World History Spring
Nationalism and Imperialism - Early 1800’s
Napoleon
- Beat all of Europe in War
- spread ^^democracy and liberalism^^
- through ==absolutism and imperialism==
- Gave the people more rights
- but took away rights of women and slaves just earned in the revolution
- Other Monarchs try to impose monarchy in france
- so people don’t get ideas
- <<continue to maintain power<<
- Offense is the best defense and invaded neighboring countries to prevent them from invading france.
- Napoleonic Code - new code of laws
- based on enlightenment principles
- women lose rights
- Economic growth
- controlled prices
- opened jobs to all based on talent
- new industries and infrastructure
- New public school system → increased education
- Napoleonic wars →1804 - 1812
- took control of europe using forceful diplomacy
- defeated the holy roman empire
Impacts in Europe
Spread revolutionary, liberal ideas - weaken monarchies
New social order
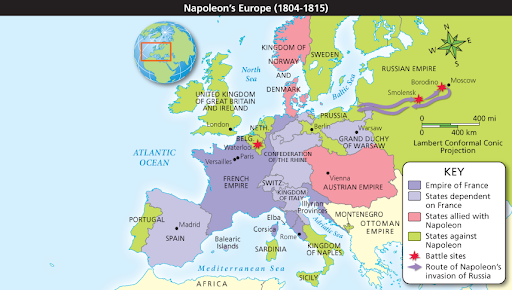
Prussia, England, Russia, and Austria are against Napoleon
People rise up in revolt - rise in Nationalism
1812 - France invades Russia
- Russians use Scorched Earth tactics
- French reach Moscow and quickly retreat because ^^winter^^
^^1813 - Napoleon defeated at Leipzig (Austria)^^
==1814 - Napoleon abdicates throne==
- exiled to alba
- escapes and returns to Paris for 100 days
%%June 18, 1815 - Battle of Waterloo%%
- french army defeated by british and prussian forces
@@1821 - Napoleon dies in Exile@@
September 1814 - June 1815
- %%Congress of Vienna%%
- meeting of diplomats and heads of state
- goal = restore stability and order
- %%Quadruple Alliance - Austria, Britain, Prussia, and Russia%%
- Peace in Europe for 100 years
New Ideologies
- political cartoons - propaganda in the form of imagery and humor
first cartoon
- metternich
- red uniform
- freedom, progress, and monarchy sign
- protesting against monarchy
- marching towards freedom
- three new ideologies
- Conservatism
- liberalism
- Nationalism
| Conservatism | Liberalism | Nationalism | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition of Ideology: Systems of thought and beliefs | Believed in the old way and conserving the monarchy | Preferred a Republic over a monarchy where rulers were limited by written constitutions and gave the people rights. | People with common heritages demanded their own state instead of being mixed up with everyone else in massive empires. |
| People Ideology Appealed to: | People who were already higher up in the social order like nobles and the monarchs but also peasants who believed in the old way. | Middle class people, business owners, bankers, writers, politicians | The larger majority ethnic groups |
| Major Goals of Supporters: | Ensure stability and prevent revolution, return to the way before 1789. | Wanted government to be based on constitutions and separation of power, elected power whose duty was to the people | Wanted to have borders and segregation based on heritage and nationality |
| Other Beliefs: | An established church, change should be slow, control of the press | Natural rights, liberty, equality, property rights, and freedom of religion |
the clashing of these beliefs lead to rebellions and civil conflict
which of the following do you most agree with about nationalism
- feeling pride in one’s country is a citizen’s responsibility
- feeling little pride in one’s country makes a person a troublemaker
- feeling too much pride in one’s country can be dangerous.
- expressing pride in one’s country - in any tradition - is a citizen’s right.
Germany
Is currently the States of the Rhine
confederation - states that band together to gain independence
1848 - revolution occurs due to austrian rule and taxes
frankfurt national assembly (1848)
- catholics favor Austria, Protestants favor Prussia
- relatively powerless and zero change
- Martin Luther was german!
- Germany is very split between catholicism and protestantism
Shows German states want to unify
^^Otto Von Bismarck^^ - Prussian representative
- Power based on practical education and military
- not ideology or morality
- Main goal = increase prussia’s power
- <<Hates divine right of monarchies<<
- ‘Blood and iron’ speech
- turns down germany’s offer so he can build up prussia enough to be able to handle the new land
@@Second Reich@@ Begins (1864 - 1870)
- Alliance w/ austria
- austro - prussian war
- franco - prussian war
German states unify under Bismarck and Prussia’s command
1871 - creation of Second Reich (second German Empire)
Kaiser - top dog of the second Reich
- summon and dismiss parliament
- inherited position
- appoint and dismiss chancellor
Chancellor
- proposed legislation to parliament
Bundesrat
- assembly of state representatives
- appointed by leaders of states
Reichstag
- Elected by manhood suffrage
- election every three years
Bismarck → first chancellor
Foreign policy - keep France weak
domestic policy - erase threats(Catholics and socialists), kulturkampf (state above religion)
Germany becomes dominant European power
- Advantages
- ample coal and iron
- disciplined and educated workforce
- growing population
- Government provided support for economic growth
- single currency
- standardized banking
- protective tariffs
Democratic Reforms
Challenges in Eastern Europe
- factories
- growth in cities
- worker discontent
- rise in socialism
Multinational Empire - many different nationalities in region
- czechs, slovaks, poles, ukrainians, serbs, croats, slovens, etc
- desire to have own government and state
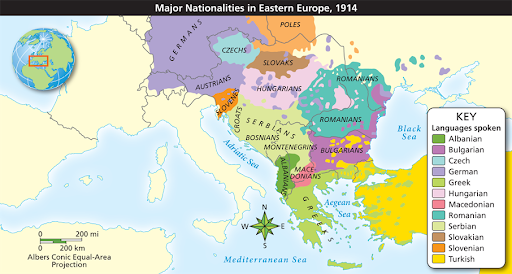
Austrian Struggles and Reforms
- Francis Joseph takes throne
- strengthen empire
- set up constitution and legislature
- Francis still has ultimate authority
- Austria is defeated by the Prussians
- led to further desire for change
- Creation of dual monarchy (Austria-Hungary)
- Ruler is Francis Joseph (Austrian)
- remain seperate states
- Austrian ministries of defense, finance and foreign affairs maintain power.
Ottoman Empire Declines
Ottoman Empire is Islam
Serbia and Greece = successful nationalist movements
The turks are showing weakness
Europeans begin dividing land
Crimean war is fought over this land
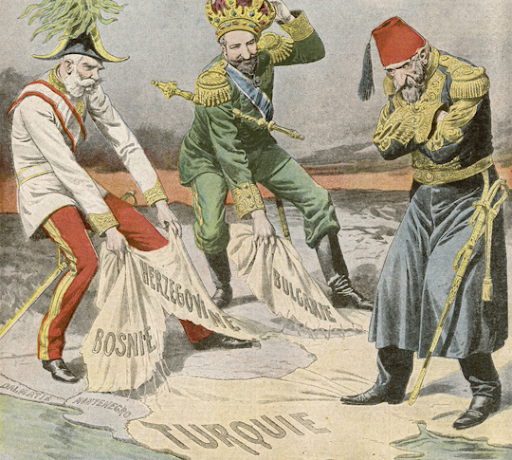

These conflicts are referred to as the “Balkan Powder Keg”
any small sparks can cause the whole thing to explode into a massive war…
Great Britain
- Queen Victoria
- Constitutional Monarchy w/ bicameral Parliament
- House of Commons (elected representatives)
- Louse of Lords (hereditary, can veto commons bills)
- Democratic reforms:
- Great Reform Act - change of seats and representation
- Chartist movement - men’s suffrage?
- Abolishing Slavery
- Women’s suffrage
- the Irish Question - how to rule over and control Ireland
United States
- Territorial expansion “manifest destiny”
- Democratic Expansion
- Abolition
- Women’s rights
- Economic Growth
- leader of the second industrial revolution
- Harsh conditions and low wages - push for reforms
- 8 hours a day
- ban child labor
- Monopoly regulation
France
Multiple revolutions and government systems
- Revolutions in 1830 & 1848
- Second Empire and Third republic
Increasingly Liberal governments over time
First country to adopt universal male suffrage
30 - 40 political parties
Dreyfus Affair
showed simmering anti-semitism existing in Europe
- Alfred Dreyfus (jew) convicted of treason for passing military secrets - imprisoned for 5 years
- Actual spy found - army forged documents to incriminate Dreyfus
- Divided military and society
Led to beginnings of Zionist Movements
- Desire for Jewish Homeland
Divisions between military and society
Imperialism
- The policy of on country’s political, economic, or cultural domination over other lands and territories
- Causes of Imperialism
- industrialization
- political and military concerns
- Humanitarian and Religious efforts
- Social Darwinism
- In africa:
- Types of Imperial Rule
- Direct rule
- Officials and military sent to colony
- Imposed culture and rule
- most common in africa
- Indirect rule
- Governor and council of advisors
- local rulers retain some authority
- Encouraged western ideas and education
- Protectorate
- Local Rulers retain authority
- expected to follow european advice
- Cheaper for European countries
- Spheres of Influence
- weak governments remain
- Outside power claims exclusive investment or trading privileges in area
Middle East and India
ottoman empire is weakened
Prominently Islam and Hinduism
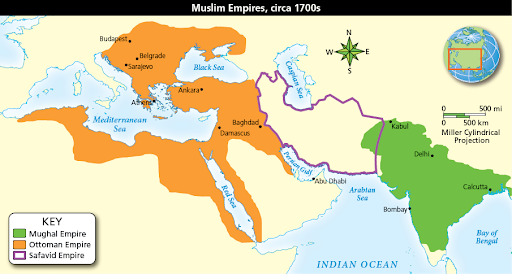
==Muslim Reform Movements== in the Middle East
- Muslim empires faced threats of European Imperialism
Imperialism in Asia:
China
silk can only be traded with gold and silver
china experiences ==surplus==
get really rich
focus on agriculture and less on industrial goods
leads to less of a surplus and evens out with britain
Britain takes initiative and starts the opium war
opium is imported into china
banned in Britain
china goes to war with britain over it
britain wipes out the chinese government
takes over chinese trade
Britain takes over Hong Kong
Ching Dynasty is Failing
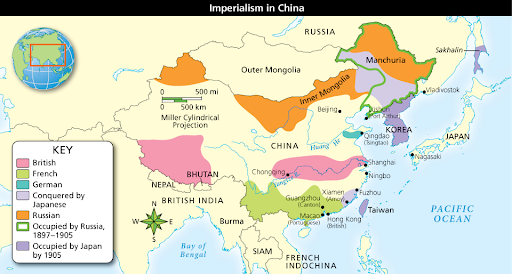
China’s land is being taken away
China takes the biggest blow when they are defeated by Japan in the Sino-Japanese War
throwing out of the old ways
Guangxu ‘hundred days of reform’
Boxer group tries to rebel
gets absolutely crushed
leaves room for european hate
nationalism
Imperialism in Japan
- Japan is far behind
- They kind of let imperialism happen bc they cant fight against it and know how far behind they are
- Japan is closed off from foreigners
- Shoguns take over
- change is wanted
- Fishbowl breaks
- Meiji revolution - strengthen Japan against European Imperialism
- Japan is no longer under control
- Japan starts to expand empire
- Goes from being Imperialized to becoming Imperials
- Sino Japanese war
- War against China
- Takes over Taiwan and Manchuria
- Russo-Japanese War
- Defeats Russia
- Controls Korea
- Iron Fist rule
- “how many Koreans can you kill in one day”
Pacific and American Imperialism
Dutch east india company sought to control spice islands
Indonesia
- plantation management and trade = huge motive
- created social class system
- Farmers must plant 1/5 land of export goods
British looking for Base to compete with Dutch
- Burma (Myanmar)
- many clashes with britain
- annexed
- Malaysia
- Singapore - world’s busiest port
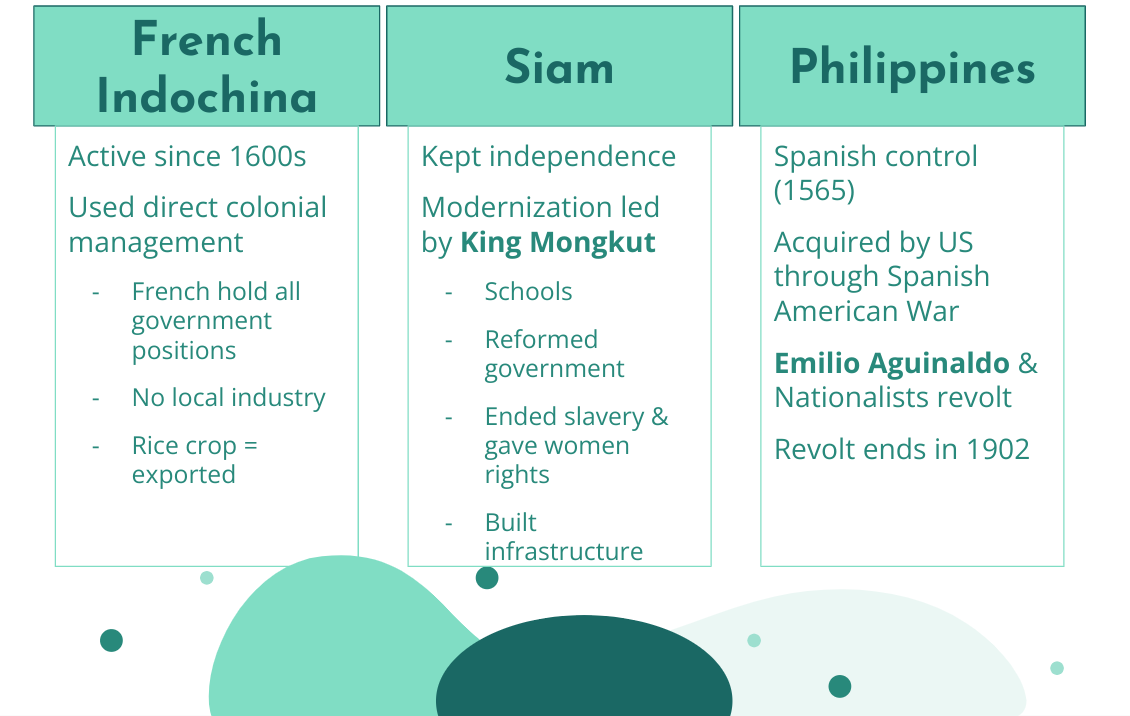
Siam = Thailand
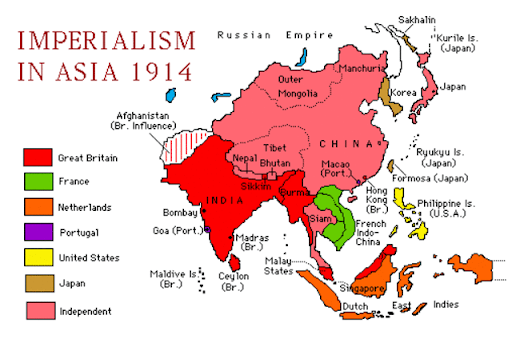
Americas
Many wars of Independence
Church = privileged
limited voting rights and racial prejudice
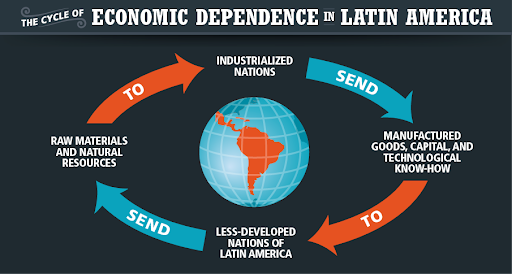
Colonialism doesn’t disappear
- Britain and US replace Spain and France
Mexico’s Search for Stability
- Texas War of Independence
- Mexican American War
Benito Juarez and La Reforma
- liberal reforms - help oppressed
- Civil war - France and Austria
General Porfirio Diaz
- strengthen army, police, and central government
- Economy advances - industry and mining
- police state
- sort of industrial revolution
Panama Canal
Allowed trade to occur quicker
Panamanian Independence Movement