Anatomy E4: UE
1/92
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
93 Terms
How many segments make up the upper limb? What are they?
4 segments
shoulder
arm
forearm
hand
muscles of supination
supinator and biceps brachii
muscles of pronation
pronator teres and pronator quadratus
Shoulder regions
pectoral, scapular, and lateral supraclavicular
Pectoral girdle is made up of
scapulae, clavicles, manubrium
What is the sternoclavicular joint (SC)?
bony articulation between pectoral girdle and axial
what makes up the arm (brachium) component?
humerus
What makes up the forearm (ante brachium) component?
radius, ulna
What makes up the hand (manus) component?
carpals, metacarpals, phalanges
How many regions make up the upper limb?
16 regions
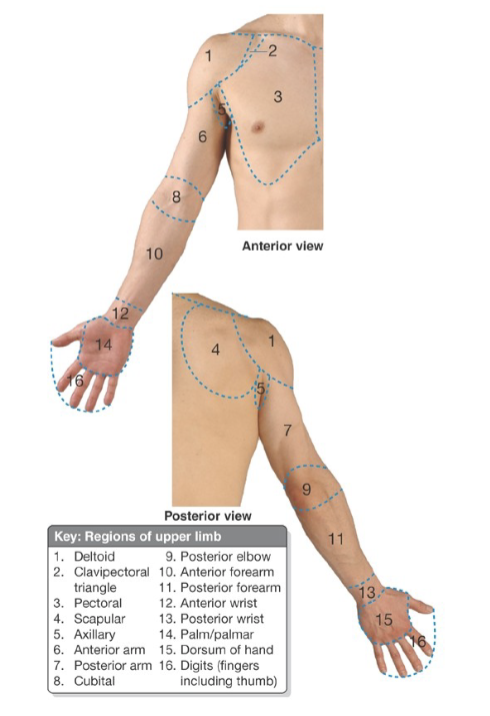
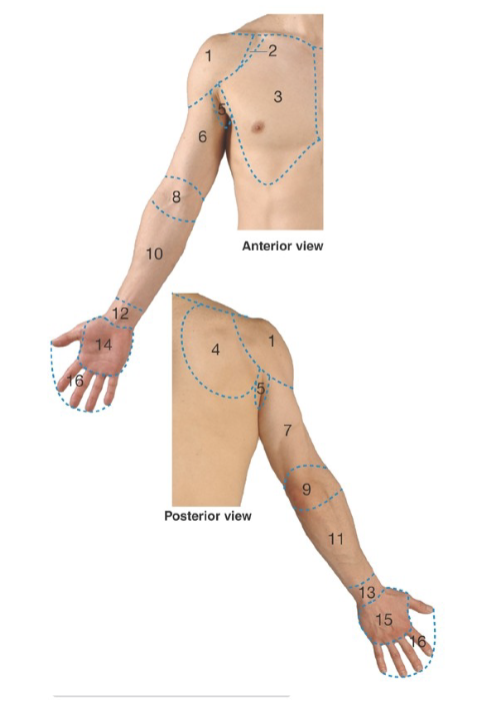
Label: what are regions 1, 2, 3, 4
1: deltoid
2: clavipectoral triangle
3: pectoral
4: scapular
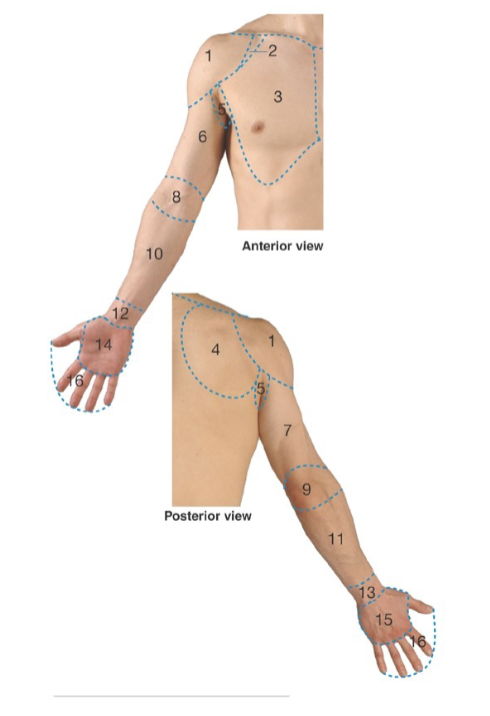
Label: what are regions 5, 6,7, 8
5: axillary
6: anterior arm
7: posterior arm
8: cubital
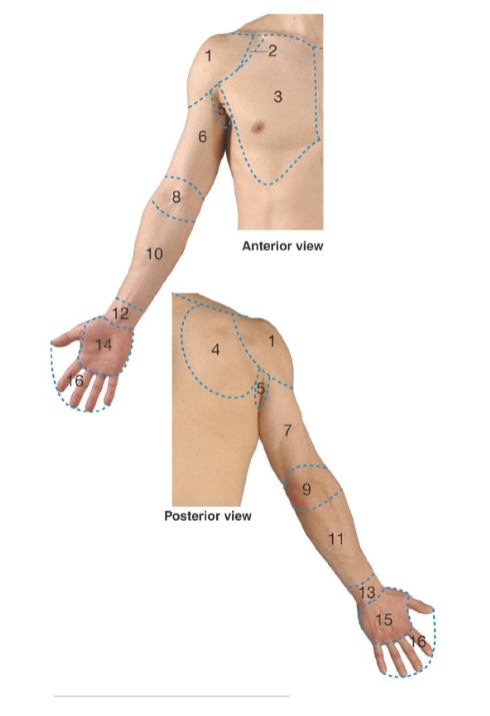
Label: what are regions 9, 10, 11, 12
9: posterior elbow
10: anterior forearm
11: posterior forearm
12: anterior wrist
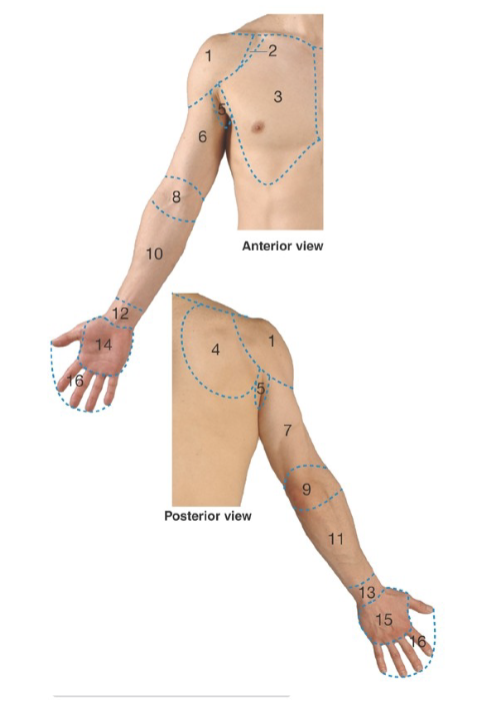
Label: what are regions 13, 14, 14, 16
13: posterior wrist
14: palm/palmar
15: dorsum of hand
16: digits (fingers & thumb)
What bones make up the upper limb?
clavicle, scapula, humerus, ulna, radius, carpal bones (8), metacarpal bones (5), phalanges
How many carpal bones are there in the hand?
8 carpals (2 rows of 4)
-make up the wrist
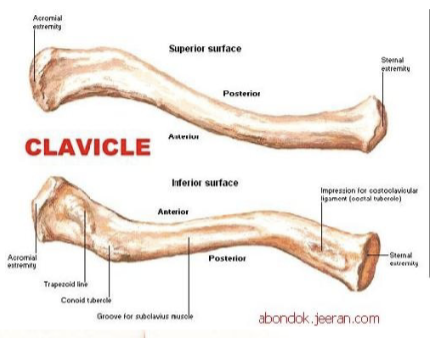
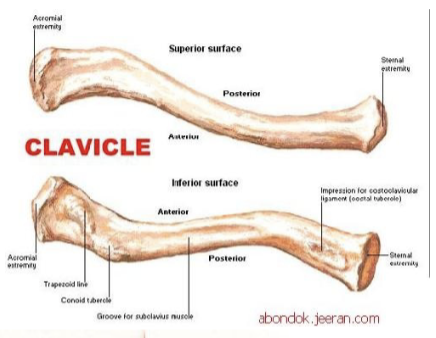
clavicle function:
protects neurovascular bundle
transmits shock/stress from upper limb to axial skeleton
Clavicle features:
sternal end: medial end enlarges where it attaches to sternum (manubrium) (SC joint)
acromial end: laterally articulates to the acromion of the scapula (AC joint)
medial 2/3 is convex anteriorly
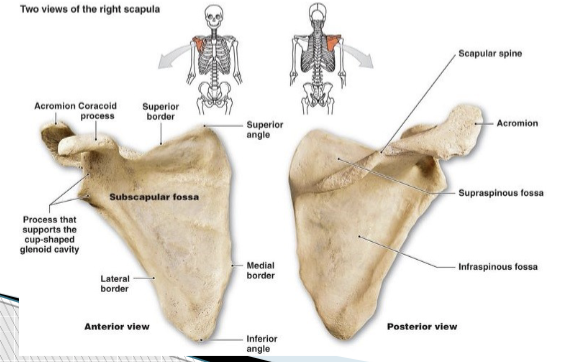
Scapula location
overlies posterolateral ribs 2-7
Scapula parts:
spine of scapula, acromion process, sub scapular fossa, coracoid process
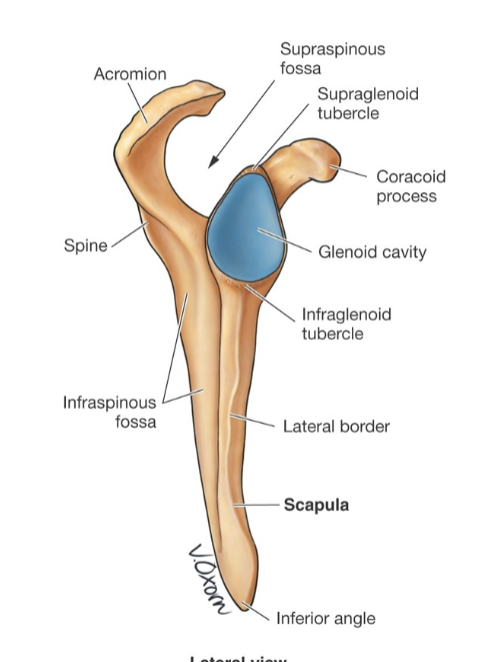
Lateral scapula features:
glenoid cavity fossa, supraglenoid tubercle, infraglenoid tubercle
Articulations of shoulder girdle
sternoclavicular joint (SC)
Acromioclavicular join (AC)
Scapulothoracic joint
Glenohumeral (scapulohumeral joint)
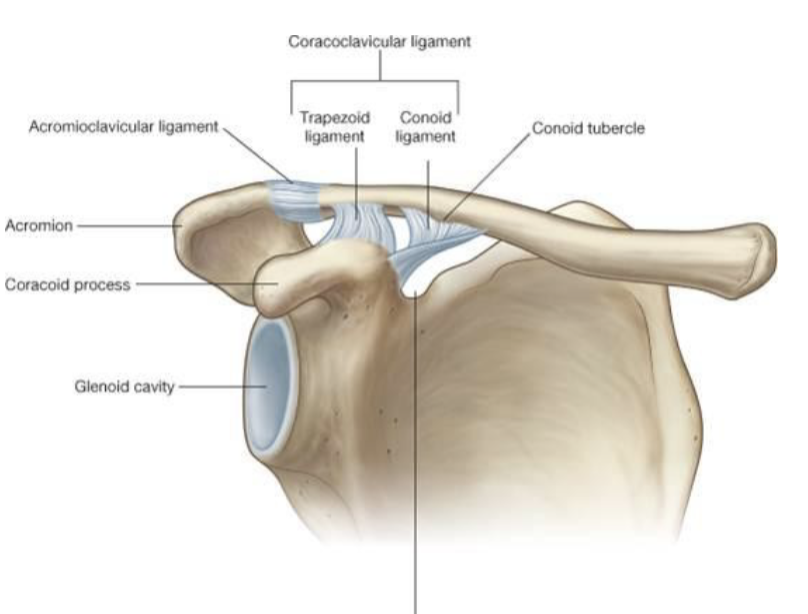
What does the clavicle articulate with?
manubrium of sternum and 1st costal cartilage
SC supports what movements?
elevation/depression
protraction/retraction
What is the function of the interclavicular ligament?
strengthens the capsule superiorly
What is the location of the costoclavicular ligament?
between sternal end of clavicle and 1st rib and its costal cartilage
What is the location of the anterior SC ligament?
between clavicle and manubrium
The AC joint supports what movement?
gliding movement
the AC joint capsule is reinforced by what?
coracoclavicular ligament
acromioclavicular ligament
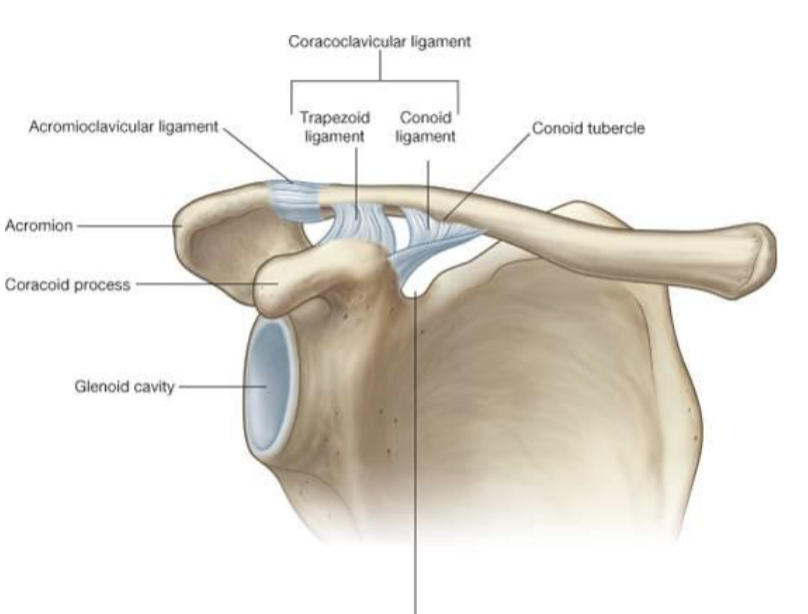
AC separation
shoulder separation: AC & CC ligament torn
-common
Scapulothoracic joint features:
no bony articulation exists between scapula and thoracic cage
What is the glenoid fossa?
part of the glenohumeral joint
-articulates with head of humerus
The glenoid fossa is unstable. what is it reinforced by?
ligaments and muscles
held in place by rotator cuff muscles
inferior part of joint capsule is the weakest area
The ball-and-socket synovial joint of the shoulder supports what types of movement?
flexion/extension
abduction/adduction
medial/lateral rotation
circumduction
ligaments of the glenohumeral joint
superior, middle, and inferior glenohumeral
Coraco-acromial ligament function
prevents superior displacement of humerus
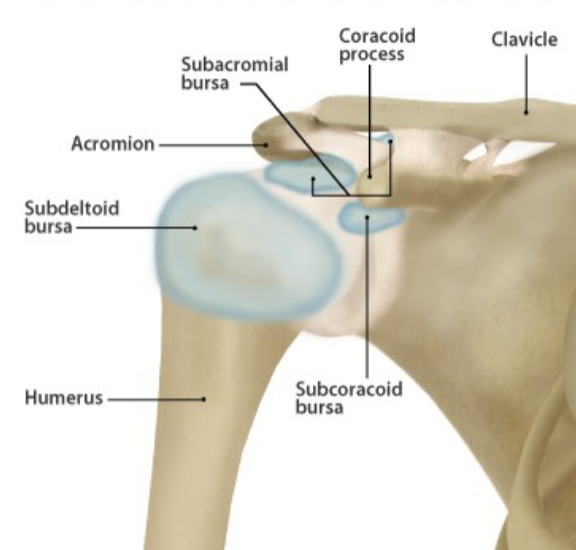
Subacromial bursa
separates acromion from supraspinatus muscle; pain felt mainly during initial stages of abduction and forward flexion
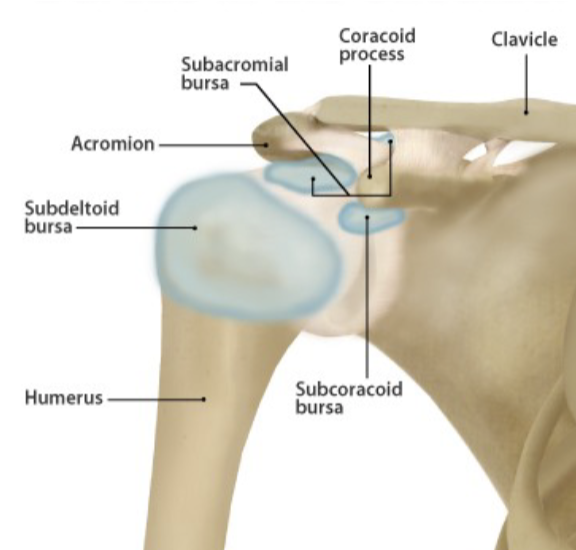
sub deltoid bursa
separates deltoid m. from head humerus
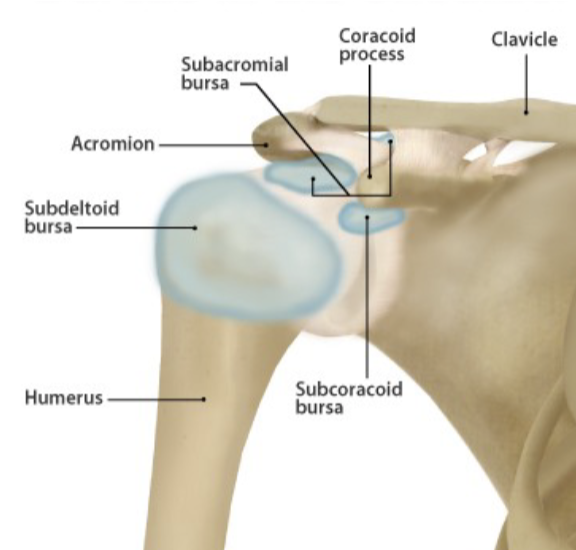
Subcoracoid bursa
located anterior to the subscapularis m. and inferior to the coracoid process
What is the largest upper extremity bone?
humerus
What features does the shaft of the humerus have?
deltoid tuberosity and radial groove
What condyles are on the humerus?
trochlea, capitulum, olecranon fossa, coronoid fossa
What do the capitulum and trochlea articulate with?
cap: articulates with radial
troch: articulates with trochlear notch
What muscles attach to the great tubercles of the humerus?
supraspinatus m, infraspinatus m, teres minor m.
What lies within the bicipital groove?
contains end of long head of biceps brachii
-located between greater and lesser tubercles
During flexion, where does the coronoid process of ulna go?
it is received by the coronoid fossa
Radius location
lateral and shorter of the 2 forearm bones
-shaft enlarges distally
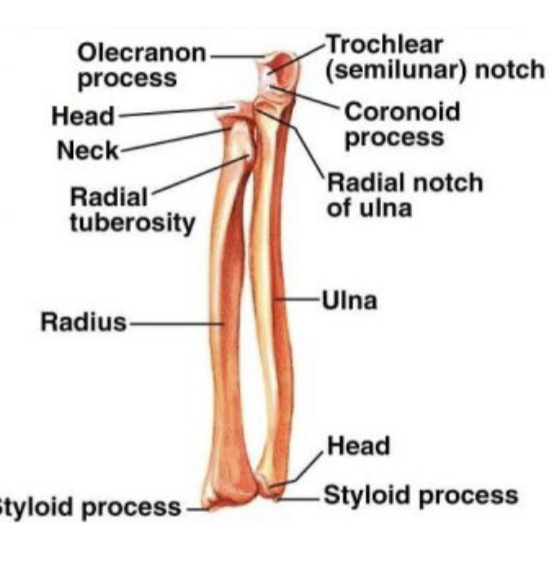
Styloid process
receives most of force from the hand
-part of the radius
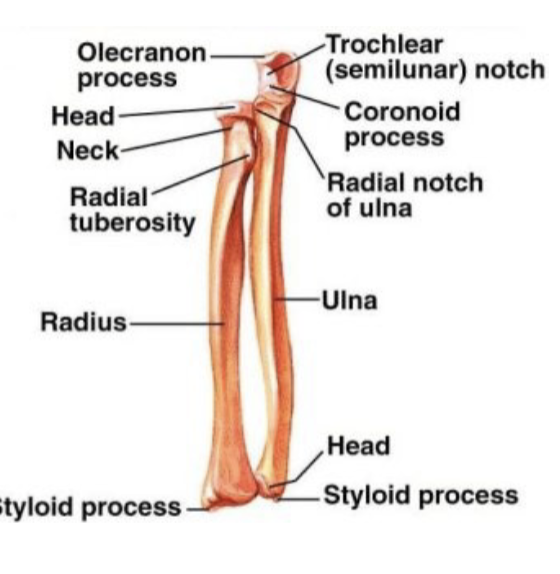
Radial styloid process
articular surfaces for scaphoid and lunate bones of wrist
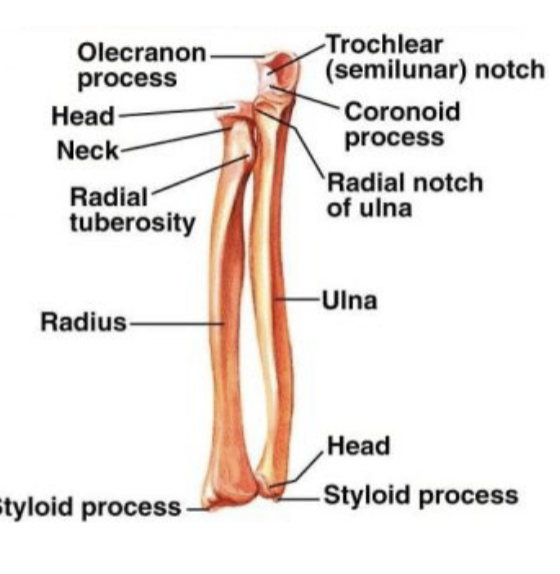
Ulna location
medial and longer of the 2 forearm bones
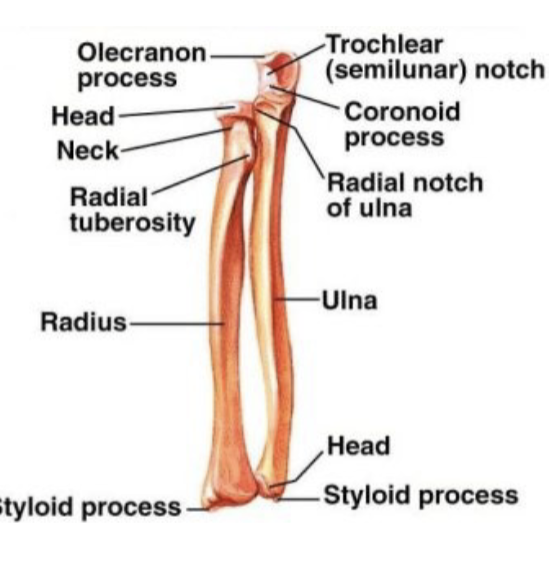
What does the trochlear notch articulate with?
trochlea of humerus
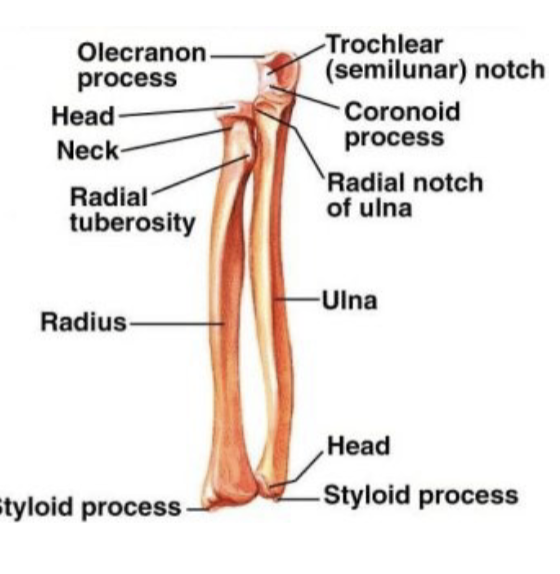
carpal bones and ulna
ulna does not articulate directly with carpal bones
What is the colles fracture?
complete fracture of distal 2cm of radius
most common forearm fracture
most common fracture in people over >50 yo
What nerves supply the elbow joint?
musculocutaneous, radial, and ulnar nerves
what bursa is located directly on the elbow and is a more common location of bursitis?
subcutaneous olecranon bursa
Carpal bone shape
shape is convex posteriorly, concave anteriorly
Wrist bone pneumonic
So long to pinky, here comes the thumb
scaphoid, lunate, triquetrum, pisiform (proximal; med→lat)
hamate, capitate, trapezoid, trapezium (distal; med→)
How many metacarpal bones are there?
5; 1st metacarpal = thumb = thickest and shortest
Which part of the metacarpals connects to the phalanges?
distal head articulate with proximal phalanges
How many phalanges are in each finger?
each digit has 3 expect the thumb
Distal phalanges
flattened with expanded(tufts) under nail beds
Proximal interphalangeal joints (PIP) location
between proximal and middle phalanges
Distal interphalangeal joints (DIP) location
between middle and distal phalanges
Brachial plexus is made up of what nerves?
C5-T1
ulnar n, radial n, median n, musuclocutaneous n
-innervates entire upper limb
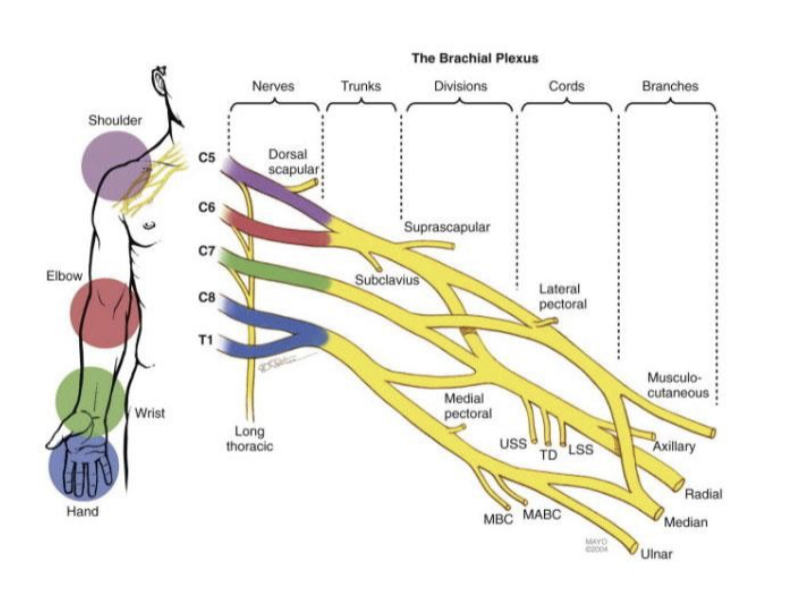
Which portion of the arm does C5 innervate?
shoulder; musculocutaneous
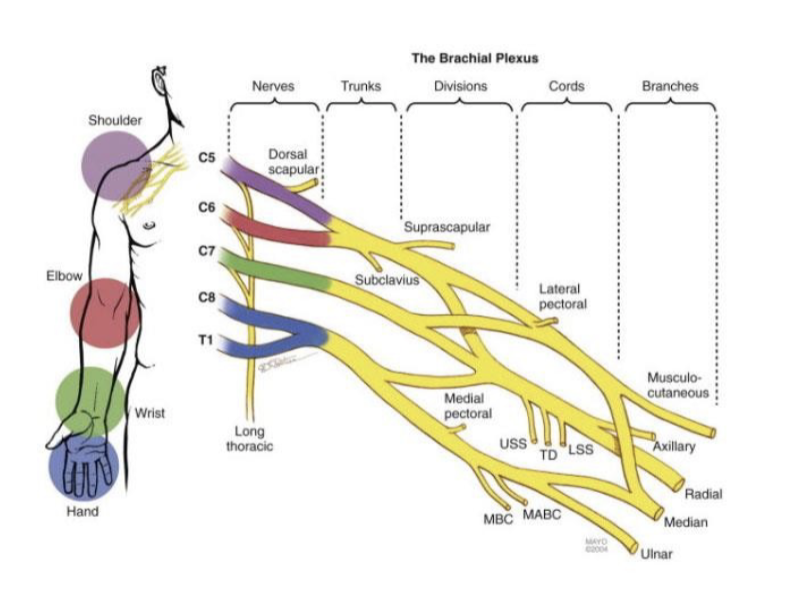
Which portion of the arm does C6 innervate?
elbow; musculocutaneous
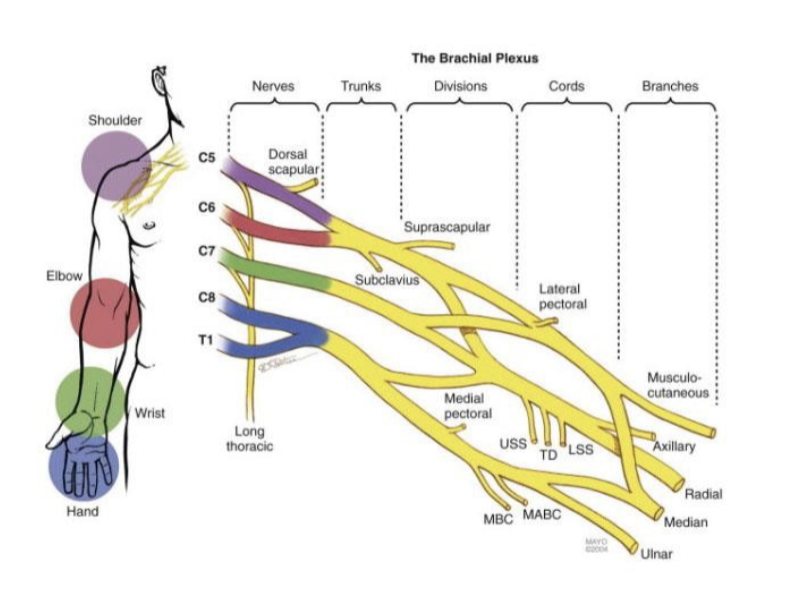
Which portion of the arm does C7 innervate?
wrist; radial
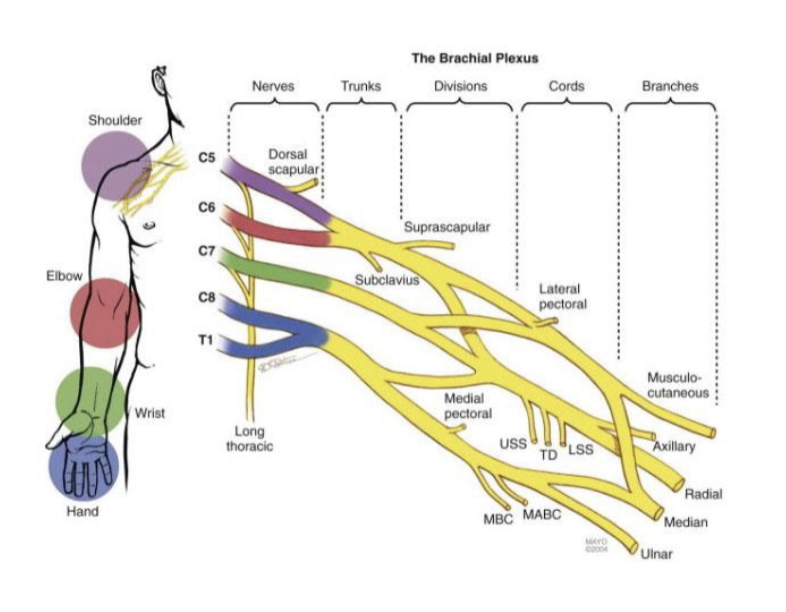
Which portion of the arm does C8 and T1 innervate?
hand; ulnar and median
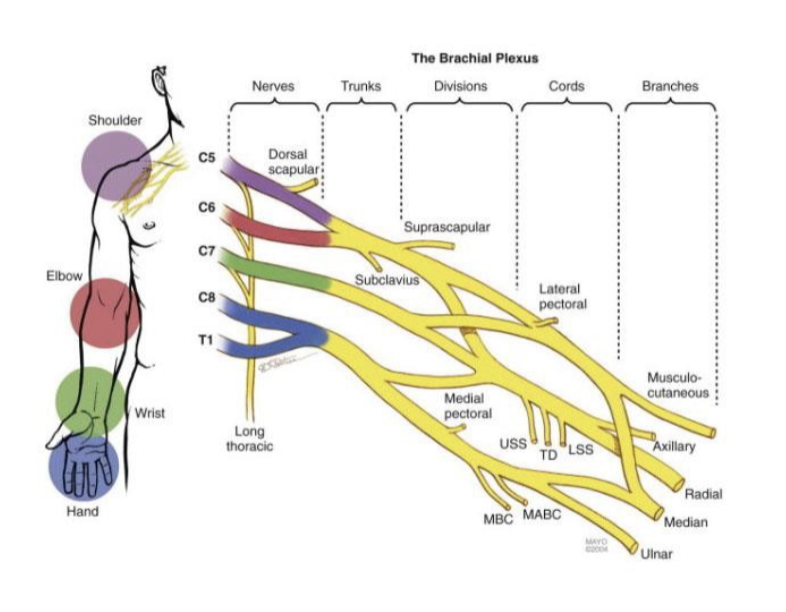
Arteries of the UE
subclavian a., axillary a., brachial a., radial a., ulnar a.
veins of the UE
ulnar, radial, median cubital, brachial axillary, subclavian
venous drainage of UE
axillary v., subclavian v. superior vena cava (SVC)
Shoulder movements
abduction, adduction, flexion, extension, medial rotation, lateral rotation, elevation/depression, protraction/retraction, rotation
What muscles do you use when you raise your arm?
first: supraspinatus m.
second: deltoid m.
third: serratus anterior m.
How many arm muscles are there?
4; 3 flexors, 1 extensor
Movements of forearm:
flexion, extension, supination, pronation
anterior groups = flexors
posterior groups = extensors
Flexion/extension of the forearm is done through…?
through the trochlea
Pronation/supination of the forearm is done through…?
through capitulum of humerus
Which nerves control forearm flexion?
musculocutaneous
-radial and median also involved
Which nerves control forearm extension?
radial
Which nerves control forearm pronation?
median
Which nerves control forearm supination?
musculocutaneous for biceps brachii m.
radial for supinator m.
Superficial veins of the arm
cephalic and basilic veins
Deep veins of the arm
brachial vein ends by merging with basilic vein to form axillary vein
Lymph nodes of UE
epitrochlear nodes, lateral axillary nodes (humeral), central axillary nodes, infraclavicular nodes
nerves of the forearm
median, radial, ulnar
Median n. innervates:
majority of flexors and pronator of forearm
Ulnar n. innervates:
supplies only flexor carpi ulnaris m. and ulnar half of flexor digitorum profudus
-becomes superficial at the wrist, running on the medial side of the ulnar artery
If the Radial n. (deep and superficial branches) is injured, this results in what condition?
Saturday nigh palsy or crutch palsy
-wrist drop
Cubital fossa
triangular shaped area rich in veins, arteries, and nerves
Anatomical Snuff box
tendon of the abductor pollicis longus and extensor pollicis brevis bound it laterally
tendon of extensor pollicis longus bound it medially
Thenar eminence
base of thumb and lateral aspect of hand
hypothenar eminence
medial and smaller portion, proximal to base of fifth finger
What are the bye-bye muscles?
lumbricals 1 and 2
-bc they flex the MCP join and extend the IP joints