Chapter 17- Energy Changes
- According to the Law of conservation of energy, energy cannot be created or destroyed, but just changed from one form to another in chemical or physical processes.
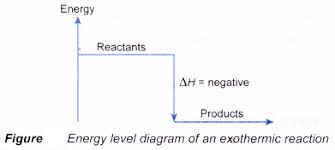
- In exothermic reactions, energy is given out as heat so the temperature of the reaction mixture rises.
- Examples of exothermic reactions: combustion, corrosion, neutralisation, respiration.
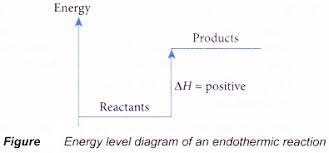
- In endothermic reactions, energy is taken in as heat so the temperature of the reaction mixture falls.
- Examples of endothermic reactions: photosynthesis, decomposition,
- Heat/enthalpy change (𐤃H) is the amount of heat energy involved in the reaction. It is measured in kilojoules (kJ)
- The enthalpy change is negative in exothermic reactions since heat is lost to the surroundings, while in endothermic reactions, it is positive as heat is gained.
ENERGY LEVEL DIAGRAMS
BOND BREAKING AND FORMATION
- Every reaction requires either bond making or bond breaking or both.
- Bond breaking is an endothermic process while bond making is an exothermic process
- Therefore, processes, where energy taken in in bond breaking, is greater than the energy given out in bond making, the process is endothermic and vice versa.
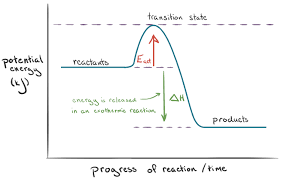
ACTIVATION ENERGY
- Some reactions do not occur at room temperature. The energy required to start the reaction is called the activation energy (Ea).
Energy profile diagrams:

- Fuels are substances burned in air to produce energy in a process called combustion.
- In presence of sufficient oxygen, complete combustion occurs producing carbondioxide and water, while incomplete combustion occurs when the oxygen is insufficient. Carbon monoxide and water are the products of incomplete combustion.
- The most common type of fuel are the fossil fuels. However, they are the biggest source of pollution.
- Fuel cells are chemical cells where reactants are continuously supplied to produce electricity directly. An example is the hydrogen-oxygen fuel cell. Due to this being eco-friendly, hydrogen might replace fossil fuels to an extent in the future.
A good fuel must:
- produce a lot of energy when burnt.
- be safe to use and convenient to store.
- cheap and readily available.
- not produce toxic gases or pollutants, or smoke.