AP PSYCHOLOGY UNIT 9 VOCAB
1/64
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
Social Psychology
Social psychology looks at how people are affected by others, including their thoughts, feelings, and behaviors.
Social Cognition
Social cognition is about how we think and understand other people and social situations.
Social Influence
Social influence is how people change their behavior or opinions because of others.
Attribution
How we explain the causes of peoples behavior.
Fundamental Attribution Error
The tendency to overemphasize internal traits (like personality) and underestimate external factors (like situation) when explaining others’ behavior.
External Attribution
Explaining behavior by looking at external or situational factors.
Internal Attribution
Explaining behavior by looking at internal traits or qualities, such as personality.
Actor-Observer Bias
The tendency to attribute our own behavior to external factors while attributing others’ behavior to internal factors.
Just-Word Hypothesis
The belief that people get what they deserve in life, leading us to assume that bad things happen to bad people and vise versa.
False Consensus Effect
The tendency to overestimate how much others share our own beliefs and behaviors.
Self-Fulfilling Prophecy
When our beliefs or expectations about a person or situation lead to behaviors that cause those beliefs to come true.
Self-Schemas
The idea and beliefs we have about ourselves that shape how we perceive and interpret info.
Gender
The social and psychological characteristics and behaviors that a culture associates with a persons biological sex.
Race
A category of humankinds that shared certain distinctive physical traits, often based on skin color.
Ethnicity
Shared cultural traits, such as language, customs, and heritage, among a group of people.
Attitude
A person’s feelings or beliefs about something, which can influence their behavior.
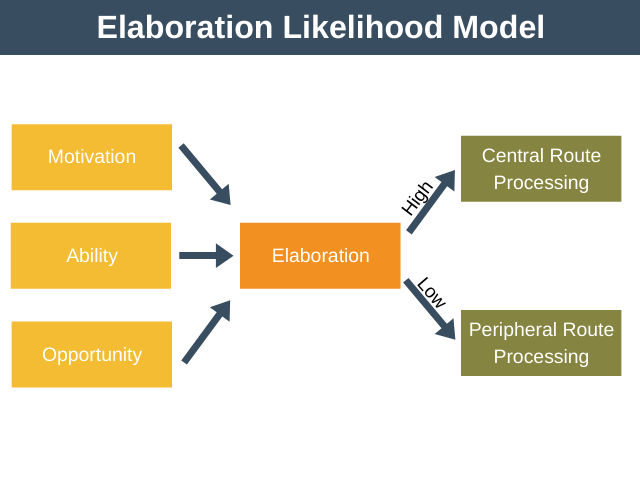
Elaboration Likelihood Model
A theory explaining how people are persuaded, either through careful thinking (central routes) or superficial cues (peripheral route.)
Central Route to Persuasion
Persuasion that happens when people carefully think about and analyze the content of a message.
Peripheral Route to Persuasion
Persuasion that occurs when people are influenced by superficial factors like attractiveness or credibility, rather than the message itself.
Foot-In-The-Door Approach
A technique where you starts with a small request to get someone to agree, then follow up with a larger request.
Door-In-The-Face Approach
A technique where you start with a large request (which is likely to be refused) and then make a smaller, more reasonable request.
Cognitive Dissonance
The mental discomfort experienced when holding two conflicting beliefs or when behavior doesn’t match beliefs, leading to changes in attitudes or behavior to reduce the discomfort.
Norms
Unwritten rules or expectations about how people should behave in a group or society.
Conformity
Adjusting your behavior or beliefs to match those of others or to fit in with a group.
Normative Social Influence
Conforming to fit in with the group and gain approval or avoid disapproval.
Informational Social Influence
Conforming because you believe others have more accurate information or better judgement.
Compliance
Agreeing to a request or following a directive, often in response to a direct ask or pressure.
3 EXAMPLES OF CONFORMITY
Peer pressure, fashion trends, and corporate culture.
Social Facilitation
When people perform better on simple or well-learned tasks when they are in the presence of others.
Social Inhibition
When people perform worse on complex or new tasks when they are around others.
Social Loafing
When people put in less effort when working in a group compared to working alone.
Deindividuation
When people lose their sense of individual identity and become more likely to act in ways they normally wouldn’t, often in a group setting.
Group Polarization
When a groups opinions become more extreme after discussing a topic together.
Groupthink
When a group values harmony and consensus over making the best decision, leading to poor decisions.
Bystander Effect
When people are less likely to help in an emergency if there are other people around.
Diffusion of Responsibility
When individuals feel less responsible to act because they believe others will take action.
Social Exchange Theory
The idea that people weigh the costs and benefits of interactions and aim to maximize their benefits to minimize their costs.
Reciprocity Norm
The expectation that people will respond to each others actions with similar actions.
Social Traps
Situations where individuals or groups act in their own self-interest but end up causing harm to everyone including themselves in the long run.
Prisoners Dilemma
a situation where two people might not cooperate, even if it would be in their best interest, because they don’t trust each other.
Superordinate Goals
Goals that require cooperation between groups or people, which can help reduce conflict and promote unity.
Prejudice
A negative attitude or feelings toward someone based on their group membership (like race or gender) often without knowing them personally.
Stereotyping
Assigning specific traits or behaviors to all members of a group, often based on oversimplified or inaccurate beliefs.
Discrimination
Treating people unfairly or unequally because of their group membership.
Ethnocentrism
Believing that ones own culture or ethnic group is superior to others.
Ingroup
A group of people you identify with or feel you belong to.
Outgroup
A group of people you do not identify with or feel is different from your own group.
Out-Group Homogeneity Bias
The tendency to see members of an outgroup as being more similar to each other than they really are, and different from members of your own.
Scapegoat Theory
Blaming a person or group for problems or negative outcomes, often to deflect blame from oneself or ones own group.
Ultimate Attribution Error
The tendency to attribute position behaviors of our own group to internal factors (like personality) and negative behaviors to external factors (like circumstances) while doing the opposite for outgroups.
Aggression
Behavior intended to harm or cause pain to others.
Frustration-Aggression Hypothesis
The idea that frustration (being blocked form achieving a goal) leads to aggression.
Social Learning
Learning behaviors by observing and imitating others, rather than through direct experience.
Altruism
Selflessly helping others without expecting any personal gain or reward.
Prosocial Behavior
Actions intended to benefit or help others, such as volunteering or cooperation.
Halo Effect
The tendency to let a persons positive traits in one area influence your overall judgement of them, making you view them more favorably in other areas as well.
Mere Exposure Effect
The tendency to develop a preference for things or people simply because they are familiar or encountered frequently.
Consummate Love
A type of love that includes passion, intimacy, and commitment- often considered the ideal form of love.
Compassionate Love
A deep, emotional bond characterized by intimacy and commitment, but typically without the intense passion seen in romantic love.
Fatuous Love
A type of love that combines passion and commitment without much intimacy, often seen in whirlwind romances or quick marriages.
Romantic Love
A type of love that includes passion and intimacy, often associated with deep emotional connection and attractions.
What is Leon Fistinger known for?
Cognitive dissonance
What is Solomon Asch known for?
Conformity experiments
What is Stanley Milgram known for?
Obedience experiments
What is Philip Zimbardo known for?
Stanford prison experiment