Introduction to Communication Sciences and Disorders Exam 3
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
outer ear
the external part of the ear that collects and directs sound waves toward the eardrum
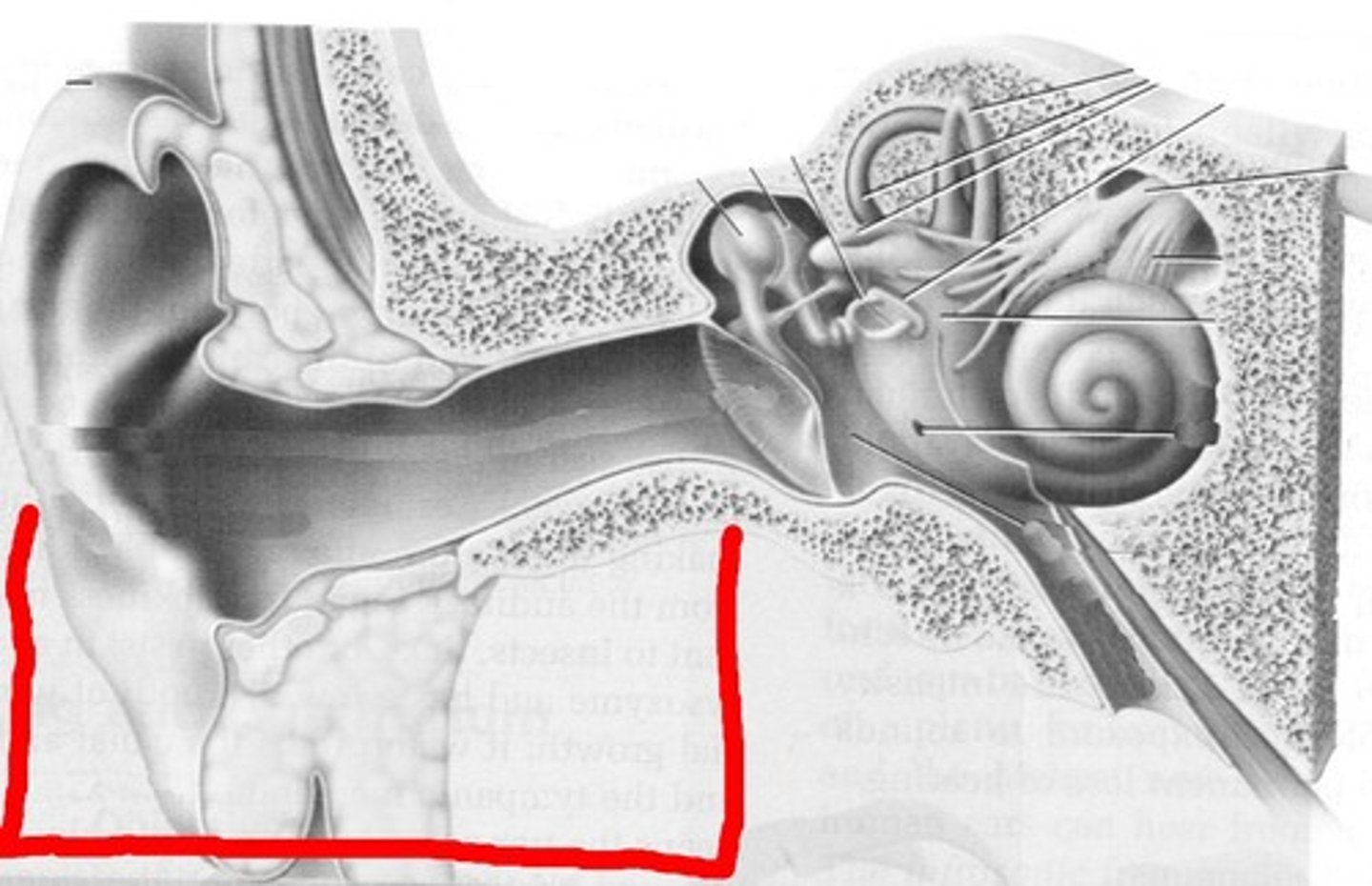
middle ear
the air-filled space containing the ossicles that amplifies and transmits sound vibrations from the eardrum to the inner ear
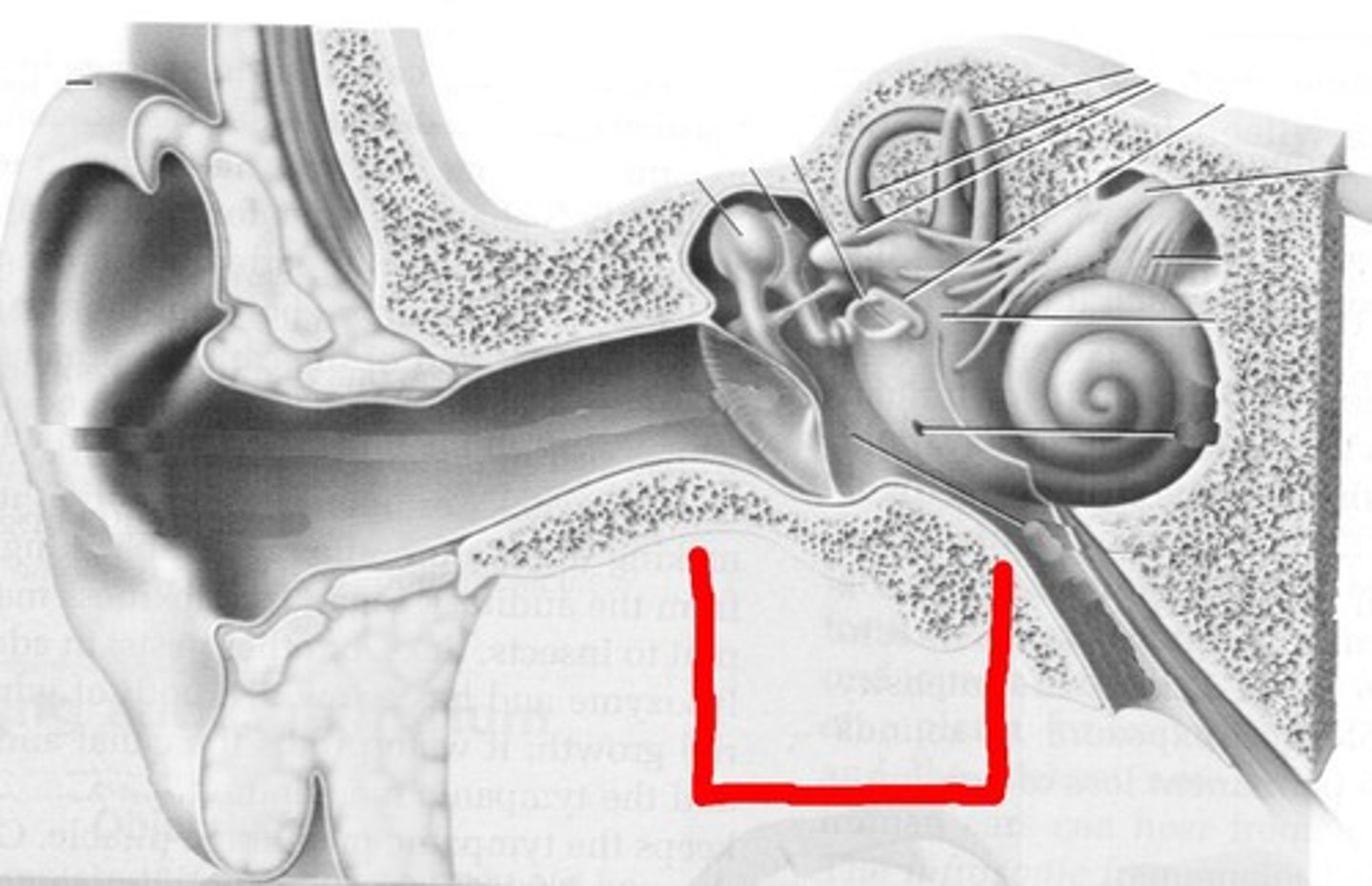
inner ear
the fluid-filled region that converts sound vibrations into nerve signals and helps maintain balance
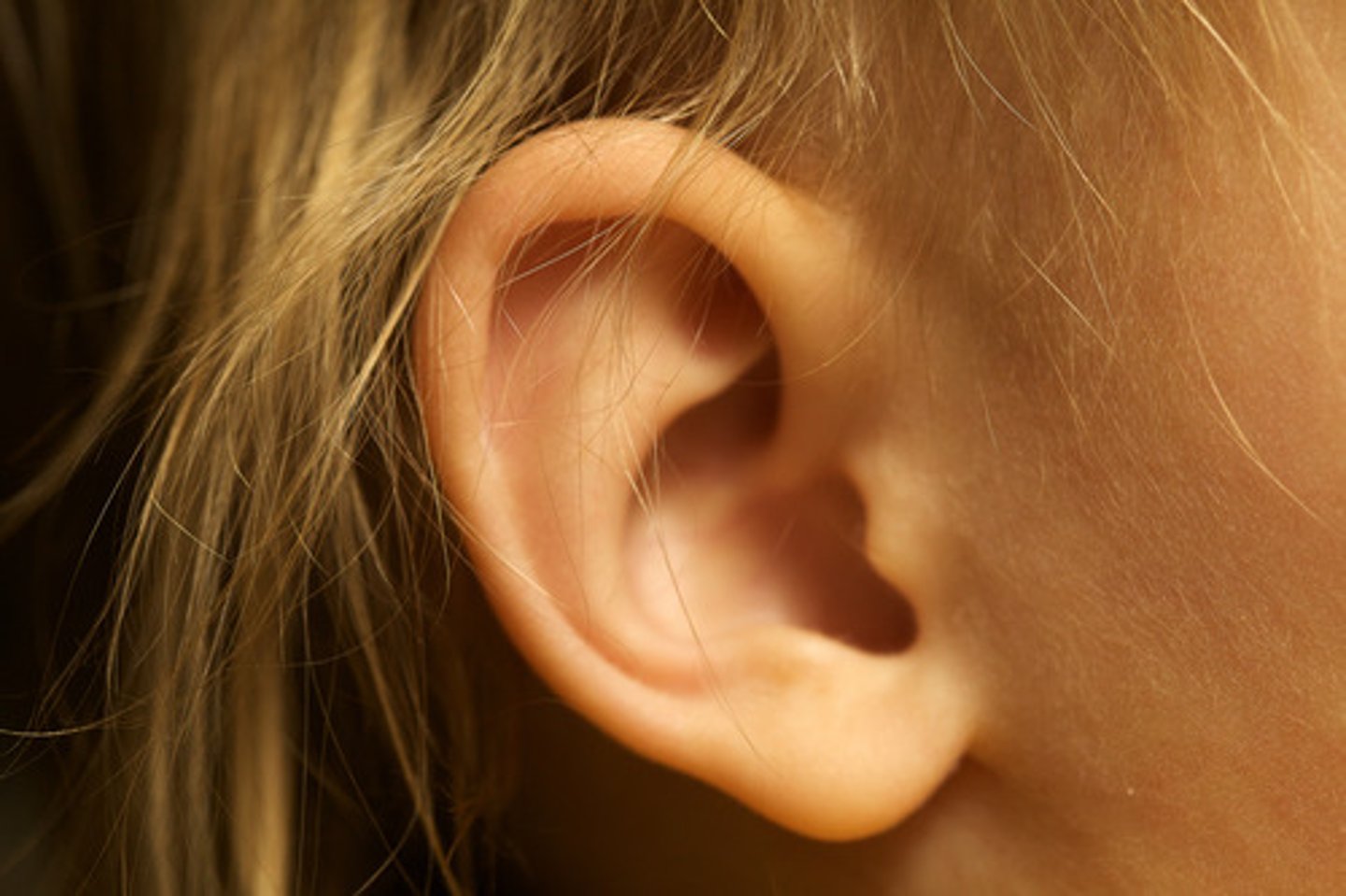
auricle / pinna
outer ear, collects sound waves and helps localize the direction of sound
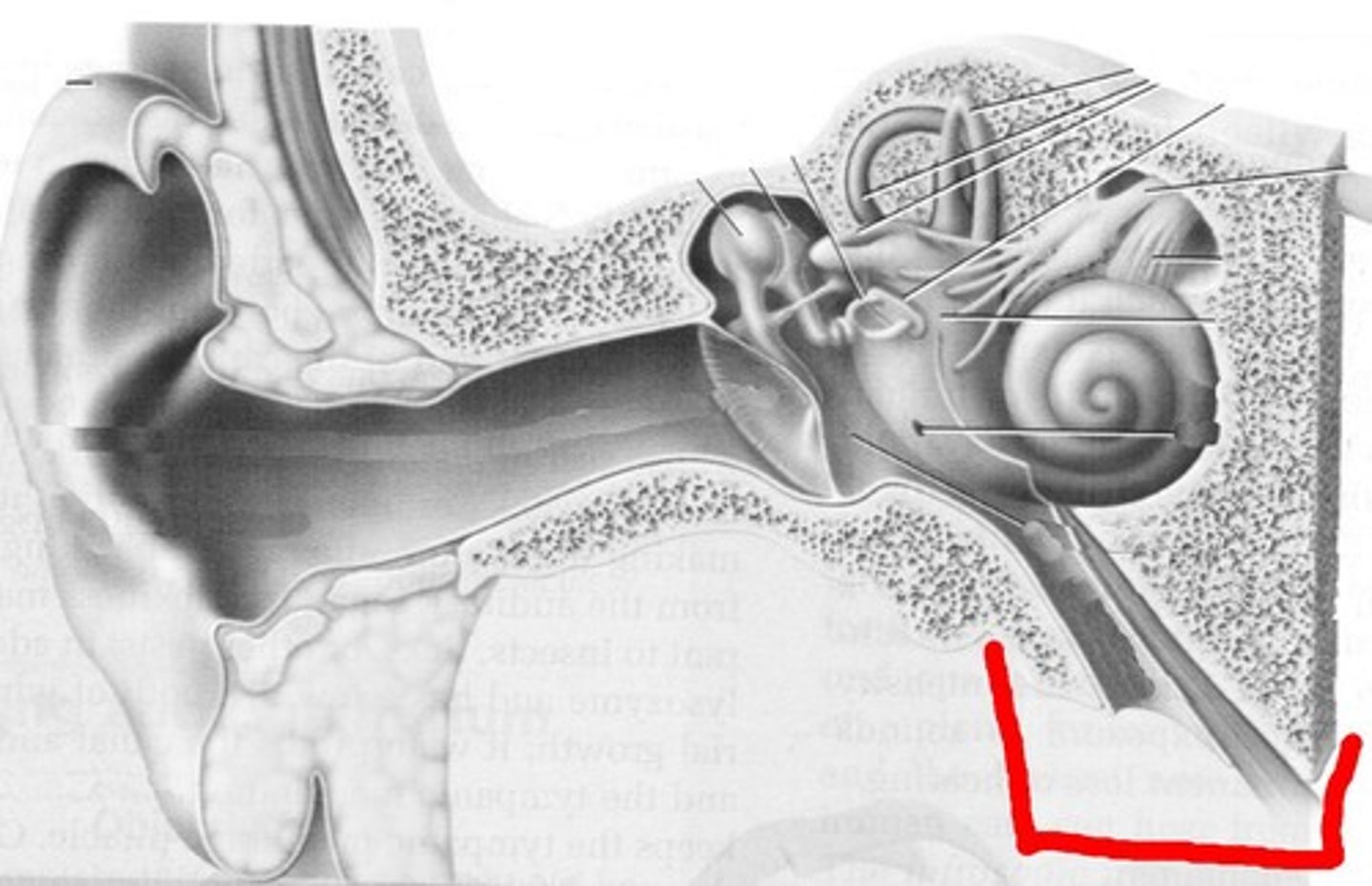
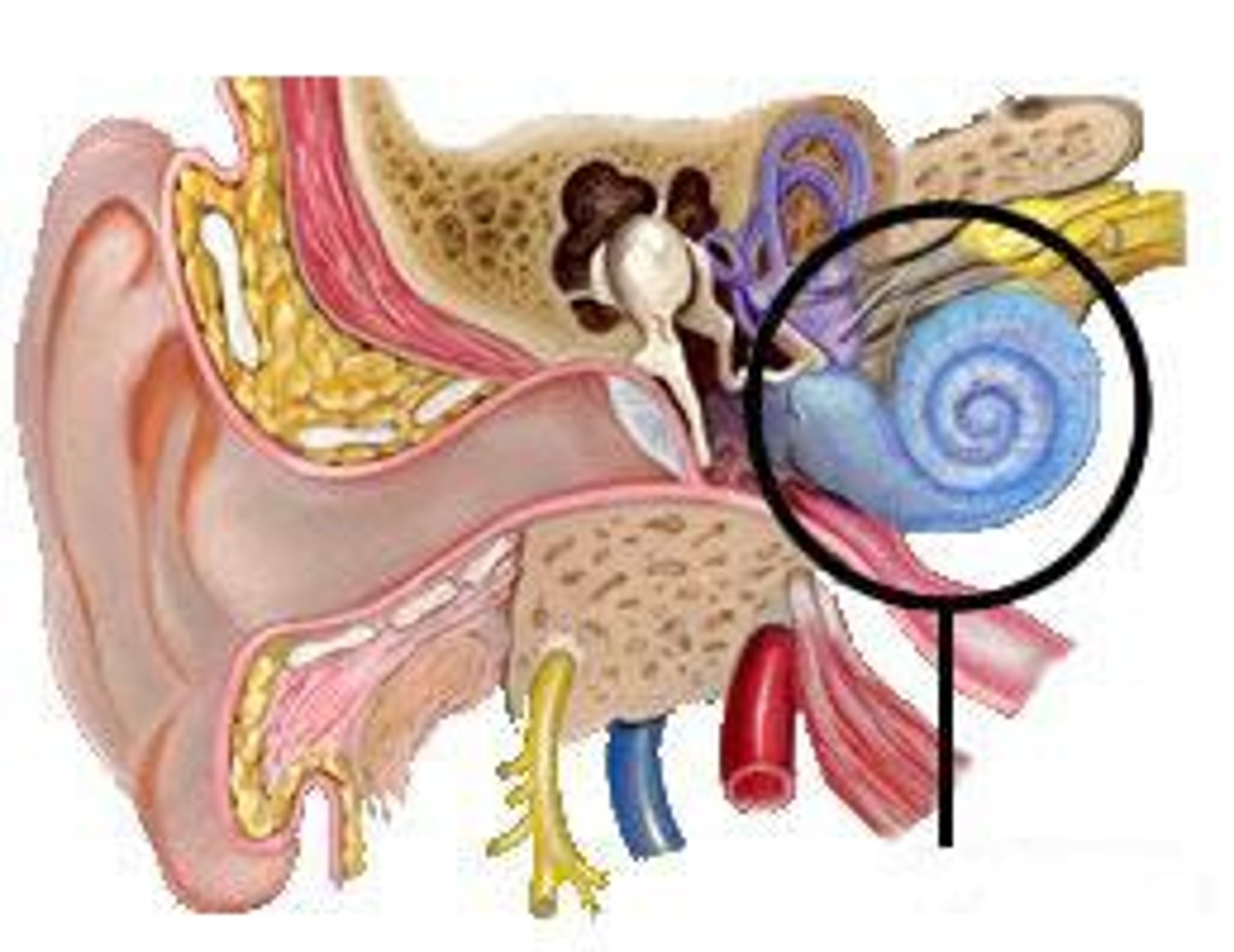
cochlea
inner ear, converts mechanical sound vibrations into electrical nerve impulses the brain can interpret
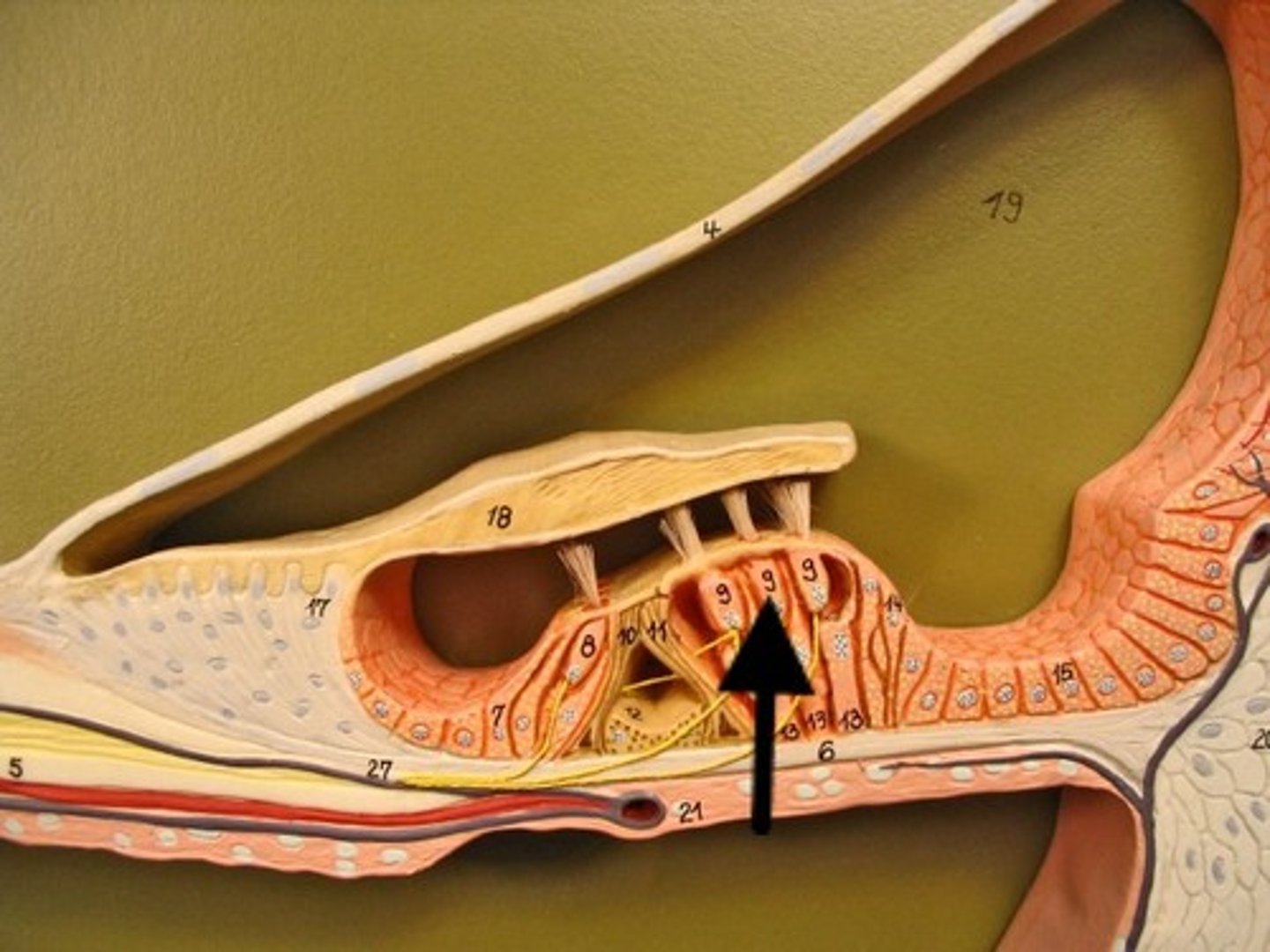
cochlea hair cells
inner ear, detect specific sound frequencies and change vibrations into neural signals
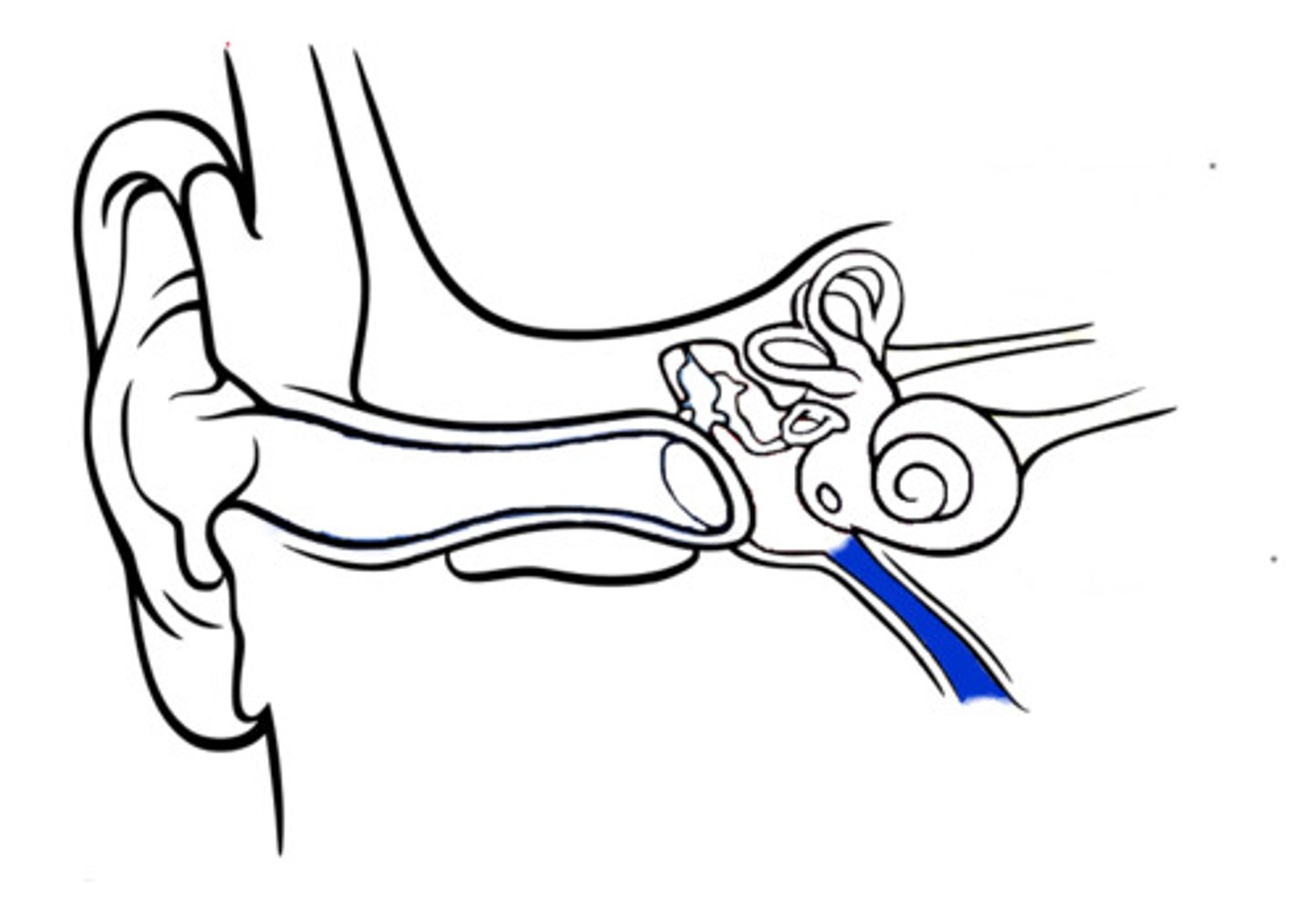
eustachian tube
equalizes air pressure between the middle ear and the atmosphere; example: ears “popping” during altitude changes
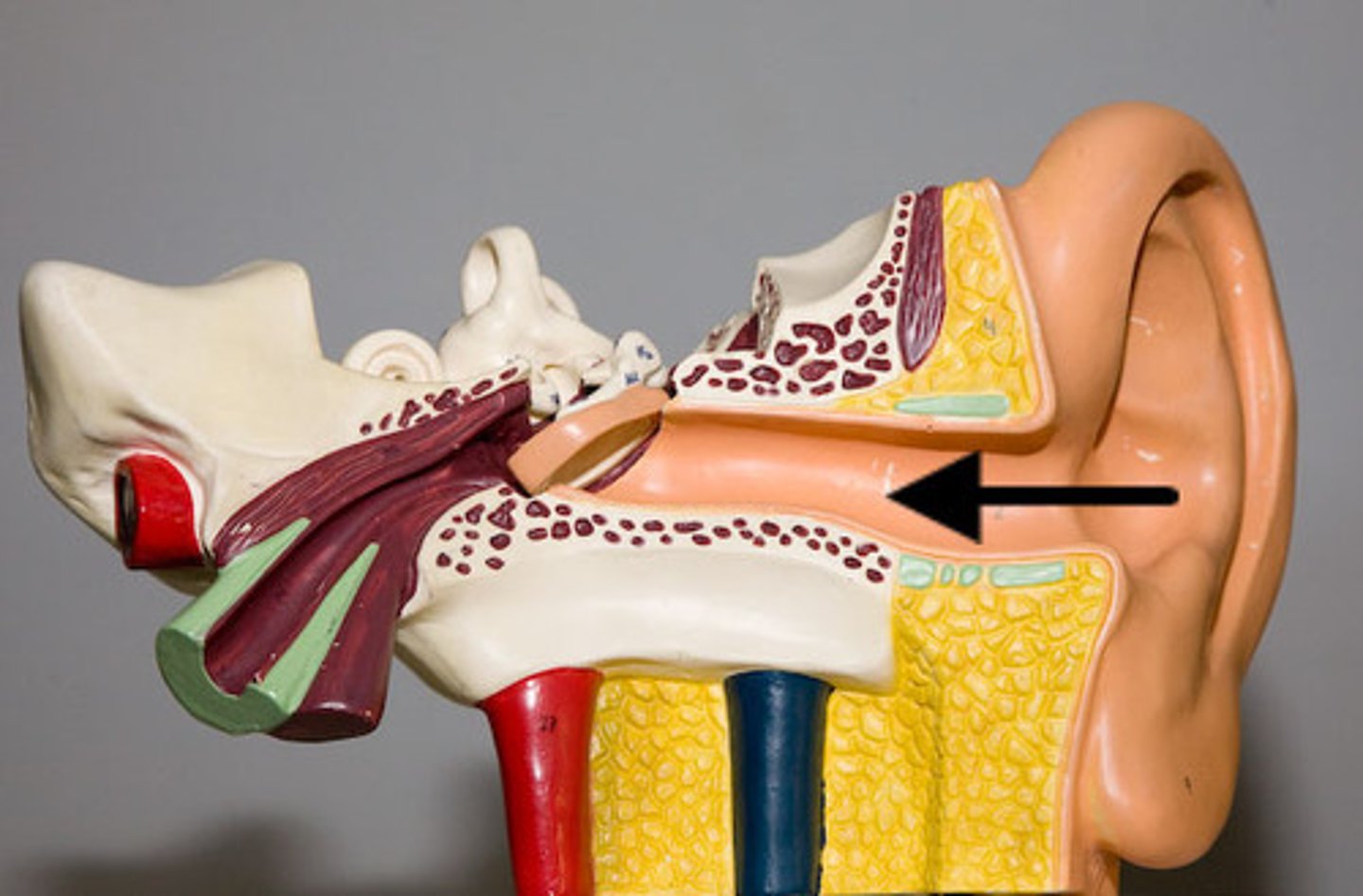
external auditory canal
channels sound waves from the outer ear to the tympanic membrane
ossicles
middle ear, amplify and transmit sound vibrations from the tympanic membrane to the oval window
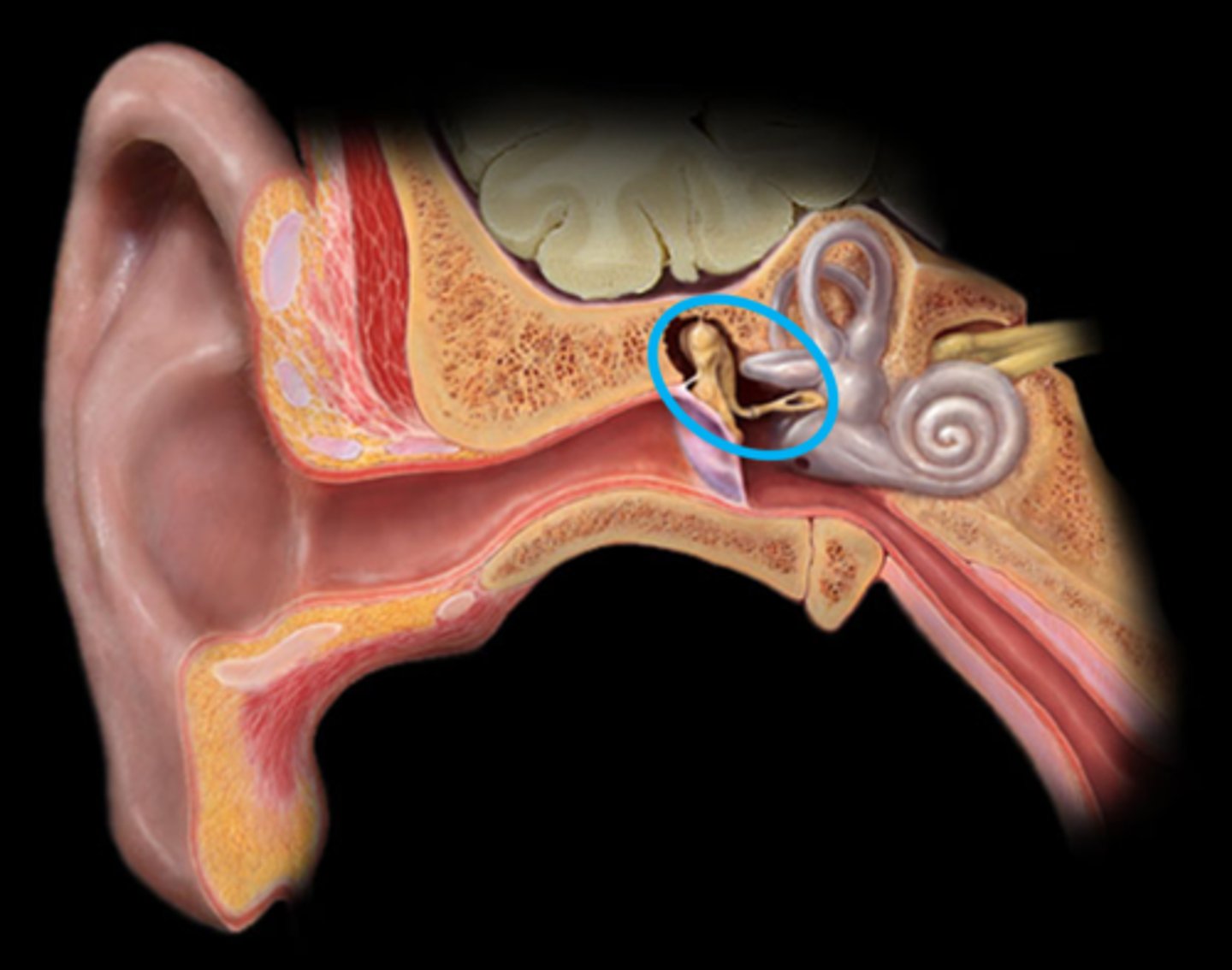
semicircular canals
inner ear, detect rotational head movements to maintain balance; example: sensing motion when spinning
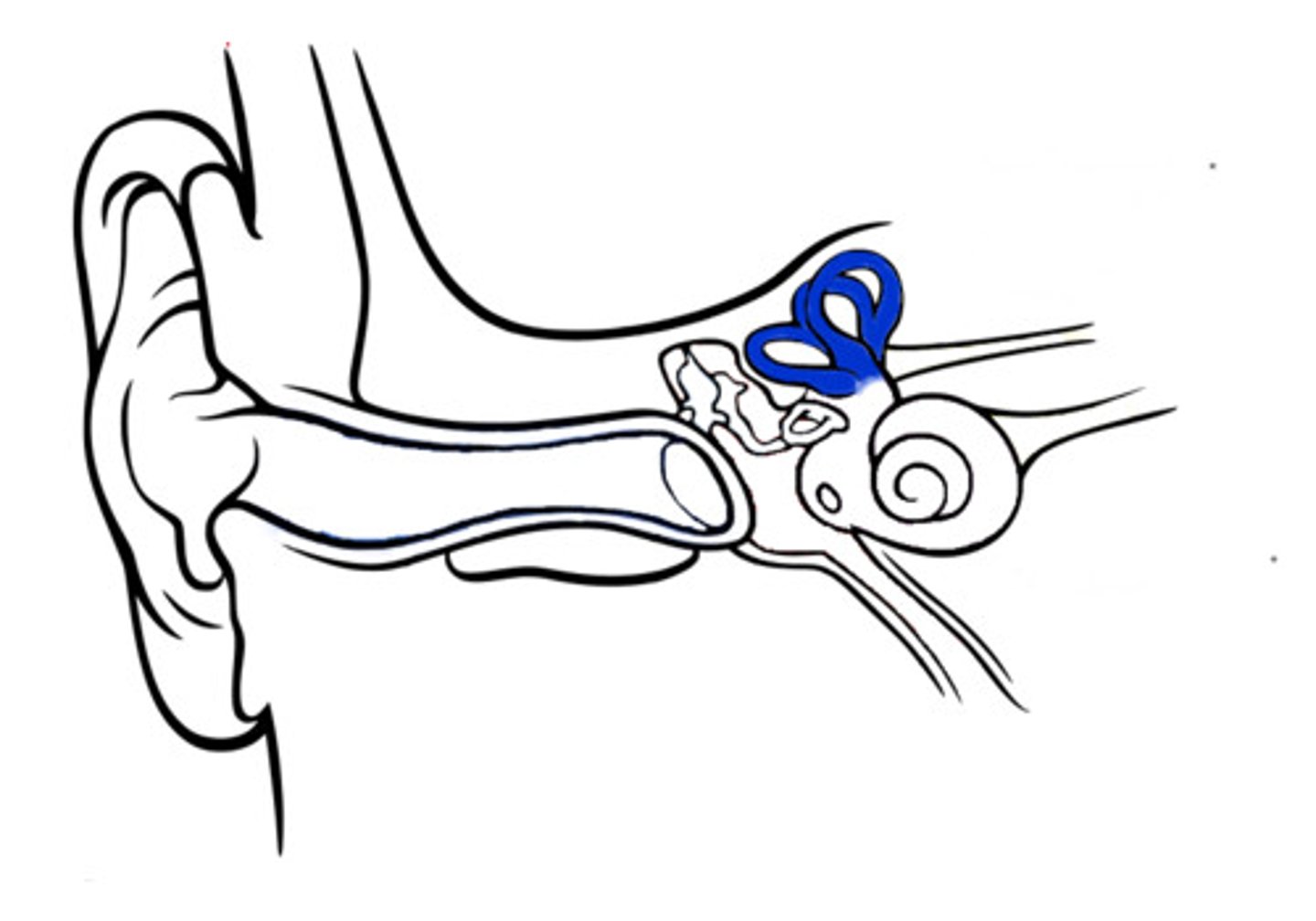
stapedius
a tiny muscle in the middle ear that dampens vibrations by pulling on the stapes bone, protecting the inner ear from loud sounds
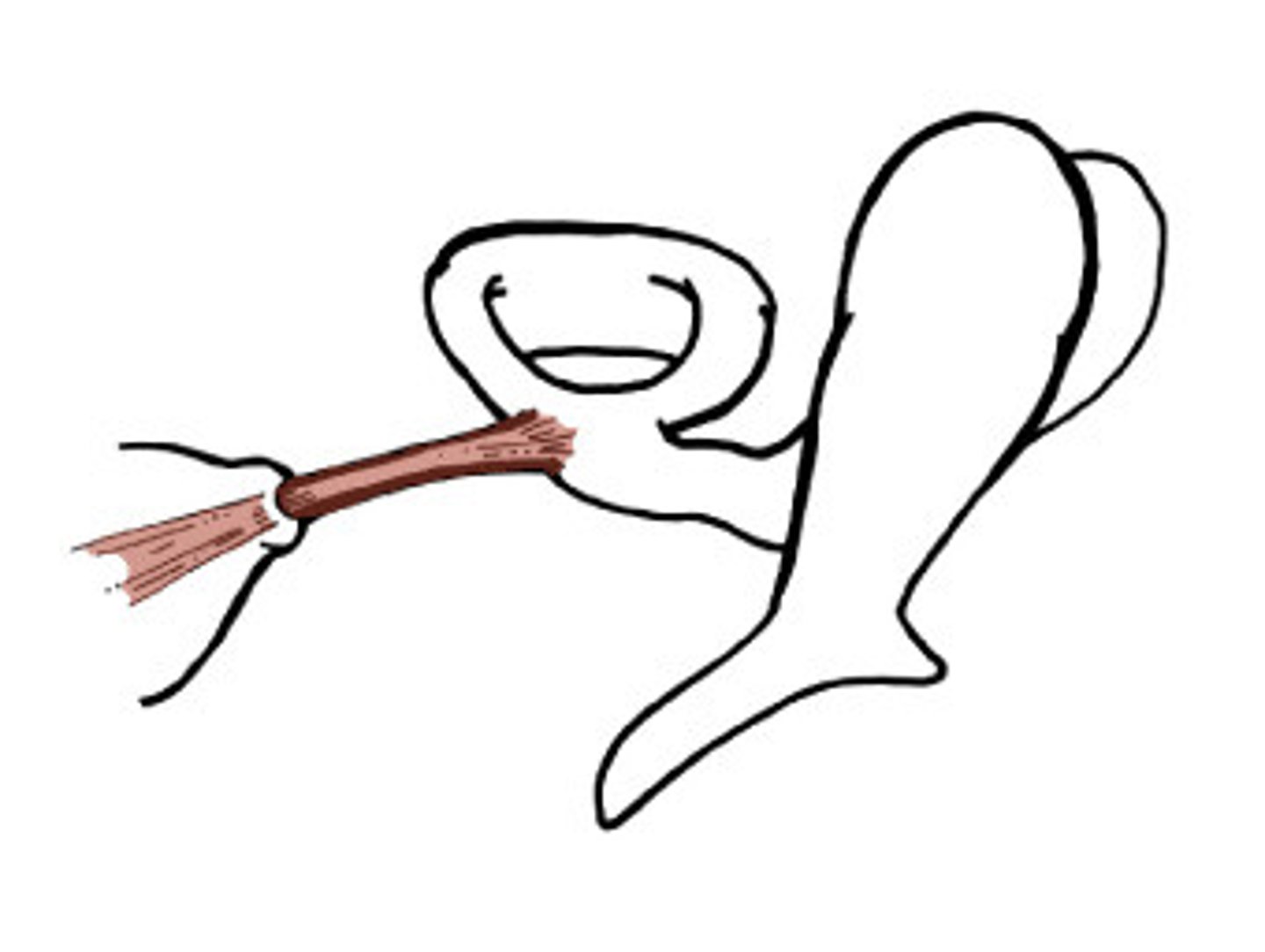

tympanic membrane (eardrum)
vibrates when struck by sound waves, a process that transmits the vibrations to the tiny bones of the middle ear to be sent to the inner ear for processing
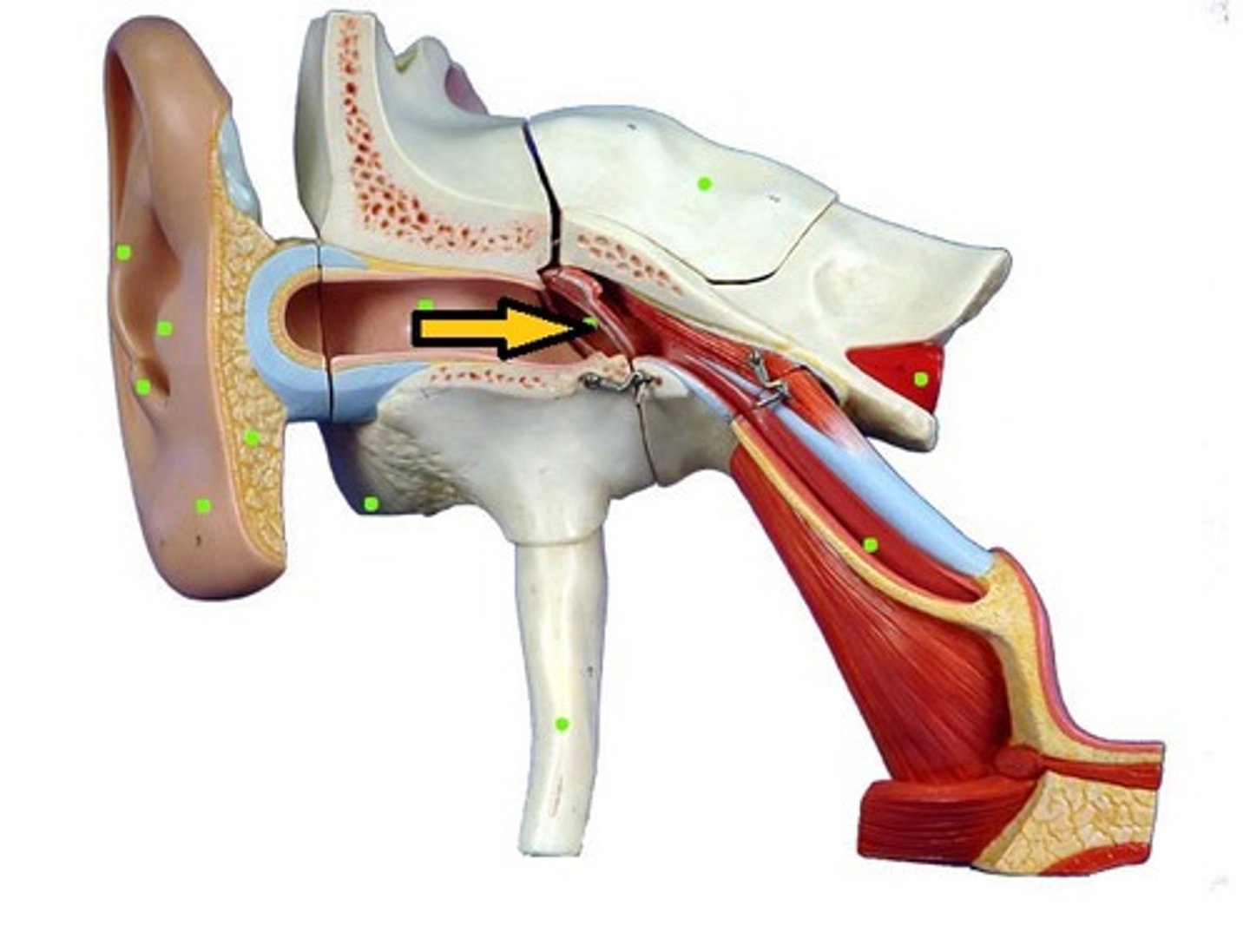
frequency (Hz)
the number of sound wave cycles per second, determining pitch
intensity / amplitude (dB)
the strength of a sound wave, perceived as loudness; example: whispering at about 30 dB versus a rock concert at 110 dB
20 Hz to 20,000 Hz
What is the range of human hearing?
air conduction
sound transmission through the air via the outer, middle, and inner ear; assessed using headphones during a hearing test
bone conduction
sound transmission through vibration of the skull directly to the inner ear; assessed using a bone oscillator placed behind the ear
acoustic, mechanical, hydraulic, electrical
process of energy transformation in hearing in order
acoustic (sound) energy
sound waves traveling through the air
mechanical energy
physical vibrations of ear structures
hydraulic (fluid) energy
movement of fluid within the cochlea
electrical (neural) energy
electrochemical nerve impulses sent to the brain
conductive hearing loss
hearing loss caused by problems in the outer or middle ear that prevent sound from being conducted efficiently to the inner ear (e.g., ear canal blockage, middle ear fluid, ossicular problems)
sensorineural hearing loss
hearing loss resulting from damage to the inner ear (cochlea) or the auditory nerve, affecting the conversion of sound into neural signals (often permanent)
mixed hearing loss
a combination of conductive and sensorineural hearing loss, involving damage in both the outer/middle ear and the inner ear or auditory nerve
eustachian tube in adults
tube is longer and more vertical, allowing better drainage and fewer hearing disorders
eustachian tube in children
tube is shorter, narrower, and more horizontal, making middle ear infections and fluid buildup more common and increasing risk of conductive hearing loss
audiogram
chart used to measure and record an individual's hearing thresholds across different frequencies and intensities to identify type and degree of hearing loss
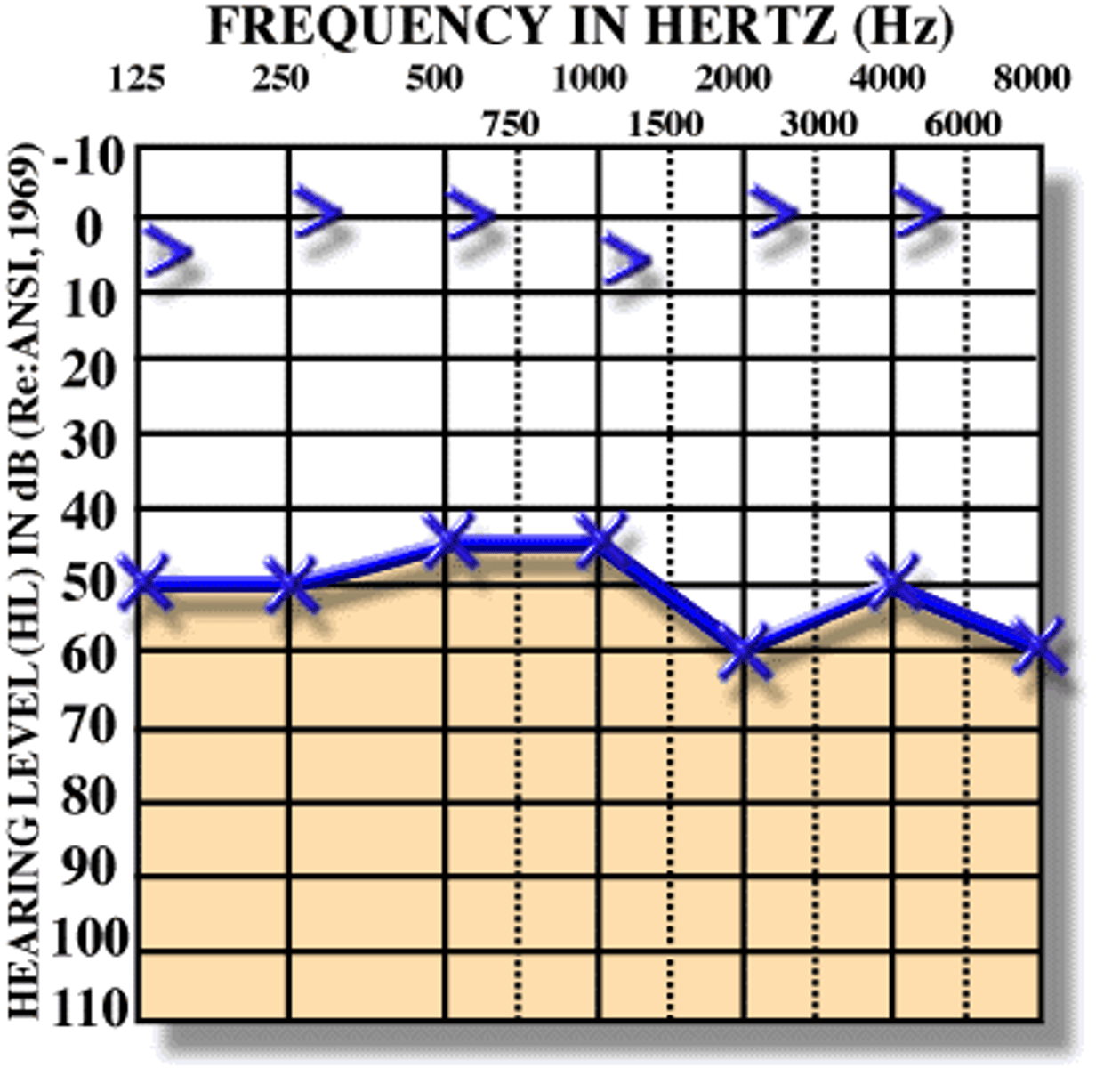
hearing disorder assessment for middle ear
assessment methods such as tympanometry and acoustic reflex testing evaluate middle ear pressure, eardrum mobility, and ossicular chain function
auditory habilitation
learning new skills, mainly for children
auditory rehabilitation
restoring lost skills after an illness or injury
World War II induced hearing loss
Why and when did audiologists first begin dispensing hearing aids?
behind-the-ear hearing aid
a hearing aid worn behind the ear that captures sound through microphones, amplifies and processes it digitally, and delivers sound into the ear canal via tubing and an earmold

Body-worn hearing aid
a portable hearing aid worn on the body that uses a microphone, amplifier, and receiver to amplify sound and transmit it to an earpiece (largely obsolete today)
Bone anchored hearing aid
a device that transmits sound vibrations through the skull directly to the inner ear via bone conduction, bypassing the outer and middle ear
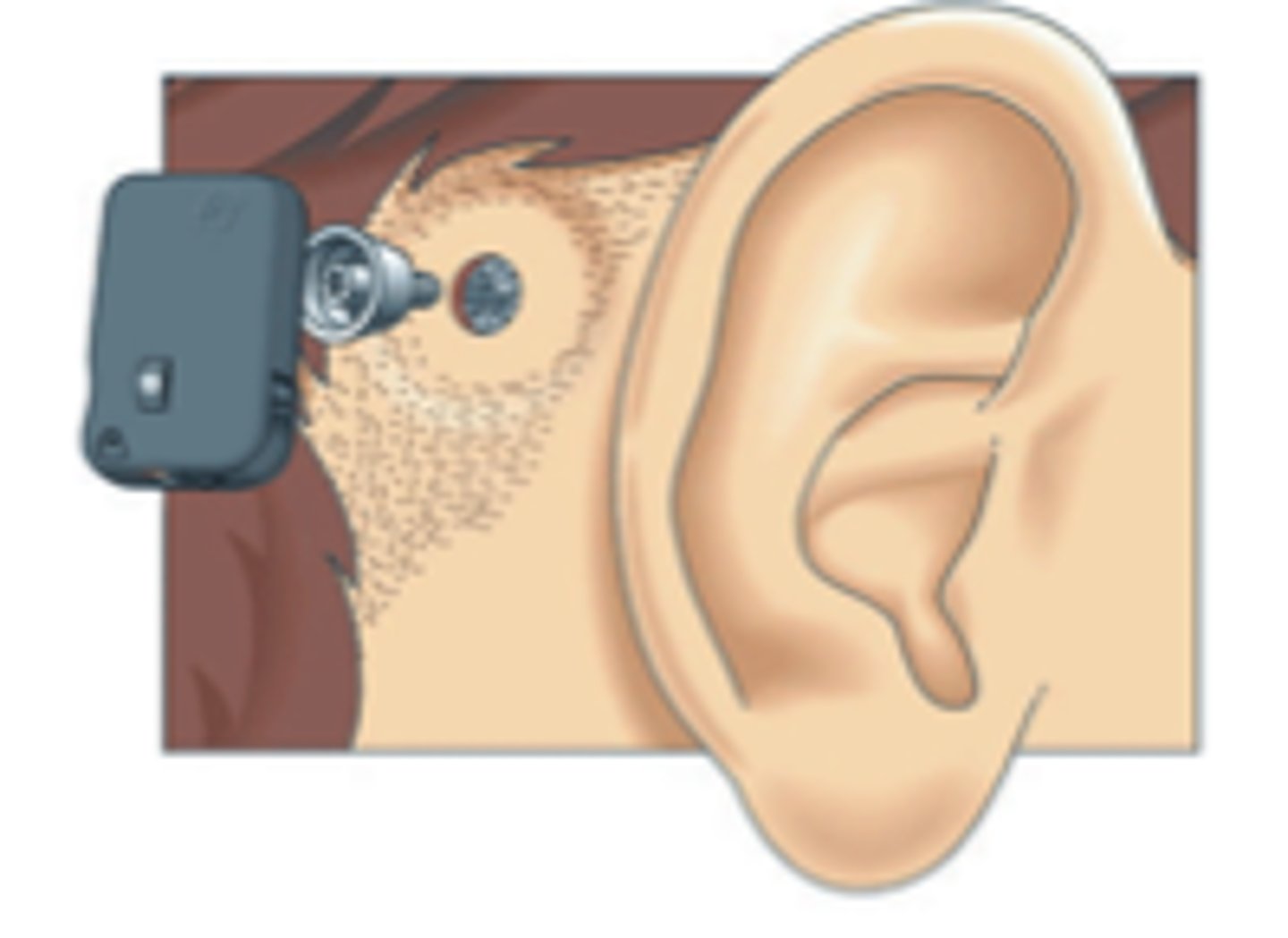
Cochlear implant
an electronic medical device that bypasses damaged cochlear structures by converting sound into electrical signals that directly stimulate the auditory nerve

FM system
a wireless assistive listening device in which a microphone worn by the speaker transmits sound via radio frequency directly to a listener's receiver, improving signal-to-noise ratio

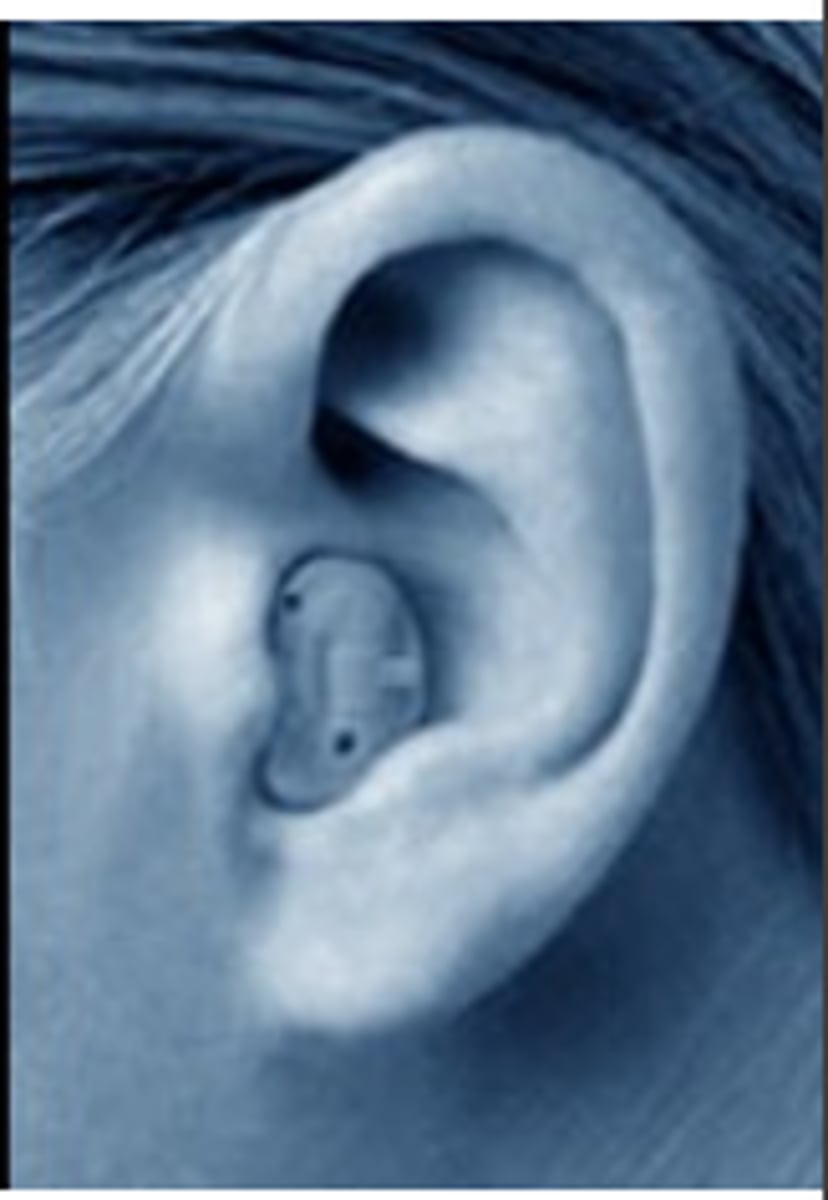
In-the-canal hearing aid
a small hearing aid that fits partly or completely inside the ear canal and amplifies sound using an integrated microphone, amplifier, and receiver
components of a hearing aid
microphone, amplifier/digital processor, receiver (speaker), power source (battery), and controls or wireless circuitry
deafness
a severe to profound hearing loss in which auditory input is insufficient for understanding speech through hearing alone, even with amplification
hard of hearing
a degree of hearing loss where auditory input is reduced but usable for speech understanding, often with the help of hearing aids
hearing loss affect on speech and language
difficulties with articulation, vocabulary development, grammar/syntax, speech intelligibility, voice quality, and listening comprehension
earlier onset hearing loss
the gradual or sudden loss of hearing that begins in childhood or young adulthood, has greater impact on speech and language development
cultural competence
ensures accurate assessment, effective intervention, respectful interactions, reduced disparities in care, and improved outcomes for individuals from diverse cultural and linguistic backgrounds
evidence-based practice (EBP)
a problem-solving approach to making clinical decisions, using best available research evidence, clinical expertise, and client preferences
importance of evidence-based practice (EBP)
promotes effective, ethical, and accountable services by integrating science with professional judgment and client needs
Augmentative and Alternative Communication (AAC)
methods, systems, tools, and strategies that support or replace spoken or written language for individuals with communication difficulties
AAC patient conditions
autism spectrum disorder, cerebral palsy, intellectual disability, developmental language disorder, apraxia of speech, ALS, stroke, traumatic brain injury, and degenerative neurological diseases
Unaided AAC system
communication methods that do not require external tools, relying solely on the user's body (e.g., speech attempts, gestures, facial expressions)

Aided AAC system
communication methods that use external tools or devices, ranging from simple picture boards to advanced speech-generating devices

No-tech or low-tech AAC
AAC systems requiring little or no technology, often inexpensive and easy to use

High-tech AAC
electronic AAC systems that use digital technology and often produce speech output

Open system
an AAC system that allows extensive customization, addition of vocabulary, and software or hardware modifications, example: C-board
Dedicated system
an AAC device designed solely for communication purposes and not usable for other functions, example: Tobii Dynavox TD Pilot

Direct AAC access
the user selects symbols directly using a body part such as a finger, hand, eye gaze, or head pointer
Indirect AAC access
the user selects symbols using an intermediary method such as scanning with a switch or partner-assisted scanning
no-tech\ low tech AAC examples
gestures, sign language, facial expressions, communication boards, picture exchange systems, alphabet boards
high-tech AAC examples
speech-generating devices, tablets with AAC apps, eye-gaze communication systems, dynamic display devices
multimodal communication
the use of multiple communication methods (e.g., speech, gestures, signs, AAC devices) together to support effective communication
AAC assessment process
a collaborative, ongoing process involving the individual, family, SLP, educators, and other professionals, focusing on communication needs, abilities, environments, and long-term participation rather than a single test session
factors in AAC assessment
motor abilities, sensory skills, cognitive and language skills, medical status, motivation, communication environments, cultural considerations, and partner support
ideal conditions for AAC system training
natural environments such as home, school, or community settings with active involvement of the user, family members, teachers, peers, and support staff
Unaided AAC
forms of communication that depend on the individual's body without external aids, such as gestures, eye gaze, and sign language
Aided AAC
forms of communication that involve external tools or devices, including picture systems, communication books, and electronic speech-generating devices
Communicative Competence
focuses on developing a person's knowledge and skills (linguistic, operational, social, and strategic) to use AAC effectively
Participation Model
identifying opportunities and barriers by comparing a person's current participation with that of their non-disabled peers