coded by one codon.
73
New cards
True
T or F: No single codon represents more than one amino acid, each three-base codon represents one amino acid.
74
New cards
stop codons
Only 61 of the possible 64 base triplets code for amino acids, the remaining three (UAA, UAG, UGA) are _______________. They tell the protein-synthesizing process when the primary structure is complete and it is time to stop adding amino acids.
75
New cards
start codon
The only ______________ is AUG which codes for the amino acid methionine. But it only functions that way when it occurs as the first codon of a sequence.
76
New cards
Initiation of Polypeptide Chain
(Step of Translation & Protein Synthesis) N-formylmethionine, initiates the growing polypeptide chain as the __N-terminal__ amino acid, once the protein is synthesized, N-formylmethionine is __cleaved__ from the protein product. The initiation process begins when mRNA is aligned on the surface of the __small ribosomal subunit__. It is aligned in such a way that the start codon occupies the __P site__.
Next, tRNA molecule with its attached fMet binds to the codon through H-bonds. The resulting complex binds to the __large ribosomal subunit__ to form the __initiation complex.__
Next, tRNA molecule with its attached fMet binds to the codon through H-bonds. The resulting complex binds to the __large ribosomal subunit__ to form the __initiation complex.__
77
New cards
Elongation of the Chain
(Step of Translation & Protein Synthesis) The __A site__ is located on the mRNA-ribosome complex next to the P site, incoming tRNA carrying the next amino acid will bond here. Each tRNA molecule can try to fit into the A site, but only the one with the correct __anticodon__ will fit properly. Once at the A site the 2nd amino acid is linked to fMet by a __peptide bond__ whose formation is catalyzed by the enzyme __peptidyl transferase__.
Now, tRNA bound to the P site is empty and the polypeptide chain is attached to the tRNA bound at the A site. The whole ribosome moves one codon along the mRNA toward its __3’__ end. As the ribosome moves, the empty tRNA is released from the P site and tRNA on A moves to P. With A available, new tRNA comes in to form another peptide bond and repeat until a chain is formed.
Now, tRNA bound to the P site is empty and the polypeptide chain is attached to the tRNA bound at the A site. The whole ribosome moves one codon along the mRNA toward its __3’__ end. As the ribosome moves, the empty tRNA is released from the P site and tRNA on A moves to P. With A available, new tRNA comes in to form another peptide bond and repeat until a chain is formed.
78
New cards
Termination of Polypeptide Synthesis
(Step of Translation & Protein Synthesis) Chain elongation continues until the ribosome complex reaches a __stop codon__. At that point, a specific protein known as a __termination factor__ binds to the codon and stops the process. The empty ribosome disciates and can then bind to another strand of mRNA and begin the process again. Several ribosomes can move along a single strand of mRNA. Therefore several identical polypeptide chains can be synthesized almost simultaneously from a single mRNA. This increases __efficiency__ and __utilization__ of the mRNA.
79
New cards
Polyribosomes
A complex of mRNA and several ribosomes (also called polysomes).
80
New cards
methionine
The first amino acid involved in protein synthesis in prokaryotic cells is a derivative of _____________.
81
New cards
translocation
Movement of the ribosome along the mRNA.
82
New cards
secondary, tertiary
Growing polypeptide chains extend from the ribosomes into the cellular cytoplasm. They then spontaneously fold to assume their 3D _____________ and __________ structures.
83
New cards
10 billion
The DNA copying mechanism is not totally error free, it’s estimated that on average 1 out of every __________ bases of DNA is incorrect.
84
New cards
Mutation
Any change resulting in an incorrect base sequence on DNA.
85
New cards
Mutagens
Certain chemicals (nitrous acid, dimethyl sulfate, etc.) can also induce mutations by reacting with DNA.
86
New cards
inhibits
Transcription of mutated DNA leads to an incorrect mRNA molecule which then leads to an incorrect amino acid sequence for a protein, or ________ the protein to be synthesized at all.
87
New cards
environmental factors
Some mutations occur naturally during DNA replication, but others can be induced by _______________________ such as ionizing radiation.
88
New cards
False
T or F: All mutations are bad and lead to lethal genetic diseases such as sickle-cell anemia, PKU, hemophilia, muscular dystrophy, etc.
89
New cards
Recombinant DNA
DNA of an organism that contains genetic material from another organism.
90
New cards
Genetic Engineering
Application of DNA technology that allows segments of DNA from one organism to be introduced into the genetic material of another organism. Has produced major advances in the fields of human healthcare, biology, and AG.
91
New cards
human insulin
An early success of genetic engineering was the introduction of the gene for _________________ into the bacterium E. Coli.
92
New cards
Restriction Enzyme
Protective enzyme found in some bacteria that catalyzes the cleaving of specific types of DNA. Were discovered in the 1960’s and they are what make genetic engineering possible.
93
New cards
foreign DNA
Restriction enzymes are normally part of a mechanism that protects certain bacteria from invasion of _____________ (viral).
94
New cards
methyl, untouched
Some of the bases in the DNA of these bacteria have _________ groups attached. The methylated DNA is ____________ by the restriction enzyme.
95
New cards
Palindromes
Sites on DNA acted on by restriction enzymes or the section in which the two strands have the same sequence but run opposite. In language, it is any word or phrase that reads the same in either direction.
96
New cards
predictable
At least 100 restriction enzymes are known and each catalyzes DNA cleavage in a specific and ______________ way. These enzymes are the tools that allow genetic engineers to cut DNA into fragments of known size and sequence.
97
New cards
DNA ligases
_______________ are also important in that they can be used to put together DNA pieces cut by restriction enzymes.
98
New cards
Vector
DNA carrier required in the introduction of a new DNA segment (gene) into a bacterial cell.
99
New cards
Plasmid
A vector that is a circular piece of double-stranded DNA found in the cytoplasm of bacterial cells. Range in size from two thousand to hundreds of thousands of nucleotides.
100
New cards
antibodies, toxins
Plasmids function as accessories to chromosomes by carrying genes that inactivate ___________ and produce _________. They have an unusual ability to replicate __independently__ of chromosomal DNA.