3.2-3.4 ionic, metallic and covalent bonding
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
Define ionic bonding
Electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions
Describe ionic bonding
Transfer of electrons from a metallic element to a non-metallic element
Define metallic bonding
The electrostatic forces of attraction between the positive metal ions and the sea of delocalised electrons
Define covalent bonding
Electrostatic forces of attraction between the shared pair of electrons and positively charged nuclei
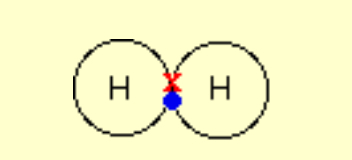
Describe the covalent bonding in H2
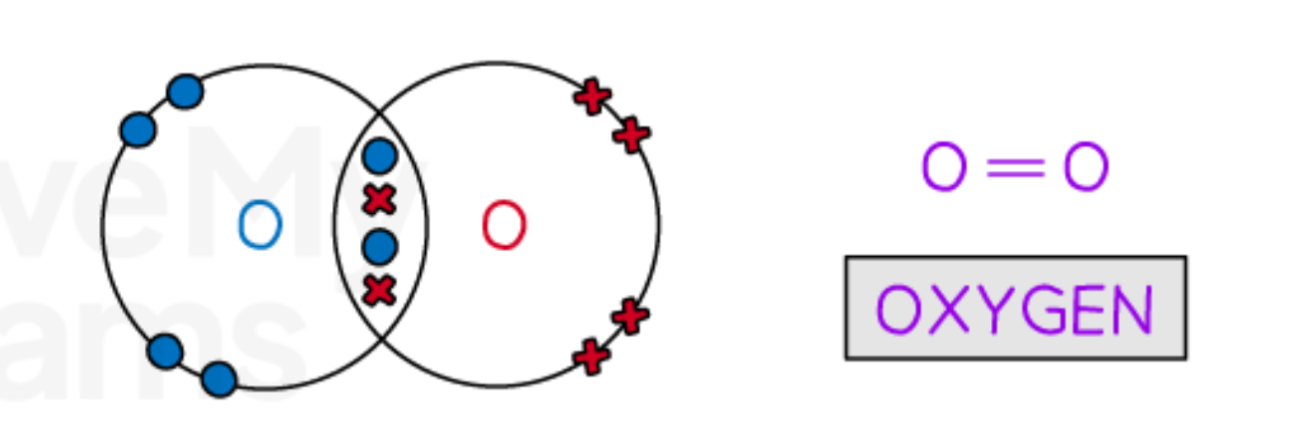
Describe the covalent bonding in oxygen
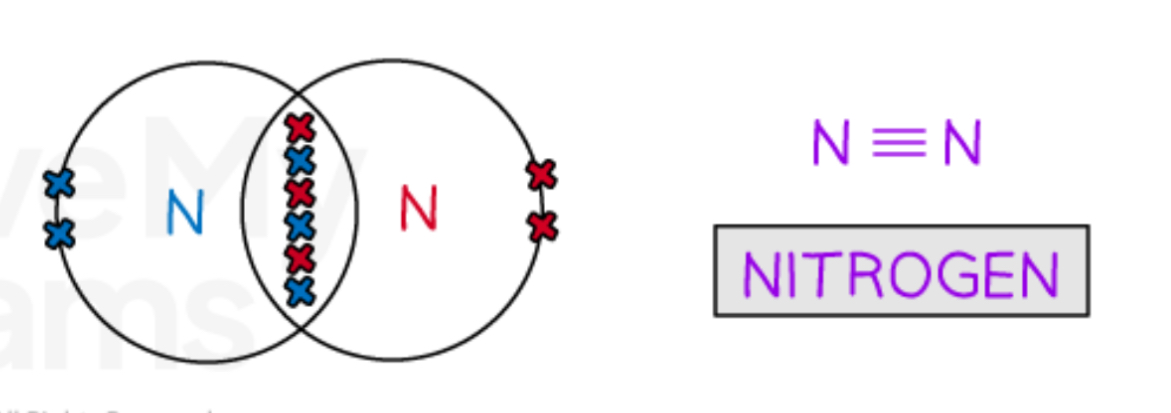
Describe the covalent bonding in Nitrogen
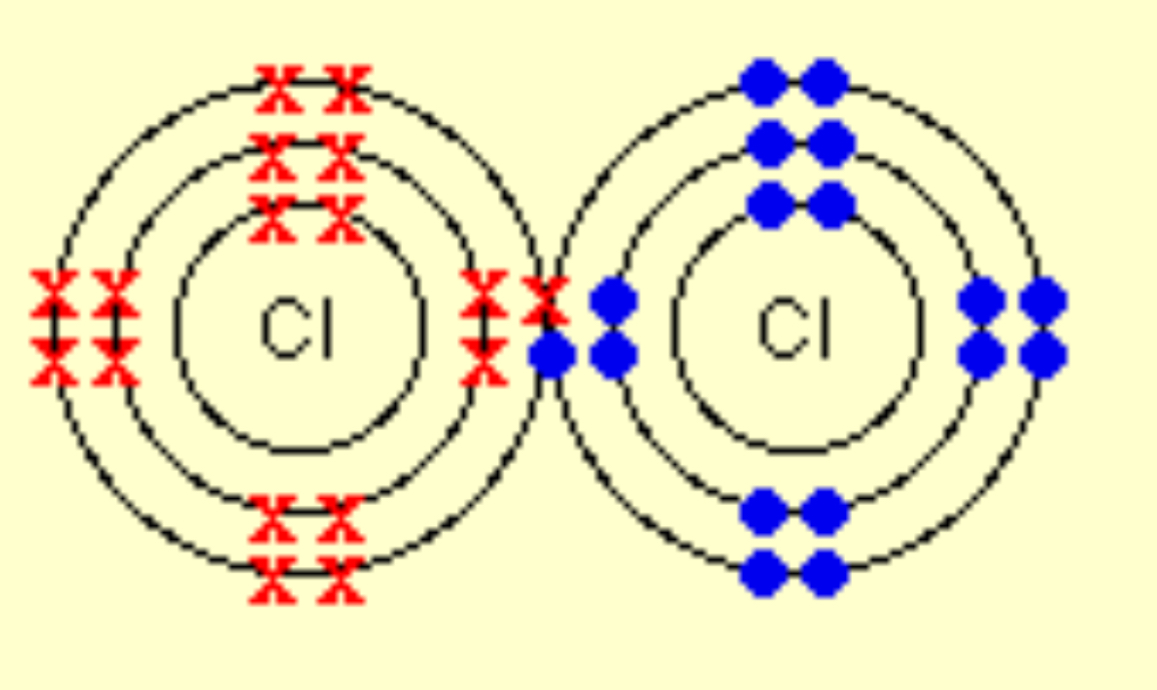
Describe the covalent bonding in Chlorine
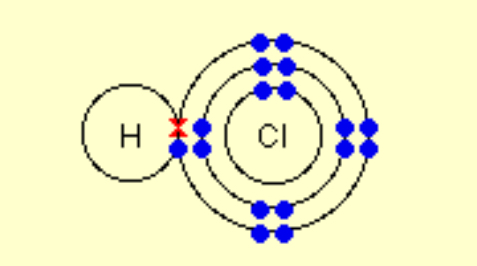
Describe the covalent bonding in HCl
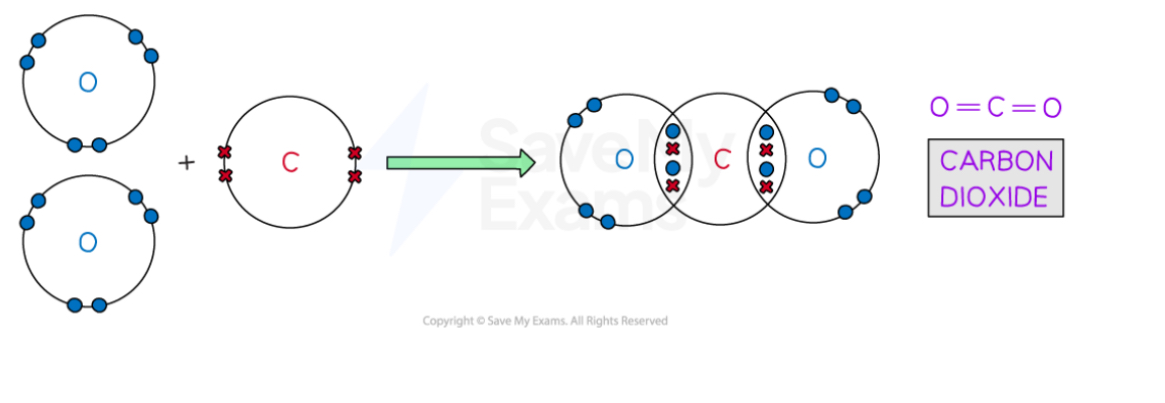
Describe the covalent bonding in CO2
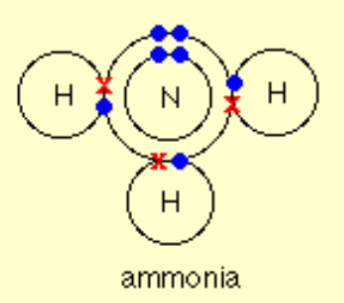
Describe the covalent bonding in Ammonia
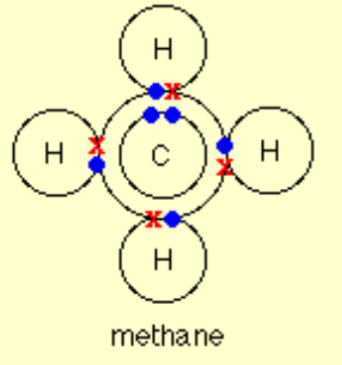
Describe the covalent bonding in Methane
Describe the covalent bonding in Ethane
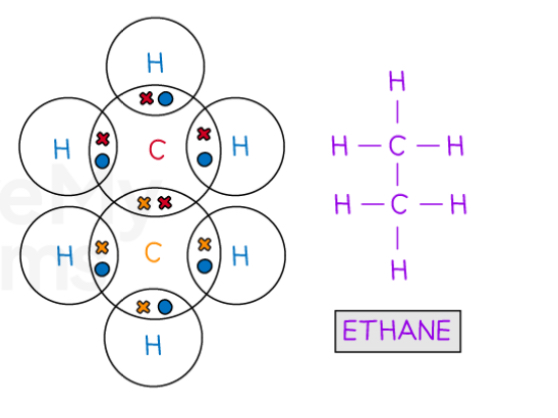
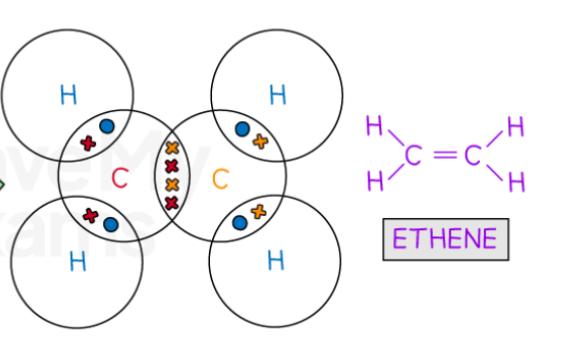
Describe the covalent bonding in ethene
What is special about covalent bonding in period 3?
Elements in period 3 can expand their octet
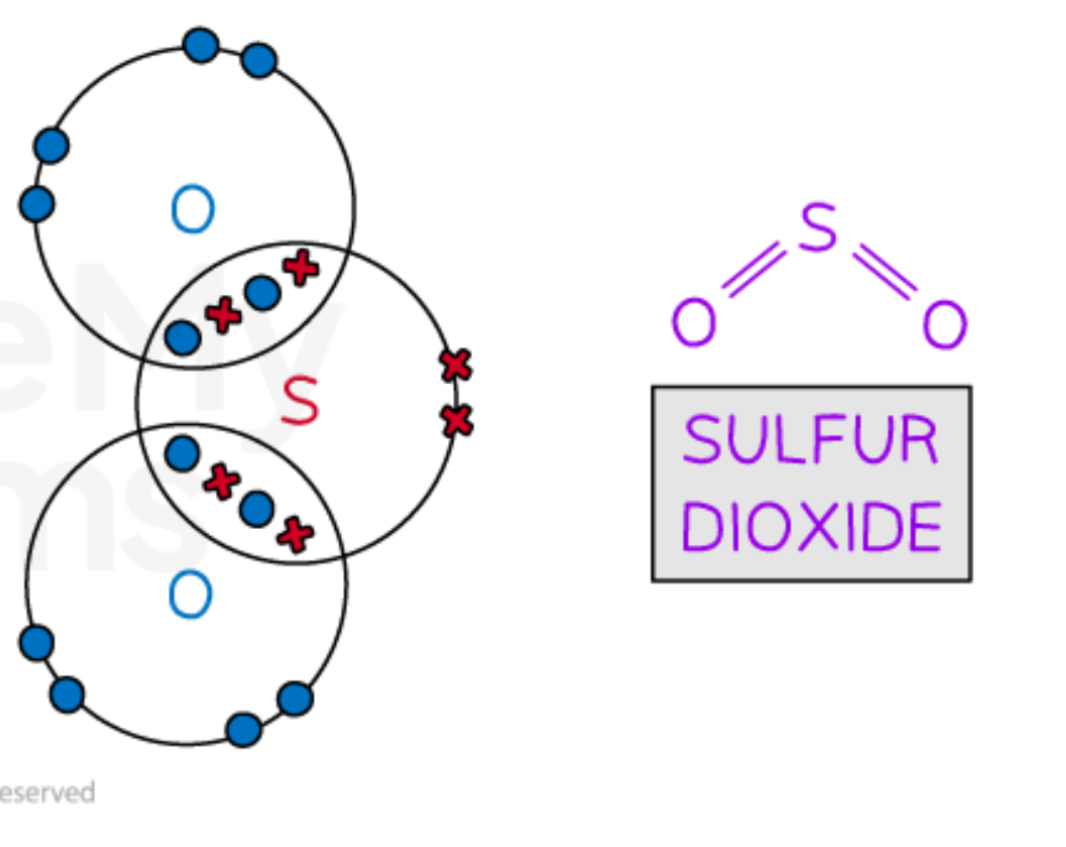
Describe the covalent bonding in SO2
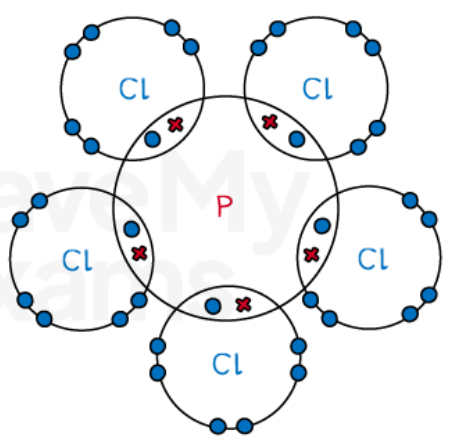
Describe the covalent bonding in PCl5
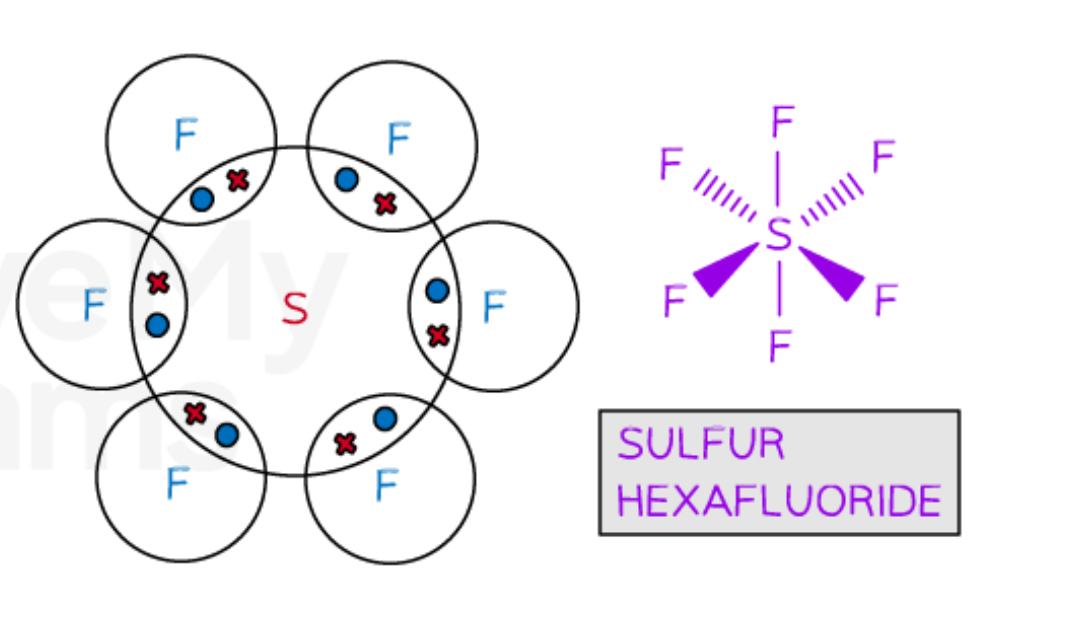
Describe the covalent bonding in SF6
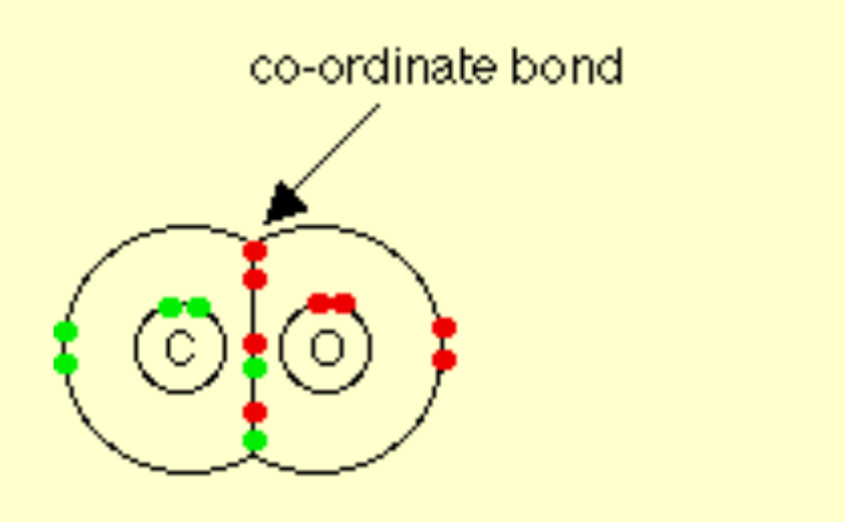
Define coordinate bonding
When both electrons in the shared pair come from the same atom
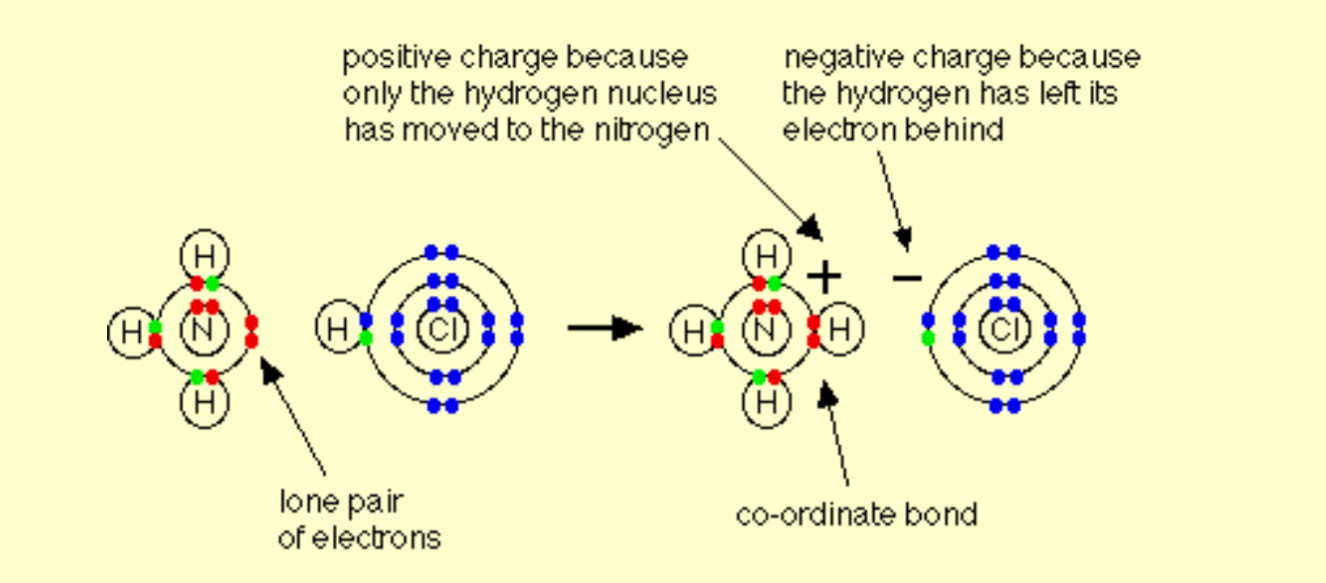
Describe the reaction between HCl and ammonia gases
NH3 + HCl → NH4Cl
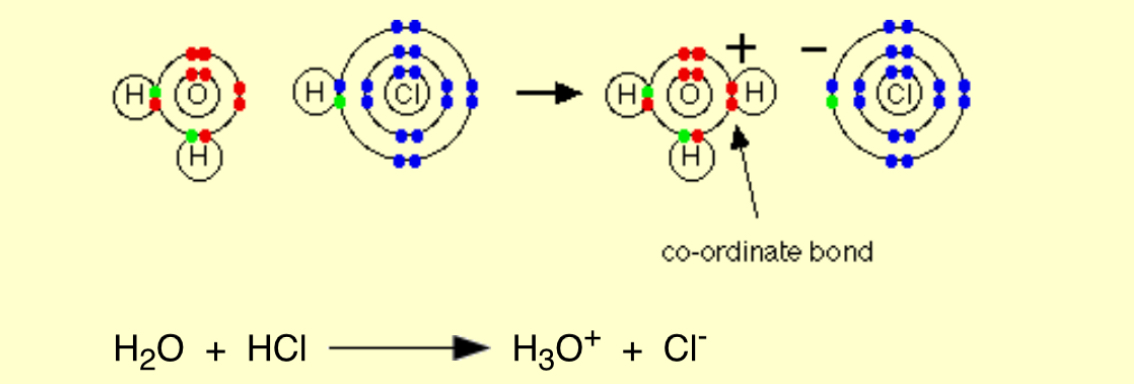
Describe the reaction of dissolving HCl in water
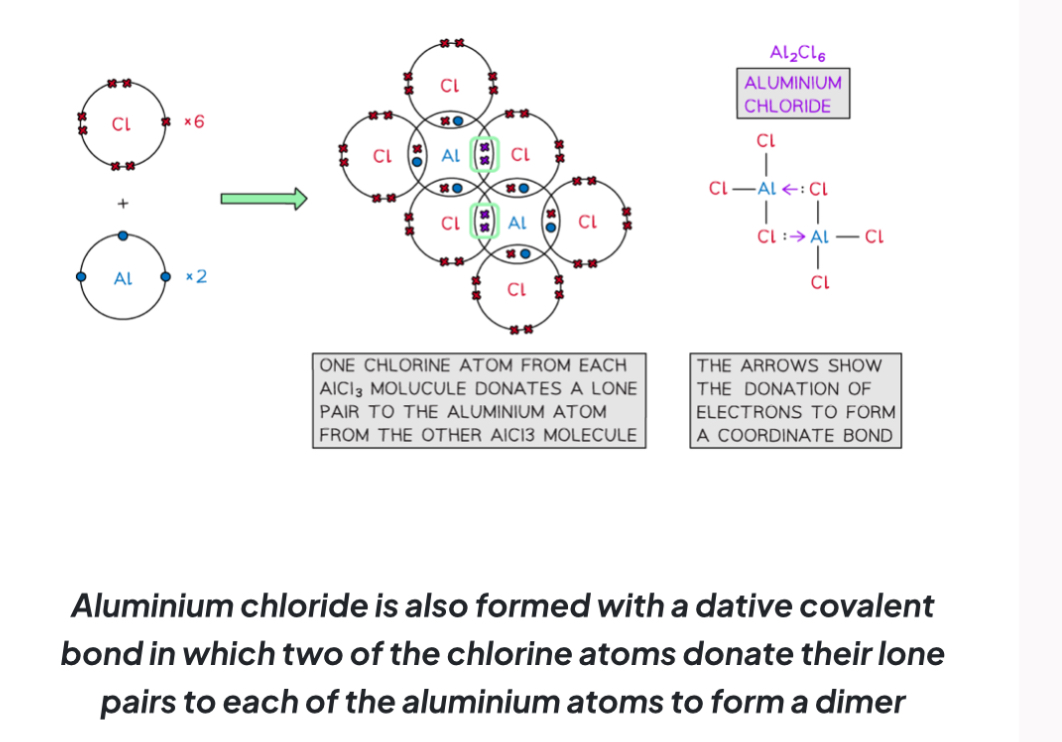
Describe the covalent bonding in Al2Cl6
Describe the covalent bonding in CO
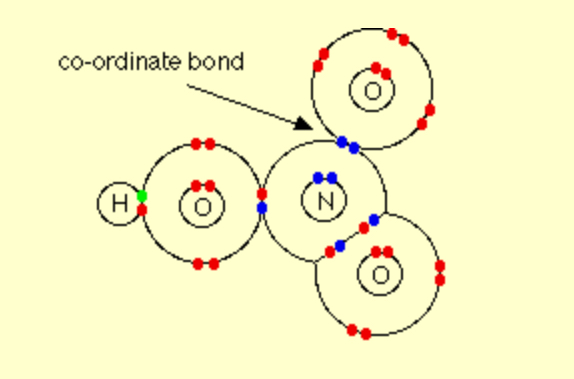
Describe the covalent bonding in HNO3
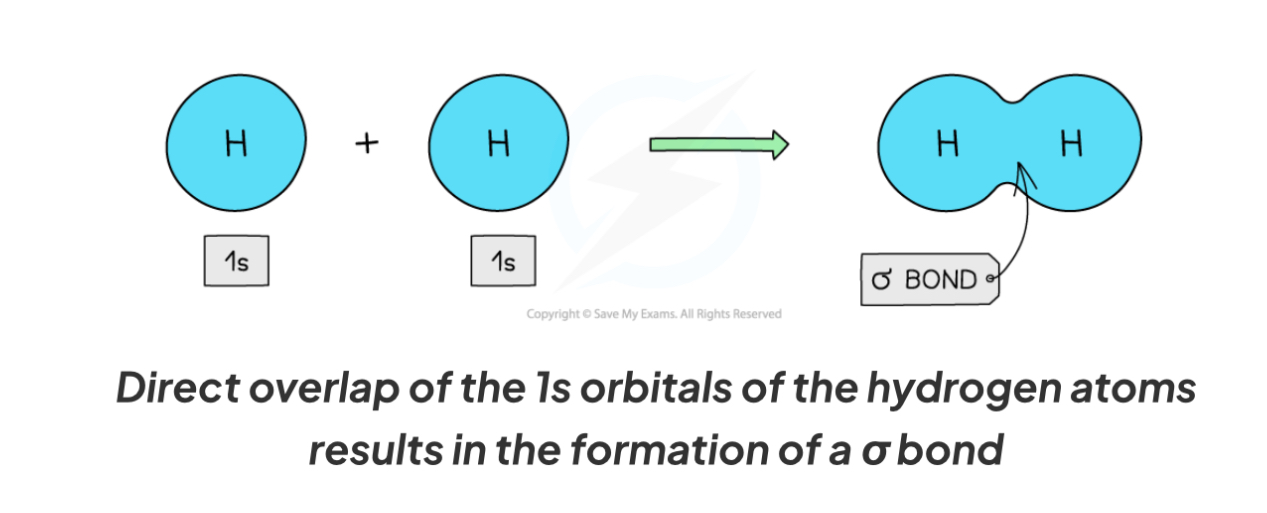
What is a Sigma bond?
Direct overlap of orbitals between the bonding atoms
What is a pi bond?
Formed by the sideways overlap of adjacent p orbitals above and below the sigma bond
How to sigma bonds form in H2
S orbitals of 2 H atoms overlap to form a sigma bond
How do sigma bonds form in C2H6
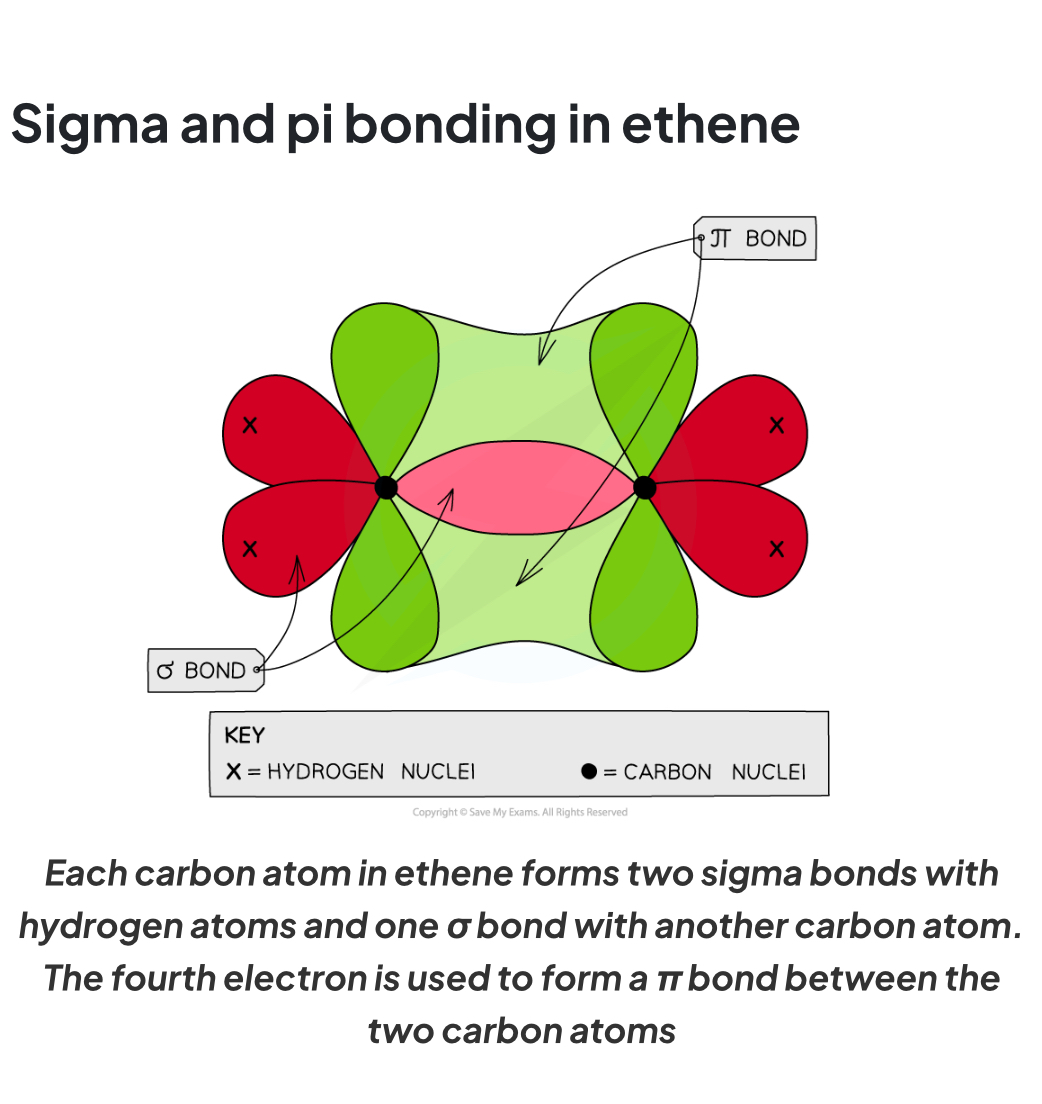
How do sigma and pi bonds form in C2H4
How do sigma and pi bonds form in HCN
Hydrogen cyanide contains a triple bond
One σ bond is formed between the H and C atom (overlap of an sp C hybridised orbital with the 1s H orbital)
A second σ bond is formed between the C and N atom (overlap of an sp C hybridised orbital with an sp orbital of N)
The remaining two sets of p orbitals of nitrogen and carbon will overlap to form two π bonds at right angles to each other
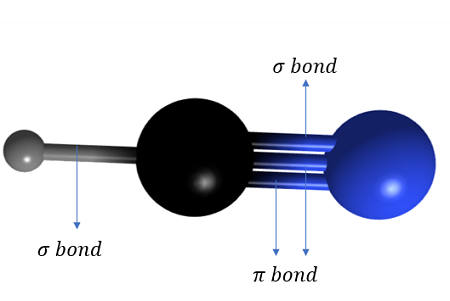
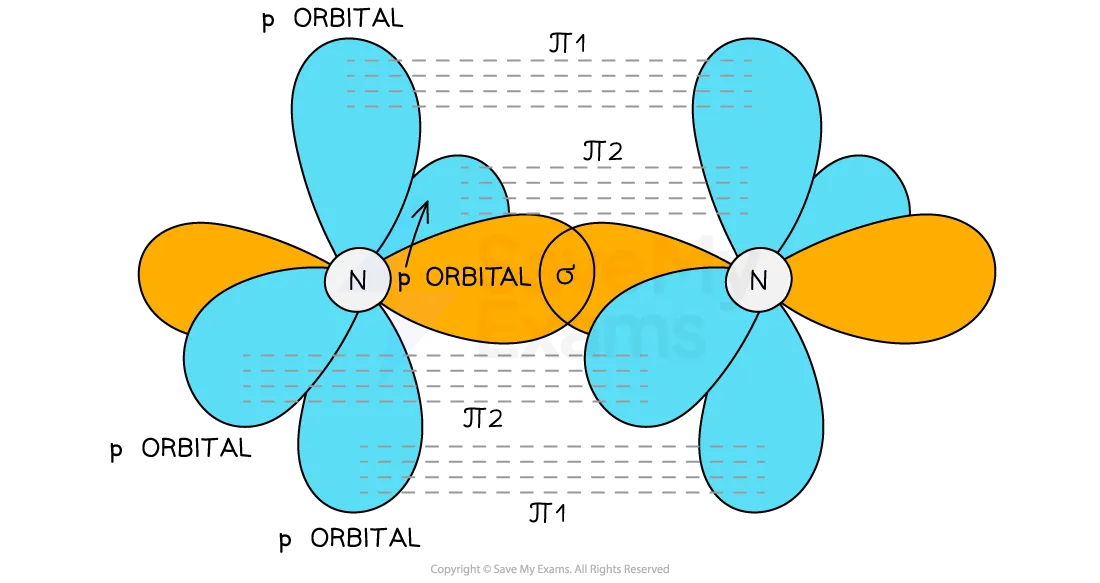
How do sigma and pi bonds form in N2
Nitrogen contains a triple bond
The triple bond is formed from the overlap of the sp orbitals on each N to form a σ bond and the overlap of two sets of p orbitals on the nitrogen atoms to form two π bonds
These π bonds are at right angles to each other
Define bond energy
The energy required to break one mole of a particular covalent bond in the gaseous state
Define bond length
Intermolecular distance of 2 covalently bonded atoms
What is sp3 hybridisation?
What is sp2 hybridisation?
What is sp hybridisation?