Kearns- Targeted Cancer Therapies
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
75 Terms
What suffix is used for monoclonal antibodies that have cancer cell growth inhibitory properties?
“mab”
The generic naming formula is prefix + ________ + ________.
What do they mean in regards of the drug?
prefix + subsystem/substem + stem
subsystem= refers to molecular target
stem= refers to the drug class
In monoclonal antibodies, the middle of the word aka a “substem or subsystem” indicates its molecular target.
What are these 3 substems?
Where do each of these target?
“-ci-” Circulatory system target
“-tu-” targets tumor growth
“-li-” targets the immune system
What is the subsystem name for each of the following:
tyrosine kinase inhibitor
proteasome inhibitor
cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor
poly ADP-ribose polymerase inhibitor
tyrosine kinase inhibitor: -tinib
proteasome inhibitor: -zomib
cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor: -cilcib
poly ADP-ribose polymerase inhibitor: -parib
Name the source of each of the following:
-ximab
-zumab
-mumab/-umab
chimeric
humanized
fully human
What drug class does the stem name “-ib” refer to?
small molecules with INHIBITORY properties
Which is bigger in size?
a. drug with -mab stem
b. drug with -ib stem
a
PRACTICE:
From the name, what can you tell me about the drug “Adalimumab”?
it is a mAb
it is fully human (aka low immunogenicity)
it targets the immune system
What are the 3 different methods mAb use to kill cancer cells?
Name the types of inhibitors that employ each method.
direct tumor cell killing
HER2, EGFR, and Leukocyte inhibitors
vascular and stromal cell ablation
aka inhibiting angiogenesis (decreasing the tumor cell’s ability to grow a blood supply)
VEGF inhibitors
immune-mediated tumor cell killing
PD1/PDL1 inhibitors
immune checkpoint inhibitors
Name the types of inhibitors that are small molecule agents used in anticancer tx?
tyrosine kinase inhibitors
proteasome inhibitors
CDK inhibitors
immunomodulators (note: she said these are not on exam)
What mAbs are HER2 inhibitors? (Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2)
Which are considered “naked”?
Trastuzumab- naked
Pertuzumab- naked
Ado-Trastuzumab- NOT naked
What does “naked” mean in terms of mAbs?
naked means NOTHING is attached to it!! aka no DRUG CONJUGATE
HER2 is what kind of receptor?
What is the MOA of all HER2 inhibitors?
Downstream Results?
is an EGFR
inhibitors MOA:
OVERALL—> binds to HER2 RECEPTOR COMPETITIVELY AND BLOCKS DOWNSTREAM PHOSPHORYLATION
more specifically: Facilitates (helps) selective recognition/ OPSONIZATION of HER2+ cancer cells
Results:
block receptor kinase activation
inhibit transcription
inhibit angiogenesis
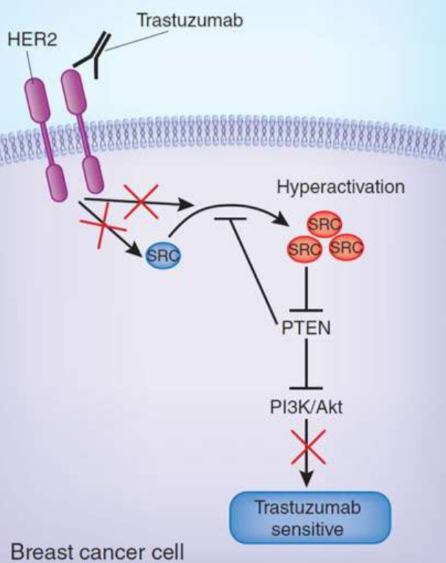
How is the MOA of Ado-Trastuzumab different from the other HER2 inhibitors? Why?
is different bc Ado-Trastuzumab is NOT NAKED it is CONJUGATED!!!!!!! is linked to EMTANSINE
in ADDITION to facilitating selective recognition/ OPSONIZATION of HER2+ cancer cells—> this drug ALSO is a tubulin inhibitor
Answer the following about each:
Generic | Class | Method of killing (direct, vascular ablation, etc.) | Type of mAb | WARNINGS |
Trastuzumab |
|
|
|
|
Pertuzumab |
|
|
|
|
Ado-Trastuzumab |
|
|
|
|
Rank each HER2 Inhibitor in order from longest to shortest washout time.
(trastuzumab, pertuzumab, ado-trastuzumab)
LONGEST TIME—→ Trastuzumab (up to 7 months)
Pertuzumab (18 days)
Ado-Trastuzumab (4 days)
Are trastuzumab and Ado-trastuzumab interchangeable? Why?
no—> bc of washout times
PRACTICE:
Which of the following would occur with administration of a HER2 antagonist?
a. dimerization of kinases
b. auto phosphorylation
c. gene transcription
d. competitive antagonism
d
What mAbs are EGFR inhibitors? (Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor)
Cetuximab
Panitumumab
Answer the following about Cetuximab:
warnings
pre-medication?
MOA
type of mAb
half-life (i don’t think imp)
dosing (i don’t think imp)
ADRs (i don’t think imp
warnings: cardiopulmonary arrest/infusion reactions
pre-medicate w/ antihistamine
MOA: inhibits EXTRACELLULAR EGFR, may also induce cell-mediated cytotoxicity
chimeric mAb
t 1/2: short (63-230 hrs)
dose q1-2 w
ADRs: fatigue, malaise, pain, neuropathy, rash, weight loss, GI
Answer the following about Panitumumab:
warnings
MOA
type of mAb
half-life (i don’t think imp)
dosing (i don’t think imp)
ADRs (i don’t think imp)
warning: potential serious derm toxicity
MOA: inhibits EXTRACELLULAR EGFR ONLY
human mAb
t 1/2- short (4-11 days)
dose q2 w
ADRs: fatigue, skin rxns, hypomag, GI, ocular toxicity
Which has a higher potential for immunogenicity?
a. Cetuximab
b. Panitumumab
a
What is the target of Leukocyte antigen inhibitors?
direct tumor killing CD antigens expressed on the surface of hematopoietic cells
What is the MOA of mAbs that are leukocyte antigen inhibitors?
mAbs that OPSONIZE CANCER CELLS
How?
active antibody-dependent cell mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC)—> phagocytosis
or/and
active complement-dependent cytotoxicity (CDC)
Classification of leukocyte antigen inhibitors is based on the target antigen. What are the 2 drugs used in anticancer therapy and their CD target??
Rituximab- CD20
Inotuzumab- CD22
Are CD’s on T cells or B cells?
B cells!!!
Which leukocyte antigen inhibitor is naked? Which is conjugated and with what drug?
Rituximab- NAKED
Inotuzumab- conjugated with ozogamicin
Answer the following about Rituximab:
class
MOA
warning
type of mAb
effect on B cells (i do not think imp)
ADRs (i do not think imp)
Leukocyte Antigen Inhibitors
binds to CD20 on B cells to initiate ADCC/CDC
WARNINGS: infusion and mucotaneous reactions, hepatitis B reactivation, progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy
CHIMERIC mAb
depletion of B cells in 6 weeks, last up to 9m
ADRs: edema, HTN, fatigue, insomnia, HA, infection, etc.
Answer the following about Inotuzumab:
Class
MOA
warning
type of mAb
linked to
ADRs (i do not think imp)
Leukocyte Antigen Inhibitors
binds to CD22, internalization of ADC-receptor complex
bc of ozogamicin—> alkylating agent that damages DNA (calicheamicin derivative)
WARNINGS: hepatotoxicity, post-HSCT non-relapse mortality
humanized mAb
linked to ozogamicin
ADRs: fatigue, HA, N/V/D/C, BMS, infection, etc.
What are the 2 VEGF inhibitors used in anticancer therapies?
Bevacizumab- our focus
Ramucirumab
What is the MOA of VEGF inhibitors?
Results?
MOA: inhibits the actions of VEGF on the VEGFRs of cancer cells
also enhances lymphocyte response
results: inhibits angiogenesis and limits tumor growth
What type of inhibitor is Bevacizumab?
COMPETETIVE INHIBITOR
Answer the following about Bevacizumab:
class
MOA
WARNINGS
what route is available?
ADRs (I don’t think imp)
VEGF inhibitor
blocks VEGFR, enhances lymphocyte response
WARNINGS: GI perforations, surgery/wound healing, hemorrhage
intravitreal (into the eye) route available
ADRs: HTN, VTE, fatigue, HA, infections, impaired healing, etc.
What mAbs are programmed cell death receptor inhibitors?
Pembrolizumab (Keytruda)
Nivolumab
Atezolizumab
Avelumab
Durmalumab
(just said to “recognize these names”)
The goal of immune checkpoint inhibitors of programmed cell death receptors is to block the interaction between ________ and ________.
PD-1 and PD-L1
Does Pembrolizumab inhibit PD-1 or PD-L1? Therefore, would it act on the T cell or tumor cell?
PD-L1, would act on the TUMOR CELL!!!!!!!
Answer the following about Pembrolizumab:
inhibits PD-__
results?
requires what diagnostic test?
type of mAb
WARNING
inhibits PD-L1
results—> immune system can recognize and attack tumor cells
requires PD-L1 IHC 22C3 test to make sure you have high PD-L1 expression
HUMANIZED mAb
WARNINGS: NOT for pregnant women
(mneumonic: Pem is just pregnancy)
If a tumor cell is growing, would it be overexpressing or under expressing PD-L1 markers?
overexpressing
PD-1 is on the ________ cell.
PD-L1 is on the _________ cell.
PD-1 is on the T cell.
PD-L1 is on the tumor cell.
What is the name of an immune checkpoint inhibitor (CTLA-4) that uses immune mediated tumor cell killing and is used in combination with Nivolumab for non-small cell lung cancer?
Ipilimumab
Bispecific T-cell engagers (BiTEs) is another way of targeting…
direct tumor killing
What is unique about BiTEs compared to other drugs in general?
binds to the T cell and tumor cell and acts on both aka “bispecific”
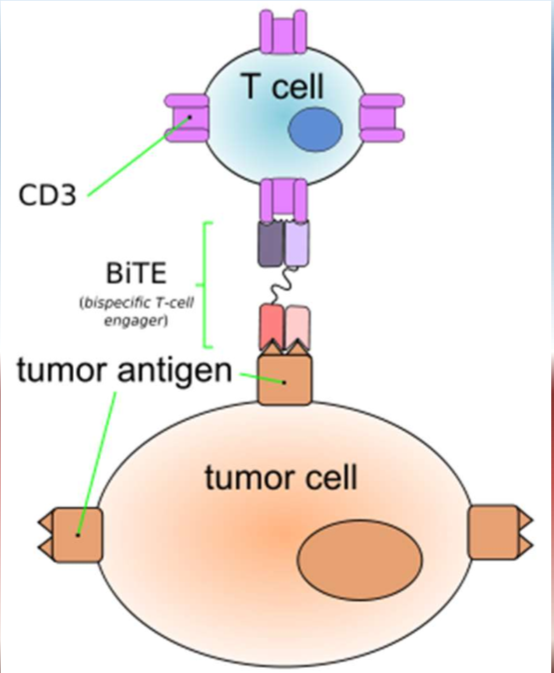
BiTEs consist of 2 single chain variable fragments. What are the 2 fragments?
Tumor-associated antigens (TAA) targeting fragment
aka binds to the tumor cell
T-cell surface antigen fragment
aka binds to the T cell
What is the unique MOA of BiTEs?
What are the results?
MOA: direct cytotoxic T-cell activity against cancer cells
forms a link between T cell and tumor cell
produces a perforin or “hole” and makes the tumor basically explode
What drug is an example of BiTEs?
Blinatumomab
Answer the following about Blinatumomab:
WARNINGS:
type of mAb
USES
ADRs (i don’t that imp)
WARNINGS: Cytokine release syndrome, neurotoxicity
murine mAb
Uses: ACUTE LYMPHOBLASTIC LEUKEMIA
note: NOT CHRONIC!!! ACUTE!!!!!
ADRs: edema, pain, HTN, rash, infection, etc.
Blinatumomab acts on what specific CDs on the tumor cell and t cell?
on tumor cell—> CD19
on T cell—> CD3
Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors (TKIs) are mainly used to tx what 3 cancers? What classes of TKIs are used for each cancer?
chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML)
BCR-ABL inhibitors
melanoma
BRAF inhibitors
MEK 1 and 2 inhibitors
MEK= mitogen-activated extracellular kinase
non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC)
EGFR inhibitors
ALK Inhibitors
ALK= anaplastic lymphoma kinase
Review:
How does the tyrosine kinase pathway normally work to have cell growth, proliferation, and differentiation?
ligand binds to ligand binding
domains come together to dimerize
tyrosine kinases on domains are phosphorylated
phosphorylation drives various cell processes like transcription
How do the mechanisms of action of mAbs that inhibit phosphorylation differ from those of tyrosine kinase inhibitors?
mAbs bind to the RECEPTOR and block downstream signaling like phosphorylation—→ EXTRACELLULARLY
the ligand binding to the ligand binding domain
tyrosine kinase inhibit dimerization/ phosphorylation of kinases INTRACELLULARLY
dimerization
PRACTICE:
If I had a glioma (brain tumor) and I needed tx immediately, would I use a TKI or mAb?
mAb (why? bc we don’t have time for the tyrosine kinase to get intracellularly and produce it’s effect. we are gonna use a mAb that quickly reaches the tumor surface to produce its effect)
What is the goal of TKIs?
inhibit tyrosine kinase activity so that cell growth and proliferation slows down
What TKIs are BCR-ABL Inhibitors and used for the tx of CML?
Imatinib mesylate
Nilotinib
Ponatinib (doesn’t target just BCR-ABL)
What are the CYP interactions with Imatinib and Nilotinib?
Imatinib- CYP3A4 inhibitors and inducers, CYP450 INDUCERS
Nilotinib- CYP3A4 inhibitors
Answer the following about Imatinib:
class
Uses
MOA
WARNINGS
BRCA-ABL inhibitor/ small molecule TKI inhibitor
Ph+ CML
MOA: antagonizes phosphorylation
WARNINGS: hepatotoxicity, hemorrhage, GI perforation, dermatologic rxns
Answer the following about Nilotinib:
class
Uses
used in adults or kids?
WARNINGS:
BRCA-ABL inhibitor/ small molecule TKI inhibitor
Ph+ CML —> ONLY IF RESISTANCE TO IMATINIB
used in adults
WARNINGS: prolongs QT interval, avoid drugs that also prolong QT interval, CYP3A4 inhibitors
Answer the following about Ponatinib:
target/class
uses
MOA
multitarget, can inhibit BCR-ABL1/ BRCA-ABL inhibitor/ small molecule TKI inhibitor
USES: for Ph+ CML when there is a T3151 MUTATION!!!!!!!!!
MOA: antagonizes phosphorylation—> antiangiogenic/antieoplastic
What is something that would cause resistance to Imatinib and would make you use Nilotinib?
if the tumor cell would activate alternative signaling pathways to increase phosphorylation and transcription not the BCR-ABL pathway
What does Ph+ or Ph- CML refer to? Why is it important?
Ph+ means you are POSITIVE for the Philadelphia chromosome aka the BCR-ABL1 gene mutation
In CML, 95% of cases are Ph+ so it’s key in the tx of CML
(think: if most cases of CML are caused by the BCR-ABL1 mutation, why would I use a BCR-ABL inhibitor on CML that doesn’t HAVE THE GENE????)
What is the T3151 mutation?
a PAN-MUTATION in BCR-ABL at site T3151!!! (means everywhere in the gene)
The EGFR pathway is initiated by what and activates what 3 pathways to result in cell proliferation, growth, progression, etc.?
initiated by binding of extracellular ligand
activates:
RAS/MAPK
PIP3K
JAK/STAT
What is the MOA of EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors?
(FYI: she didn’t really mention any specific drugs for this class just talked about the class in general)
small molecule EGFR TKIs bind to the kinase domain and block function of the EGF receptor
What drug is a TKI that inhibits VEGF?
Sunitinib
Answer the following about Sunitinib:
class
MOA
results
WARNINGS!!!
VEGF inhibitor/ small molecule TKI
MOA: competitively inhibit binding of ATP to TK domain on the VEGF RECEPTOR
Results: inhibit angiogenesis
WARNINGS: HEPATOTOXICITY
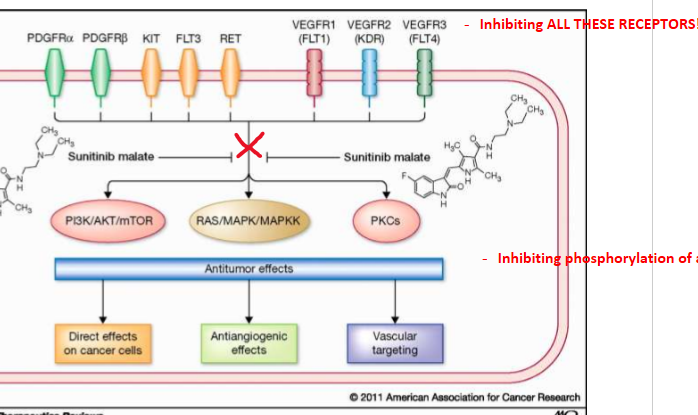
In general, what are some mechanisms of resistance to ALL TKIs?
point mutations in the kinase domain that prevent binding of the drug and lock the enzyme in the open position
amplification of kinase gene
drug efflux (ex: Pg-p)
altered kinase trafficking
What do proteasome inhibitors do in targeted anticancer therapies? Results?
inhibitors bind the proteasome and inhibit protein degradation
prevent the proteolytic degeneration of TF NF-kb
results: decrease anti-apoptotic factors, cell adhesion, and proliferation
What is the overall strategy proteasome inhibitors use?
cancer cells make lots of extra proteins and use proteasomes to degrade them so they don’t die
we inhibit the proteasome so that all the extra proteins build up and kill the cancer cell!!
What drug is a proteasome inhibitor?
Bortezomib
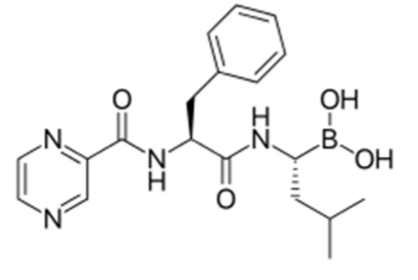
Answer the following about Bortezomib:
admin (route, formulation)
MOA
Metabolism
Resistance with ___________________.
admin: IV/SQ administered DIPEPTIDE for relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma
MOA: dipeptide boronic acid inhibitor that INHIBITS 26S PROTEASOME
Metabolism: CYP3A4, CYP2C19
resistance with prolonged tx
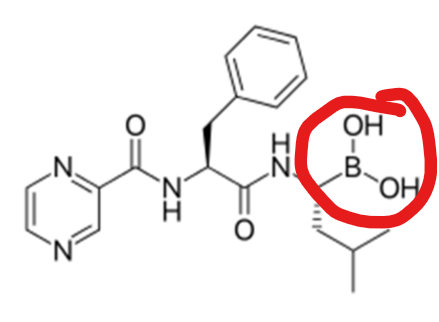
Specifically, how does Bortezomib inhibit the 26S proteosome?
the boronic acid on Bortezomib is specific for the active site of the proteasome and forms a complex. this inhibits the proteolysis activity of the proteasome
Cyclin-dependent kinases play an important role in ___________________.
cell cycle regulation
Overall, CDK inhibitors inhibit…
cell cycle progression
What is the most present cyclin in G1 phase?
cyclin D
What small molecule targeted anti-cancer drug is a CDK inhibitor?
Palbociclib
Answer the following about Palbociclib:
MOA
results
Uses
admin
METABOLISM
SELECTIVE INHIBITOR of CDK4 and CDK6
results: blocks phosphorylation of retinoblastoma tumor suppressor protein, G1 phase arrest
breast cancer
oral
CYP3A4 METABOLISM—> avoid strong inhibitors/inducers