Bio 225 Exam 1 - Endocrine System - Lloyd
1/34
Earn XP
Description and Tags
UofM Biology 225 Exam 1 - Endocrine System
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
Types of cell signaling
autocrine/paracrine, nervous, endocrine, direct cell signaling (inter-individual)
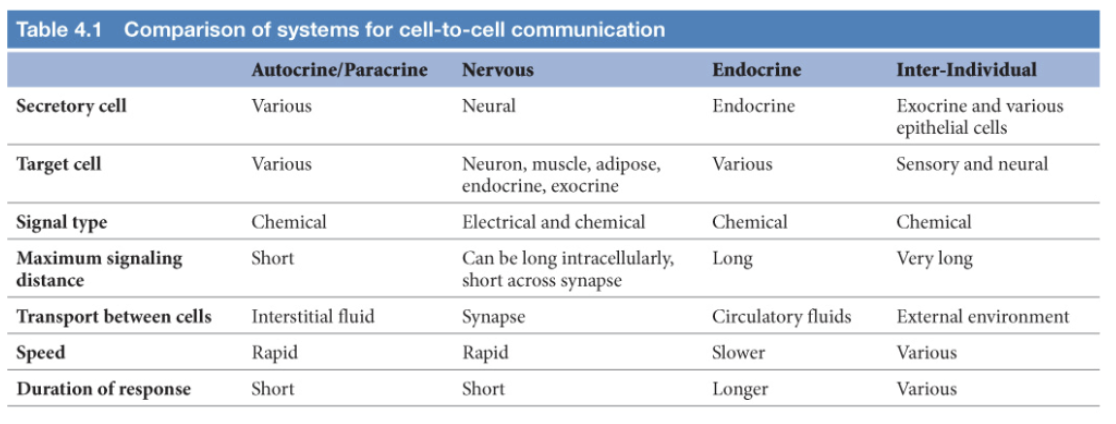
Secretory cell, target cell, signal type, max. signaling distance, transport b/w cells, speed, and duration of response for autocrine/paracrine cell signaling
various; various; chemical; short; interstitial fluid; rapid; short
Secretory cell, target cell, signal type, max. signaling distance, transport b/w cells, speed, and duration of response for nervous cell signaling
neural; neuron, muscle, adipose, endocrine, exocrine; electrical and chemical; can be long intracellularly, short across synapse; synapse; rapid; short
Secretory cell, target cell, signal type, max. signaling distance, transport b/w cells, speed, and duration of response for endocrine cell signaling
endocrine; various; chemical; long; circulatory fluids; slower; longer
Secretory cell, target cell, signal type, max. signaling distance, transport b/w cells, speed, and duration of response for inter-individual cell signaling
exocrine and various epithelial cells; sensory and neural; chemical; very long; external environment; various; various
Classes of chemical messengers
peptides (hydrophilic), steroids (hydrophobic), amines (hydrophilic), lipids, purines, gases (we study firsts 3)
hormones are
chemical substances released by one cell which act on another
The ____ of the messenger effects the ______ _______
structure; signaling mechanism
ex: hydrophobicity
Hormones are divided into two different groups based on
hydrophobicity
Hydrophilic messengers (hormones): storage, secretion, transport, receptor, effects
Intracellular vesicles; exocytosis; dissolved in extracellular fluids; transmembrane; rapid
Hydrophobic messengers (hormones): storage, secretion, transport, receptor, effects
synthesized on demand; diffusion across membrane; short distance: dissolved in extracellular fluid, long distances: bound to carrier proteins; intracellular or transmembrane; slower or rapid
Peptide/Protein hormones
hydrophilic; soluble in aqueous solutions; travel to target cell dissolved in extracellular fluid; rapid effects on target cells
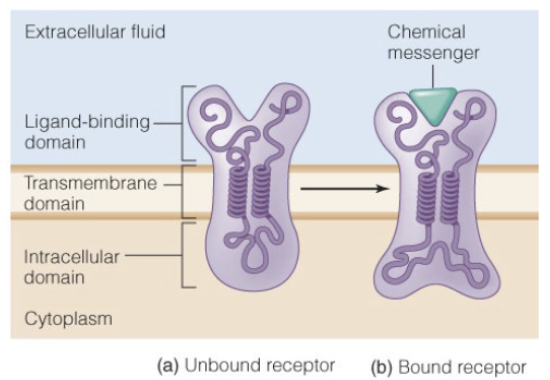
Peptide/Protein hormones bind to
transmembrane receptors causing signal transduction
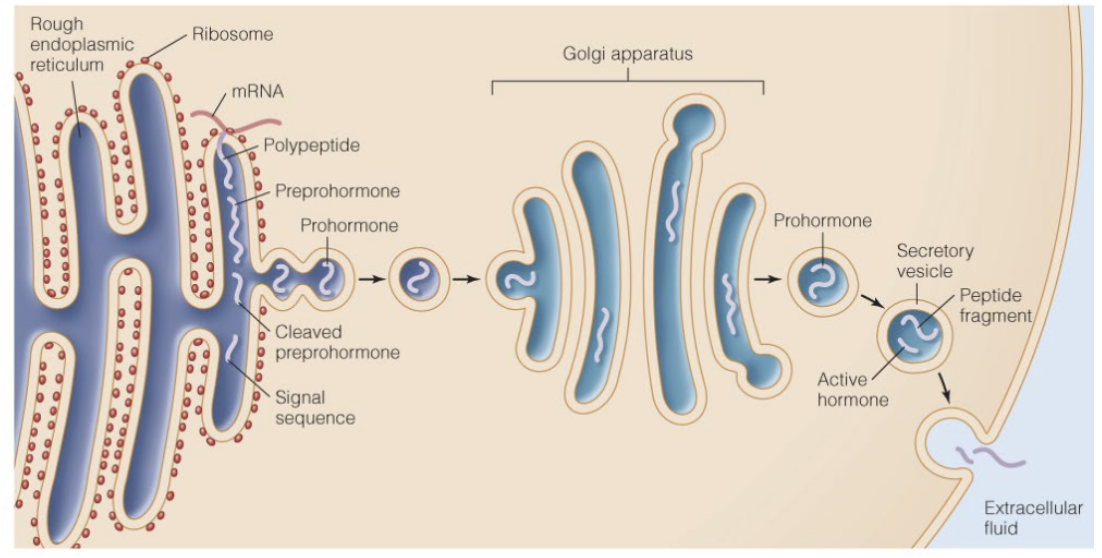
Peptide hormone production and release
Synthesized in RER as preprohormone —> preprohormone cleaved to prohormone —> Golgi apparatus for protein modification and packaging into vesicle —> prohormone in vesicle cleaved into peptide fragment and active hormone —> active hormone released
AVP aka
vasopressin and antidiuretic hormone
Function of AVP
works to control blood pressure by 1) increases H20 reabsorption and 2) constricts arterioles which increases BP
Synthesis and secretion of AVP
RER: arginine vasopressin apart of larger polypeptide as preprovasopressin (includes neurophysin and glycoprotein and signal peptide —> signal peptide cleaved making provasopressin —> leaves RER —> modified packaged by Golgi apparatus into secretory vesicle —> cleavage again into AVP (and glycoprotein and neurophysin)
Secretory vesicles: cleavage again to separate AVP
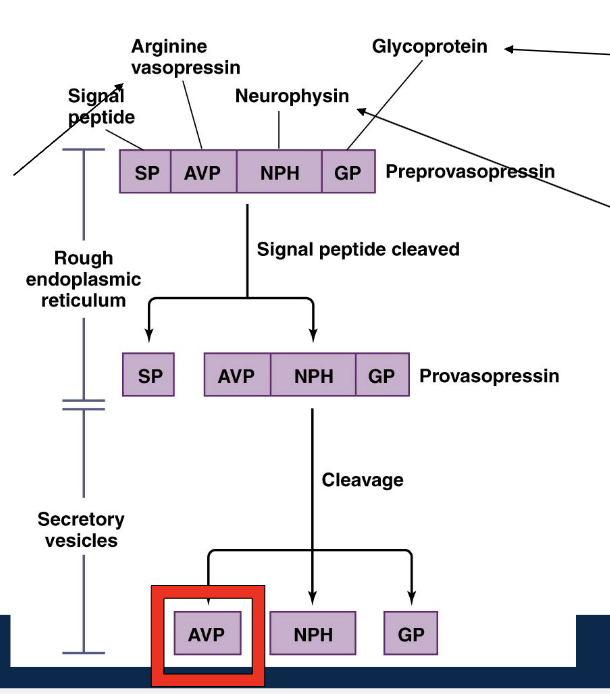
glycoprotein
protein w/ an oligosaccharide side chain
neurophysin
carrier protein for oxytocin and vasopressin
Amine hormones are
hormones that possess amine group (-NH2)
most hydrophilic (thyroid hormones are hydrophobic)
examples of amine hormones
acetylcholine, catecholamines (dopamine, norepinephrine, epinephrine), serotonin, melatonin, histamine, thyroid hormones
amine hormones are sometimes called and naming
biogenic amines
end in -ine
amine hormones are what kind of hormones
some”true” (endocrine) hormones, some neurotransmitters, some both
amine hormones have
diverse effects
Steroid hormones are derived from
cholesterol (three 6-C rings and one 5-C ring)
Steroid hormone examples
pregnenolone, progesterone (cortisol, testosterone, corticosterone —> aldosterone)
3 classes of steroid hormones
mineralocorticoids, glucocorticoides, reproductive hormones
steroid hormones synthesized by
smooth ER or mitochondria
steroid hormone naming
end in -one
Mineralocorticoids
electrolyte balance (water ion balance)
glucocorticoides
stress hormones
reproductive hormones
reglate sex-specific characteristics
Steroid hormones
hydrophobic (can diffuse thru plasma membrane)
cannot be stored in cell; must be synthesized on demand
Steroid hormones pathway
synthesized on demand —> the chemical messenger binds to carrier proteins (most not all) —> circulatory system carries the free and bound messenger to target cell —> free messenger binds to intracellular or transmembrane receptors (usually intracellular)
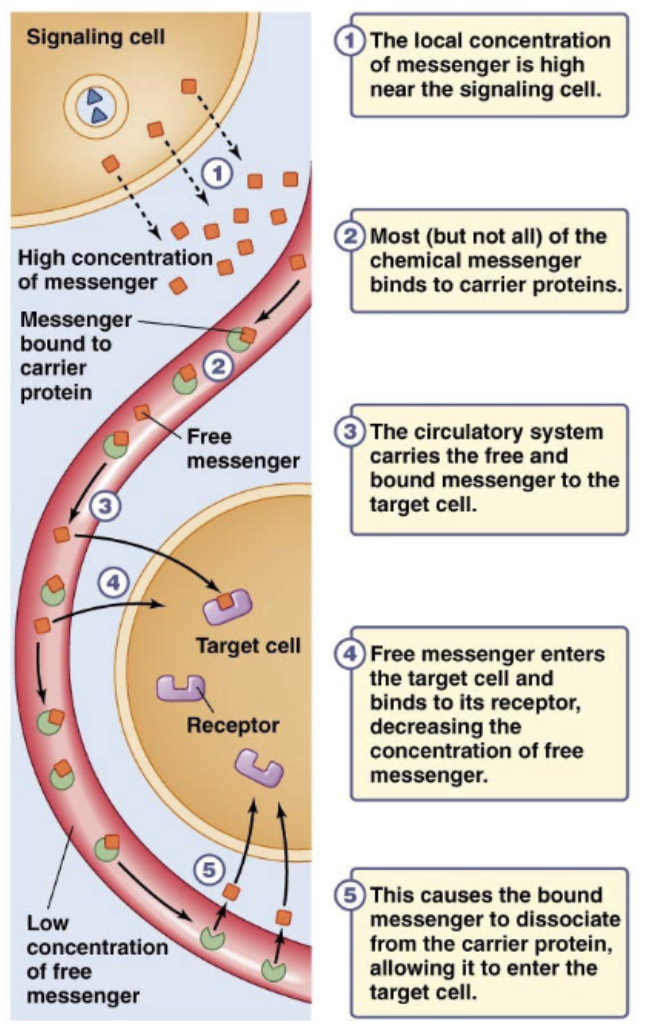
steroid hormone effect speed
slow effects on target cell (gene transcription)
stress hormone cortisol has rapid non-genomic effects