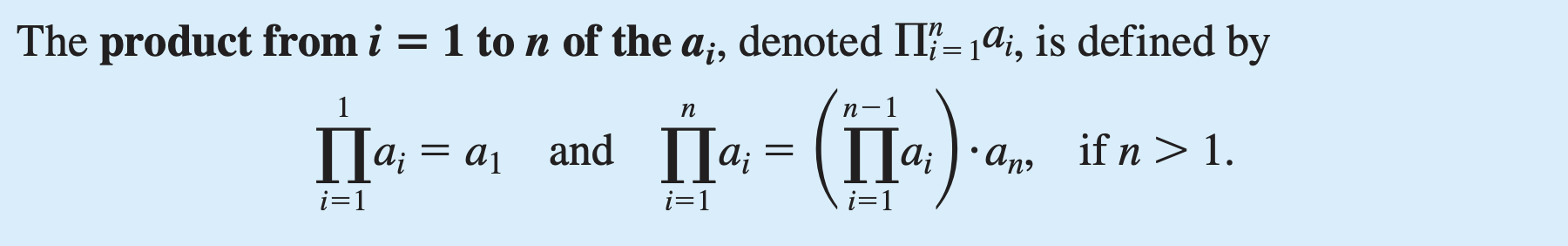Chapter 5 - Sequences, mathematical induction, and recursion
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
A function whose domain is either all the integers between two given integers or all the integers greater than or equal to a given integer. Represented as a set of elements written in a row (am, am+1, am+2, ..., an).
each individual element ak
The k in ak
A rule that shows how the values of ak depend on k.
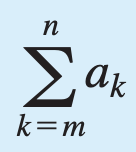
The sum of all the terms am, am+1, am+2, ..., an.
am + am+1 + am+2, ... + an.
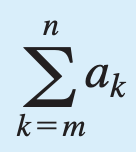
What are k, m, and n?
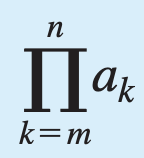
the product from k equals m to n of a-sub-k (if m and n are integers and m ≤ n).
The product from k equals m to n of a-sub-k
The product of all the terms am, am+1, am+2, ... , an.
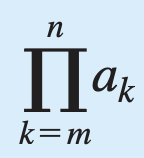
We write
am * am+1 * am+2 * ...* an
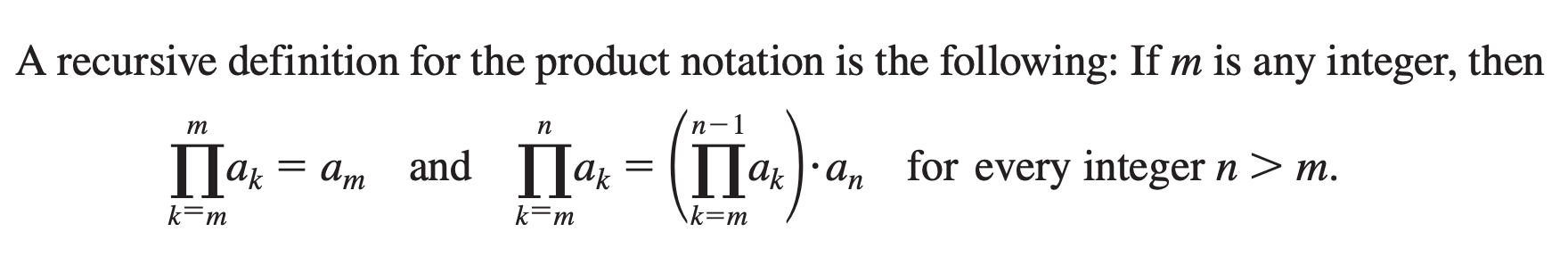
Recursive definition for the product notation
The summation from i = 1 to n of the ai
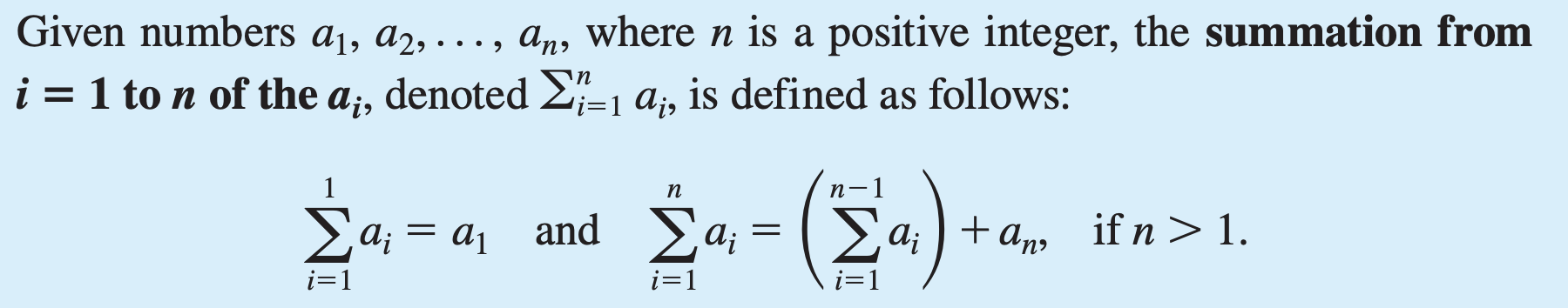
The product from i = 1 to n of the ai