sickle cell anaemia
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
sickle cell anaemia
blood disorder caused by a gene mutation where one base is substituted for another (point mutation). results in abnormal haemoglobin causing crescent shaped red blood cells

sickle shaped red blood cells
carry reduced amounts of oxygen causing individual to feel constantly tired
dies sooner resulting in fewer than normal red blood cells (anaemia)
blocks blood flow through tiny blood vessels to chest, abdomen, joints causing episodic pain
sickle cell disease
sickle cell anaemia is recessive; individual must have 2 copies of recessive allele (paternal, maternal) to have the disease
sickle cell diseased individuals
homozygous for sickle cell allele, and die at an early age (lethal)
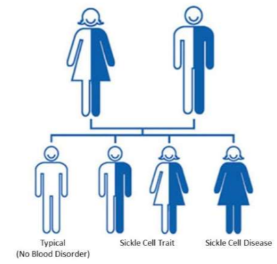
sickle cell traited individual (carrier)
heterozygous for sickle allele, individuals are resistant to malaria providing survival advantage, and live healthy lives
more frequent in african populations
due to heterozygous advantage and natural selection. malaria acts as selection pressure increasing sickle allele frequency in gene pool, as it helps survival (where malaria present)
malaria
10% of human pop infected by malaria, 90% of all cases in africa. caused by parasitic microorganisms transmitted by mosquitoes (malaria plasmodium), which infects red blood cells. people producing normal red cells are good hosts; easily get disease
cure
can potentially be cured by bone marrow stem cell transplantation
how sickle allele became common in malaria regions of world
sickle cell anaemia trait provides immunity against malaria, which causes more mortality than sickle-cell anaemia. thus, sickle cell trait is a genetic advantage, and are passed onto the next generation from heterozygous individuals, becoming more prominent due to natural selection