Bio 101 Final Exam
1/135
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Cumulative
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
136 Terms
Chemistry
the study of the interaction between molecules and atoms
Matter
anything that occupies space and possesses mass
Protons
positively charged particles located within nucleus
Electrons
negatively charged particles that orbit nucleus
properties: no definitive size or shape, carry energy
Neutrons
neutral particles located within nucleus
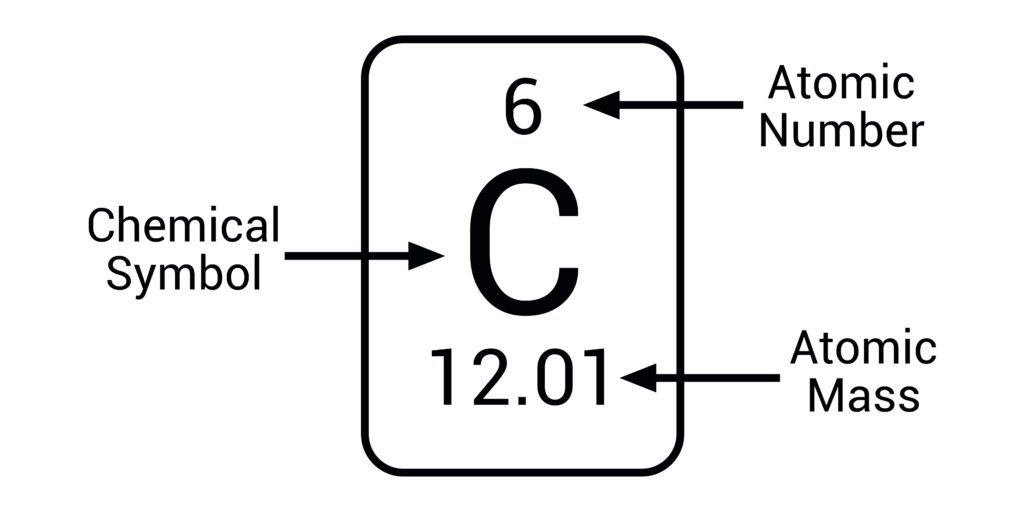
Atomic number
number of protons in an atom, determines atomic properties
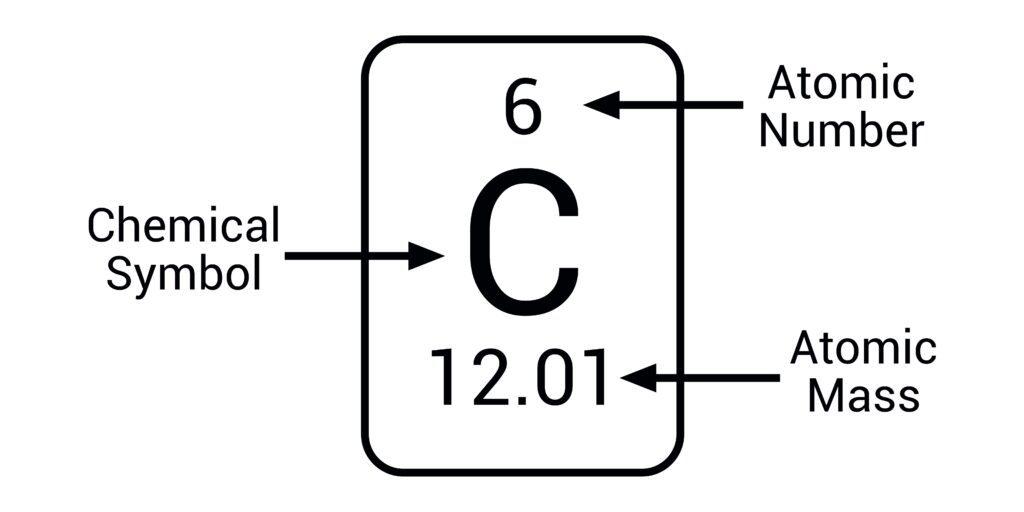
Atomic mass
number of protons and neutrons in an atomic nucleus
Elements
lots of one molecule or types of molecules, two or more types of atoms
Compounds
two or more types of molecules/elements bonded together
Isotopes
slightly different than an element, similar properties
Radioisotope
unstable atom that breaks up spontaneously
Radioactive decay
degradation of atomic nucleus
predictable consistent process
some isotopes break down more consistently, used to measure concentration and ratio to predict age (half life)
Electron orbitals
contain two electrons max.
multiple orbitals per energy level or shelf
electrons gain energy by filling orbitals
pattern: 2(n²)
Shell Model
first shell has one orbital, every other holds four
Valence shell
last shell, determines how element interacts with other elements based on electron number/reactivity
Energy levels/shells
determine reactive potential
Reactive elements
have a greater chance to move to the next energy level
desire stability, filling valence shell
Chemically inert
no desire to fill shell, all filled
all noble gasses
Chemical bonds
the way two atoms interact and electron vacancies are filled
Polarity
separation of charges
Electronegativity
ability/desire to pull electrons from other atoms
dependent on size, vacancies, and reactivity
Ionic bonds
held together by opposite charges
each substance retains charge
polar
donating/stealing electron
Covalent bonds
sharing of electrons to fill an orbital
very strong
increase in bonds equals increase in bond strength
multiple covalent bonds
polar and nonpolar
Hydrogen bonds
attraction between hydrogen atoms and other covalently bonded atoms
not ‘true’ chemical bonds
water caries a neutral charge
polar covalent bond
able to covalently bond with many molecules
very weak but numerous bond
other atom exerts more pull on the shared electron than hydrogen
Polar molecule
attracts water and molecules around it
Chemistry of water
universal solvent
polarity
covalent bond
displays cohesion and adhesion
large heat capacity
high heat of evaporation
density
Density
uniquely less dense when cold and solid
pH
amount of hydrogen ions floating in solution
acidic: 0-6
neutral: 7
alkaline: 8-14
Acid
hydrogen ion surplus in a solution
strong vs weak acids
pH < 7
Base
lack of hydrogen in a solution
pH>7
OH
Buffer
stabilizes pH of a solution by accepting or donating hydrogen ions (H^+)
Acids and bases
biological properties function within pH range
influx of acids or vases
damage and environmental effects
Organic compounds
composed of primarily carbon and hydrogen atoms
on Earth prior to life
Carbon characteristics
versatile bonding: can form four covalent bonds, four vacancies
can form shapes with bonds: chain/ring
form a wide variety of compounds
Hydrocarbons
organic molecule composed of only carbon and hydrogen
Functional group
atom or molecular group covalently bonded to a carbon atom of an organic compound
determines characteristics of compound
pH and polarity
determines chemical behavior
Isomer
molecules with same formula but different structures
Reaction
process that results in a molecular change
Hydrolysis
requires water
Condensation
forms water
metabolic water
dehydration
organic macromolecules
carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acid, and proteins
monomer
subunit of a larger molecule
polymer
composed of multiple monomers
Carbohydrates
organic compounds that consist of CHO
fuel source and energy storage
carbon/hydrogen bonds
structural components
sugars and carbs
1:2:1
monosaccharides
simple sugar, carbohydrates when broken down yields non-carbohydrate molecules
monomer/subunit
solubility enables them to move in biological systems easily
polarity
energy source
structural sugar
glucose
C6 H12 O6
Disaccharide
complex carb composed of two monosaccharides: lactose and sucrose
Polysaccharide
complex carb composed of many monosaccharides forming a complex structure
hundreds of thousands of simple sugars
difficult to break down or delayed energy release
cellulose
chitin
Cellulose
structural component of plants
indigestible
very ridged structure
insoluble fiber
herbivorous animals
Chitin
structural component of arthropods
indigestible
exoskeleton
Lipids
a macromolecule composed of CHO
more carbon and hydrogen bonds than carbs
nonpolar molecules
insoluble
energy storage
fatty acids and glycerol monomers
Fat
fatty acid bonded to glycerol
triglyceride
Triglyceride
fats with three fatty acid tails
Fat vs. Oil
Fat is solid at room temperature, oil is liquid
Glycerol
head of triglyceride molecule
first monomer of fats/lipids
Fatty acid
long chains of hydrocarbons that form the tail on triglycerides
second monomer
Saturated fat
all carbons are bonded to two hydrogen atoms
no double bonds
can pack tightly
unsaturated fat
at least one carbon is bonded to a single atom
at least one double bond
cant be packed tightly
phospholipids
phosphate head with two hydrocarbon tails
polar and nonpolar sections
cell membranes
phospholipids bilayer
Wax
lipids with usually one long fatty acid tail connected to alcohol
packed very tightly
water/air resistance
plants (leaves) and animals like birds
Steroids/sterols
lipids without fatty acid tails
formed into rings
physiological functions
cholesterol and hormones
Cholesterol
reinforces cell membranes, in between
formed from saturated fats
cholesterol build-up: too ridged prevents proper function
Hormone
regulates growth and development
testosterone and estrogen
Proteins
organic molecule with a very wide variety of functions because of the wide variety in structure
composed if CHON
diet
Amino acids
monomer of proteins
composed of carboxyl group, amino acid group, and “side chain”
type of side chain determines type of amino acid
determines properties
20 different types naturally occurring
different combinations form different proteins
Protein structure
primary
secondary
tertiary
quaternary
importance: confers/determines function
peptide (covalent) bond
chemical bond that connects amino acids
forms chains of peptides
polypeptide chains join to other chains forming proteins
polypeptide
multiple amino acids bonded together
Nucleic acids
preform cellular information delivery and storage
Nucleotide
monomer of nucleic acids
composed of pentose sugar, phosphate group, nitrogenous base
DNA
nucleic acid with deoxyribose sugar
storage of genetic material
double helix
thymine base
RNA
nucleic acid with a ribose sugar
protein synthesis
single stranded, linear
uracil base
Cell theory
every living organism is made of cells
smallest unit of life
arise from preexisting cells
discovered by Antoni Leeuwenhoek
animalcules
Robert Hook
Cells carry out metabolism and homeostasis
cellular metabolism dependent upon surface area
cellular function
SA to volume ratio
cell membranes
Plasma membrane
layer that regulates what enters and exits cell
not always outermost layer
Cytoplasm
intracellular fluid composed primarily of water, sugar, and ions
cytosol
suspends materials
Ribosome
synthesizes proteins
Eukaryotes
possess nucleus
very large cells
contain membrane-bound organelles
animals, plants, fungi, protists
Prokaryotes
lack of nucleus
very small cells
simple structures/organelles
bacteria and archaea
Prokaryotic organism cellular components
ribosomes: polypeptide assemblage
plasmids: circles of DNA
small amount of genes
nucleotide: region containing majority of DNA
cell wall: protection, structure, support
on top of plasma membrane
different components in archaea and bacteria
Superficial elements:
capsule: adhesive outer surface
fimbriae: aids in adhesion
flagellum/flagella: mobility
biofilm: commercial microorganisms
living in close proximity
“slimy” appearance
colonization of hostile environments
Endosymbiont theory
many eukaryotic organelles were once prokaryotic organisms absorbed or ingested
Plant cells
cell wall
central vacuole
chloroplasts
Animal cells
lack cell wall and central vacuole
have a centriole
Eukaryotic organelles and structures
Nucleus: stores cell’s genetic material
regulates cellular function
double membrane bound organelle
Nuclear membrane: membrane surrounding nucleus
connected to rough endoplasmic reticulum
nuclear pores
Nucleolus: produces ribosomes
center of nucleus
ribosomes and nuclear pores
Endomembrane system: series of organelles that utilize vesicles to preform a variety of functions
vesicle: membrane enclosed sac with a specific function
formed from the budding of organelles
material transportation
Rough endoplasmic reticulum
synthesizes and distributes proteins for extracellular use
attached to nuclear membrane
covered in ribosomes
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
synthesizes and distributes lipids and carbohydrates
detoxification
intra and extracellular use
Golgi apparatus/body
modifies the vesicle and its contents then distributes them into or out of cell
receives vesicles from plasma membrane or RER/SER
Lysome
break down cellular waste and debris
formed from Golgi
digestive enzymes
Peroxisome
membrane enclosed sac that breaks down fatty acids
hydrogen peroxide and catalase
formed by ribosomes
Vacuoles
membrane-bound sac that stores nutrients
animals have a lot
Central vacuoles
large vacuoles that are primarily composed of water
hydrostatic/turgor pressure
helps maintain shape by pushing out from inside
plant cells
maintain plant shape
Chloroplast
organelle specializing in photosynthesis
contain their own DNA, ribosomes, metabolic processes
endosymbionnt theory: certain organelles are the decedents of ancient bacteria
chlorophyl
double membrane bound
plant cells
structure:
stroma
thykaloids
granum
Stroma
fluid within chloroplast
thykaloids
membranes on which photosynthesis occurs
contain photosystems and pigments
phospholipid bilayer
granum
stacks of thykaloids
mitochondrion
organelle responsible for cellular respiration in eukaryotes
produces ATP
own DNA and ribosomes
double membrane bound
Nucleic acid
matrix
mitochondrial internal fluid
citric acid cycle
cristae
fingerlike projections within mitochondria
ETP/ETC
H+ gradient
cytoskeleton
system of structures that reinforce the cell, organizes components, and move structures
composed of protein fibers
cellular locomotion
forms weblike structure in cell
cytoskeleton intermediate filament
reinforces cellular shape and structure
strengthens cell
8-11nm diameter
cytoskeleton actin filament
reinforces cellular shape and structure and mobility
uses and motor protein myosin
7nm diameter