LEC 8.1: Asepsis & Infection Prevention
1/78
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Asepsis, Infection, Chain of Infection, Factors Increasing Susceptibility, NANDA
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
79 Terms
Infection
Growth of microorganisms in the body tissue where they are not usually found
Infection
The following is an example of what?
E. Coli is a normal flora in the small intestine but there’s a bacteria that limits it’s growth. However, when one takes antibiotics, that limiting bacteria decreases, allowing E. Coli to increase. When one has poor hygiene in cleaning their perineum, E. Coli may be able to enter through the urethral orifice and cause UTI.
Asymptomatic/Subclinical Infection
Microorganism produces no clinical evidence of disease
Disease
Detectable alteration in normal tissue function
Virulence
Severity or harmfulness of a microorganism
Virulence
The following is an example of what?
Comparing the common cold and COVID, COVID has more severe effects.
Communicable Disease
Condition resulting from transmission of an infectious agent from one individual to another
Communicable Disease
The following is an example of what?
COVID is airborne, enabling it to stay in the air for long time periods and allow for easy transmission.
Pathogenicity
Ability to produce disease
Pathogen
A microorganism that causes disease
Opportunistic Pathogen
Causes disease only in a susceptible individual
Opportunistic Pathogen
The following is an example of what?
Candida albicans is a normal bacteria in the oral cavity that is normally limited by another bacteria. However, if one takes antibiotics that reduces that limiting bacteria, the candida albicans is able to increase and results in the formation of Candidiasis.
Bacteria
Viruses
Fungi
Parasites
4 Types of Microorganisms that cause Infection
Bacteria
A microorganism that causes infection
Most common
Live and can be transported through air, water, food soil, body tissues & fluids & inanimate things
Virus
A microorganism that causes infection
Consist primarily of nucleic acid
Needs to enter living cells in order to reproduce
Virus
The following is an example of what type of microorganism that causes infection?
Helper T-Cells normally help in detecting foreign bodies and calling other immune cells to destroy such bodies. However, HIV attaches to the Helper T-Cell, causing the Helper T-Cell to be unable to call other immune cells, allowing the HIV to reproduce.
Fungi
A microorganism that causes infection
Include yeast and molds
Fungi
The following is an example of what type of microorganism that causes infection?
Candida albicans is a normal flora in the vaginal canal which becomes opportunistic when the good bacteria that controls it is lessened.
Parasites
A microorganism that causes infection
Live on other living organisms
Include protozoa (ex. malaria) and arthropods (mites, fleas, ticks)
Local vs. Systemic
Acute vs Chronic
2 MAIN Types of Infection
Local Infection
Type of infection
Limited to a specific part of the body where the microorganisms remain
Local Infection
The following is an example of what type of infection?
One is experiencing a runny nose.
Systemic Infection
Type of infection
Microorganisms spread and damage different parts of the body
Systemic Infection
The following is an example of what type of infection?
One is experiencing a fever.
Bacteremia
Part of Systemic Infection
Culture of the person’s blood reveals microorganisms
Septicemia
Part of Systemic Infection
Bacteremia results in a systemic infection
Acute Infection
Type of infection
Appear suddenly or last a short time
Chronic Infection
Type of infection
Occur slowly, over a long period, and may last months or years
Chronic Infection
The following is an example of what type of infection?
A person with Tuberculosis needs to drink antibiotics for 3 months.
Acute or Chronic Infection
The following is an example of what type of infection?
For some, COVID is only experienced for a week. For others, COVID causes remnant symptoms even after a year of initial symptom experience.
Asepsis
Freedom from disease-causing microorganisms
Aseptic Technique
The way to decrease the possibility of transferring microorganisms from one place to another
Medical Asepsis
Surgical Asepsis
2 Types of Aseptic Technique
Medical Asepsis
One of the types of Aseptic Technique
Includes all practices intended to confine a specific microorganism to a specific area, limiting the number, growth & transmission of microorganisms
Clean
Part of Medical Asepsis
Absence of almost all microorganisms
Dirty
Part of Medical Asepsis
Likely to have microorganisms
Surgical Asepsis/Sterile Technique
One of the types of Aseptic Technique
Refers to activities that keep area or object free of all microorganisms
Spores
Microscopic dormant structure formed by some microorganisms that are very hardy and often survive common cleaning techniques
When suitable environment is found, it “hatches” and replicates
Destroyed in sterile technique
False (Surgical Asepsis destroys spores.)
True or False: Medical Asepsis destroys spores.
Nosocomial Infections
Infections that originate in the hospital
Develop during a client’s stay in a facility or manifest after discharge
May also be acquired by a personnel working in the facility
48 Hours
How many hours after discharge should an infection manifest to be considered a Nosocomial Infection?
Health Care-Associated Infections (HAIs)
What are Nosocomial Infections a sub group of?
Endogenous Source
Nosocomial infection that originated from the client themself.
Endogenous Source
The following is an example of what source of Nosocomial Infection?
Human skin has normal flora on the epidermis. If sterile technique is not done when performing an intravascular insertion, the patient potentially may have an infection through the puncture or cannula.
Exogenous Source
Nosocomial infection that originated from the client’s environment and hospital personnel.
Exogenous Source
The following is an example of what source of Nosocomial Infection?
The hospital room, like the telephone, call light, linens, and walls can introduce microorganisms.
A nurse with poor hygiene may introduce microorganisms to the patient.
Latrogenic Infections
Compromised Host
2 Possible Factors in Nosocomial Infections
Latrogenic Infections
One of the possible factors in nosocomial infections
Direct result of diagnostic or therapeutic procedures
Compromised Host
One of the possible factors in nosocomial infections
Normal defenses have been lowered by treatment or illness
Etiologic Agent
Reservoir (includes Carriers)
Portal of Exit
Mode of Transmission
Portal of Entry
Susceptible Host
6 Links of Chain of Infection
Etiologic Agent
One of the links of chain of infection
Any microorganism capable of producing infection
Will depend on the following:
Number present (the more microorganism present, the more it causes an infection)
Virulence (ability to produce disease) and potency
Ability to enter the body
Susceptibility of the host
Ability to live in the host’s body
Reservoir
One of the links of chain of infection
Sources of microorganisms
Common Examples:
Other humans
Client’s own microorganisms
Plants
Animals
General environment
Carrier
Reservoir of a specific infectious agent that usually does not manifest any clinical signs of disease
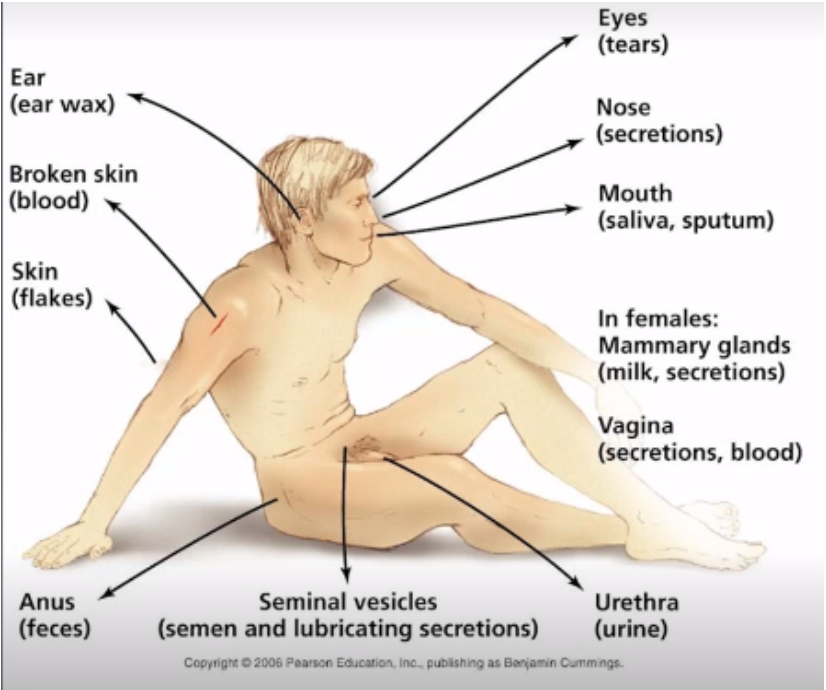
Portal of Exit
One of the links of chain of infection
Where the microorganisms leave the reservoir
Method of Transmission
One of the links of chain of infection
Means of transmission to reach another host
3 mechanisms
Direct transmission
Indirect transmission
Airborne transmission
Direct transmission
Indirect transmission
Airborne transmission
3 Methods of Transmission
Direct Transmission
One of the methods of transmission
Involves immediate & direct transfer of microorganisms from person to person
E.g. touching, biting, kissing or sexual intercourse
Droplet Spread
Droplet Spread
Specific type of Direct Transmission
Occurs if source & host are within 3 feet of each other
Sneezing, coughing, spitting, singing & talking
Indirect Transmission
One of the methods of transmission
Includes
Vehicle-borne transmission
Vehicle: any substance that serve as an immediate means to transport & introduce an infectious agent into a susceptible host through a suitable portal of entry
E.g. fomites (inanimate objects), water, food, blood & plasma
Vector-borne transmission
Vector: an animal or insect that serves as an intermediate means of transporting the infectious agent
Vehicle
Part of Indirect Transmission
Any substance that serve as an immediate means to transport & introduce an infectious agent into a susceptible host through a suitable portal of entry
E.g. fomites (inanimate objects), water, food, blood & plasma
Fomites
Another word for inanimate objects
Vector
Part of Indirect Transmission
An animal or insect that serves as an intermediate means of transporting the infectious agent
E.g. Mosquitoes, rats, birds, chickens, bats, dogs
Airborne Transmission
One of the methods of transmission
Transmitted by air currents
May involve droplets or dust
Droplet Nuclei
Form of Airborne Transmission
Residue of evaporated droplets emitted by an infected host
Can remain in the air for long periods
Can cause virions that can remain in the air for a long time
Dust
Form of Airborne Transmission
May contain infectious agents such as spores of C. difficile
Airborne Transmission: Dust
The following is an example of what Method of Transmission?
Anthrax
Portal of Entry
One of the links of chain of infection
Where microorganisms enter a body
Often, the microorganisms enter the body of the host by the same route they used to leave the source
Susceptible Host
One of the links of chain of infection
Any person who is as risk for infection
Compromised Host: A person at increased risk, an individual who for one or more reasons is more likely than others to acquire an infection
Compromised Host
A person at increased risk, an individual who for one or more reasons is more likely than others to acquire an infection
Age
Hereditary
Level of Stress
Nutritional Status
Current Medical Therapy
Preexisting Disease
6 Factors Increasing Susceptibility
Age
One of the factors increasing susceptibility
The younger and older the host, the poorer the immune system
With the younger clients, their immune system is not fully developed
With older clients, their immune system also becomes older.
Hereditary
One of the factors increasing susceptibility
Sometimes, there are clinical presentations wherein the patient has low or poor antibodies, increasing susceptibility to infection.
Level of Stress
One of the factors increasing susceptibility
In stress, there is an increased production of cortisol - a hormone produced by the adrenals. When cortisol is too much, also makes the immune system weak.
Cortisol
What hormone released when stressed weakens the immune system?
Nutritional Status
One of the factors increasing susceptibility
The nutrients , vitamins and minerals needed for the reproduction of good cells in the immune system are lacking, of course, the immune system could not function properly as expected.
Current Medical Therapy
One of the factors increasing susceptibility
Chemotherapy and radiation therapy tends to affect the function of the immune system. The purpose of killing cancer cells can also kill normal white blood cells that are very important in fighting infections.
Preexisting Disease
One of the factors increasing susceptibility
There are certain disease that would actually place the person at risk or susceptible to having an infection.
Examples: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD), Diabetes Mellitus, Leukemia
Risk for Infection
NANDA Nursing Diagnosis
State in which an individual is at increased risk for being invaded by pathogenic microorganisms
Inadequate primary defenses
Inadequate secondary defenses
Risk factors for Risk for Infection