Histology Quiz 11
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/34
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
1
New cards
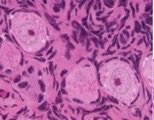
primordial
what type of follicle?
2
New cards
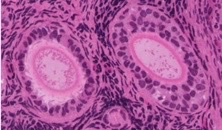
primary
what type of follicle?
3
New cards
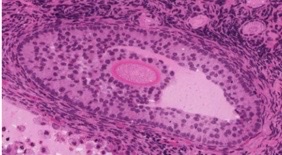
antral
what type of follicle?
4
New cards
1
how many follicles mature during each monthly cycle in humans?
5
New cards
atresia
degeneration process that other follicles undergo so only 1 dominant follicle can mature
6
New cards
corona radiata
layer of cells that surround oocyte in mature follicle and remain with oocyte during fertilization
7
New cards
antrum
grows in size in a mature follicle
8
New cards
cumulus oophorus
narrow stalk that connects the oocyte to granulosa and theca (ruptures during ovulation)
9
New cards
apoptosis of granulosa and oocyte, degeneration of follicle structure, phagocytosis
what is involved in follicular atresia?
10
New cards
mature, granulosum in tact
mature or atretic follicle? why?
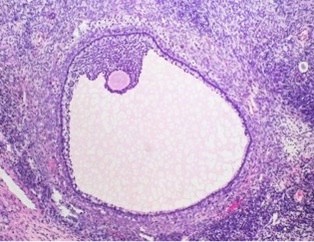
11
New cards
atretic, granulosum in damaged
mature or atretic follicle? why?
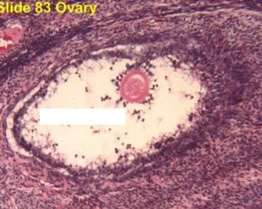
12
New cards
progesterine
hormone produced by corpus luteum that induces growth of the uterine lining in preparation for possible fertilization and embryo implantation
13
New cards
temporary endocrine structure that produces estrogens to regulate uterus
function of corpus luteum
14
New cards
granulosum and follicular theca left behind by ovulated mature oocyte
what is the corpus luteum made of?
15
New cards
corpus albicans
what does the corpus luteum degenerate into if there is no fertilization?
16
New cards
it shrinks and is converted to ovarian stromal tissue
what happens to the corpus albicans over time?
17
New cards
atretic follicle
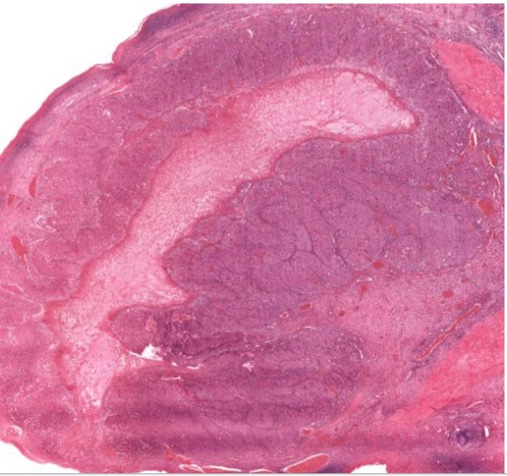
atretic follicle, corpus luteum, or corpus albicans?
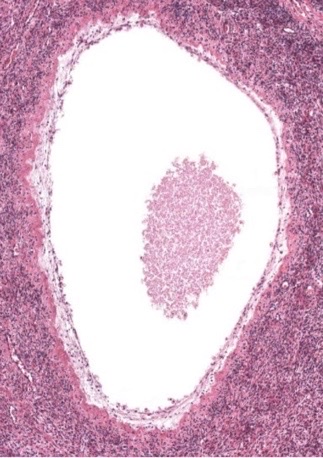
18
New cards
corpus albicans
atretic follicle, corpus luteum, or corpus albicans?
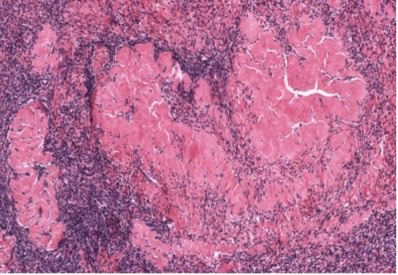
19
New cards
corpus luteum
atretic follicle, corpus luteum, or corpus albicans?
20
New cards
receive oocyte form ovary, site of fertilization, mediate movement of eggs sperm and embryos
functions of oviducts
21
New cards
simple columnar with peg cells and ciliated cells
oviduct epithelium
22
New cards
highly folded mucosa with underlying muscularis
oviduct structure
23
New cards
peg cells
– Darker staining, non-ciliated cells \n – Secretory cells that produce multiple products
24
New cards
Fluid for lumen, Metabolic support for eggs and sperm, Factors for sperm capacitation
what do peg cells produce?
25
New cards
create current for movement, capture sperm during capicitation
functions of ciliated cells
26
New cards
embryo implantation, placenta formation, muscular contractions for childbirth
functions of the uterus
27
New cards
perimetrium, myometrium, endometrium
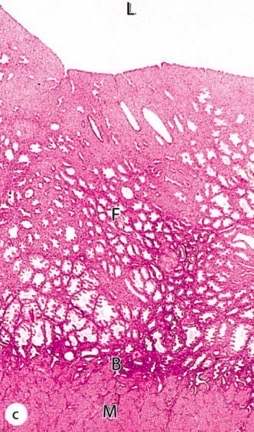
layers of the uterus (outside to inside)
28
New cards
3
how many layers/strata in the uterus myometrium?
29
New cards
outer and inner strata have parallel arrays but the middle layer has fiber bundles in many different directions
how are the myometrium fibers oriented?
30
New cards
downregulated
During pregnancy, gap junctions in the smooth muscle cells are _________ to prevent contractions
31
New cards
apical layer
“functional” endometrium layer that changes dramatically throughout the menstrual cycle
32
New cards
estrogens
what causes the changes in the endometrium during the ovarian cycle?
33
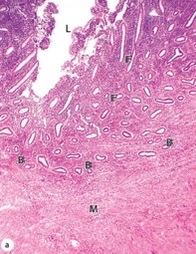
New cards
proliferative
which uterine stage?
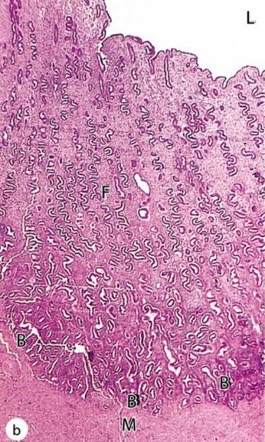
34
New cards
secretory
which uterine stage?
35
New cards
menstrual
which uterine stage?