Cell Organelles and Cell Transport (copy)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/43
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 2:14 PM on 9/5/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
1
New cards
Cell Theory
All organisms are composed of cells
All cells come from pre-existing cells
The cell is the basic unit of life
2
New cards
what is the cell/plasma membrane
3
New cards
Phospholipid Bilayer
double layer Phospholipid molecules with hydropholic tails pointing inward and the hydrophilic heads facing outwards
4
New cards
Protein Molecules
1.Transport ions and molecules across the plasma membrane
2.Enzymes to carry out chemical reactions
3.Receptors for hormones
2.Enzymes to carry out chemical reactions
3.Receptors for hormones
5
New cards
Cholesterol Molecules
found between phospholipids tails to prevent them from sticking together.
6
New cards
Carbohydrate Chain
1.Adhesion to other cells
Recognition of molecules at the membrane surface
Recognition of molecules at the membrane surface
7
New cards
Passive Transport
Movement of materials through the plasma membrane
Does not require energy
Ex: oxygen, carbon dioxide molecules, water, lipids
Does not require energy
Ex: oxygen, carbon dioxide molecules, water, lipids
8
New cards
Diffusion
Form of passive transport
Movement of ions or soluble molecules that move from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration
High Concentration- a lot of molecules in a smaller area
Low Concentration- molecules are very spread out
Diffusion results from the random movement of molecules
Movement of ions or soluble molecules that move from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration
High Concentration- a lot of molecules in a smaller area
Low Concentration- molecules are very spread out
Diffusion results from the random movement of molecules
9
New cards
Osmosis
The diffusion of water through the plasma membrane, or any semipermeable membrane
Ex: vacuoles
Water moves from an area of low solute concentration to an area of high solute concentration
Solute- the substance that gets dissolved
Ex: sugar water- sugar is the solute
Ex: vacuoles
Water moves from an area of low solute concentration to an area of high solute concentration
Solute- the substance that gets dissolved
Ex: sugar water- sugar is the solute
10
New cards
Facilitated Diffusion
A type of passive transport
No energy required
Passage of molecules and ions bound to specific carrier proteins, across the membrane, down their concentration gradients
Carrier Protein:
a. Protein responsible for transporting specific substances through the cell membrane
b. Fixed and part of the membrane
Move down the concentration gradient- high to low
Sugar and Amino Acids move this way
a. Too big to move directly through the membrane
Active Transport
No energy required
Passage of molecules and ions bound to specific carrier proteins, across the membrane, down their concentration gradients
Carrier Protein:
a. Protein responsible for transporting specific substances through the cell membrane
b. Fixed and part of the membrane
Move down the concentration gradient- high to low
Sugar and Amino Acids move this way
a. Too big to move directly through the membrane
Active Transport
11
New cards
Active Transport
Movement of materials AGAINST a concentration gradient
a.Low solute concentration to high solute concentration
-ENERGY REQUIRED!!!
a.Low solute concentration to high solute concentration
-ENERGY REQUIRED!!!
12
New cards
Endocytosis
Materials are ingested by the cell
The membrane forms a vesicle around the material ingested
The membrane forms a vesicle around the material ingested
13
New cards
Exocytosis
How bulky particles or large molecules are transported out of a cell
Vesicle binds with the plasma membrane and the particle is pushed out
Vesicle binds with the plasma membrane and the particle is pushed out
14
New cards
Fluid Mosaic Model
what makes up the plasma membrane, A model of cell membrane structure representing the dynamic nature of membrane lipids and proteins
15
New cards
Prokaryotes
Cell membranes and cell wall
No real Nucleus- just a large circular molecules of DNA
Smaller cells
No real Nucleus- just a large circular molecules of DNA
Smaller cells
16
New cards
Eukaryotes
Cell membrane and some have cell wall
True Nucleus- DNA found within a nuclear envelope
Larger cells
True Nucleus- DNA found within a nuclear envelope
Larger cells
17
New cards
Cell Wall
Only found in plant cells
Made up of the polysaccharide cellulose
Made up of the polysaccharide cellulose
18
New cards
Nucleus
Carrier of heredity information
Surrounded by the nuclear envelope/ contain nuclear pores
Monitors the cell- ensures that the complex molecules that the cell requires are synthesized
Surrounded by the nuclear envelope/ contain nuclear pores
Monitors the cell- ensures that the complex molecules that the cell requires are synthesized
19
New cards
Nucleolus
Found inside the nucleus ribosomes are constructed here
20
New cards
Cytoplasm
the substance that fills the cell, a jellylike fluid inside the cell in which the organelles are suspended
21
New cards
Cytosol
Solution of ions, small molecules and proteins, the semifluid portion of the cytoplasm
22
New cards
Homeostasis
Balanced and stable internal environment, process by which organisms maintain a relatively stable internal environment
23
New cards
Regulation
Control and coordination of various activities ex: Nucleus
24
New cards
Cytoskeleton
Anchors the organelles, network of protein filaments within some cells that helps the cell maintain its shape and is involved in many forms of cell movement
25
New cards
Organelles
Membrane bound compartments
26
New cards
Ribosomes
Small organelles for protein synthesis
The can be attached to the Endoplasmic Reticulum or free floating
The can be attached to the Endoplasmic Reticulum or free floating
27
New cards
Golgi body
Looks like stacks of flattened sacs
It's the packing and distribution center
Packages, modifies, and transports proteins to be sent out to other parts of the cell
It's the packing and distribution center
Packages, modifies, and transports proteins to be sent out to other parts of the cell
28
New cards
Vesicles
The Golgi body produces this organelle
A little sac that carries products to the plasma membrane
A little sac that carries products to the plasma membrane
29
New cards
Vacuoles
Filled with water and solutes
It's a supporting element
Much larger in plant cells
Contains waste products
It's a supporting element
Much larger in plant cells
Contains waste products
30
New cards
Mitochondria
Powerhouse of the cell
Site of cellular respiration
1. Converting energy from organic molecules into useful energy for cell
Has an oblong shape
Site of cellular respiration
1. Converting energy from organic molecules into useful energy for cell
Has an oblong shape
31
New cards
Nutrition
Nutrients the cell needs for other functions
32
New cards
Excretion
Removal of cellular waste products
33
New cards
Growth
Utilizes the products of synthesis and requires energy
34
New cards
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
WITHOUT ribosomes
Used for lipid synthesis, detoxification, and makes hormones
Used for lipid synthesis, detoxification, and makes hormones
35
New cards
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
WITH ribosomes
Used for protein synthesis, and transport of proteins & other materials throughout the cell
Used for protein synthesis, and transport of proteins & other materials throughout the cell
36
New cards
Lysosomes
The organelle that contains digestive enzymes to break down or digest organic compounds and old worn out organelles
37
New cards
Centrioles
Only in animal cells
Most active during cell division
Produce special fibers to pull chromosomes to opposite ends of cell
Most active during cell division
Produce special fibers to pull chromosomes to opposite ends of cell
38
New cards
Cilia/Flagellum
Found on the outside of cells
Locomotive purposes in single celled organisms (movement)
Locomotive purposes in single celled organisms (movement)
39
New cards
Chloroplast
Only found in plant cells
Site of photosynthesis
Site of photosynthesis
40
New cards
Transport
Absorption and distribution of materials with an organism
41
New cards
Synthesis
Large molecules built from smaller ones (ex: building proteins)
42
New cards
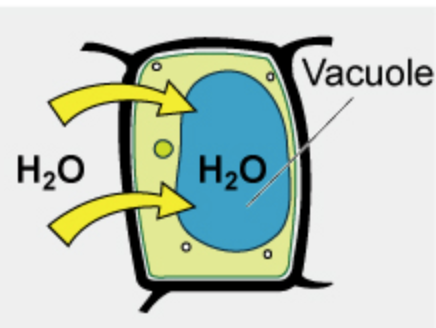
when water moves into a cell because the solute is greater inside the cell
hypotonic
43
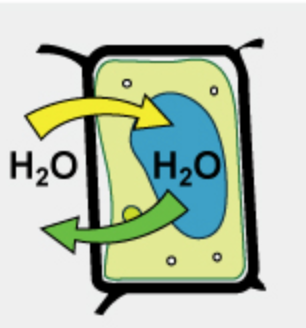
New cards
when water moves randomly in/out of the cell
isotonic
44
New cards
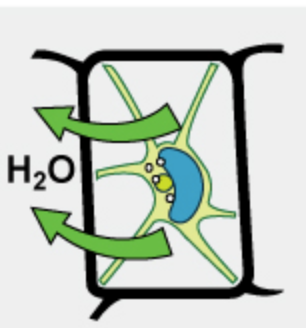
when water moves from the inside of the cell outside due to a higher solute concentration outside the cell.
hypertonic