Intro to Petroleum Engineering
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
Name the 3 Exploration Well Evaluation Techniques
Physical Samples of Underground Rocks
Core samples
Cutting samples
Well Log
Drillers log, the driller keeps a record of rock and fluid types, encountered & the time it took to drill through a particular layer
Wireline log, a sonde is lowered into wellbore at end of wireline. Sonde measures electrical, radioactive or acoustic properties of formations
Logging while drilling
Well Testing
Drill Stem Test
Wireline formation tester
Helps detect mobile hydrocarbons
Expensive due to cost of tech and rig time
What are the 5 phases of field development and their objectives
Exploration, Identifying potential reservoir
Evaluation, Identifying prospect reservoir
Development, Design and set-up facilities
Production, Maximising efficiency
Abandonment, Safety and security
What are the three types of stratigraphy and what data do they analyse?
Lithostratigraphy, Rock types
Biostratigraphy, Fossil content
Sequence stratigraphy, Arrangement or grouping of layers
What are the different types of survey’s and what do they measure
Magnetic Survey
Anomalies (slight variations) in the earth’s magnetic field due to magnetic properties of subsurface rocks
Gravity Survey
Measure anomalies in the earth’s gravitational field, due to variation in the density of sub-surface rocks
Seismic Surveys
Measure the time taken for sound waves to travel through sub-surface rocks due to variation in the density, depth and mineralogy of rocks
What are the three main parts of the drilling operation and their descriptions
Drilling top hole, High rate of penetration
Middle hole, Lower rate of penetration
Reservoir sections, Minimise formation damage
What are the criteria for starting coring
Special depth given by geologist
Increase in penetration rate, indicating porous zone
Hydrocarbon indications (visual signs of oil/gas)
Cutting showing transition from capstone to reservoir rock
What technique is used for induction Log and what information do you get from it
Tool has one source and two detectors held on callipers against the formation and a counter picks up gamma ray diffused by the formation towards the borehole. Number counted is related to number of electrons, which is related to formation density, which is used to get porosity.
What are the different types of recovery and what methods do they contain
Primary
Gas-cap
Solution-gas
Water
Gravity
Compaction
Combination
Secondary
Water injection
Gas injection
Tertiary
Near miscible gas injection
Steam-injection
What are the pressure, production and gas-oil-ratio behaviours for the solution gas mechanism
Production will result in a rapid decline in pressure; hence, low recovery is expected, 5-30% STOIIP. Gas-oil ratio starts low then rises to a maximum
What phrases refer to the phase behaviour of a gas reservoir
Wet gas
Gas-condensate
Is this statement true “Because of small thermal capacity and surface area of porous reservoir, flow processes in a reservoir occur at variable temperature”
No
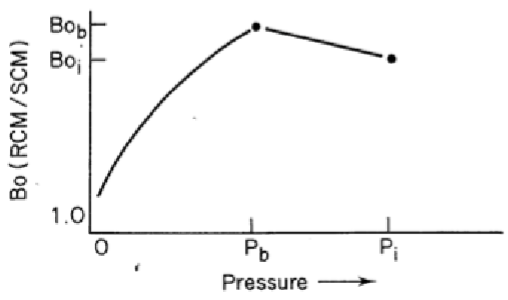
What does a typical volume factor (Bo) vs pressure profile
Trends
Above the bubble point oil expands as pressure is reduced hence Bo increases
Below the bubble point oil shrinks as gas comes out of solution therefore Bo. decreases
What assumptions can be made for Darcy’s law for single-phase flow
Laminar flow
Homogenous rock
What are parts of the phase behaviour for a single-component pure system
Vapour-Pressure line
Critical point
Tripple point
What are flow regimes that can occur in a reservoir and a key characteristic pressure behaviour for it
Semi-steady-state flow:pressure gradient is constant but abs pressure declines
Transient flow regime: When the flow starts in the well, there is an immediate reduction in pressure. This pressure perturbation moves through fluid at a rate dictated by rock permeability and fluid properties. Producing a pressure variation along the model.
What is the conceptual separation process taking place in gravity separators
Driven by density difference between the gas, oil and water phases. Gas flashes from the well-head fluid as the pressure is reduced.
Why would water separated from the field production be injected back into the oil reservoir
Reservoir pressure support
Oil sweep from injectors to producers
What does the cemented and perforated bottom-hole completion look like
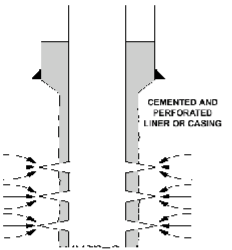
Why would cemented and perforated bottom-hole production be preferred in a heterogeneous, multi-phase saturated
Cemented & Perforated production liner/casing would be preferred in a heterogenous, multi-phase saturated reservoir because of its ability to control the zonal inflow of unwanted fluids
if the well productivity index increases what would you expect to happen to the wellbore pressure
It will increase (more pressure is required to pump fluid up well)
What are the 5 Exploration Techniques
Previous geological/geophysical data
Large collections of data
General depositional trends
Aerial and Satelite Images
Geophysical Methods
Applies physics to study subsurface geology
Measurements of earth’s magnetism, gravity and seismic vibrations to determine thickness of sediments and shape of geophysical structures
Oil and Gas Seeps
Most obvious sign
slow difficult to read
most have already been exploited
Exploration Drilling
Based on previous methods a location is selected
Data on lithology, porosity, permeability, fluid distribution and saturation evaluated to predict if resv has enough oil or gas to justify completion of exploratory well
What are the main objectives and required information for evaluation
Objectives
Determination of fluids in place
Estimation of amount of hydrocarbon and recovery factor
Information
Identification of depositional sequences, thickness and mineralogy of layers
Info relating to porosity, permeability, fluid distribution and saturation
Data on reserve and production capacity of resv
What are the objectives for an appraisal well
To delineate reservoir boundaries if exploration successful
Appraisal wells drilled in succession
Ideally intersect contacts between oil and water and oil and gas
How are the different types of rock formed and what is their porosity
Igneous
By crystallisation of molten material
They have very low or no porosity, no permeability
Metamorphic
Recrystallisation of older rocks, either by direct heating or by heating accompanied by pressure and deformation
Very low or no porosity
Sedimentary Rocks
Formed by accumulation of particles as sediment
Depends on rock texture
What is stratigraphy and the different types
The study of the history of deposition of layers deposited in a basin is called stratigraphy
Types
Rock types: Lithostratigraphy
Fossil Content: Biostratigraphy
Chemical Composition: Chemostratigraphy
Magnetic Signatures: Magnetostratigraphy
Arrangement or grouping of layers into sequences: Sequence stratigraphy
What are the types of petroleum migration and what are their definitions
Primary Migration
Expansion of sufficient amount of generated petroleum causes the source rock to fracture and allow fluid to escape
Secondary Migration
Petroleum then migrates away from source rock and through pore spaces of surrounding rocks upwards and sometimes along the beds
What is Petroleum Entrapment
Petroleum which is prevented from reaching the surface due to a ‘trap’ (Impermeable seal rock unit)
The resv seal and trap must be in place before hydrocarbon formation
What are the types of hydrocarbon traps
Stratigraphic
Formed during deposition of reservoir beds
Unconformity or Lenticular (Pinch out)
Structural
Created by tectonic processes after deposition of the resv beds
Anticline/dome, fault and salt dome plug
Combination
Formed by a combination of those during deposition and by tectonic activities
Resv could occur in an anticline that is faulted and associated with unconformity
What is the definition for reserves
Quantities of petroleum that are anticipated to be commercially recovered from accumulations from a given date forward
What are the degrees of uncertainty in reserves
Proved
Commercially recoverable from known resvs and current economic conditions and regulations (at least 90% probability)
Unproved
Probable
more likely to be recovered than not (50% probability)
Possible
Less likely to be recovered than recovered (10% probability)
What are the causes of abnormal pressure
Thermal effects
Expansion or contraction of sealed fluids in rock
Rapid burial of sediments
consisting of layers of sand and clay. Speed of burial does not allow fluids to escape from the pore space
Clay diagenesis
Montmorillonite diagenesis to illite produces water from the clay particles as they compact
Osmotic effects
via salinity differences. Clay acts as a semipermeable membrane across which water may glow if there are different salt solutions on either side of the barrier
Depletion
Production from the reservoir, natural or man-made
Geological changes
What are the pressure gradients for hydrocarbon pressure regimes
Gas: 0.08
Oil: 0.36
Water: 0.45
What are the types of electric logs
Spontaneous potential log
Record of weak electric potential that is developed naturally in the rock
Resistivity log
Sonde sends an electrical signal through the formation and relays it back to a receiver at the surface
Induction log
measures. conductivity created by a electromagnetic field
Electric log
measured is measured in uncases sections of the borehole
What are the types of non-electric log
Nuclear logs
Record natural and induced radioactivity
Gamma ray log
Neutron log
Sonic Log
Acoustic sonde transmits and receives sound waves
What factors affect porosity
Particle shape
Particle packing
Particle size distribution and arrangement
Cementing material, bugs and fractures
What is the permeability of a rock
The ease at which fluid flows through the pore structure
What assumptions are made for Darcy’s law
Steady state flow
Laminar flow
Single phase only occupying 100% of porosity
No reaction between fluid & rock
Homogenous rock
|What are methods of estimating permeability
Empirical correlation
Lab measurements
Well test data
What is wettability
The relative degree to which a fluid will spread on or coat a solid surface in the presence of other immiscible fluid
it is a function of both rocks and fluids which depends on the compositions of the fluids solid surface
a wetting phase is one which spreads over the solid and preferentially wets the solid
What are the three flow regimes and their descriptions
Instead-state or transient flow: Transient pressure data without boundary effects
Semi-steady( (pseudo-steady state): Closed no flow boundary
Steady-state: Strong aquifer support or injection wells
What are the classification of reservoir fluids
Black oil
Volatile oil
Gas-condensate
Wet gas
Dry gas
What is an FPSO and what does it have
Floating production system which is moored permanently and connected to wells by flexible risers
what it has
shape of a ship
Controls well operations
Required production & processing facilities
Crude oil storage tanks built into hull
Oil export by shuttle tanker or pipeline
No drilling