PAC555 Clinical Applications Quiz I
1/117
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
118 Terms
The major goals of clinical anatomy applications are to discuss the relationships between human anatomy and human __________ as well as to correlate anatomy with clinical __________
Disease; Diagnostic imaging
Diagnostic imaging can allow for evaluation of multiple __________ and can allow for simultaneous evaluation of neurological, vascular, and __________ etiologies of a complaint
Organ systems; Musculoskeletal
Preliminary abnormal findings on imaging at the point of care may help to __________ patients who need care most in communities with limited access to medical specialists
Triage
__________ accidentally discovered X-rays in his laboratory and was the first to use X-rays to visualize image of human __________. He was awarded a Novel prize in physics in 1901
Wilhem Roentgen (Germany, 1895); Bones
__________ developed prototype fluoroscope intended for use in the home. However, he abandoned his work with X-rays after his assistant, Clarence Dally, died of cancer related to radiation exposure in 1904
Thomas Edison (1896)
__________ discovered the radioactive compound radium chloride. She subsequently purified radium and discovered __________
Marie Curie (1989); Polonium
__________ is the only person to win a Nobel prize in two different scientific fields— Physics in 1903 and Chemistry in 1911
Marie Curie
Marie Curie died of __________ due to radiation exposure and is buried in a lead-lined grave due to radioactivity
Aplastic anemia
Radium was a prime form of medical misinformation in the mid 1900s and was used to promote male __________ health and was a __________ holder
Sexual; Cigarette
__________ was an Austrian psychiatrist and neurologist known for the first clinical use of ultrasound
Karl Dussik (1942)
Ultrasound does not pass through __________ and is therefore no longer used for brain imaging
Bone
__________ worked in EMI Laboratories in Britain and was noted to have developed the first CT scan. He was awarded a Nobel Prize in Medicine in 1979
Godfrey Hounsfield (1971)
What are the 3 fates of ionizing radiation in diagnostic imaging?
It can be transmitted, absorbed, or scattered
Transmitted Radiation…
Passes through the patient (creates image)
Absorbed Radiation…
Energy from x-rays is transferred to the patient’s tissues (exposes patient to radiation)
Scattered Radiation…
Changes its path away from the patient (exposes healthcare worker to radiation)
How do we measure radiation exposure?
Via absorbed doses, equivalent doses, and effect doses
An absorbed dose refers to energy deposited in __________ of tissue
1 kilogram
The SI unit of an absorbed dose is __________
The gray (Gy)
1 Gy = __________ rad
100 rad
Absorbed doses measure the __________ of energy, not the biological effect
Amount
Equivalent doses are an adjustment for biological effect caused by different types of __________
Radiation— not all forms of radiation do the same amount of damage even if the absorbed energy is the same
Alpha particles are approximately __________ times more damaging than X-rays, gamma rays, or electrons
20
Equivalent dose uses a __________ that corrects for the different biological effects of different types of radiation
Coefficient
The SI unit for equivalent dose is __________
Sievert (Sv)
1 Sv = __________ rem
100 rem
Effective doses are an adjustment for biological __________ caused by radiation in different tissues, depending upon the tissue exposed
Effects
Some tissues are more susceptible to the effects of __________ radiation than others
Ionizing
Radiation exposure to the bone marrow or endocrine tissue is much more biologically significant than radiation to the __________
Skin
Effective dose uses a __________ that corrects for the different biological effects of radiation on different tissues
Coefficient
The SI unit for effective dose is __________
Sievert (Sv)
Ionizing radiation can damage any cellular __________, either by directly disrupting bonds between atoms or by generating __________ which affect structure
Macromolecule; Free radicals
The most concerning biological effect of ionizing radiation is damage to __________, which may result in cancers or heritable mutations
DNA
What are the two groups of biological effects of ionizing radiation?
Deterministic effects + stochastic effects
Deterministic effects refers to direct __________ damage by radiation which exceeds physiological mechanisms for repair
Macromolecule
In deterministic effects, damage occurs when a threshold is met. __________ and __________ increase with increasing dose
Probability; Severity
Deterministic effects require a __________ dose (usually > .5 Gy). Most diagnostic procedures do not reach the threshold dose of these effects
High
Stochastic effects refer to probability increases with increasing __________ dose, but severity is independent of dose. These may occur at any level of exposure
Cumulative
Stochastic effects are usually due to DNA damage by __________
Free radicals
Many diagnostic procedures involving radiation exposure over the lifespan may result in adverse __________ effects of radiation
Stochastic
Doses as low as __________ mSv statistically increase risk of developing cancer
10 mSv
__________ refers to the principle of keeping radiation doses as low as reasonably achievable to avoid stochastic effects
ALARA
ALARA stands for…
As Low As Reasonably Achievable
What are the three ways to reduce external radiation exposure?
Keep distance, place something heavy in between (shielding), and shorten time while being close to radioactive materials
The simplest form of diagnostic imaging is __________
X-ray
X-ray requires two elements— what are they?
An x-Ray generator and a photosensitive surface that detects X-rays passing through the tissue
An X-ray generator emits radiation only when __________ and is not radioactive on its own
Energized
A photosensitive surface is either __________ or an electronic detector
Film
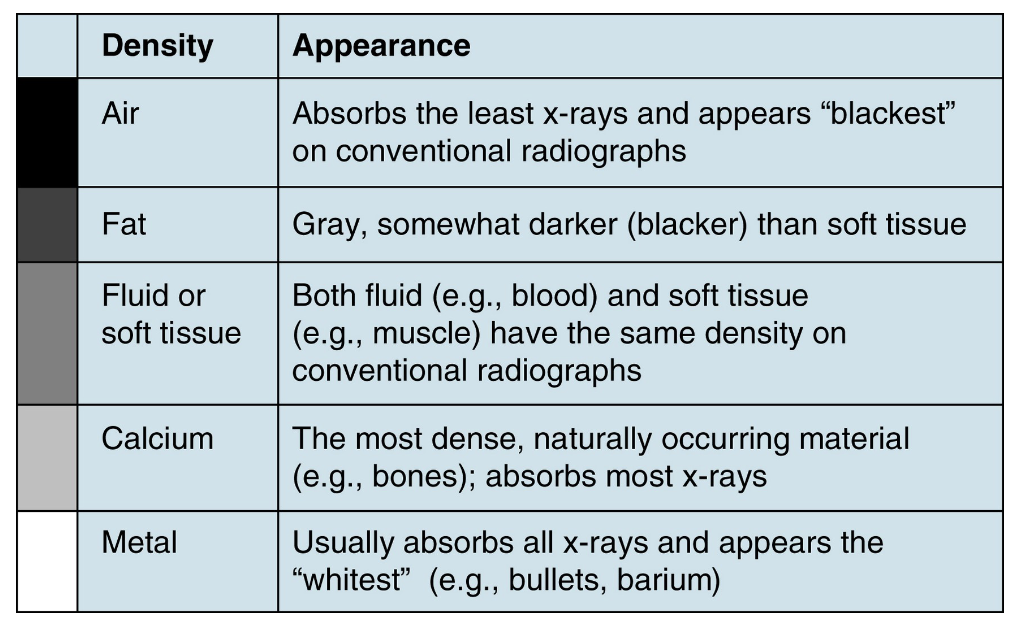
X-rays show 5 basic densities based upon the amount of radiation that is absorbed through the material- what are they?
Air, Fat, Fluid or soft tissue, Calcium, and Metal
On an x-ray, __________ appears black and absorbs the least x-rays on conventional radiographs
Air
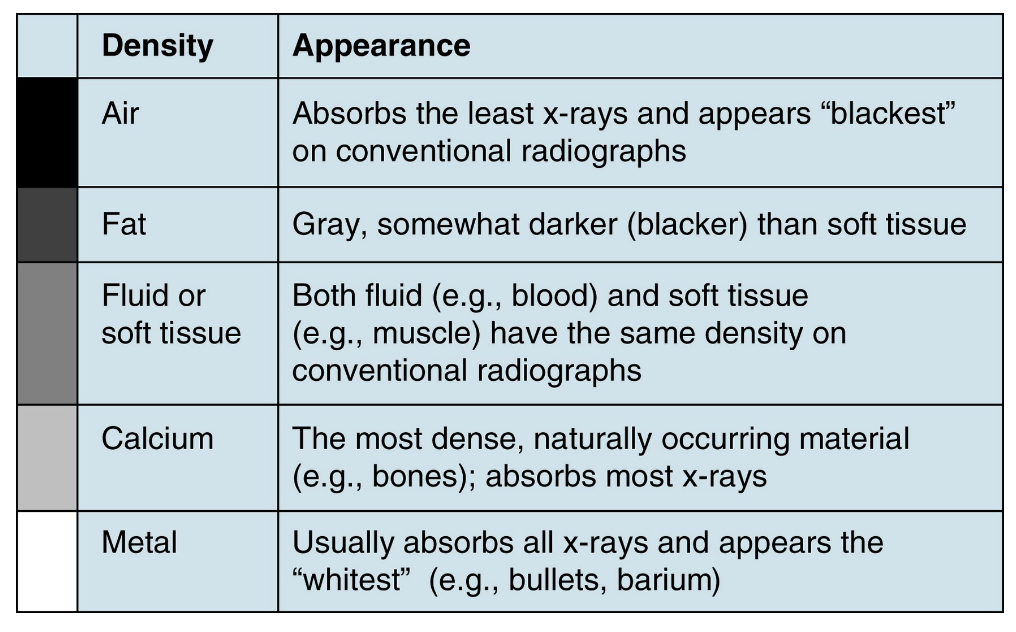
On an x-ray, __________ is gray, somewhat darker than soft tissue
Fat
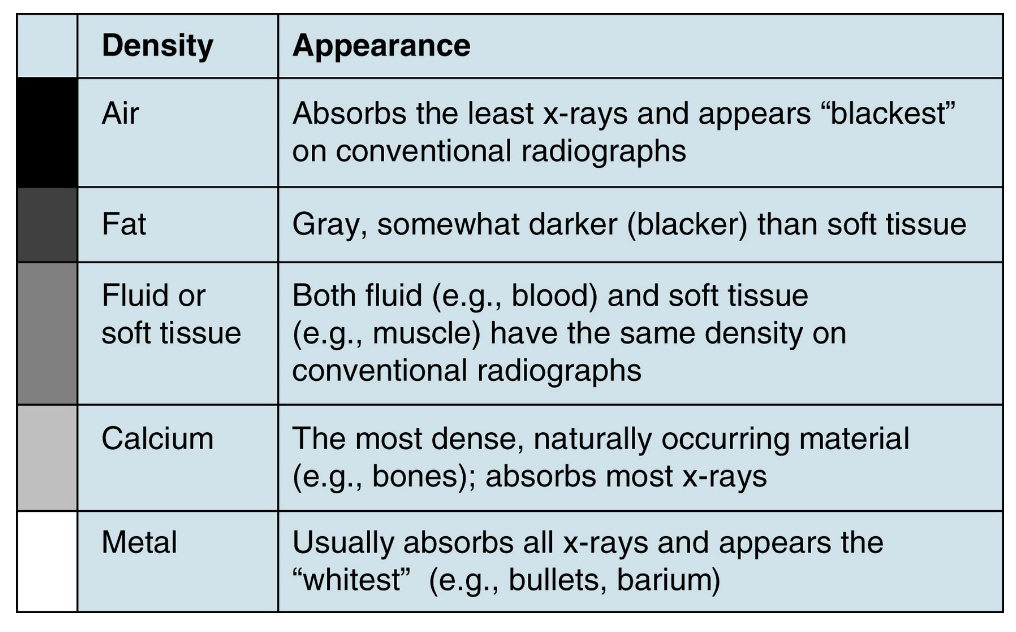
On an x-ray, __________ appears medium-gray
Fluid or soft tissue
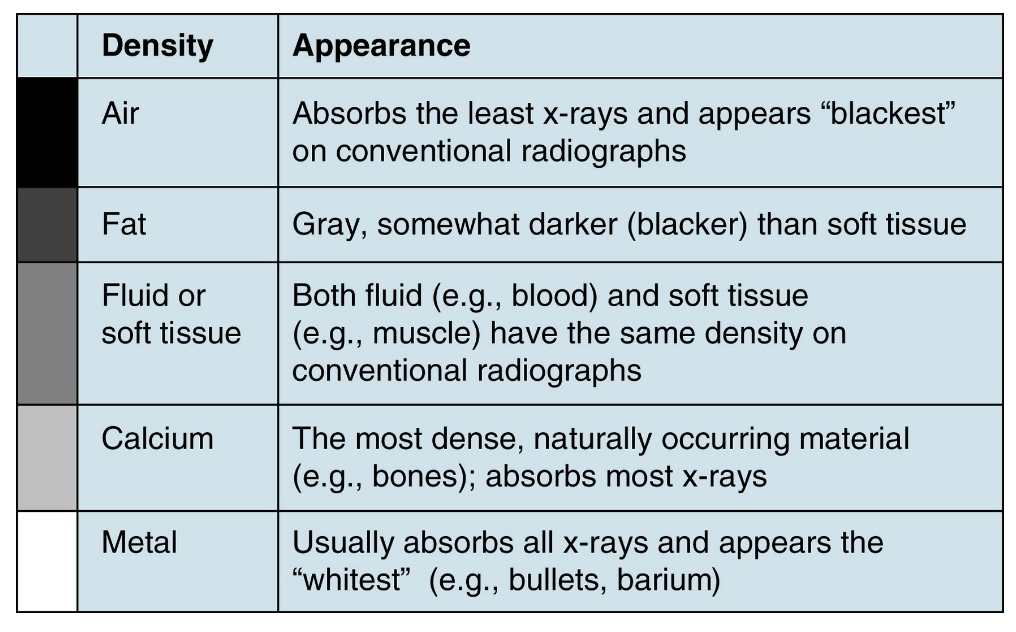
__________ and __________ have the same density on conventional radiographs
Fluid (e.g. blood); Soft tissue (e.g. muscle)
On an x-ray, __________ is the most dense, naturally occurring material and absorbs the most x-rays. It appears light gray
Calcium
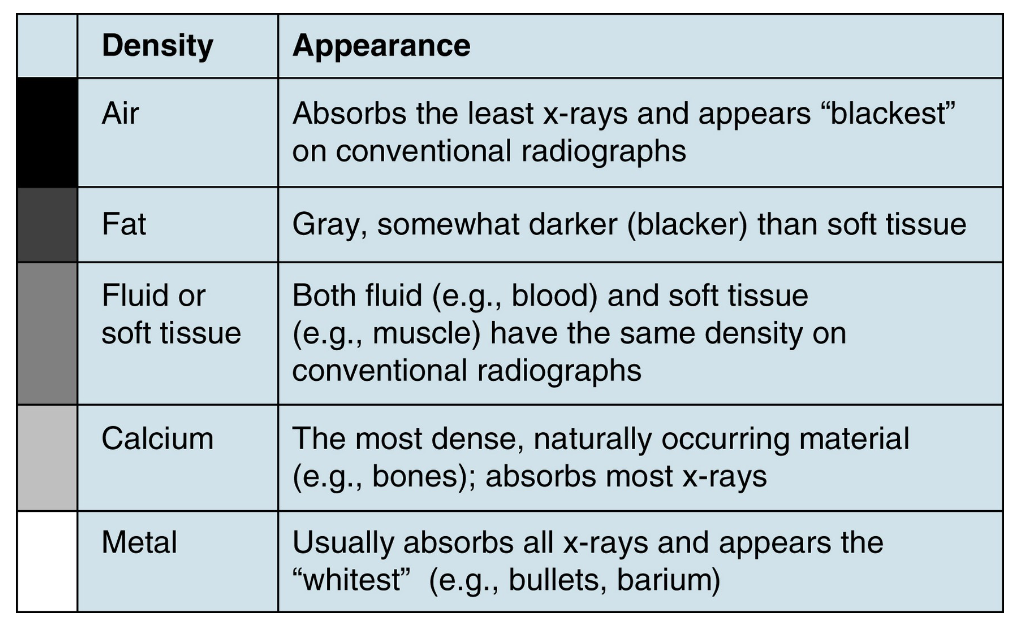
On an x-ray, __________ usually absorbs all x-rays and appears the whitest
Metal
What are the advantages of x-ray? (3)
-Relatively quick
-Inexpensive
-Semi-portable (can be done at bedside in hospital or with mobile imaging unit)
What are the disadvantages of x-ray? (5)
-Requires ionizing radiation
-Limited range of density (only 5)
-Reduces 3D structure to 2D image (usually need to obtain at least two images)
-Acquiring images usually requires a licensed X-ray tech or special license for the provider
-Is a snapshot in time— does not show change
__________ is essentially a “x-ray video”
Fluoroscopy
Fluoroscopy uses ionizing radiation to visualize events in the body in __________
Real-time
Fluoroscopy can be used to guide invasive procedures as the camera and table __________ freely to obtain the best projection
Move
Computed Tomography (CT) uses __________ to obtain serial images through various regions of the body
X-rays
In a CT, the x-ray source and detectors are mounted on a __________ that rotates around the patient
Gantry
What are the advantages of CT over conventional x-ray? (3)
-Can quickly obtain images through large volumes of body
-Processed via computer algorithms that allow for better differentiation between tissue densities
-Can be post-processed into 3D reconstructions to allow for better visualization
CTs can be considered as a __________— a 2D image depicted by the computer as a single pixel in an image matrix
Slice
CT “slices” have a discrete __________, so each pixel corresponds to a volume of space in the body, This volume of space is called a __________
Thickness; Voxel
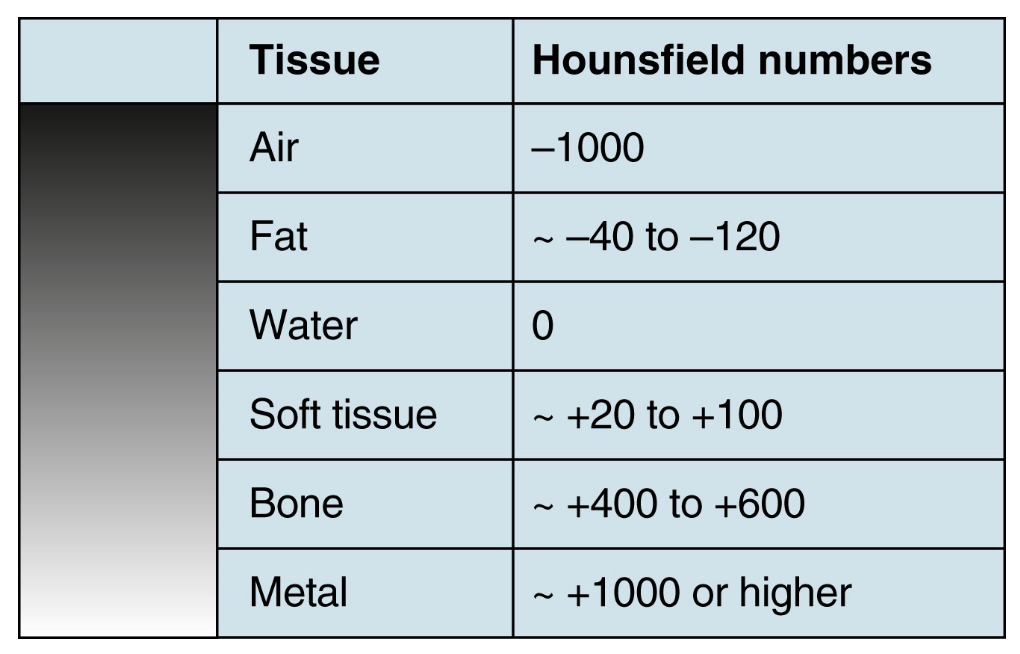
In CT, each voxel is assigned a specific numerical value based on its density. This value is called the __________ unit
Hounsfield unit
Structures that are more dense have a higher __________ and will have more positive Hounsfield units
Attenuation
Structures which are less dense have a lower __________ and will have more negative Hounsfield units
Attenuation
Like conventional X-ray, __________ structures appear white and __________ structures appear black
More dense; Less dense
What are the 6 densities measured in CT and what are their Hounsfield numbers?
What is Window Level (WL)?
Hounsfield unit value in the center of the window width
What is Window Width (WW)?
Range of Hounsfield units displayed
CT images are obtained in one or more of 3 imaging planes. What are they and what do they divide?
Axial: Divides the body into upper and lower sections
Sagittal: Divides the body into right and left sections
Coronal: Divide the body into anterior and posterior sections
What are the advantages of CT? (4)
-Expanded gray scale allows for greater ability to differentiate between various tissue densities
-Widely available
-Rapid
-Ability to created 3D image reconstruction
What are the disadvantages of CT? (3)
-Utilizes ionizing radiation at a higher dose than conventional x-ray
-Equipment and staffing is expensive
-More complex to interpret
Ultrasound probes (or transducers) contain a __________ that converts electrical signals into sound waves, and vise-versa
Piezoelectric crystal
__________ allows a single transducer to both transmit sound waves into a tissue and receive the sound waves that reflected back
Piezoelectric crystal
True or False: The ultrasound transducer can transmit and listen at the same time
False- it cannot
Ultrasound waves are sent in __________, followed by a pause to “listen” to returning sound waves as they are reflected off tissue surfaces
Pulses
The sound waves transmitted into tissue are described by their…
Wavelength, frequency, and amplitude
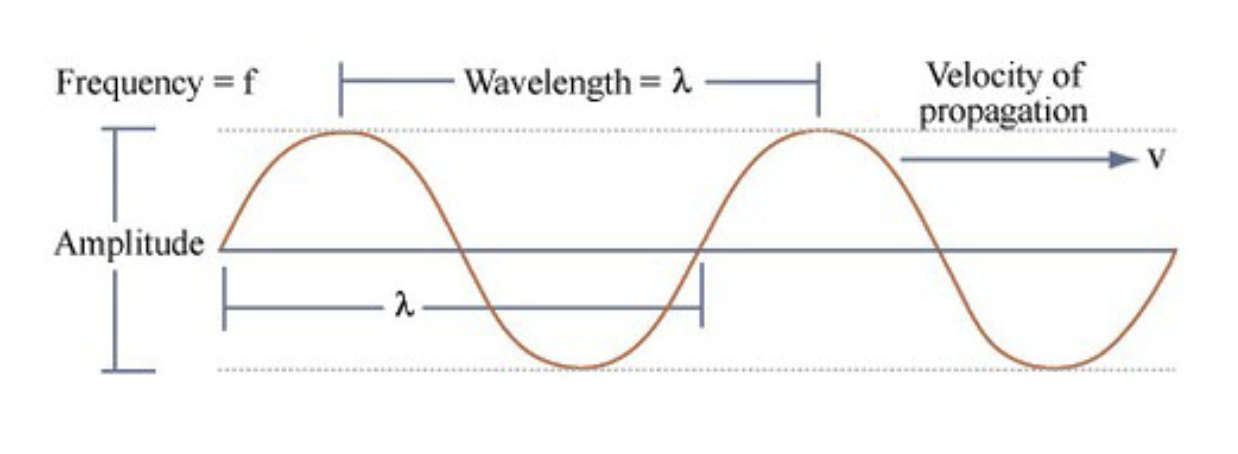
In ultrasound, c = __________
c= speed of sound (a constant for a specific tissue)
In ultrasound, λ = __________
wavelength of the transmitted wave
In ultrasound, f = __________
Frequency of the transmitted wave
High frequencies (low wavelengths) provide __________ resolution, but at the expense of being able to see deeper structures
High
Low frequencies allow imaging of __________ structures and obese patients, but at the expense of resolution
Deep
__________ is a property of the ultrasound transducer that cannot be easily adjusted with ultrasound machine controls
Frequency
The appearances of an ultrasound image depends on the type of __________ used
Transducer
__________ transducers are used for vascular and musculoskeletal applications and produce a rectangular image
Linear
__________ transducers (used for abdominal imaging) and __________ transducers (used for cardiac imaging) produce a cone-shaped image known as sector format
Curvilinear; Phased array
In a sector format image, the narrow part of the cone-shaped image is __________ to the ultrasound probe
Closest
The portion of the image nearest the ultrasound probe is called the __________
Near field
The portion of the image furthest from the ultrasound probe is called the __________
Far field
Areas between the near field and far field are called the __________
Mid field
Anechoic:
Completely black, often a fluid-filled structure (vessel or cyst). Occurs due to no echo
Hypoechoic:
Darker than surrounding tissues
Isoechoic:
Same color/appearance as surrounding tissues
Hyperechoic:
Brighter than surrounding tissues
What are the advantages of ultrasound? (5)
-Portable
-Allows visualization of physiology in real time
-Extremely safe (no ionizing radiation)
-Safe for children + pregnant patients
-Can be used for procedure guidance
What are the disadvantages of ultrasound? (3)
-Cannot penetrate bones or air
-Image quality is suboptimal in obese patients
-Image acquisition requires training and practice
__________ makes use of the magnetic properties of hydrogen atoms to generate images
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)