Session 2: Dermatomes and Segmental Innervation of the Limbs
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
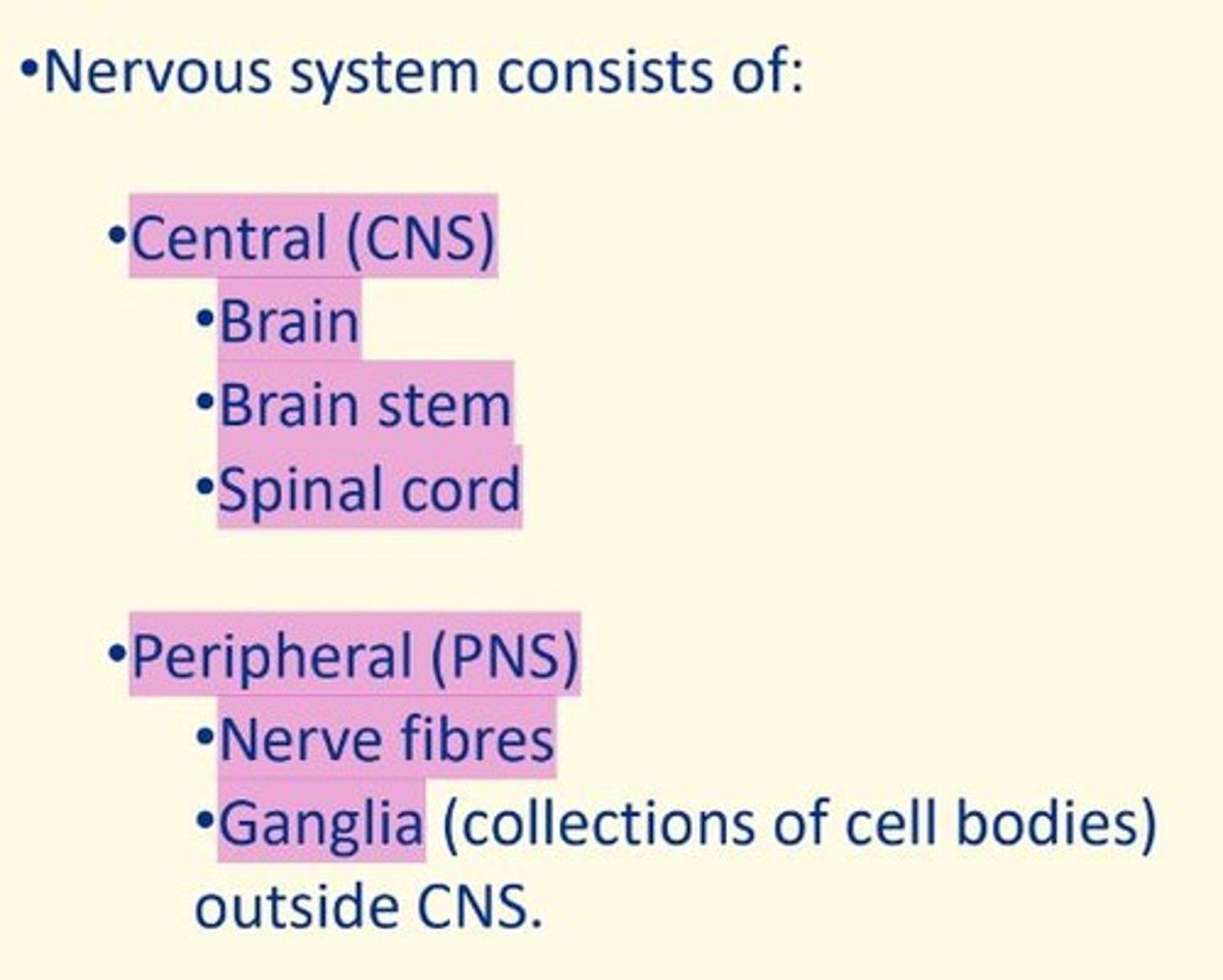
What are the anatomical divisions of the nervous system?
CNS = brain, brainstem, spinal cord
PNS = nerve fibers, ganglia (collection of cell bodies)
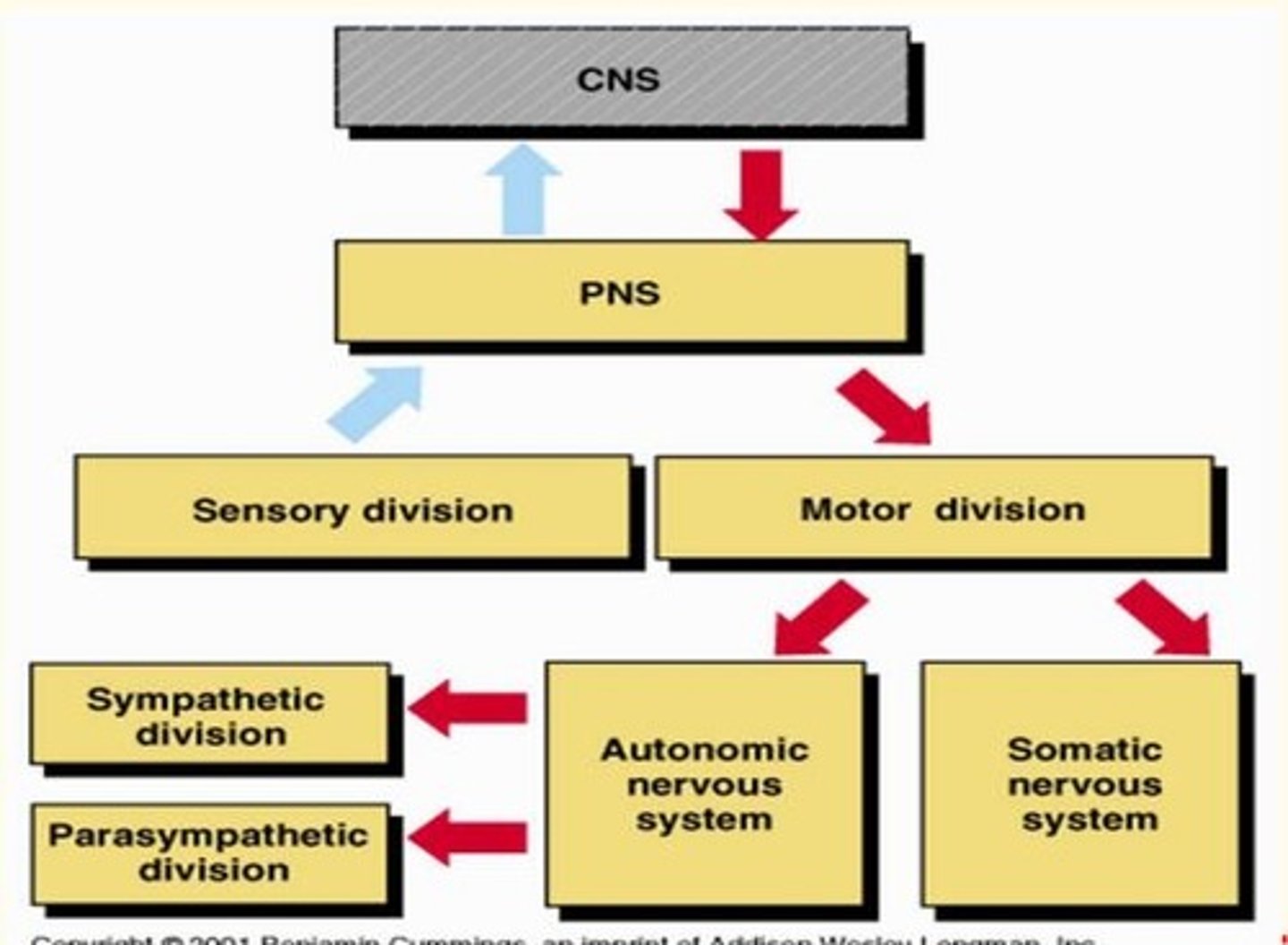
What are the functional divisions of the nervous system?
PNS = sensory division + motor division
Motor division = somatic (voluntary) + autonomic (involuntary)
ANS = sympathetic (speeds up) + parasympathetic (slows)
How many cranial nerves do we have?
12 pairs of cranial nerves
2 pairs emerge from brain
10 pairs emerge from brainstem
How many spinal nerves do we have?
31 pairs of segmental nerves from spinal cord
Most are mixed - carry afferent and efferent signals
Spinal nerves are examples of mixed nerves. What does this mean?
Spinal nerves are mixed nerves. This means they carry both afferent and efferent signals.
Afferent neurons
Nerve cells that carry (sensory) impulses towards the central nervous system
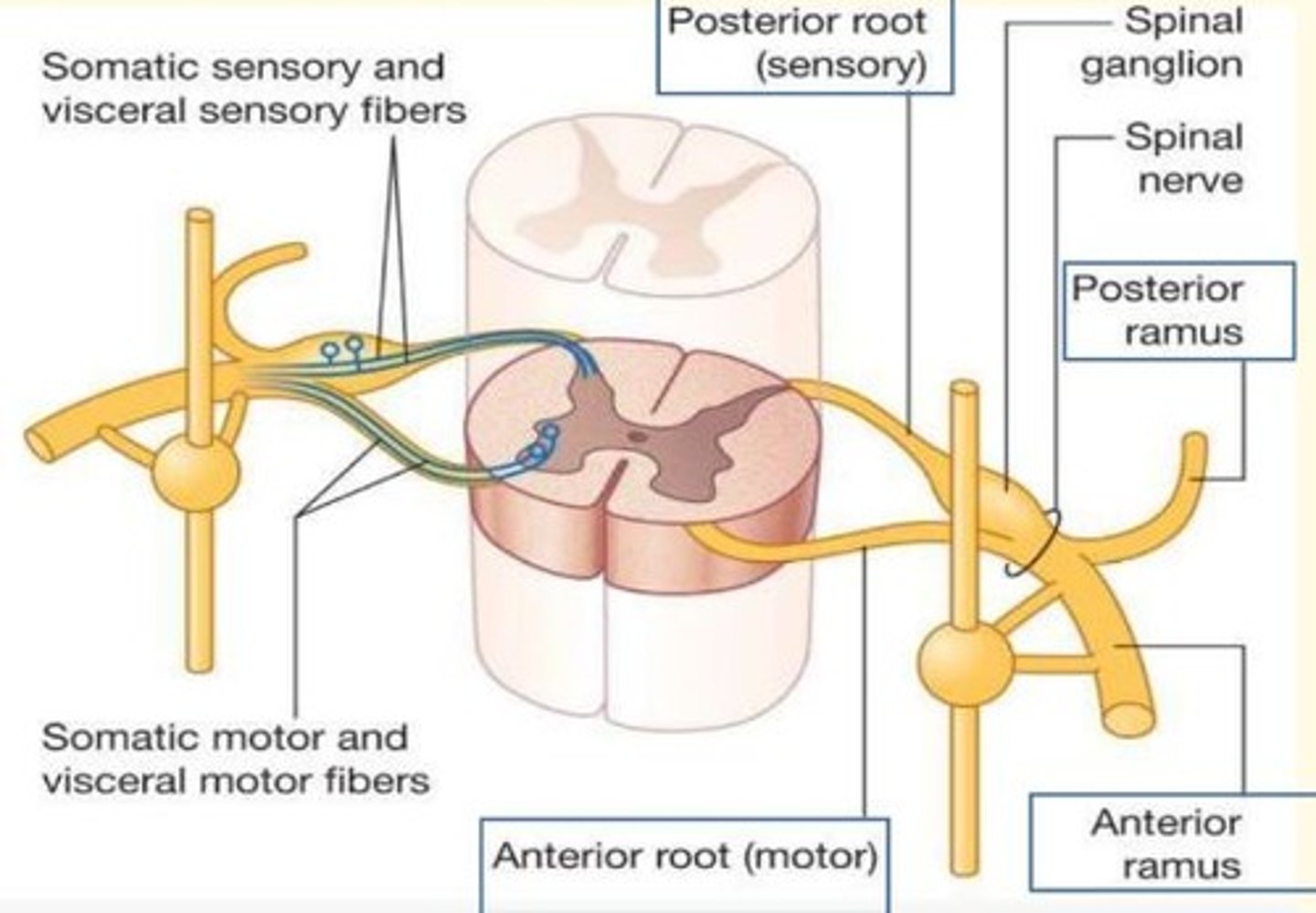
Efferent neurons
Nerve cells that carry (motor) impulses away from the CNS to the muscles/glands of body in order to initiate an action.
The CNS is segmented. What does this mean?
Each segment of nervous tissue connects independently to the periphery.
Sensory nerves serve discrete territories of skin.
Motor nerves serve myotomal territories.
Each segment has left and right sides.
Each segment is also known as a ___ ___
Neural level
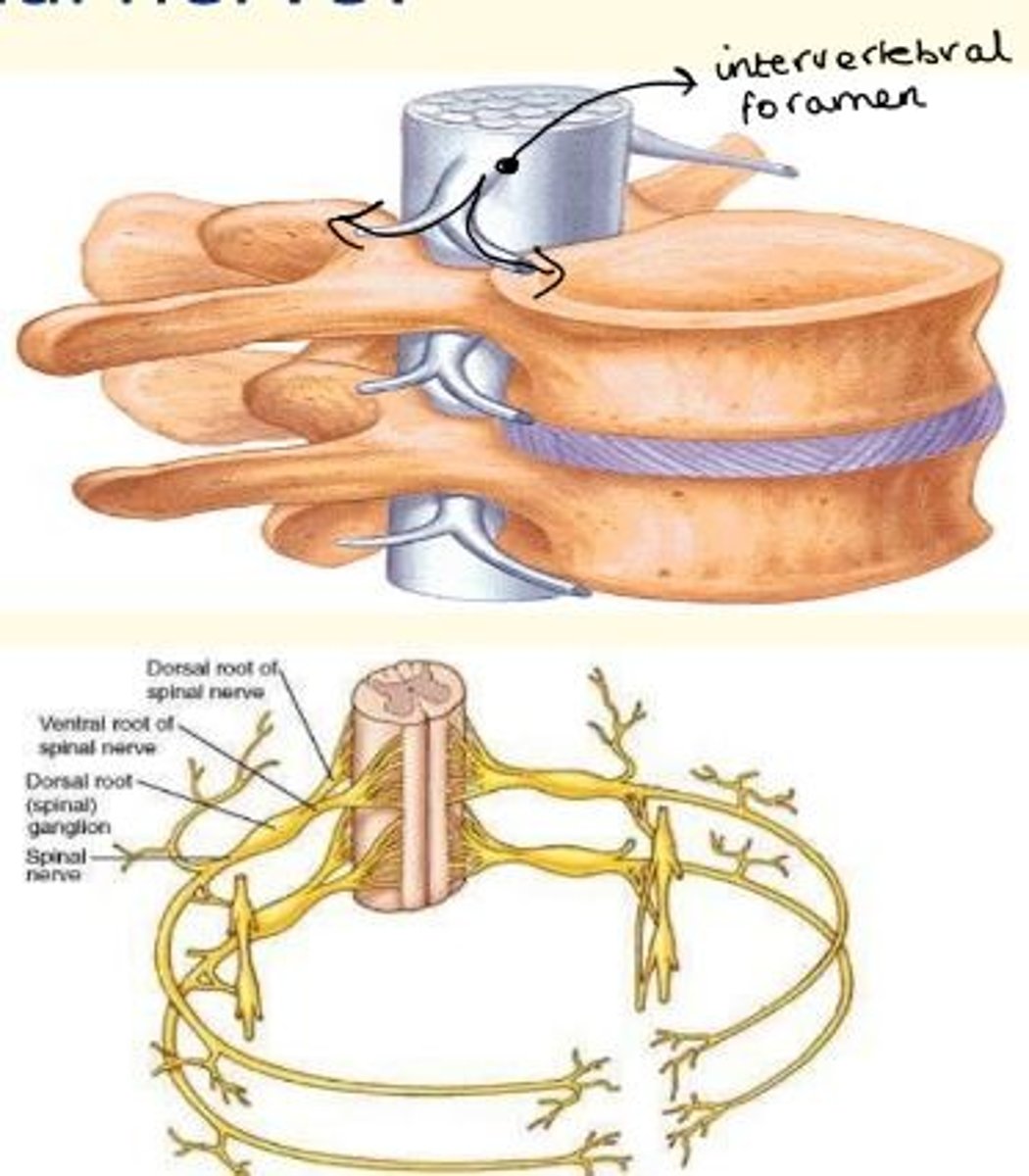
What is a segmental spinal nerve?
At each vertebral level, the spinal cord gives out a pair of nerves - left and right.
These exit the vertebral column via the intervertebral foramina.
The adult spinal cord ends at...
L1
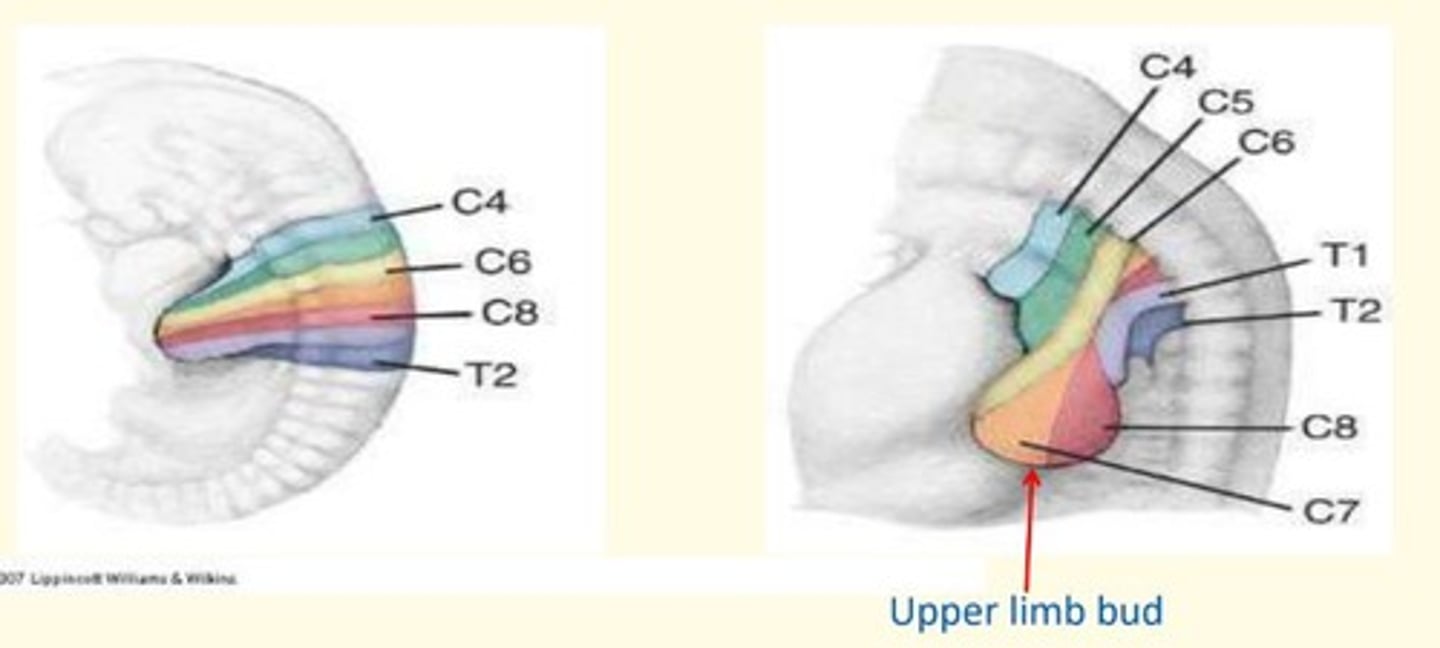
The segmented embryonic spinal cord
C4-C8
T1-T2
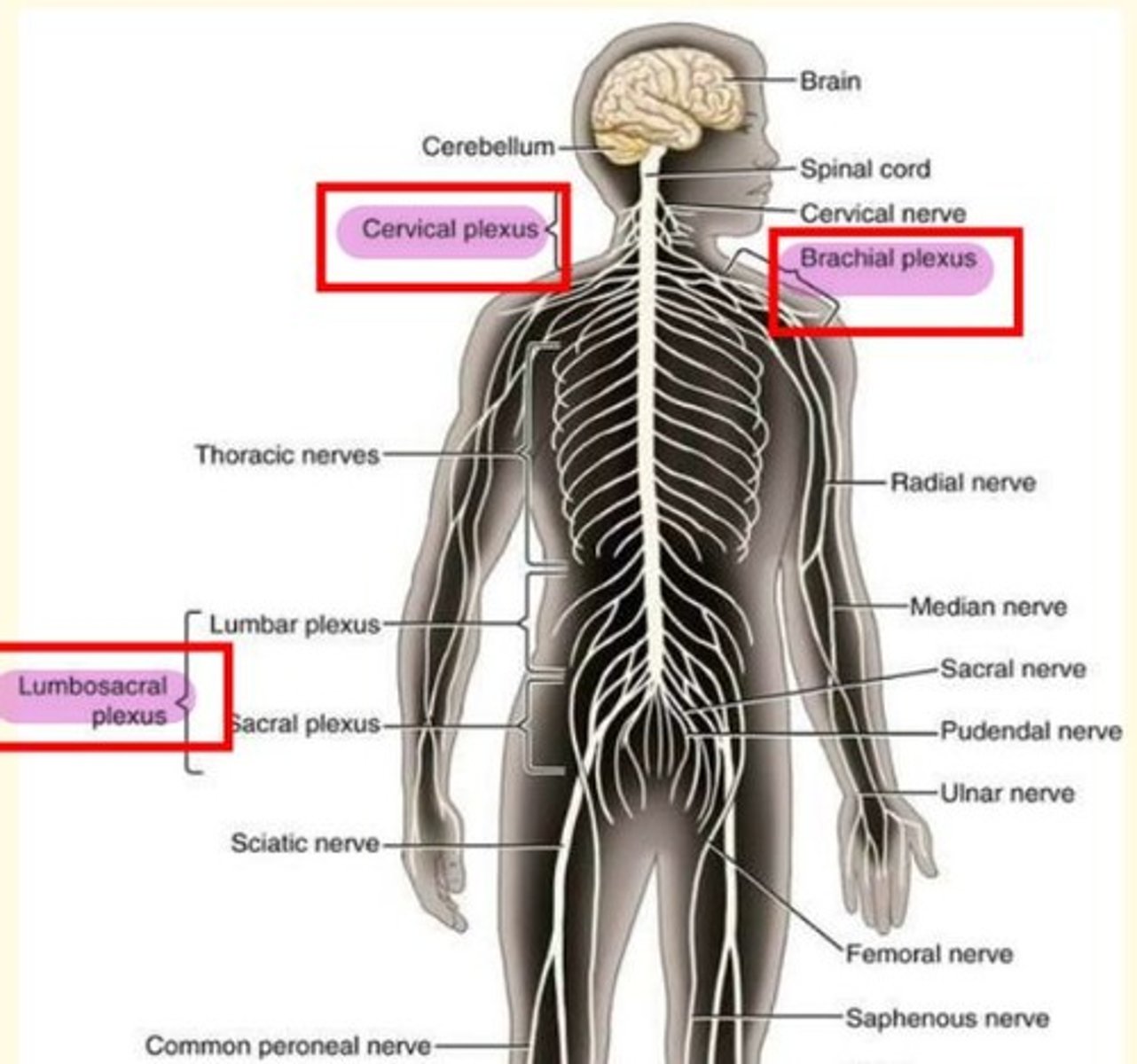
Why is having a plexus important?
Having a plexus means that damage to a spinal nerve won't leave the entire limb paralysed
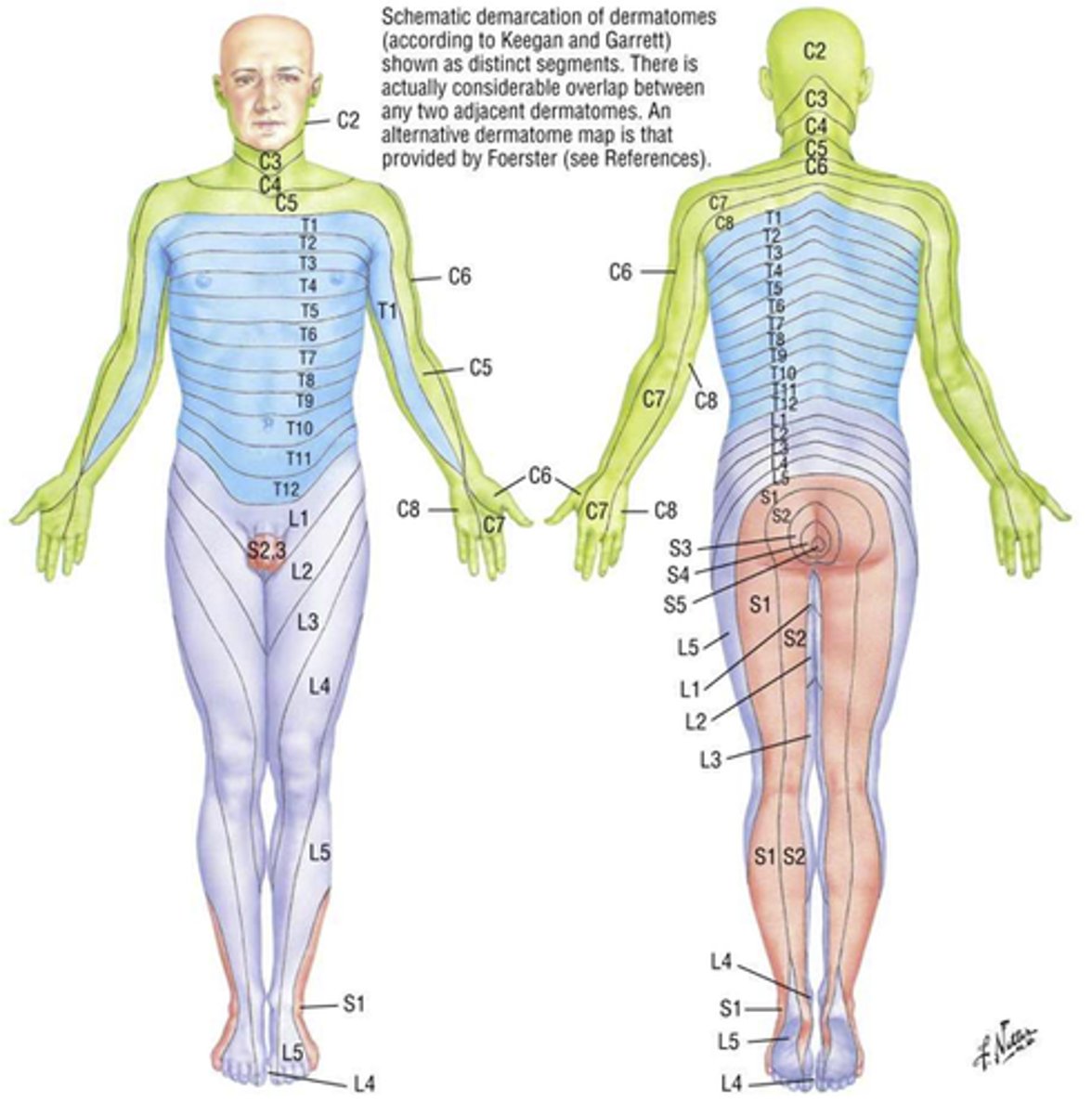
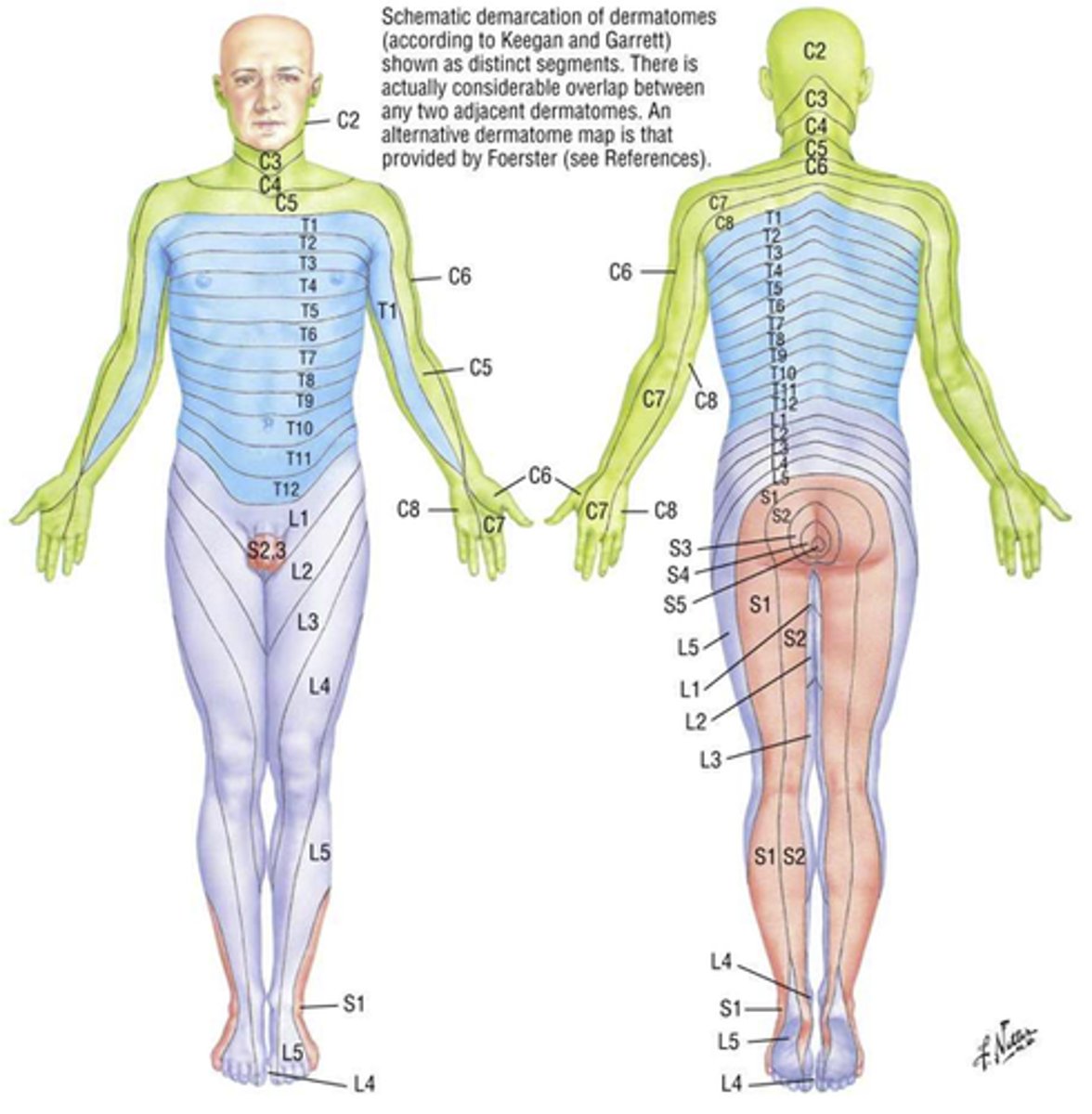
Dermatome
Area of skin supplied by a single spinal nerve
Some overlap
Myotome
Group of muscles that a single spinal nerve innervates
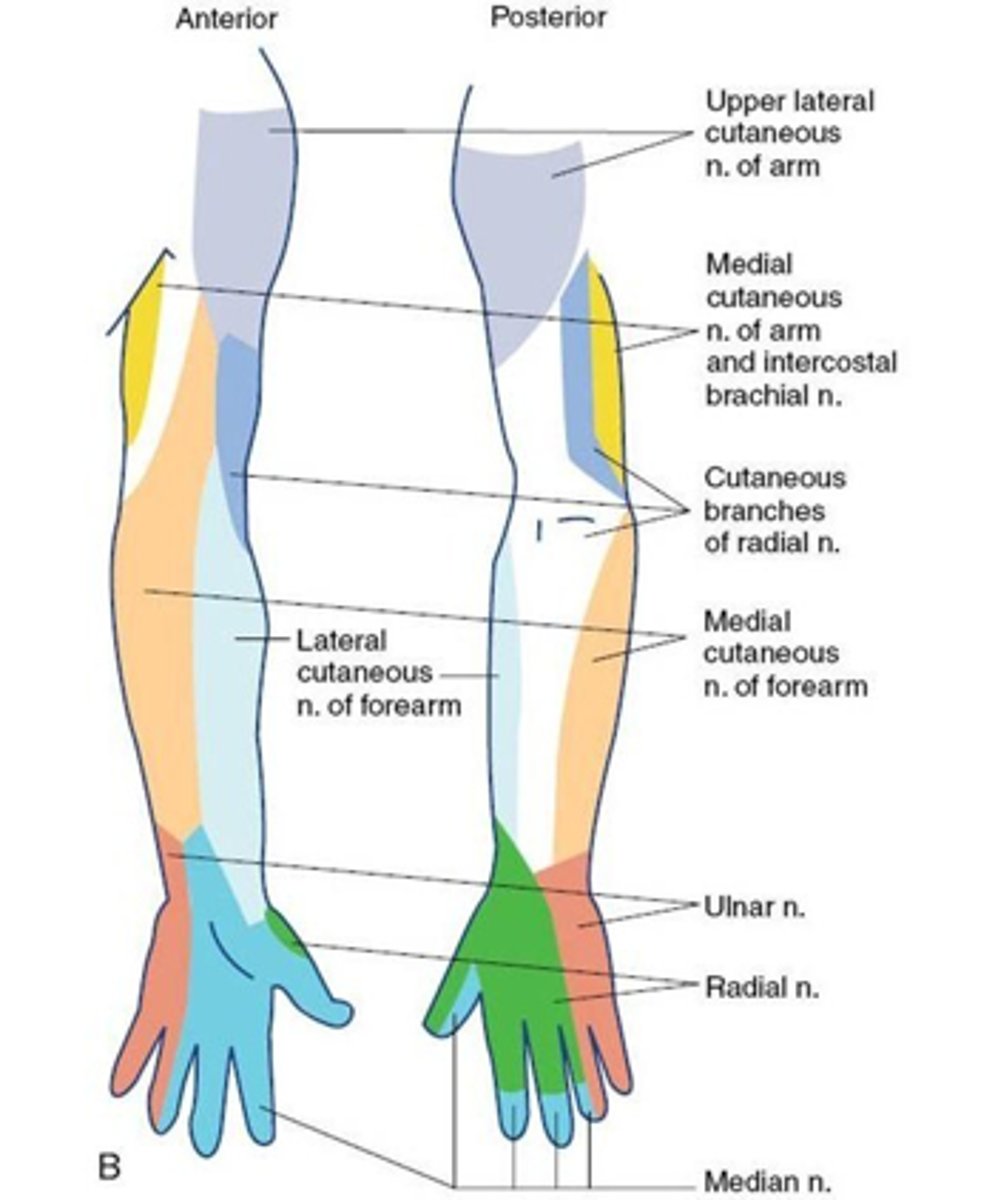
Cutaneous distribution of a peripheral nerve
Area of skin the peripheral nerve innervates - nerve fibers form several spinal roots
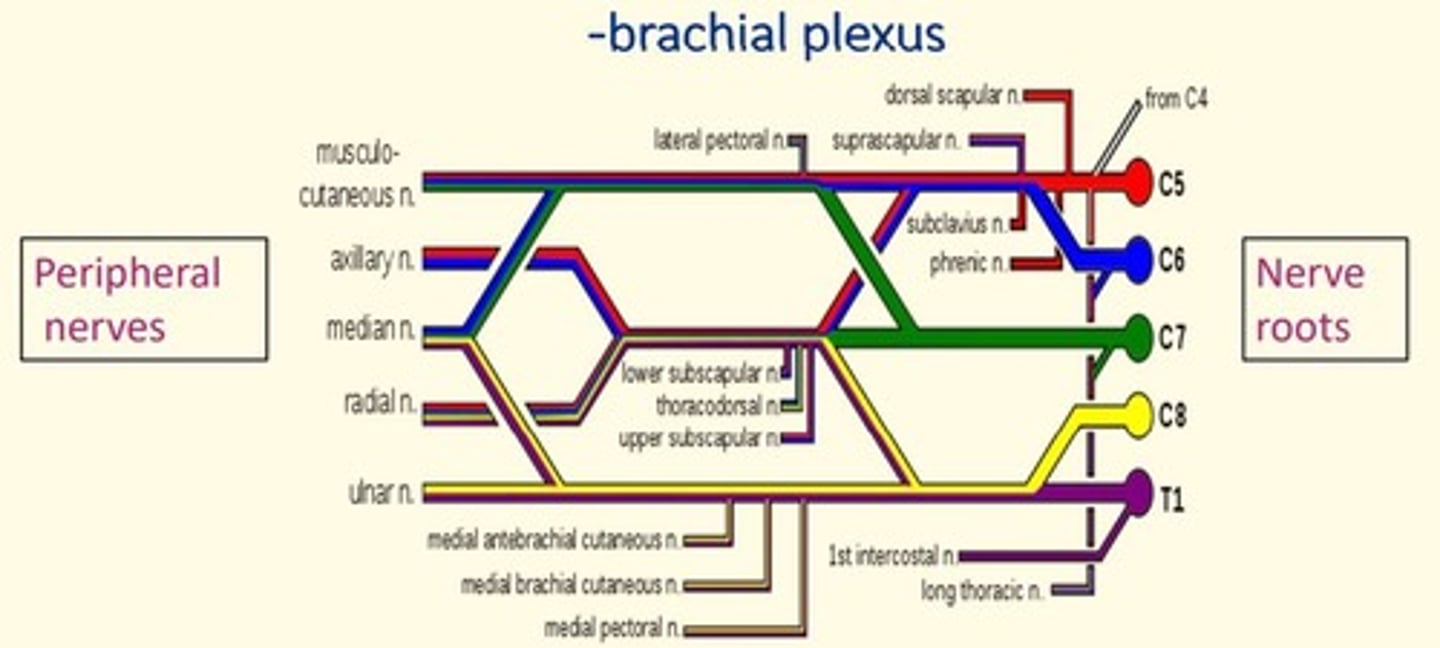
Brachial plexus
Network of interlacing nerves found in the upper arm area
C5-C8, T1
Dermatome
Cutaneous area of skin innervated by a single spinal nerve.
Neurons from a spinal nerve can travel from dermatome via multiple routes/nerves.
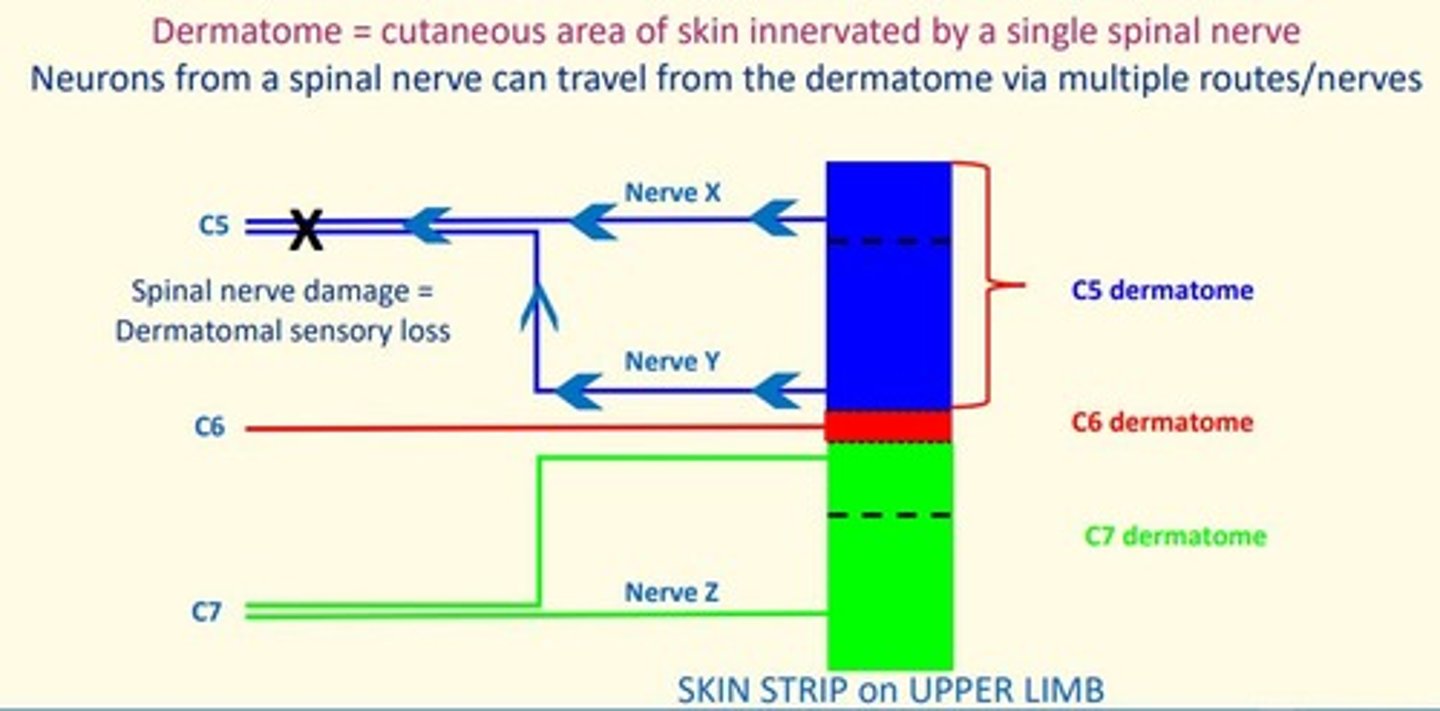
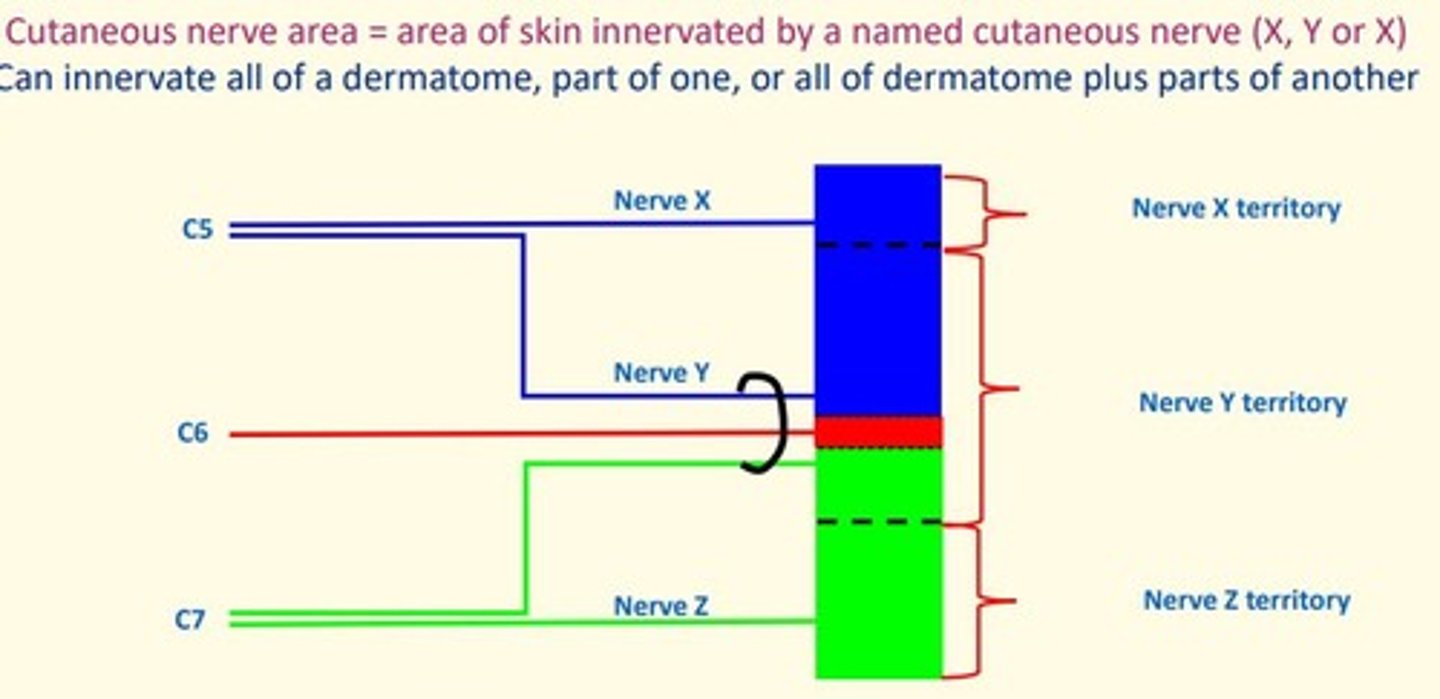
Cutaneous nerve area
Area of skin supplied by a named cutaneous nerve
There are different patterns of loss which occur depending on the ___ of the lesion
There are different patterns of loss which occur depending on the level of the lesion
Lesion of the spinal root (close to spinal cord) will result in loss of sensation in dermatome and myotome.
Distal lesion (e.g., axillary nerve in axilla) will result in loss of sensation in peripheral nerve field (regimental badge area)
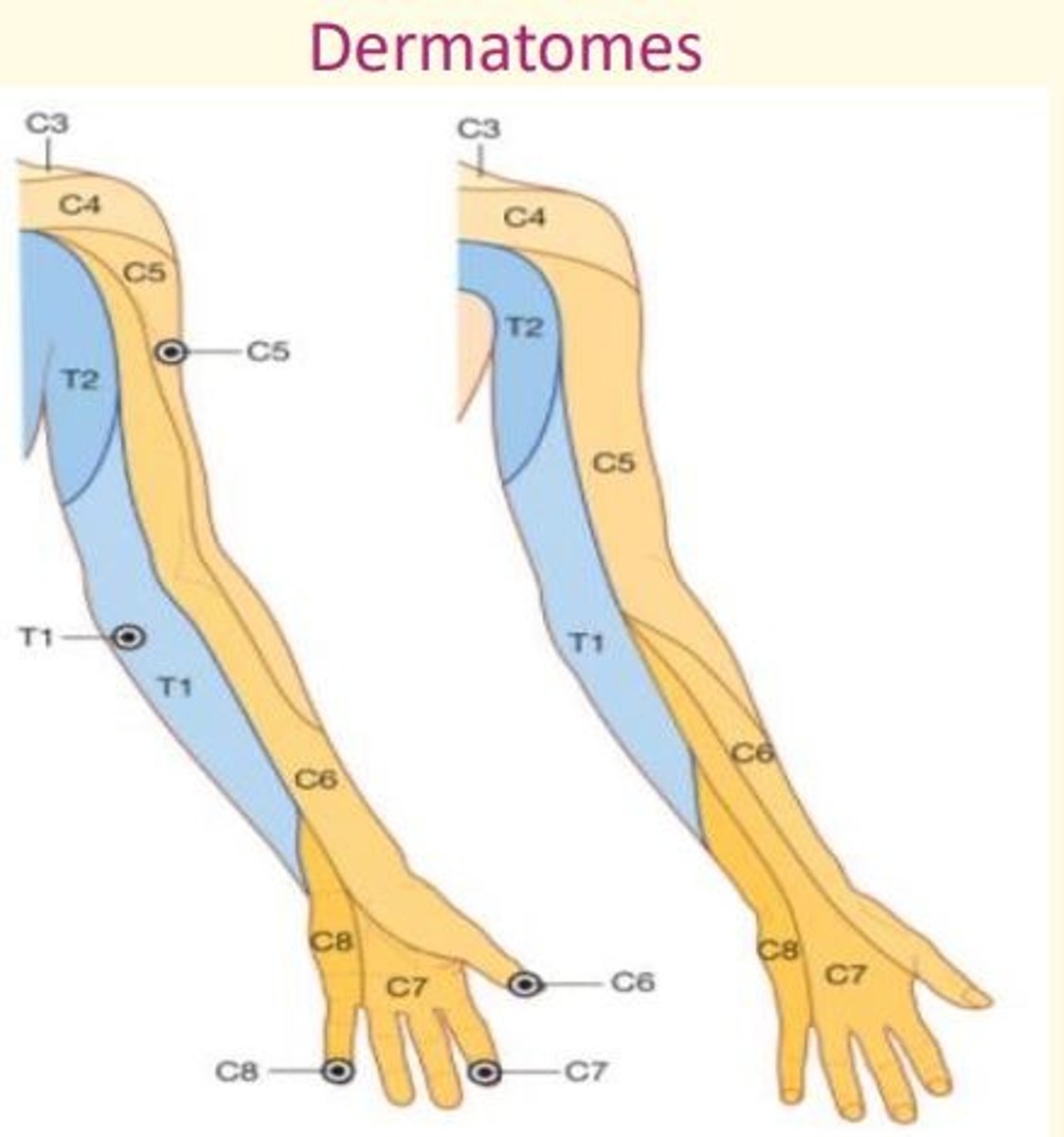
Dermatomes of the upper limbs
Innervated by ventral rami from C5-T1
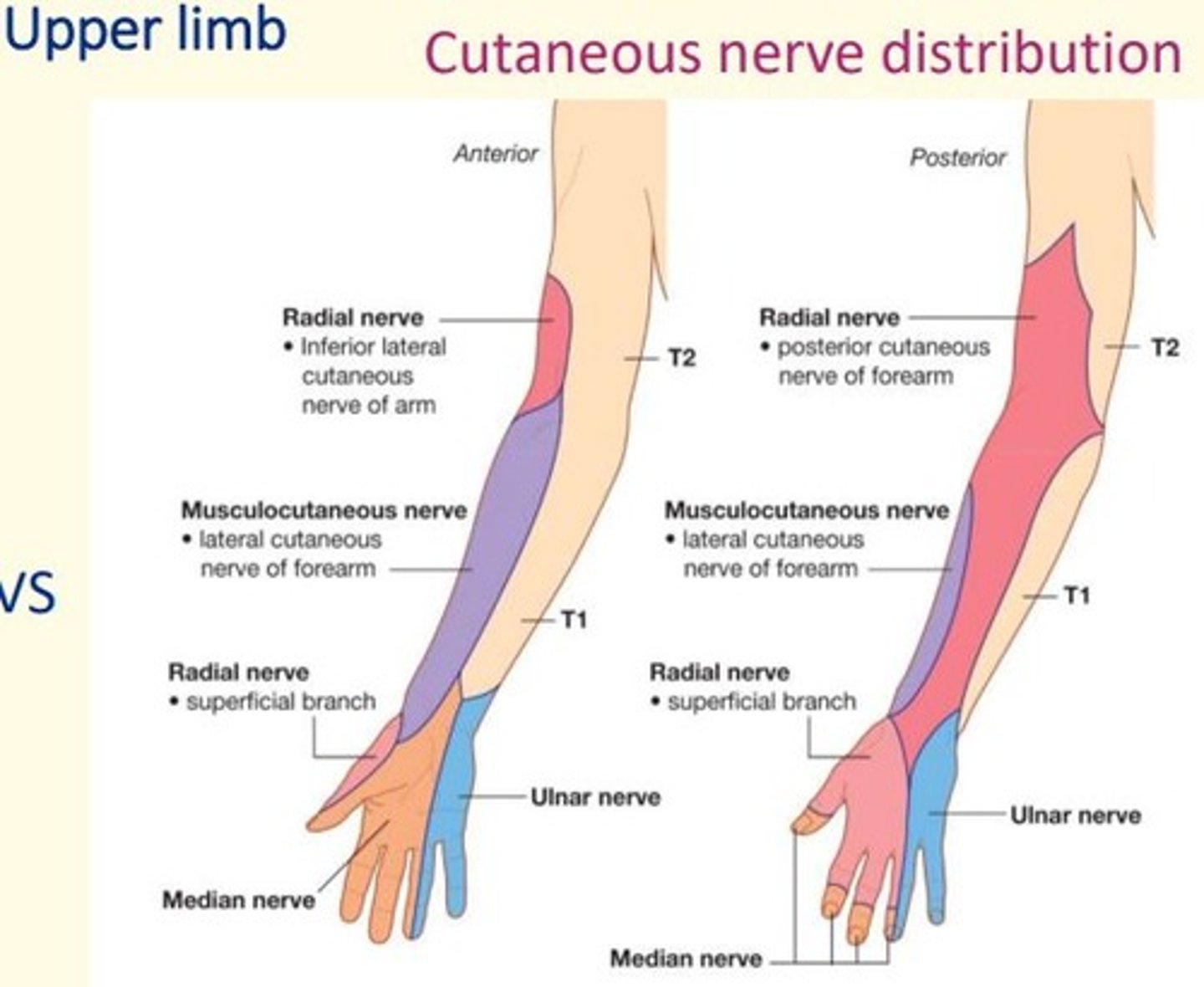
Cutaneous nerve distribution of the upper limbs
T1 T2 to posterior and lateral side of arm
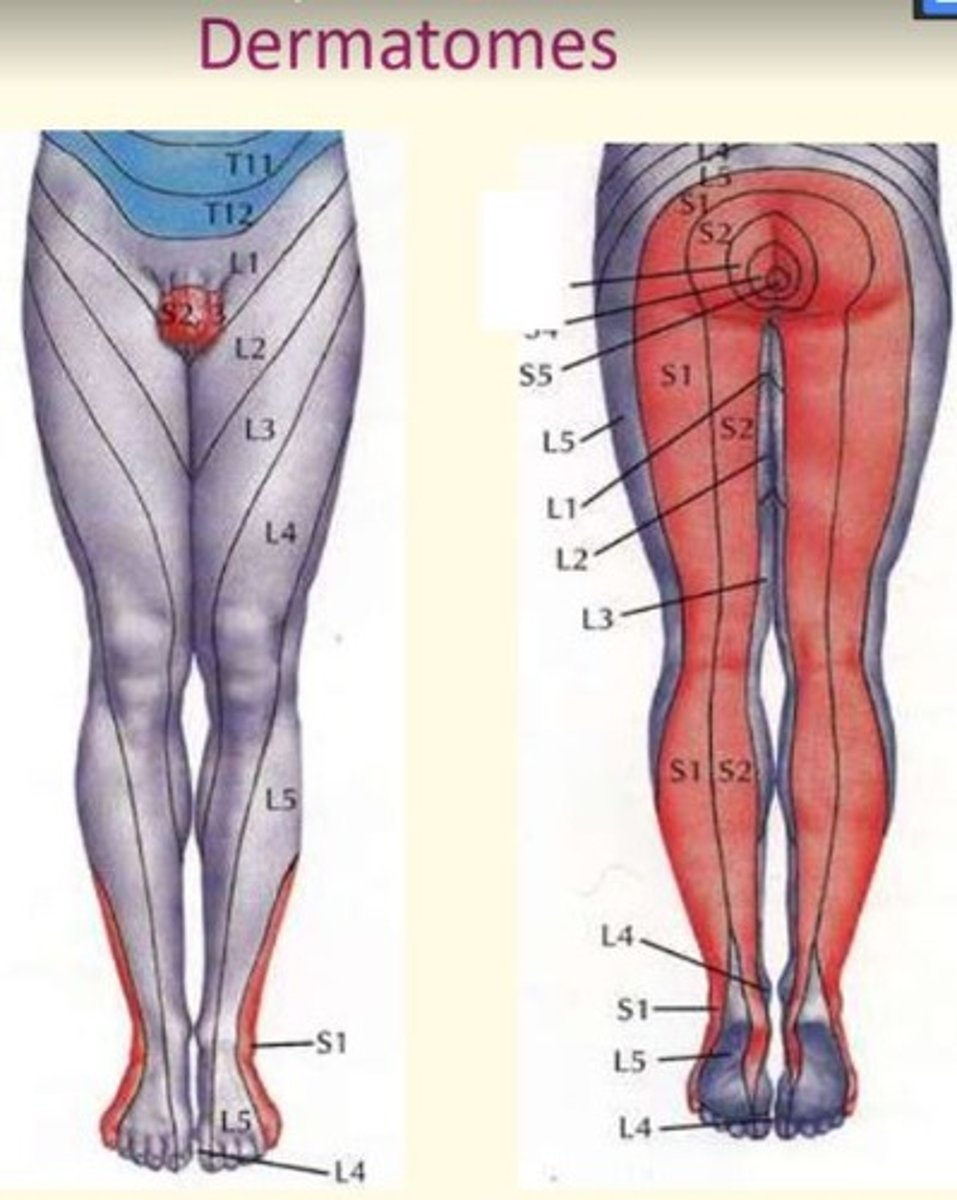
Dermatomes of the lower limbs
Lumbar serves most anterior surfaces
Sacral serves most posterior surfaces
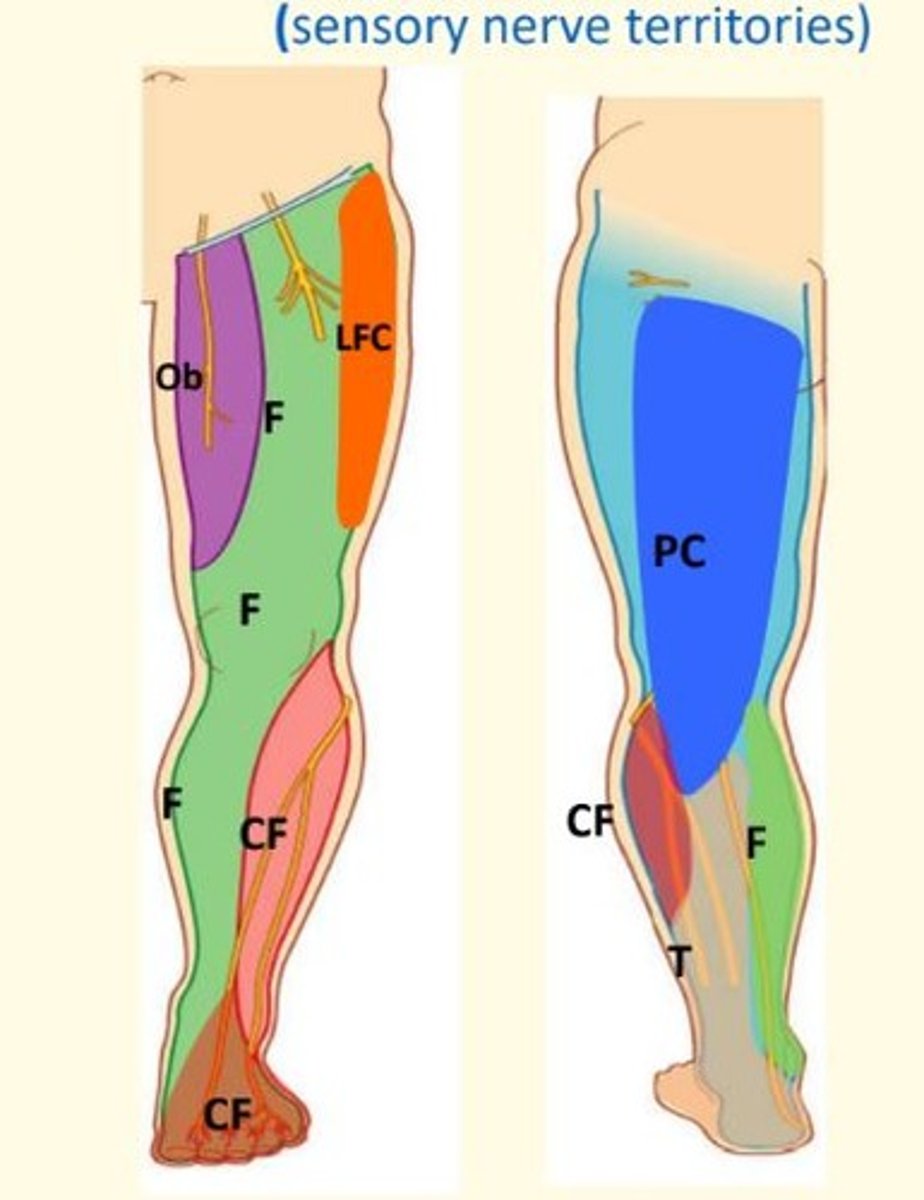
Cutaneous nerve distribution of the lower limbs
lateral femoral cutaneous nerve (lateral thigh), saphenous nerve (anteromedial leg and foot), and posterior cutaneous nerve of the thigh (posterior thigh).
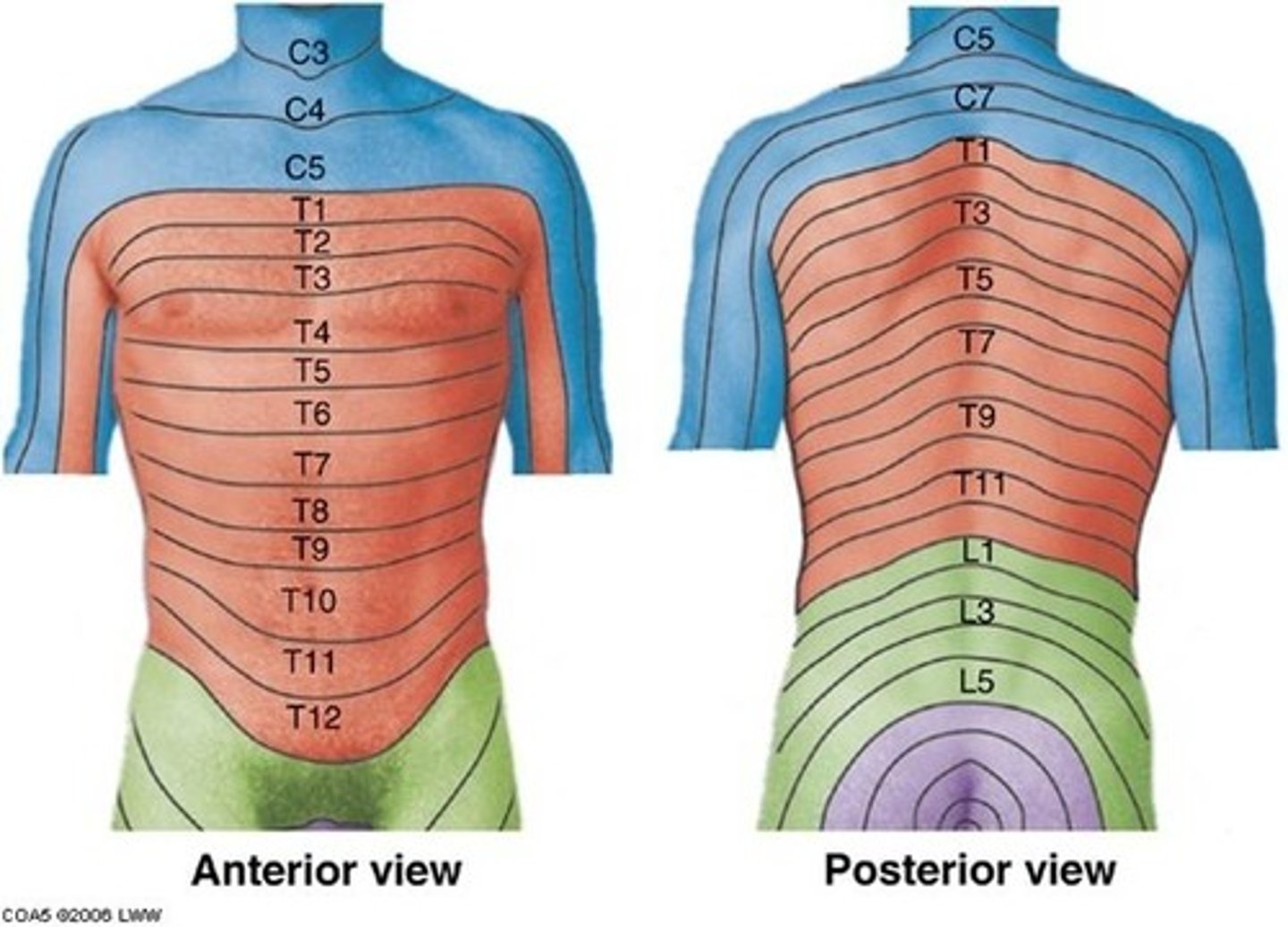
Trunk dermatomes
T1 = medial side of forearm to base of finger
T2 = axillary region
T4 = nipple area
T6 = xiphoid process level
T10 = umbilicus level
T12 = anterior superior iliac crest level
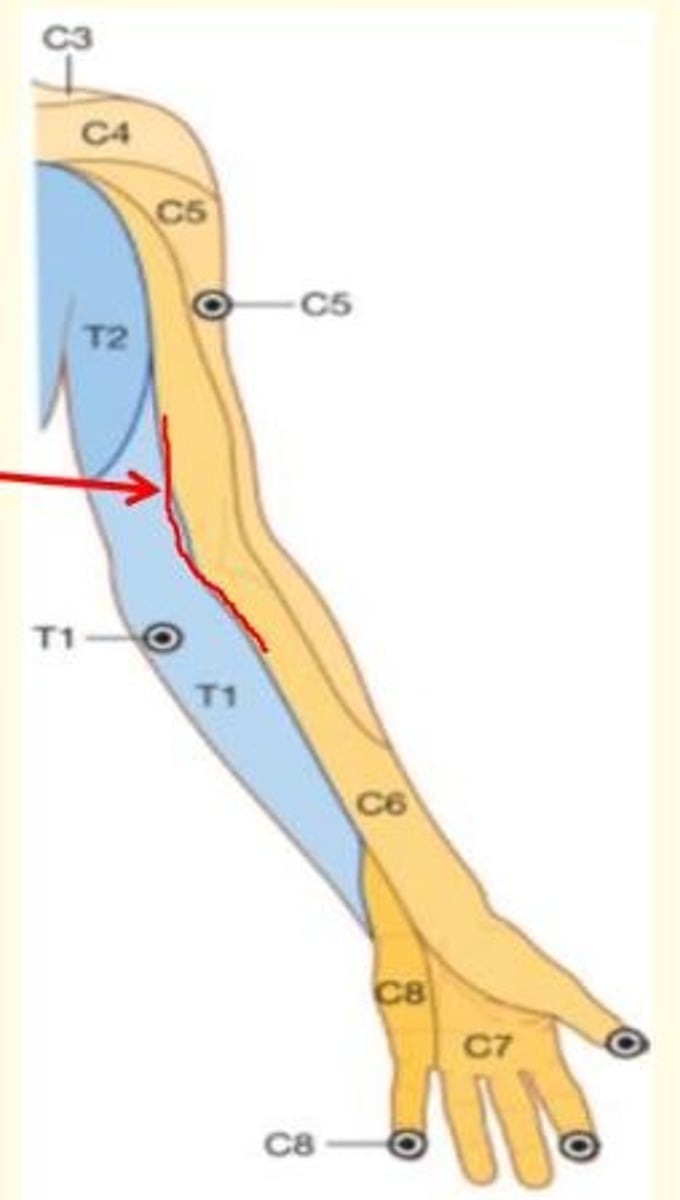
Axial lines of upper limb
Line of junction of two dermatomes supplied from discontinous spinal levels (e.g., C6 and T1 in this image)
There is no overlap
Anterior and posterior axial lines
Pre- and post- axial borders
These are the boundaries between flexor and extensor compartments. They are marked out by veins.
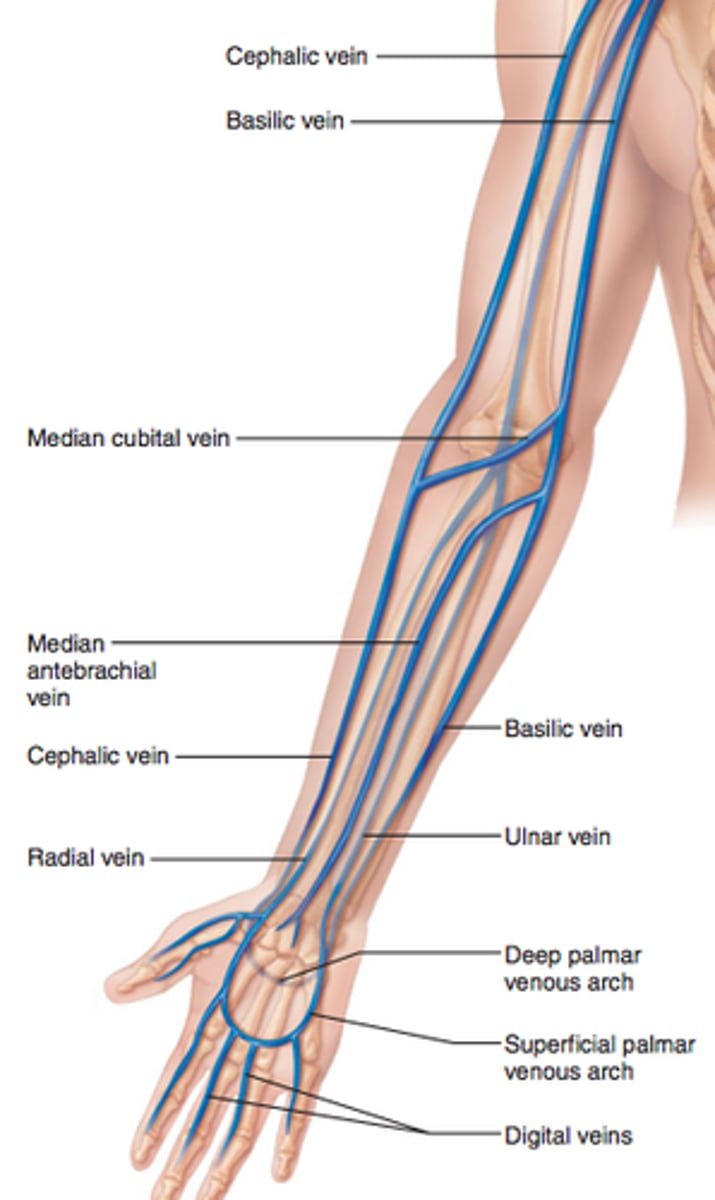
Pre- and post- axial borders of upper limb
Cephalic & Basilic veins
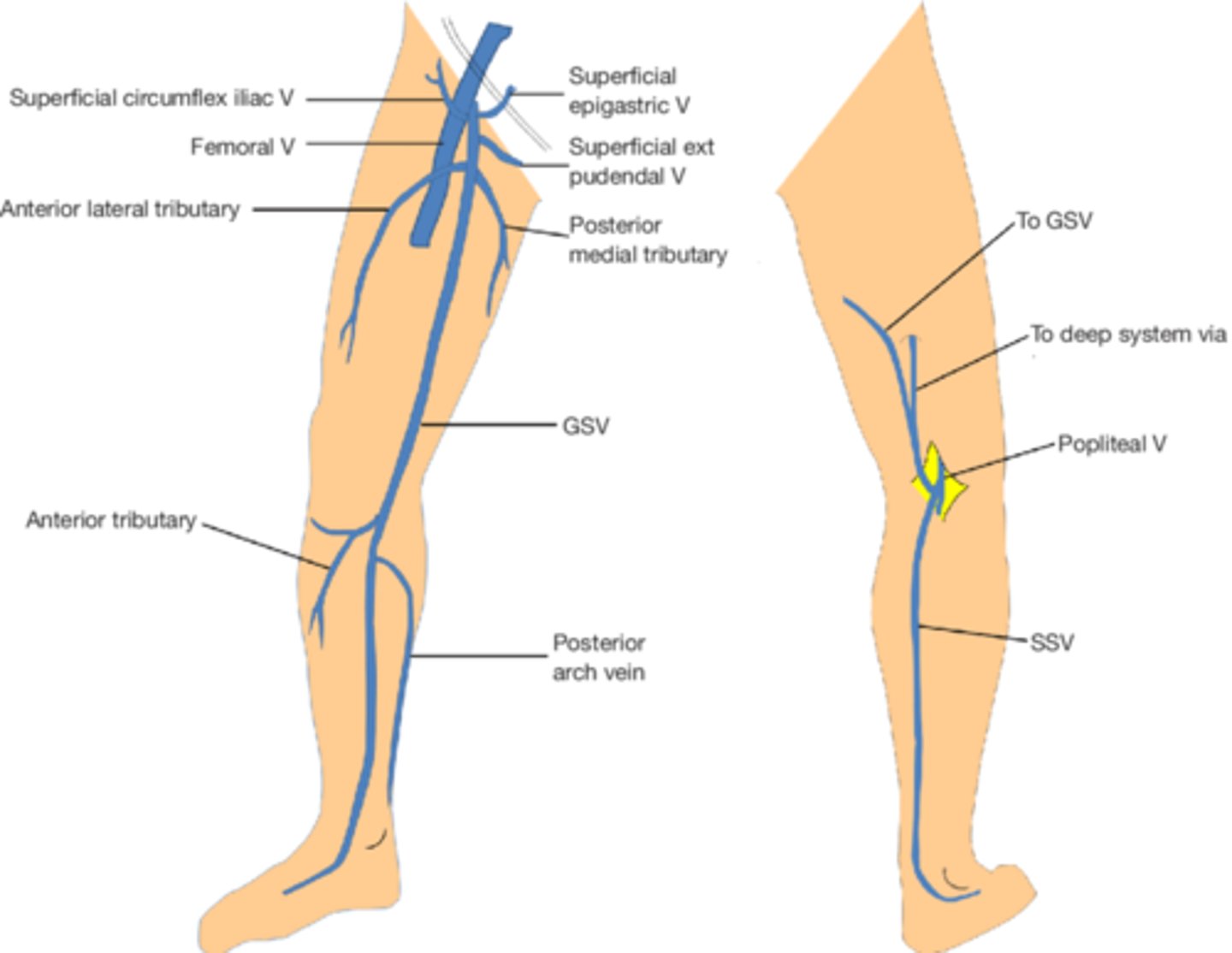
Pre- and post- axial borders of lower limb
Great Saphenous Vein (GSV) and Small Saphenous Vein (SSV)
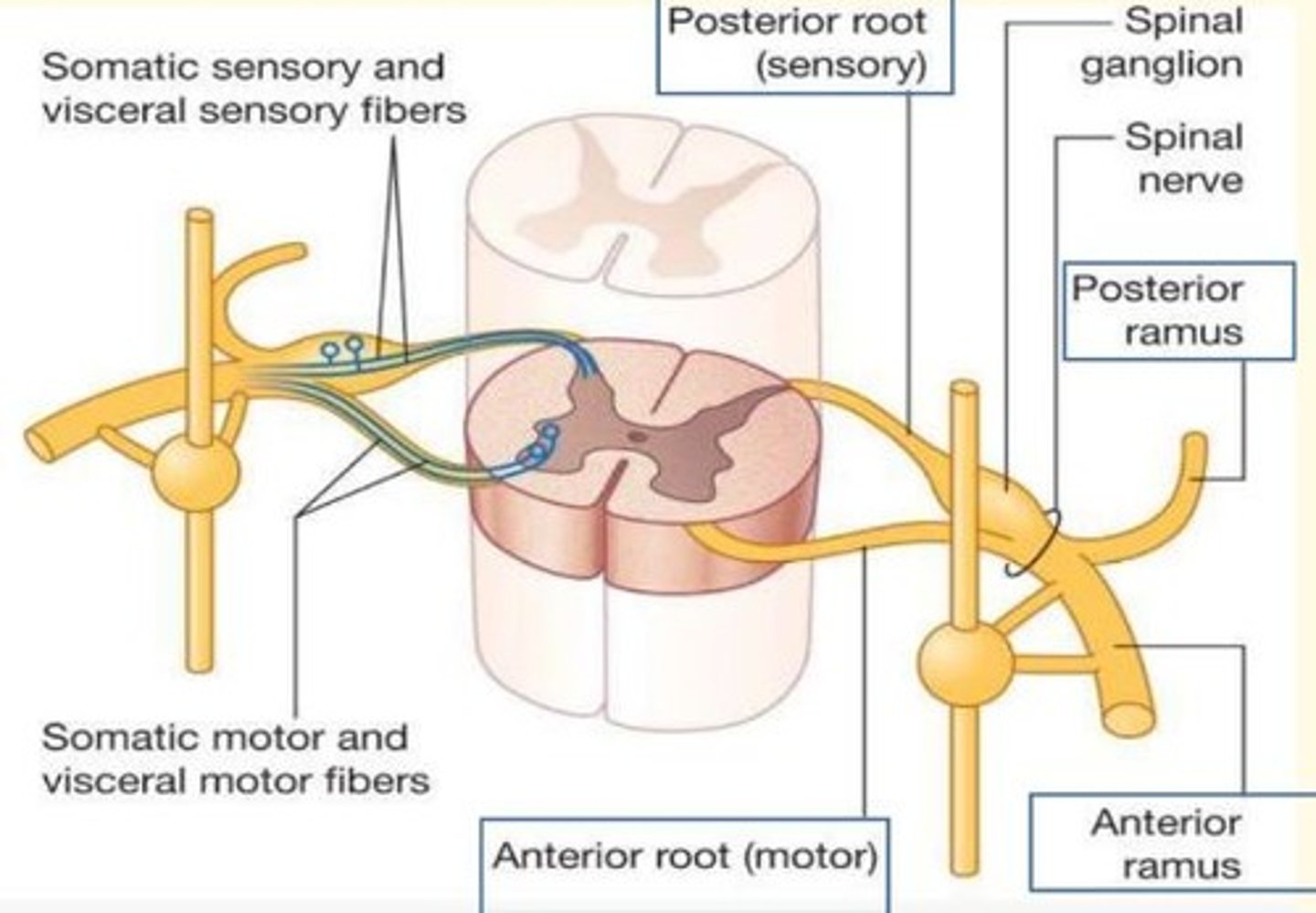
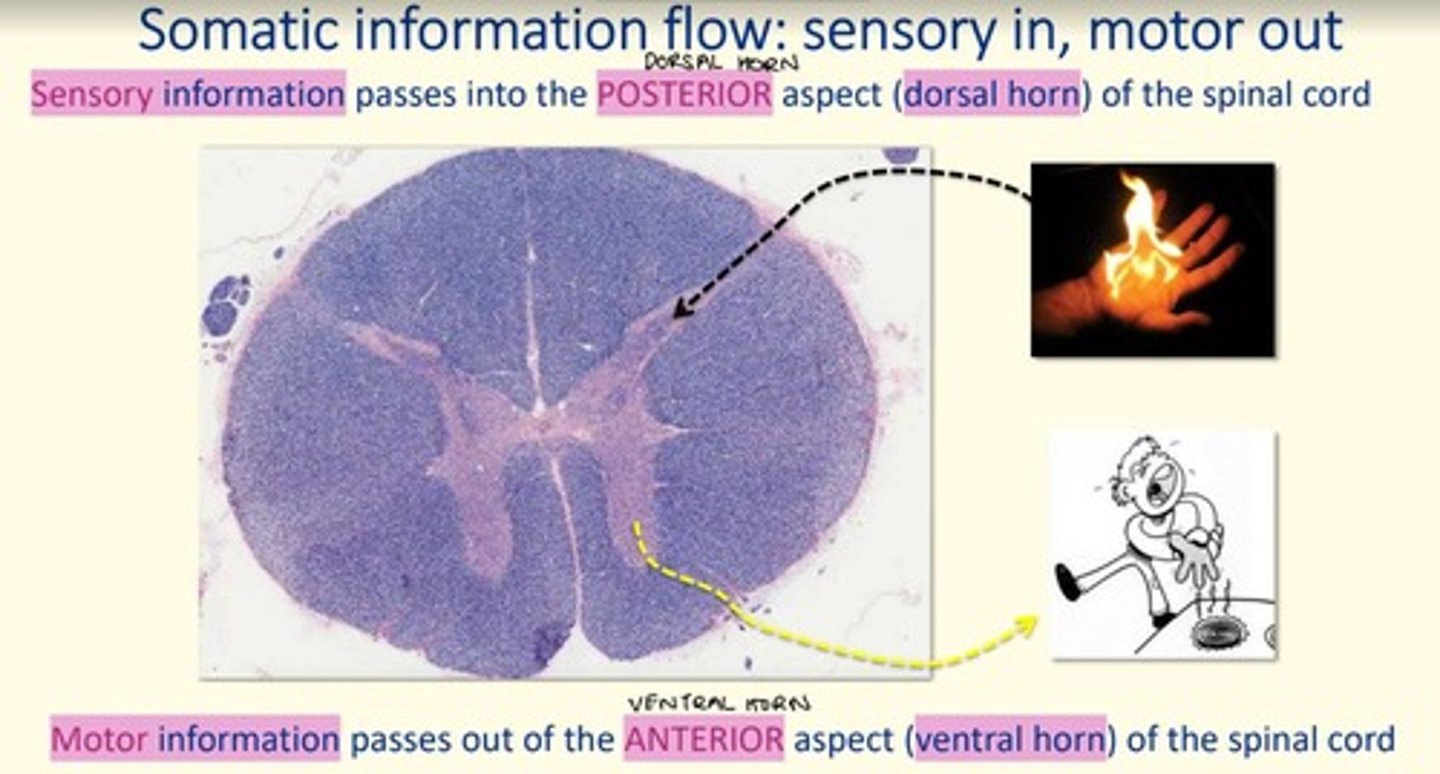
Sensory information passes into the posterior aspect (___ horn) of the spinal cord via ___ neurons
Sensory information passes into the posterior aspect (dorsal horn) of the spinal cord via afferent neurons
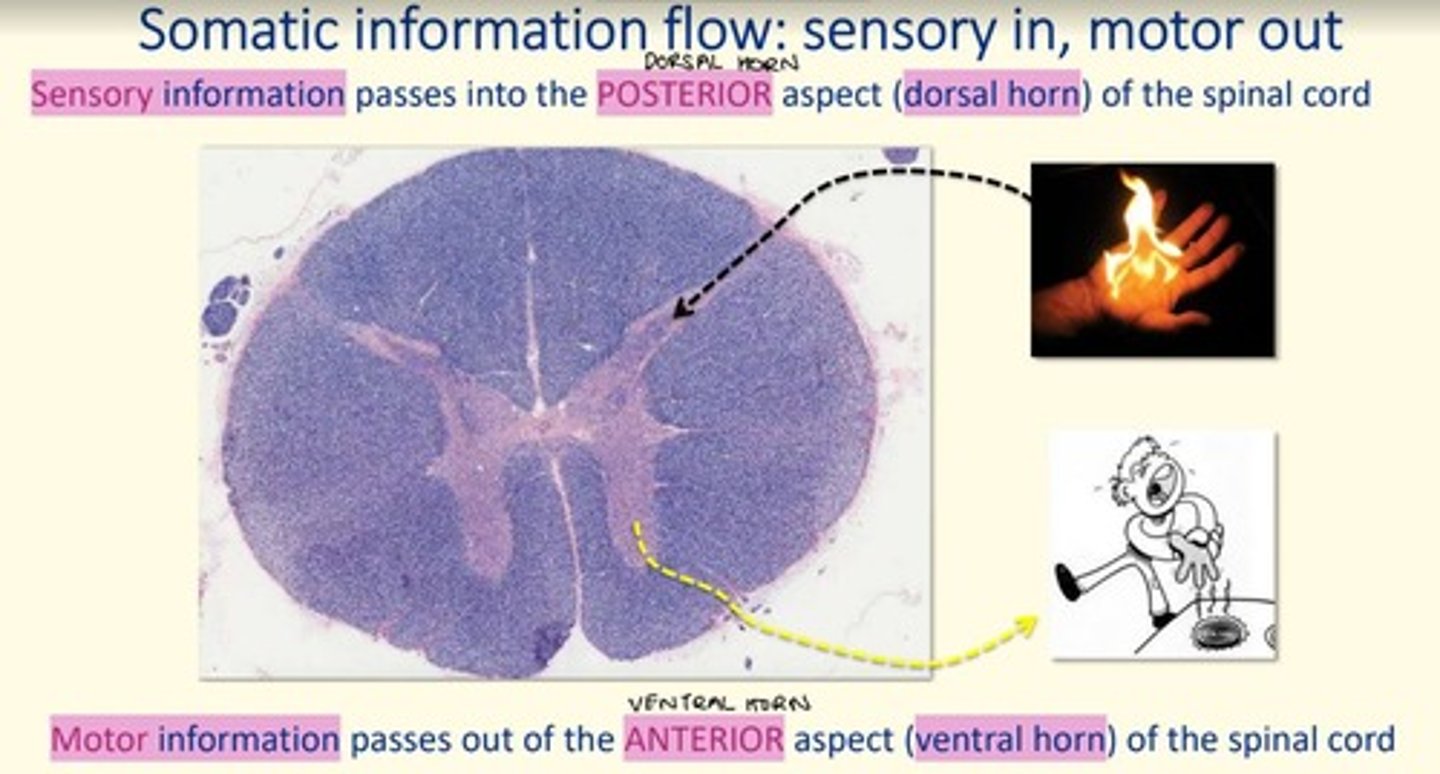
Motor infomration passes out the anterior aspect (___ horn) of the spinal cord via ___ neurons
Motor infomration passes out the anterior aspect (ventral horn) of the spinal cord via efferent neurons
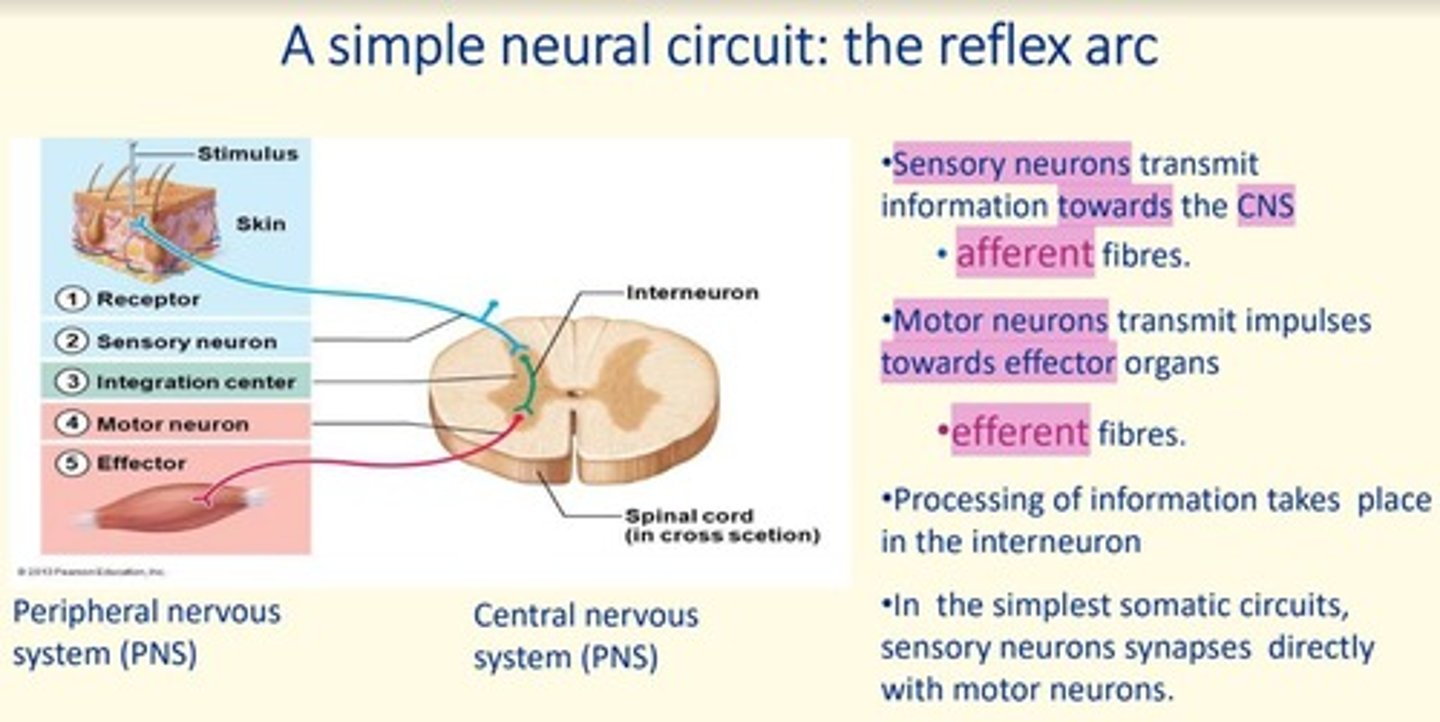
Sensory neurons transmit information ___ the CNS via ___ fibres
Sensory neurons transmit information towards the CNS via afferent fibres
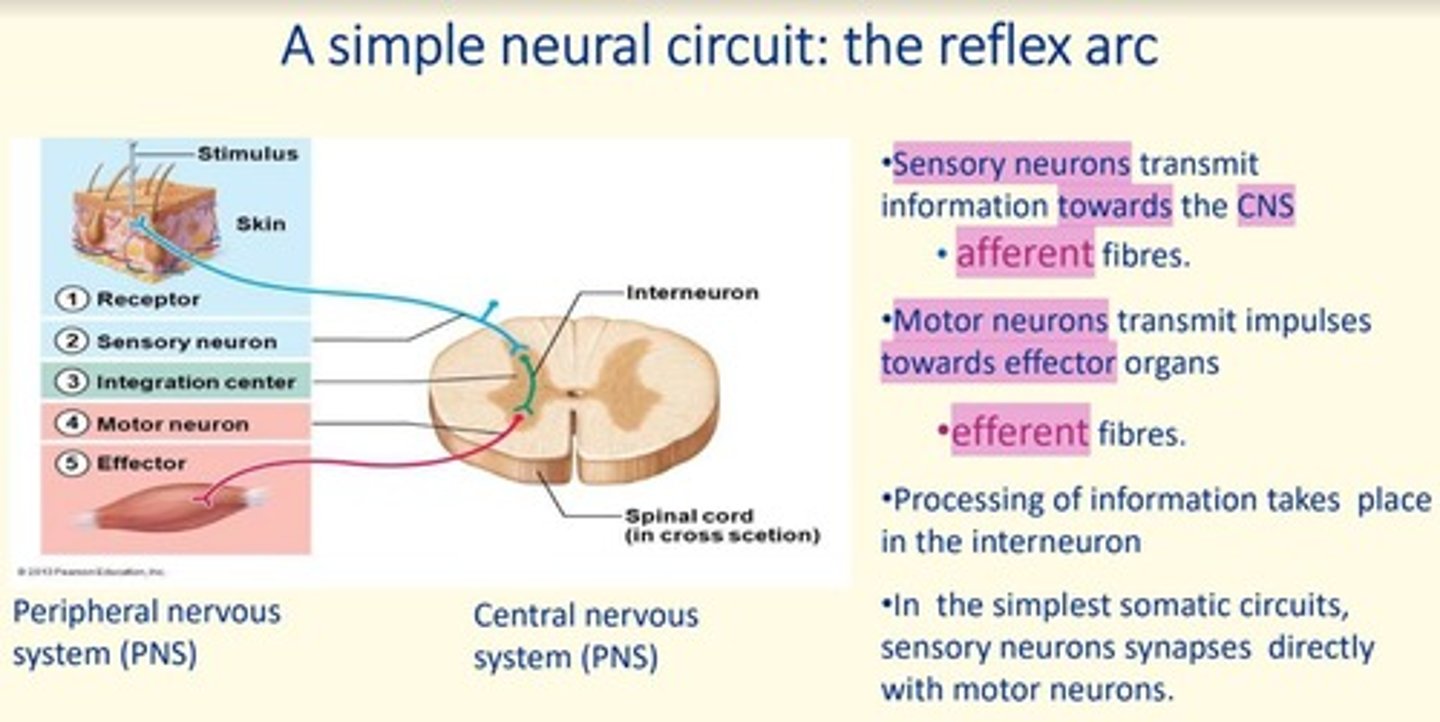
Motor neurons transmit impulses ___ from the CNS, towards ___ organs via ___ fibres
Motor neurons transmit impulses away from the CNS, towards effector organs via efferent fibres
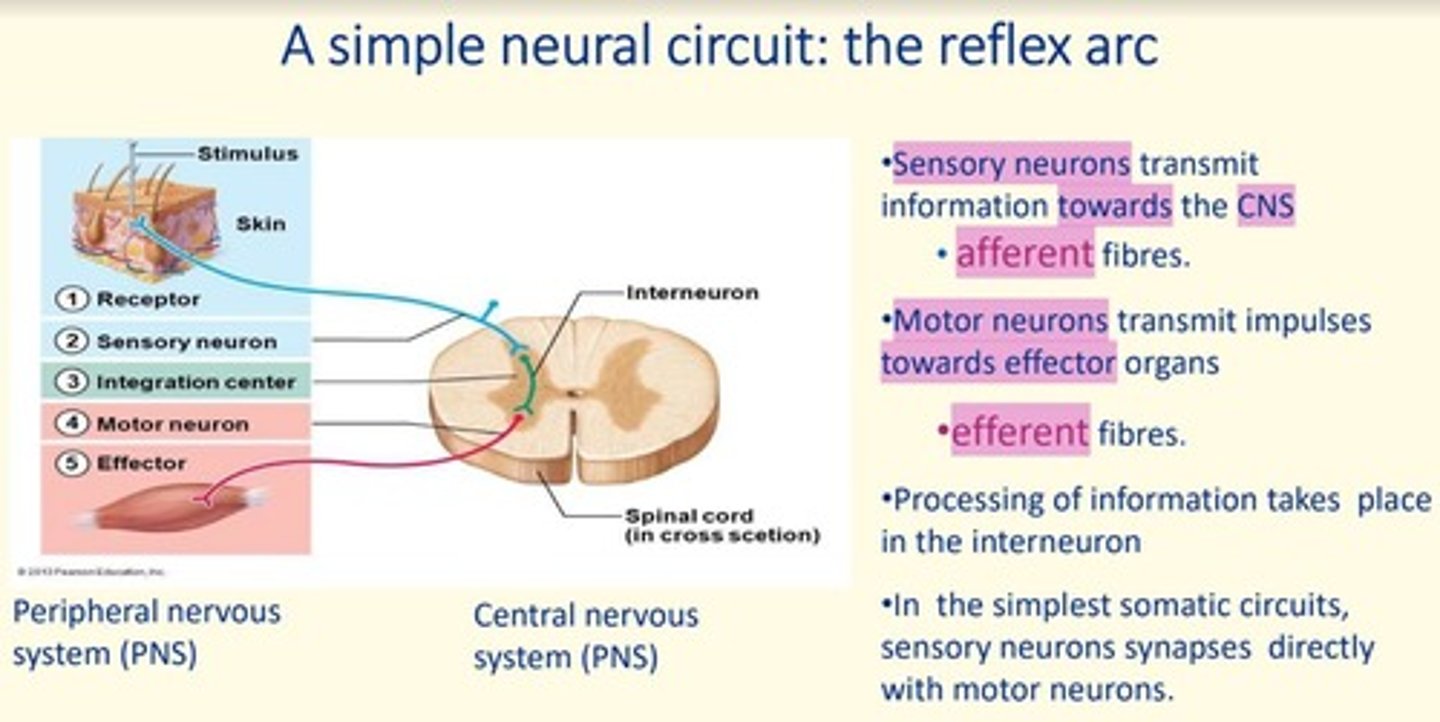
Where does processing of information take place in the simple reflex arc?
In the interneuron
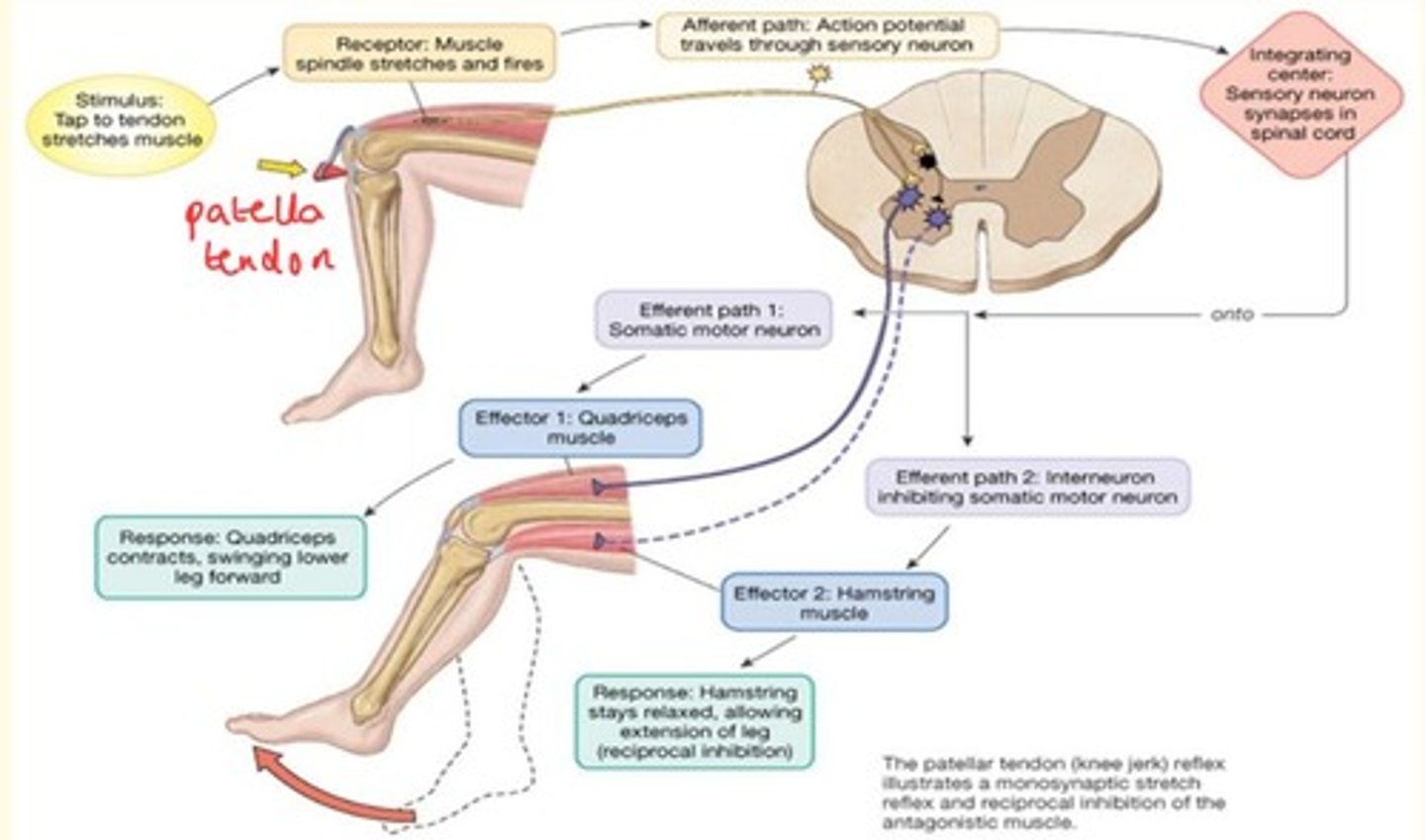
Knee jerk reflex
Sends afferent signal to spinal cord, bypasses the brain.
Effector 1 = Quadriceps muscle which contracts (extension)
Effector 2 = Hamstring muscle stays relaxed, allowing for extension of leg
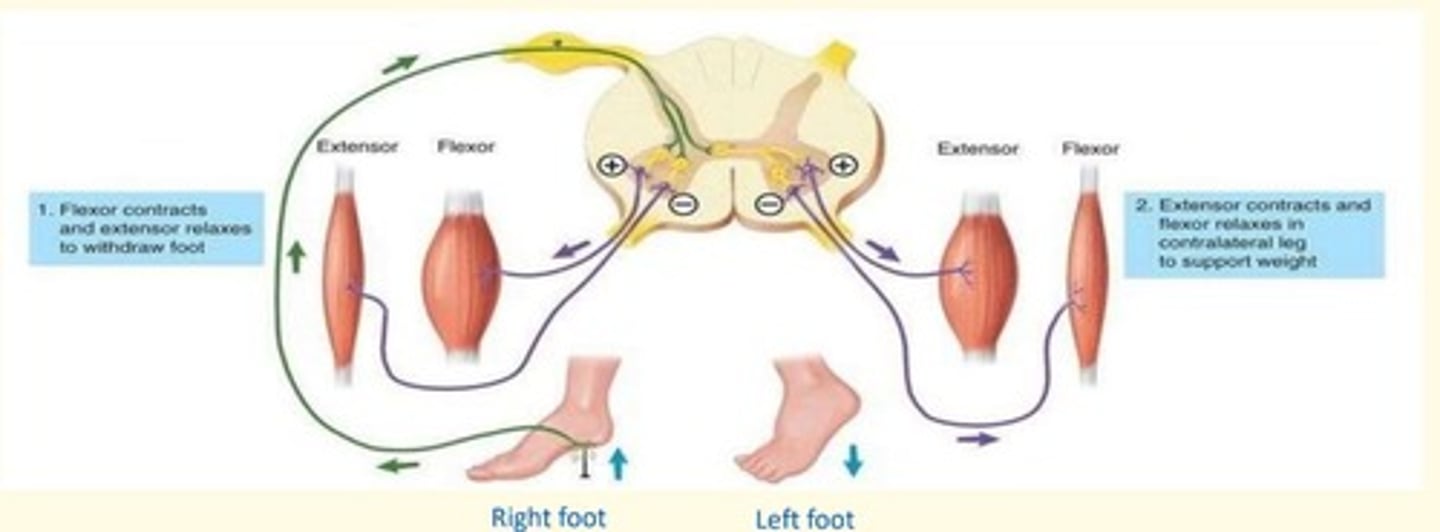
Crossed extensor reflex
When a withdrawal reflex is initiated in one lower limb, the crossed extensor reflex causes extension of contralateral (opposite) lower limb to support weight
In the affected foot = flexor contracts, and extensor relaxes to withdraw foot from painful stimuli
In the other foot = extensor contracts, flexor relaxes in contralateral leg to support weight (so you don't fall over)
The connective sheath covering an entire muscle bundle is known as the...
Epimysium
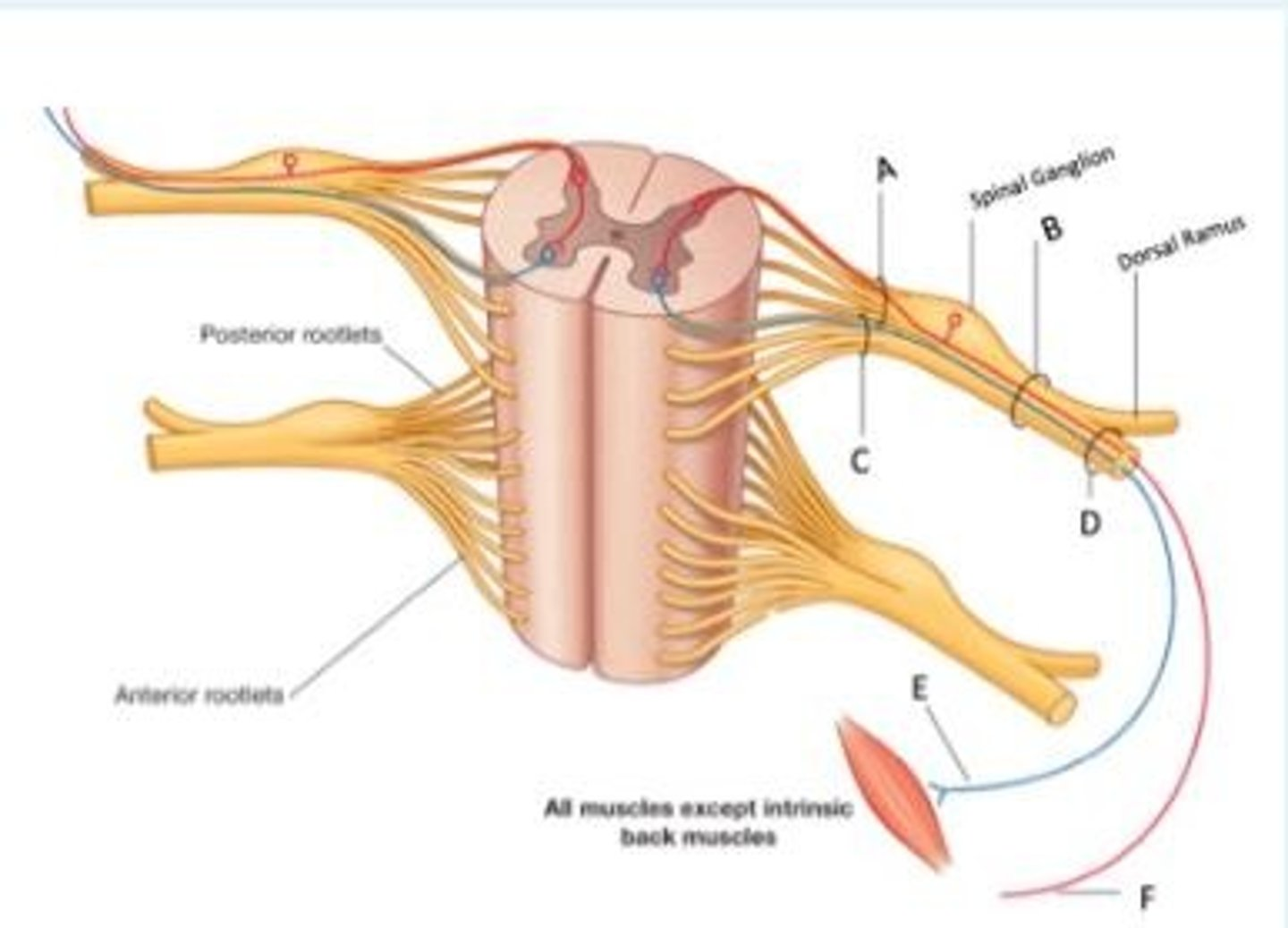
Look at the cross section of the spinal cord below. Identify the letter that represents a mixed nerve (sensory and motor)?
B
Look at the cross section of the spinal cord below, and use the appropriate letters to fill in the following statement...
___ indicates the somatic sensory nerve ending in the skin which conveys sensory signals toward the spinal cord. Sensory signals enter the spinal cord via ___. The signal is processed (either in the spinal cord or in the brain) and a motor signal leaves the spinal cord via ___ to eventually reach a muscle through ___ which is a somatic motor nerve fiber.
F indicates the somatic sensory nerve ending in the skin which conveys sensory signals toward the spinal cord. Sensory signals enter the spinal cord via A. The signal is processed (either in the spinal cord or in the brain) and a motor signal leaves the spinal cord via C to eventually reach a muscle through E which is a somatic motor nerve fiber.
What is a myotome?
A myotome is a group of muscles whose nerve supply all originates from one spinal nerve root
What is the difference between a dermatome and the cutaneous distribution of a peripheral nerve and why is it clinically significant?
A dermatome is an area of skin supplied by a single spinal nerve whereas the cutaneous distribution of a peripheral nerve is an area of skin supplied by a peripheral nerve - this nerve would have arisen from a plexus which receives input from many spinal root nerves - therefore one peripheral nerve may have many spinal root innervations.
It is clinically significant in order to locate where damage/disease has occurred ie. at a spinal level, higher level or peripheral level?
The spinal cord receives ___ fibers which carry ___ nerve fibers through the dorsal roots. It sends out ___ fibers which carry ___ and ___ nerve fibers through the ventral roots
The spinal cord receives afferent fibers which carry sensory nerve fibers through the dorsal roots. It sends out efferent fibers which carry motor and autonomic nerve fibers through the ventral roots
The deep muscles of the back are supplied by a branch of a spinal nerve called...
Dorsal Ramus
Think of the ventral side of your thumb. What dermatome and what cutaneous nerve area would this include?
C6 and Median nerve