Applications of fermentation (lec 5)
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
Applications of fermentation:
Microbial biomass
Single cell protein
Baker’s yeast in baking industry
Microbial insecticides
Food production: vinegar
Metabolites production
Amino acids
Glutamic acid
Lysine
Organic acids
Citric acid
Lactic acid
Secondary metabolites production: antibiotics (penicillin)
Biopolymers
Glycocalyx
Xanthan
Biosurfactants
Rhamnolipids
Bioremediation
Biotransformation
Biofuels
Bioleaching
Immunological production
Vaccine production
Polio inactivated vaccine
Monoclonal antibody production
Muromunab-CD3
Nivolumab
Ex. of single cell protein used as dietary supplements:
Central Africa: Blue-green algae (cyanobacteria) human supplement “spirulina”
BP: petroleum fraction + candida sp.= torpina animal feed
ICI: methanol+ M. methylotropha bacteria= pruteen animal feed.
The m.o. used in production of Baker’s yeast is……………………………
Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Yeast is harvested by…………………..
centrifugation.
Give example of bacteria microbial insecticides:
Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) dried spores + prototoxins that solubilize the protein in the alkaline digestive tract of insects.
Summarize vinegar production.
Step 1: Alcoholic fermentation
Sugars are fermented by yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) into ethanol & CO2 (anerobic conditions)
Step 2: Acetic acid fermentation
Acetobacter bacteria oxidizes ethanol into acetic acid in an aerobic process.
Enzymes used in industry are mostly………………….
hydrolases.
Uses of microbial enzymes in industry:
Production of nutritive sweeteners from starch
Detergent industry (proteases & lipases)
Textiles industry (a-amylases, cellulase, proteases)
Leather bating (proteases)
Medical uses (penicillinases, fungal dextranases, proteases)
Common enzyme immobilization techniques.
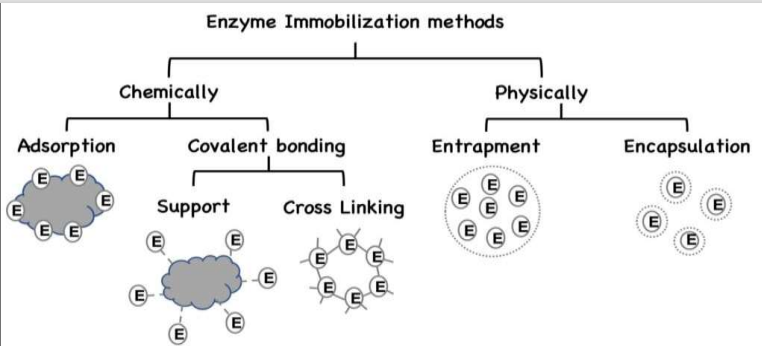
Give advantages, disadvantages and when to use immobilized cells over immobilized enzymes:
Advantages:
Cost effective
Convenient
Disadvantages:
Difficulty of substrate & production permeability
Byproducts may be formed
Lower yield
When to use:
When a cost-effective method is needed
When reaction has many metabolic steps
When enzyme extraction is difficult
Applications of immobilized enzymes:
Immobilized glucose oxidase in biosensors (glucose meters)
Immobilized glucose isomerase for high-fructose corn syrup production
Therapeutic amino acids and their uses include:
Glutamic acid production for neuropathic diseases
Lysine production for wound healing
Limiting biotin in glutamic acid production causes:
Increased permeability in bacterial cell wall to release the amino acid.
Inhibits enzyme, so that a-ketoglutarate gets mostly converted to glutamic acid, not oxaloacetate.
Overproduction of lysine amino acid require…………………of C. glutamicum, so we get a defective………………..enzyme and no threonine.
Homoserine mutant
Homoserine dehydrogenase
In citric acid, solid state fermentation is done on…………………………….
rice bran on aluminum pans.
In citric acid submerged fermentation, highest yield is in………………..phase. pH should be lower than………………………….
accumulation
3.5
To increase yield of citric acid in submerged fermentation,……………or…………….can be added.
ethanol or methanol
………………………….gives higher-yield of lactic acid in continuous fermentation.
Cell immobilization
Citric acid fermentation is………………….while lactic acid fermentation is……………………………
aerobic
anaerobic
Most important components in fermentation media for penicillin production:
The side-chain precursor, phenylacetic acid
Sulfur compounds because penicillin has sulphur
Fermentation phases in penicillin production:
First phase (trophophase) 30 hrs fungal growth
Second phase (idiophase) 5-7 days; penicillin production
Third phase: depleted C & N sources; production stops.
In penicillin production, why is it important to add sidechain precursor?
to avoid production of various natural penicillin mixtures which are difficult to separate.
In penicillin recovery, filtration is done by………………………. Extraction uses solvent…………………..and re-extraction needs ………………………..
Rotary vacuum filter
Butyl acetate
Aq. potassium buffer
Example of natural biopolymer:
glycocalyx on bacterial cell wall.
In the recovery of xanthan, precipitation is done by…………………………
alcohol.
Properties & applications of xanthan.
Properties:
Viscous
Thermally stable
Pseudoplastic
Applications:
Thickener in food
Hydrogel in pharmaceutics
Painting
Enhanced oil recovery
Applications of rhamnolipids:
Cleaning (eco-friendly detergent)
Antimicrobial activity
Enhanced oil recovery
In recovery/downstream processing of rhamnolipids, the end residue is………………….
honey-colored.
Microbes used in bioremediation:
genetically engineered Pseudomonas putida
Give examples of steroids biotransformation.
Plant-derived diosgenin or animal-derived cholesterol—→ Progesterone—→ by fungus—→Cortisone.
Cortisol—→ Corynebacterium simplex cells—→ prednisolone.