6 Developmental Psychology
1/83
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
84 Terms
developmental psychology
a branch of psychology that studies physical, cognitive, and social change throughout the life span
zygote
the fertilized egg; it enters a 2-week period of rapid cell division and develops into an embryo
embryo
the developing human organism from about 2 weeks after fertilization through the second month
fetus
the developing human organism from 9 weeks after conception to birth
teratogens
agents, such as chemicals and viruses, that can reach the embryo or fetus during prenatal development and cause harm
fetal alcohol syndrome (FAS)
physical and cognitive abnormalities in children caused by a pregnant woman's heavy drinking; in severe cases, symptoms include noticeable facial disproportions
habituation
decreasing responsiveness with repeated stimulation; as infants gain familiarity with repeated exposure to a visual stimulus, their interest wanes and they look away sooner
maturation
biological growth processes that enable orderly changes in behaviour, relatively uninfluenced by experience
cognition
all the mental activities associated with thinking, knowing, remembering, and communicating
schema
a concept or framework that organizes and interprets information
assimilation
interpreting our new experiences in terms of our existing schemas
accommodation
adapting our current understandings (schemas) to incorporate new information
sensorimotor stage
in Piaget's theory, the stage (from birth to about 2 years of age) during which infants know the world mostly in terms of their sensory impressions and motor activities
object permanence
the awareness that things continue to exist even when not perceived
preoperational stage
in Piaget's theory, the stage (from about 2 to 6 or 7 years of age) during which a child learns to use language but does not yet comprehend the mental operations of concrete logic
conservation
the principle (which Piaget believed to be a part of concrete operational reasoning) that properties such as mass, volume, and number remain the same despite changes in the forms of objects
egocentrism
in Piaget's theory, the preoperational child's difficulty taking another's point of view
theory of mind
people's ideas about their own and others' mental states, and about their feelings, perceptions, and thoughts, and the behaviours these might predict
autism spectrum disorder (ASD)
a disorder that appears in childhood and is marked by significant deficiencies in communication and social interaction, and by rigidly fixated interests and repetitive behaviours
concrete operational stage
in Piaget's theory, the stage of cognitive development (from about 6 or 7 to 11 years of age) during which children gain the mental operations that enable them to think logically about concrete events
formal operational stage
in Piaget's theory, the stage of cognitive development (normally beginning about age 12) during which people begin to think logically about abstract concepts
autism
a disorder that appears in childhood and is marked by deficient communication, social interaction, and understanding of others' states of minds
stranger anxiety
the fear of strangers that infants commonly display, beginning by about 8 months of age
attachment
an emotional tie with another person; shown in young children by their seeking closeness to the caregiver and showing distress on separation
critical period
an optimal period shortly after birth when an organism's exposure to certain stimuli or experience produces proper development
imprinting
the process by which certain animals form attachments during a critical period very early in life
temperament
a person's characteristic emotional reactivity and intensity
basic trust
according to Erik Erikson, a sense that the world is predictable and trustworthy; said to be formed during infancy by appropriate experiences with responsive caregivers
self-concept
our understanding and evaluation of who we are
gender
in psychology, the biologically and socially influenced characteristics by which people define male and female
aggression
physical or verbal behaviour intended to hurt someone
gender role
a set of expected behaviour for males or for females
role
a set of expectations (norms) about a social position, defining how those in the position ought to behave
gender identity
our sense of being male or female
social learning theory
the theory that we learn social behaviour by observing and imitating and by being rewarded or punished
gender typing
the acquisition of a traditional masculine or feminine role
transgender
un umbrella term describing people whose gender identity or expression differs from that associated with their birth sex.
adolescence
the transition period from childhood to adulthood, extending from puberty to independence
identity
our sense of self; according to Erikson, the adolescent's task is to solidify a sense of self by testing and integrating various roles
social identity
the "we" aspect of our self-concept; the part of our answer to "Who am I?" that comes from our group memberships
intimacy
in Erikson's theory, the ability to form close, loving relationships; a primary developmental task in late adolescence and early adulthood
emerging adulthood
for some people on modern cultures, a period from the late teens to mid-twenties bridging the gap between adolescent dependence and full independence and responsible adulthood
X chromosome
the sex chromosome found in both men and women; females have two & males have one; one from each parent produces a female child
Y chromosome
the sex chromosome found only in males; when paired with an X chromosome from the mother, it produces a male child
testosterone
the most important of the male sex hormones; both males & females have it, but the additional amount in males stimulates the growth of the male sex organs in the fetus and the development of male sex characteristics during puberty
puberty
the period of sexual maturation, during which a person becomes capable of reproducing
primary sex characteristics
the body structures (ovaries, testes, and external genitalia) that make sexual reproduction possible
secondary sex characteristics
non-reproductive sexual characteristics, such as female breasts and hips, male voice quality, and body hair
menarche
the first menstrual period
AIDS (acquired immune deficiency syndrome)
a life-threatening, sexually transmitted infection caused by the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). ___ depletes the immune system, leaving the person vulnerable to infections
sexual orientation
an enduring sexual attraction toward members of either one’s own sex (homosexual orientation), the other sex (heterosexual orientation), or both sexes (bisexual orientation).
menopause
the time of natural cessation of menstruation; also refers to the biological changes a woman experiences as her ability to reproduce declines
cross-sectional study
a study in which people of different ages are compared with one another
longitudinal study
research in which the same people are restudied and retested over a long period
social clock
the culturally preferred timing of social events such as marriage, parenthood, and retirement
Kohlberg
sought to describe the development of moral reasoning by posing moral dilemmas to children and adolescents, such as "Should a person steal medicine to save a loved one's life?"
preconventional morality
in Kohlberg’s stages of moral development, children before age 9 typically exhibit self-interest, obeying rules to avoid punishment or gain concrete rewards
conventional morality
one of Kohlberg’s stages of moral development during early adolescence characterized by the desire to uphold laws and rules to gain social approval or maintain social order
postconventional morality
in Kohlberg's stages of moral development, during adolescence and beyond, individuals' actions reflect their belief in basic rights and self-defined ethical principles
sex
biologically influenced characteristics that define male or female
androgyny
a blend of traditional masculine and feminine psychological characteristics
neurocognitive disorder
condition, previously dementia, that decreases blood flow to the hippocampus over time. risk increases with age
conception
a single sperm cell penetrates the outer coating of the egg and fuses to form one fertilized cell
innate reflexes
infants are born with reflexes that aid in survival, such as blinking, grasping, rooting, stepping, sucking, swimming, tonic neck, startle and the Babinski reflex
infantile amnesia
the earliest age of conscious memory is around 3.5 years, attributed to the lack of developed language abilities at that age, although associations between actions and results can still be learned
authoritarian parenting
parenting style in which parents impose rules and expect obedience
permissive parenting
parenting style in which parents submit to children’s demands
authoritative parenting
parenting style in which parents are demanding but responsive to their children. correlates with social competence
neglectful parenting
parenting style in which parents are uninvolved, careless, inattentive and don’t seek a relationship
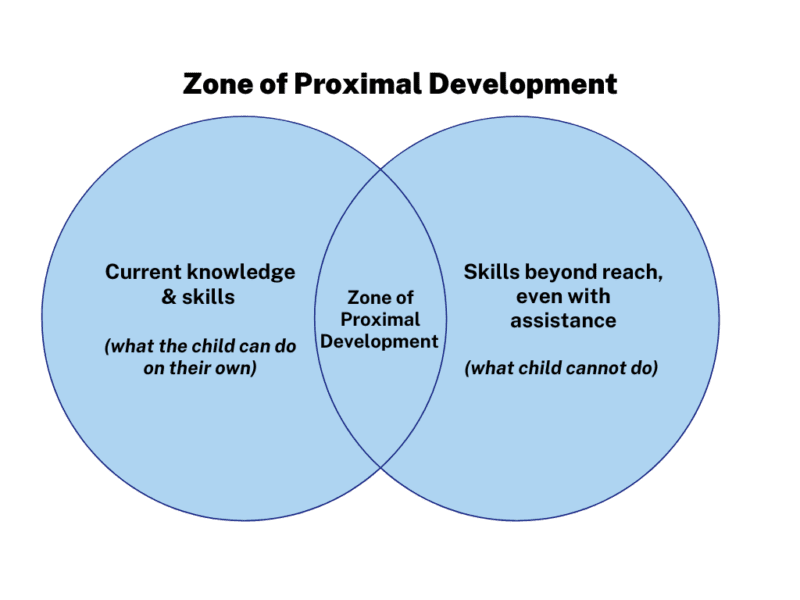
Lev Vygotsky
proposed that temporary supports are offered to children as the mind grows with interaction with the social environment so that children learn in a zone of proximal development
secure attachment
type of emotional bond expressed by approximately 60% of children when placed in a strange situation; they exhibit a willingness to explore their environment happily in the presence of their mothers. however, upon their mother's departure, they demonstrate distress. common with mothers who are sensitive and responsive.
insecure attachment
emotional bond expressed by approximately 40% of children when placed in a strange environment. children tend to cling to their mothers or caregivers and are less likely to explore their environment. common with mothers who are insensitive and unresponsive.
avoidant attachment
emotional bond in which people are clingy out of fear of rejection which can increase conflict in a relationship
anxious attachment
emotional bond displayed by people constantly craving acceptance and being alert to possible rejection
separation anxiety
displayed by infants that have higher heart rates and become more easily agitated. parents using more sensitive responding will help attachment
Erikson’s stage of psychosocial development during infancy
trust vs. mistrust
Erikson’s stage of psychosocial development during toddlerhood
autonomy vs. shame and doubt
Erikson’s stage of psychosocial development during preschooler
initiative vs. guilt
Erikson’s stage of psychosocial development during elementary school
competence vs. inferiority
Erikson’s stage of psychosocial development during adolescence
identity vs. role confusion
Erikson’s stage of psychosocial development during young adulthood
intimacy vs. isolation
Erikson’s stage of psychosocial development during middle adulthood
generativity vs. stagnation
Erikson’s stage of psychosocial development during late adulthood
integrity vs. despair
The imaginary audience phenomenon
refers to the belief that a person is under constant, close observation by peers, family, and strangers