business management
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
as
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Managerial Levels
• First-Line Managers: manage the work of employees
• Middle Managers: manage the work of first-line managers
• Top Managers: responsible for making plans and decisions that affect the entire organization
Efficiency vs. Effectiveness
Efficiency: Low waste when attaining goals
• Effectiveness: Attains the goals needed
Social Media Management
Managers must be concerned with social media because these forms of communication are becoming important and valuable tools in managing
Geocentric Attitude
focusing on a global, "world-oriented" perspective when making staffing decisions and managing operations. It's about hiring the best talent regardless of their nationality or location and establishing a global mindset within the organization.
Employee Turnover
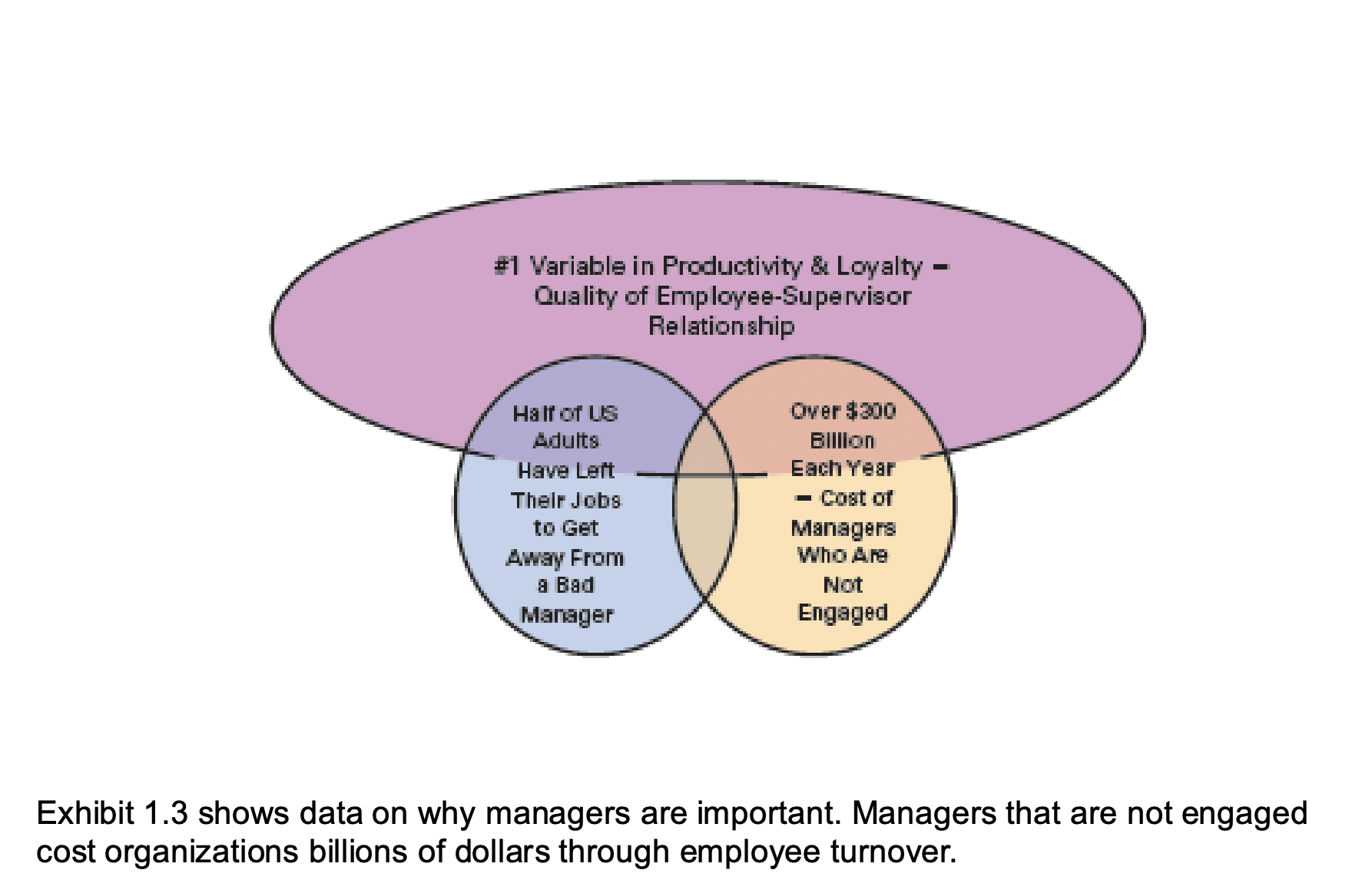
Universality of Management
• The reality that management is needed in all types and sizes of organizations, at all organizational levels, in all organizational areas, and in organizations no matter where located
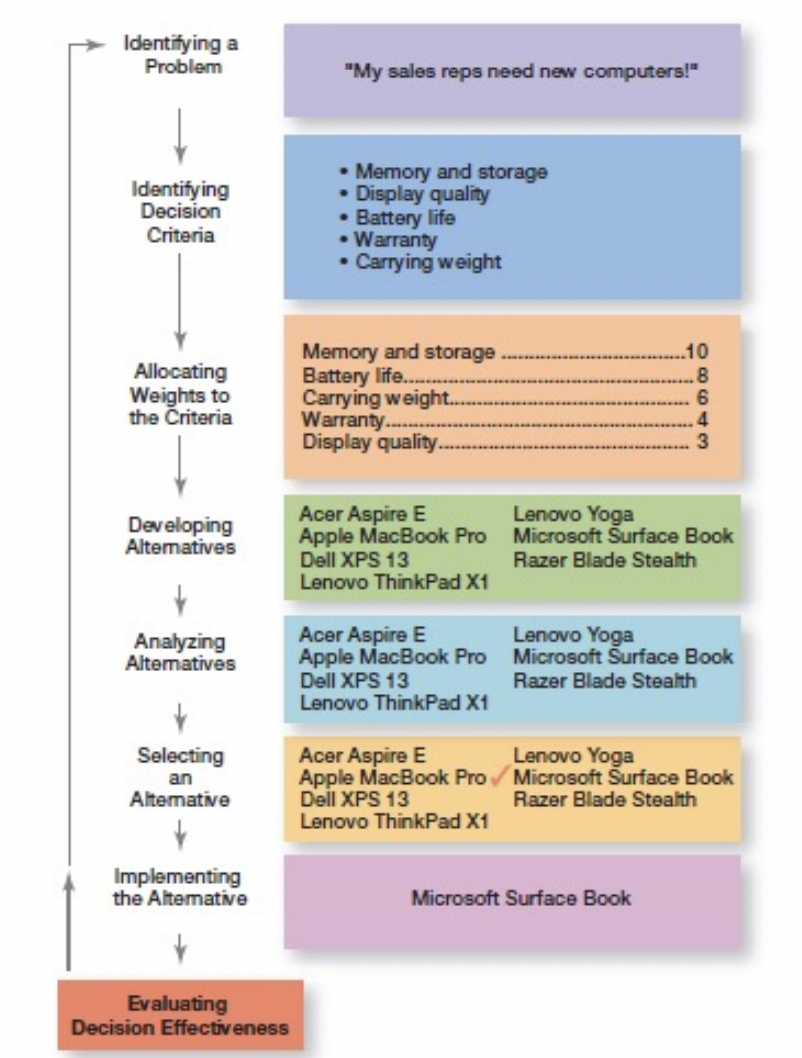
Decision Making Process
Rationality vs. Bounded Rationality
Rational Decision Making: choices that are logical and consistent and maximize value
Bounded rationality: decision making that’s rational, but limited by an individual’s ability to process information (accepting solutions that are “good enough”)
Bias in decision making
Overconfidence – Overestimating your abilities or knowledge
Anchoring effect – Relying too heavily on the first piece of info you receive
Selective perception – Only noticing information that supports your views
Confirmation bias – Seeking out info that confirms what you already believe
Framing – Decisions influenced by how information is presented
Availability bias – Judging based on information that comes to mind easily
Representativeness bias – Judging based on how similar something is to a stereotype
Self-serving bias – Attributing success to yourself and blaming failure on others
Hindsight bias – Believing, after the fact, that the outcome was predictable
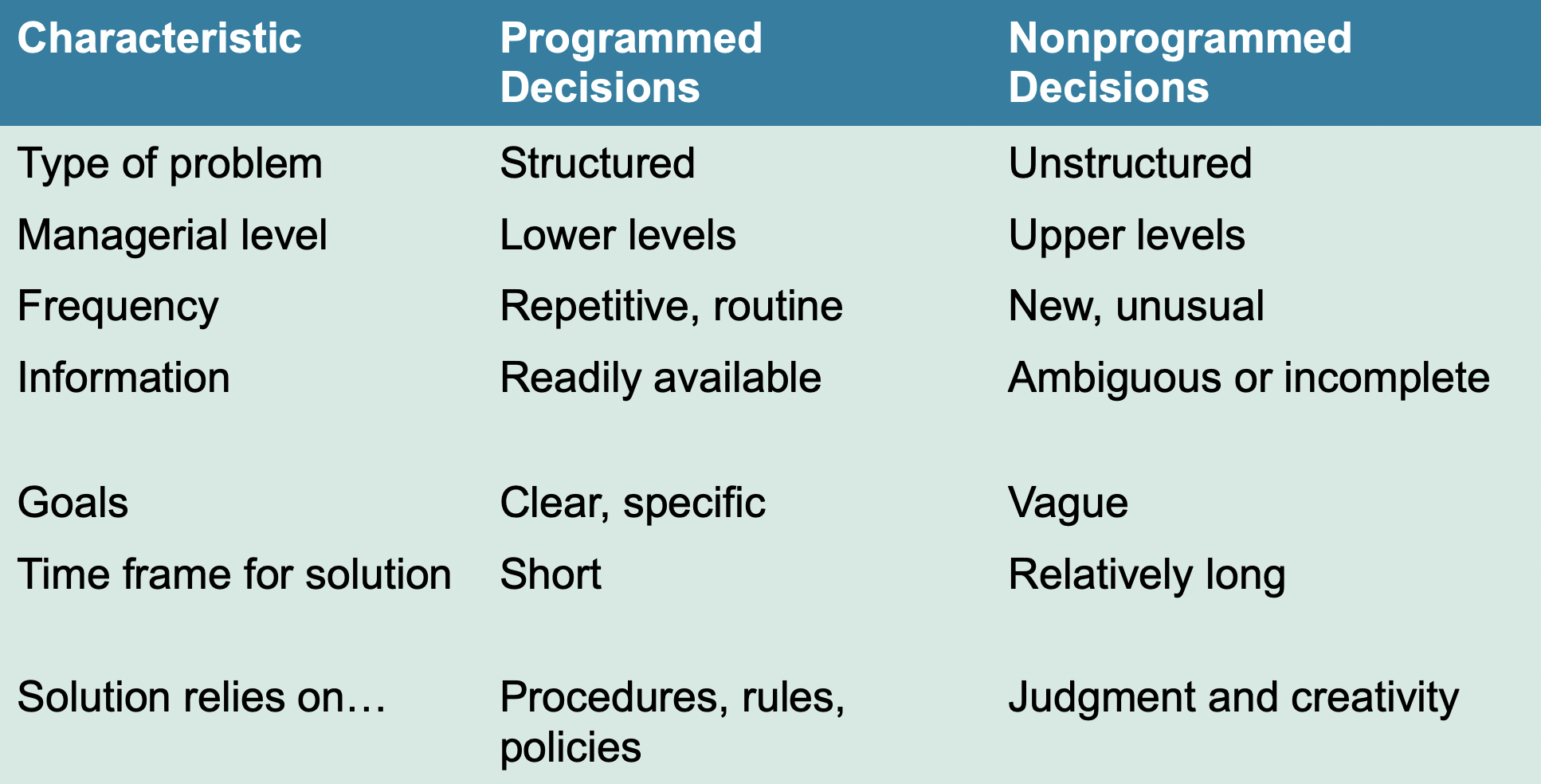
Programmed vs. Nonprogrammed decisions
Design thinking
Design thinking is a human-centered, creative problem-solving approach that focuses on understanding user needs and developing solutions that meet those needs. It's a process of iteratively empathizing with users, defining problems, ideating solutions, prototyping, and testing.
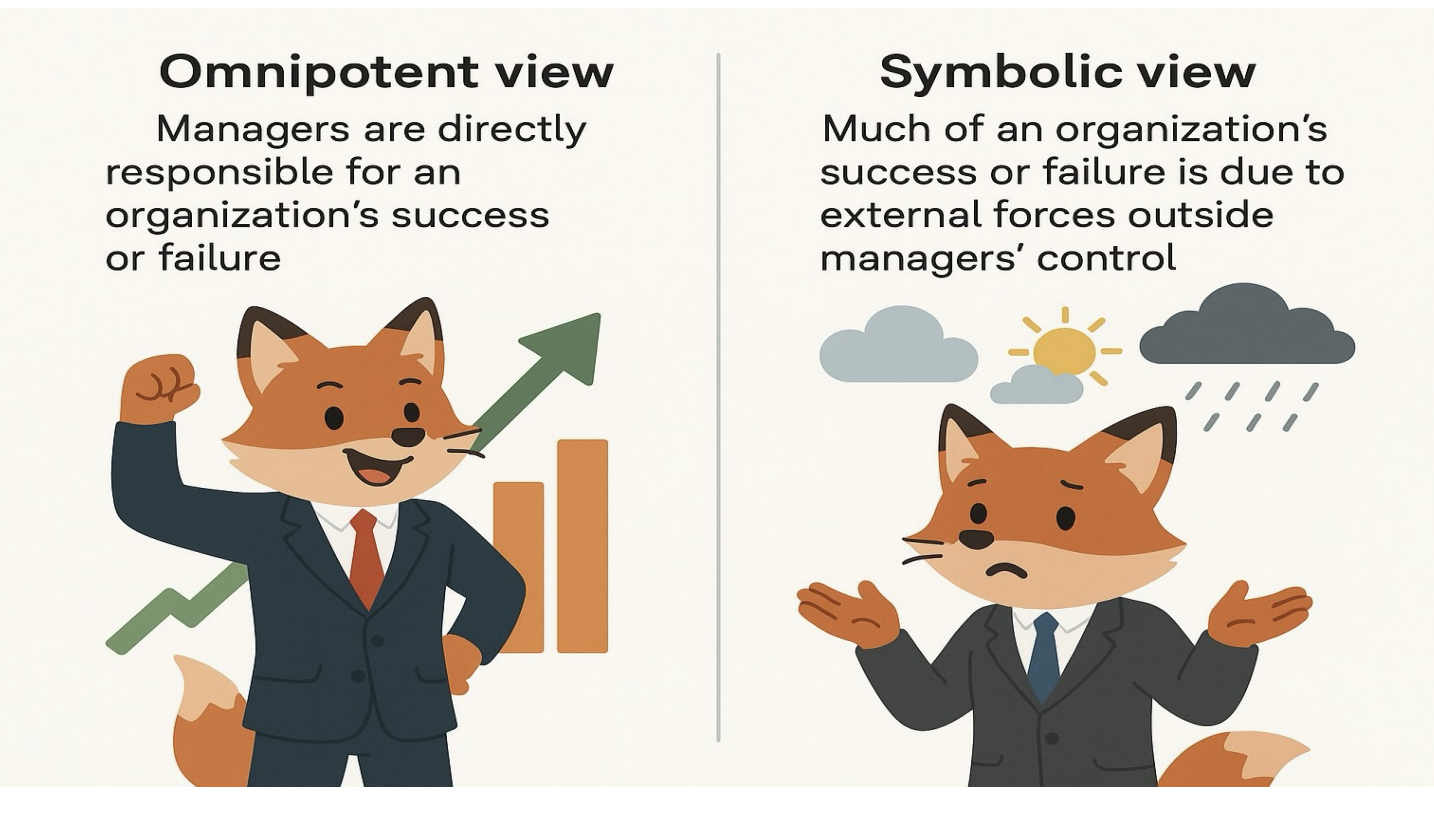
Managerial Views
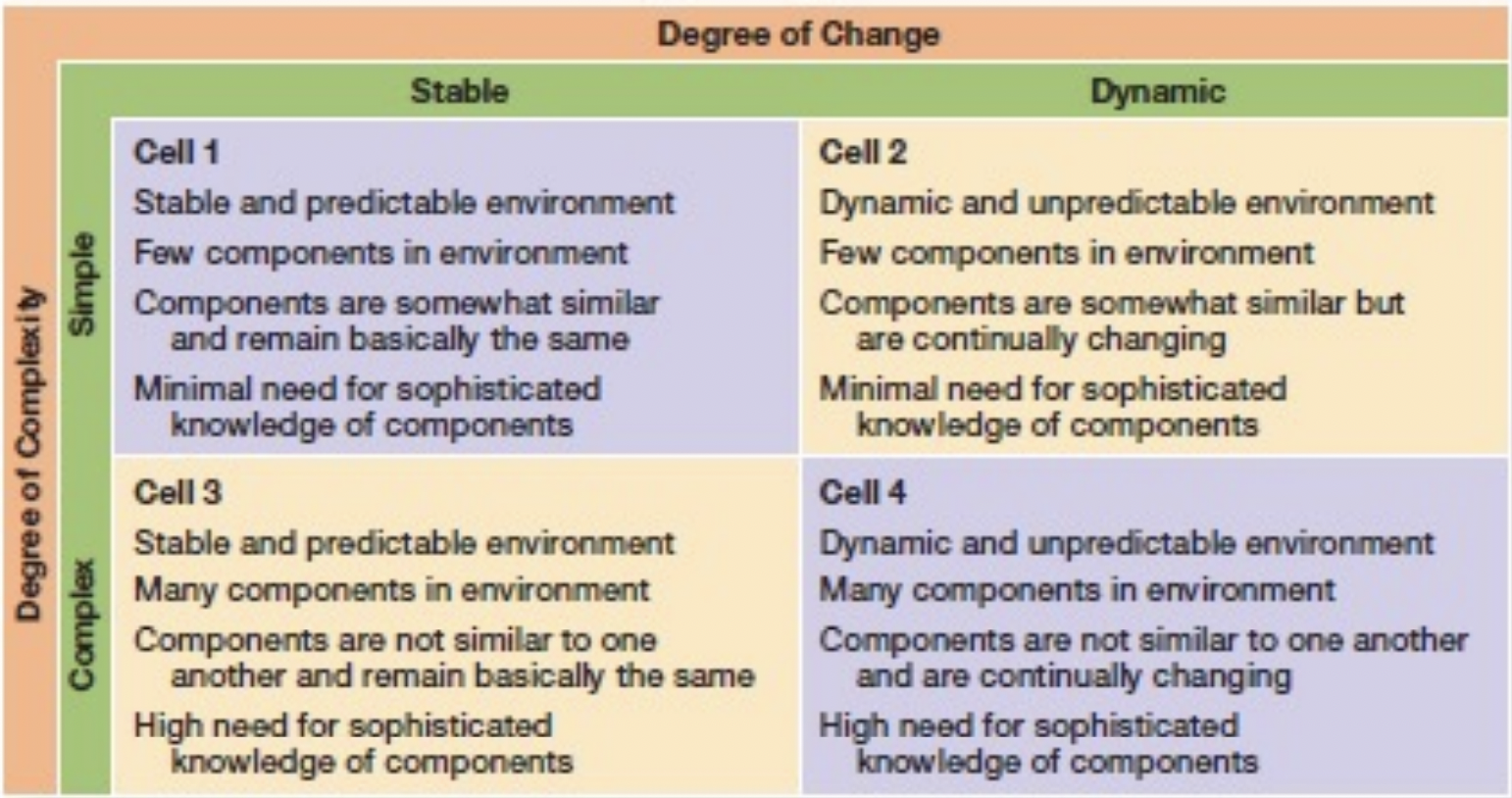
Environmental Uncertainty
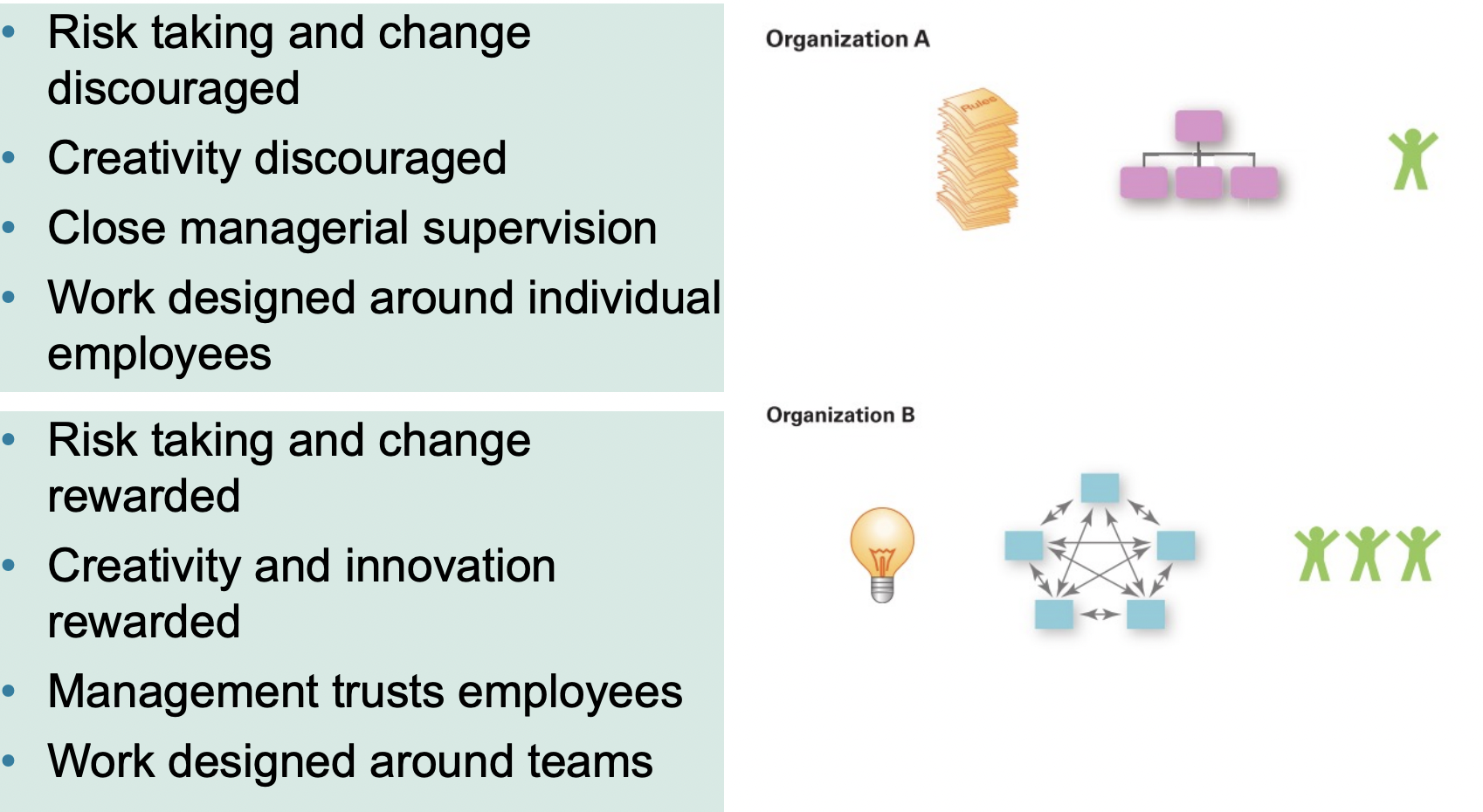
Strong vs. Weak cultures

How employees learn culture
Artifacts: Material symbols in organizations include physical elements like office layout, dress code, executive cars, corporate jets, office size, furnishings, perks (like health club memberships), fitness centers, dining facilities, and reserved parking, all of which reflect and reinforce the organization’s culture and values.
Stories: Organizations use stories to connect past events to present values and teach cultural norms.
Rituals: Repeated rituals, like ceremonies or daily meetings, reinforce key values and goals.
Language: Unique jargon and acronyms help unify members and create a shared identity.
Organizational change in Strong vs. Weak cultures
Global Attitude Conflict
• Ethnocentric: view that home country has best work practices
• Polycentric: view that managers in the host country know the best approaches
• Geocentric: world-oriented view; wants to use best practices from around the globe
Global Sourcing Dilemma
Companies often source globally to reduce costs, but this can create problems like:
Critics of globalization maintain that jobs were leaving developed high labor cost nations and flowing to cheap labor nations.
Cheap goods worldwide created wage stagnation for the middle class.
Globalization and capitalism together have increased wealth inequality.
Some groups are harmed by globalization
Multi domestic Strategy
A multidomestic strategy is when a company adapts its products, marketing, and operations to fit the specific needs and preferences of each country it operates in. It treats each market as unique and independent, rather than using one global approach.
WTO
– World Trade Organization (W T O) monitors and promotes trade relationships between foreign countries.
Transnational Organization Structure
A transnational organization—an M N C that has eliminated artificial geographical barriers
1. Global Headquarters
Sets overall strategy, ensures efficiency, maintains brand identity.
Coordinates knowledge-sharing across countries.
2. Regional or National Subsidiaries
Operate semi-independently.
Adapt products, marketing, and policies to fit local cultures, laws, and preferences.
3. Integrated Global Teams
People from different countries work together across time zones.
Collaboration is high to share best practices and innovations.
4. Matrix Structure (often used)
Employees report to both global and local managers.
Encourages balance between central control and local freedom.
Strategic Alliance Benefit
Strategic Alliance: partnership between an organization and foreign company partner(s) in which both share resources and knowledge in developing new products or building production facilities
A strategic alliance allows companies to share resources, expertise, and markets without merging, helping them enter new markets, reduce costs, innovate faster, and compete more effectively while maintaining independence.
Management Change
Organizational change: any alteration of people, structure, or technology in an organization
Change agent: someone who acts as a catalyst and mostly assumes the responsibility for managing the change process

Resistance to change
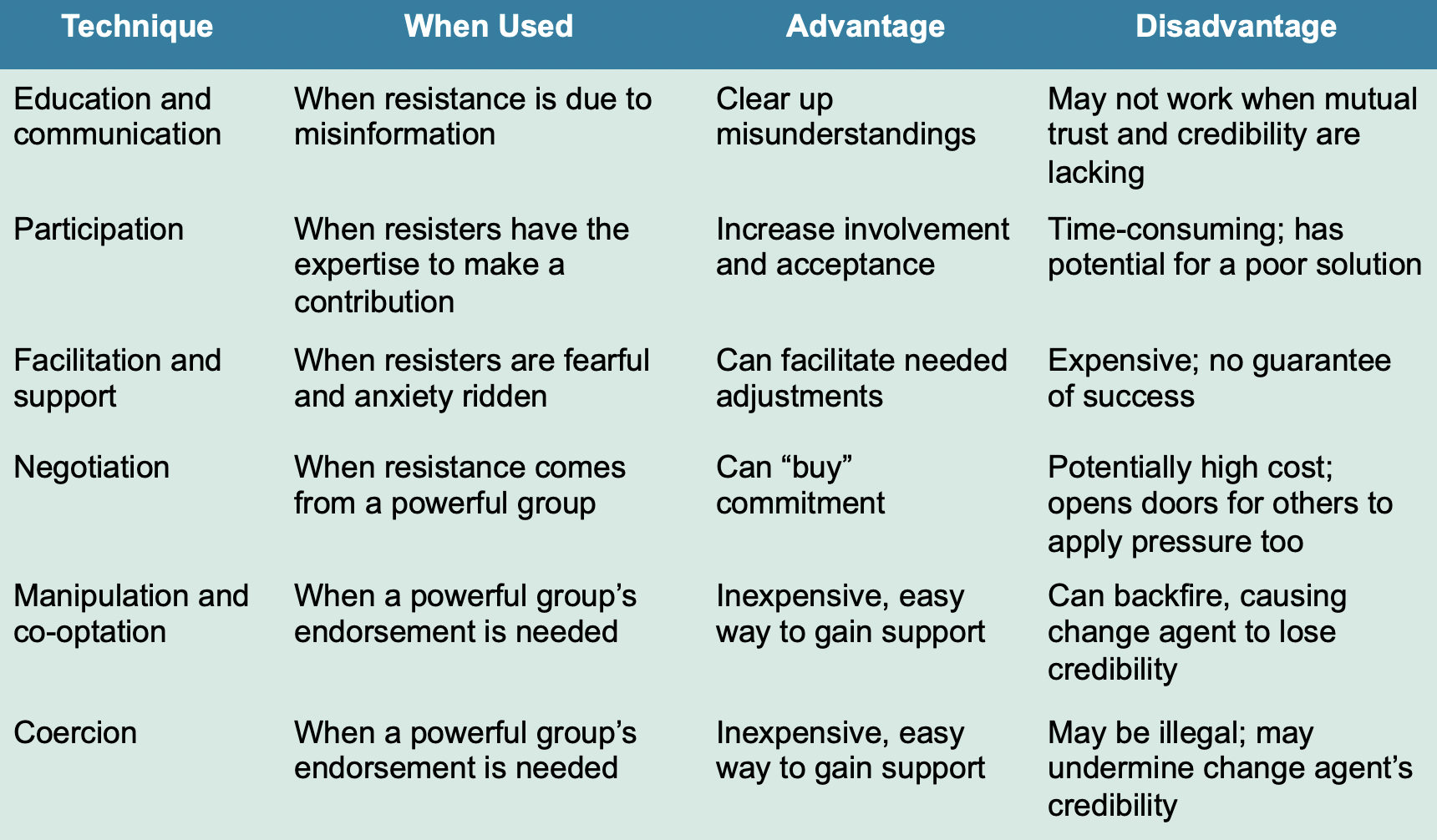
OD techniques
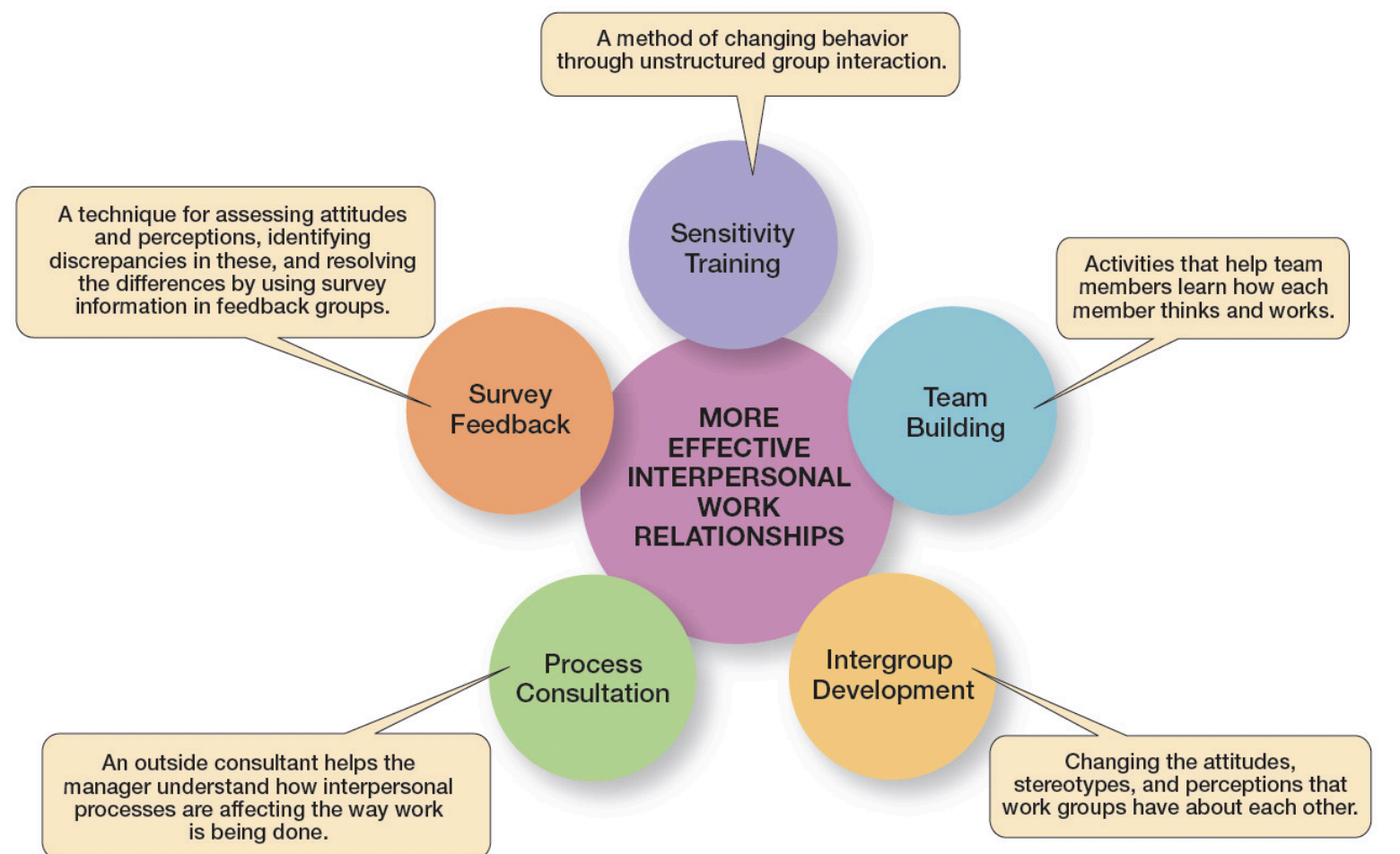
Changing an Organizations Culture
Set the tone through management behavior; promote employees who adopt new values.
Clearly specified expectations.
Shake up current subcultures through job transfers, job rotation, and/or terminations.
Attain high employee participation, gathers higher level of trust.
Lewin’s 3 step change process
Unfreeze: A company preparing to adopt a new digital sales platform starts by explaining to employees why the old system is outdated, shares performance data, and holds meetings to address fears and gather input.
Change: The company rolls out the new platform with hands-on training sessions, assigns mentors to support users, and encourages feedback to help staff adjust to the new workflow.
Refreeze: After the transition, the company updates official procedures, rewards employees who adapt quickly, and fully integrates the platform into daily operations to make it the new norm.
White water rapids metaphor
the lack of environmental stability and predictability requires that managers and organizations continually adapt and manage change actively to survive. – preparation may not be applicable
