3d: Light and sound
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/72
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
73 Terms
1
New cards
is visible light longitudinal or transverse
transverse
2
New cards
can light be refracted
yes
3
New cards
can light be reflected
yes
4
New cards
sound waves
vibration of air molecules
5
New cards
are sound waves longitudinal or transverse
longitudinal
6
New cards
can sound waves be refracted
yes
7
New cards
can sound waves be reflected
yes
8
New cards
what are reflected sound waves called
echo
9
New cards
angle of incidence
angle of the wave approaching the boundary
10
New cards
angle of reflection
angle of wave leaving the boundary
11
New cards
law of reflection
angle of incidence = angle of reflection (i=r)
12
New cards
how are angles measured
between the wave direction and a line at 90 degrees to the boundary
13
New cards
where does the arrow of the incident ray point
towards the boundary
14
New cards
where does the arrow of the reflected ray point
away from the boundary
15
New cards
snell's law
n = sin i / sin r
16
New cards
what happens to light when it enters a denser medium
it bends towards the normal
17
New cards
which factor affects how much the light bends
density of the material
18
New cards
less dense to more dense medium
light bends towards the normal
19
New cards
more dense to less dense medium
light bends away from the normal
20
New cards
angle of incidence of light (notation)
i
21
New cards
angle of reflection of light (notation)
r
22
New cards
refractive index (notation)
n
23
New cards
relationship between refractive index, angle of incidence and angle of refraction
n = sin i / sin r
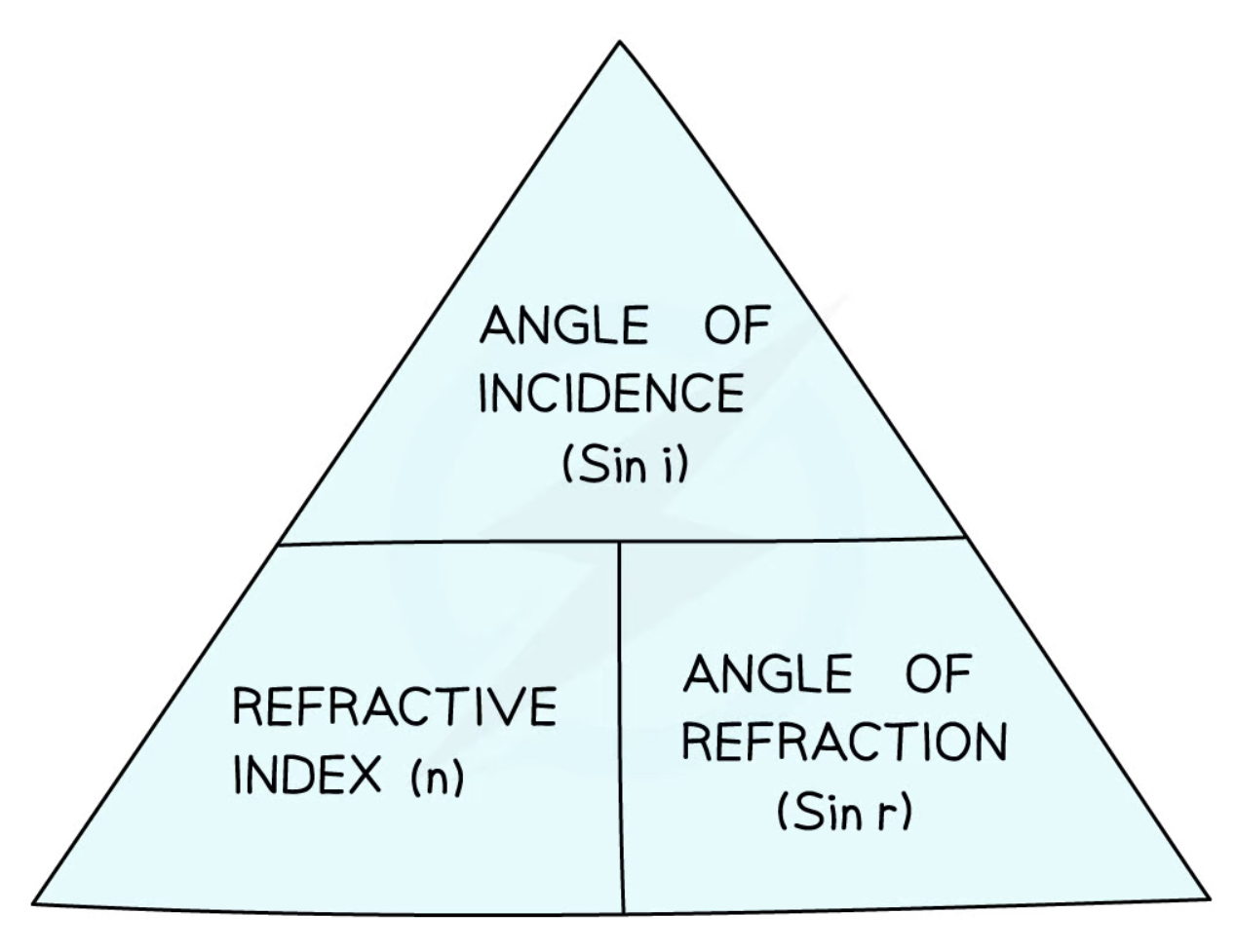
24
New cards
total internal reflection
when light is reflected when moving from a denser medium towards a less dense one
25
New cards
when does total internal reflection occur
when the angle of incidence is greater than the critical angle and the incident material is denser than the second material
26
New cards
two conditions for total internal reflection
- angle of incidence > critical angle
- incident material is denser than second material
- incident material is denser than second material
27
New cards
where is total internal reflection utilised
- optical fibres
- prisms
- prisms
28
New cards
total internal reflection - optical fibres
light travelling down an optical fibre is totally internally reflected each time it hits the edge of the fibre
29
New cards
total internal reflection - where is it used along optical fibres
- communications
- endoscopes
- decorative lamps
- safety reflectors
- endoscopes
- decorative lamps
- safety reflectors
30
New cards
total internal reflection - prisms
the light totally internally reflects in both prisms
31
New cards
total internal reflection - where is it used along prisms
- periscopes
- binoculars
- telescopes
- cameras
- binoculars
- telescopes
- cameras
32
New cards
periscope
a device that can be used to see over tall objects consisting of two right-angled prisms
33
New cards
what happens to the angle of incidence once the angle of refraction is exactly 90
it's known as the critical angle
34
New cards
angle of incidence larger than critical angle
refracted ray is reflected
35
New cards
relationship between critical angle and refractive index
sin c = 1/nl
36
New cards
large refractive index of a material
small critical angle
37
New cards
frequency range for human hearing
20 - 20000 Hz
38
New cards
what can be observed by an oscilloscope
changing signals like sound waves and alternating current
39
New cards
what happens to the longitudinal sound wave when a microphone is connected to an oscilloscope
it is displayed as though a transverse wave on the screen
40
New cards
what does the time base measure
time period of the wavew
41
New cards
what does the height of the wave measured from the centre of the screen tell us
amplitude
42
New cards
what does the number of waves on the screen tell us
frequency
43
New cards
more waves displayed
increased frequency
44
New cards
less waves displayed
decreased frequency
45
New cards
high pitch
high frequency of vibrationl
46
New cards
low pitch
low frequency of vibration
47
New cards
loud sound
large amplitude
48
New cards
soft sound
small amplitude
49
New cards
investigating refraction - variables
independent variable: shape of block
dependent variable: direction of refraction
control variables: width and frequency of light
dependent variable: direction of refraction
control variables: width and frequency of light
50
New cards
investigating refraction - equipment
- ray box
- protractor
- paper
- pencil
- ruler
- perspex blocks
- protractor
- paper
- pencil
- ruler
- perspex blocks
51
New cards
investigating refraction - method
- place glass box on a sheet of paper
- draw around rectangular perspex
- direct a beam of light at the face of the box using the ray box
- mark the paper
- draw a dashed line at right angles to the outline of the block where the points are
- remove block and join marked points
- replace block with outline and repeat at a different angle
- repeat for each shape of perspex block
- draw around rectangular perspex
- direct a beam of light at the face of the box using the ray box
- mark the paper
- draw a dashed line at right angles to the outline of the block where the points are
- remove block and join marked points
- replace block with outline and repeat at a different angle
- repeat for each shape of perspex block
52
New cards
investigating refraction - marking the paper
- point on the ray
- point where the ray enters
- point where the ray exits
- point on the exit light ray
- point where the ray enters
- point where the ray exits
- point on the exit light ray
53
New cards
investigating refraction - refraction patterns for different blocks
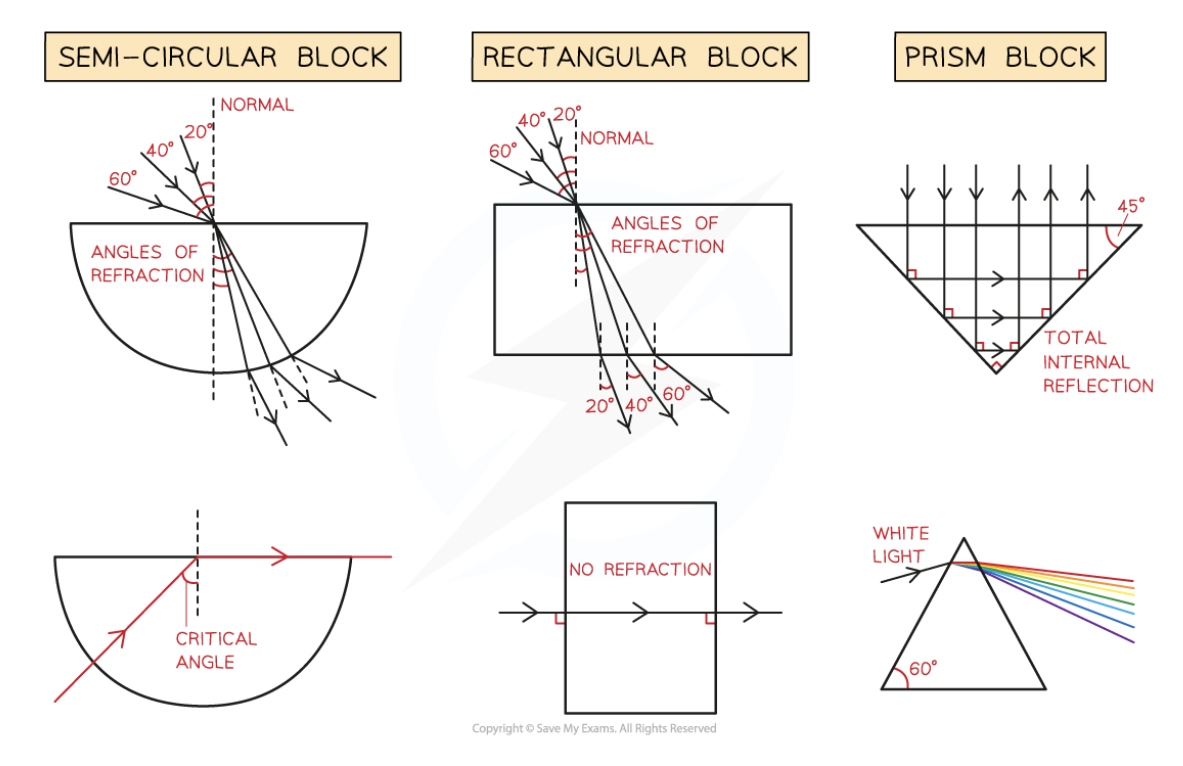
54
New cards
investigating refraction - analysis
i and r are measured from normal
55
New cards
investigating refraction - systematic errors
incorrectly drawn lines
56
New cards
investigating refraction - random errors
- inaccurately marked points
- protactor resolution
- protactor resolution
57
New cards
investigating refraction - safety considerations
- ray box light could cause burns
- light might damage eye
- keep all liquids away
- light might damage eye
- keep all liquids away
58
New cards
investigating refractive index - variables
independent variable: angle of incidence
dependent variable: angle of refraction
control variables: use of perspex block, width and frequency of light beam
dependent variable: angle of refraction
control variables: use of perspex block, width and frequency of light beam
59
New cards
investigating refractive index - method
same as investigating refraction
60
New cards
investigating refractive index - method
same as investigating refraction
61
New cards
investigating refractive index - analysis
n = sin i / sin r
62
New cards
investigating refractive index - systematic errors, safety consideration
same as investigating refraction
63
New cards
investigating the speed of sound - equipment
- trundle wheel
- wooden blocks
- stopwatch
- oscilloscope
- microphones
- tape measure
- wooden blocks
- stopwatch
- oscilloscope
- microphones
- tape measure
64
New cards
investigating the speed of sound - measuring the speed of sound between two points (variables)
independent variable: distance
dependent variable: time
control variable: same location
dependent variable: time
control variable: same location
65
New cards
investigating the speed of sound - measuring the speed of sound between two points (method)
- measure distance between 2 people
- 1 person should hold two wooden blocks to bang together above their head
- the other should hold a stopwatch which they start when they see the blocks bang together and stop when they hear it
- repeat for average
- repeat with various distances
- 1 person should hold two wooden blocks to bang together above their head
- the other should hold a stopwatch which they start when they see the blocks bang together and stop when they hear it
- repeat for average
- repeat with various distances
66
New cards
investigating the speed of sound - measuring the speed of sound between two points (analysis)
speed = distance / time
67
New cards
investigating the speed of sound - measuring the speed of sound with oscilloscopes (variables)
independent variable: distance
dependent variable: time
control variables: same location, same set of microphones
dependent variable: time
control variables: same location, same set of microphones
68
New cards
investigating the speed of sound - measuring the speed of sound with oscilloscopes (method)
- connect two microphones to an oscilloscope and place them 2 m
- set up the oscilloscope so that it triggers when the first microphone detects a sound and adjust the time base so that the sound arriving at both microphones can be seen on the screen
- make a large clap using the two wooden blocks next to the first microphone and use the oscilloscope to determine the time at which the clap reaches each microphone and the time difference between them
- repeat at several distances
- set up the oscilloscope so that it triggers when the first microphone detects a sound and adjust the time base so that the sound arriving at both microphones can be seen on the screen
- make a large clap using the two wooden blocks next to the first microphone and use the oscilloscope to determine the time at which the clap reaches each microphone and the time difference between them
- repeat at several distances
69
New cards
investigating the speed of sound - measuring the speed of sound with oscilloscopes (analysis)
speed = distance / time
70
New cards
using an oscilloscope - variables
independent variables: tuning forks of different frequencies
dependent variable: time period
dependent variable: time period
71
New cards
using an oscilloscope - equipment
- tuning forks
- microphone
- oscilloscope
- wires
- microphone
- oscilloscope
- wires
72
New cards
using an oscilloscope - method
- connect the microphone to the oscilloscope and test it
- adjust the time base of the oscilloscope until the signal fits on the screen
- strike the tuning fork on the edge of a hard surface to generate sound waves of a pure frequency
- hold the tuning fork near to the microphone and observe the sound wave on the oscilloscope screen
- freeze the image on the oscilloscope screen
- measure and record the time period of the wave signal on the screen
- repeat for varying tuning forks
- adjust the time base of the oscilloscope until the signal fits on the screen
- strike the tuning fork on the edge of a hard surface to generate sound waves of a pure frequency
- hold the tuning fork near to the microphone and observe the sound wave on the oscilloscope screen
- freeze the image on the oscilloscope screen
- measure and record the time period of the wave signal on the screen
- repeat for varying tuning forks
73
New cards
using an oscilloscope - analysis
frequency = 1 / time period