A&P Ch. 14 Autonomic Nervous System
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
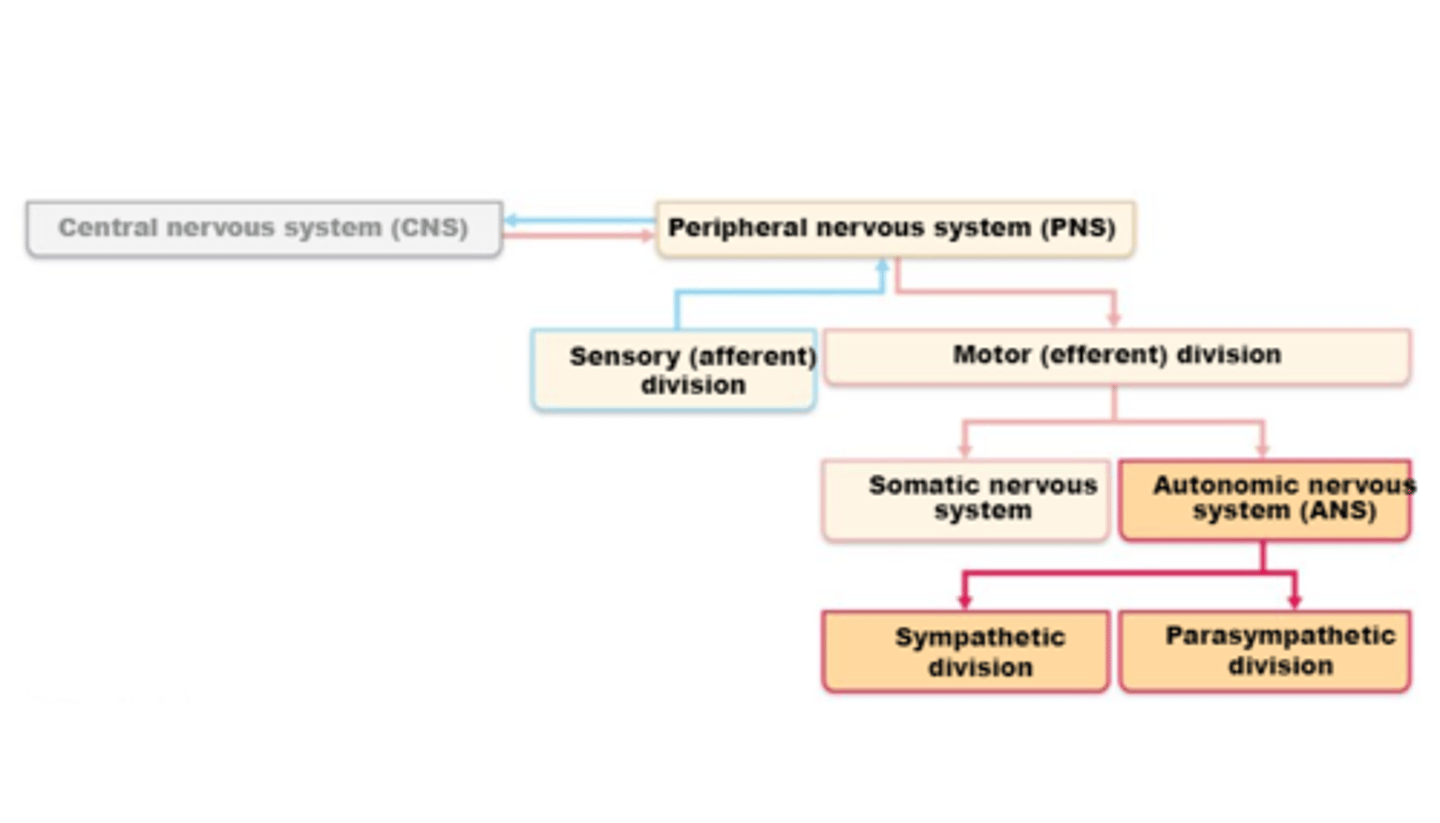
ANS consists of motor neurons that:
1) Innervate smooth and cardiac muscle and glands.
2) Make adjustments to ensure optimal support for body activities.
3) Operate via subconscious control.
4) Have viscera as most of their effectors.
Differences between the ANS and SNS
Effectors,
Efferent pathways,
Target organ responses to their neurotransmitters
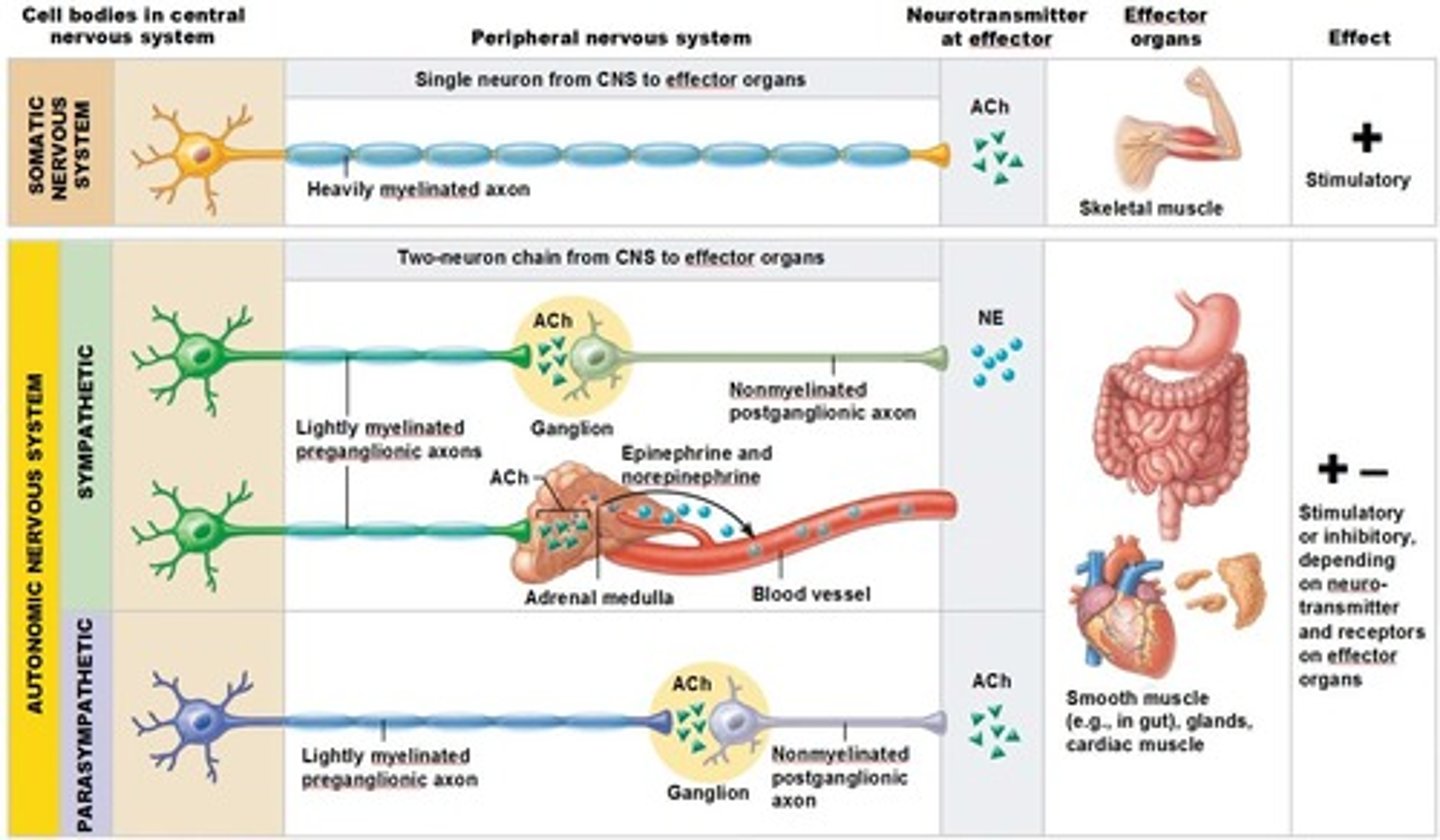
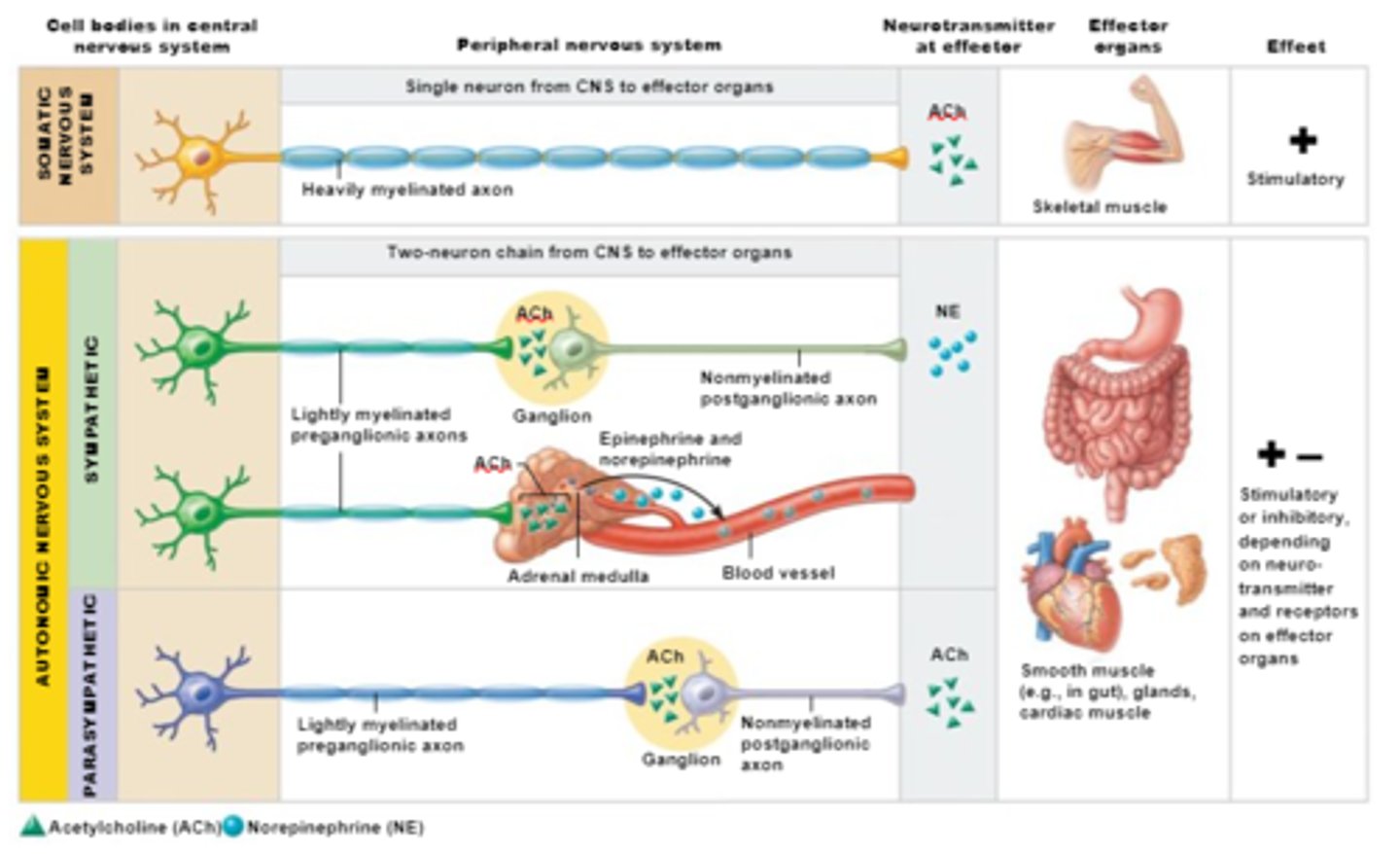
Effectors of Somatic Nervous System
skeletal muscles
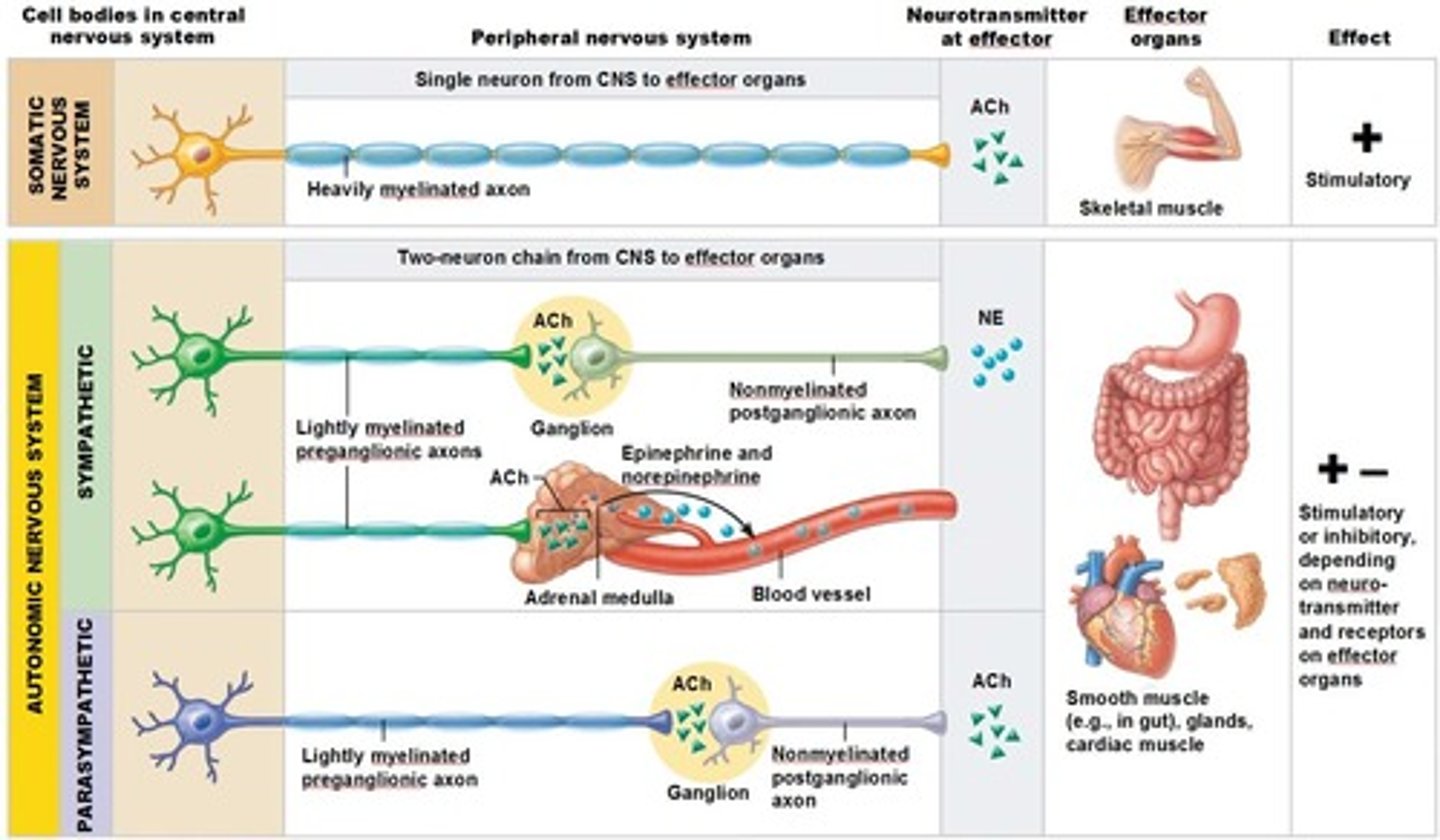
Effectors of Autonomic Nervous System
Cardiac Muscles,
Smooth Muscles,
Glands

Efferent pathways of Somatic Nervous System
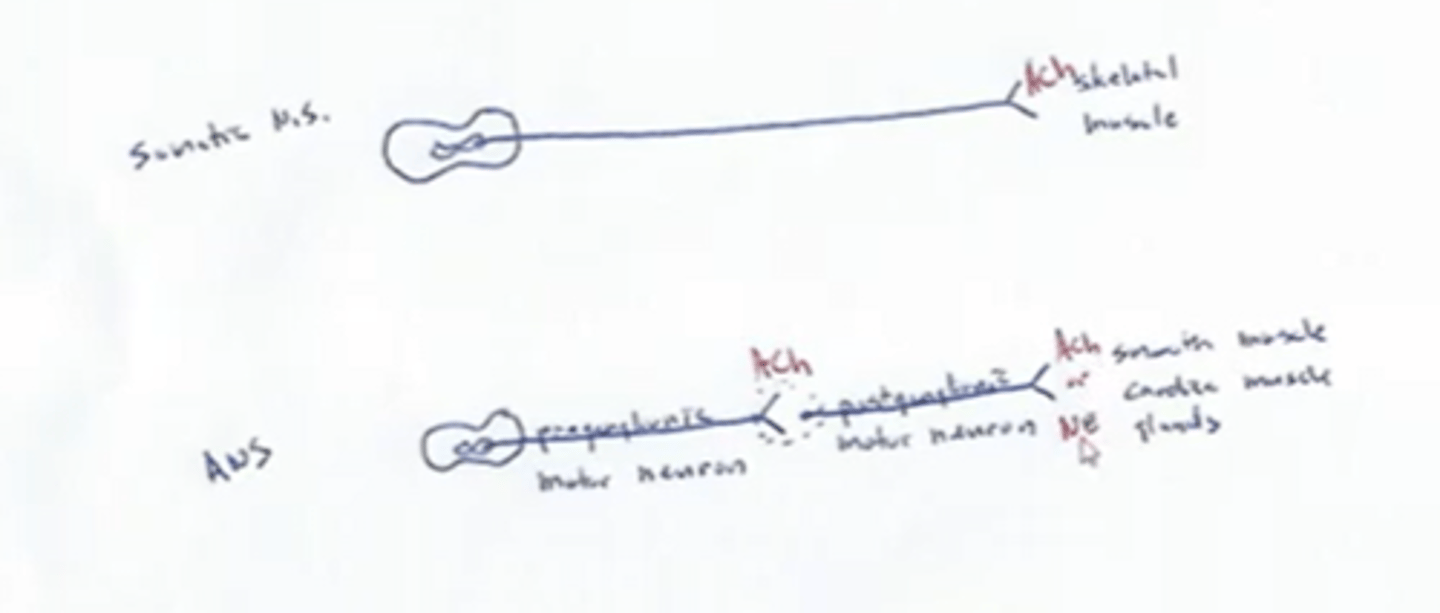
Heavily myelinated axons of the somatic motor neurons extend from the CNS to the effector
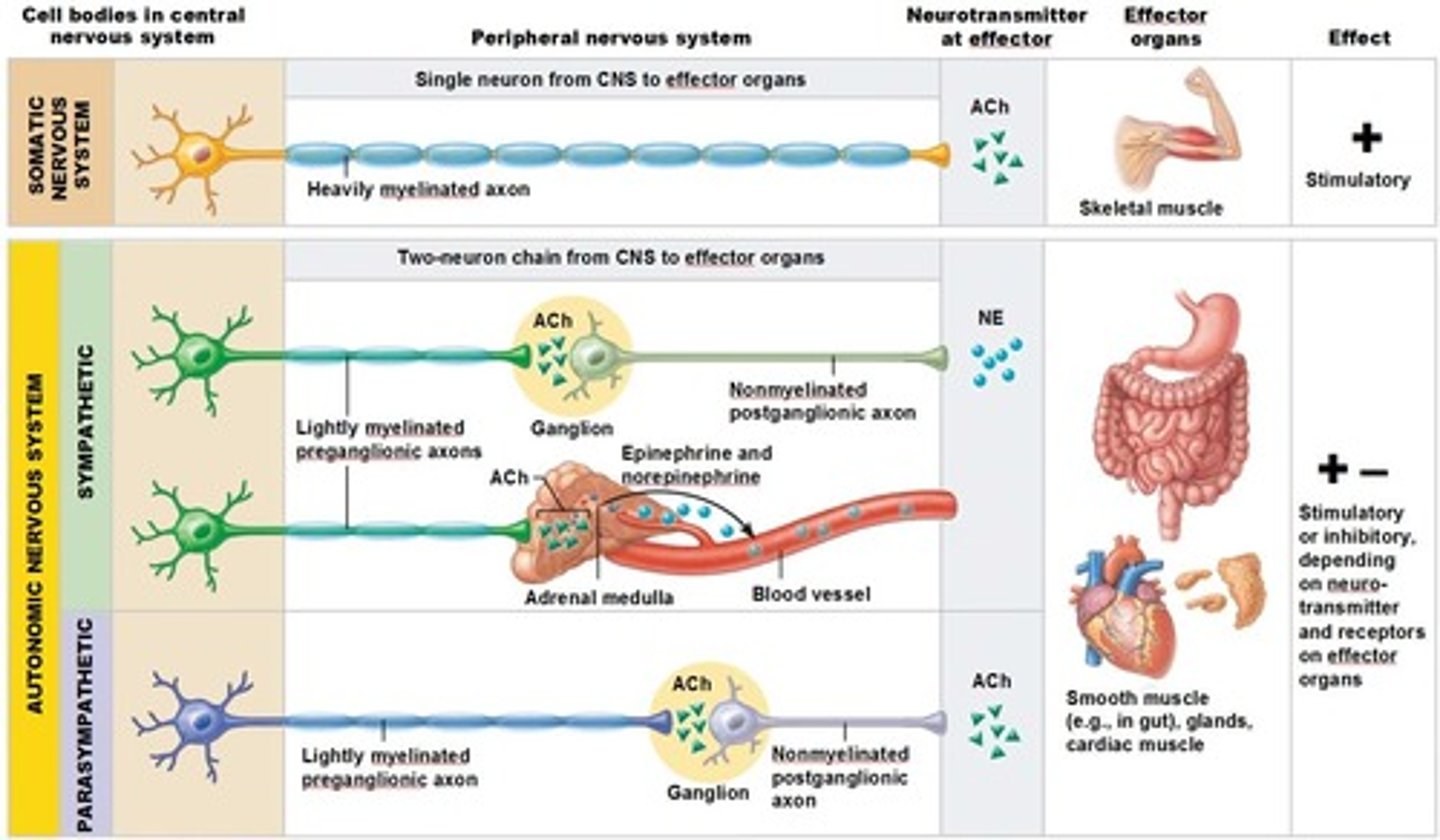
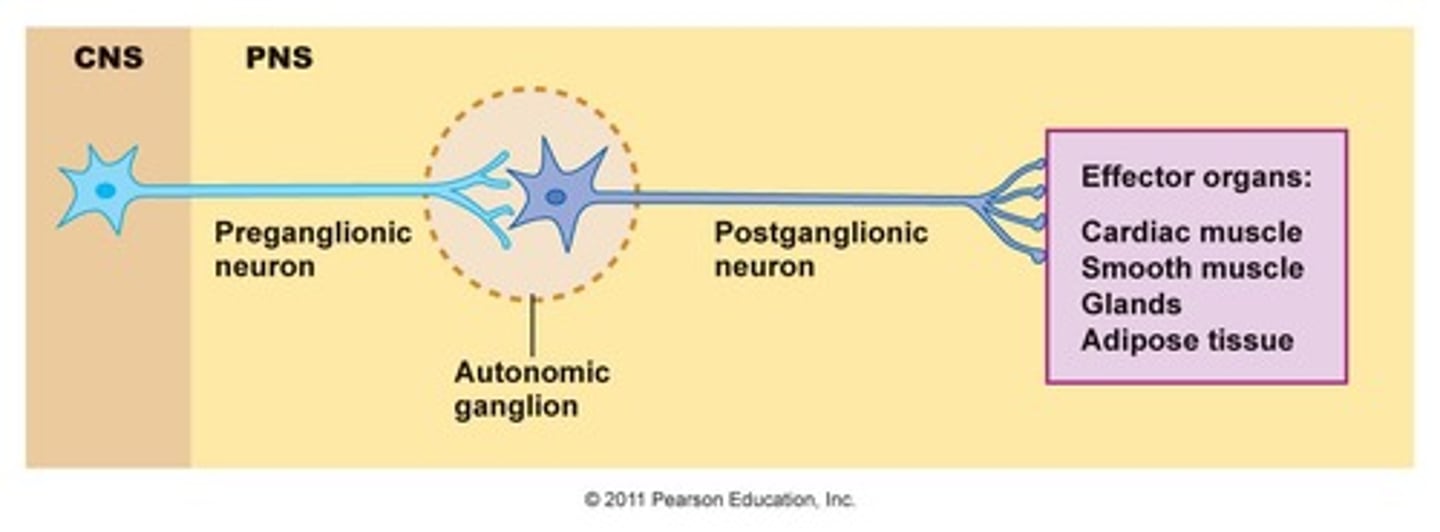
Axons of the ANS are a two-neuron chain
-The preganglionic (first) neuron has a lightly myelinated axon
-The ganglionic (second) neuron extends to an effector organ
Preganglionic Neuron
Has a lightly myelinated axon
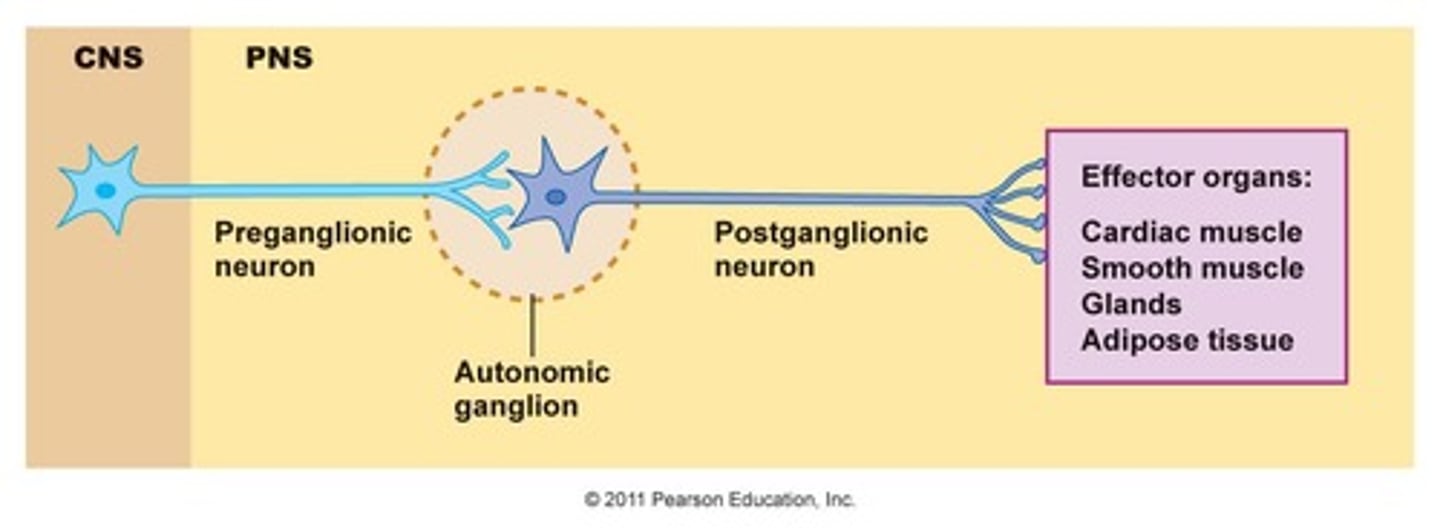
Postganglionic Neuron
Extends to an effector organ
Target organ responses to the Somatic Nervous System neurotransmitter
All somatic motor neurons release Ach, which has an excitatory effect

Target organ responses to the Autonomic Nervous System neurotransmitter
1) Preganglionic fibers release Ach
2) Postganglionic fibers release norepinephrine (NE) or Ach and the effect is either stimulatory or inhibitory
3) ANS effect on the target organ is dependent upon the neurotransmitter released and the receptor type of the effector
Divisions of the Autonomic Nervous System
Sympathetic Nervous System,
Parasympathetic Nervous System
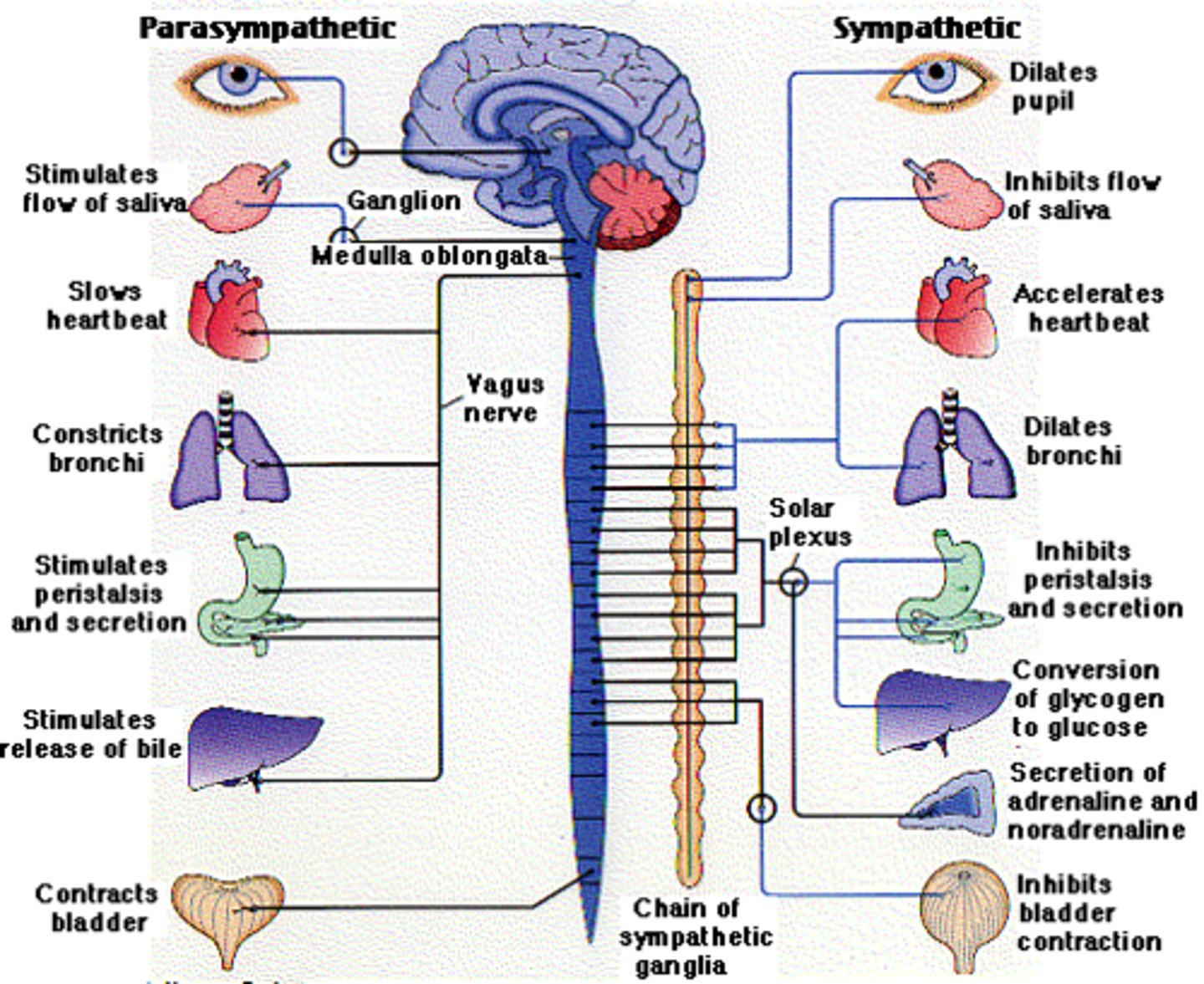
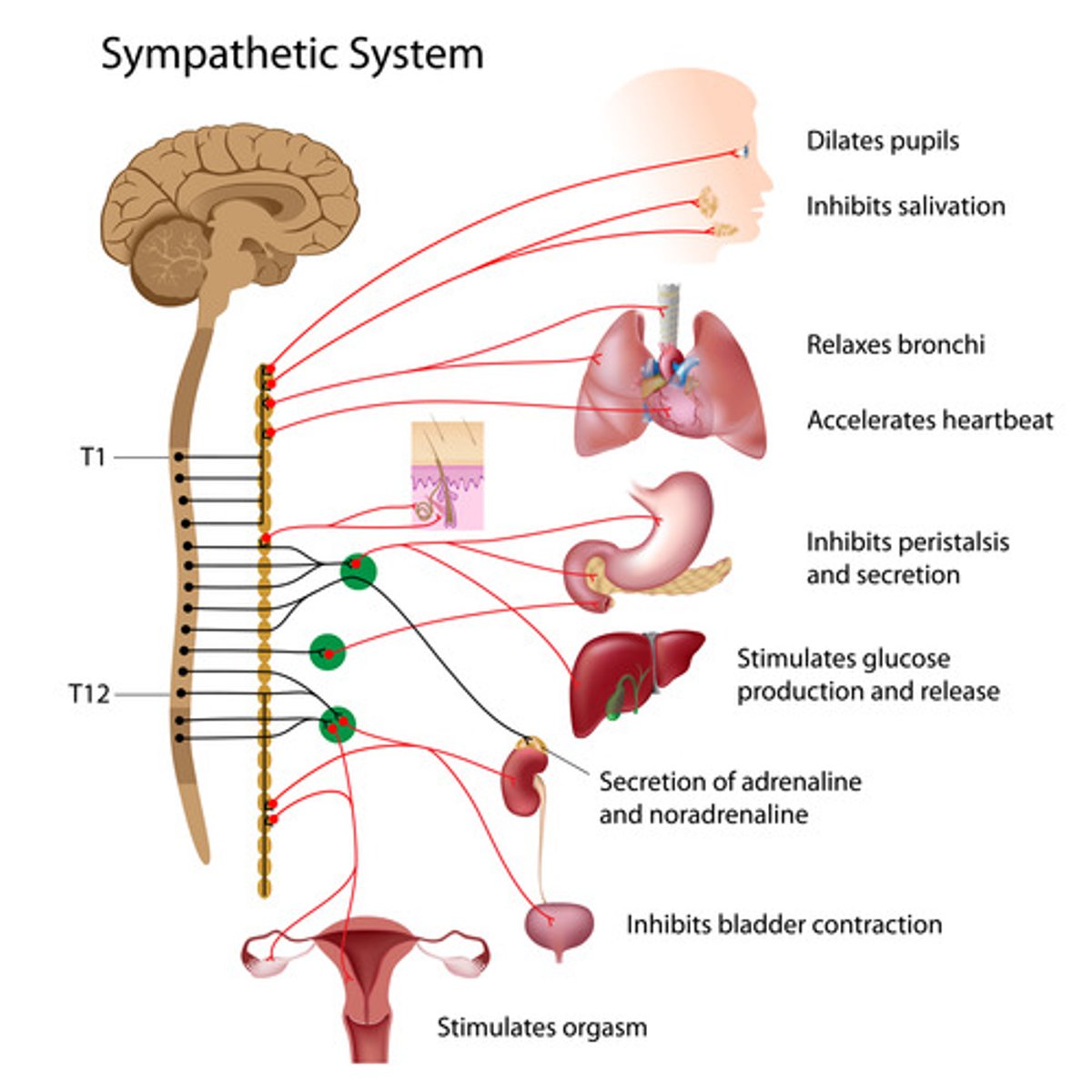
Sympathetic Nervous System
1) Mobilizes the body during extreme situations (the "fight-or-flight" system)
- Involves "E activities"- exercise, excitement, emergency, and embarrassment
- Promotes adjustments during exercise -blood flow to organs is reduced, flow to skeletal muscles and heart is increased
- Its activity is illustrated by a person who is threatened (Increase in HR, breathing is rapid and deep, skin is cold and sweaty, and the pupils dilate)
Parasympathetic Nervous System
1) Performs maintenance activities and conserves body energy
- Involves the "D activities"- digestion, defecation, and diuresis (urination)
- Its activity is illustrated in a person who relaxes after a meal
---BP, HR, and respiratory rates are low
---GI tract activity is high
---Skin is warm and pupils are constricted
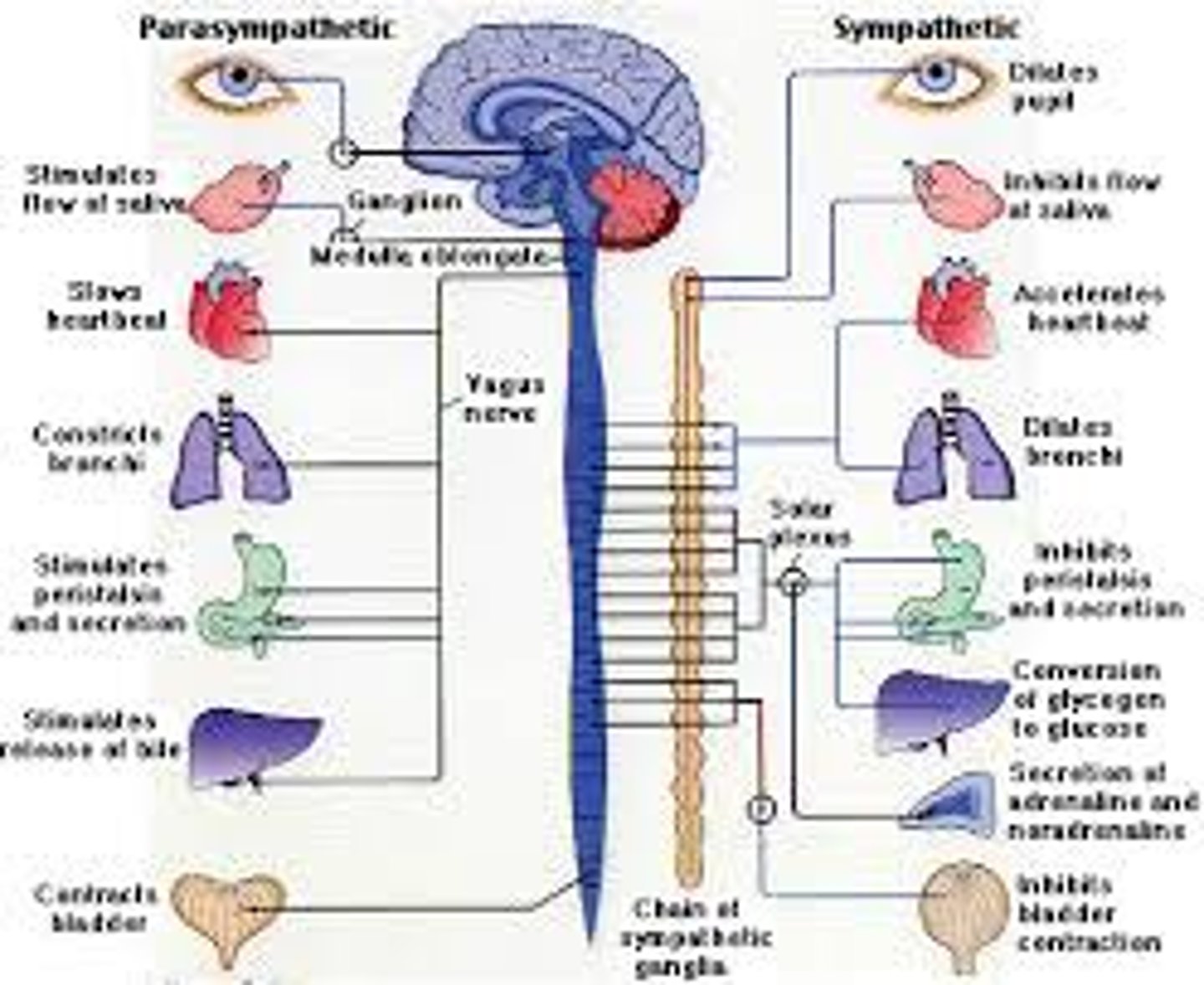
How do the two divisions counterbalance each other's activity?
Dual innervation of organs
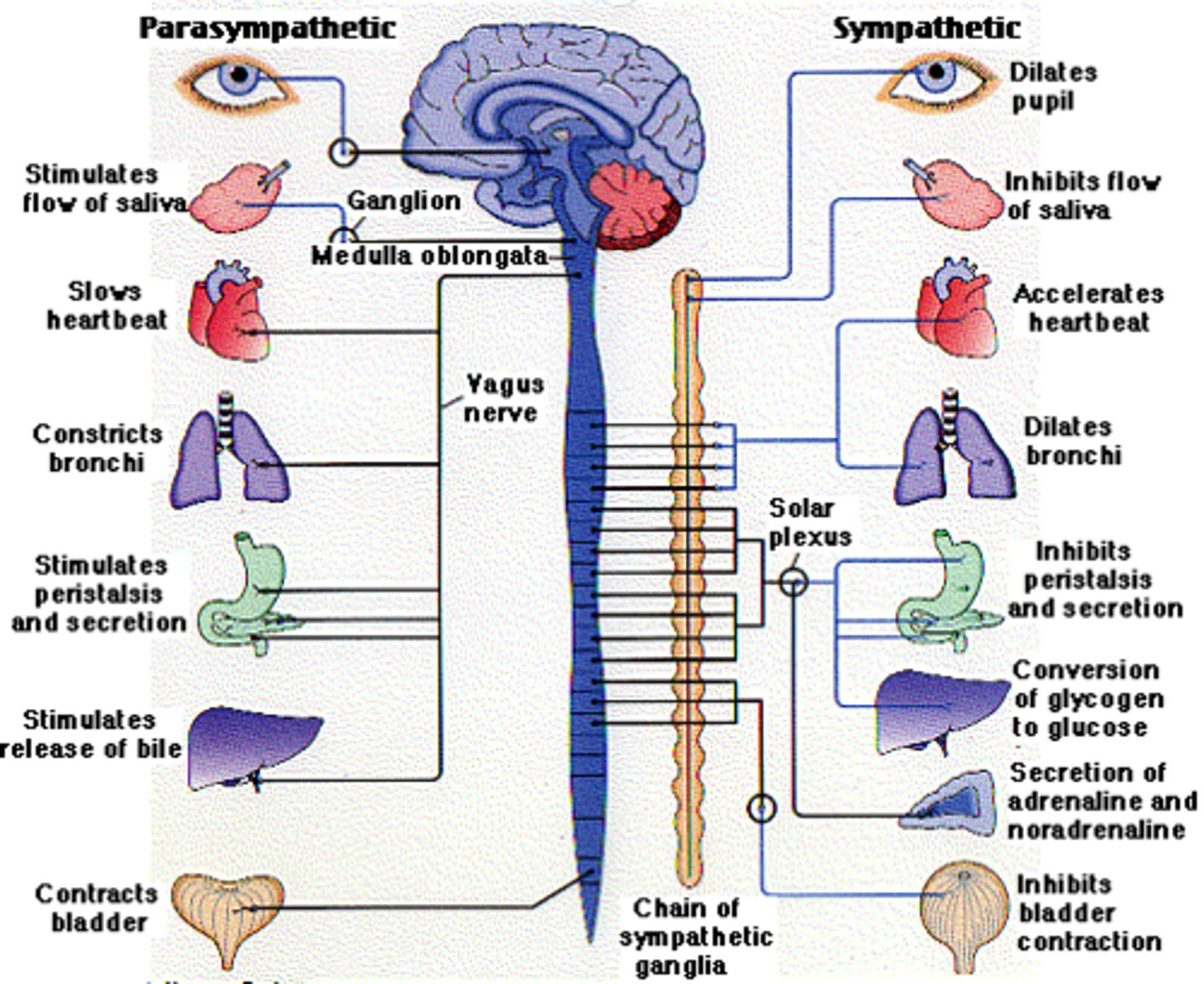
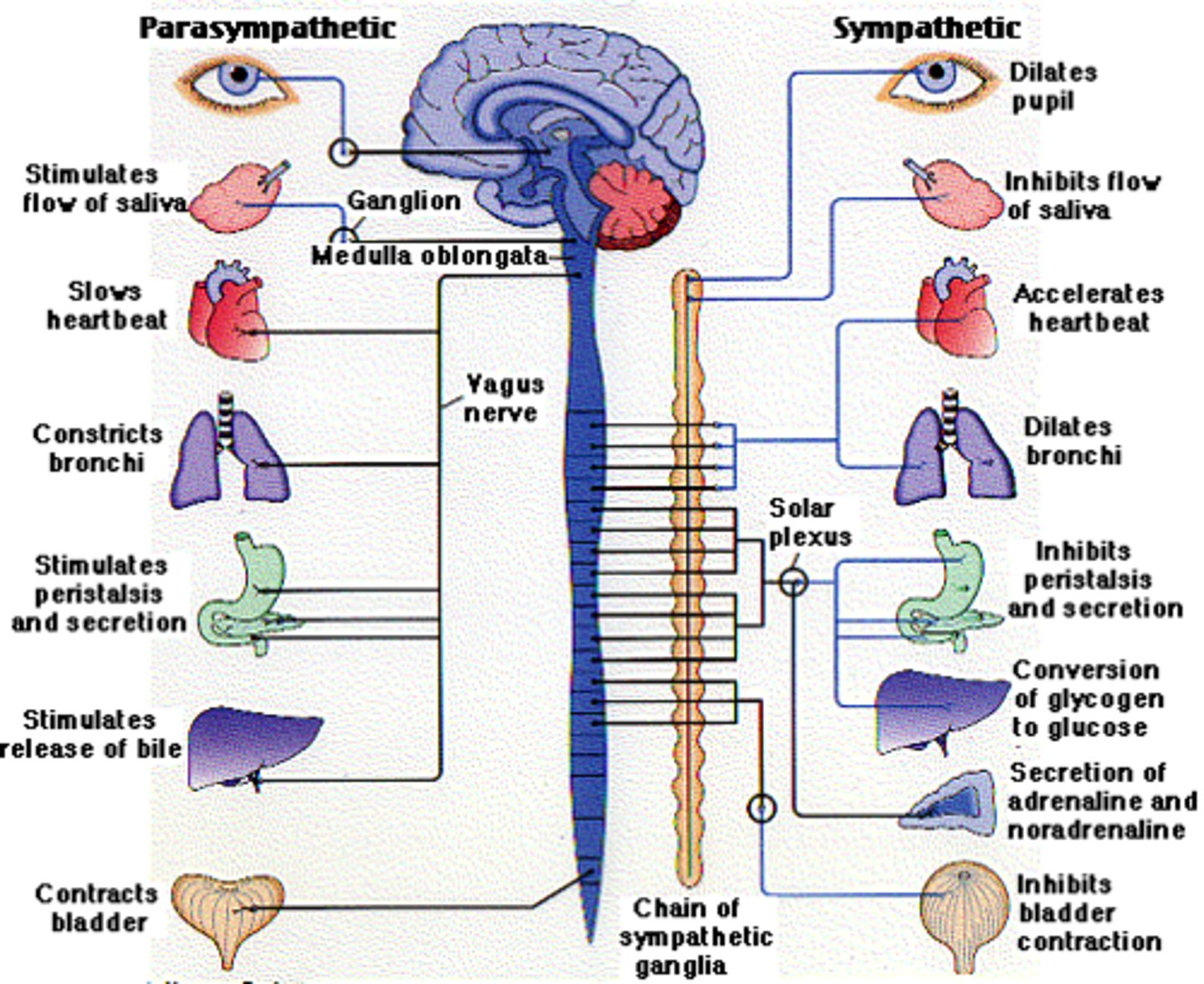
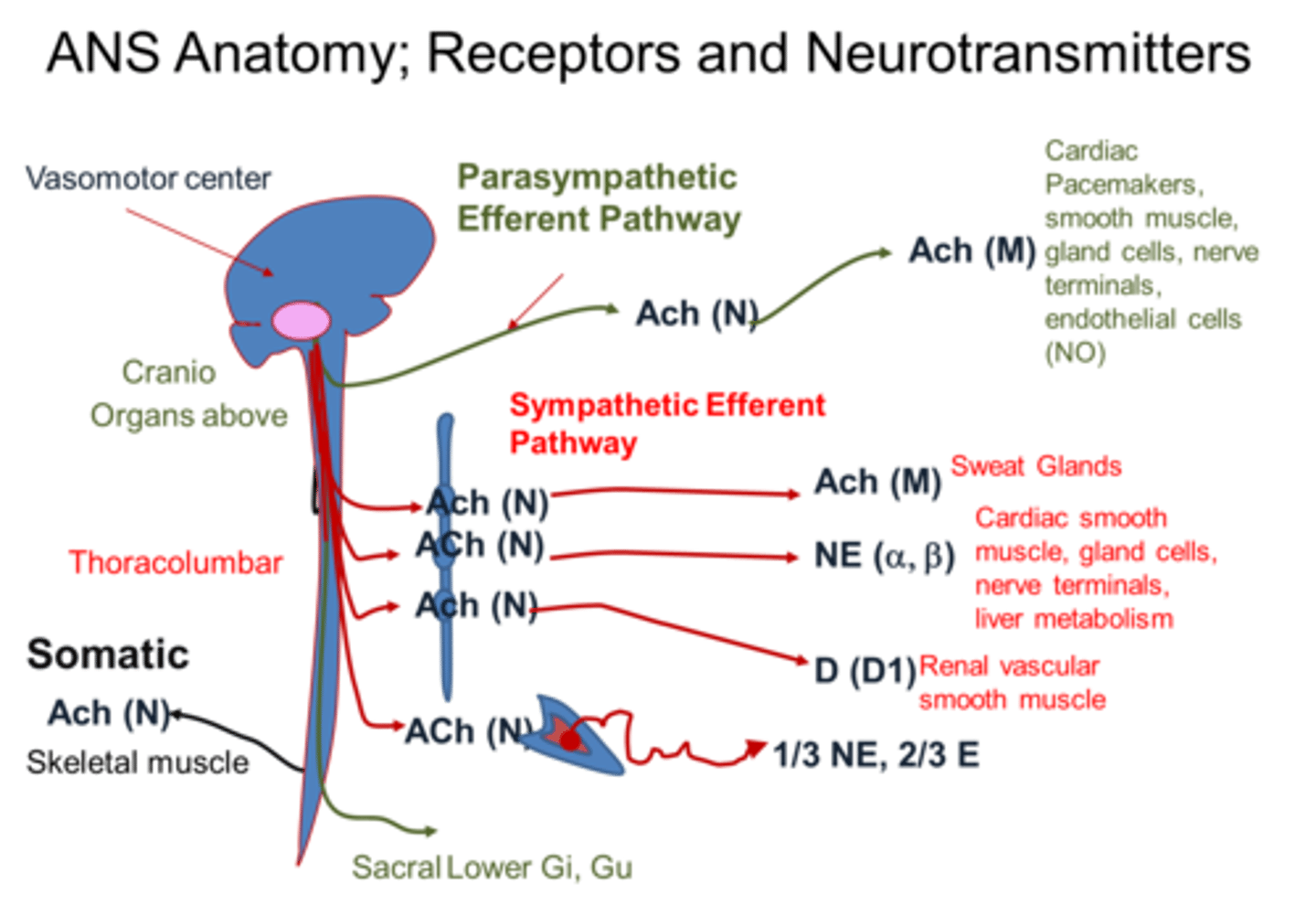
autonomic nervous system anatomy
1) Sympathetic and parasympathetic division are distinguished by their:
- Unique origin sites
- Relative lengths of their fibers
- Location of their ganglia
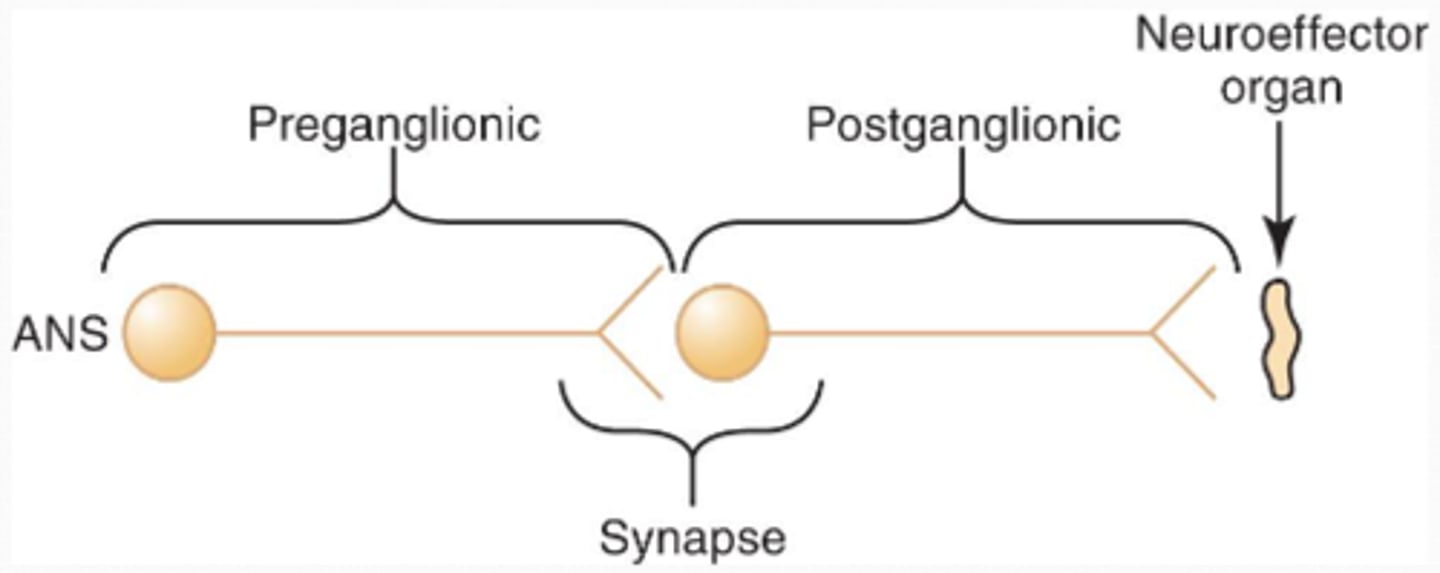
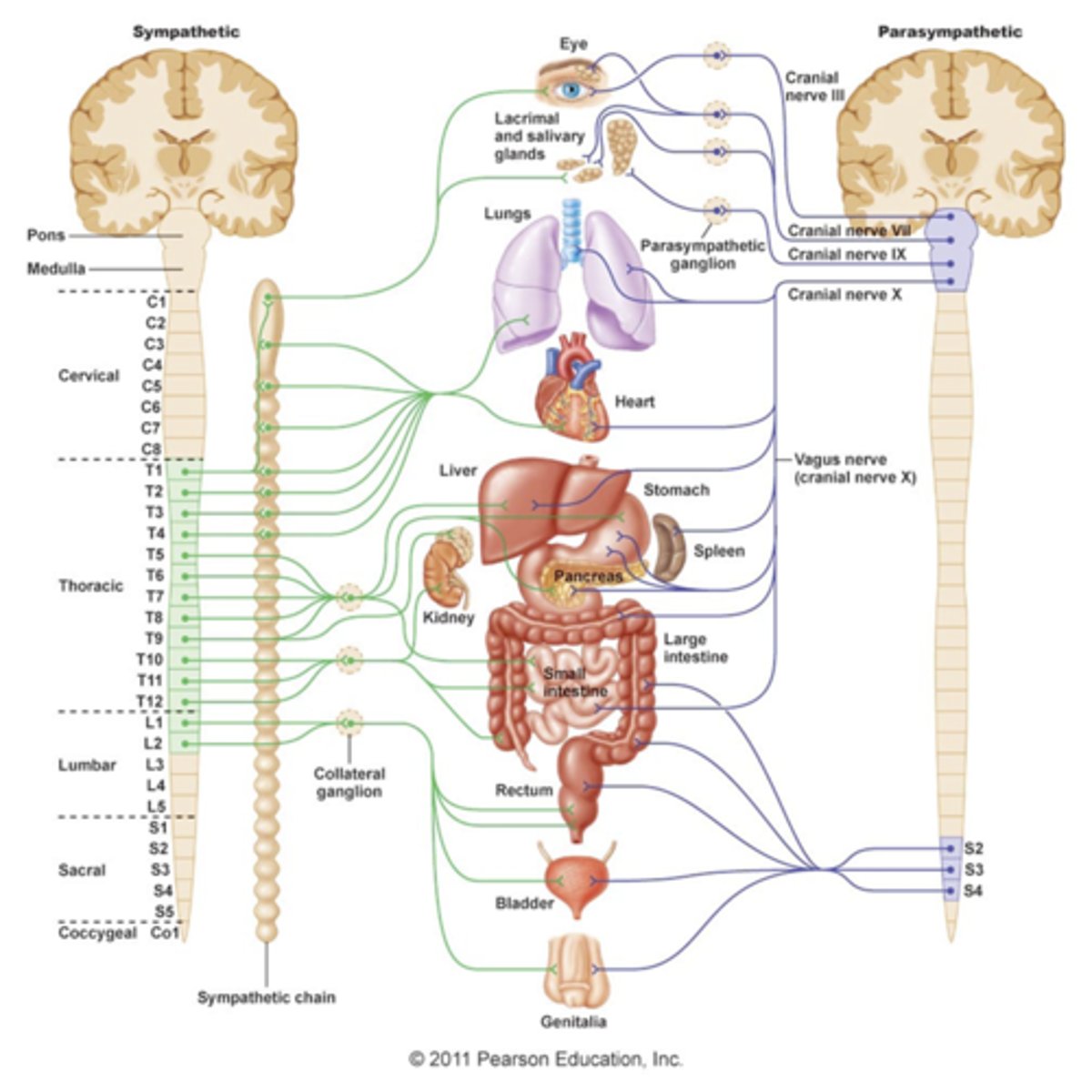
ANS Unique origin sites
1) Sympathetic fibers originate from thoracolumbar region of the spinal cord
2) Parasympathetic fibers originate from brain and sacral regions of the spinal cord
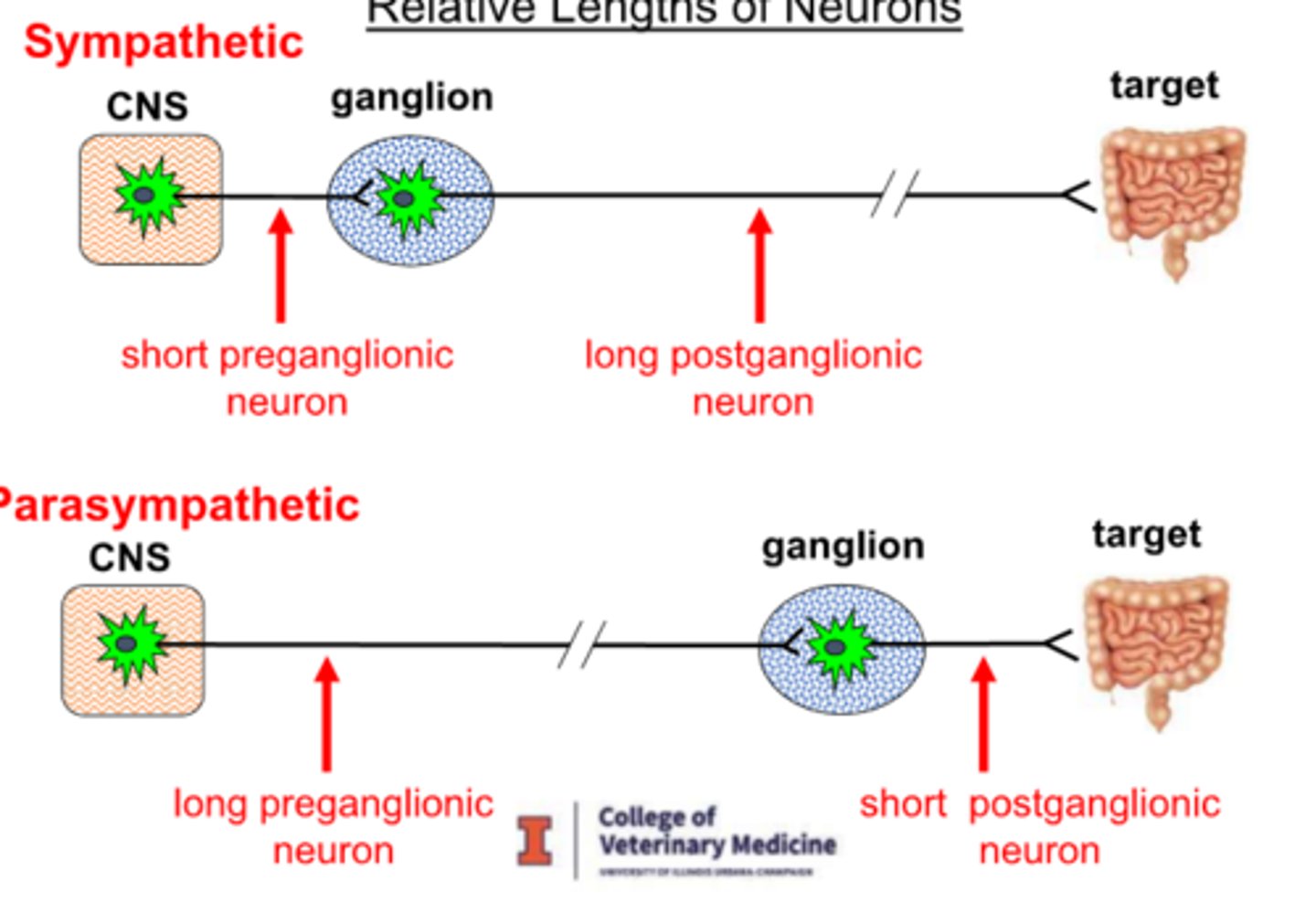
Relative lengths of their fibers in ANS
1) Sympathetic contains short preganglionic and long postganglionic fibers
2) Parasympathetic contains long preganglionic and short postganglionic fibers
Location of their ganglia in ANS
1) Sympathetic ganglia are located close to the spinal cord
2) Parasympathetic ganglia are located in the visceral effector organs
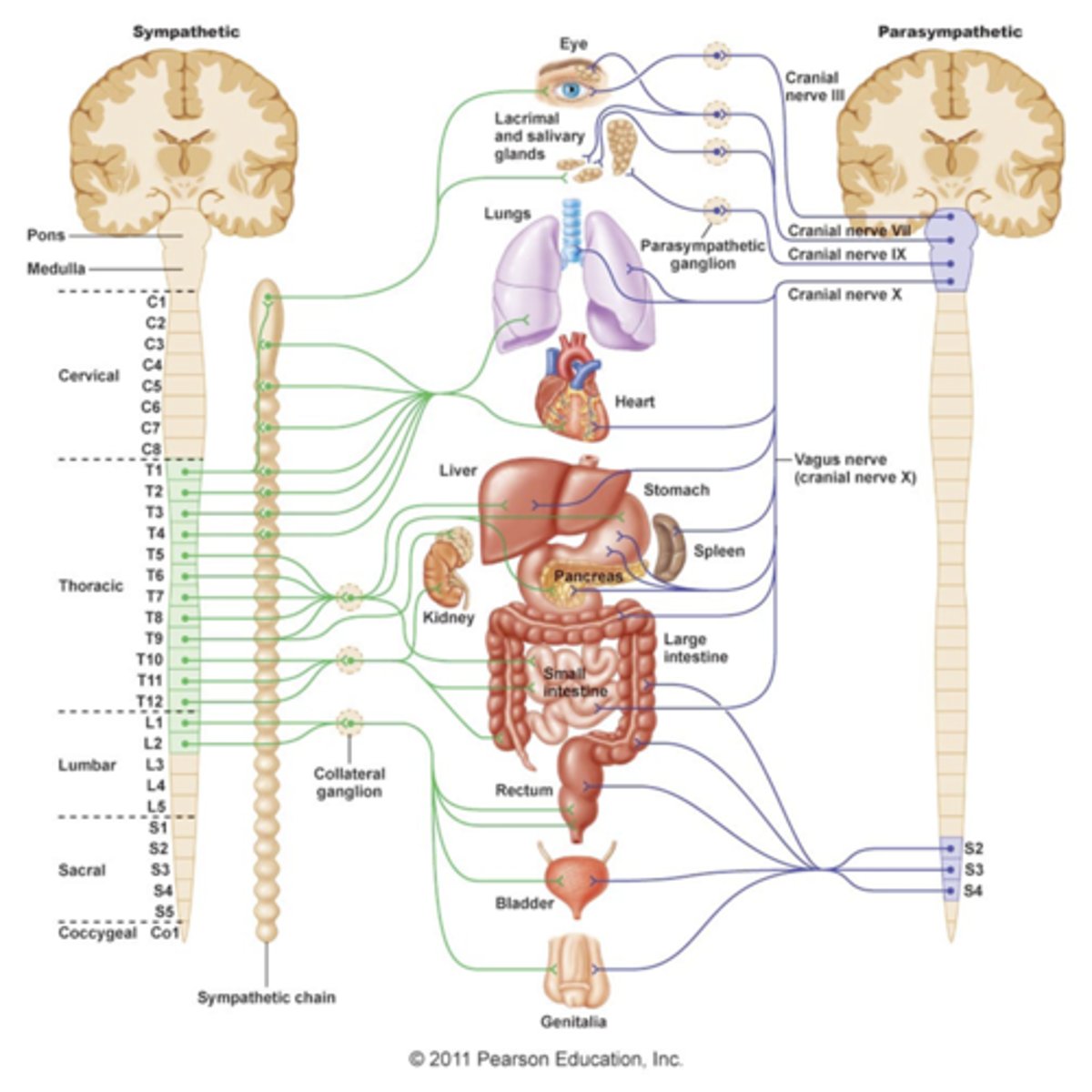
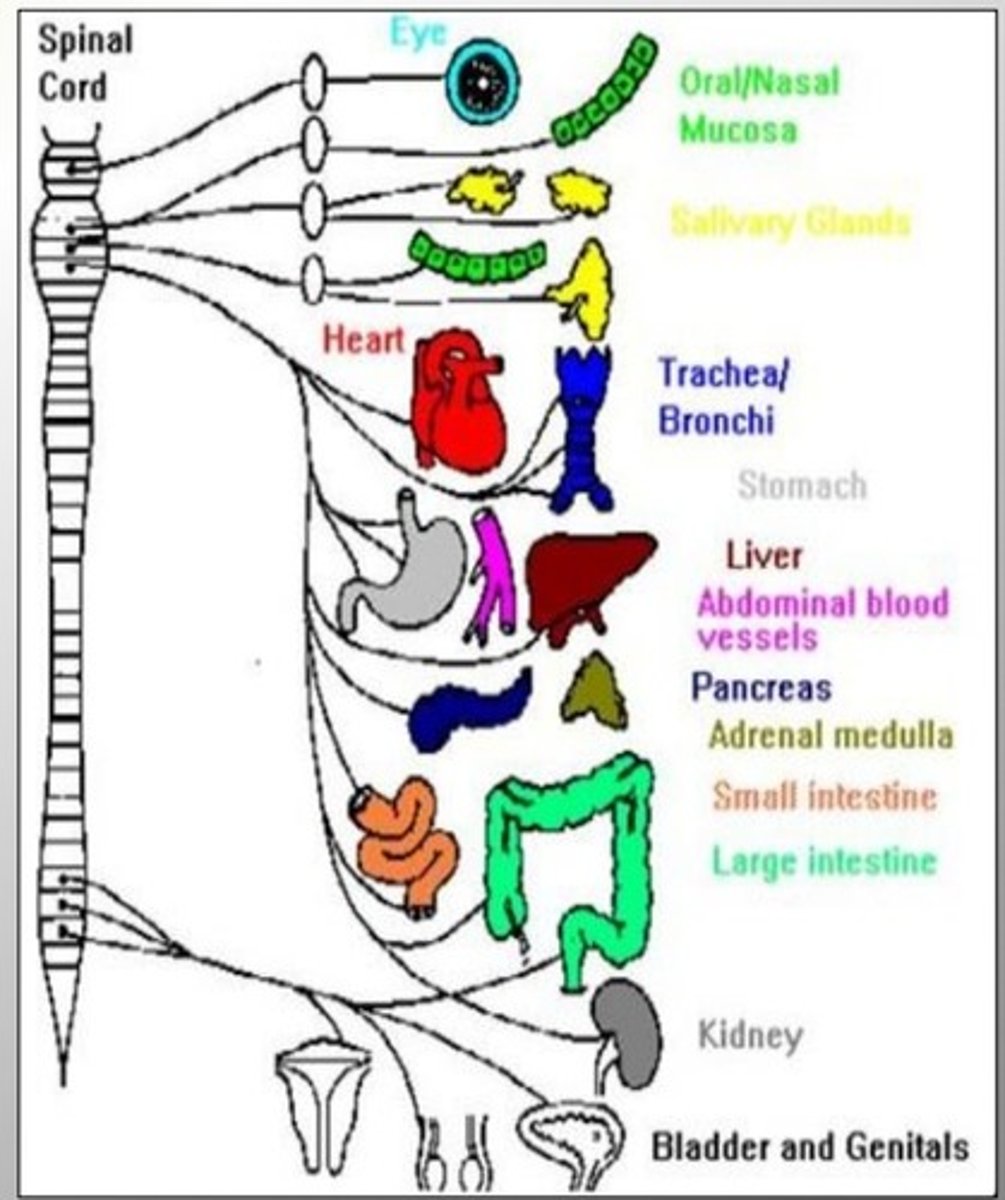
ANS outflow of Parasympathetic (craniosacral) Division
1) Cranial outflow
- Cranial nerves- Occulomotor, Facial, Glossopharyngeal, Vagus, etc.
--Effector organs- salivary, nasal, and lacrimal glands; heart, lungs, and most visceral organs.
2) Sacral outflow
- S2-S4
-- Effector organs- large intestine, urinary bladder, ureters, and reproductive organs
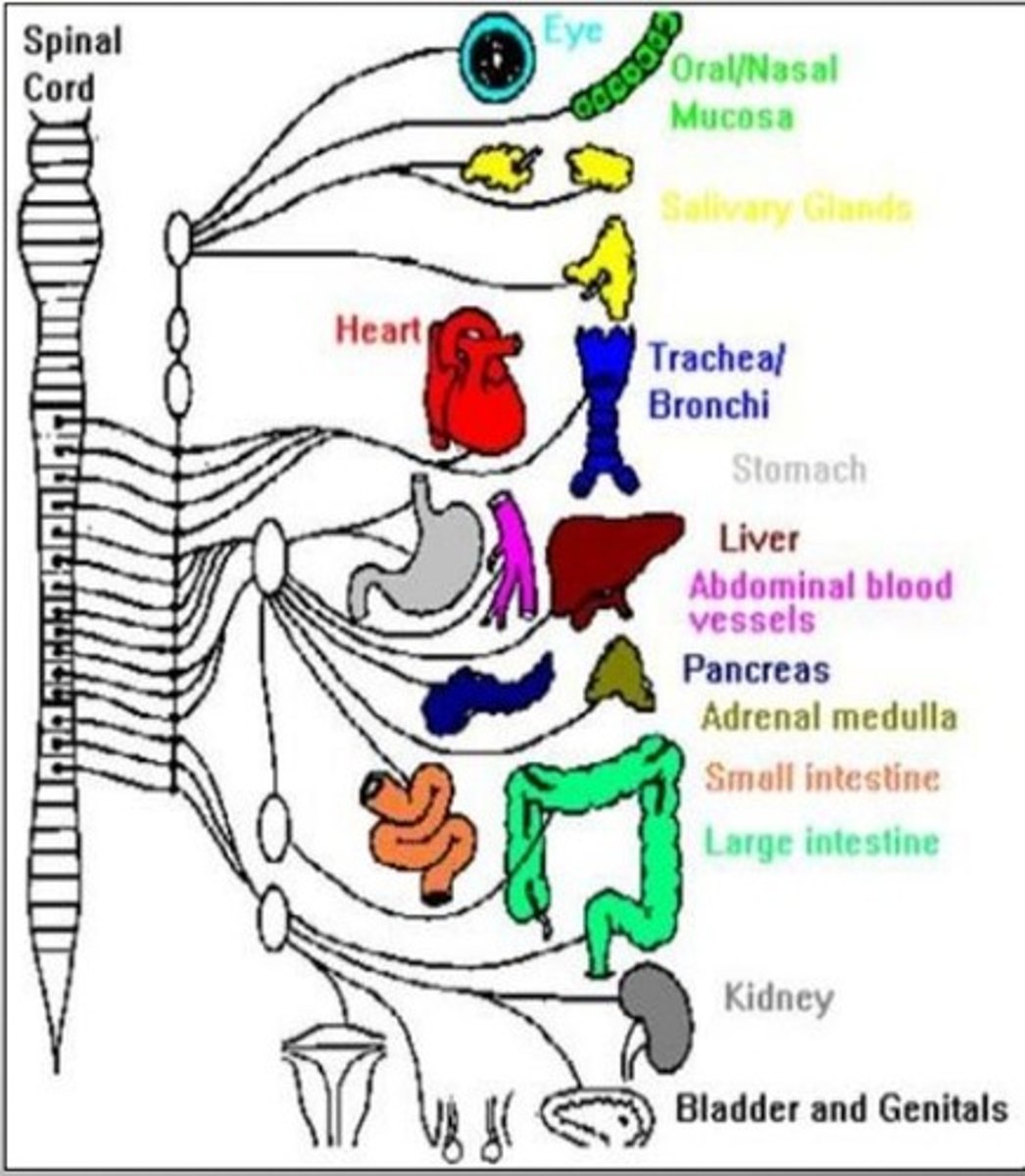
ANS outflow of Sympathetic (thoracolumbar) Division
1) Outflow
-T1-L2
-- Preganglionic fibers pass through the white rami communicates and synapse in the chain (paravertebral) ganglia
--Postganglionic fibers innervate the numerous organs of the body
-Effector organs- head and neck, heart, bronchi and lungs, esophagus, stomach, spleen, pancreas, liver, small intestine, kidney, reproductive organs, large intestine, ureter, urinary bladder, etc.
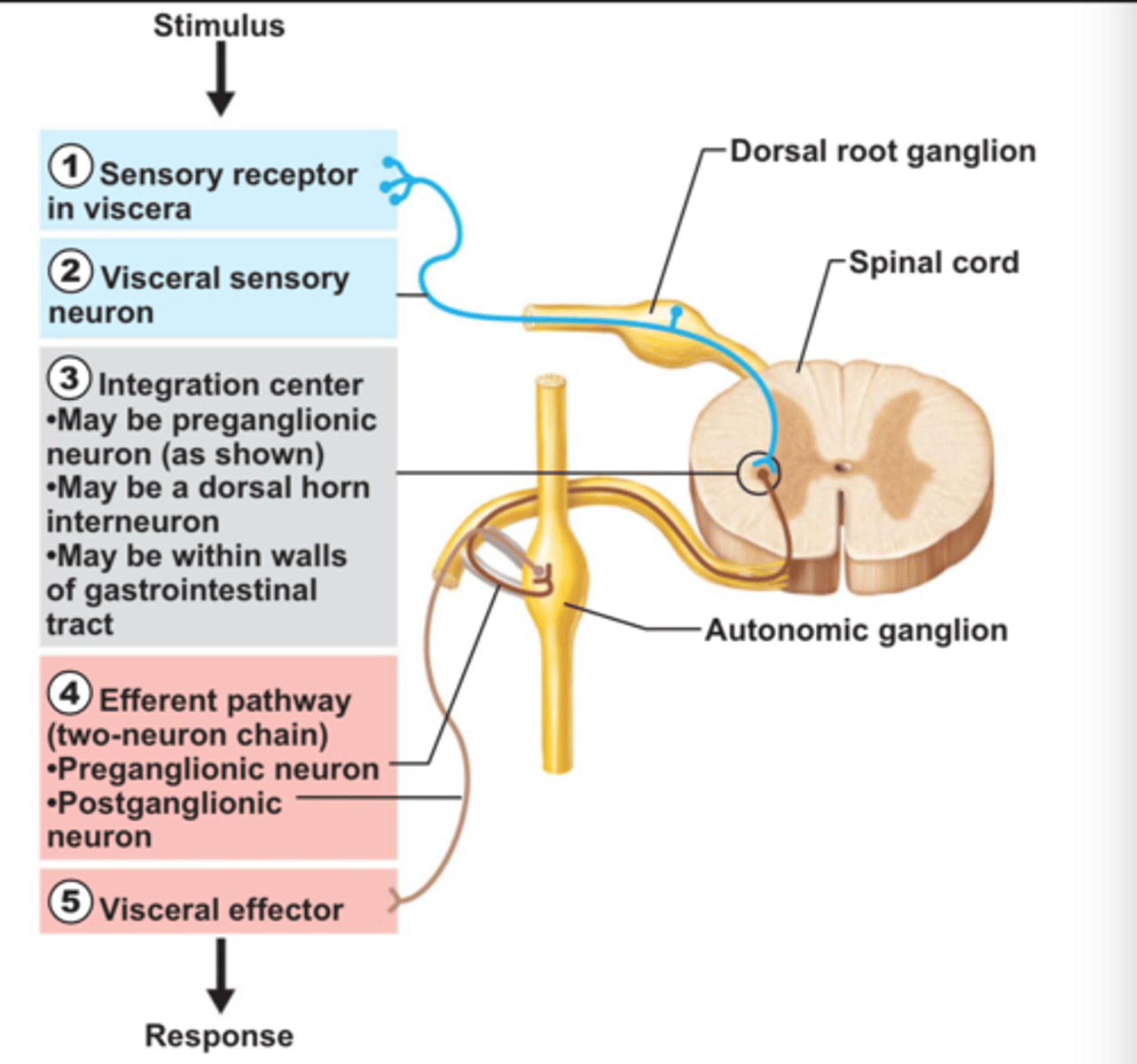
Components of Visceral reflexes
Receptors,
Sensory (afferent) Neurons,
Integration Center,
Motor (efferent) Neurons: Preganglionic Neuron & Postganglionic Neuron,
Effector
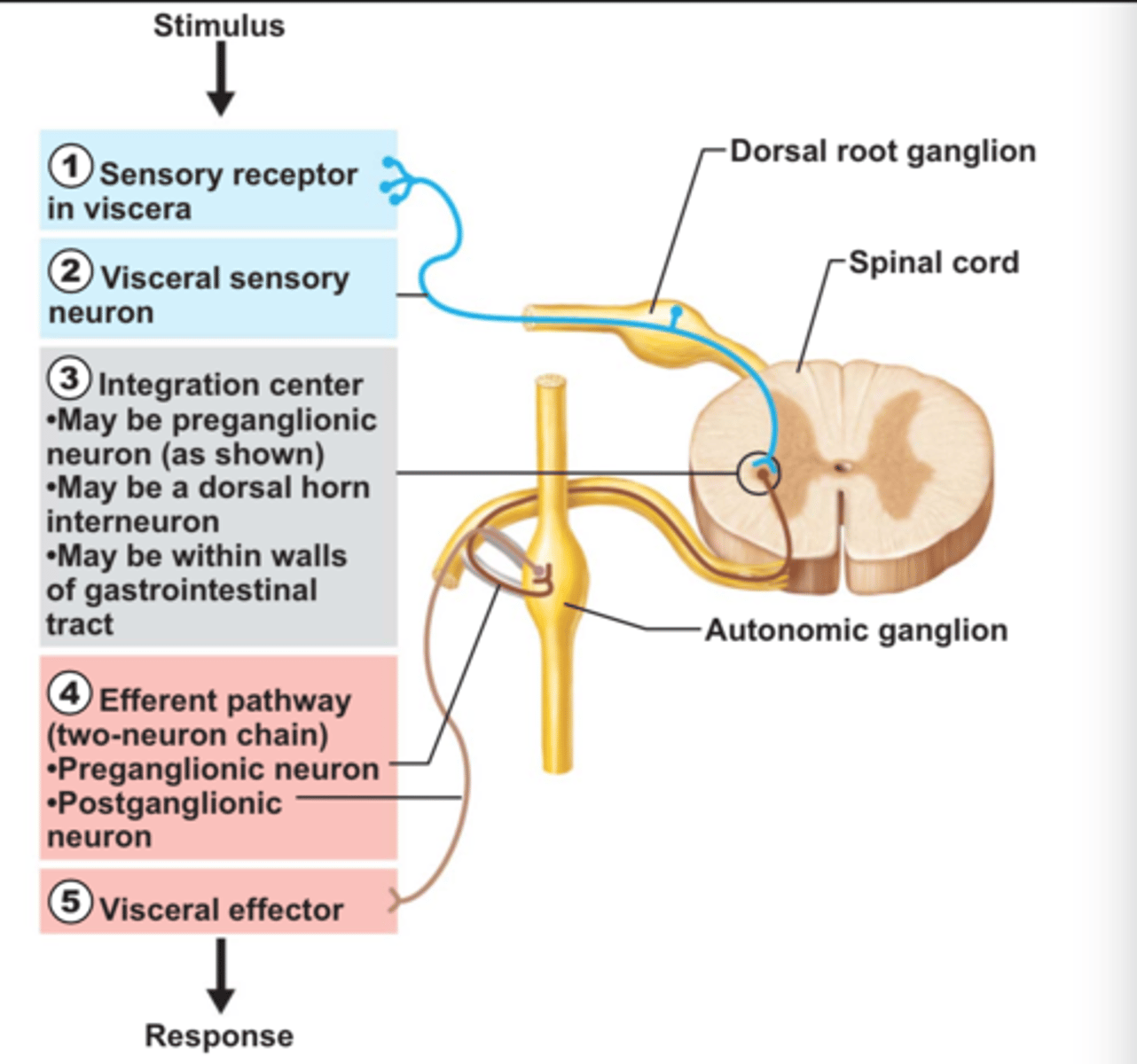
Visceral reflexes
Visceral reflexes have the same elements as somatic reflexes
Referred Pain
1)Pain stimuli arising from the viscera are perceived as somatic in origin
2)This may be due to the fact that visceral pain afferents travel along the same pathways as somatic pain fibers
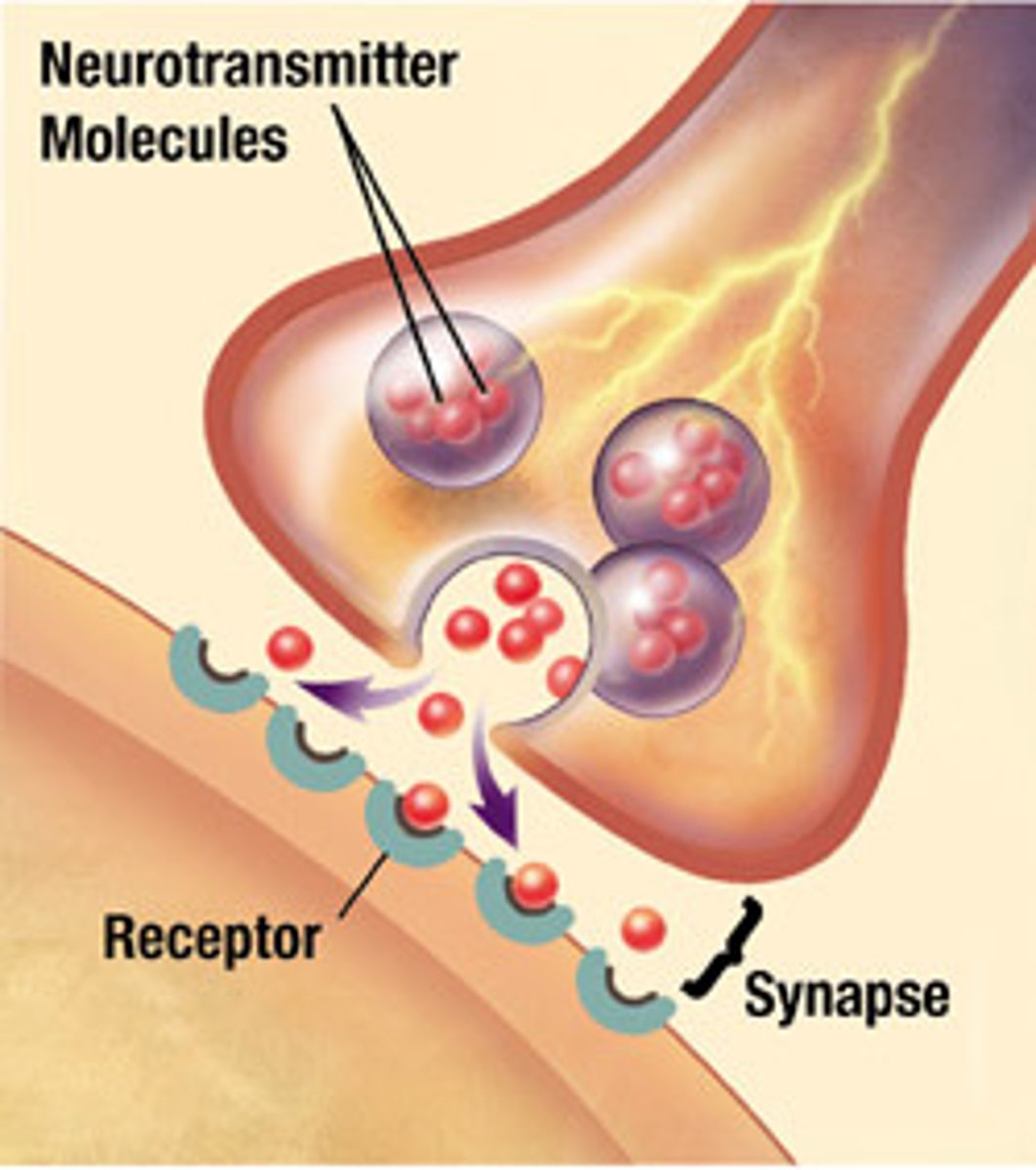
ANS Physiology: Neurotransmitters and Receptors
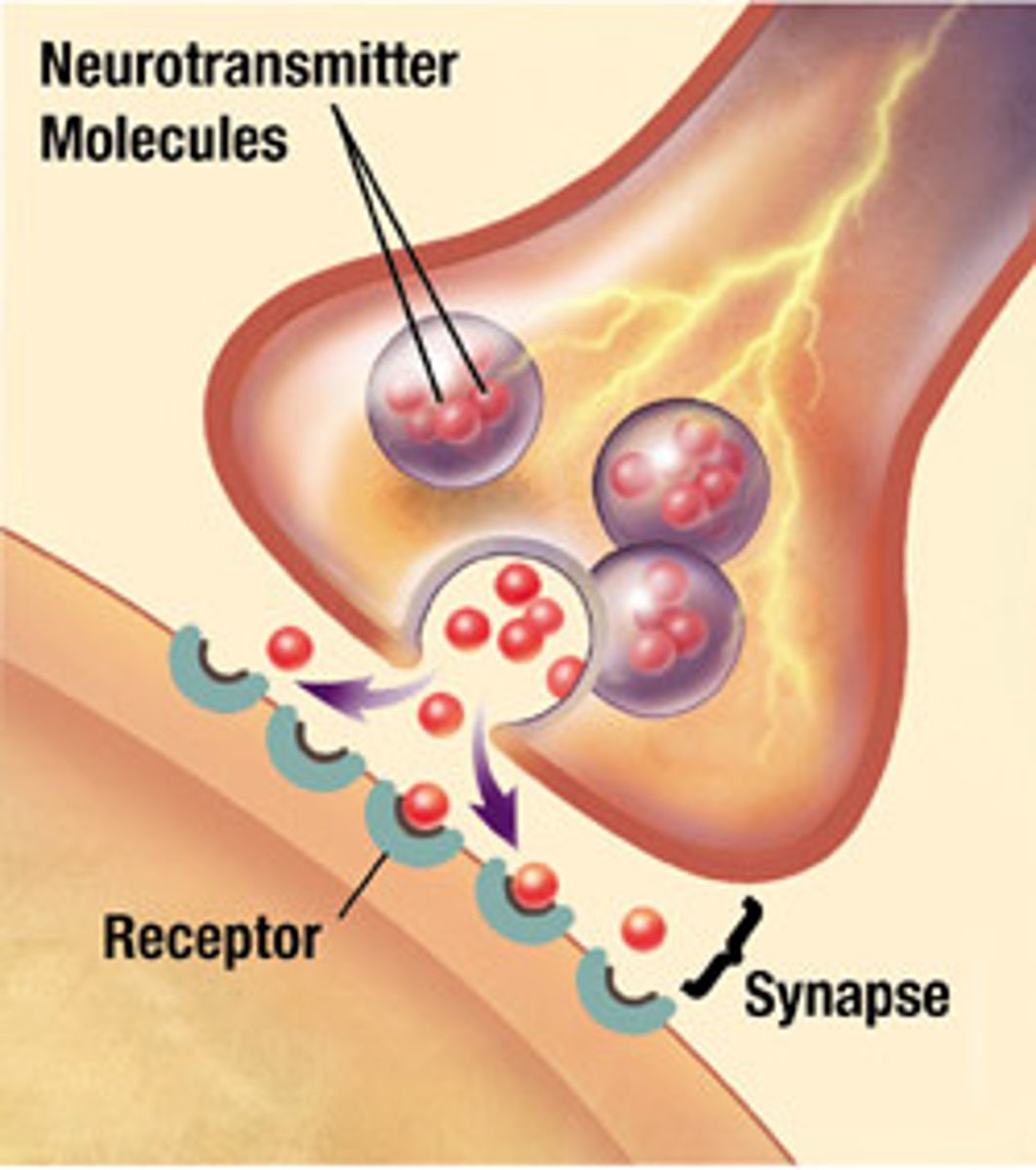
Ach and norepinephrine (NE) are the two major NTs of the ANS
-Ach
-NE
-NT effects can be excitatory or inhibitory depending upon the receptor type
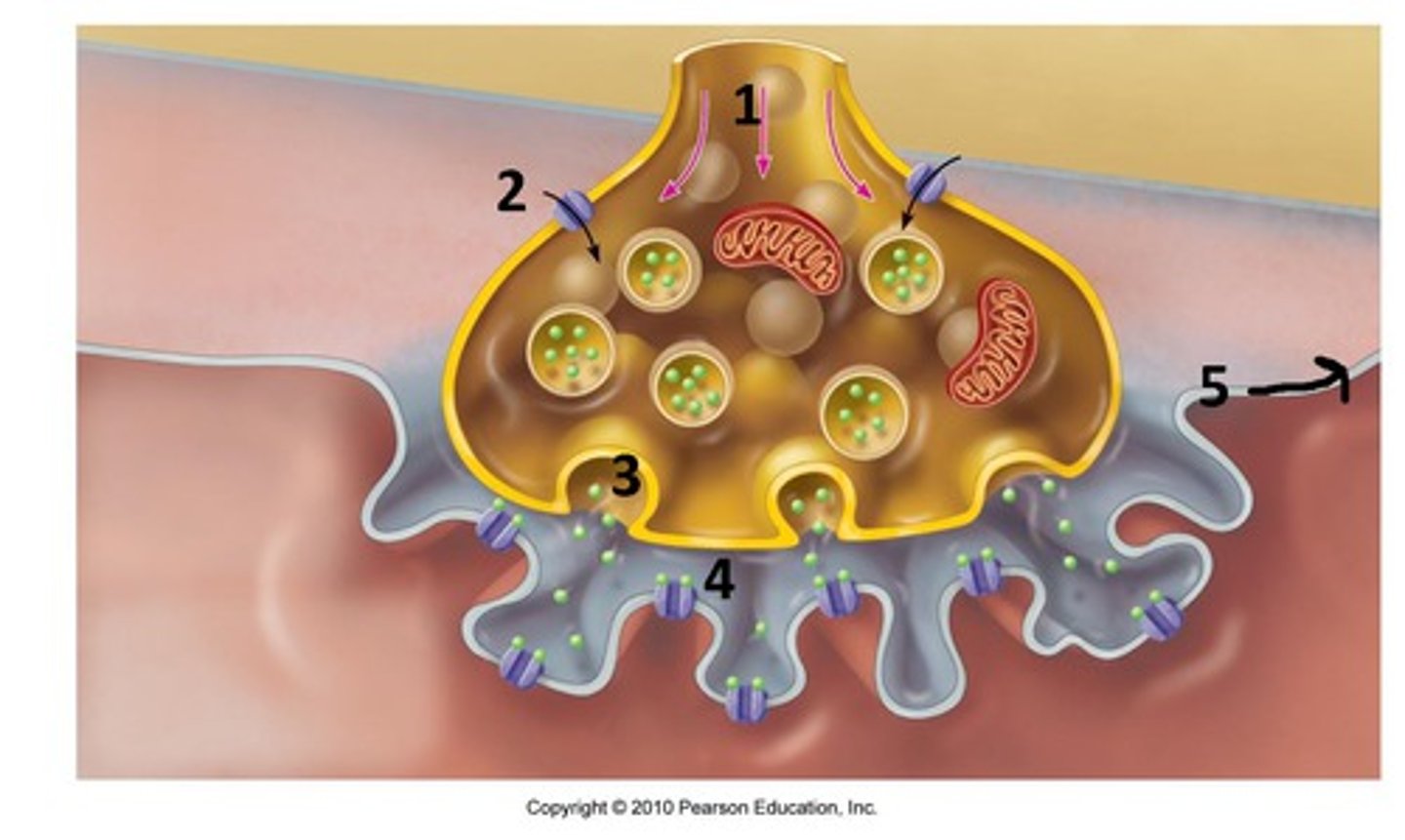
Ach released by:
All preganglionic axons,
All parasympathetic postganglionic axons
-Ach releasing fibers are called cholinergic fibers
Cholinergic Fibers
Ach releasing fibers
NE released by:
most sympathetic postganglionic axons
NT effects can be what?
NT effects can be excitatory or inhibitory depending upon the receptor type
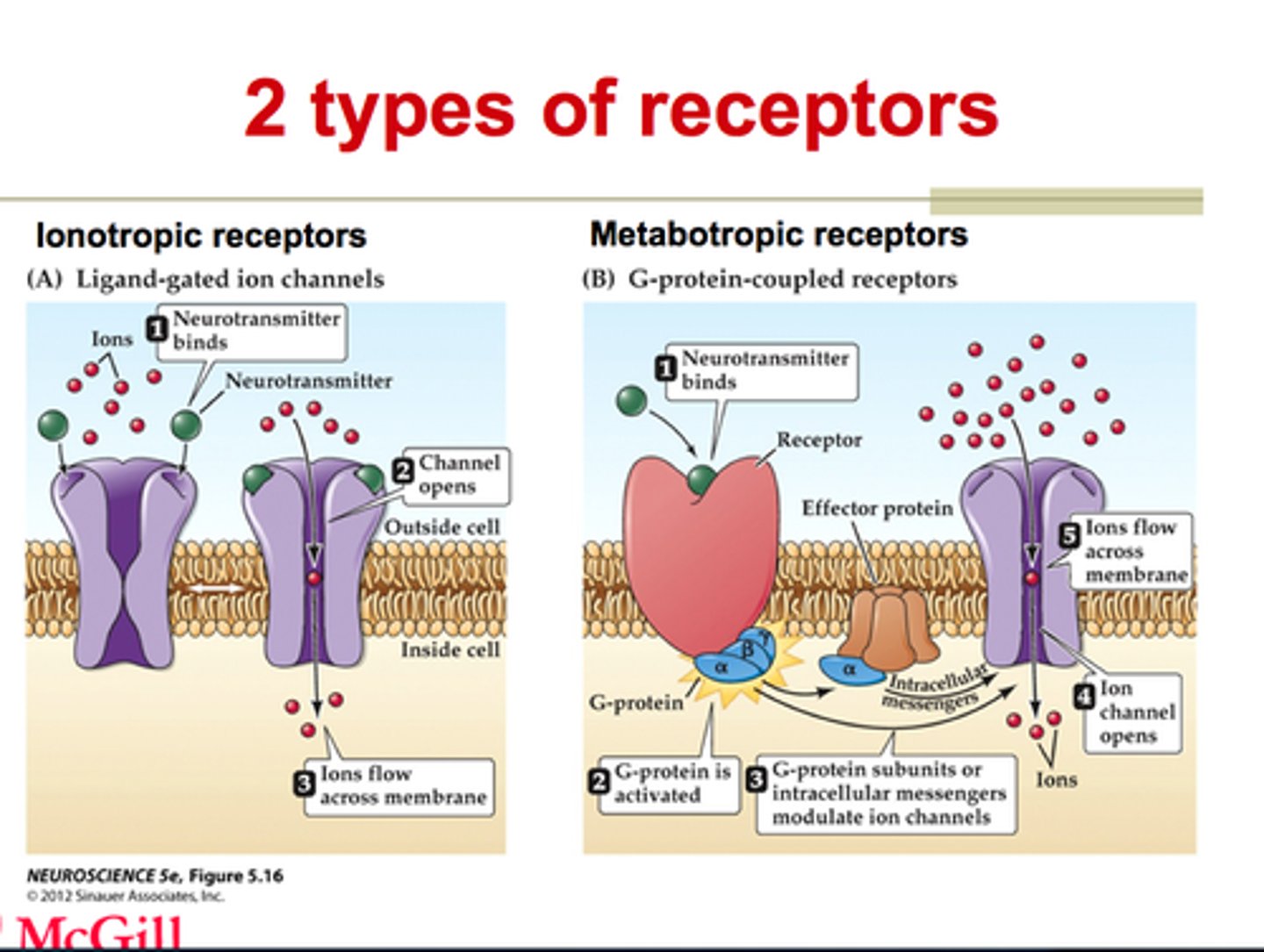
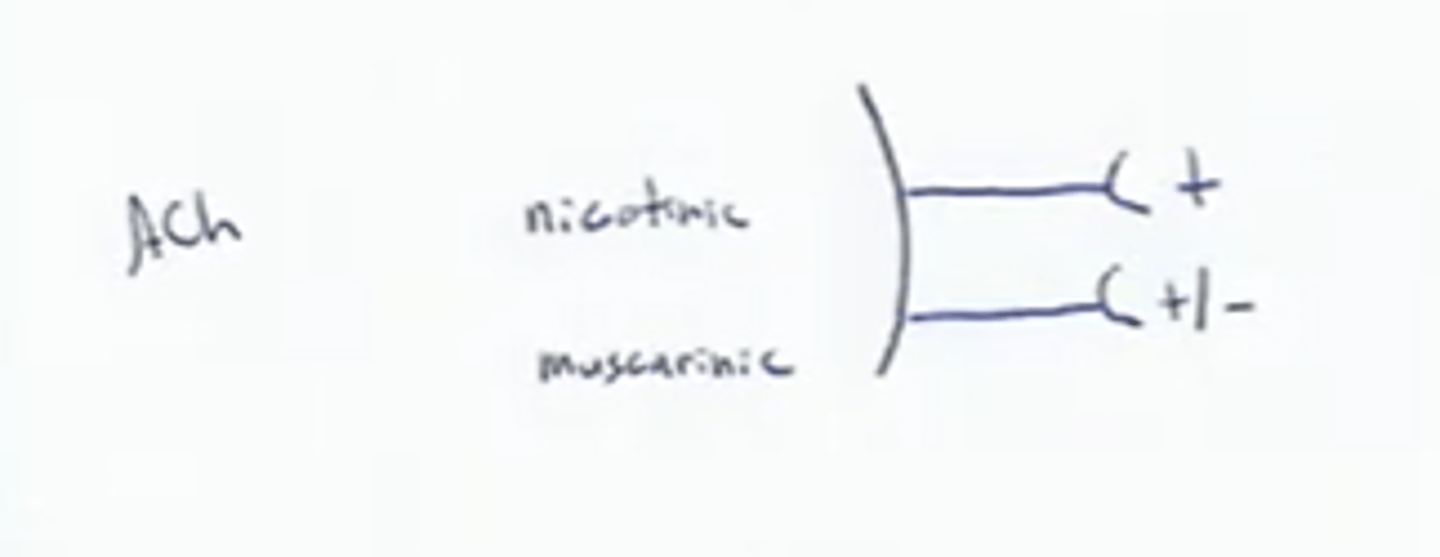
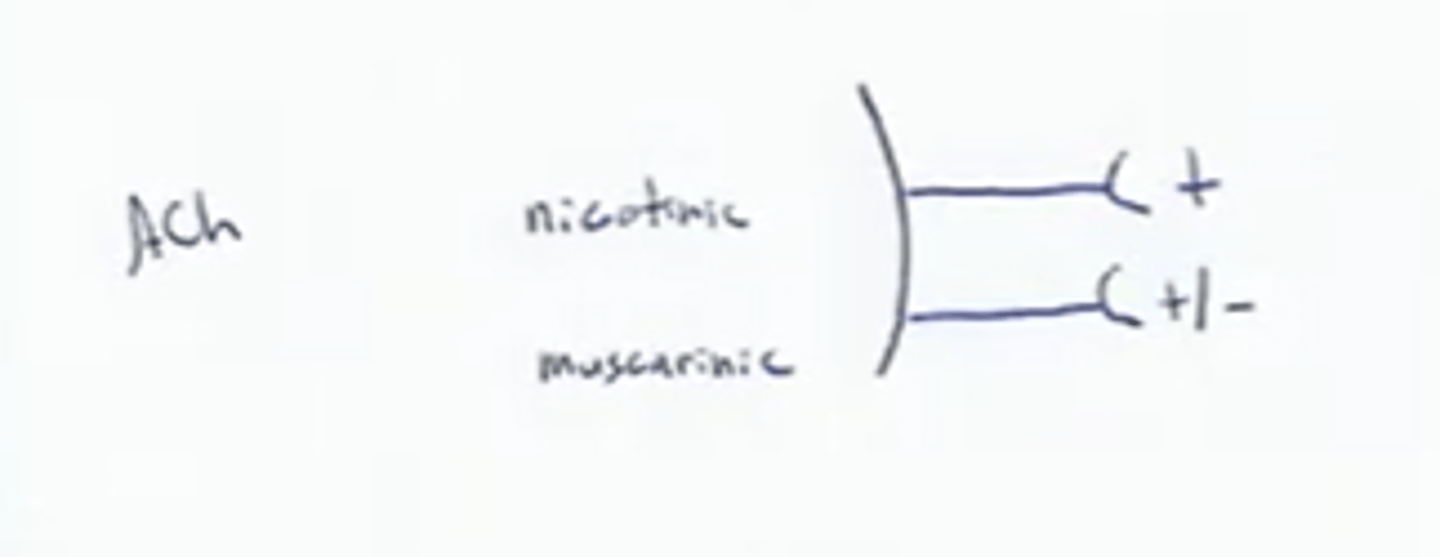
ANS physiology receptors:
1) Cholinergic receptors (bind Ach)
-has 2 types
2) Adrenergic receptors (bind NE)
Two types of Cholinergic Receptors
Nicotinic Receptors,
Muscarinic Receptors
Nicotinic Receptors
Effect of Ach binding is always stimulatory
Muscarinic Receptors
Effect of Ach binding can be either inhibitory or excitatory depending on the receptor type on the target organ
Types of Adrenergic Receptors
1) alpha and beta
2) Each type has 2-3 subclasses (a1, a2, B1, B2, B3)
3) Effectors of NE binding to:
-a receptors are generally stimulatory
-B receptors are generally inhibitory
4) A notable exception- NE binding to B receptors of the heart is stimulatory
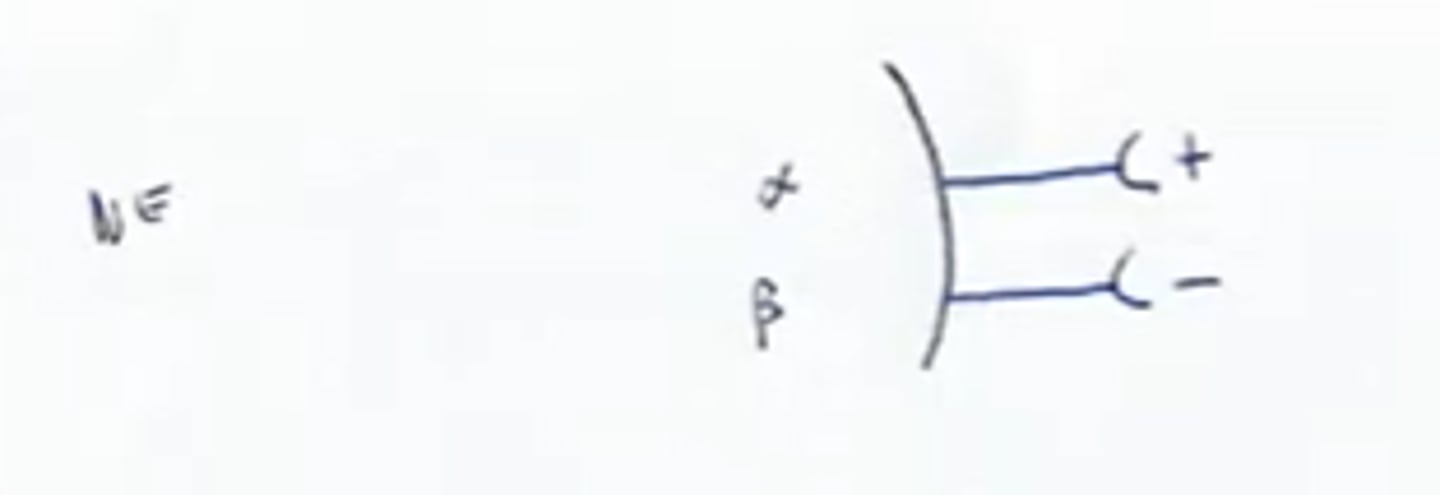
Alpha Receptors
Type of Adrenergic receptor that are generally stimulatory
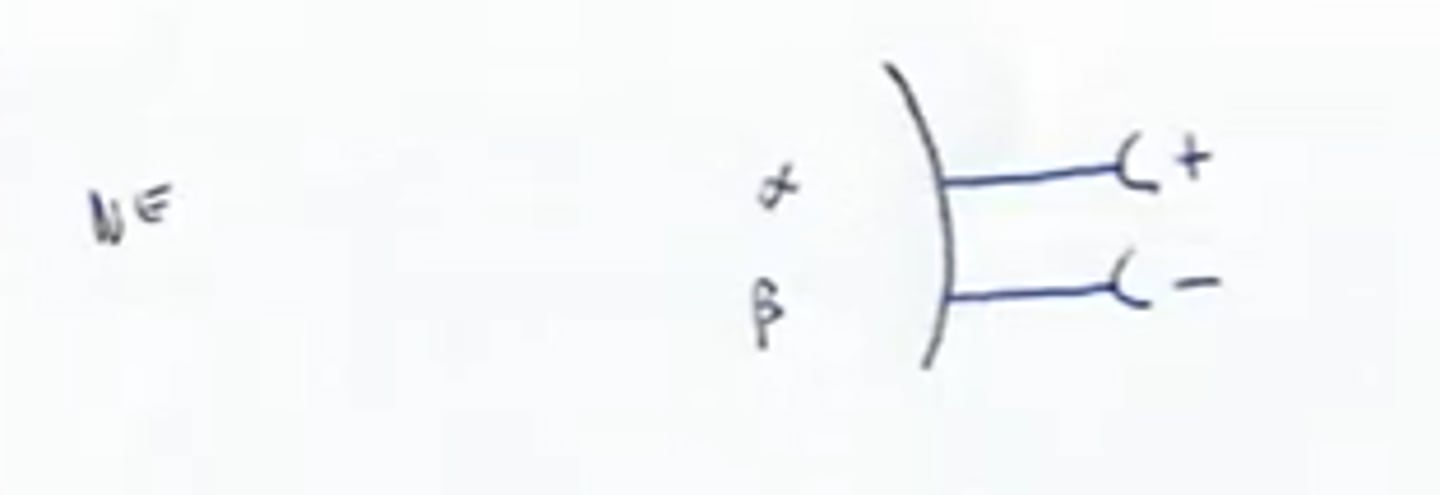
Beta Receptors
Type of Adrenergic receptors that are generally inhibitory
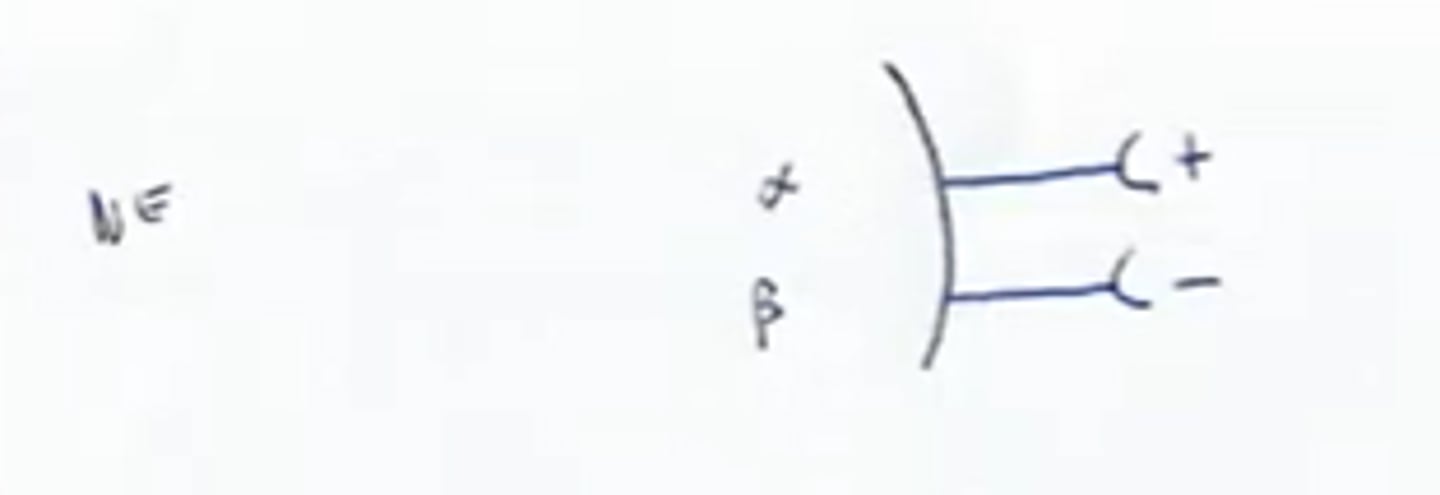
Effect of drugs: Atropine
Blocks parasympathetic effects
Effect of drugs: Neostigmine
inhibits AchE and is used to treat myasthenia gravis
Effect of drugs: Tricyclic antidepressants
Prolong the activity of NE on postsynaptic membranes
Effect of drugs: Over-the-counter for colds, allergies & nasal congestion
Stimulates alpha-adrenergic receptors
Effect of drugs: Beta-blockers
attach mainly to B1 (Beta1) receptors and reduce HR and prevent arrhythmias
Antagonistic interactions of the autonomic divisions
Most visceral organs are innervated by both sympathetic and parasympathetic fibers that precisely control visceral activity
-Sympathetic fibers increase heart and respiratory rates, and inhibit digestion and elimination.
-Parasympathetic fibers decrease heart and respiratory rates, and allow for digestion and the discarding of wastes
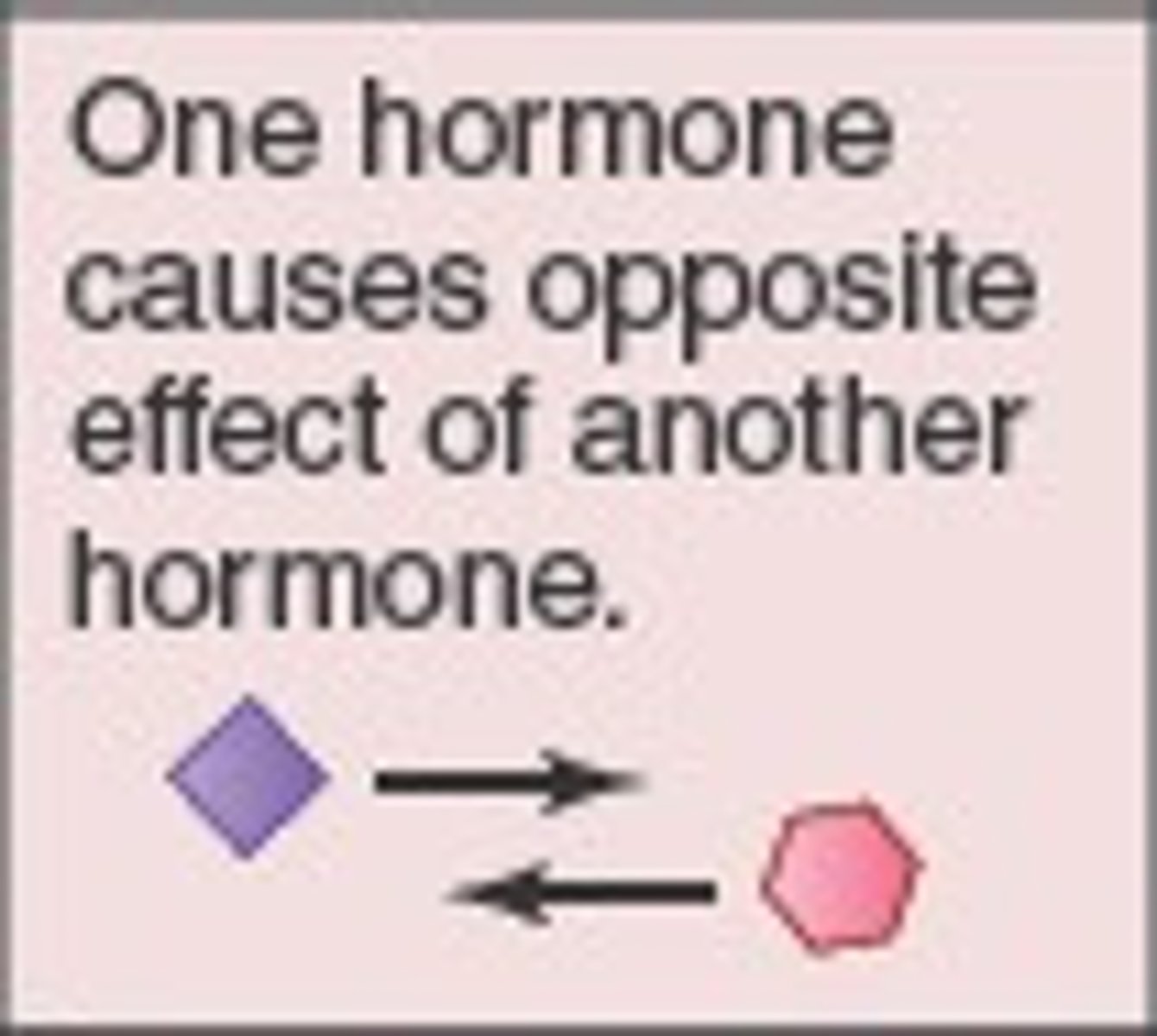
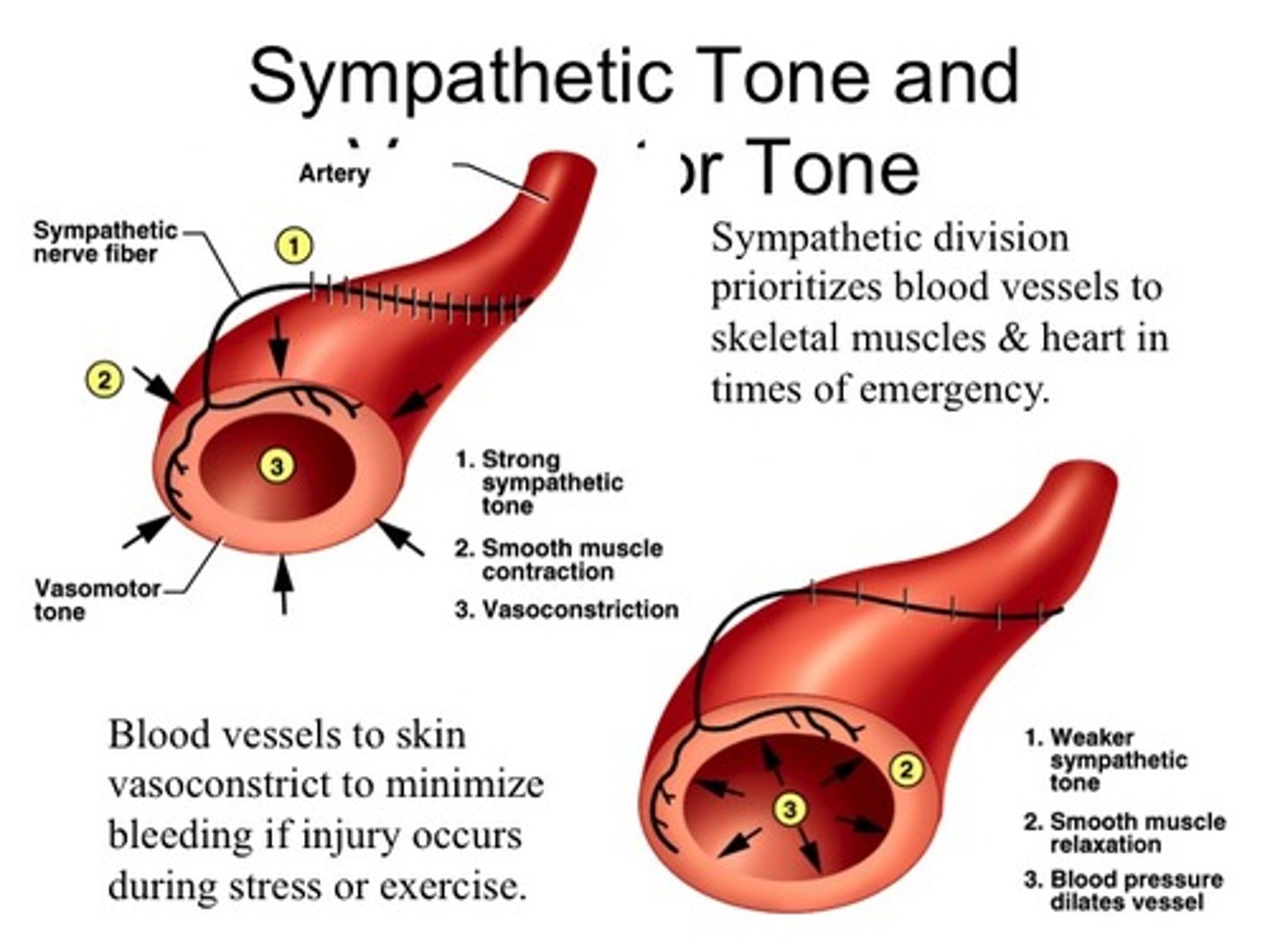
Sympathetic Tone
1) Controls BP and keeps the blood vessels in a continual state of partial constriction
2) This sympathetic tone (vasomotor tone) next card info
3)Alpha-blocker drugs interfere with vasomotor fibers and are used to treat hypertension
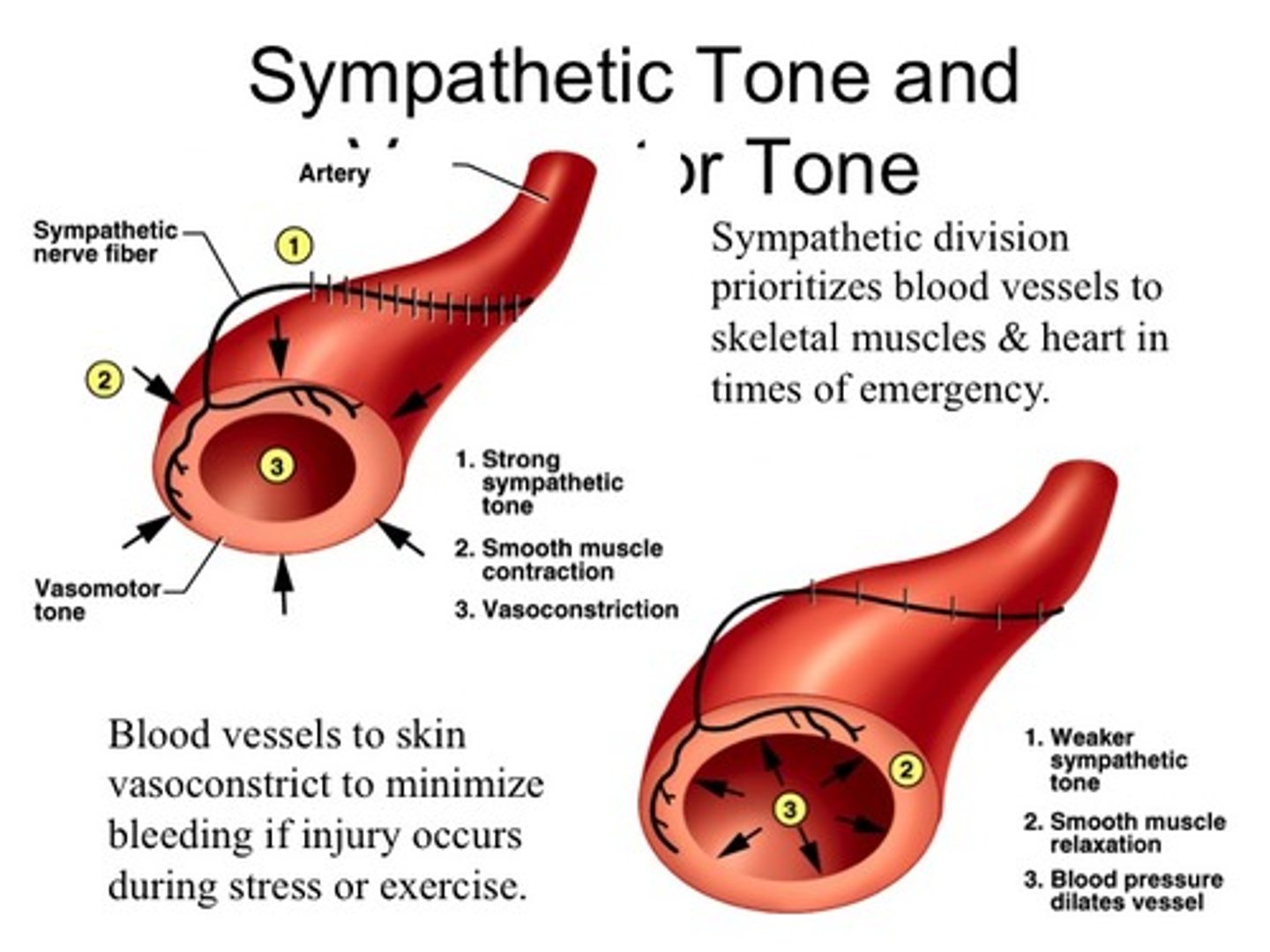
Vasomotor tone
1) Constricts blood vessels and causes BP to rise as needed
2) Prompts vessels to dilate if BP is to be decreased
Parasympathetic Tone
1) Slows the heart
2) Dictates normal activity levels of the digestive and urinary systems
3) Sympathetic division can override these effects during times of stress
Sympathetic Division
Controls thermoregulatory responses to heat,
Release of renin from the kidneys to increase BP,
Metabolic effects
Cooperative effects of sympathetic and parasympathetic tone
ANS cooperation is best seen in control of the external genitalia
-Parasympathetic fibers cause vasodilation and are responsible for erection of the penis and clitoris
- Sympathetic fibers cause ejaculation of semen in males and reflex peristalsis in females
Unique roles of the sympathetic division
Regulates many functions not subject to parasympathetic influence
These include ...
The sympathetic division controls:
1) Thermoregulatory responses to heat
2) Release of renin from the kidneys to increase BP
3) Metabolic effects...
Metabolic effects the sympathetic division controls are:
1) Increases the metabolic rate of body cells
2) Raises blood glucose levels
3) Mobilizes fat as a food source
4) Stimulates the reticular activating system (RAS) of the brain, increasing mental alertness
Control of ANS functioning
1) Hypothalamus is the main integration center of ANS activity...
2)Subconscious cerebral input via limbic lobe connections influence hypothalamic function
3) Other controls come from the cerebral cortex, the reticular formation, and the spinal cord
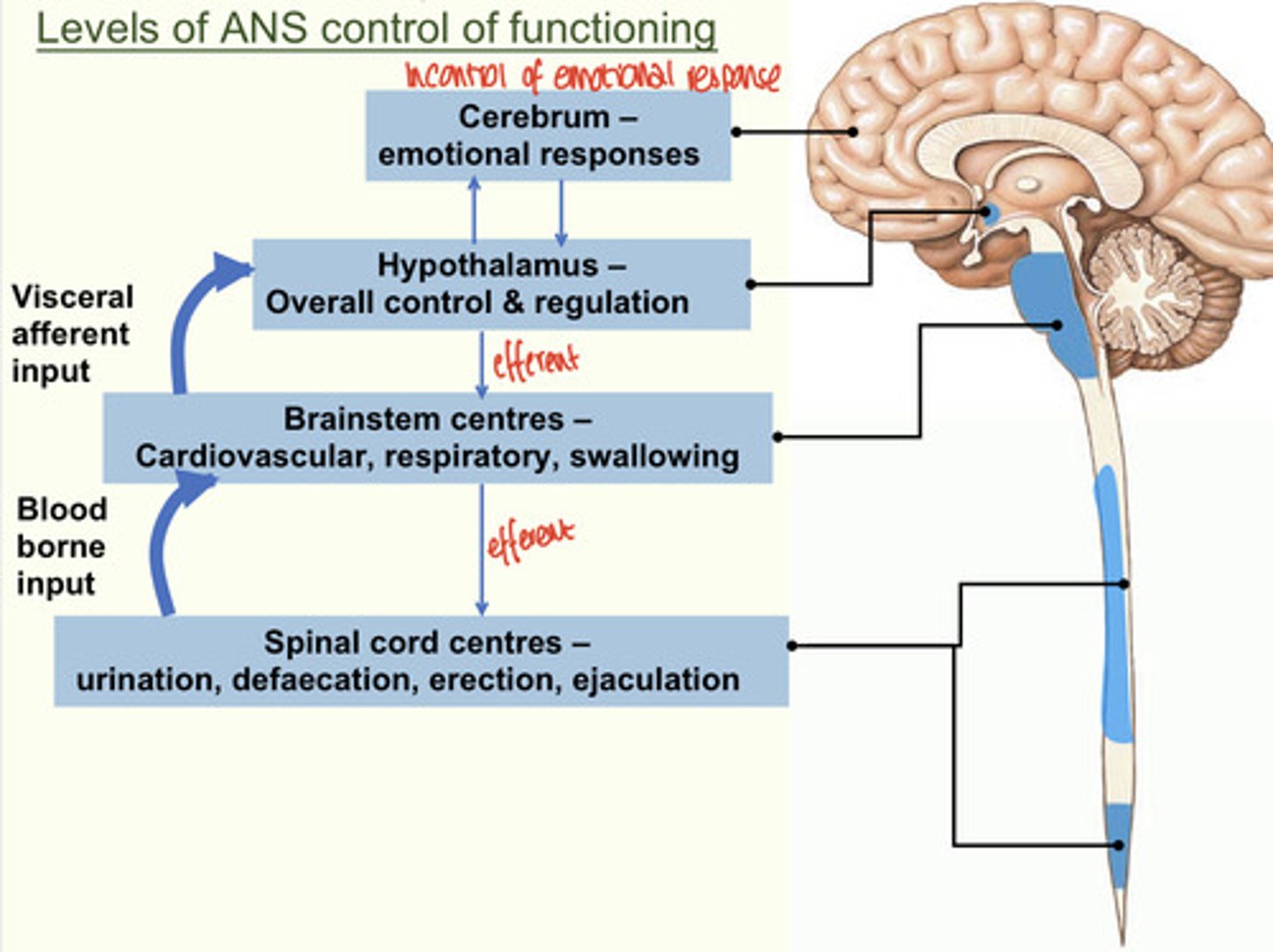
Hypothalamus is the main integration center of ANS activity...
Controls heart activity, BP, body temperature, water balance, endocrine activity, emotional stages (rage, pleasure), biological drives (hunger, thirst, sex), and reactions to fear and the "fight-or-flight" system.
Homeostatic Imbalances of the ANS
1) Hypertension
2) Raynaud's disease
3) Mass Reflex reaction
