Skull pt. 1
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
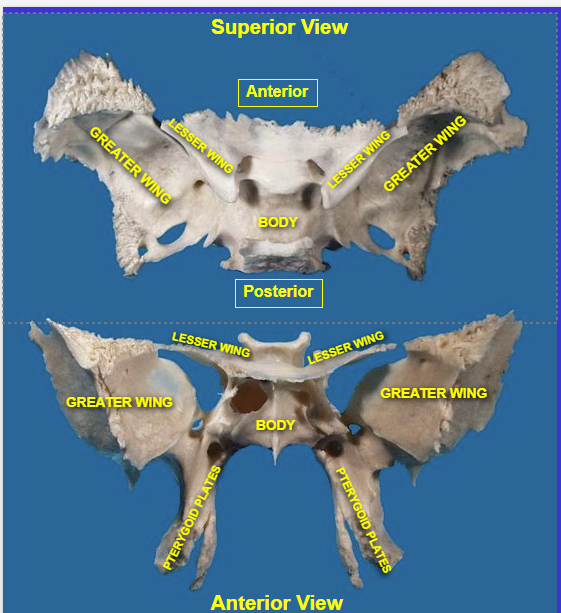
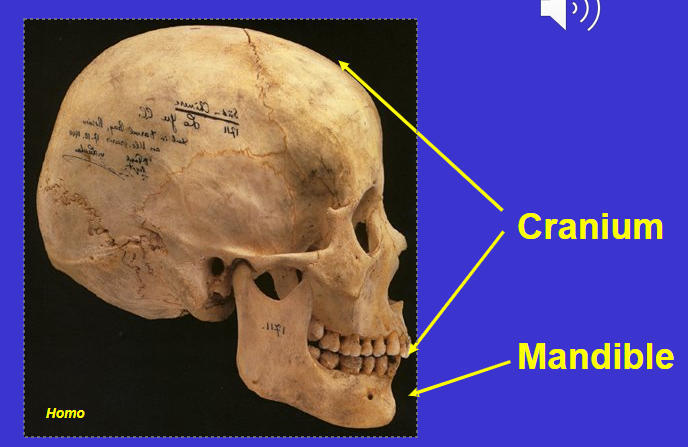
Skull
Mandible & cranium
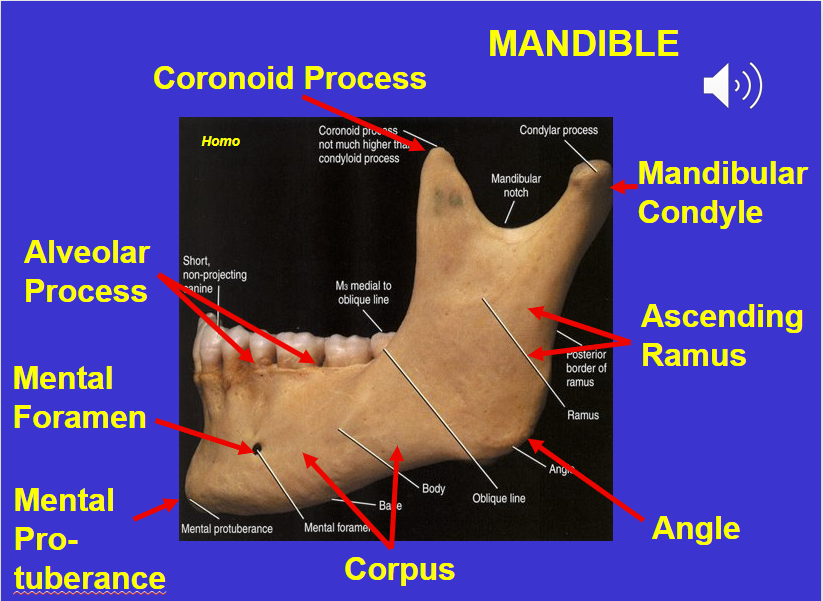
Coronoid process (in the mandible)
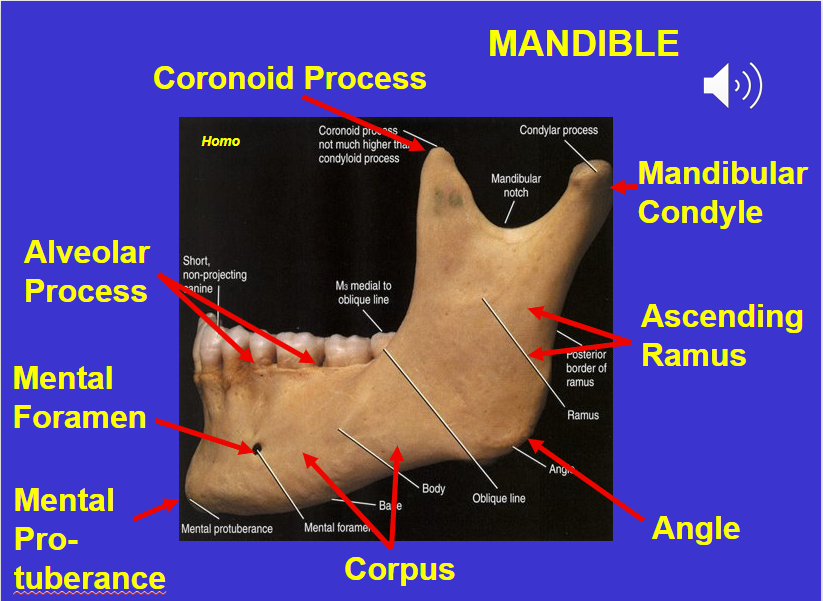
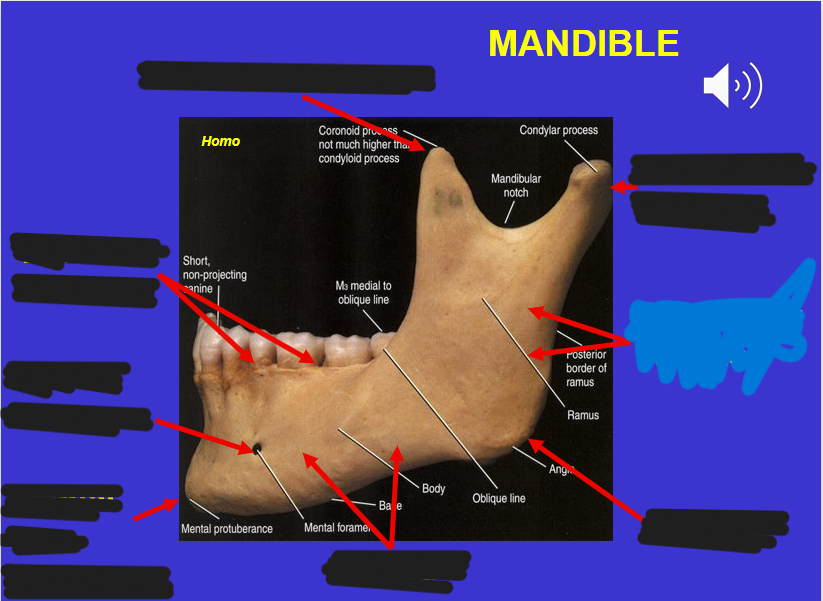
Alveolar process (in the mandible)
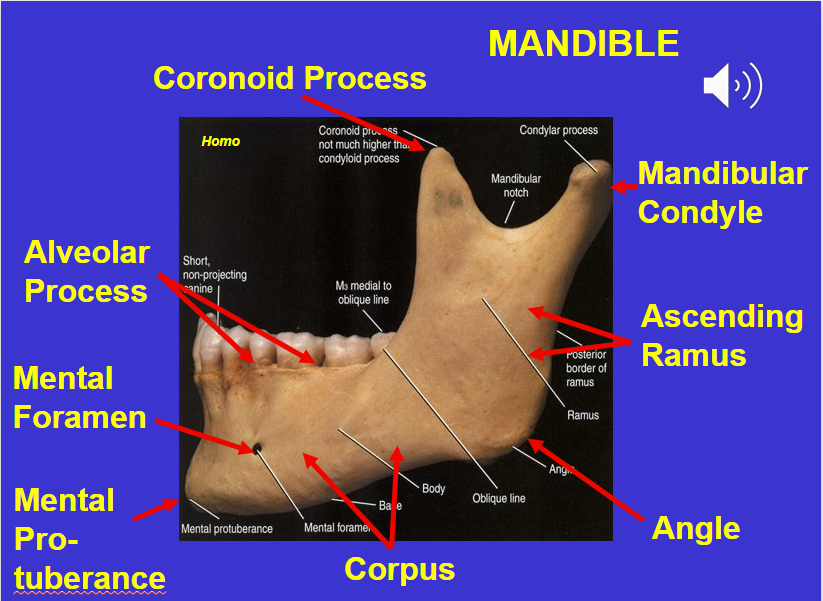
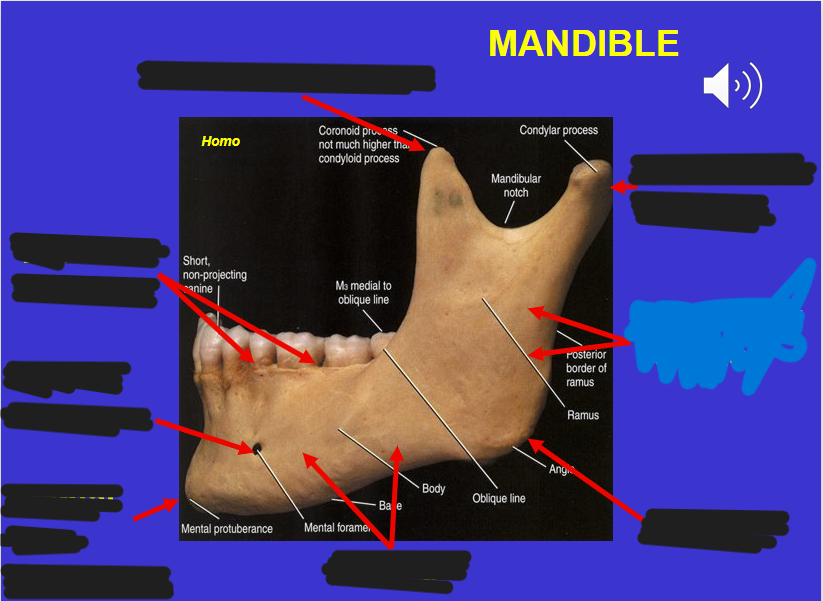
Mental foramen (in the mandible)
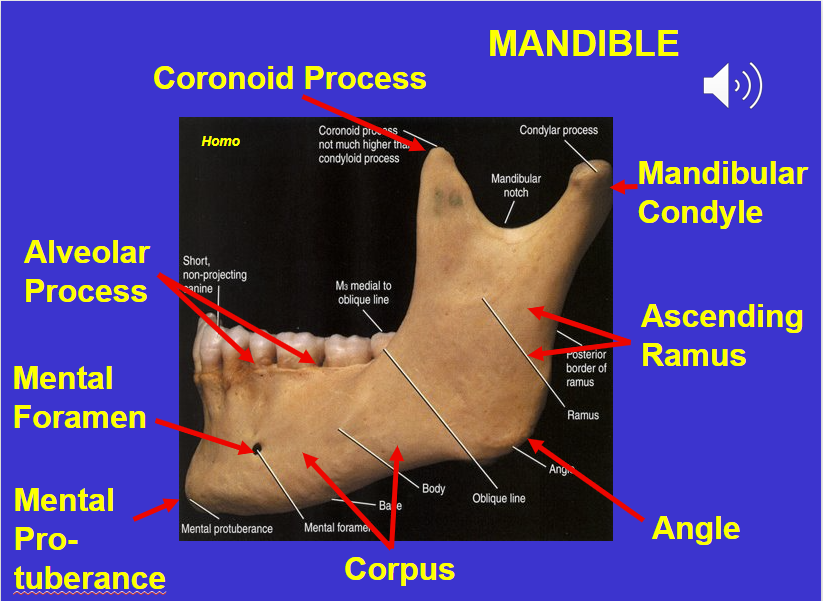
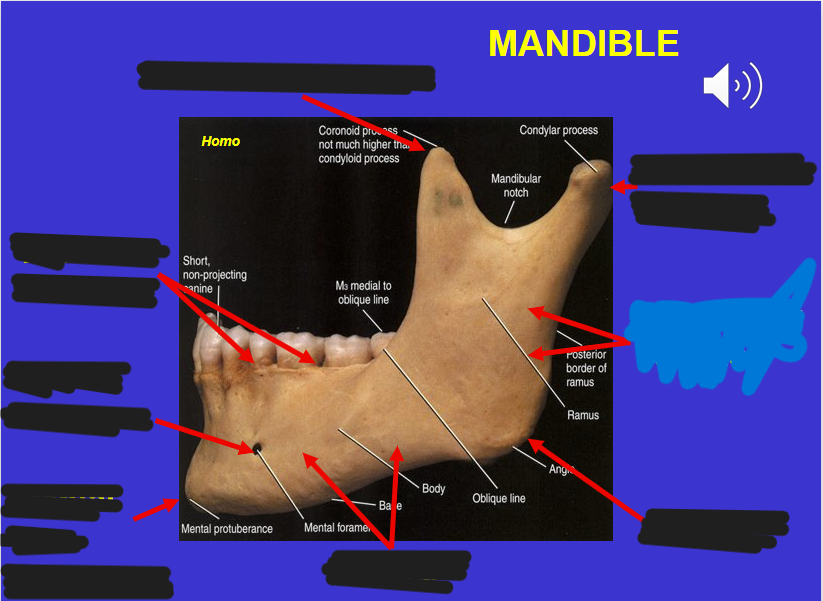
Corpus (in the mandible)
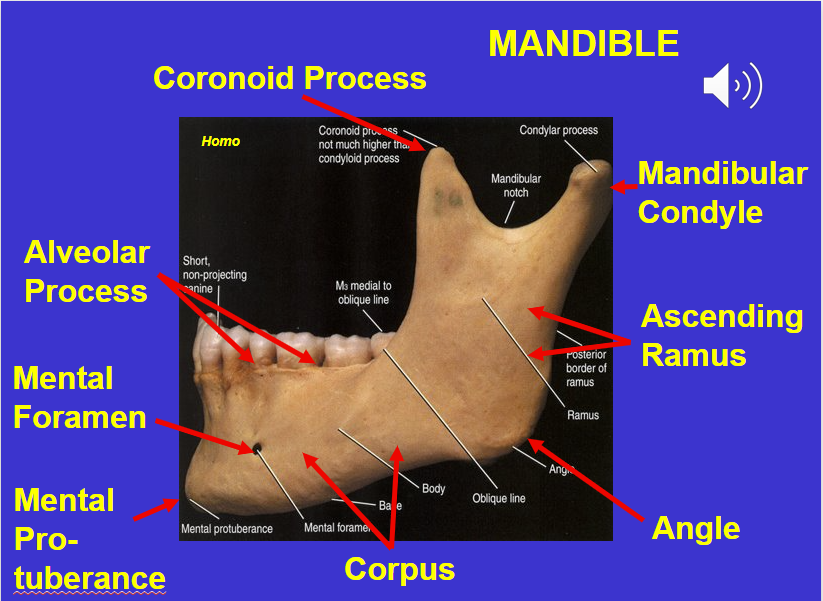
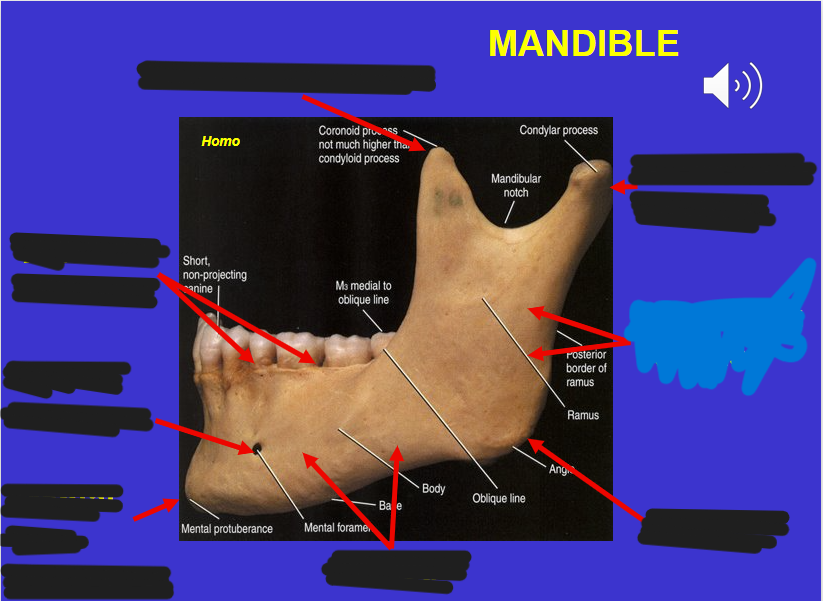
Angle (in the mandible)
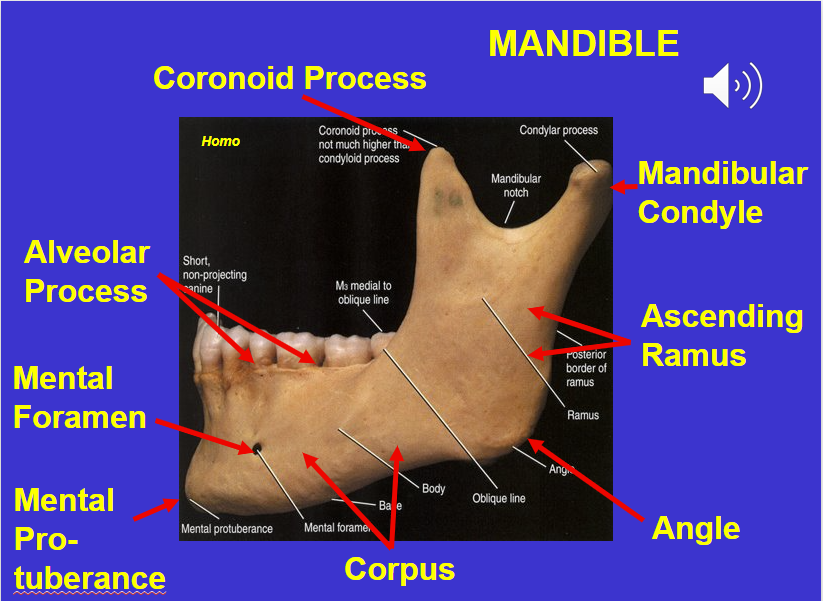
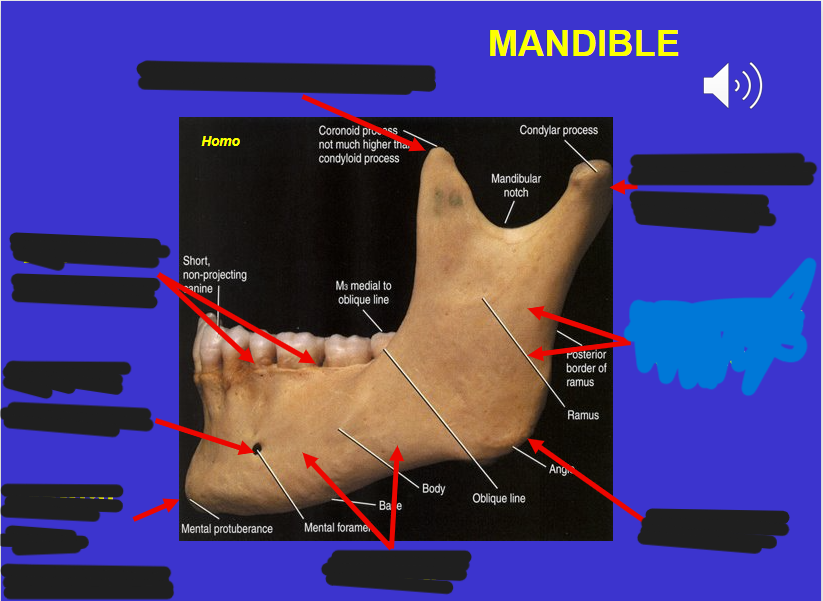
Ascending ramus (in the mandible)
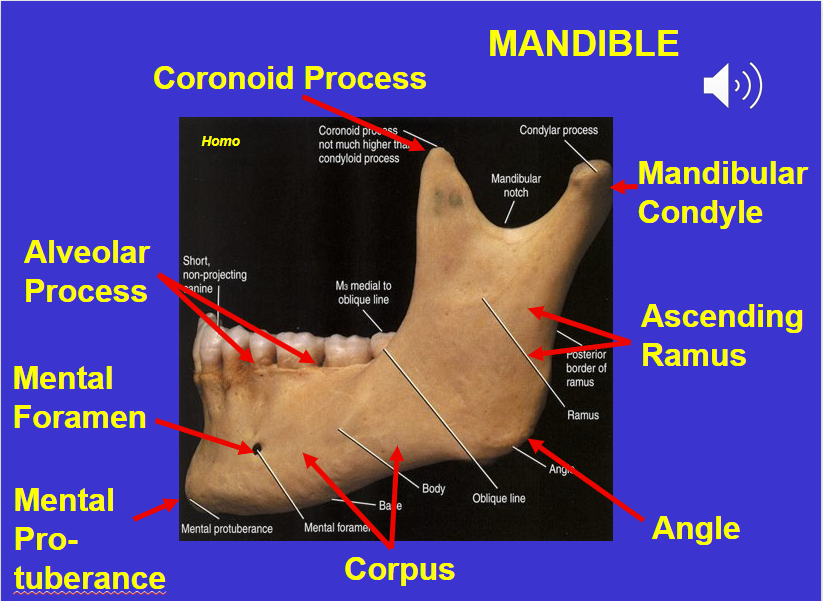
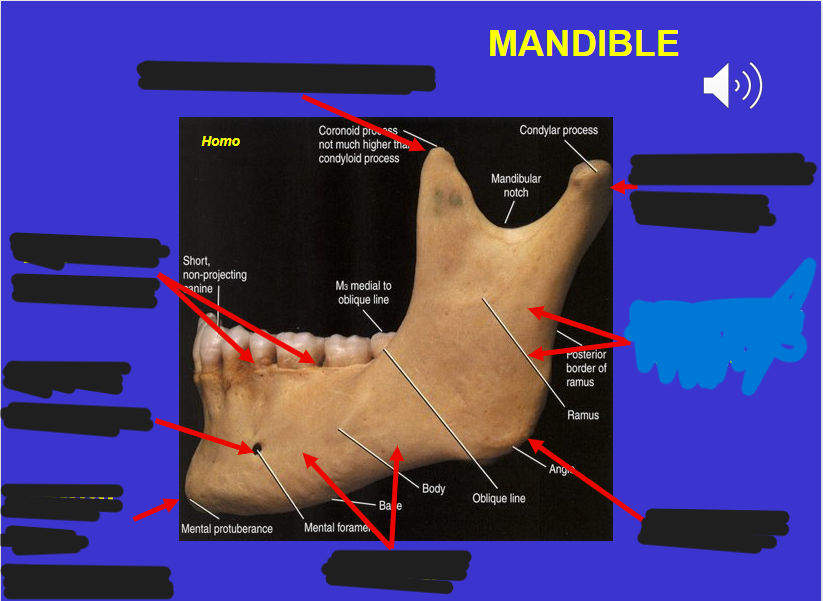
Mandibular condyle (in the mandible)
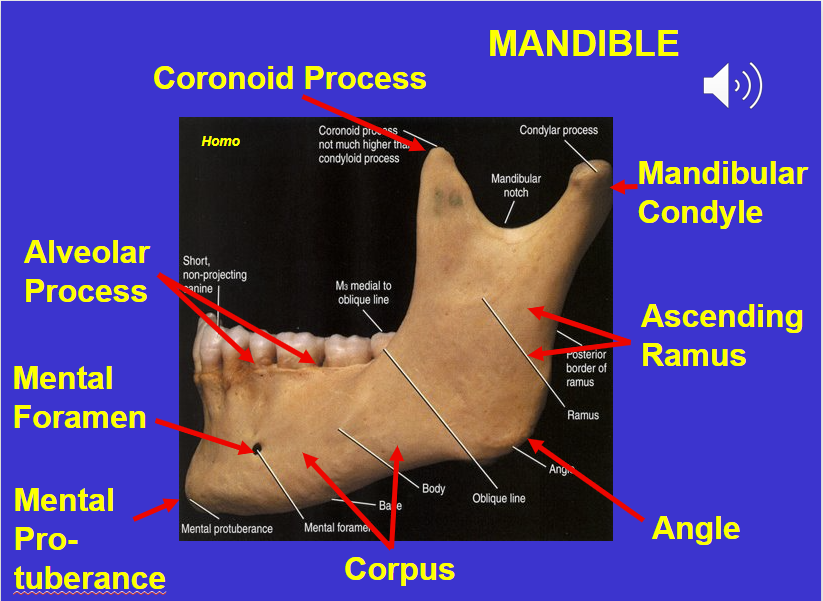
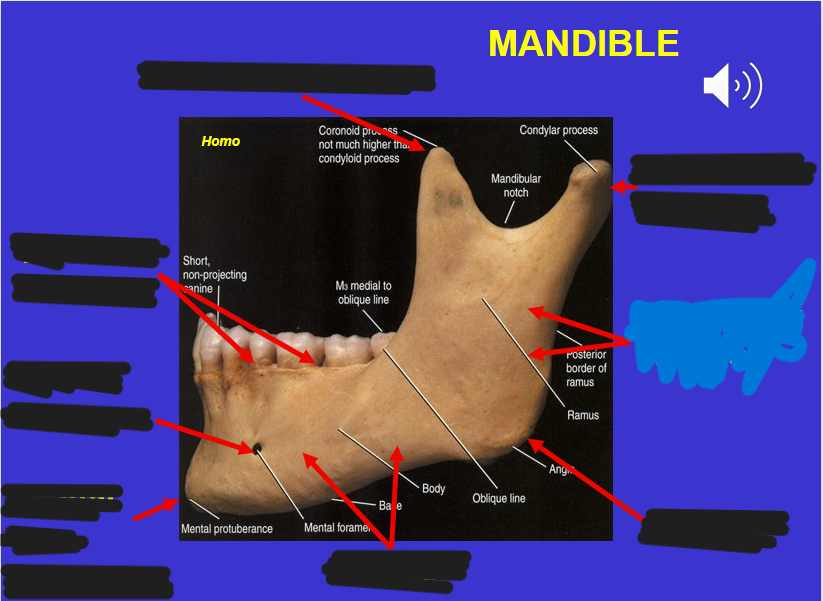
Mental protuberance (in the mandible)
What is the anterior region of the cranium called?
Splanchnocranium or Facial skeleton
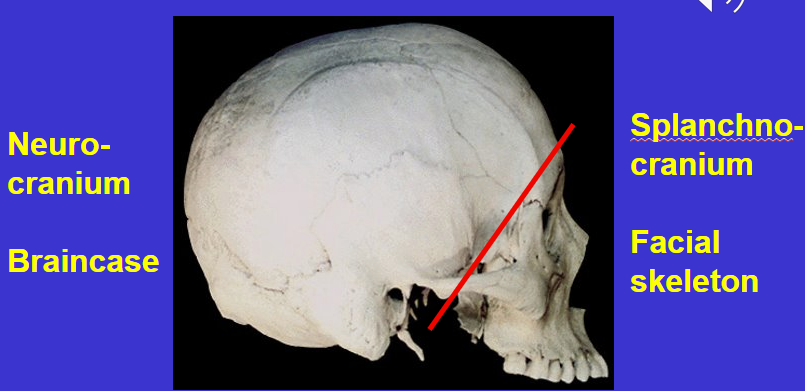
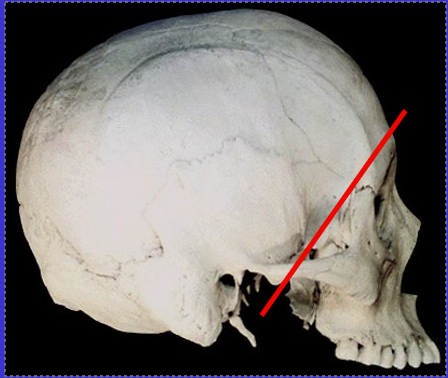
What is the posterior region of the cranium called?
Neurocranium or braincase
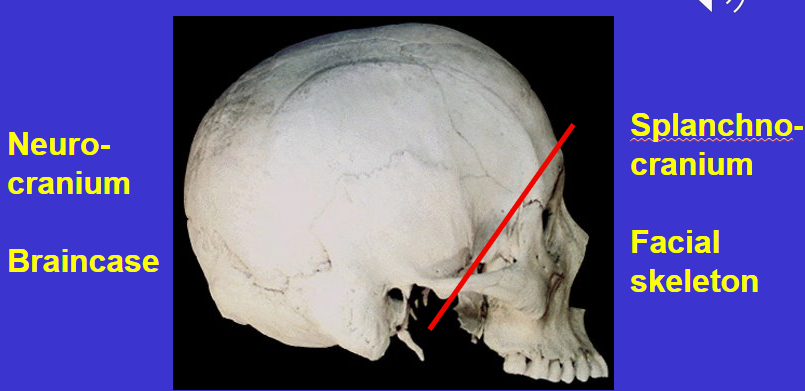
What is the basicranium? Where is it found?
The inferior surface region of neurocranium
Place where most vessels/nerves enter & exit
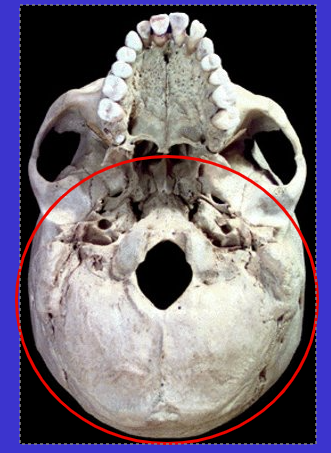
How many regions of the cranium are there?
three
Basicranium
Neurocranium
Splanchnocranium
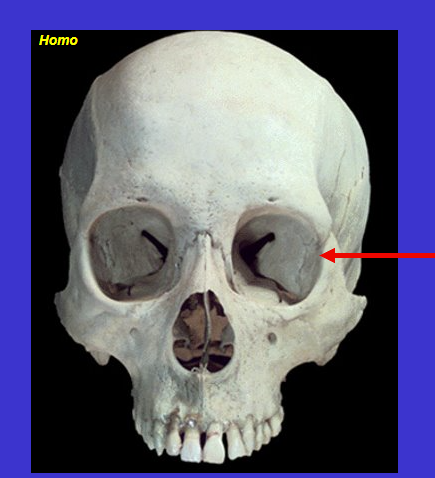
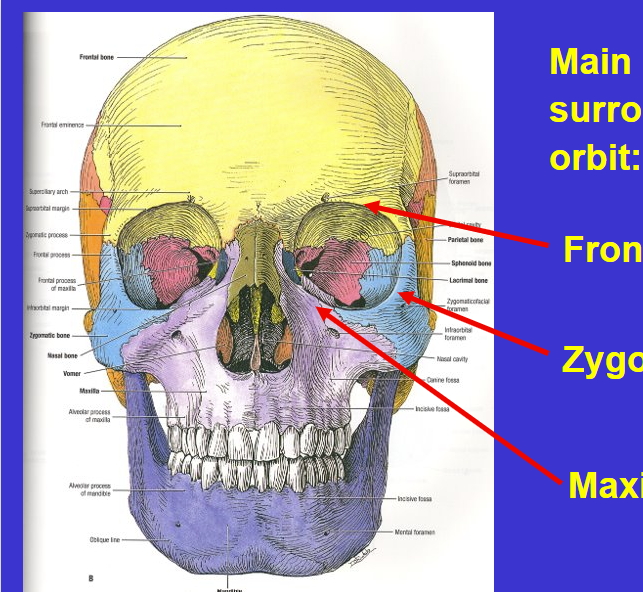
The arrow is pointing to…
orbit (eye socket)
Surrounded by…
Frontal, Zygomatic, & Maxilla bone
Lacrimal on the side next to maxilla (dark green) & Sphenoid bone in the back (in pink)
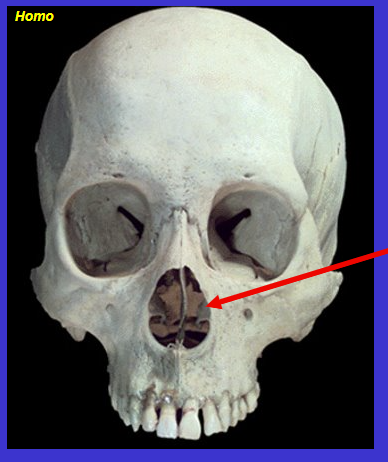
The arrow is…
The piriform or nasal aperture
surrounded by maxilla & nasal bones
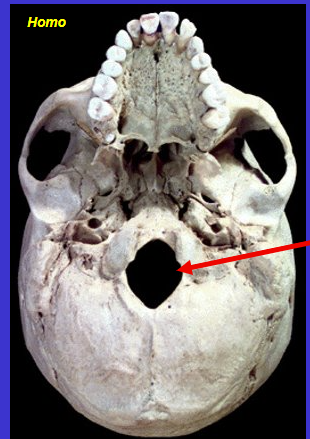
What is the arrow
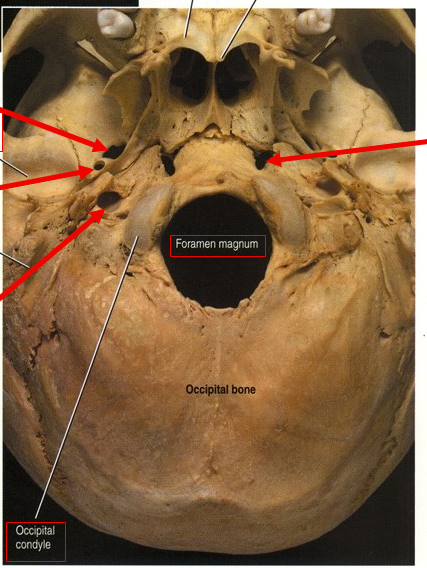
Foramen magnum (transmits spinal cord)
What does foramen mean?
Hole in a bone
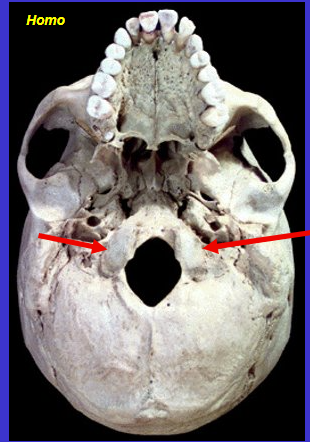
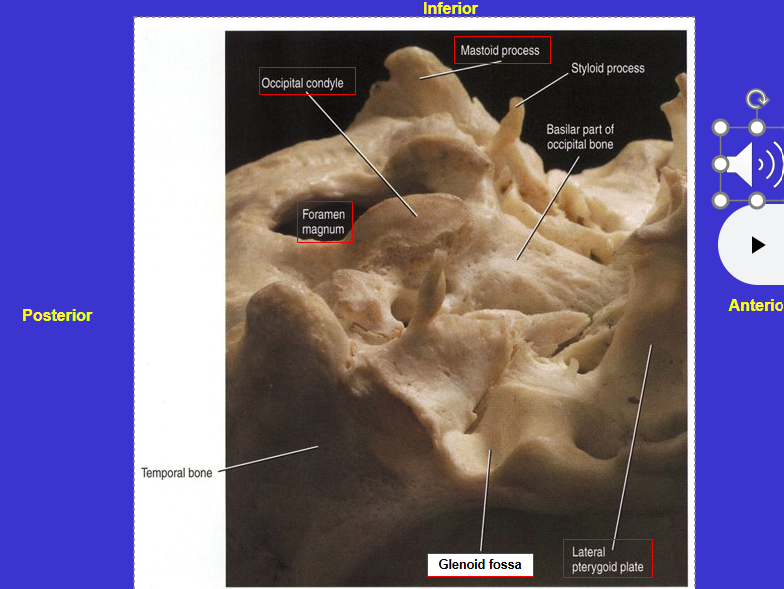
What is the arrow?
Occipital condyles (where cranium articulates with vertebral column (spin))
where base of cranium articulates with vertebra
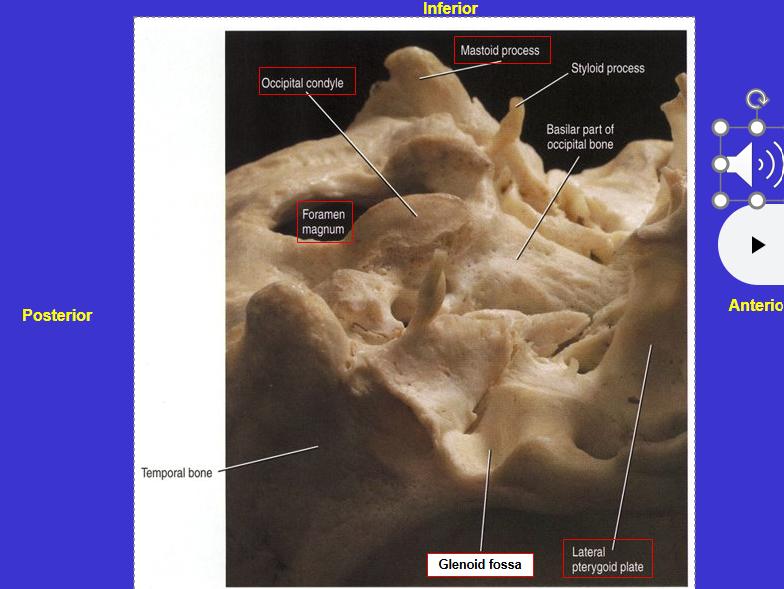
What is an articulation?
Place where bones meet (forming a joint)
What is a condyle
Rounded or ellipsoidal mobile articular surface
Occipital condyles
Mandibular condyle
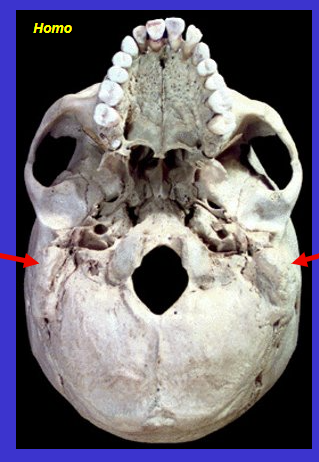
What is the arrow?
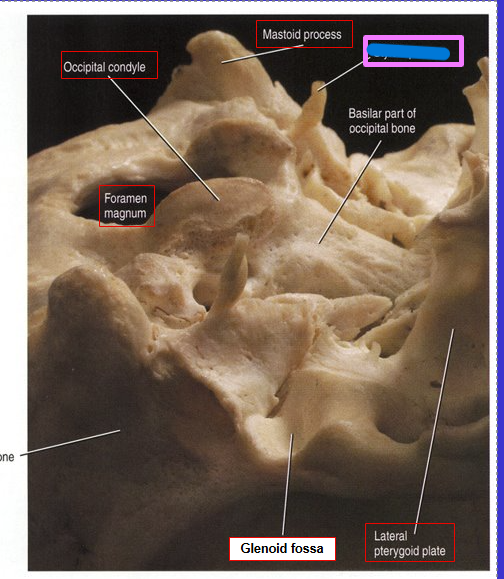
Mastoid process
Mastoid = breast shaped
Process = bump or projection on a bone
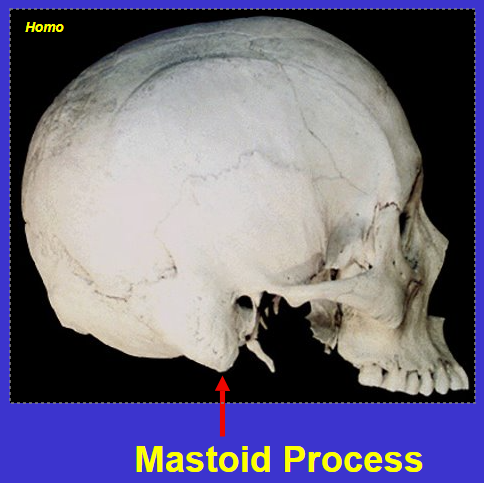
What is a process?
Bump or projection on a bone
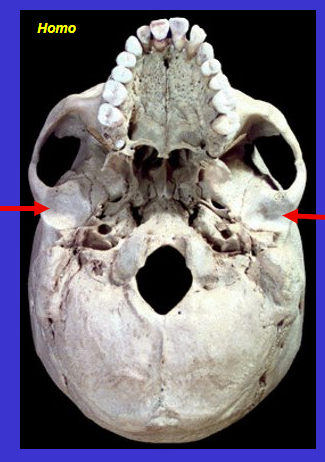
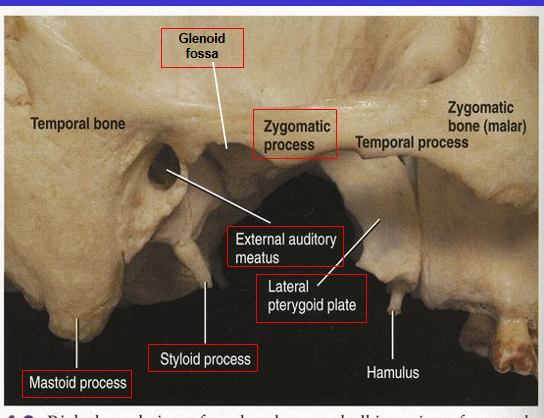
What is the arrow
Glenoid fossa (where cranium articulates with mandible)
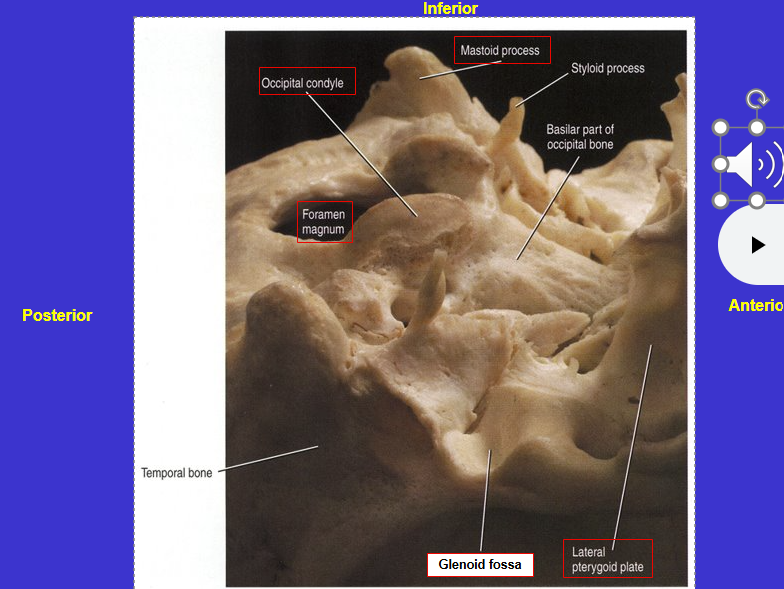
What does fossa mean?
Depression on a bone’s surface or space enclosed by bone
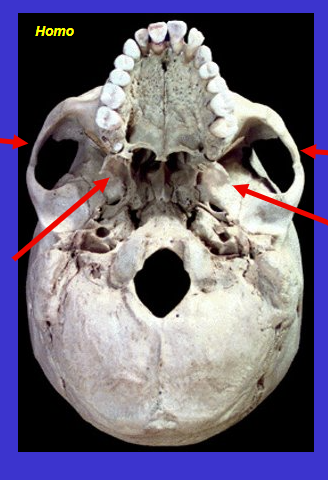
What are the 2 top arrows? What are the 2 bottom arrows? What are they both for/purpose?
Top = Zygomatic arches
Bottom = Pterygoid plates (medial to zygomatic arch)
sites of chewing muscle attachment
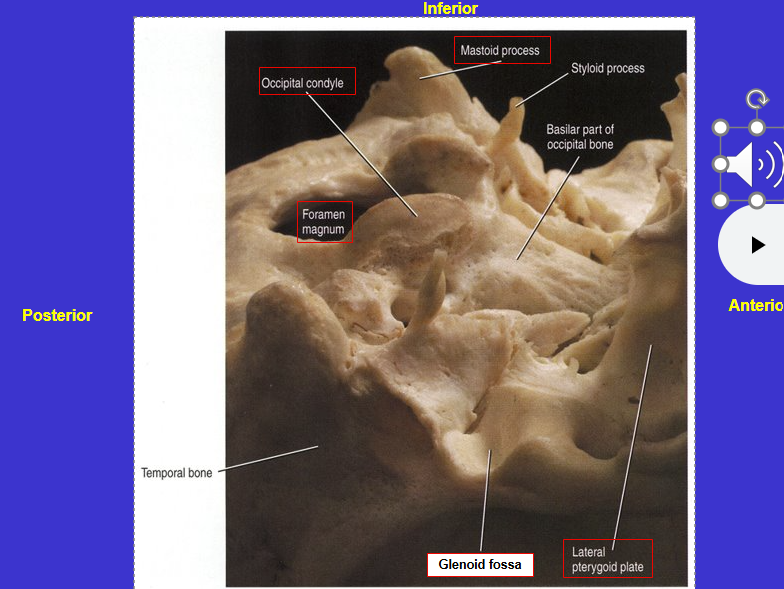
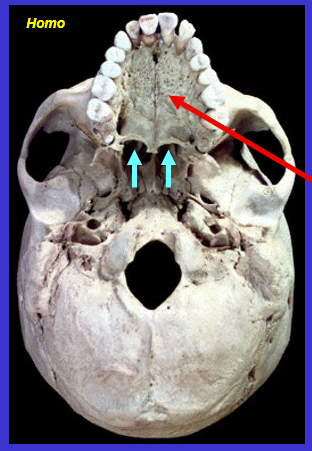
What is the red arrow?
Hard palate
Largely formed by maxilla (and some from palatine)
(the blue arrows are the soft palate - for swallowing)
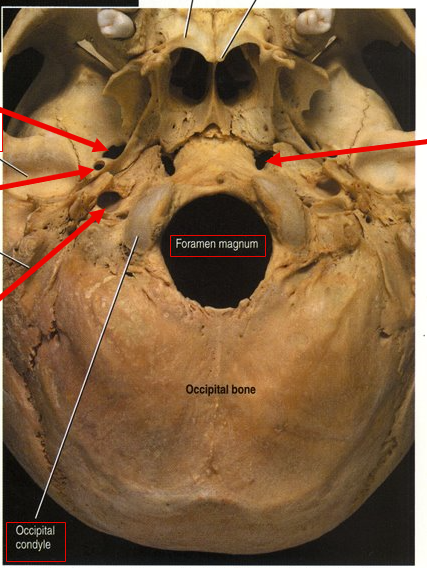
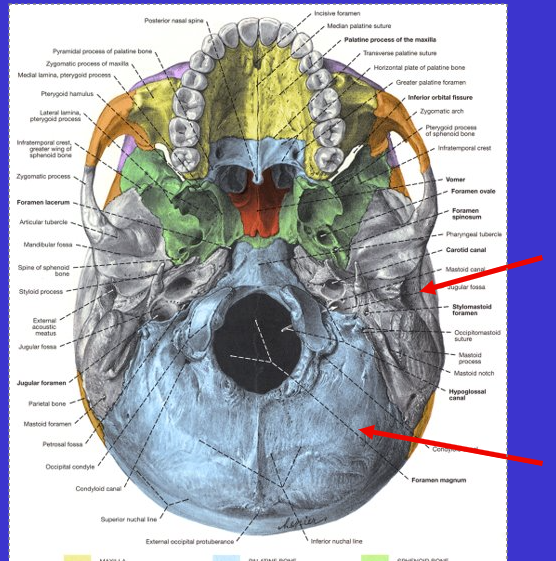
What is the top left arrow?
Foramen ovale (nerve runs through)
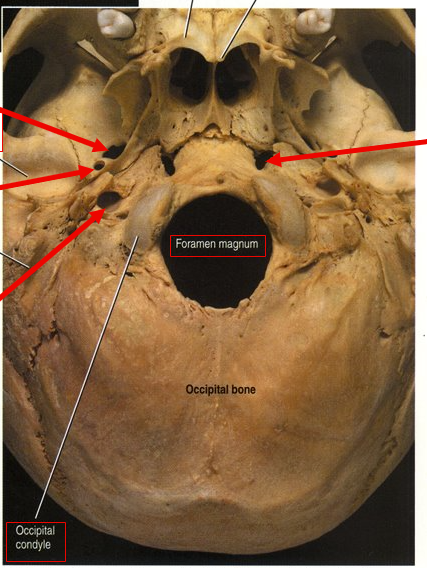
What is the left middle arrow?
Foramen spinosum (meninges arteries run through)
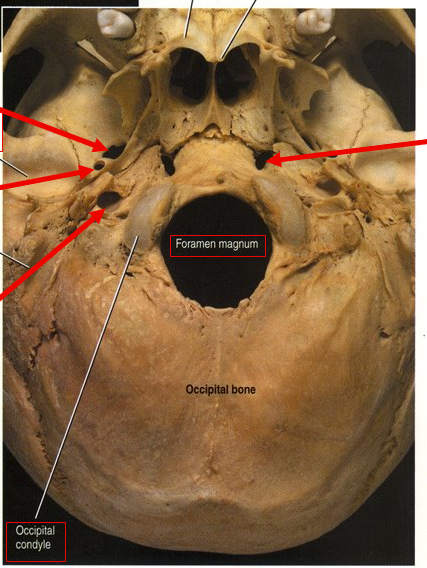
What is the bottom left arrow?
Carotid foramen (Carotid artery runs to brain)
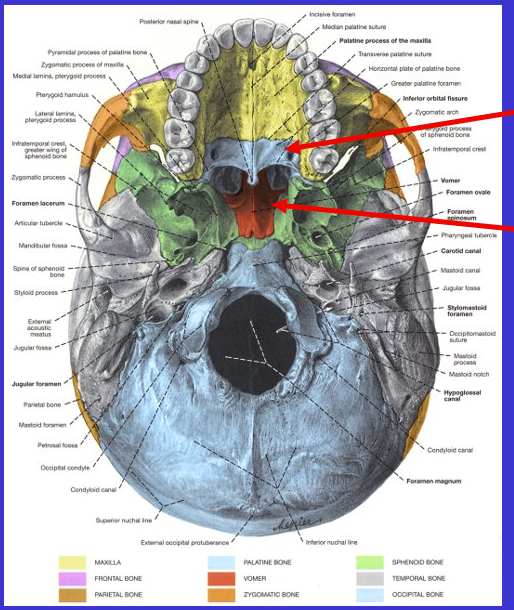
What is the right arrow?
Foramen lacerum (closed by cartilage through life)
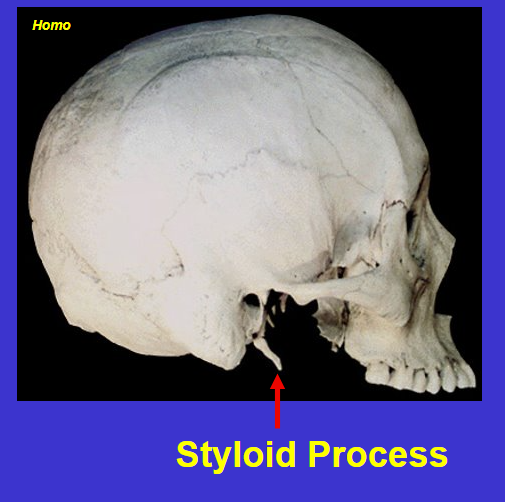
What is the pink box?
Styloid process (anterior and medial to mastoid process)
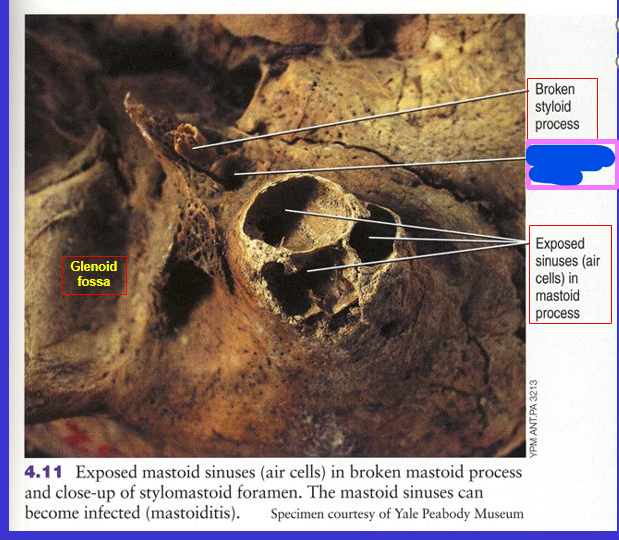
What is the pink box?
Stylomastoid foramen (hole between styloid process and mastoid process)
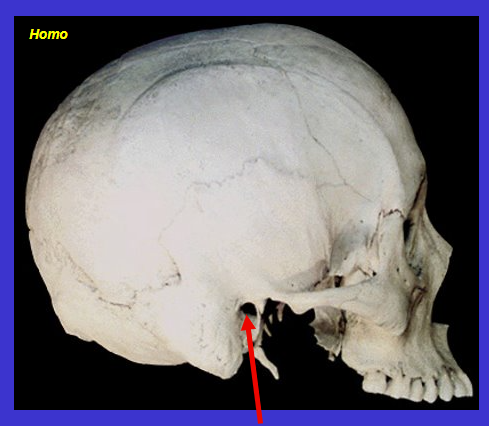
What is the arrow?
External acoustic (auditory) meatus
is the ear hole
what is the arrow?
Maxilla
Holds upper teeth
there’s a right and left
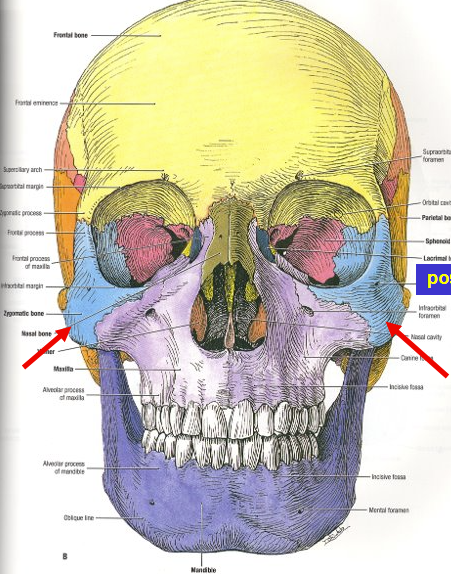
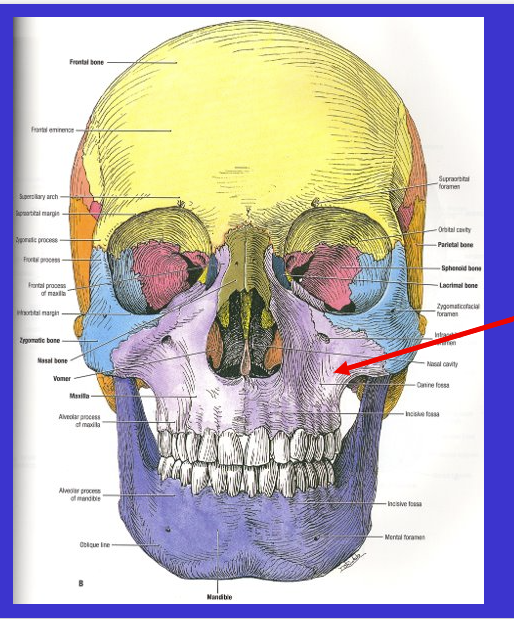
What is in blue/pointed to by arrow
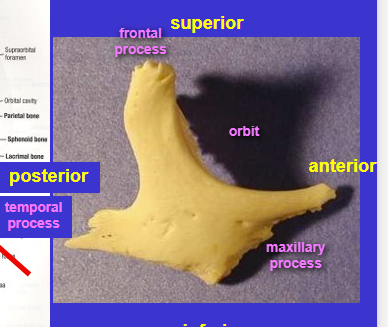
Zygomatic bone (check bones)
Has three major processes (Shown in image)
What is the arrow?
Nasal bones (form the bridge of nose)

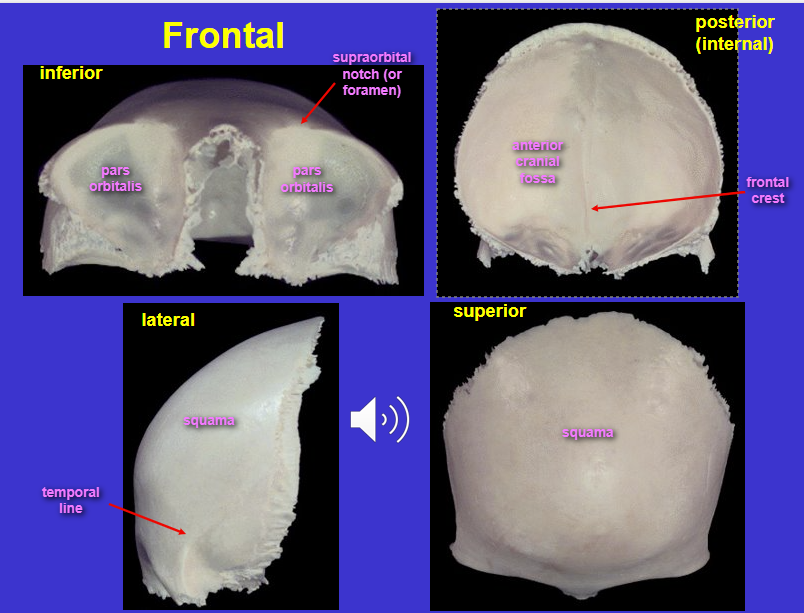
What is the yellow bone/arrow?
Frontal bone
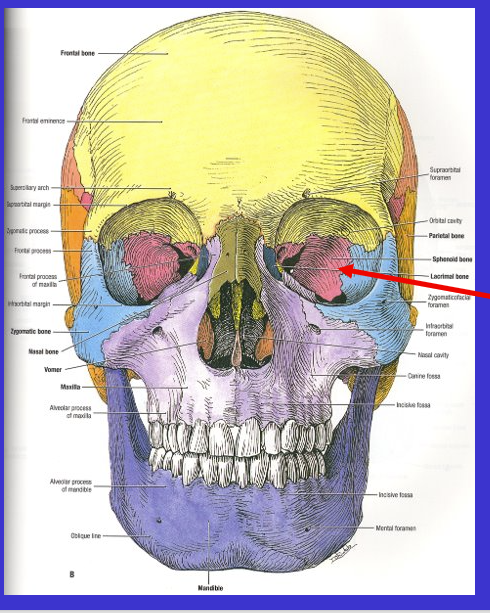
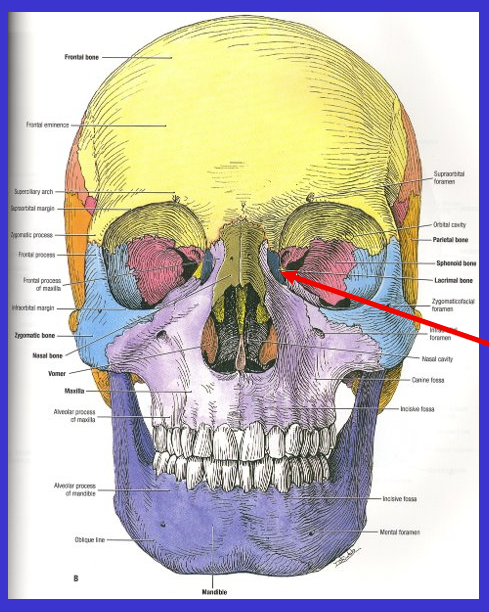
What is the arrow?
Sphenoid
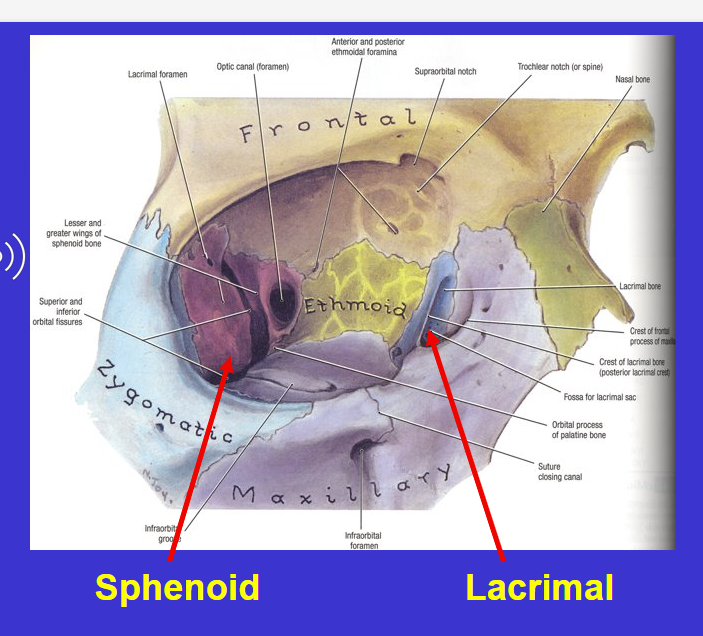
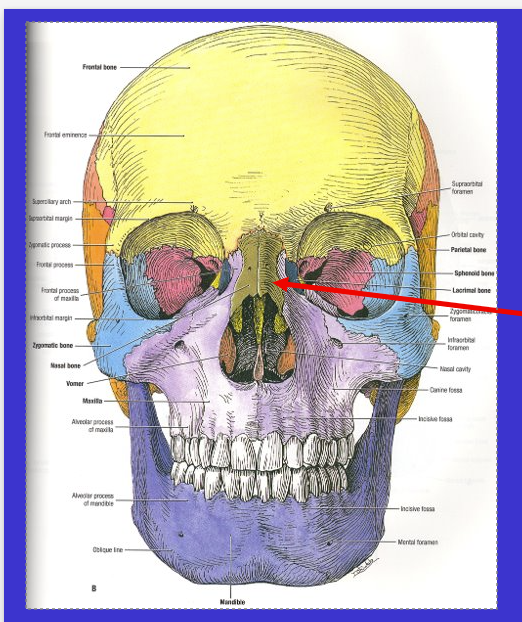
What is the arrow?
Lacrimal bone
supports lacrimal sac (tear fluid)
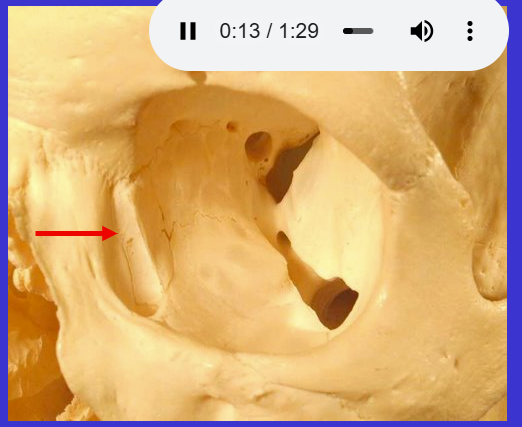
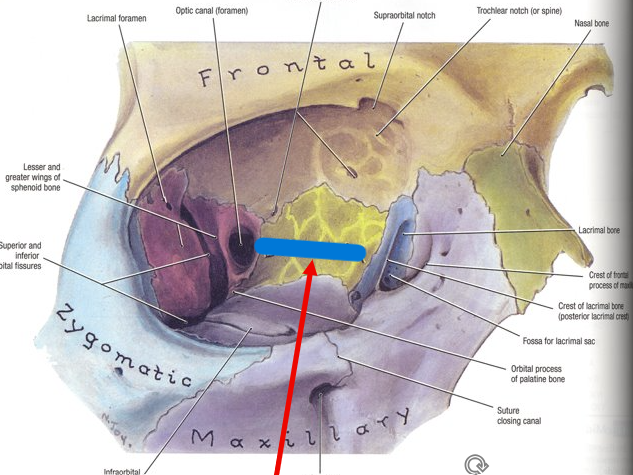
What is the arrow?
Ethmoid bone (visible from orbit)
surrounds cribriform plate & crista galli
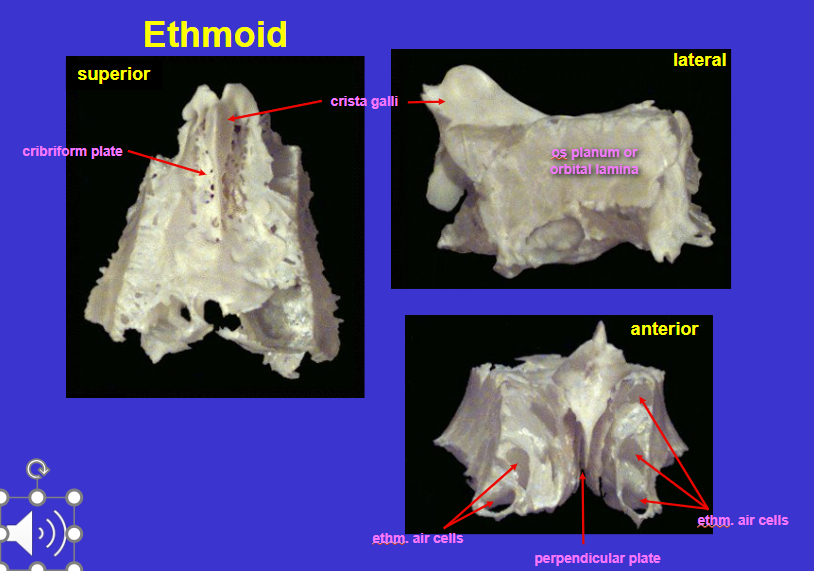
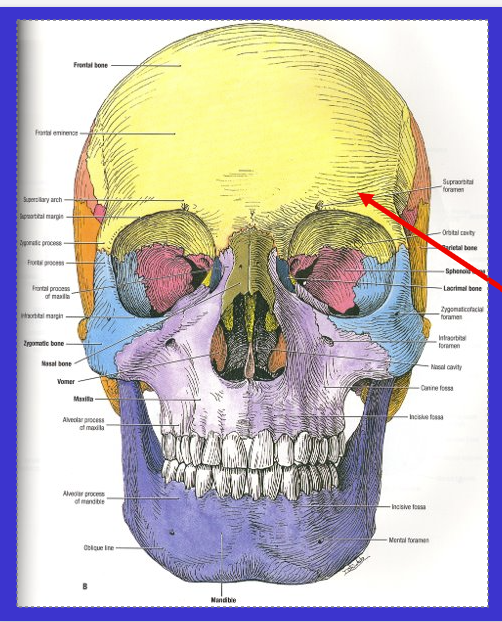
What is the top arrow?
Parietal bone
completely flat bone
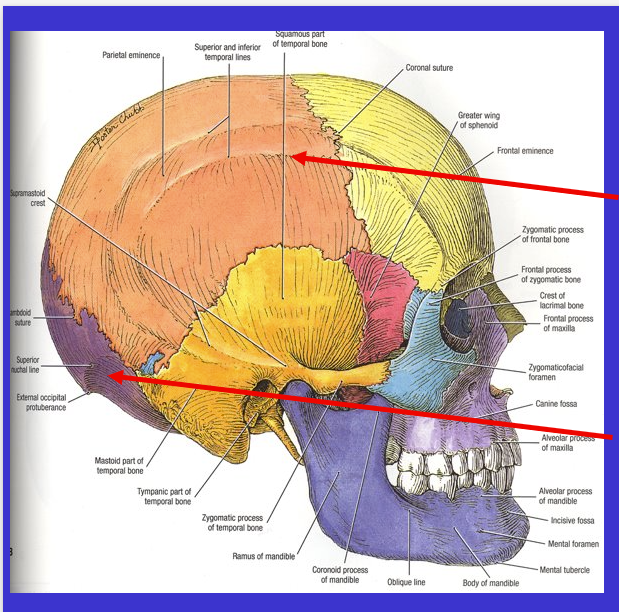
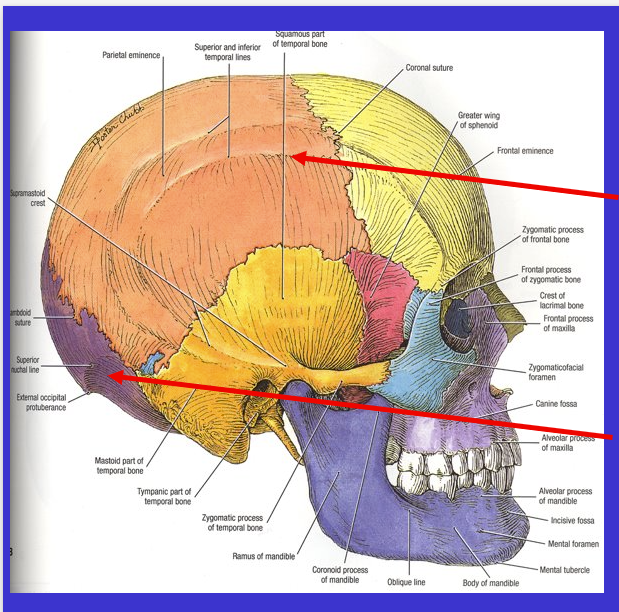
What is the bottom arrow?
Occipital bone
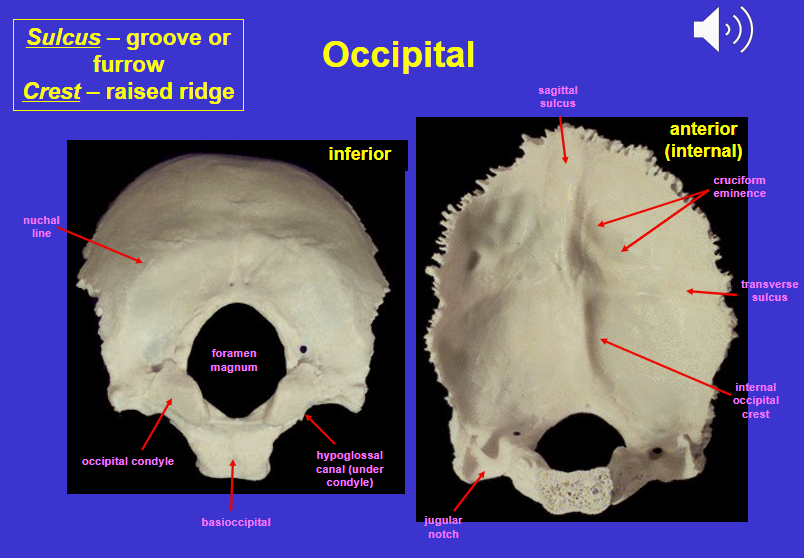
What is a sulcus
Groove or furrow
What is a crest
Raised ridge
What is the flat part of the occipital bone? Circled
Occipital squama (flat part contributing to brain case)
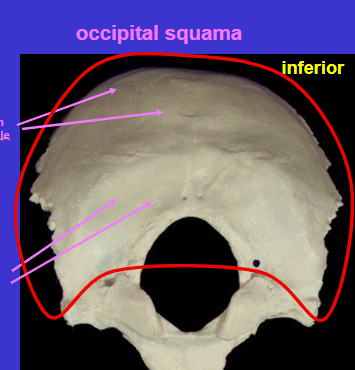
What is the top region called? What is the bottom region called?
Top = Planum occipitale
Bottom = Planum nuchale
*separated by nucal line

What are the arrows?
Meningeal grooves (accommodate meningeal)
What is a Wormian bone?
A highly variable little bone

What is a suture?
Immobile joint between neurocranial bones
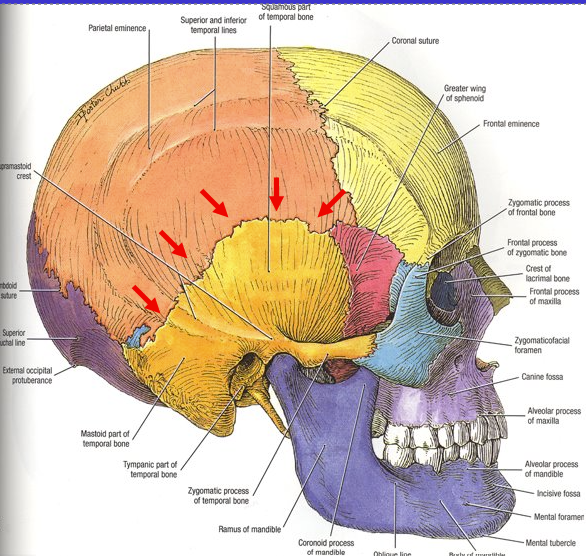
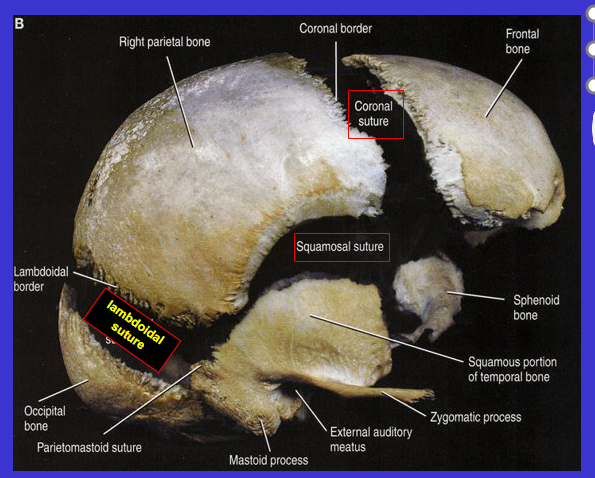
Which suture is the arrow pointing to?
Squamosal suture
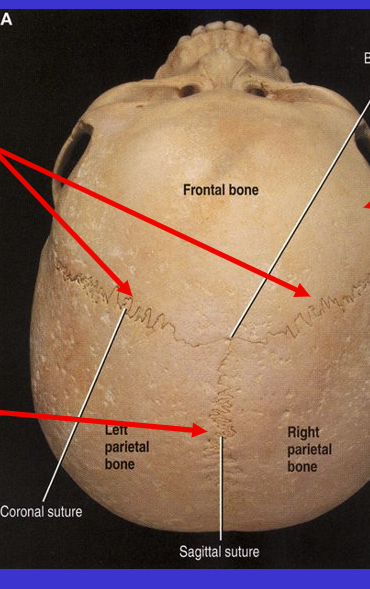
What are the top 2 sutures?
Coronal suture (because kind of align with coronal plane)
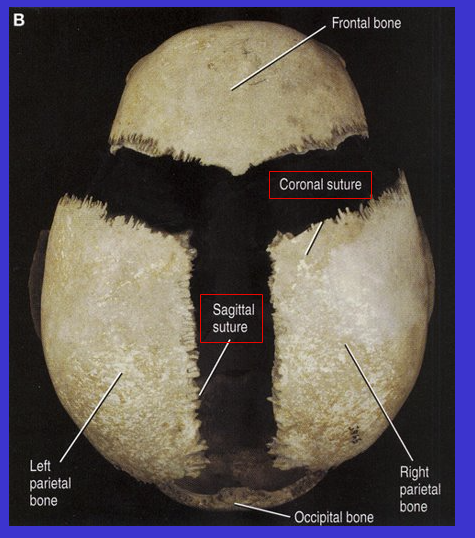
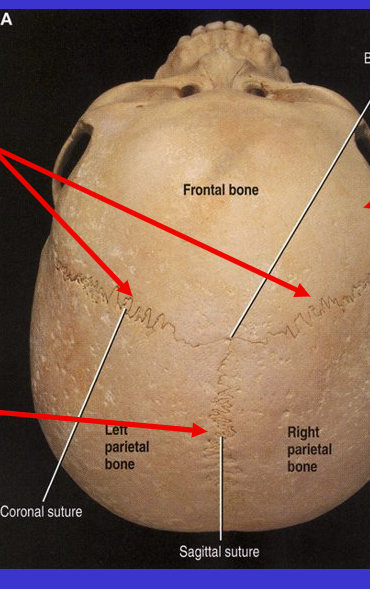
What is the bottom arrow suture?
Sagittal suture (because it aligns with the sagittal plane)
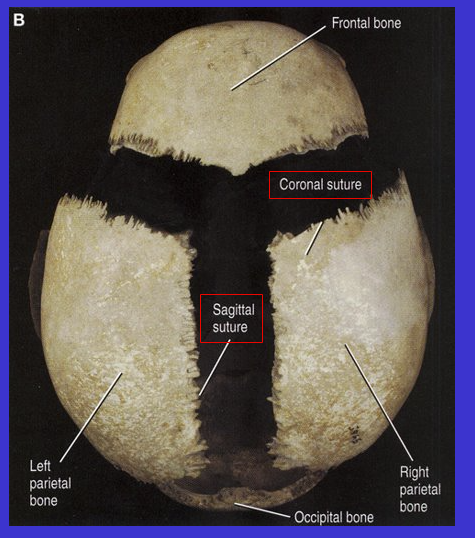
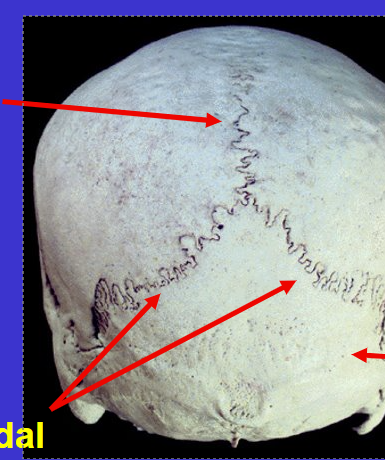
What suture is the bottom 2 arrows?
Lambdoidal suture (because it kind of looks like a Lamda) (the top suture is the sagittal suture)
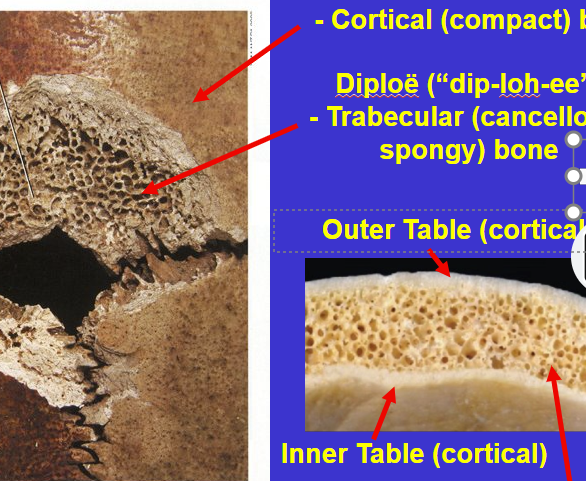
What 3 characteristic layers do flattened bones of the braincase have?
Outer Table = Cortical (compact) bone
Diploe = Trabecular (cancellous, spongy) bone with rounded spaces
Inner table = cortical bone
What is the top arrow?
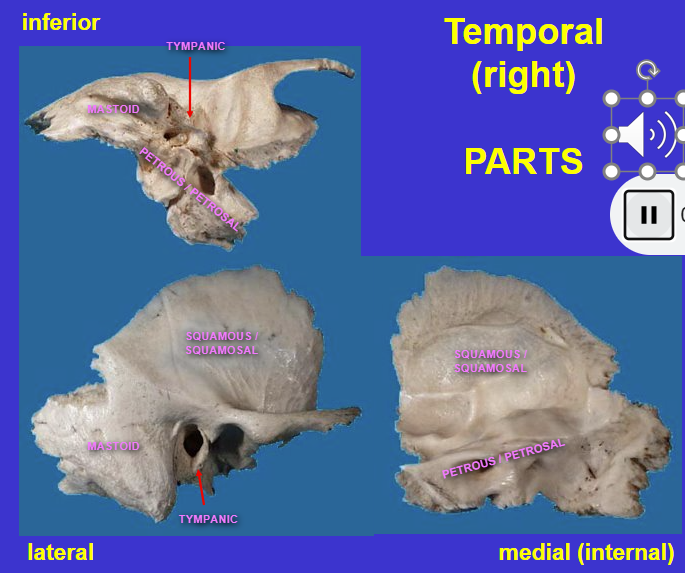
Temporal bone
very complex bone because it’s formed from separate bones throughout evolutionary history
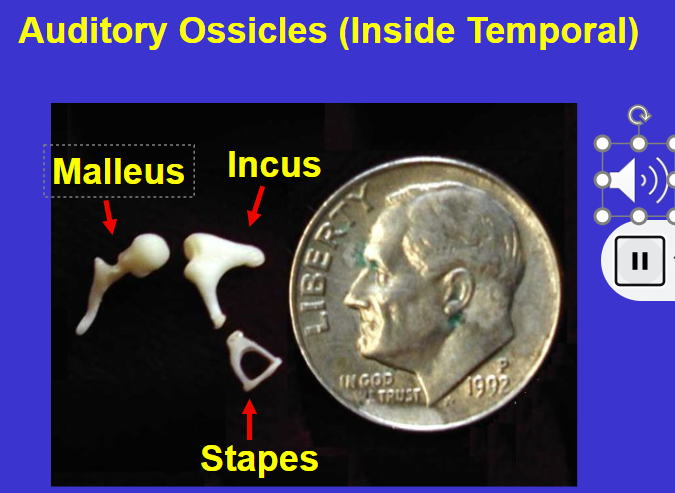
What are the 3 auditory ossicles (inside temporal)
Malleus (hammer)
Incus (anvil)
Stapes
*Air space in temporal bones/connect ear drum
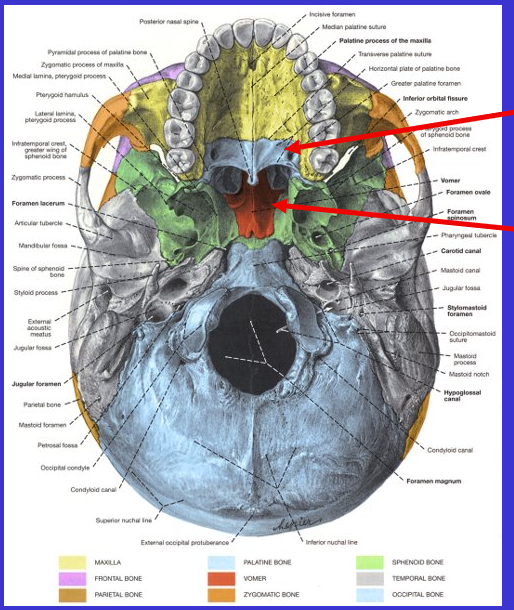
What is the top arrow?
Palatine bone (posterior part of hard palate, connecting it to soft palate)
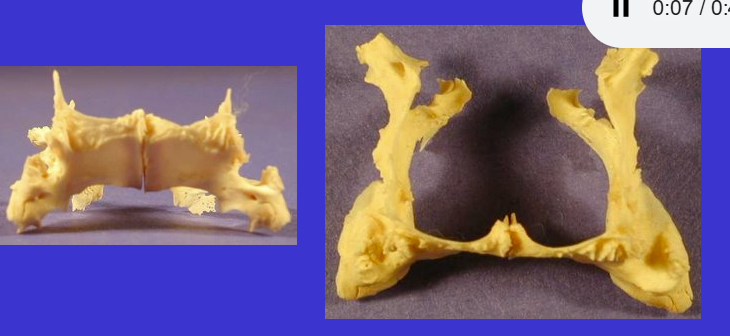
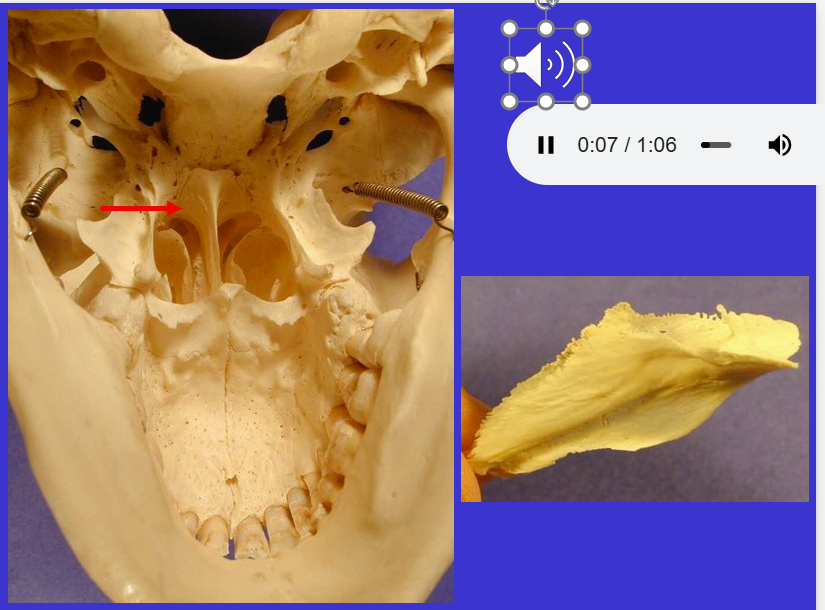
What is the bottom arrow?
Vomer (unpaired midline structure that forms nasal septum)
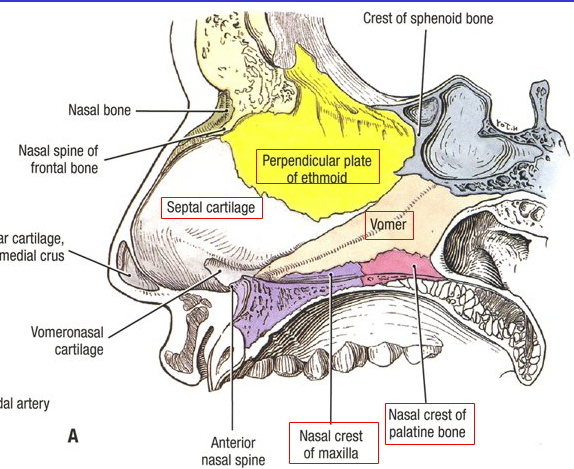
What are the 5 structures that make up the nasal septum?
Perpendicular plate of ethmoid
Septal cartilage
Nasal crest of maxilla
Nasal crest of palatine bone
Vomer
*Both the left and right nasal fossa (nose holes) are separated by nasal septum)
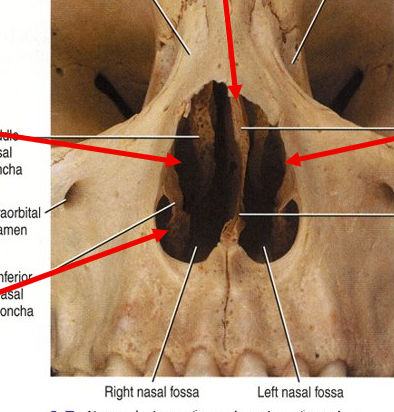
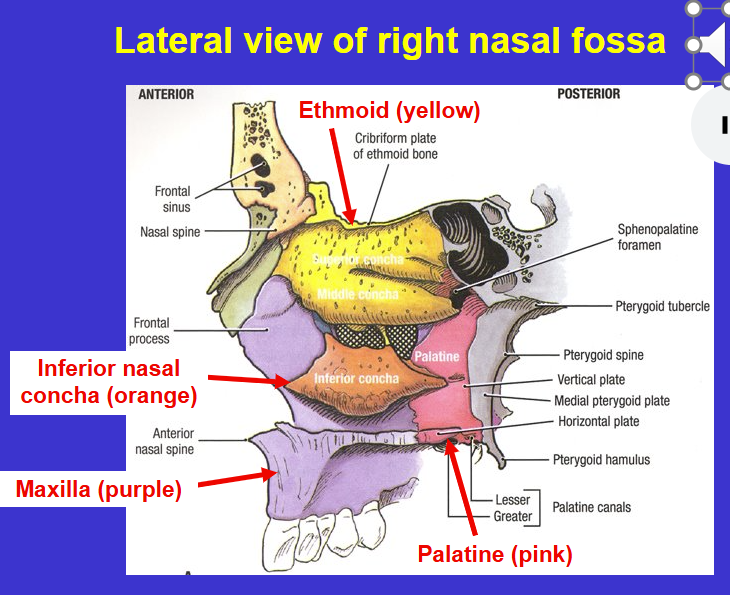
What is the bottom left arrow?
Inferior nasal concha bone (separate bone that’s covered in mucus membrane to humidify the air)
What does a isolate sphenoid look like?
Like an owl and similarly called like it