Market structures (Theme 4)
1/18
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
what are the barriers to entry and exit?
legal - intellectual property rights
set up costs and sunk costs
branding
knowledge needed
fixed costs and economies of scale
lack of access to suppliers and customers
destroyer pricing?
what is a lack of contestability?
When is is hard to enter and exit markets
what are some assumptions made with perfect competition?
infinite firms
perfect information and mobility
no barriers to entry
firms are profit maximisers
this means that it is productively and allocatively efficient
it provides a theoretical benchmark that is a target and we can compare existing markets with
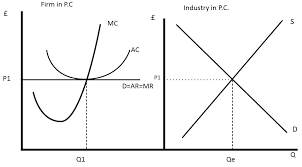
what does the diagram for perfect competition look like?
It features a horizontal demand curve at the market price, representing perfect elasticity, with marginal cost and average cost curves intersecting at the firm's equilibrium output level.
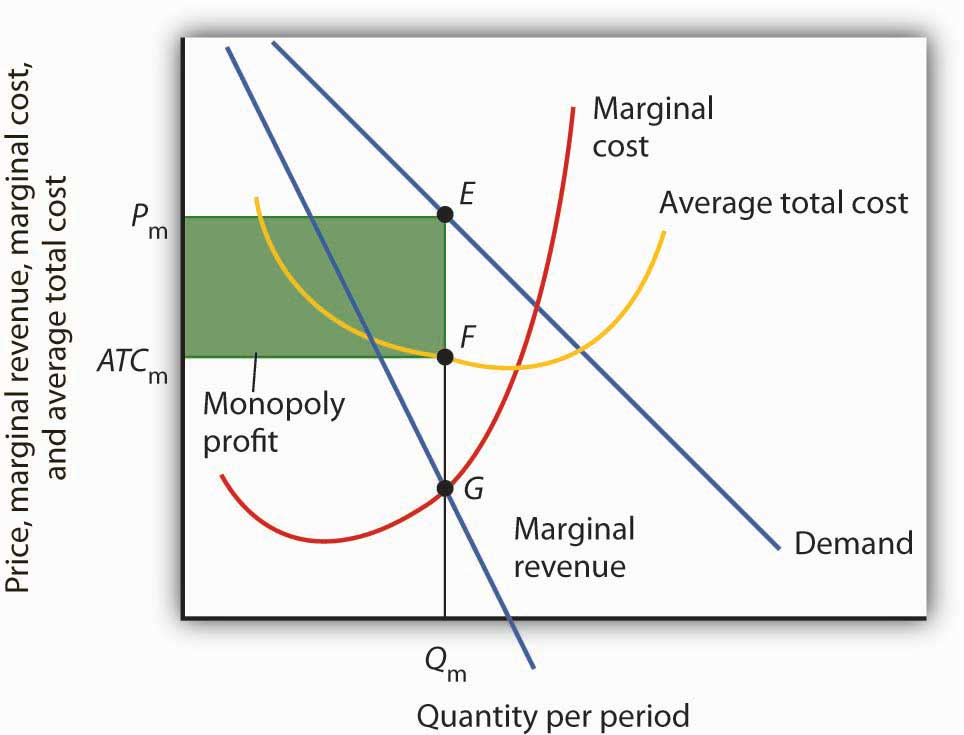
what does the diagram for monopoly demand look like and why?
demand slopes downwards. Market demand is the same as demand for the firm.
marginal cost and average cost cross the curve at different points
assuming that firms are profit maximisers, they can sell the quantity where mc=mr at a much higher cost to make abnormal profits
what effect does a monopoly/market dominance have on consumers?
high prices
supply can be restricted to maximise profits
lack of choice
potential monopsony as the firm may be their sole buyer
lack of quality and innovation (no incentive)
what are advantages of monopolies?
profits can be reinvested - R&D possible
natural monopolies - long run AC fall over a wide range of output levels, so only one firm can exploit economies of scale and achieve productive efficiency.
natural monopolies can occur in utilities due to huge fixed costs of building and maintaining networks
what does the government do about monopolies?
control prices
nationalise them
monitor them - Ofwat, Ofgem (energy), CMA
do not allow cartels and stop unfair practices
what are oligopolies?
A few large firms competing
Non price competition - differentiated products
some barriers to entry
what are some oligopoly strategies?
there tends to be a market leader and follower
collusions are possible - price determination, market division, production quotas
normal non-price competition but there may be aggressive price competition (if good are homogenous)
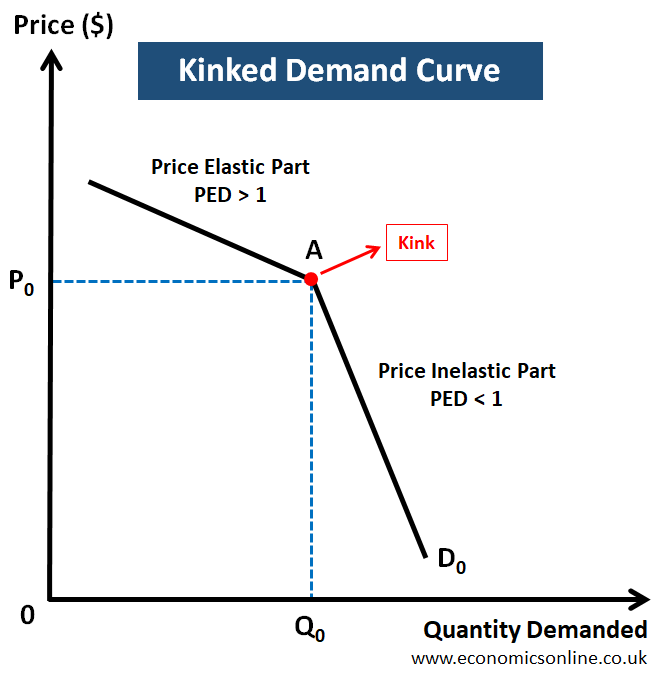
what is the kinked demand curve and why does it look like that?
this is to do with game theory.
if a firm raises their prices it is assumed that competitors will not do the same, so demand falls by a larger amount
but if they put prices down, they do not gain much since competitors are likely to follow
therefore there is an optimum price point
what are some factors to consider when deciding what a firm in an oligopoly should do?
there is a different between long run and short run
game theory, what will firms do in response?
what objectives do you have?
what information do you have?
what is monopolistic competition?
products are differentiated and there are few barriers to entry, so a large number of firms
what does the sma do?
investigate mergers
conduct market studies
investigates cartels and anti-competitive behaviour - pricing, practices
enforces consumer protection law
when does the cma analyse mergers?
whee combined turnover is over £70 milllion or market share is greater than 25%
what power does the cma have?
they can stop mergers and fine companies up to 10% of worldwide turnover
what are the benefits of being a monopsony buyer?
can get low prices
more power over workers and supplier (depending on competition)
can get more power over things like delivery times and quality
what are benefits for other stakeholders?
economies of scale and lower overall costs (due to only contract and easier negotiation) can help the supplier
low costs may be passed down to consumers
what are some disadvantages of monopsonies?
suppliers treated unfairly
cost reductions are likely not to be passed on
added risk for suppliers if there is a monopoly
if a monopsony occurs for labour, this can drive down wages
there may be poorer ethical standards