Primitive Reflexes & Atypical Development
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
Reflex =
Stereotyped response to sensory input
primitive reflexes
Reflexes that develop in the womb to facilitate postural control, health and safety of the infant
Predictable Motor Response triggered by proprioceptive, tactile, and vestibular stimulation
Purpose is to facilitate typical development for purposes of survival and new movement patterns
Postural Reflexes
(supine flexion, prone extension)
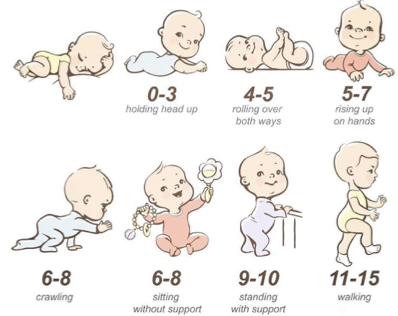
goal of primitive reflexes
is to help an individual move against gravity and develop voluntary movement
integration
•Typically integrate in 1st year of life
•When a reflex is “integrated” it has developed into a more mature movement pattern.
•The reflex is no longer present
persistence
•RETAINED
•May indicate atypical development
•The reflex is still present
•The more mature movement pattern has not developed
•Child did not experience enough movement related to that reflex and the response.
•lower-level developmental delays
• Hindered development of the advanced stage of the nervous system
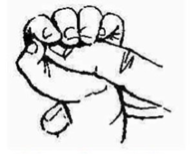
Palmar Grasp Reflex
Onset: Birth
Integration: 5-6 Months
Voluntary Grasp replaces it
Automatic flexing fingers to grab objects
Palmar Grasp Reflex test
Placing your finger or an object into your baby's open palm, which will cause a reflex grasp or grip
Retained Reflex:
Poor manual dexterity, Poor pencil grip, Messy handwriting,
palmar grasp reflex case example
10m old female baby with PMH of torticollis and low tone.
OT referral: Increased flexion of digits when crawling
Standardized Assessment: PDMS-2
Grasping Standard score 6; VMI standard score 7 (Below average)
Grasp
Immature grasp with ulnar side of hand; gross raking without thumb, no clear open web space
Index finger not integrated with grasp; pincer grasp not observed
VM:
Poor precision with Put in tasks (removing pegs) Poor graded control (placing cubes in cup)
Goal Areas: Promote radial digital grasp, WB with full wrist and digit extension; Graded control with grasp and release
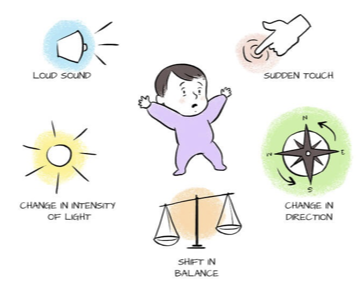
MORO Reflex
Onset: 28 Weeks Gestation
Integration: 4-6 Months
Occurs in response to unexpected changes in environment
Noise
Change in position
Light
Sudden Touch
Function: Flight or Fight Response
Moro reflex test
Rapidly Drop Head Backwards
Response
Phase 1: Arm Extension & Abduction
Phase 2: Arm Flexion & Adduction
moro reflex integrated test results
test: •Rapidly Drop Head Backwards
•Result: NO Arm Extension/Flexion & Abduction/Adduction
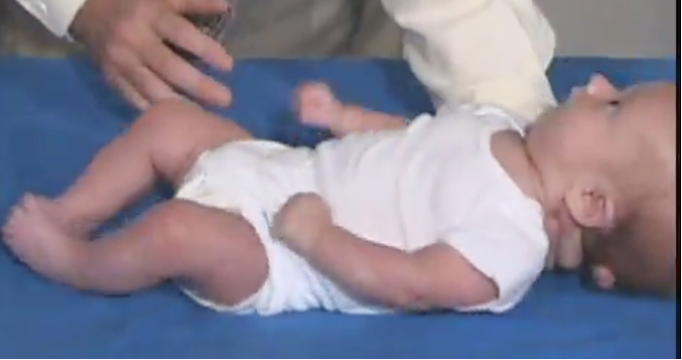

Retained Moro Reflex
•Persistence Effects: Impacts sensory modulation, hypersensitivity
•Visual, auditory, vestibular: Decreased balance and coordination, Gravitational Insecurity
•Constant state of “fight or flight”
•Poor impulse control: Distractibility
•Mood swings, emotional outbursts
Onset: 37 Weeks Gestation
Integration: 4-6 Months
Function: Precursor to Hand Eye Coordination
Rolling over stomach
Crawling
Reading/writing
Crossing Midline
Distribution of Muscle tone
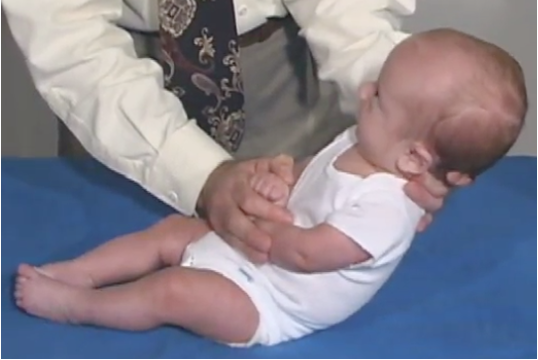
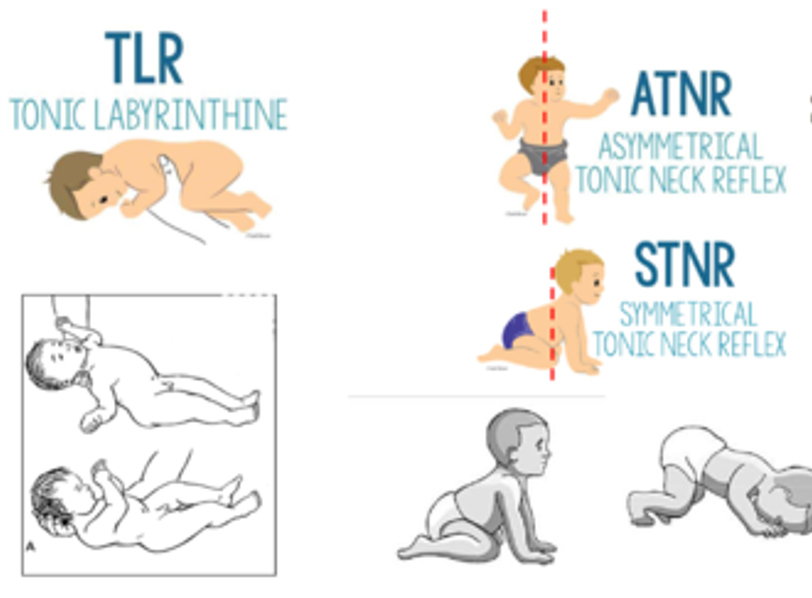
Asymmetrical Tonic Neck Reflex (ATNR) test
•Test: Position Baby in Supine & Rotate Head
•to 90 Degrees.
•Response
•Face Side: Arm Extension
Skull Side: Arm Flexion
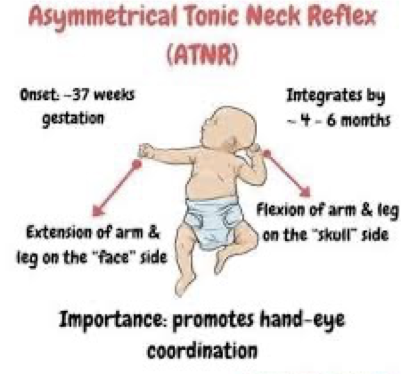
Persistence Effects of ATNR
Unable to Cross Midline (eyes/hands): impacts creeping and crawling
Poor Reading Comprehension
Poor Visual Tracking & Eye Pursuits
Poor Handwriting
Poor Hand Eye Coordination
Poor bilateral coordination
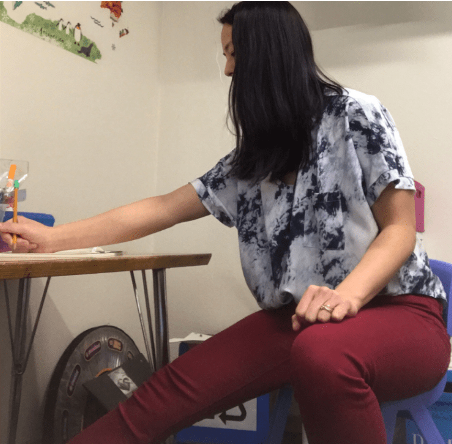

Writing compensations bc of ATNR
tight pencil grasp, turning paper, decreased fluency, extended arm, writing w/ slant, letter reversals

Tonic Labyrinthine Reflex (TLR)
•Onset: 37 Weeks Gestation
•Integration: 6 Months
•Function:
•Development of Balance, Body Position & Stability
•Balances Flexion and Extension Tone
•Head Neck Alignment and control
•Body/Head Trunk Dissociation
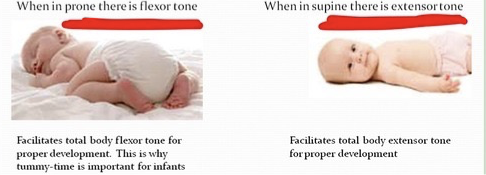
There are 2 aspects of TLR:
TLR Test
TLR PRONE and TLR Supine.
Retained: TLR: prone flexion and supine extension

persistence effects of TLR
Difficulty with Prone Extension (Increased Flexor Tone)
Difficulty with supine to sit (Increased Extensor Tone)
Poor Posture (W sit)
Poor Coordination
Impacts Auditory Processing
Impacts Visual Perception
Low muscle tone
Decreased chin tuck (impacts feeding)

Symmetrical Tonic Neck Reflex (STNR)
Onset: 4-6 months
Integration: 8-12 Months
Function: Precursor to Crawling –
Ability to sustain static Quadruped Position
Disassociation of the upper and lower body
Assists in Bilateral Patterns of Movement
Allows for antigravity movement
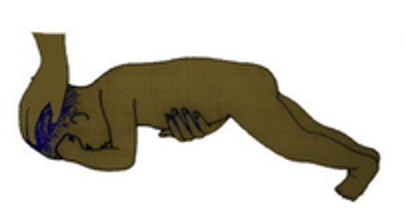
STNR Test
place in crawling position and flex the head → arms flex, legs extend
place in crawling position and extend the head → arms extend, legs bend
UB & Head = same response -> NO UB & Head Dissociation
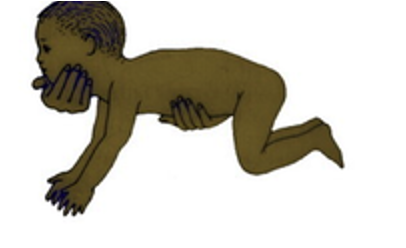
persistence effects of STNR
•Difficulty sitting up from supine
•Poor muscle tone and posture (W-sit)
•Impacts Focus

Research Connection Retained Reflexes and ADHD
•Survival-oriented and automatic movements are not integrated within infant development
•Prone to hyperactivity or impulsivity due to sensory and motor dysfunction
•Systematic Review (189 articles)
•Retained primitive reflex results in over active brainstem; which inhibits the limbic system and cerebral cortex which may lead to neurodevelopmental disorders
•Systematic Review (189 articles)
•Significant positive and moderate Correlation between primitive reflexes and ADHD.
•Higher the degree of ATNR and STNR non-integration, more severe the ADHD symptoms in children.
•Correlation with ADHD and retained ATNR: anxiety, impulsivity-hyperactivity, and learning problems in children with ADHD.
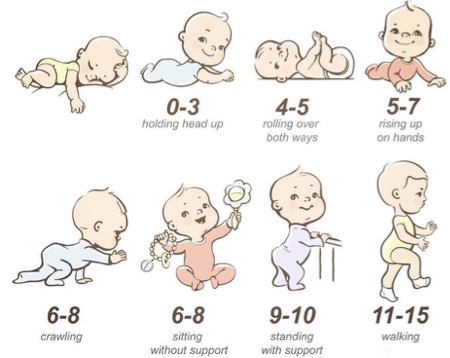
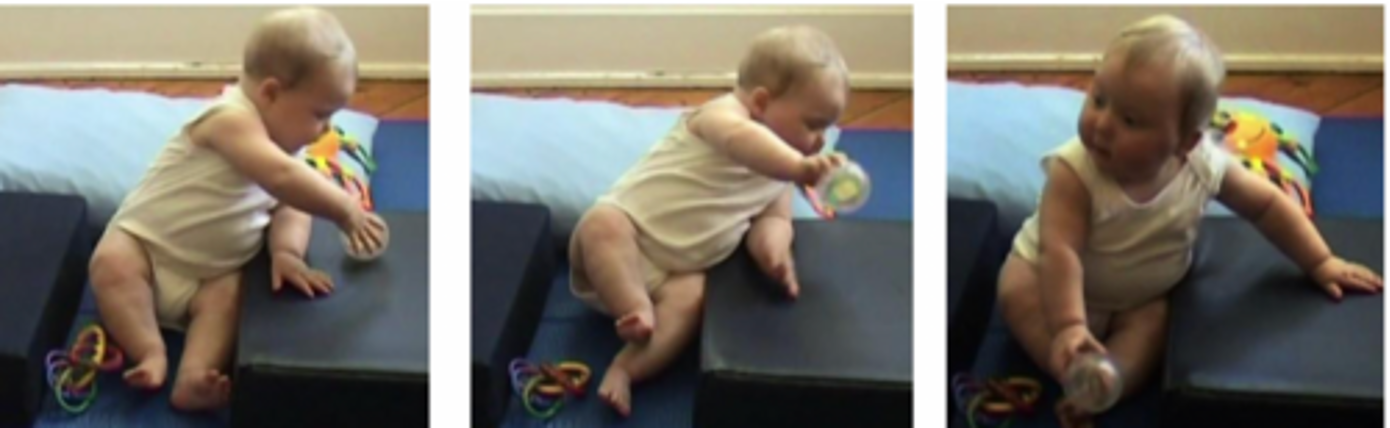
Primitive Reflex Integration Impact on Motor Milestones at 4-6 M
Moro and ANTR
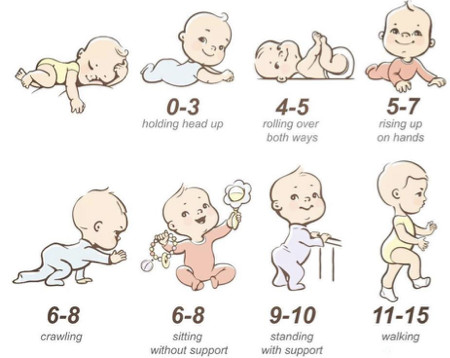
Primitive Reflex Integration Impact on Motor Milestones at 6 M
TLR reflex
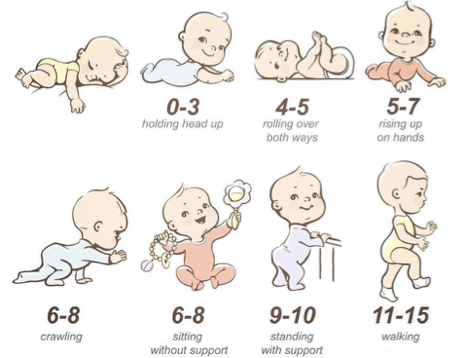
Primitive Reflex Integration Impact on Motor Milestones at 8-12 M
STNR
Primitive Reflexes: Take Away
•GOAL: Help integrate Reflexes that are retained longer than usual
•Choose standardized tools to connect impairment to occupational performance.
•Always Link it to Occupation!
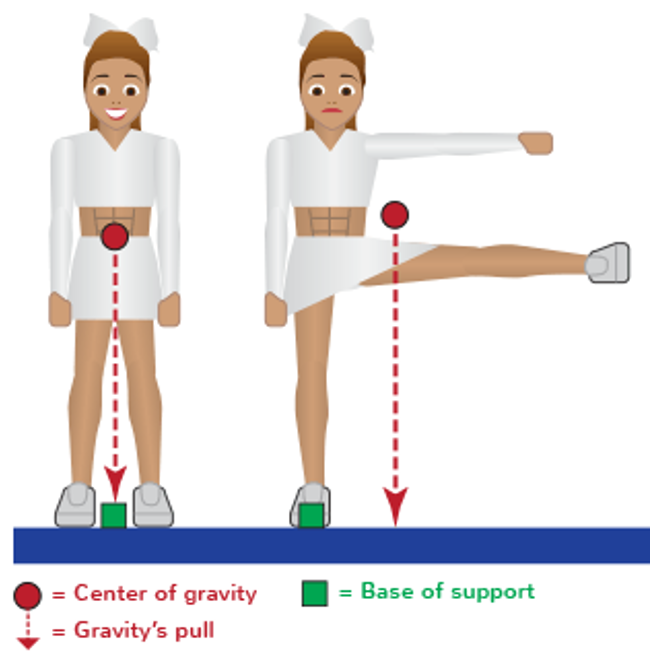
postural control
•Foundation for movement:
•Postural stability allows for distal mobility
•Ability to control center of mass in relation to base of support
•Postural Reflexes:
•Supine Flexion
•Prone Extension
assessment of movement
Quality of Movement and Postural Control
Impact on Occupational Performance:
Feeding, Play, Functional Mobility, Dressing
Consideration in all Pediatric Settings
NICU
In patient Rehabilitation
Acute
School
Early Intervention
Outpatient
Development of Postural Control
ring
long
side
tailor

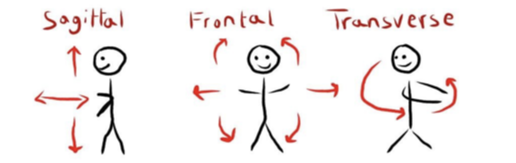
sagittal plane of movement (double check)
right and left
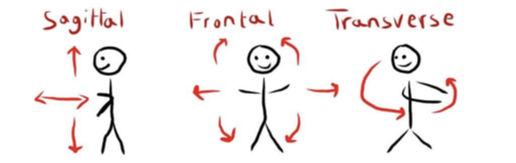
frontal plane of movement (double check)
up and down
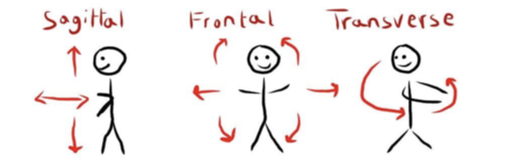
transverse plane of movement (double check)
cross body
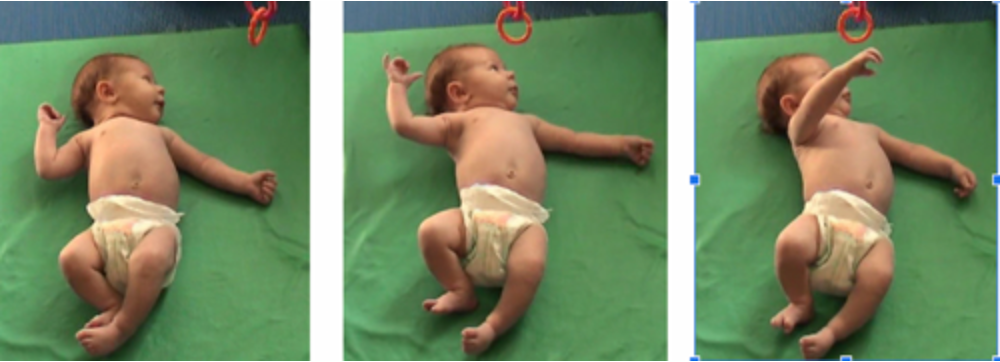
sagittal weight shifts
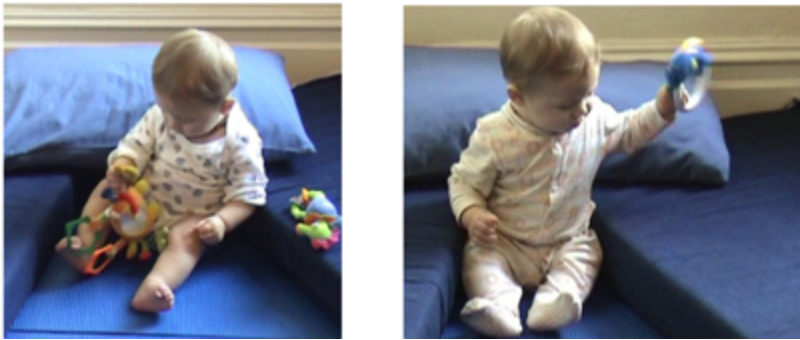
frontal weight shifts
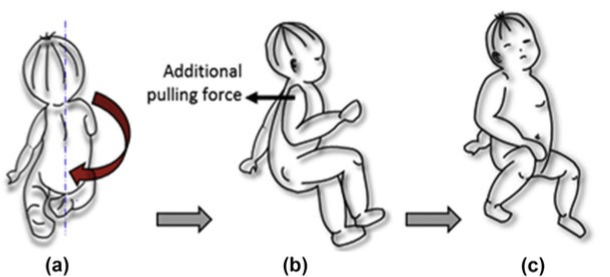
Transverse Weight Shifts

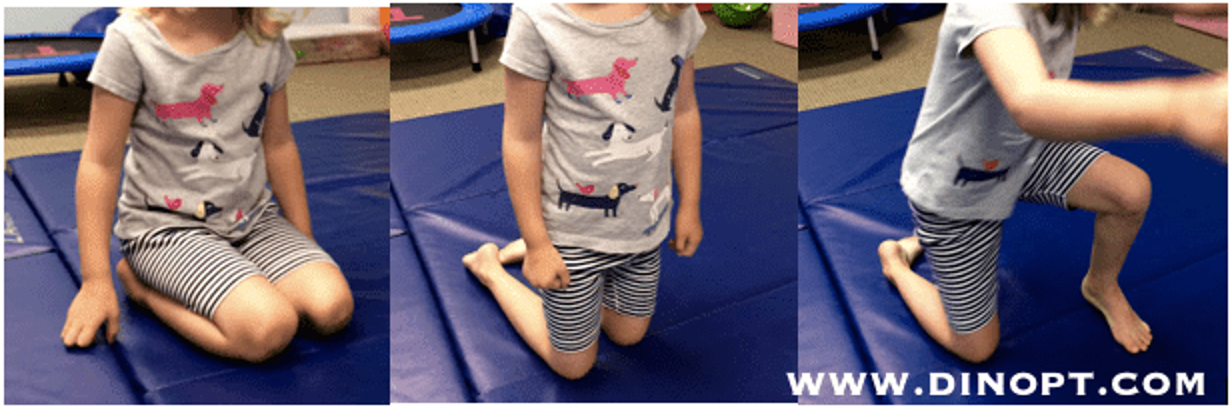
Prone to sit: Moving Different planes

Transitional Movements (sit)

transitional movements: 4 point/Quadruped

transitional movements: half kneel → tall kneel → tall kneel to stand

