Marketing
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/158
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
159 Terms
1
New cards
Marketing is all about lying
Wrong
* consumers not naive
* consumers will realise that the product is deceptive and will punish companies on social media
* deceptive advertising is prohibited !
* consumers not naive
* consumers will realise that the product is deceptive and will punish companies on social media
* deceptive advertising is prohibited !
2
New cards
Marketing = sales
Wrong
* marketing and sales are ==distinct== function units in the organization
* marketing comes ==before== sales
* marketing and sales are ==distinct== function units in the organization
* marketing comes ==before== sales
3
New cards
Tell me the evolution of marketing
* production concept : large production low price when demand > supply
* product concept : buy when good quality
* selling concept : buy when enough selling efforts
* marketing concept : customers satisfaction key, sell what consumers want and desire
* product concept : buy when good quality
* selling concept : buy when enough selling efforts
* marketing concept : customers satisfaction key, sell what consumers want and desire
4
New cards
Explain to me the selling concept
* starting point : factory
* focus : existing products
* means : selling and promoting
* ends : profits trough sales volume
\
* focus : existing products
* means : selling and promoting
* ends : profits trough sales volume
\
5
New cards
Explain to me the marketing concept
* starting point : market
* focus : customer needs
* means : integrated marketing
* ends : profits trough customer satisfaction
* focus : customer needs
* means : integrated marketing
* ends : profits trough customer satisfaction
6
New cards
Marketing is used by companies to sell products to consumers
Wrong
* marketing can be used by many different organizations : NGO’s, political parties, individuals, events
* no just to sell also for exemple get votes for political party
* marketing not always directed to consumers Ex.: public service announcment
* marketing can be used by many different organizations : NGO’s, political parties, individuals, events
* no just to sell also for exemple get votes for political party
* marketing not always directed to consumers Ex.: public service announcment
7
New cards
What is marketed ?
* goods
* services
* events
* experiences
* persons
* places
* propreties
* organizations
* ideas
* services
* events
* experiences
* persons
* places
* propreties
* organizations
* ideas
8
New cards
What is marketing?
Marketing is all about common sense
\
* built on academic research in psychology, sociology, economics and neuroscience, as well as real business practices
* creating, communicating, delivering and exchanging offerings that have value for customers
* creating and exchanging products that are needed and wanted by consumers
\
* built on academic research in psychology, sociology, economics and neuroscience, as well as real business practices
* creating, communicating, delivering and exchanging offerings that have value for customers
* creating and exchanging products that are needed and wanted by consumers
9
New cards
What is marketing management?
* superior customer value
* before product oriented → sales before marketing => push product
* now customers oriented → analyze customer needs and create satisfaction, loyalty
* before product oriented → sales before marketing => push product
* now customers oriented → analyze customer needs and create satisfaction, loyalty
10
New cards
What is marketing? 3P
creating value : 3P
* people
* planet
* profit → prosperity
* people
* planet
* profit → prosperity
11
New cards
What are the core marketing concepts?
* understanding consumer behaviour
* strategic marketing
* operational marketing
* strategic marketing
* operational marketing
12
New cards
what is a need?
the basic human requirements such as air, food, water, clothing and shelter
13
New cards
what is a want?
specific objects that might staisfy a need
14
New cards
what is a demand?
wants for specific products backed by an ability to pay
15
New cards
what is the marketing process in an organization?
1. opportunity
2. segmentation and targeting
3. marketing mix
4. implementation and control
16
New cards
what are the major market forces?
* technology
* globalization
* physical environment
* social responsability
* globalization
* physical environment
* social responsability
17
New cards
What are the new consumer capabilities?
* can search, communicate and purchase on the move
* can use internet as a powerful information and purchasing aid
* cant tap into social media to share opinions and express loyalty
* can actively interact
* can reject marketing they find inappropriate (Adblock)
* can use internet as a powerful information and purchasing aid
* cant tap into social media to share opinions and express loyalty
* can actively interact
* can reject marketing they find inappropriate (Adblock)
18
New cards
What are the new companies capabilities?
* can use the internet as a powerful information and sales channel, including for individually differentiated goods
* can collect fuller and richer information about markets, customers, prospects and competitors
* can reach customers quickly and efficiently via social media and mobile marketing, sending targeted ads, coupons, and information
* can collect fuller and richer information about markets, customers, prospects and competitors
* can reach customers quickly and efficiently via social media and mobile marketing, sending targeted ads, coupons, and information
19
New cards
What are the new competitive environment?
* retail transformation (Amazon, multiverse etc)
* heightened competition
* heightened competition
20
New cards
What are the new marketing realities?
* from exclusive (only Western world/culture) → to inclusive (others)
* science & data based
* hiring, training and motivating employees to serve consumers well
* science & data based
* hiring, training and motivating employees to serve consumers well
21
New cards
What is environmental scanning?
refers to possession and utilization of information about occasions, paterns and relationships within a company’s internal and external environment
22
New cards
What is the purpose of environmental scanning?
* identify trends
* identify opportunities/threats
* evaluate the company’s strenghts/weaknesses
* identify opportunities/threats
* evaluate the company’s strenghts/weaknesses
23
New cards
What is the macro environment?
consists of a number of brad forces that affect not only the company, but also the other actors in the micro environment
24
New cards
Does companies have control on the macro environment?
NO !!!!
25
New cards
What is a fad?
unpredictable, short-lived and without social, economic and political significance
26
New cards
What is a trend?
more predicticable and durable than a fad; trends reveal the shape of the future and can provide strategic direction
27
New cards
What is the PESTEL analysis?
* political
* economical (income distribution)
* social (demographic and cultural)
* technological
* environmental (corporate environmentalism)
* legal
* economical (income distribution)
* social (demographic and cultural)
* technological
* environmental (corporate environmentalism)
* legal
28
New cards
What is the micro environment?
consists of actors in the firm’s immediate environment or business system that affect its capabilities to operate effectively in the chosen markets
\
HAVE CONTROL !!
\
HAVE CONTROL !!
29
New cards
What is the market (demand)?
refers to the group of consumers or organizations that is interested in the product, has the ressources to purchase the product, and is permitted by law and other regulations to acquire the product
30
New cards
How do you estimate futur demand?
* composite of sales force opinions
* expert opinion
* past-sales analysis
* survey of buyers’ intentions
* expert opinion
* past-sales analysis
* survey of buyers’ intentions
31
New cards
What is consumer behavior?
the study of how individuals, groups and organizations select, buy, use, and dispose of goods, services, ideas or experiences to satisfy their need and wants
32
New cards
What influences consumer behavior?
* cultural
* social
* personal factors
* social
* personal factors
33
New cards
What is hedonic?
= feelings involved
VS rational
not depend on product category
VS rational
not depend on product category
34
New cards
What determines age and life-cycle?
determines what consumer buys at each stage of life
35
New cards
What is personality?
set of distinguishing human psychological traits that lead to relatively consistent and enduring responses to environment stimuli
36
New cards
When a need becomes a motive?
whent it is aroused to a sufficient level of intensity to drive us to act
37
New cards
What is motivational strenght?
the degree to which a person is willing to expend energy to reach one goal as opposed to another reflects their underlying motivation to attain that goal
38
New cards
what is motivational direction?
they are goal oriented in that they drive us to satisfy specific needs
39
New cards
What are motivational conflicts?
* positively valued goals
* consumers are motivated to approach the goal and will seek out products that will be instrumental in attaining it
* avoiding negative goals
* consumers are motivated to avoid a negative outcome structuring their purchases or consumption activities
* consumers are motivated to approach the goal and will seek out products that will be instrumental in attaining it
* avoiding negative goals
* consumers are motivated to avoid a negative outcome structuring their purchases or consumption activities
40
New cards
What is Freud’s theory?
behavior is guided by subconscious motivations
41
New cards
What is Maslow’s Hierarchy of needs?
behavior is driven by lowest, unmet need
1. psychological needs
2. safety needs
3. social needs
4. esteem needs
5. self-actualization needs
\
1. psychological needs
2. safety needs
3. social needs
4. esteem needs
5. self-actualization needs
\
42
New cards
What is Herzberg’s two-factor theory?
behavior is guider by dissatisfiers and satisfiers
43
New cards
What is consumer product involvement?
the consumer’s level of interest in making a particular purchase, which can range from inertia t very high involvment
44
New cards
What is message-response involvement?
the consumer’s interest in processing marketing communications
45
New cards
What is perception?
the process by which we select, organize and interpret information inputs to create a meaningful picture of the world
46
New cards
What is a perceptual map?
tool which evaluates the relative standing of competing brands along relevant dimensions (scensory receptors)
47
New cards
What is selective attention?
the inclination for consumers to pay attention to messages that connect with their needs, beliefs, interests, and values
48
New cards
What is selective distortion?
how consumers interpret brand messaging in a way that fits with their preconceptions of that brand
49
New cards
what is selective retention?
how customers remember brand messaging based on their previously established needs, beliefs, interests, and values
50
New cards
what is sensory marketing?
stimulating 5 senses
* seeing
* hearing
* touching
* smelling
* tasting
* seeing
* hearing
* touching
* smelling
* tasting
51
New cards
How adding emotions to advertising helps?
more
* perception
* attention
* shares on social media
* perception
* attention
* shares on social media
52
New cards
what is experiential marketing?
samples
53
New cards
what are nostalgic brands?
used by consumers to retreive memories about past experiences and are often valued for their ability to do this
ex.: nutella, la laitière etc
ex.: nutella, la laitière etc
54
New cards
What are the stages of the buying decision process?
* problem recognition
* the buyer recognizes a problem/need triggered by internal/external stimuli
* information search
* internal/external
* deliberate/accidental
* pre-purchase / ongoing
* evaluation of alternatives
* purchase decision
* post-purchase behavior
* the buyer recognizes a problem/need triggered by internal/external stimuli
* information search
* internal/external
* deliberate/accidental
* pre-purchase / ongoing
* evaluation of alternatives
* purchase decision
* post-purchase behavior
55
New cards
what are beliefs?
descriptive thought that a consumer holds about something
56
New cards
what are attitudes?
person’s enduring favourable or unfavourable evaluations, emotional feelings and action tendencies toward some object or idea
57
New cards
What are the 3 types of attitude?
* conative : will to act
* emotional : feelings
* cognitive : knowledge
* emotional : feelings
* cognitive : knowledge
58
New cards
What are the bundle of attributes?
* core product
* actual product : packaging, style, desing, brand name
* augmented product : after-sale service, warranty, installation, delivery&credit
* actual product : packaging, style, desing, brand name
* augmented product : after-sale service, warranty, installation, delivery&credit
59
New cards
What is a product?
anything that can be offered to a market to satisfy a want or need
* ~~owning~~ ==> solution to a specific need
* ~~owning~~ ==> solution to a specific need
60
New cards
what is greenwashing?
exagerate “green” features and communicate on sustainability but they are not
\
ex.: TUI flights
\
ex.: TUI flights
61
New cards
what is packaging?
all the activities of designing and producing the container for a product
\
used as a marketing tool
* self-service
* consumer affluence
* company and brand image
* innovation opportunity
\
used as a marketing tool
* self-service
* consumer affluence
* company and brand image
* innovation opportunity
62
New cards
what is a planogram?
plan made by retailers in collaboration with brands to make sure that everything is at the right spot
* best product below because people would make the effort to grab them
* eye level to promote products
* best product below because people would make the effort to grab them
* eye level to promote products
63
New cards
what are the objectives of packaging?
* identify the brand
* convey descriptive and persuasive information
* facilitate product transportation and protection
* assist at-home storage
* aid product consumption
* convey descriptive and persuasive information
* facilitate product transportation and protection
* assist at-home storage
* aid product consumption
64
New cards
what is the customer journey?
* pre purchase
* during purchase
* post purchase
* during purchase
* post purchase
65
New cards
what is adoption?
an indivdual’s decision to become a regular user of a product
* awareness
* interest
* evaluation
* trial
* adoption
* awareness
* interest
* evaluation
* trial
* adoption
66
New cards
what are the factors that influence the adoption process?
* readiness to try new products
* personal influence
* personal influence
67
New cards
what defines market attractiveness?
* merket forces
* competitive intensity
* market accessibility
* competitive intensity
* market accessibility
68
New cards
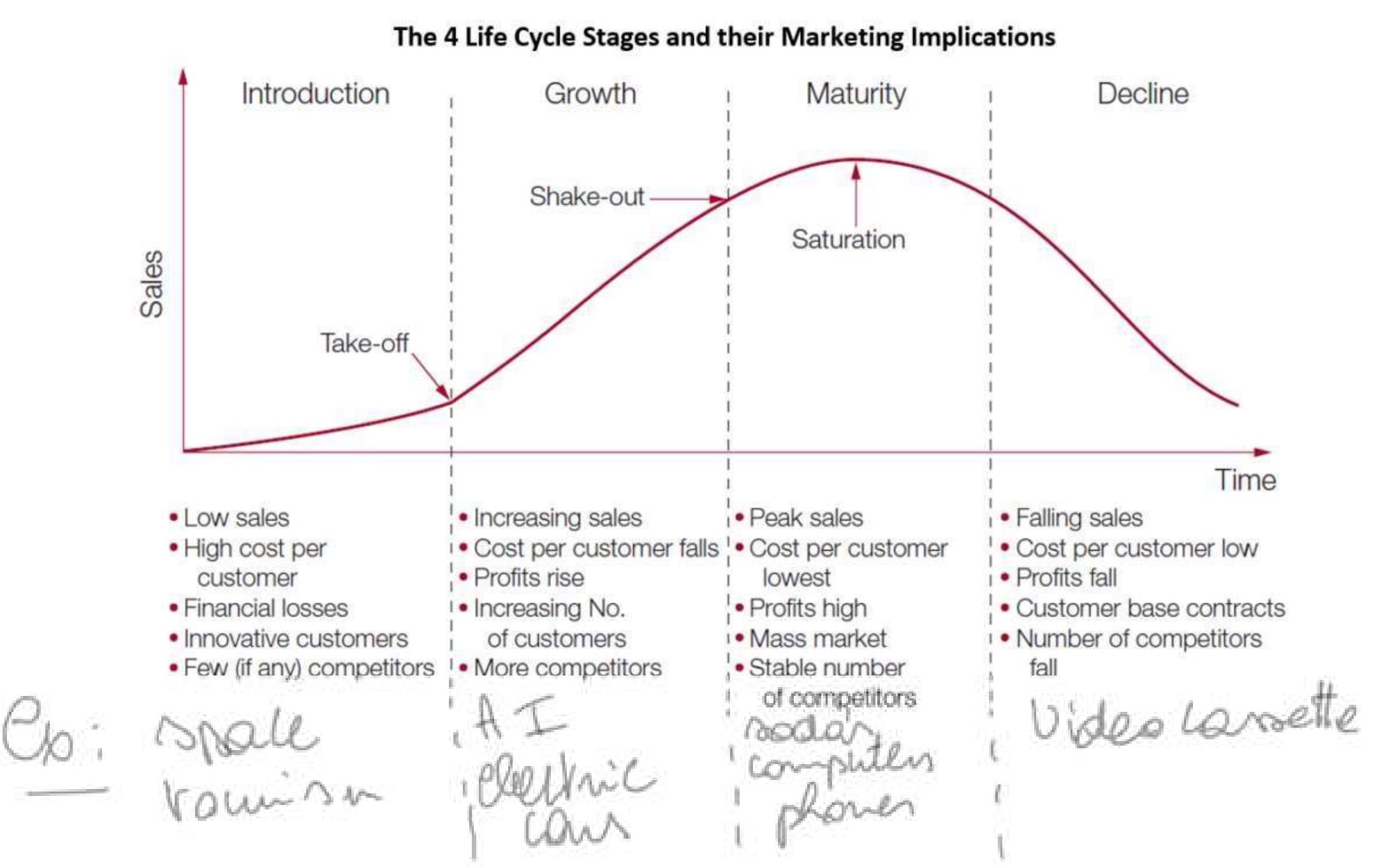
what is the product lifecycle model? (market forces)
* introduction
* growth
* maturity
* decline
* growth
* maturity
* decline
69
New cards
explain the introduction stage of the product lifecycle model
* pioneering advantages
* recall of brand name
* establishes product class attributes
* recrutes more consumers
* pioneering drawbacks
* imitators can surpass innovators
* once leadership is lost, it’s rarely regained
* recall of brand name
* establishes product class attributes
* recrutes more consumers
* pioneering drawbacks
* imitators can surpass innovators
* once leadership is lost, it’s rarely regained
70
New cards
explain the growth stage of the product lifecycle model
to sustain rapid market share growth
* improve product quality/ add new features
* new models/flanker products
* new market segments
* increase distribution coverage and new distribution channels
* shift from awareness and trial communication to preference and loyalty communication
* lower prices to attract price-sensitive buyers
* improve product quality/ add new features
* new models/flanker products
* new market segments
* increase distribution coverage and new distribution channels
* shift from awareness and trial communication to preference and loyalty communication
* lower prices to attract price-sensitive buyers
71
New cards
explain to me the maturity stage of the lifecycle product model
* market modification
* product modification
* market program modification
* product modification
* market program modification
72
New cards
explain to me the decline stage of the product lifecycle model
* eliminating weak products
* harvesting and divesting
* harvesting and divesting
73
New cards
How can we measure competitive intensity?
Porter’s 5 forces
* competitive rivalry
* threat of new entry
* byer power
* threat of substiution
* supplier power
* competitive rivalry
* threat of new entry
* byer power
* threat of substiution
* supplier power
74
New cards
Give me the caracteristics of perfect competition
number of firms : very large
type of product : standardized
control over price : none
entry conditions : no barriers
type of product : standardized
control over price : none
entry conditions : no barriers
75
New cards
Give me the caracteristics of monopolistic competition
number of firms : many
type of product : diffenrentiated
control over price : slight
entry conditions : no barriers
type of product : diffenrentiated
control over price : slight
entry conditions : no barriers
76
New cards
Give me the caracteristics of oligopoly
number of firms : few
type of product : standardized or diffenrentiated
control over price : considerable
entry conditions : large barriers
type of product : standardized or diffenrentiated
control over price : considerable
entry conditions : large barriers
77
New cards
Give me the caracteristics of monopoly
number of firms : one
type of product : unique
control over price : considerable if not regulated
entry conditions : large barriers
type of product : unique
control over price : considerable if not regulated
entry conditions : large barriers
78
New cards
what are the different types of competitors?
* direct competition
* indirect competition
* generic competition
* indirect competition
* generic competition
79
New cards
what are the Porter’s generic strategies?
* overall cost leadership
* shein, primark
* differentiation
* nike, addidas
* focus
* chanel, clothes for dissabled people
* shein, primark
* differentiation
* nike, addidas
* focus
* chanel, clothes for dissabled people
80
New cards
What are the targeting strategies?
* undifferentiated : baton mars
* partial undifferentiated : alcool
* differentiated : volksvagen
* partial differentiated : BMW
* concentrated : david loyd
* partial undifferentiated : alcool
* differentiated : volksvagen
* partial differentiated : BMW
* concentrated : david loyd
81
New cards
What is positioning?
* reason for being / value proposition
* benefits that differentiate brands
* benefits that differentiate brands
82
New cards
What are points-of-difference? PODs
attributes/benefits that consumers strongly associate with a brand, positively evaluate and believe they could not find to the same extent with a competitive brand
83
New cards
What are the PODs criteria?
* desirable
* deliverable
* differentiating
* deliverable
* differentiating
84
New cards
What are points-of-parity? POPs
attribute/benefit associations that are not necessarily unique to the brand but may in fact be shared with other brands
85
New cards
What are POPs criteria?
* category
* correlational
* competitive
* correlational
* competitive
86
New cards
what are the growth strategies?
* diversification growth
* integrative growth
* intensive growth
* integrative growth
* intensive growth
87
New cards
what is intensive growth?
corporate management should first review opportunities for improving existing businesses
* market penetration strategy
* market development strategy : geographic / new segmentation
* product development strategy
* diversification strategy : new product but close to your existing product
* market penetration strategy
* market development strategy : geographic / new segmentation
* product development strategy
* diversification strategy : new product but close to your existing product
88
New cards
what is integrative growth?
business can increase sales and profits through backward, forward or horizontal integration within its industry
89
New cards
what is diversification growth?
makes sense when good opportunities exist outside the present business
90
New cards
what is branding?
the process of endowing products and services with the power of a brand
91
New cards
what is a brand?
is a name, term, sign, design, symbol to identify the goods or services
92
New cards
what is the brands’ role for consumers?
* set nd fulfill expectations
* simplify decison making
* take on personal meaning
* simplify decison making
* take on personal meaning
93
New cards
what is the brands’ role for firms?
* secure competitive advantage
* create brand loyalty
* practicality
* create brand loyalty
* practicality
94
New cards
what are the types of brand name?
* “name” brand : IKEA, Google (mot)
* “figurative” brand : nike, apple (image)
* “semi-figurative” or “combined” brand : lacoste, bacardi (mot + image)
* “figurative” brand : nike, apple (image)
* “semi-figurative” or “combined” brand : lacoste, bacardi (mot + image)
95
New cards
what are the caracteristic of a brand value proposition?
* emotional value
* the utility derived from the feelings or affective states that a product generates
* social value
* the utility derived frome the product’s ability to enhance social self-concept
* functional value (price/value for money)
* the utility derived from the product due to the reduction of its perceived short term and loger term costs
* functional value (performance/quality)
* the utility derived from the perceived quality and expected performance of the product
* the utility derived from the feelings or affective states that a product generates
* social value
* the utility derived frome the product’s ability to enhance social self-concept
* functional value (price/value for money)
* the utility derived from the product due to the reduction of its perceived short term and loger term costs
* functional value (performance/quality)
* the utility derived from the perceived quality and expected performance of the product
96
New cards
what is brand identity?
the set of messages sent by a unique brand
97
New cards
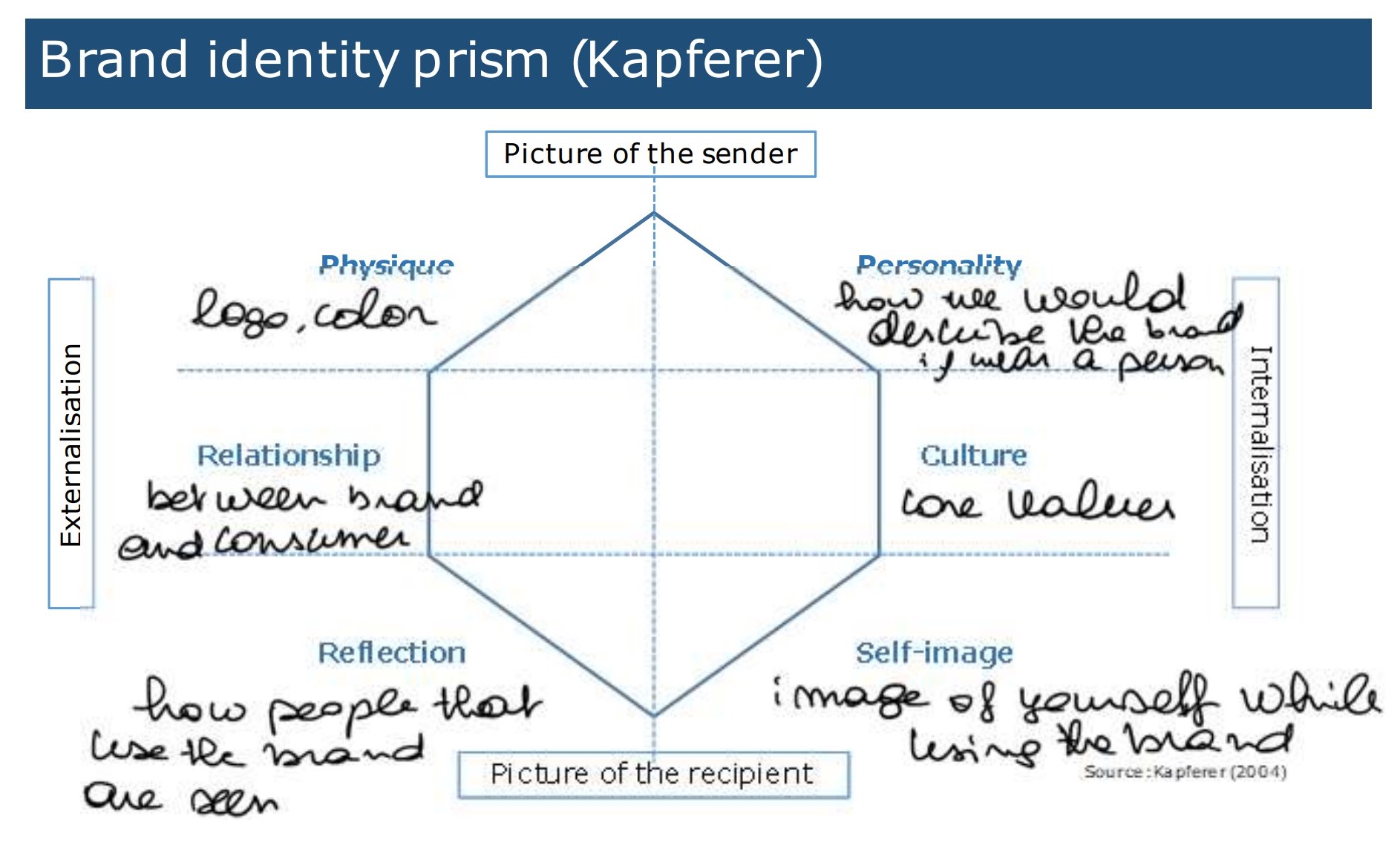
what is the brand identity prism
* physique
* personality
* relationship
* culture
* reflection
* self-image
* personality
* relationship
* culture
* reflection
* self-image
98
New cards
what is brand image?
the set of mental representations, both affective and cognitive, that an individual or a group of individuals associates with a company or a brand (= message received)
99
New cards
what is the difference between reflection and brand image
reflection : how people/consumers are supposed to be seen
brand image : how the message is perceived/ how they are effectively seen
brand image : how the message is perceived/ how they are effectively seen
100
New cards
what is brand equity?
* added value
* strenght of a brand
* strenght of a brand