BUS 206 FINAL
1/121
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
122 Terms
Elasticity
measure of responsiveness of one variable to a change in another variable
price-elasticity of demand
a measure of the responsiveness of quantity demanded of a good to a change in its price when all other influences on a buyer’s plans remain the same
measures the percentage change in Qd compared to the percentage change in the price of the good
elasticity units
none!
% change in price (not midpoint)
just replace p with q for quantity
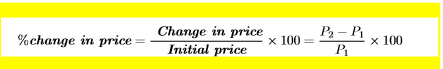
price elasticity of demand equation
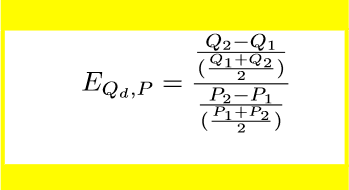
% change in price OR quantity using midpoint formula
just replace p with q for quantity

why is price elasticity of demand always negative?
because P and Qd move in opposite directions
necessities have _____ substitutes, so the demand for them is _______
poor, inelastic
luxuries have _______ substitutes, so the demand for them is _______
many, elastic
The more time that passes after the price of a good changes, the _____ elastic the demand is for the good
more
along a linear demand curve, elasticity _______ as the price falls
decreases
elastic demand
|Ed| > 1
a given change in price results in a greater change of Qd
inelastic demand
|Ed| < 1
a given percentage change in price results in a smaller percentage change in Qd
unit elastic
|Ed| = 1
percentage change in price = percentage change in Qd
perfectly elastic
Ed = ∞
small percentage change of price and big percentage change of Qd
horizontal supply/demand curve
Perfectly inelastic
Ed = 0
vertical supply/demand curve
If price increases and total revenue increases
price increase is stronger than Qd decrease
% change P > % change Q
|Ed| < 1
Inelastic
if price increases and total revenue decreases
Qd decrease stronger than P increase
% change Q > % change P
|Ed| > 1
elastic
if price increases and no change to total revenue
Q decrease as strong as P increase
% change Q = % change P
If EQxPy > 0 then x and y are __________
substitutes
If EQxPy < 0 then x and y are __________
complements
If EQxPy = 0 then x and y are _________
unrelated
cross price elasticity of demand
measures the percentage by which Qd of one good changes in response to a 1% change in the price of another good
income elasticity of demand
the percentage change in Qd of a good when a consumer’s income changes divided by the percentage change of the consumers income
cross price elasticity of demand equation
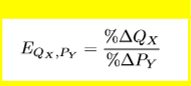
if Eqdm < 0 then
good is inferior
if Eqdm > 0 then
good is normal
if 0 <Eqdm < 1
good is inelastic
if Eqdm >1
good is elastic
price elasticity of supply
measures the percentage change in quantity supplied that occurs in response to a 1 percent change in price
price of elasticity of supply equation
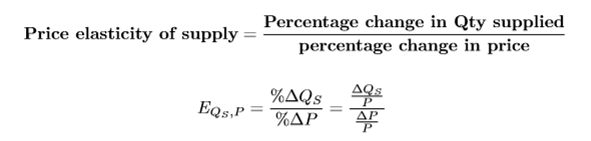
productive efficiency
producing the maximum possible output
allocative efficiency
situation in which quantities of goods/services produced are those that the people value most highly
which point on the PPC is the best?
Resource Allocation Methods
market price *
command *
majority rule
contest
1st come 1st served
sharing equally
lottery
market price resource allocation
people who can afford it will buy it
command resource allocation
government controls how much money you an have via taxes
taking from someone to give to someone else
marginal benefit
benefit people receive from consuming one more unit of a good/service
willingness to give up
principle of decreasing marginal benefit
the more we have of any good or service, the smaller our marginal benefit for it is
direction of MB curve
downward
how is marginal benefit measured
by what you are willing to give up
what are allocation decisions based of off
marginal benefit and marginal cost
marginal cost
the opportunity cost of producing one more unit of a good or service
what you must give up
how is marginal cost measured?
by the slope of the PPC
what direction is the marginal cost curve
upward
Efficient allocation
resources are allocated efficiently only when MB=MC
point on PPC where MB and MC intersect
chose level of activity where MB>MC and stop where MB<MC
what do if MB>MC
increase activity level
what do if MC>MB
decrease activity level
deadweight loss
the reduction in economic surplus resulting from a market not being at competitive equilibrium
Best/Efficient Choice
obtained where MB=MC
as big as total benefit can be where MB>MC
value
what we get and the price we pay
2 building blocks of market efficiency
consumer surplus
producer surplus
An MB curve is also a ________ curve
demand
consumer surplus
difference between price consumers would be willing to pay for a good (MB) and the price they actually have to pay
individual consumer surplus
net gain to an individual buyer from the purchase of a good
willingness to pay - price paid
total consumer surplus
area below demand curve but above market price`
welfare economics
includes consumer/producer/total surplus, deadweight loss, and market failures
individual producer surplus
net gain to an individual seller from selling a good
price received - seller’s cost
marginal cost curve is also ________ curve
supply
total producer surplus
area below market price and above the supply curve
total surplus
CS + PS
free competitive markets are _________
efficient
competitive equilibrium condition
MB=MC (D=S)
when is economic surplus maximized in a competitive market with many buyers and sellers and no government restrictions?
when the market is at competitive equilibrium
underproduction
production in market is smaller than equilibrium
market failure
situation in which the market delivers an inefficient outcome
is market capitalism omnipotent?
no! market failure happens
equity
fairness
equality
everyone gets the same thing
Can consumer surplus be negative? If so, when?
Yes, when you buy something with a price higher than the original amount you were willing to pay cause you really want it
why can’t healthcare be a free market?
because there are not many sellers of health insurance and they would have too much market power
2 broad reasons for market failure
overproduction and underproduction
what occurs when there is over or underproduction
deadweight loss
producer surplus on a unit
price - marginal cost
reasons for market failure
externalities *
public goods and common resources *
price/quantity regulations
taxes and subsidies
monopoly
high transaction cost
externality
cost or benefit that affects someone other than the seller or buyer
public good
benefits everyone and no one can be excluded from its benefits (national defense)
causes free-rider problem
common resource
owned by no one but used by everyone (atlantic salmon in alaska)
types of price regulations
price floor
price ceiling
excise taxes
based on quantity
gas
ad valorem taxes
percentage of value
tarrifs
do free markets exist
no, they’re the ideal benchmark
type of quantity regulation
quota
price ceiling
a maximum price that can be legally charged for a good/service
4 bad results of price ceilings
shortage
increased search activity
inefficiently low quality
shadow market/ illegal activity
binding price ceiling
price ceiling < equilibrium price
effective
creates shortage because of underproduction
nonbinding price ceiling
price ceiling > equilibrium price
ineffective
inefficiently low quality
sellers offer low quality goods at a low price even though buyers are willing to pay more
price floor
a legally established minimum price for a good or service
binding price floor
price floor > equilibrium price
effective
creates surplus
nonbinding price floor
price floor < equilibrium price
ineffective
price support
government buys surplus goods brought on by price floor
how does minimum wage cause unemployment
quantity of workers supplied > quantity of workers demanded
characteristics of public goods
nonrivalry
nonexcludable
free-rider problem
characteristics of private goods
rivalry
excludability
bad effects of price floor
inefficiently low quantity demanded
inefficient allocation of sales among sellers
wasted resources
inefficiently high quality
shadow market
Pigouvian tax
a tax or charge levied on the production of a product that generates negative externalities
will offset overallocation/overproduction
negative externalities are associated with ________allocation
over
positive externalities are associated with _________allocation
under
Pigouvian subsidy
A payment designed to encourage activities that yield external
benefits.
3 options for correcting positive externalities
subsidies to buyers
subsidies to producers
government provisions