N5 BIO multicellular organisms
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/104
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
105 Terms
1
New cards
chromosome complement
number of chromosomes a cell contains
2
New cards
reasons for cell division
* reproduce (unicellular)
* growth and repair (multicellular)
* growth and repair (multicellular)
3
New cards
diploid
cell with a double set of chromosomes
4
New cards
unicellular
organism composed of one cell
5
New cards
mulitcellular
organism composed of multiple cells
6
New cards
its important the chromosome compliment in daughter cells is maintained so that…
no information is lost and the cell can carry out the same functions as the parent cell
7
New cards
mitosis stage 1 & 2
1. each __chromosome doubles__ to form 2 identical __chromatids__
2. __chromosomes__ shorten & coil up. __Nuclear membrane__ starts to disappear
8
New cards
mitosis stage 3 & 4
3. __chromatids__ line up at the __equator__ and __spindle fibres__ attach to the __centromeres__
4. spindle fibres __pull apart__ pair of identical chromatids to __opposite poles of the cell__
9
New cards
mitosis stage 5 & 6
5. __new nuclear membranes form__, cytoplasm divides
6. 2 daughter cells are formed, the __daughter cells are identical to each other and the parent cell__
10
New cards
embryonic stem cells
* found in very early embryos
* have ability to develop into any type of cell the body requires
* can develop into complete organs
* have ability to develop into any type of cell the body requires
* can develop into complete organs
11
New cards
tissue/adult stem cells
* only regenerate cells associated with the tissues in which they are found
12
New cards
stem cells
* unspecialised cells found in animals
* can divide to produce more stem cells
* can divide to produce more stem cells
13
New cards
specialised cell
cell that has become differentiated to perform a specific function e.g. nerve cell, red blood cell, sperm cell
14
New cards
therapeutic application of stem cells
* bone marrow transplant
* skin grafts
* repairing heart muscle
* cornea repair
* skin grafts
* repairing heart muscle
* cornea repair
15
New cards
organise cell types
cells → tissue → organs → systems
\
e.g.
muscle cells → muscle tissue → heart → circulation system
\
e.g.
muscle cells → muscle tissue → heart → circulation system
16
New cards
main parts of CNS
* brain
* spinal cord
* spinal cord
17
New cards
CNS is connected to the rest of the body by…
neurons (nerves)
18
New cards
brain
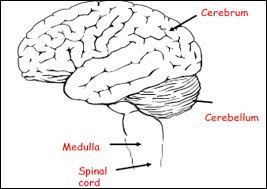
19
New cards
cerebrum
controls conscious thoughts, memory and personality
20
New cards
cerebellum
controls muscle coordination and balance
21
New cards
medulla
controls breathing and heart rate
22
New cards
CNS system
stimulus→ receptor→ sensory neuron→ inter neuron(in CNS)→ motor neuron→ effector→ response
23
New cards
reflex arc
* rapid reflex actions provides protection against possible harmful stimuli
\
* e.g. swallowing-(stimuli=touch/pressure)-(effect=muscle contract)-(protective role=prevent choking)
\
* e.g. swallowing-(stimuli=touch/pressure)-(effect=muscle contract)-(protective role=prevent choking)
24
New cards
synapse
* the space where two neurons meet
25
New cards
hormones
chemical messengers produced by endocrine glands
26
New cards
factors that increase risk of diabetes
* overweight
* age
* genetics (type 1)
* age
* genetics (type 1)
27
New cards
type 1 diabetes
* early, rapid onset
* no insulin produced
* requires injections
* no insulin produced
* requires injections
28
New cards
type 2 diabetes
* overweight, elderly
* resistance to insulin
* healthy, balanced lifestyles
* resistance to insulin
* healthy, balanced lifestyles
29
New cards
pancreas detects increase in blood sugar…
insulin released → insulin converts glucose into glycogen to remove glucose from blood → normal blood sugar level
30
New cards
pancreas detects decrease in blood sugar…
glucagon release increased → glucagon broken down into glucose → normal blood sugar level
31
New cards
H__i__ → __i__nsulin
(high blood sugar)
(high blood sugar)
glucose is gone → glucagon
(low blood sugar)
(low blood sugar)
32
New cards
diploid cells
each cell contains two matching sets of chromosomes
33
New cards
haploid cells
each cell contains one set of chromosomes
34
New cards
fertilisation
the nucleus of the male gamete: sperm (haploid) fuses with the nucleus of the female gamete: egg (haploid) to form a zygote (diploid)
35
New cards
plant
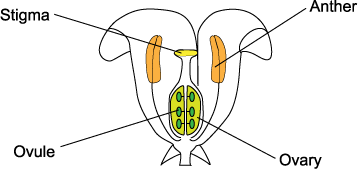
36
New cards
plant male gamete
pollen produced in the anther
37
New cards
plant female gamete
ovule produced in the ovary
38
New cards
animal male gamete
sperm produced in the testis
39
New cards
animal female gamete
egg cell produced in the ovary
40
New cards
male
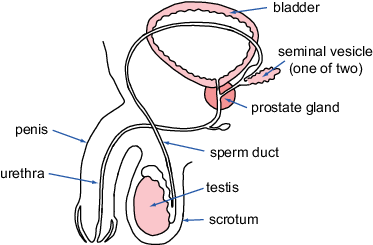
41
New cards
female
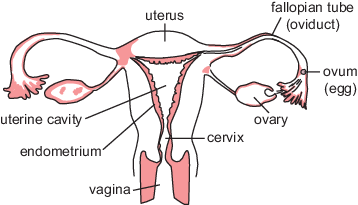
42
New cards
fertilisation in animals occurs inside…
the female in the oviduct
43
New cards
continuous variation
the inherited characteristic shows a range of values between a minimum to a maximum (cannot be put in distinct groups e.g. height)
44
New cards
discrete variation
the characteristic cannot be measured so forms distinct groups with no continuation of the characteristic in between e.g. eye colour
45
New cards
polygenic inheritance
* most phenotypes show continuous variation
* type of inheritance involving several genes acting together
* type of inheritance involving several genes acting together
46
New cards
gene
section of DNA strand that codes for a protein that gives the organism its characteristics
47
New cards
allele
different forms of a gene
48
New cards
phenotype
description if the appearance of the organism
49
New cards
genotype
the genes that an organism possesses, giving rise to the phenotype
50
New cards
homozygous
organism that has a genotype with 2 identical alleles either dominant or recessive
51
New cards
heterozygous
organism that has a genotype with 2 different alleles, one dominant and a hidden recessive allele
52
New cards
the reason why actual results differ is…
because fertilisation is a random process. Introducing the element of chance
53
New cards
upper epidermis function
thin outer layer - has no chloroplasts so allows light to pass through to mesophyll cells
54
New cards
palisade mesophyll function
* main site of photosynthesis
* cells contain many chloroplasts
* cells arranged to allow maximum absorption of light energy
* cells contain many chloroplasts
* cells arranged to allow maximum absorption of light energy
55
New cards
spongy mesophyll function
cells are loosely packed with moist air spaces between them to allow gases to diffuse quickly into the cells
56
New cards
vein
contains xylem and phloem vesseles
57
New cards
lower epidermis
lower layer of cells containing many pores called stomata (singular, stoma)
58
New cards
stoma
allows water vapour to leave and is site of gas exchange
59
New cards
guard cells
* cells that surround the stomata & control the opening and closing of the stomata
* stomata allow entry and exit of excess water vapour and oxygen
* stomata allow entry and exit of excess water vapour and oxygen
60
New cards
use of transport systems in plants
* allow water and minerals to travel to leaf cells
* allow sugar to move around
* allow sugar to move around
61
New cards
water & soil minerals are absorbed through…
root hair cells by osmosis and transported up the plant to the leaves in xylem
62
New cards
xylem vessels
* dead hollow tubes
* water and minerals move in upward direction
* supports the plant due to lignin
* water and minerals move in upward direction
* supports the plant due to lignin
63
New cards
xylem is supported by…to…
* lignin
* to withstand changes in pressure as water moves up the plant
* to withstand changes in pressure as water moves up the plant
64
New cards
transpiration
loss of water by the evaporation from the leaves of a plant
65
New cards
why do root hairs have a large surface area?
to increase absorption of water
66
New cards
factors affecting rate of transpiration
* change in temperature
* change in wind speed
* change in humidity
* surface area
* change in wind speed
* change in humidity
* surface area
67
New cards
transport of sugar
* transported in phloem tissue
* phloem tissue is alive
* sugars move up and down
* phloem is made up of: sieve tubes, companion cells
* phloem tissue is alive
* sugars move up and down
* phloem is made up of: sieve tubes, companion cells
68
New cards
potometer
measure rate of transpiration/rate of water uptake
69
New cards
red blood cell
* carries oxygen around the body
* biconcave
* contain haemoglobin
* don’t have a nucleus
* biconcave
* contain haemoglobin
* don’t have a nucleus
70
New cards
white blood cell
protects body from infection
71
New cards
plasma
liquid component of blood in which cells and other materials are carried
72
New cards
blood transports
* oxygen
* carbon dioxide
* glucose
* carbon dioxide
* glucose
73
New cards
RBC equation
haemoglobin + oxygen (lungs)
74
New cards
white blood cells destroy
pathogens
75
New cards
pathogens
* bacteria
* fungi
* virus
* fungi
* virus
76
New cards
main types of white blood cell
1. phagocytes
2. lymphocytes
77
New cards
phagocytes
destroy pathogens through a process called phagocytosis
78
New cards
lymphocytes
* produce antibodies which destroy pathogens
* each antibody is specific to a particular pathogen
* each antibody is specific to a particular pathogen
79
New cards
phagocytosis
1. phagocyte moves towards pathogen
2. phagocyte engulfs pathogen
3. pathogen destroyed by enzymes in phagocyte
80
New cards
left ventricle has a thicker muscle than right ventricle bc…
right ventricle only pumps blood a short distance to the lungs but the left ventricle pumps blood a greater distance to all other body parts
81
New cards
valves are found…
between the atria and ventricles and between the ventricle and the arteries leaving the heart
82
New cards
function of valve
prevent backflow of blood
83
New cards
artery
* function: carries blood away from the heart at high pressure
* structure: thick muscular walls to withstand pressure & narrow central cavity
* structure: thick muscular walls to withstand pressure & narrow central cavity
84
New cards
vein
* function: carries blood towards the heart at low pressure
* structure: contain valves to prevent backflow of blood, wide central cavity & thick muscular wall (but not as thick as artery)
* structure: contain valves to prevent backflow of blood, wide central cavity & thick muscular wall (but not as thick as artery)
85
New cards
capillaries
* smallest blood vessel
* found in dense networks close to body cells
* where exchange of materials between blood and body cells take place
* found in dense networks close to body cells
* where exchange of materials between blood and body cells take place
86
New cards
capillary features
* very thin walls- fast exchange of gases and nutrients
* found in dense networks- rich blood supply so more exchange of materials
* large surface area- maximum exchange of materials
* found in dense networks- rich blood supply so more exchange of materials
* large surface area- maximum exchange of materials
87
New cards
coronary arteries
blood supply to the heart muscle
88
New cards
blood flow through the heart, lungs & body (deoxygenated blood)
vena cava → right atrium → right ventricle → pulmonary artery → lungs
89
New cards
blood flow through the heart, lungs & body (oxygenated blood)
lungs → pulmonary vein → left atrium → left ventricle → aorta → body cells + tissue-(also deoxygenated)
90
New cards
aorta
carries blood away from the heart
91
New cards
atria
Upper chambers of the heart that pass blood to the lower ventricles
92
New cards
pulmonary artery
Artery that carries deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs
93
New cards
pulmonary vein
Vein that carries oxygenated blood from the lungs to the heart
94
New cards
vena cava
Blood vessels that carry deoxygenated blood to the heart from the body
95
New cards
ventricles
Lower chambers of the heart that receive blood from the upper atria
96
New cards
materials required to be absorbed into cells
* oxygen for respiration
* nutrients
* nutrients
97
New cards
waste material that needs to be removed from cells
carbon dioxide
98
New cards
where do materials travel around the body
bloodstream
99
New cards
features of surfaces that carry out absorption exchange
* large surface area
* thin walls
* rich blood supply
* thin walls
* rich blood supply
100
New cards
lungs
* gas exchange organs
* have a large number of alveoli
* have a large number of alveoli