Task #1 Entire Deck
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/107
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
108 Terms
1
New cards
Crimes against the person
crimes that direct violence or the threat of violence against others (assault)
2
New cards
crimes against the sovereign
killing the king
3
New cards
driving offences
Offences that involve breaking the rules of the road, such as speeding or not wearing a seatbelt
4
New cards
preliminary offences
Attempts, conspiracy
5
New cards
victimless crimes
violations of law in which there are no obvious victims (drug use)
6
New cards
economic crimes
an act committed in violation of the criminal law for the purpose of monetary gain and financial benefits (money laundering)
7
New cards
Public order offences
Acts that are deemed to disturb the public order in some way e.g. indecent language or behaviour
8
New cards
Regulatory offences
Breach of water restrictions, fire restrictions or public transport rules
9
New cards
doli incapax
A Latin term meaning "incapable of wrong"; the presumption that a child under 10 years of age cannot be held legally responsible for his or her actions and cannot be guilty of a criminal or civil offence
10
New cards
what is the minimum age of responsibility in australia
10
11
New cards
doli incapax for 10-13 yr olds
PROSECUTION must prove child has criminal intent and knew the law
12
New cards
doli incapax for 14-18 yr olds
They are deemed old enough to know their actions are wrong, but they are still offered protection in multiple ways under the law.
13
New cards
Actus Reus
'a guilty act'; the physical element of a crime
14
New cards
mens rea
criminal intent (guilty mind), fault elements
15
New cards
physical elements
voluntariness, omission. NO MENTAL IS TAKEN INTO ACCOUNT
16
New cards
Voluntariness
whether it was your decision or not (muscle spam, sleepwalking are INVOLUNTARY)
17
New cards
omission
not doing something that should have been done (feeding children)
18
New cards
fault elements (from highest to lowest level of severity)
intent, recklessness, negligence
19
New cards
Intent
intention or purpose (meant to rob a bank)
20
New cards
Recklessness
The state of being aware that a risk does or will exist and nevertheless acting in a way that consciously disregards this risk. Reasonably forseeable (driving with eyes closed)
21
New cards
Negligence
unknown consequence, but the result was so extreme it's a crime. (going to a country w/h a law about all boys wearing blue shirts, but tourist doesn't since they didn't know about law and gets arrested)
22
New cards
Common Law
made through judicial decisions; based on precedent
23
New cards
precedent
judges follow the other ruling judges have made in similar cases
24
New cards
Statute Law
Law made by parliament; introduced in a bill, then (if passed) becomes an act
25
New cards
crime
an act or omission against the community at large, which is punishable by the state; an act society has deemed to be criminal
26
New cards
context for crime
social and economic factors - culture, history, religion, political systems, social attitudes
27
New cards
perspectives
concepts on morality change geographically over time
28
New cards
Stakeholders
people/groups who are affected by the law and have interests in the issue
29
New cards
Law reform
the process of constantly updating and changing the law so it remains relevant and effective
30
New cards
Law Reform Process
find the problem, consults with stakeholders, consults with community, try to fix problems
31
New cards
Criminal law includes
investigation, enforcement, prosecution, defence, criminal trial, sentencing, punishment
32
New cards
Criminal law is concerned with
a wrong against the public as a whole
33
New cards
criminal law is about crimes
against a person, state or property
34
New cards
prosecution
the state or crown
35
New cards
police and/or director of public prosecution
prosecute offender in court parties
36
New cards
offender
a person who commits a crime; the accused or defendant
37
New cards
what is the standard of proof
The prosecution must prove that the accused is guilty beyond reasonable doubt
38
New cards
accused
a person officially charged with a crime
39
New cards
prosecute
(v.) to bring before a court of law for trial; to carry out
40
New cards
crown
state party that commences a criminal action in a court of law
41
New cards
Actus Reus
Criminal conduct- specifically, intentional or criminally negligent (reckless) action or inaction that causes harm.
42
New cards
Mens Rea
the intention or knowledge of wrongdoing that constitutes part of a crime, as opposed to the action or conduct of the accused.
43
New cards
Do all crimes require mens rea?
no, speeding doesn't
44
New cards
are there various levels of actus rea?
yes - murder
45
New cards
physical elements
these are the elements that are tangible or can be visually seen.
46
New cards
fault element
intention, recklessness
47
New cards
Summary offence
A minor (less serious) criminal offence that can be heard in a Magistrates' Court without a jury.
48
New cards
Indictable offence
a serious offence generally heard before a judge and a jury
49
New cards
Parties to a crime
All those who take part in the commission of a crime, including those who aid and abet and are therefore criminally liable for the offense.
50
New cards
Principal in the first degree
person who actually commits the act, likely to recieve the highest sentence
51
New cards
An example of principal in the first degree
in an armed robbery, this is the person who pointed the gun and stole the money
52
New cards
Principal in the second degree
A person who was present at the crime scene and who aided, abetted, counseled, or encouraged the principal. May be given an lesser sentence (depending on circumstance)
53
New cards
Principle in the second degree example
in an armed robbery, this can be the lookout
54
New cards
Accessory before the fact
A person who orders a crime or helps the principal commit the crime but who is not present during the crime
55
New cards
Accessory after the fact
A person, who, knowing a crime has been committed, helps the principal, or an accomplice avoid capture or helps them escape
56
New cards
Accessory after the fact example
Driving getaway car, disposing of evidence
57
New cards
Ratify
sign or give formal consent to (a treaty, contract, or agreement), making it officially valid.
58
New cards
Constitution
outlines the rules for the government body of a nation; broad principles not specific rules
59
New cards
How do you change the constitution?
referendum - all people of voting age must vote, and they must get a majority yes in the vote and majority in states
60
New cards
Rule of Law
No one is above the law and it applies to everyone. A fundamental law
61
New cards
Separation of Powers
Constitutional division of powers among the legislative, executive, and judicial branches, with the legislative branch making law, the executive applying and enforcing the law, and the judiciary interpreting the law
62
New cards
Checks and Balances
A system that allows each branch of government to limit the powers of the other branches in order to prevent abuse of power
63
New cards
3 powers of government
Legislative, Executive, Judicial
64
New cards
3 powers of government are set in
the constitution
65
New cards
Constitutional Monarchy
A King or Queen is the official head of state but power is limited by a constitution.
66
New cards
who is the king represented by
governor general
67
New cards
Governer General
Represents the Queen in Australia
68
New cards
what does the governor general do
appoints federal judges, commander-in-chief of defence forces
69
New cards
Legislative Branch
the branch of government that makes and amends the laws; parliment
70
New cards
Who is in the legislative branch?
Senate and House of Representatives
71
New cards
Executive Branch
puts law into action; implements laws, present bills
72
New cards
Who is in the Executive Branch?
PM and cabinet, government departments
73
New cards
Cabinet
group of officials who head government departments and advise the PM - corruption is an option
74
New cards
Judiciary Branch
Interprets the laws
75
New cards
Who is in the Judiciary branch?
federal courts and high court
76
New cards
Judicial Review
Allows the court to determine the constitutionality of laws
77
New cards
judicial independence
insulating judges from the need to be accountable to voters or elected officials so that they can make impartial decisions based on the law
78
New cards
Drukheim
wrote anomie
79
New cards
Anomie
a sense of aimlessness or despair that arises when we can no longer reasonably expect life to be predictable; too little social regulation; normlessness
80
New cards
Anomie requires
rules and order to function happily within society
81
New cards
anomie example
rapid inequality, structured racism, mass wealth, rapid political change (with social upheaval), class divides, significant personal trauma, major economic crisis
82
New cards
what does anomie say about why crimes are committed
an individual's lack of belonging in society can lead to deviant/criminal behaviour
83
New cards
What did Foucault write
Discipline and Punish
84
New cards
what is discipline and punish
police, judges etc are above normal society, power is used for control, there is no rehabilitation
85
New cards
retribution
a repayment; a deserved punishment 'an eye for an eye'
86
New cards
Incapacitation
an approach to punishment that seeks to protect society from criminals by imprisoning or executing them
87
New cards
who wrote carcere e fabbrica
melossi and pavarini - 'The prison and the factory' in english
88
New cards
carcere e fabbrica
calls for a reconsideration of mass imprisonment to better reflect social change - why prison?
89
New cards
Minister of Education is a member of the….
executive
90
New cards
What does not relate to the fault elements of crime?
omission
91
New cards
What must be proved when prosecuting a strict liability offence?
actus reus
92
New cards
strict liability offence
Strict liability offences are offences which do not require proof that you intended to commit the crime. INDIVIDUAL
93
New cards
strict liability offences example
speeding, drink driving and drug driving.
94
New cards
Foucault argued that the criminal justice system was organised with the primary aim of:
maximising social control
95
New cards
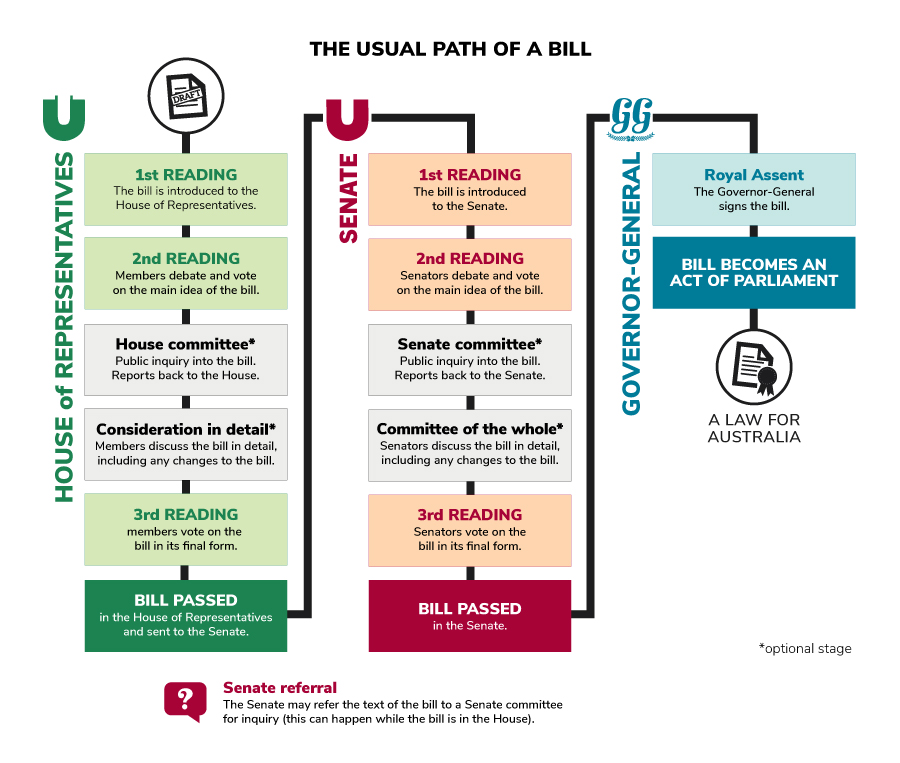
Which of the following statements about the federal legislative process is not true?
Only members of the governing party can introduce bills to the House of Representatives.
96
New cards
What are some true statements about the federal legislative process?
1. The Governor General must provide royal assent for a bill to become law.
\
1. A double majority vote (*majority overall and in each state*) is required to pass a bill.
\
1. The Senate debates and votes on bills only *after* they have passed with a majority in the House of Representatives.
97
New cards
Define anomie and explain its relation to criminal behaviour
The person chooses criminal activity because the individual believes that there is no reason not to. In other words, the person is alienated, feels worthless and that their efforts to try and achieve anything else are fruitless
98
New cards
Explain the concept of a strict liability offence using one example
a strict liability defence is applicable only when it meets the following requirements –
* No fault elements exist – it includes recklessness, intention, knowledge, etc. on the part of the accused) – responsible for the physical elements of the offence
* The defence of reasonable and honest mistake exists
\
An excellent example to describe such a case would be an individual caught driving while their license – their legal right to drive – was suspended for whatever reasons. The police will charge them with a strict liability offence. In the event that they can successfully bring sufficient evidence that they were mistaken – not aware about their license suspension – they may be able to successfully defend their case.
* No fault elements exist – it includes recklessness, intention, knowledge, etc. on the part of the accused) – responsible for the physical elements of the offence
* The defence of reasonable and honest mistake exists
\
An excellent example to describe such a case would be an individual caught driving while their license – their legal right to drive – was suspended for whatever reasons. The police will charge them with a strict liability offence. In the event that they can successfully bring sufficient evidence that they were mistaken – not aware about their license suspension – they may be able to successfully defend their case.
99
New cards
explain fault elements
**A fault element for a particular physical element may be intention, knowledge, recklessness or negligence.**
100
New cards
explain intention
A person has intention with respect to conduct if he or she means to engage in that conduct