chapter 9 - muscle tissues
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
functions of skeletal muscle? list 4
produces body movements
stabilize body positions
store proteins, calcium, glucose
helps regulate body temperature
properties/functions of muscle? list 4
excitable = produces APs when enough stimulation
contractile = generate force by shortening and pulls structures together
extensibility = can stretch w/o damage; critical to moving or for movement to happen
elastic = muscle tissue stretched = can go backt o resting length afterwards w/o damage
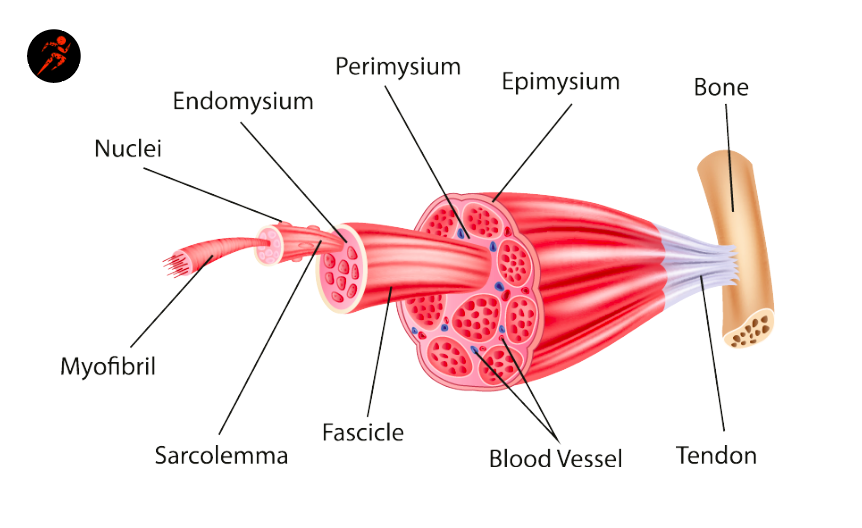
STRUCTURE OF A SKELETAL MUSCLE: what is muscle belly?
numbers?
truth?
arrangement?
a body of muscle connected to skeleton by tendons
hundreds to thousands of muscle fibers
highly vascular
may be arranged in a variety of shapes depending on function
STRUCTURE OF A SKELETAL MUSCLE: what are tendons?
bundles?
shapes?
made up of dense regular ct and minimally vascular
parallel bundles of collagen fibers with few fibroblasts to maintain dense regular ct
many shapes depending on function
can be broadsheaths
CT COVERINGS: endomysium
type of ct?
function?
carries?
innermost layer that covers each muscle fiber
reticular; loose ct = lots of elastic fiber
bind muscle fibers while allowingn them to move freely
carries small blood supply called capillaries
CT COVERINGS: perimysium
what is fassicle?
ct?
movement?
carries?
covers each fasicle and holds the muscle bundle together. allows muscle fibers to act w/o interrupting e/o
dense irregular ct
allows some freedom of movement
carries blood vessels
CT COVERINGS: epimysium
ct?
function?
truth?
covers muscle belly on top of the outside, outer most layer
dense irregular
binds fasicles together
continuous layers, fibers interwoven to keep muscles together
MICROSCOPIC ANATOMY: mature muscle fibers size?
develops from?
mature fiber?
what can it not do?
10-100 micrometer in diameter, 10-30 cm long
develop from fusion of 100+ myoblasts (immature muscle stem cells)
mature fiber: single cell with 100+ nuclei
cannot divide = terminally differentiated
MICROSCOPIC ANATOMY: hypertrophy
truth?
increased…?
fiber?
function?
enlargement of existing fibers
muscle growth is due to hypertrophy
increased production of myofibrils, mitochondria, organelles
fiber increases in diameter
capable of more forceful contractions (can lift heavy things)
MICROSCOPIC ANATOMY: satellite cells
what can it do?
ability?
damage effect?
myoblasts in mature skeletal muscles scattered through diff muscles and muscle groups
can divide and fuse to make new muscle fibers
limited ability to regenerate muscle fibers after damage
significant muscle damage leads to muscle fibers replaced with scar tissue
MICROSCOPIC ANATOMY: what is scar tissue?
dense ct; cannot contract but reduces power and connect and stretch. muscle is less functional than before
MICROSCOPIC ANATOMY: myostatin
knocked down: signals not as strong as they should be
knocked out: not sending signals at all; myostatin not made
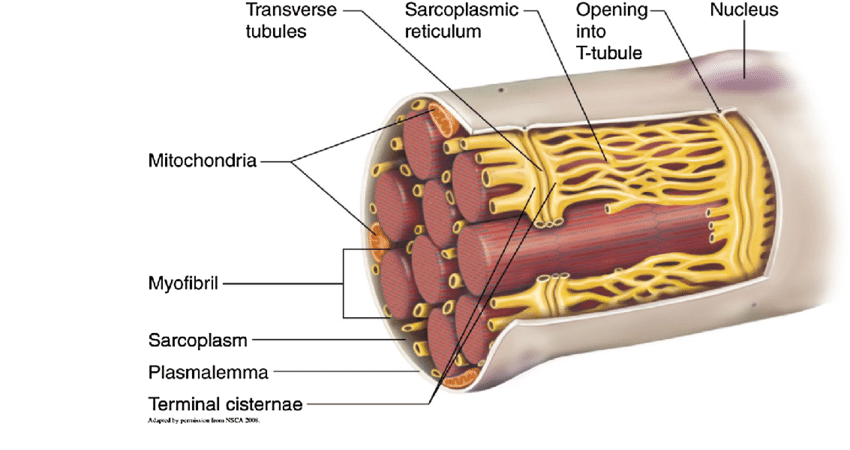
MICROSCOPIC ANATOMY: sarcolemma, sarcoplasm (truth?), myoglobin, mitochondria
sarcolemma: plasma membrane of muscle fibers
sarcoplasm: cytoplasm of a muscle fiber (evreything inside the muscle fiber but not the nucleus)
has lots of glycogen that stores glucose to release and generate ATP
myoglobin: protein, binds to oxygen to carry out blood.
mitochondria: present in rows throughout fiber
MICROSCOPIC ANATOMY: transverse tubules / aka
what is it
looks like
opens to
importance
t tubules
invaginations (inward folding) of sarcolemma
tunnel from surface toward center of each fiber
open to the outside, filled with interstitial fluid surrounding the cells
importance: signal to contract spreads, signals go through and stimulates to contract together
MICROSCOPIC ANATOMY: sarcoplasmic reticulum
similar to
expanded section is called
what’s triad
system of membranous sacs
smooth er, stores calcium to trigger contraction
terminal cisterns = end sacs against t tubules
triad: 1 t tubule + 2 terminal cisterns
MICROSCOPIC ANATOMY: myofibrils vs filaments
myofibrils = contractile elements
bundles of contractile protein filaments
striated
filaments
thin = 8 nm diameter, made primarily of actin
thick = 16nm, made primarily of myosin
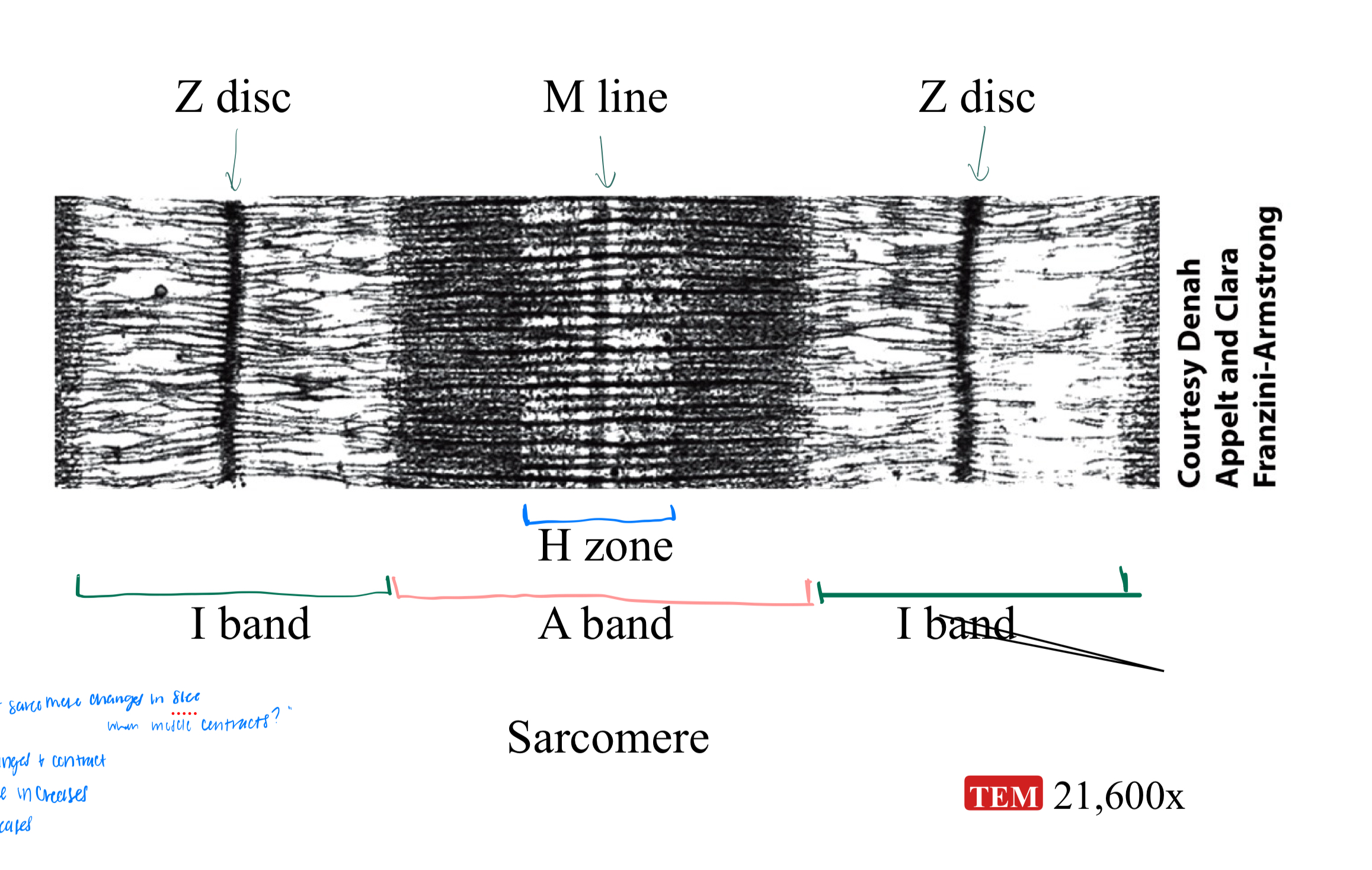
MICROSCOPIC ANATOMY: sarcomere, z-discs, I band, A band
sarcomere = basic functional unit of a myofibril
z discs = narrow regions of dense protein, separate one sarcomere from the next (start and stop of a sarcomere)
I band = thin filaments only, lighter region
A band = length of thick filament, darker region
MICROSCOPIC ANATOMY: A band regions:
zone of overlap
h zone
m line
zone of overlap = edges of A band, where thin and thick filaments overlap
H zone = center of A band, thick filaments only
M line = center of H zone, line of proteins holding thick filaments in place
PRACTICE: what part of sarcomere changes in size when a muscle contracts?
think: I band, overlap zone, H zone
i band changes and contract
overlap zone increases
h zone decreases
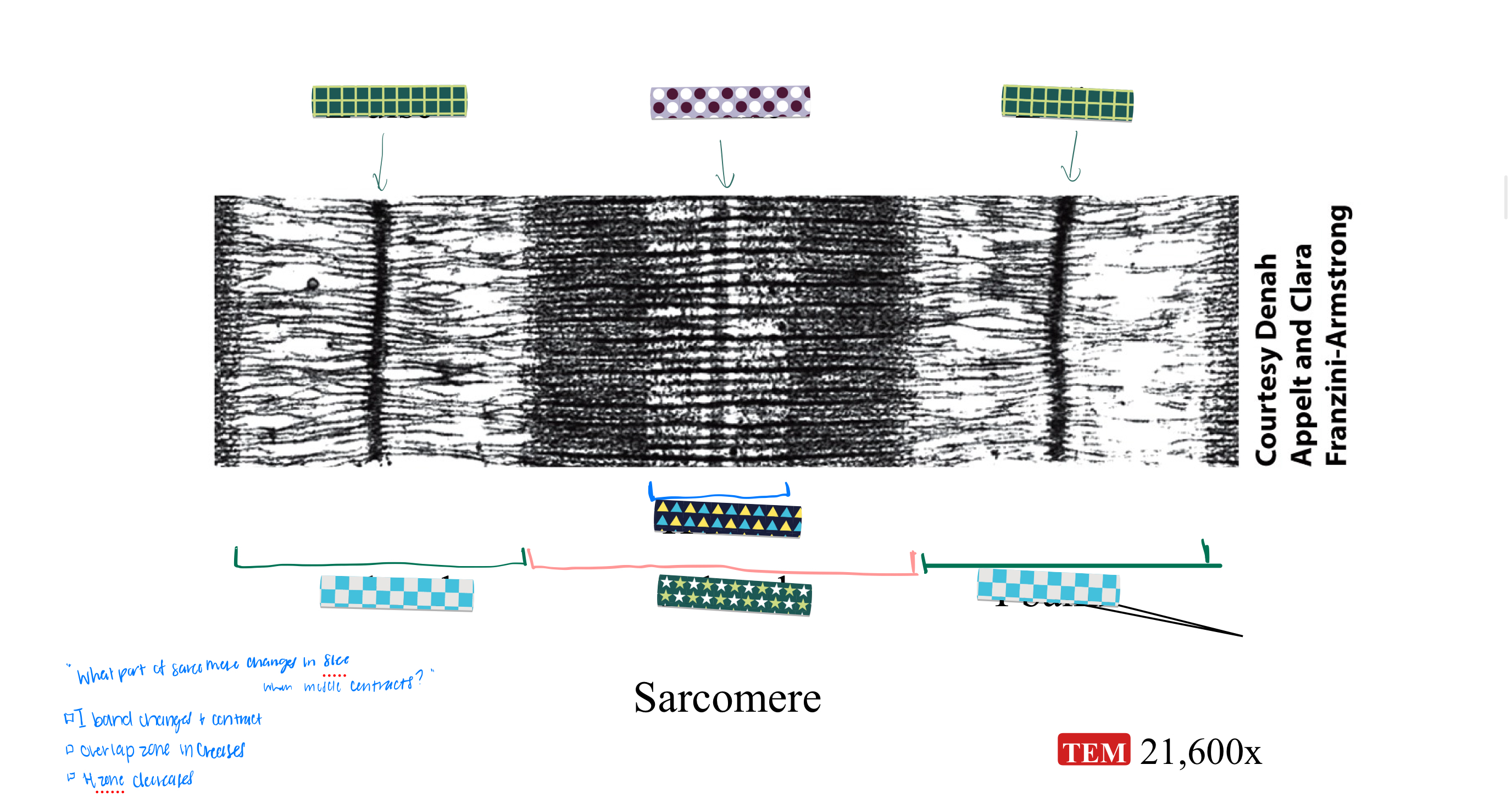
PRACTICE: label this sarcomere
CONTRACTILE MUSCLE PROTEINS: what are contractile proteins?
myosin
motor protein
generate force occuring w/ contraction
myosin: main component of thick filaments, type of contractile protein
motor protein: converts chemical energy from ATP to mechanical energy
300 molecules of myosin from 1 thick filament
CONTRACTILE MUSCLE PROTEINS: myosin 2 components
tails = point towards M line, line parallel to each other
heads = extend towards thin filaments
break ATP = functional area to hold myosin together
CONTRACTILE MUSCLE PROTEINS: actin
truth?
main component of thin filaments
each has a myosin binding site where myosin heads can attach
can’t break ATP = can’t generate force
acts like a rope that myosin pulls to generate force
REGULATORY MUSCLE PROTEINS: what are they?
type: tropomyosin
turn contraction on and off; associated with actin to regulate myosin’s access to actin
tropomyosin: covers myosin binding sites on actin to get in between thin and thick proteins to block contraction
REGULATORY MUSCLE PROTEINS: troponin
bounded to
complex proteins holding tropomyosin in place; regulates its location
when bound to calcium, will move tropomyosin away from myosin binding sites and changes its shape
contraction only happens when calcium is present
STRUCTURAL MUSCLE PROTEINS: what are they
how many?
contribute to alignment of thin and thick filaments, stability, elasticity, and extensibility of myofibrils
dozen identified
STRUCTURAL MUSCLE PROTEINS: titin
3rd most abudant protein in skeletal muscle
extends from z disc to m line
largest known protein
anchors thick filament to both z discs and m line, stabilizes position of the filament
accounts for elasticity and extensibility of myofibrils
STRUCTURAL MUSCLE PROTEINS: myomesin vs nebulin
myomesin = forms M line stabilizing thick filaments, binds to titin
nebulin = anchors thin filaments to Z discs and hold it in place
STRUCTURAL MUSCLE PROTEINS: dystrophin
links think filaments to integral membrane proteins of sarcolemma, transmits tension to tendons
CONTRACTION: sliding filament mechanism/theory
myosin heads walk along thin filaments and pulls the thin filaments towards M line so sarcomere shortens
REMEMBER: thick and thin filaments are not shortened, just overlapping them more
SKELETAL MUSCLE FIBERS: red vs white fibers
red fibers = high myoglobin (related to hemoglobin)
ex: red liquid on meat packaging is myoglobin leaking out from the meat, not blood
white fibers = low myoglobin
SKELETAL MUSCLE FIBERS: slow oxidative fibers
aka SO or type 1
dark red - lots of myoglobin; stockpile of oxygen
generate atp aerobically; uses atp efficiently
slow contraction, uses atp slowly
fatigue resistant = capable of sustained contraction, endurance
SKELETAL MUSCLE FIBERS: fast oxidative glycolytic fibers
FOG or type IIa
red = contains some myoglobin
generate atp both aerobically and anaerobically (glycolysis)
faster contraction with some fatigue resistance
uses atp faster
used for walking and jogging
SKELETAL MUSCLE FIBERS: fast glycolytic fibers
FG or type IIb
white = low myoglobin
stores lots of glycogen
generates ATP by glycolysis; anaerobic, least sufficient with 2 atp
contracts strong and fast and fatigues quickly
intense anaerobic movements of short duration; ex weight lifting
contraction of type 1, type 11a and type 11b
type 1 motor units = fast > weak contractions
type i + type iia = stronger contraction
type 1 slowest, type 11a second slowest, type 11b fastest in terms of fatigue
most skeletal muscle contain all 3 fiber types
SKELETAL MUSCLE FIBERS: exercise and muscle fibers
affects characteristics of existing fibers
endurance exercises = gradual transformation of some FG fibers to FOG
high intensity exercises = increase size and strength of FG fibers
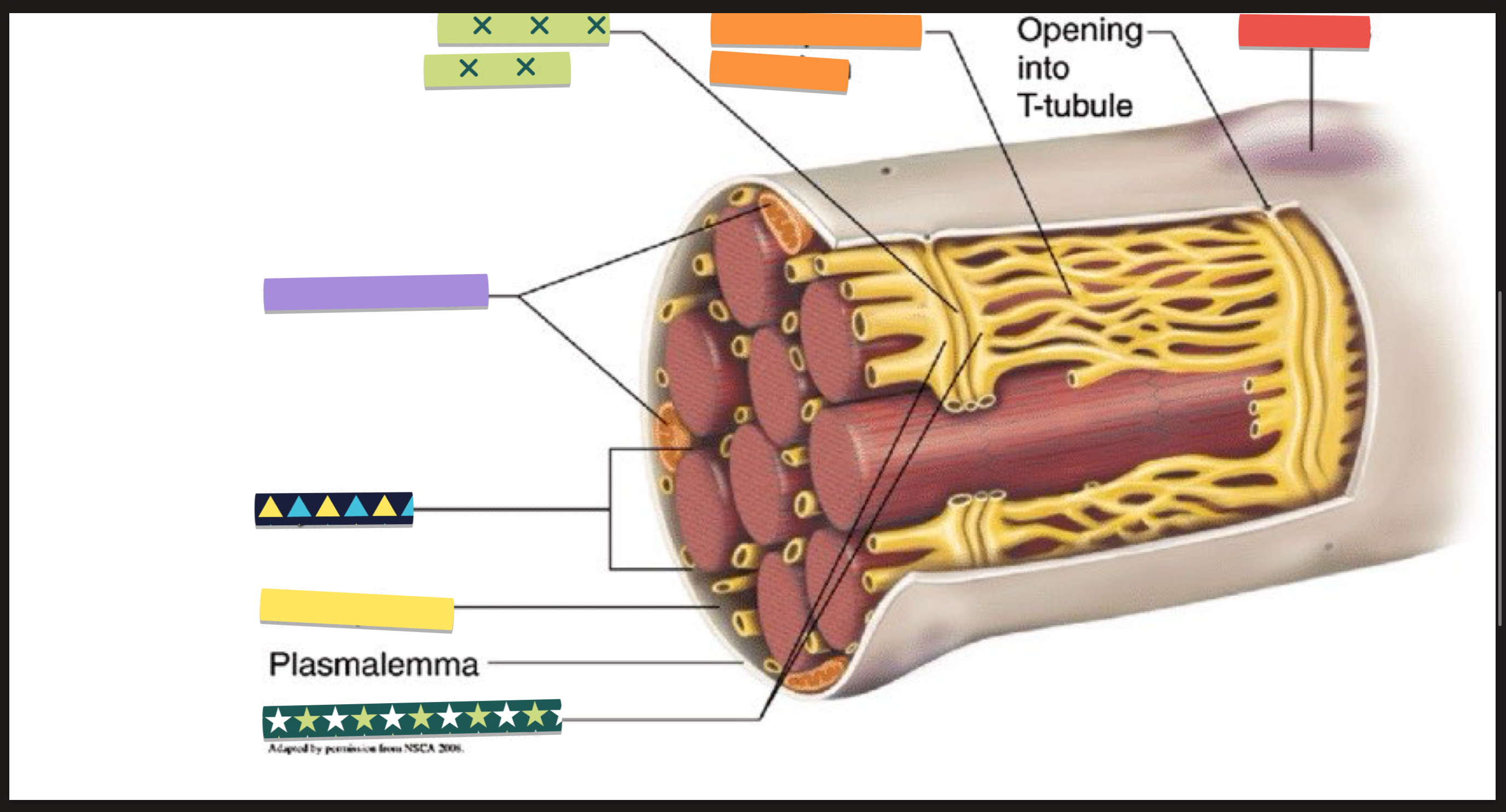
PRACTICE: label this muscle fiber
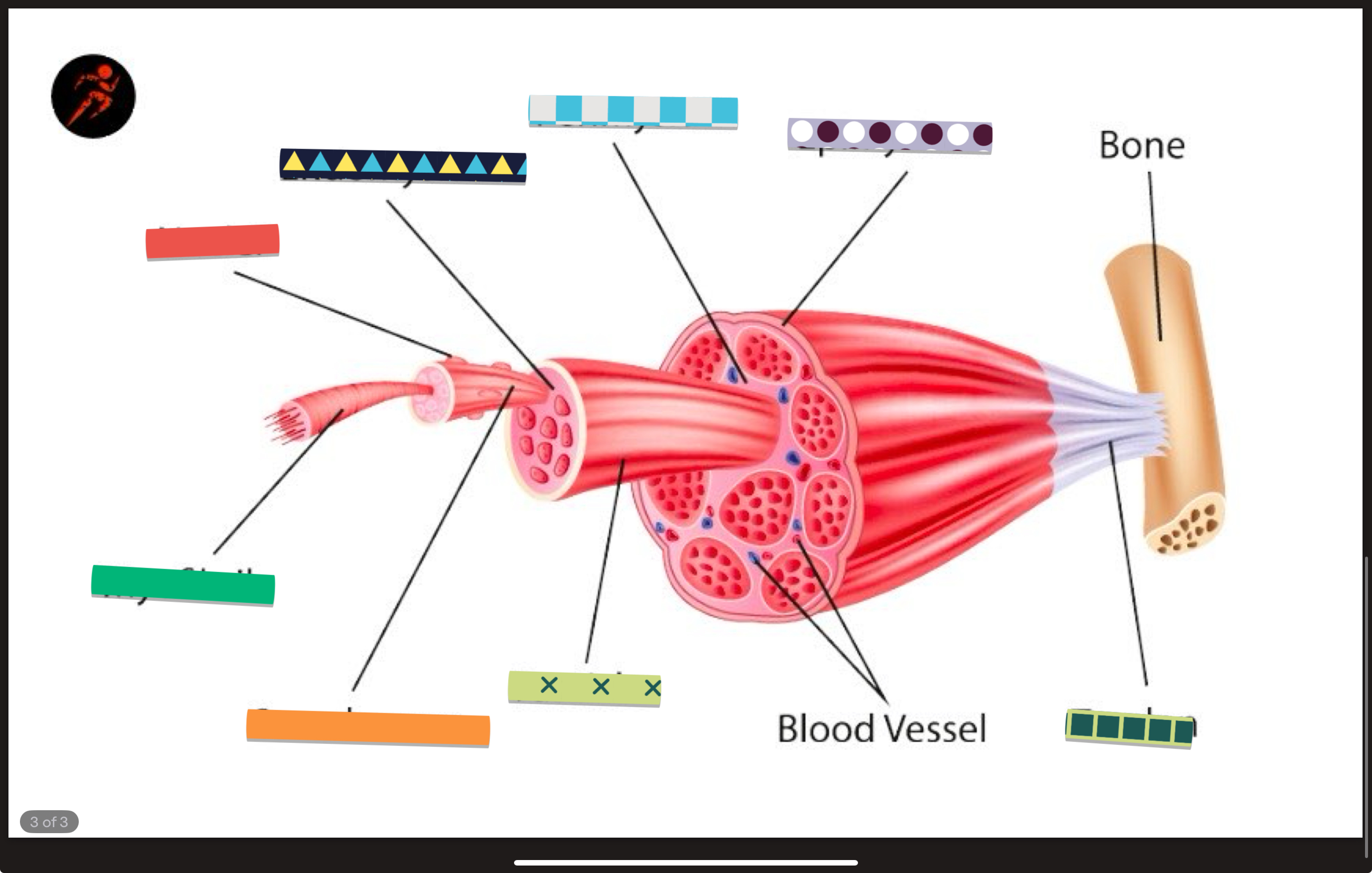
PRACTICE: label this