BIO test 1: Macromolecules and parts of the cell
1/98
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
99 Terms
carbon backbone, functional groups
what do all macromolecules have in common?
monomers
small, individual, similar subunits
building blocks of macromolecules
polymer
chains of covalently linked monomers
polymerization
the process of monomers coming together to form polymers
Condensation/dehydration reaction
monomer in, water out
add covalent bond
decreases, increases
when condensation reactions occur, entropy ___, and when hydrolysis occurs, entropy ____
hydolysis
water in, monomer out
braks covalent bond
monosaccharides
monomers for carbohydrates
simple sugars
i
isomers
molecules with the same chemical formula but different chemical structures
aldehyde group and oxygen
what causes a carbon ring to form?
alpha carbon
carbon one that has this configuration
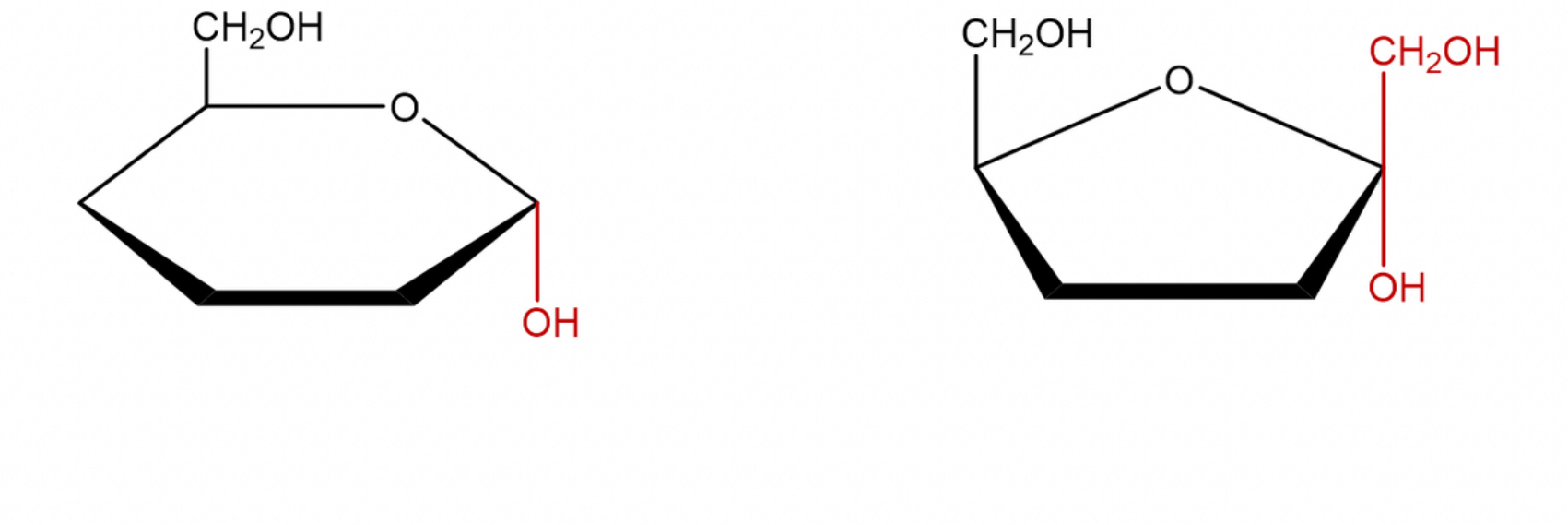
beta carbon
carbon one that has this configuration

glucose
one main example of monosaccharides
polysaccharide
thousands of monosaccharide molecules attached to each other by covalent bond
glycosidic bond
what type of bond forms between monosaccharides?
lipids
largely nonpolar and hydrophobic
composed primarily of C and H
not technically a polymer
chemically diverse
fats
triglycerides, lipids composed of fatty acids connected to a glycerol molecule
steroids
composed of many carbon atoms bonded to form rings
phospholipid
glycerol backbone, 2 fatty acid chains, and a phosphate containing head group
glycerol
3 carbon molecule with 3 hydroxyl groups
fatty acid
long unbranched chains of carbon and end with a carboxyl functional group
flexible
one quality of saturated fatty acids is that they are ____ and carbond atoms can rotate around the single bonds
3 fatty acids, glycerol
triacylglycerol is made of
energy storage
triglycerides are mainly for ____
ester bonds
bonds that form during condensation reactions for lipids
high
high carbon content, nonpolar bonds, has ____ chemical energy
saturated fat
lots of hydrogen atoms
straight and packed tightly
high melting temp
solid at room temp
unsaturated fat
double nonds
kinked
not packed tightly
low melting point
liquid at room temp
hydrogenated oils
double bonds broken and hydrogen atoms added to give a certain structure
more solid at room temp
amphipathic molecules
contain hydrophilic and hydrophobic regions
spontaneously, arrange
amphipathic molecules ___ arrange themselves in a way that ___ interactions with water to the hydrophilic part of the molecule
amino acids
monomers, subunits of proteins
central carbon, carboxyl group, amino group, hydrogen, variable group
what are amino acids made of?
alpha carbon
what is the name of the carbon in amino acids?
20
how many types of amino acids are there?
R group
determines the identity of each amino acid and its chemical properites when it is part at a larger protein
amino group, NH3+
when amino acids ionize, what becomes a base?
carboxyl group, COO-
when an amino acid ionizes, what becomes an acid ?
stay in solution and affect chemical reactivity
what does ionization of the amino group do?
hydrophilic
when amino acids have electrically charged or polar side chains they are ____
Determining amino acid properties
R-group negative charge? if yes=acidic
R-group positive charge? if yes=basic
R-group uncharged with oxygen atom? if yes=polar
r-group uncharged with no oxygen? if yes=nonpolar
peptide bond
the kind of bond is formed between amino acids in polypeptides
covalent bond
amino and carboxyl
between what two groups does a condensation reaction occur in amino acids?
residue
individual amino acid
polypeptide
chain of amino acids
more than 20 AA
side chains
what part of polypeptides interact with water and each other?
directionality
monomers attached in the same orientation form their end terminus to their C terminus
amino terminus
free amino group at one end when linked to form polypeptides
oligoprotein
a few amino acids linked together
fewer than 20 AA
protein
any chain of AA residues
refer to the complete, functional form of the polypeptide
primary protein structure
the unique sequence of amino acids in the polypeptide, form the N-terminal to the C-terminal end
single change in AA impact the way a protein behaves
R-groups affect chemical reactivity and solubility of protein
common to all proteins
secondary protein structure
created by interactions (hydrogen bond) between Carboxyl=Oxygen and Amino group-H functional groups of different residues
a-helix
B-sheet (pleated)
Tertiary Protein Structure
due to the interactions that involve atoms on the side chain of amino acids
hydrogen bonds btwn R and carboxyl
hydrophobic interactions: NP substance to aggregate
disulfide bond
ionic bond
disulfide bond
between cysteine residue and side chain
quarternary structure
two or more polypeptides assemble to form a larger protein molecule
folding
what is crucial to a protein’s function?
chaperones
specialized proteins that help other proteins fold correctly
Ex: heat shock proteins help refold proteins denatured by high temps
prion
infectious disease causing agents that were once normal proteins that were induced into incorrect folding
can cause a chain reaction
selective permeability
lipid bilayers have ___
higher; lower
lipid bilayer with short and unsaturated hydrocarbon tails have ___ permeability and fluidity, while one iwth long and saturated hydrocarbon tails have ___
lipoproteins
spherical structures made of phospholipids
extracellular fluid
keep stuff you don’t need outc
cytoplasm
keeps the stuff you need in
fluid mosaic model
the cell membrane is fluid and flexible with lateral movement of lipids or proteins and diverse arrangement
lipid composition , temperature
membrane fluidity depends on ____
transmembrane proteins
span the entire bilayer
integral proteins
embedded in bilayer
can be hydrophobic and hydrophilic
peripheral membrane proteins
associated with one face
anchored membrane protein
covalently bonded to lipids that are inserted intot he membrane
glycoprotiens
carbohydrate attached to the outer surface of proteins
glycolipids
carbohydrates are attached tot he outer surface of lipids
recognition sites
interact with external environment
detergents
amphipathic, water soluble molecules that can form micelles
hydrophobic tails of _____ molecules interact with hydrophobic portions of transmembrane proteins to allow isolation
surface carbohydrates
thought of as a molecular signature
allow cells to be identifiable based on their surface features
cell structure
plasma membrane
proteins perform most cell functions
carbohydrates provide energy and support
contain genetic material
cytoplasm and ribosomes
prokaryotic cells
don’t have membrane bound organelles
no nucleus
unicellular: bacteria and archaea
small
DNA in nucleoid
may have plasmids
cell wall
plasmids
contain genes but are physically independent of the main chromosome
help adapt to unusual circumstances
flagella
swimming
fimbriae
attachment to other cells or surfaces
eukaryotes
eukarya—4 kingdoms
multicellular and unicellular
contain organelles
has a nucleus
organelles
specialized internal compartments defined by membranes
compartmentalization
division of labor efficiency and regulation
domain eukarya
protists
fungi
plants
animals
endomembrane system functions
carry and direct newly synthesized proteins
make necessary modifications to the proteins as they are moved
nucleoulus
where RNA is manufactured
Ribosomal subunits are also assembled here
Nuclear envelope
double membrane (inner and outer) and has nuclear pores
smooth ER
site of lipid production, detoxification
rough er
associated with ribosomes that are synthesizing proteins
studded with ribosomes
endoplasmic reticulum
wraps around the nucleus
smooth and rough
ribosomes
macromolecular machines that manufacture proteins
composed of protiens and RNA
for eukaryotes it is scattered in cytosol and is associated with ER
not considered an organelle or part of the endomembrane system
golgi apparatus
stacks of flat membrane bound sacs (cisternae)
modify proteins, lipids
cis face to trans face
receives from ER
directs proteins and lipids to other organelles
uses glycosylation
glycosylation
attachement of small carbohydrates
glycolipids and glyoproteins
lysosome
recycling center of the cell
part of endomembrane system
enzymes break down biomoleules that are damaged, defective, or no longer needed
perform hydrolysis
integral membbrane proteins pump protons into here
mitochondrion
two membranes
supplies energy in the form of ATP
has its own DNA
chloroplast
2 membranes
converst sunlight into chemical energy with photosynthesis
contains copies of its own chromosome
mitochondria, chloroplast
which two organelles are believed to be once free living bacteria and have their own dna
vacuoles
very large, found in pants, fungi and some other eukaryotes where lysosomes are not present
storage depots
peroxisomes
contain enzyme that catalyze oxiddation reactions important for cellular function
nucleus
largest organelle
surrounded by nuclear envelope with pores
DNA and helps with transcription and assembles ribosomes