Alkanes and Alkenes - year 11 IGCSE chemistry
1/7
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
Alkanes
A group of saturated hydrocarbons
General formula: CnH2n+2
Unreactive compounds but they do undergo combustion reactions
Saturated
To only have single carbon-carbon bonds, no double bonds
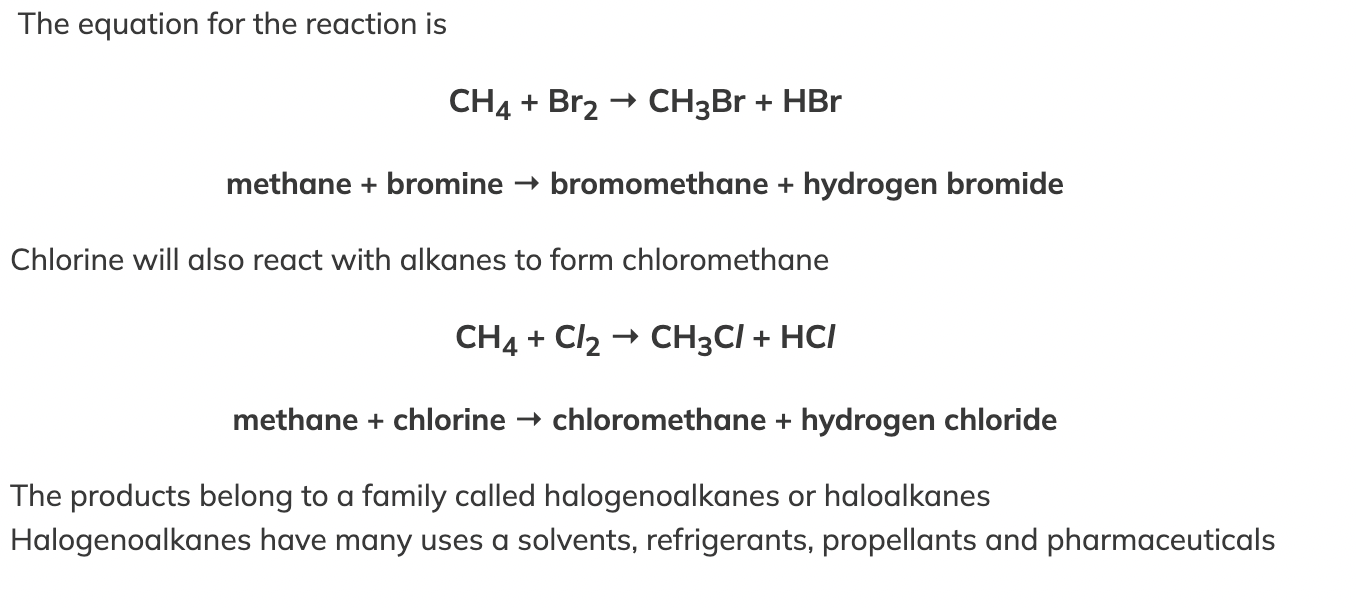
Relationship between alkanes and halogens
Alkanes undergo a substitution reaction with halogens in the presence of ultraviolet radiation
Alkenes
Contains a double-carbon bond
Unsaturated (because of the double bond
Much more reactive than alkanes
General formula: CnH2n
Characteristics of alkene’s double bond
The double bond alkenes have means they can make more bonds with other atoms by opening up the C=C bond and allowing incoming atoms to form another single bond with each carbon atom of the functional group
Define pent-n-tene (n could be any number)
n signifies the position (counting from the left) of the carbon double bond in the alkene. For example, pent-2-ene would mean that the carbon double bond is between the 2nd and 3rd carbon atom
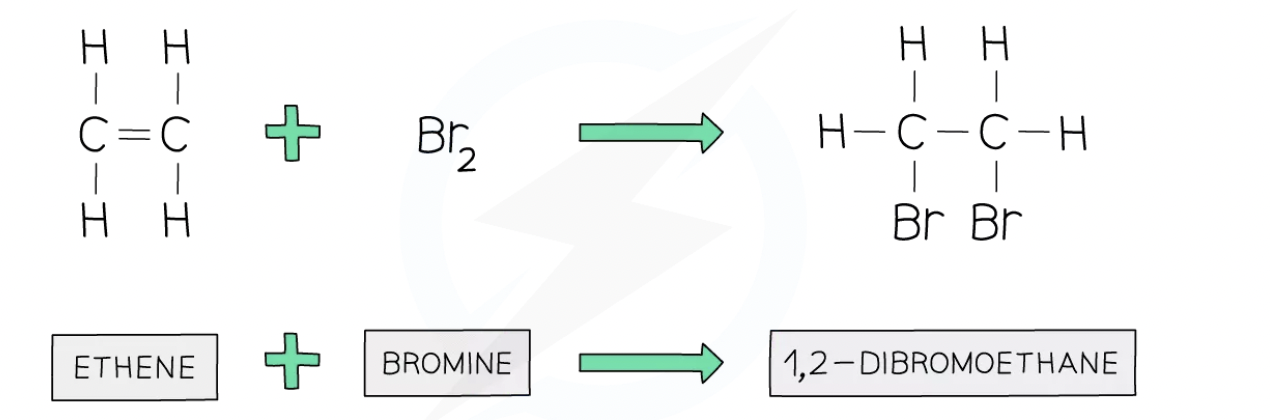
Relationship between halogens and alkenes
Alkenes undergo addition reactions in which atoms of a halogen add across the C=C double bond
Bromine water test
This determines whether a compound is an alkane or an alkene, this works because alkenes are much more reactive:
- If the bromine water decolors, it is an alkene (it reacts)
- if the bromine water stays orange, it is an alkane